Hemodialysis as a Risk Factor for Lower Right Internal Jugular Stenosis in Cardiac Surgery Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Committee Approval
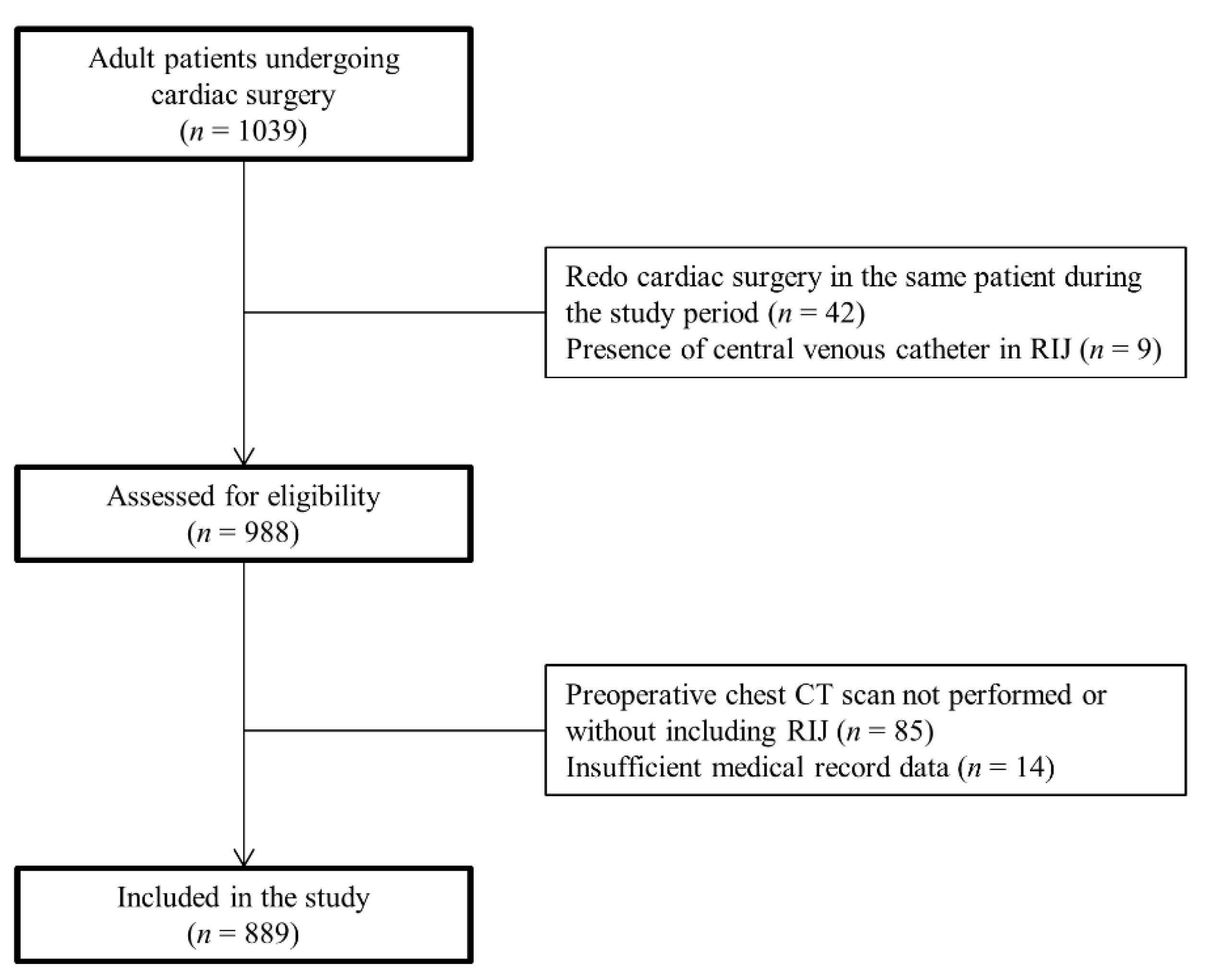
2.2. Study Population
2.3. CVC and Data Collection
2.4. CT Review
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kayir, S.; Ozyalcin, S.; Dogan, G.; Diken, A.I.; Turkmen, U. Internal Jugular Vein Catheterization: The Landmark Technique versus Ultrasonography Guidance in Cardiac Surgery. Cureus 2019, 11, e4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defalque, R.J. Percutaneous catheterization of the internal jugular vein. Anesth. Analg. 1974, 53, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, S.S.; Desai, N.K.; Kalra, A.; Gajera, M.; Cavanaugh, S.K.; Brampton, W.; Young, D.; Harvey, S.; Rowan, K.; Ss, R.; et al. Pulmonary artery catheters for adult patients in intensive care. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parienti, J.-J.; Mongardon, N.; Mégarbane, B.; Mira, J.-P.; Kalfon, P.; Gros, A.; Marqué, S.; Thuong, M.; Pottier, V.; Ramakers, M.; et al. Intravascular Complications of Central Venous Catheterization by Insertion Site. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Na, H.S.; Koh, W.U.; Ro, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.H. Complications in internal jugular vs subclavian ultrasound-guided central venous catheterization: A comparative randomized trial. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brass, P.; Hellmich, M.; Kolodziej, L.; Schick, G.; Af, S.; Patrick, B.; Martin, H.; Laurentius, K.; Guido, S. Ultrasound guidance versus anatomical landmarks for internal jugular vein catheterization summary of findings for the main comparison. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, CD006962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apsner, R.; Sunder-Plassmann, G.; Muhm, M.; Druml, W. Alternative puncture site for implantable permanent haemodialysis catheters. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 1996, 11, 2293–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillinger, F.; Schillinger, D.; Montagnac, R.; Milcent, T. Post catheterisation vein stenosis in haemodialysis: Comparative angiographic study of 50 subclavian and 50 internal jugular accesses. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1991, 6, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, G.S.; Lee, S.W.; Park, J.B.; Lee, J.J.; Ko, J.S. Preoperative ultrasonographic findings of internal jugular veins and carotid arteries in kidney transplant recipients. Korean J. Anesth. 2016, 69, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimochowski, G.E.; Worley, E.; Rutherford, W.E.; Sartain, J.; Blondin, J.; Harter, H. Superiority of the internal jugular over the subclavian access for temporary dialysis. Nephron 1990, 54, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.K. Central vein stenosis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 61, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammers, R.; de Haan, M.W.; Planken, N.R.; van der Sande, F.M.; Tordoir, J.H.M. Central vein obstruction in hemodialysis patients: Results of radiological and surgical intervention. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2003, 26, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, O.O.; El-Magzoub, A.-R.A.; Elamin, S. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Central Venous Stenosis among Prevalent Hemodialysis Patients, a Single Center Experience. Arab J. Nephrol. Transplant. 2014, 7, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Gonsalves, C.F.; Eschelman, D.J.; Sullivan, K.L.; DuBois, N.; Bonn, J. Incidence of central vein stenosis and occlusion following upper extremity PICC and port placement. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2003, 26, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, A.G.; Jensen, G.; Prescott, E. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism: Results from the copenhagen city heart study. Circulation 2010, 121, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandoni, P.; Bilora, F.; Marchiori, A.; Bernardi, E.; Petrobelli, F.; Lensing, A.W.A.; Prins, M.H.; Girolami, A. An Association between Atherosclerosis and Venous Thrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y. Association between hypertension and deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2016, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.-K.; Lee, H.-K.; Jeon, Y.-T.; Hwang, J.-W.; Lim, S.-M.; Park, H.-P. Clinical significance of the cross-sectional area of the internal jugular vein. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2013, 27, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labropoulos, N.; Borge, M.; Pierce, K.; Pappas, P.J. Criteria for defining significant central vein stenosis with duplex ultrasound. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 46, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, L.; Ahern, J.; Galea, S.; van der Laan, M. Estimating Effects with Rare Outcomes and High Dimensional Covariates: Knowledge is Power. Epidemiol. Method 2016, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehn, F.E.; Schwartz, K.M.; Hunt, C.H.; Eckel, L.J.; Campeau, N.G.; Carter, R.E.; Allred, J.B.; Kallmes, D.F. Prevalence of incidental narrowing of the superior segment of the internal jugular vein in patients without multiple sclerosis. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2014, 24, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Wang, Z.; Guan, J.; Jin, K.; Ding, Y.; Ji, X.; Meng, R. Clinical characteristics and neuroimaging findings in eagle syndrome induced internal jugular vein stenosis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipo, R.; Ciciarello, F.; Attanasio, G.; Mancini, P.; Covelli, E.; Agati, L.; Fedele, F.; Viccaro, M. Chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency in patients with Ménière’s disease. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.T.; Chang, K.C.; Hu, K.L.; Ting, C.K.; Chan, K.H.; Chang, W.K. Catheter-related right internal jugular vein thrombosis after chest surgery. Br. J. Anaesth. 2017, 119, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, V.N.; Eason, J.B.; Allon, M. Central Venous Occlusion in the Hemodialysis Patient. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 68, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosetti, M.; Meloni, C.; Gandini, R.; Galderisi, C.; Pampana, E.; Nicoletti, M.; Gallucci, M.T.; Simonetti, G.; Casciani, C.U. Late symptomatic venous stenosis in three hemodialysis patients without previous central venous catheters. Artif. Organs 2000, 24, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cui, T.; Yu, Y.; Liu, F.; Fu, P.; Zhou, L.; Li, X. Successful tunneled catheter placement in a hemodialysis patient with idiopathic multiple central venous stenoses. Hemodial. Int. 2014, 18, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.A.; Lee, D.Y.; Segall, J.A.; Landry, G.J.; Liem, T.K.; Mitchell, E.L.; Moneta, G.L. Characterizing resolution of catheter-associated upper extremity deep venous thrombosis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 51, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, K.; Groller, R.; Nadgir, R.N.; Fujita, A.; Qureshi, M.M.; Sakai, O. Variability in the cross-sectional area and narrowing of the internal jugular vein in patients without multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, E.B.; Sulek, C.A.; Moody, R.L.; Morey, T.E. Cross-sectional area of the right and left internal jugular veins. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 1999, 13, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vats, H.S.; Bellingham, J.; Pinchot, J.W.; Young, H.N.; Chan, M.R.; Yevzlin, A.S. A comparison between blood flow outcomes of tunneled external jugular and internal jugular hemodialysis catheters. J. Vasc. Access 2012, 13, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanz, S.; Gordon, D.H.; Lipkowitz, G.S.; Butt, K.M.H.; Hong, J.; Sclafani, S.J.A. Axillary and subclavian vein stenosis: Percutaneous angioplasty. Radiology 1988, 168, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Stenotic Group | Non-Stenotic Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 35) | (n = 854) | ||
| Demographics | |||
| Age (years) | 63 (56.5–70.5) | 64.5 (55–72) | 0.935 |
| Female | 11 (31.4%) | 322 (37.7%) | 0.566 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.1 (21.7–26.0) | 23.8 (21.5–26.0) | 0.989 |
| Smoking | 8 (22.9%) | 157 (18.4%) | 0.656 |
| Past medical history | |||
| Hypertension | 18 (51.4%) | 411 (48.1%) | 0.833 |
| Diabetes | 14 (40.0%) | 221 (25.9%) | 0.097 |
| Dyslipidemia | 9 (25.7%) | 147 (17.2%) | 0.285 |
| Angina | 19 (54.3%) | 330 (38.6%) | 0.093 |
| Myocardial infarction | 3 (8.6%) | 58 (6.8%) | 0.946 |
| Hemodialysis | 9 (25.7%) | 57 (6.7%) | <0.001 |
| Stroke | 4 (11.4%) | 132 (15.5%) | 0.682 |
| Previous pacemaker | 1 (2.9%) | 18 (2.1%) | 1.000 |
| Previous IJV catheterization (side not specified) | 5 (14.3%) | 54 (6.3%) | 0.131 |
| ASA physical status | 0.896 | ||
| 1 | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (0.5%) | |
| 2 | 7 (20.0%) | 224 (26.2%) | |
| 3 | 27 (77.1%) | 592 (69.3%) | |
| 4 | 1 (2.9%) | 33 (3.9%) | |
| 5 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (0.1%) | |
| Surgery profiles | |||
| CABG only | 17 (48.6%) | 289 (33.8%) | 0.106 |
| Combined CABG and valvular | 1 (2.9%) | 108 (12.6%) | 0.142 |
| Cardiac redo before the study period | 3 (8.6%) | 73 (8.5%) | 1.000 |
| Emergency | 5 (14.3%) | 116 (13.6%) | 1.000 |
| Preoperative medication | |||
| Aspirin | 14 (40.0%) | 290 (34.0%) | 0.578 |
| Clopidogrel | 7 (20.0%) | 139 (16.3%) | 0.726 |
| ACE inhibitor | 2 (5.7%) | 69 (8.1%) | 0.851 |
| ARB | 14 (40.0%) | 247 (28.9%) | 0.222 |
| β blocker | 6 (17.1%) | 142 (16.6%) | 1.000 |
| Calcium channel blocker | 17 (48.6%) | 317 (37.1%) | 0.233 |
| Diuretics | 14 (40.0%) | 288 (33.7%) | 0.558 |
| Digoxin | 5 (14.3%) | 92 (10.8%) | 0.706 |
| Oral hypoglycemic agent | 8 (22.9%) | 182 (21.3%) | 0.993 |
| Warfarin | 5 (14.3%) | 130 (15.2%) | 1.000 |
| Heparin before CT scan | 3 (8.6%) | 72 (8.4%) | 1.000 |
| Statin | 12 (34.3%) | 300 (35.1%) | 1.000 |
| Preoperative laboratory data | |||
| Hematocrit (%) | 35.4 (33.6–38.5) | 34.7 (32.0–37.5) | 0.250 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.0 (0.8–1.3) | 0.9 (0.8–1.1) | 0.492 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.1 (3.6–4.4) | 4.1 (3.7–4.3) | 0.904 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 140 (125.5–169.5) | 131 (102–168) | 0.113 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 0.2 (0.1–0.6) | 0.2 (0.1–0.6) | 0.835 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 223 (176–262) | 204 (167–249) | 0.394 |
| LV ejection fraction (%) | 56 (53–63) | 58 (53–63) | 0.754 |
| Preoperative coagulation profile | |||
| aPTT (s) | 33.4 (31.0–39.2) | 32.8 (30.6–36.9) | 0.924 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 322 (266.5–362.5) | 309 (262–370) | 0.588 |
| Prothrombin time (INR) | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | 0.923 |
| Stenotic Group | Non-Stenotic Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 35) | (n = 854) | ||
| Duration of surgery (min) | 370 (315–441) | 380 (325–455) | 0.741 |
| Duration of anesthesia (min) | 455 (395–515) | 455 (396–534) | 0.803 |
| CRRT | 2 (5.7%) | 19 (2.2%) | 0.445 |
| Surgical site infection | 0 (0.0%) | 15 (1.8%) | 0.903 |
| Seizure | 0 (0.0%) | 9 (1.1%) | 1.000 |
| Stroke | 2 (5.7%) | 30 (3.5%) | 0.824 |
| Death from any cause | 3 (8.6%) | 62 (7.3%) | 1.000 |
| Death from cardiac cause | 1 (2.9%) | 30 (3.5%) | 1.000 |
| In-hospital mortality | 1 (2.9%) | 22 (2.6%) | 1.000 |
| KDIGO stage | 0.465 | ||
| 0 | 19 (54.3%) | 512 (60.0%) | |
| 1 | 8 (22.9%) | 218 (25.5%) | |
| 2 | 3 (8.6%) | 62 (7.3%) | |
| 3 | 5 (14.3%) | 62 (7.3%) | |
| Delirium | 5 (14.3%) | 103 (12.1%) | 0.896 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 6 (17.1%) | 183 (21.4%) | 0.692 |
| Postoperative length of hospital stay (days) | 18 (14.5–23) | 17 (13–25) | 0.339 |
| Stenotic Group | Non-Stenotic Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 35) | (n = 854) | ||
| Smallest diameter (mm) | 5 (3.5–7.2) | 10.6 (8.5–12.6) | <0.001 |
| Smallest CSA (mm2) | 27.2 (13.7–37.9) | 88.5 (61.8–119.6) | <0.001 |
| Smallest perimeter (mm) | 20.3 (13.5–24.6) | 32.6 (27.1–37.9) | <0.001 |
| Largest diameter (mm) | 13.4 (11.3–16.8) | 14.1 (11.3–16.8) | 0.791 |
| Largest CSA (mm2) | 143.7 (89.9–192.7) | 153.6 (104.1–209.6) | 0.496 |
| Largest perimeter (mm) | 41.6 (33.2–51.0) | 43.0 (35.2–50.6) | 0.743 |
| Diameter ratio | 0.37 (0.34–0.47) | 0.76 (0.66–0.88) | <0.001 |
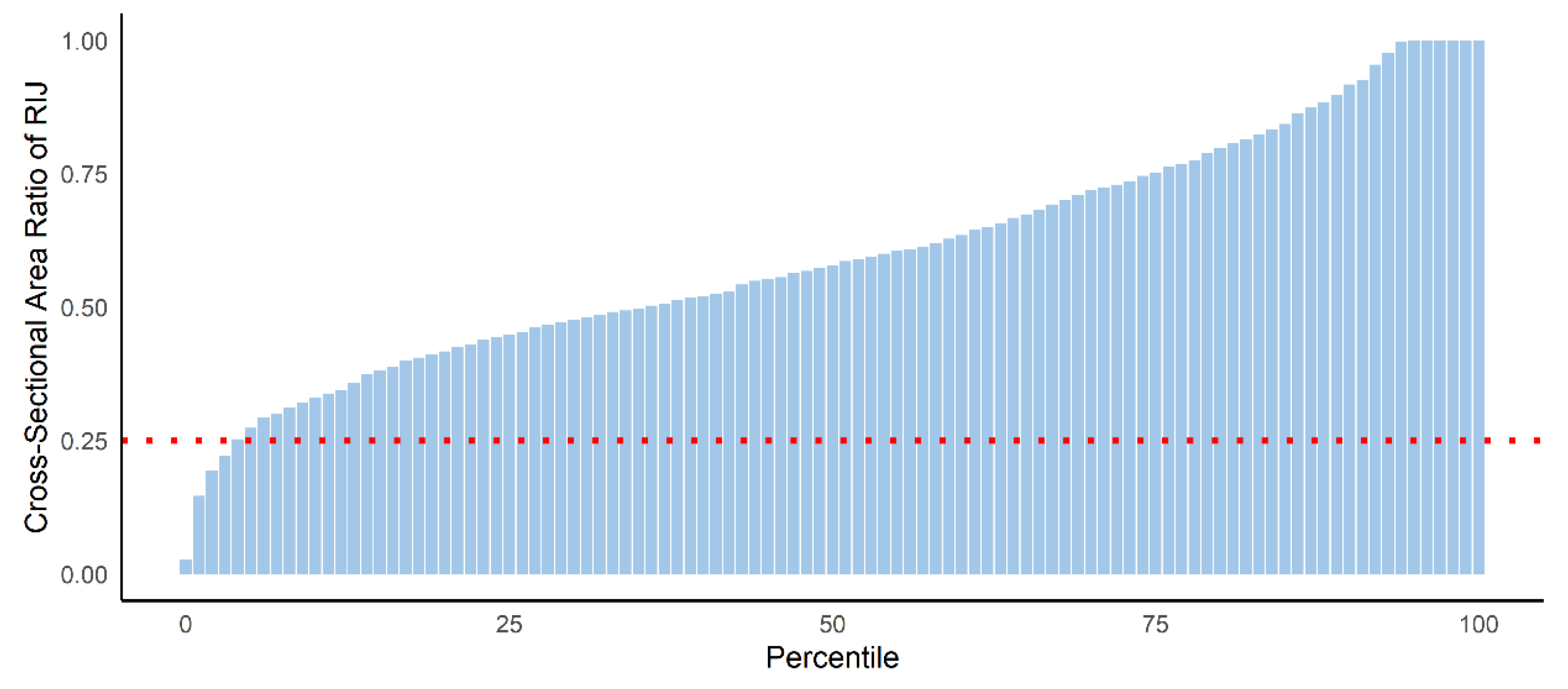
| CSA ratio | 0.18 (0.14–0.21) | 0.59 (0.47–0.76) | <0.001 |
| Perimeter ratio | 0.47 (0.40–0.50) | 0.77 (0.67–0.88) | <0.001 |
| Univariable Regression Analysis | Multivariable Regression Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 1.001 (0.976–1.027) | 0.939 | ||
| Female | 0.757 (0.366–1.567) | 0.453 | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 1.036 (0.939–1.142) | 0.481 | ||
| Smoking | 1.315 (0.586–2.95) | 0.506 | ||
| Hypertension | 1.141 (0.58–2.244) | 0.702 | ||
| Diabetes | 1.91 (0.955–3.82) | 0.068 | 1.36 (0.639–2.891) | 0.425 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1.665 (0.764–3.627) | 0.199 | 1.235 (0.527–2.894) | 0.627 |
| Angina | 1.886 (0.956–3.719) | 0.067 | 1.233 (0.564–2.698) | 0.600 |
| Myocardial infarction | 1.287 (0.382–4.328) | 0.684 | ||
| Hemodialysis | 4.84 (2.166–10.817) | <0.001 | 3.54 (1.472–8.514) | 0.005 |
| Stroke | 0.706 (0.245–2.032) | 0.518 | ||
| Previous pacemaker | 1.366 (0.177–10.533) | 0.765 | ||
| Previous IJV catheterization (side not specified) | 2.469 (0.921–6.619) | 0.072 | 1.666 (0.574–4.838) | 0.348 |
| ASA physical status | 1.253 (0.644–2.437) | 0.507 | ||
| Aspirin | 1.297 (0.65–2.587) | 0.461 | ||
| Clopidogrel | 1.286 (0.551–3.002) | 0.561 | ||
| ACE inhibitor | 0.69 (0.162–2.935) | 0.615 | ||
| ARB | 1.638 (0.82–3.274) | 0.162 | 1.402 (0.682–2.883) | 0.358 |
| β blocker | 1.037 (0.423–2.545) | 0.936 | ||
| Calcium channel blocker | 1.6 (0.813–3.149) | 0.174 | 1.259 (0.617–2.568) | 0.527 |
| Diuretics | 1.31 (0.657–2.615) | 0.444 | ||
| Digoxin | 1.38 (0.523–3.646) | 0.515 | ||
| Oral hypoglycemic agent | 1.094 (0.489–2.449) | 0.827 | ||
| Warfarin | 0.928 (0.354–2.436) | 0.88 | ||
| Heparin before CT scan | 1.018 (0.304–3.407) | 0.977 | ||
| Statin | 0.963 (0.473–1.964) | 0.918 | ||
| Hematocrit (%) | 1.048 (0.969–1.134) | 0.241 | ||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.099 (0.912–1.324) | 0.322 | ||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 0.761 (0.393–1.475) | 0.419 | ||
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 1.002 (0.996–1.008) | 0.571 | ||
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 1.002 (0.905–1.109) | 0.971 | ||
| Platelet (×109/L) | 1 (0.995–1.005) | 0.949 | ||
| LV ejection fraction (%) | 1.001 (0.971–1.032) | 0.946 | ||
| aPTT (s) | 0.999 (0.981–1.019) | 0.952 | ||
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 1.001 (0.997–1.005) | 0.753 | ||
| Prothrombin time (INR) | 0.549 (0.068–4.456) | 0.575 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ju, J.-W.; Oh, Y.; Yang, H.J.; Lee, S.; Bae, J.; Nam, K.; Cho, Y.J.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, T.K. Hemodialysis as a Risk Factor for Lower Right Internal Jugular Stenosis in Cardiac Surgery Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051042
Ju J-W, Oh Y, Yang HJ, Lee S, Bae J, Nam K, Cho YJ, Jeon Y, Kim TK. Hemodialysis as a Risk Factor for Lower Right Internal Jugular Stenosis in Cardiac Surgery Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(5):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051042
Chicago/Turabian StyleJu, Jae-Woo, Yoomin Oh, Hyo Jun Yang, Seohee Lee, Jinyoung Bae, Karam Nam, Youn Joung Cho, Yunseok Jeon, and Tae Kyong Kim. 2021. "Hemodialysis as a Risk Factor for Lower Right Internal Jugular Stenosis in Cardiac Surgery Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 5: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051042
APA StyleJu, J.-W., Oh, Y., Yang, H. J., Lee, S., Bae, J., Nam, K., Cho, Y. J., Jeon, Y., & Kim, T. K. (2021). Hemodialysis as a Risk Factor for Lower Right Internal Jugular Stenosis in Cardiac Surgery Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(5), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10051042






