Improvement in Quality of Life with Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Biofeedback in Patients with Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Electromyographic-Biofeedback as an Adjunct Therapy
1.2. Pelvic Floor Muscle Training for BPS/IC Treatment
1.3. Quality of Life and Health Indicators
1.4. Objective
2. Method
2.1. Sample Selection
2.2. Study Groups
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Studied Variables
- Result of SF-36-HRQOL questionnaire equal or greater than 80 points; or
- Increase in 30 or more points in the SF-36-HRQOL questionnaire compared to the initial score.
- Result of SF-36-HRQOL questionnaire below 80 points; and
- Increase lower than 30 points in the SF-36-HRQOL questionnaire compared to the initial score.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Issues
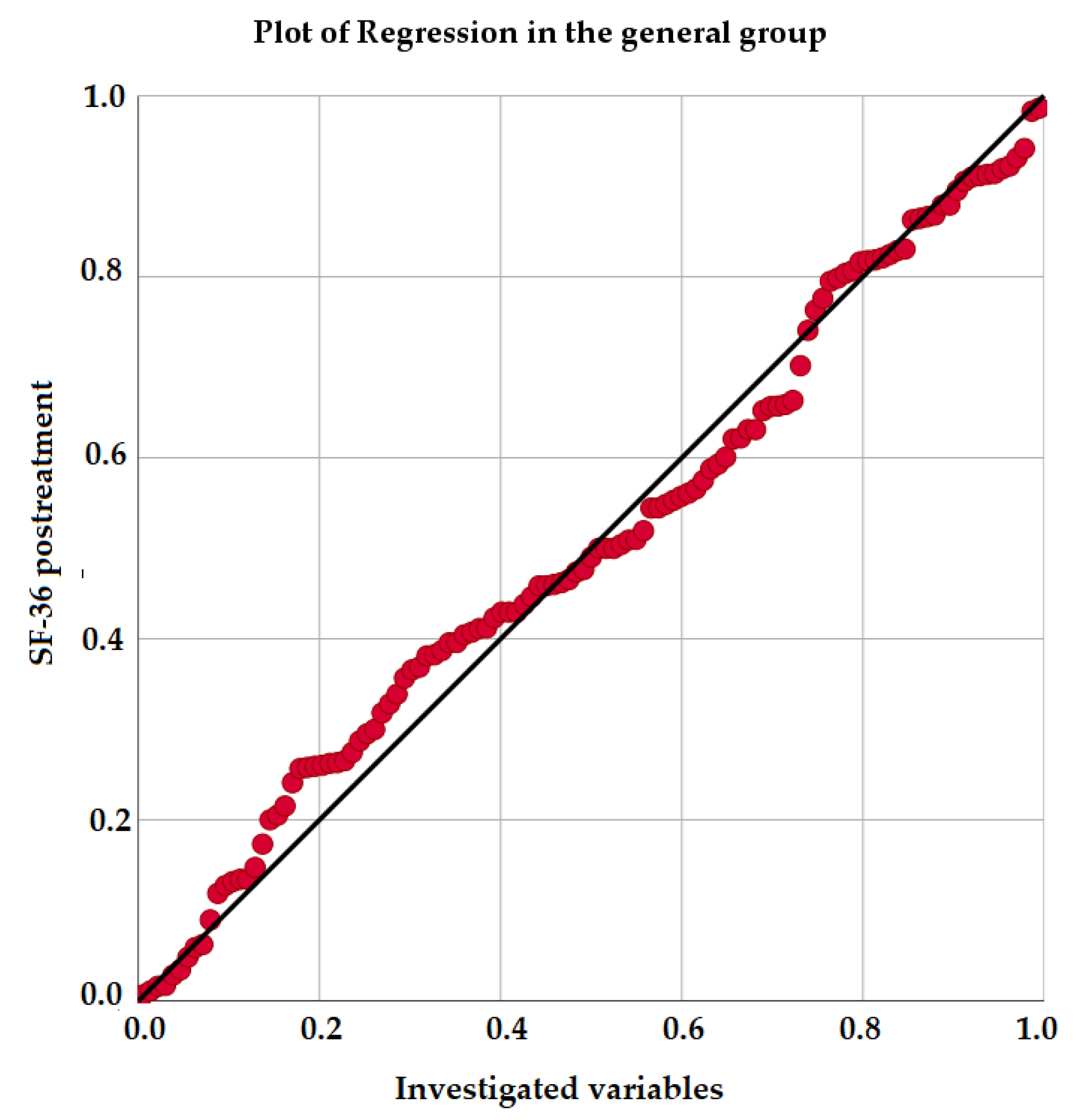
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Results in Quality of Life
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APFIEQ-CyL | Promotion of Training and Research in Surgical Specialties in Castilla and León |
| BCG | Bacillus Calmette-Guerin |
| BFB | Biofeedback (BFB) |
| BFB+ | Group receiving adjuvant biofeedback |
| BFB− | Group of patients who did not receiving biofeedback of pelvic floor. |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BPS | Bladder pain syndrome |
| BTX-A | Botulinum toxin type A |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CPP | Chronic pelvic pain |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EAU | The European Association of Urology |
| EMDA | Electromotive drug administration |
| EMG-BFB | Electromyographic biofeedback |
| ESSIC | The International Society for the Study of BPS (formerly, European Society for the Study of Interstitial Cystitis) |
| GAG | Intravesical glycosaminoglycans |
| HBO | Hyperbaric oxygen |
| HT | Hypertension |
| HRQOL | Health-related quality of life |
| IASP | The International Association for the Study of Pain |
| IC | Interstitial cistitis |
| IPD-1151T | Suplatast tosilate |
| LD | Length of disease |
| RTX | Resiniferatoxin |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TUR | Transurethral resection |
| UI | Urinary incontinence |
| UTI | Urinary tract infection |
References
- Lorenzo-Gómez, M.-F.; Gomez-Castro, S. Physiopathologic relationship between interstitial cystitis and rheumatic, autoimmune, and chronic inflammatory diseases. Arch. Esp. Urol. 2004, 57, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Engeler, D.; Baranowski, A.P.; Berghmans, B.; Borovicka, J.; Cottrell, A.M.; Dinis-Oliveira, P.; Elneil, S.; Hughes, J.; Messelink, E.J.; de C Williams, A.C.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Chronic Pelvic Pain; European-Association-of-Urology-2020: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Merwe, J.P.; Nordling, J.; Bouchelouche, P.; Bouchelouche, K.; Cervigni, M.; Daha, L.K.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Irwin, P.; et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: An ESSIC proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, C. Management of Urinary Tract Infections: Historical Perspective and Current strategies: Part I—Before antiobiotics. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Gómez, M.F.; Lorenzo-Gómez, A.; Gómez-Castro, S.; García-Criado, F.J.; Urrutia-Rodríguez, M.; Sánchez-González, N.; Escarpa-González, J.L.; Urrutia-Avisrror, M. Comparación del tratamiento de la cistopatía intersticial con ácido hialurónico endovesical frente a amitriptilina vía oral. In Proceedings of the LXIX Congreso Nacional de Urología, Oviedo, España, 4–6 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, C.L.; Koprowski, P.F. Interstitial cystitis: Successful management by increasing urinary voiding intervals. Urology 1991, 37, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennamsetty, A.; Ehlert, M.J.; Peters, K.M.; Killinger, K.A. Advances in diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2015, 17, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.M.; Carrico, D.J.; Kalinowski, S.E.; Ibrahim, I.A.; Diokno, A.C. Prevalence of pelvic floor dysfunction in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology 2007, 70, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.M. Pelvic floor myofascial trigger points: Manual therapy for interstitial cystitis and the urgency-frequency syndrome. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 2226–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, M.P.; Payne, C.K.; Lukacz, E.S.; Yang, C.C.; Peters, K.M.; Chai, T.C.; Nickel, J.C.; Hanno, P.M.; Kreder, K.J.; Burks, D.A.; et al. Randomized multicenter clinical trial of myofascial physical therapy in women with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome and pelvic floor tenderness. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Jimenez, P.-S.; Lorenzo-Gomez, M.-F.; Borrego-Jiménez, J.; Borrego-Jiménez, P.; Garcia-Criado, F.; Silva-Abuin, J. Fisioterapia y personas con discapacidad: Papel de la fisioterapia coadyuvante en la discapacidad física y psicosomática causada por la cistopatía intersticial. Fisioterapia 2009, 31, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, J.; Rapariz, M. Reeducación vésico-esfinteriana. In Urodinámica Clínica; Salinas, J., Rapariz, J., Eds.; Jarpyo: Madrid, España, 1994; p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- Oxford-University-Press. Oxford Languages; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; Available online: https://languages.oup.com/ (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Perry, J. General Letter for Insurance Appeals (Biofeedback) Pelvic Muscle Rehabilitation (EMG Biofeedback) for Urinary & Fecal Incontinence and Related Disorders Using Perry Vaginal TM and Perry Anal TM Sensors; Biofeedback Society of California: Petaluma, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Repilado-Grillo, F. Cistitis recurrentes: Una consulta frecuente en la farmacia. El Farm. Profesión Y Cult. 2017, 551, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Stamm, W.; Raz, R. Factors Contributing to Susceptibility of Postmenopausal Women to Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oyama, I.A.; Rejba, A.; Lukban, J.C.; Fletcher, E.; Kellogg-Spadt, S.; Holzberg, A.S.; Whitmore, K.E. Modified Thiele massage as therapeutic intervention for female patients with interstitial cystitis and high-tone pelvic floor dysfunction. Urology 2004, 64, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loving, S.; Nordling, J.; Jaszczak, P.; Thomsen, T. Does evidence support physiotherapy management of adult female chronic pelvic pain? A systematic review. Scand. J. Pain 2012, 3, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama’i, M.S.; Javan, A.; Vyas, N.; Lovasz, S.; Singh, N.; Cervigni, M.; Pandey, S.; Wyndaele, J.J.; Taneja, R. Bladder Pain Syndrome and Interstitial Cystitis Beyond Horizon: Reports from the Global Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Society (GIBS) Meeting 2019 Mumbai-India. Anesthesiol. Pain Med. 2020, 10, e101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandwala, S.; Cruff, J. The Role of Yoga in the Management of Bladder Pain Syndrome: A Single-Arm Pilot Study. Adv. Mind-Body Med. 2020, 34, 4–9. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla-Fernandez, B.; Gomez-Garcia, A.; Hernandez-Alonso, M.; Garcia-Cenador, M.; Mirón-Canelo, J.; Geanini-Yagüez, A.; Silva-Abuin, J.; Lorenzo-Gomez, M. Biofeedback With Pelvic Floor Electromyography as Complementary Treatment In Chronic Disorders Of The Inferior Urinary Tract. In Electromyography; Radja, M., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croacia, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 287–311. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Gómez, M.; Padilla-Fernández, B.; García-Criado, F.; Mirón-Canelo, J.; Gil-Vicente, A.; Nieto-Huertos, A.; Silva-Abuin, J. Evaluation of a therapeutic vaccine for the prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections versus prophylactic treatment with antibiotics. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2013, 24, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J., Jr.; Sherbourne, C. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med. Care 1992, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.; Prieto, L.; Antó, J.M. The Spanish version of the SF-36 Health Survey (the SF-36 health questionnaire): An instrument for measuring clinical results. Med. Clin. 1995, 104, 771–776. [Google Scholar]
- Del Río, C.; Montero, J. Exploración neurológica y neurofisiológica del suelo pelviano. Cirugía Española 2004, 76, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.L.; Padilla-Fernandez, B.; Garcia-Criado, F.; Gomez-Garcia, A.; Miron-Canelo, J.; Geanini-Yaguez, A.; Silva-Abuin, J. The Usefulness of Electromyography in Diagnosis of Functional Status of Pelvic Floor Muscles in Women with Urinary Incontinence; Catriona Steele: Rijeka, Croacia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maizels, M.; Firlit, C.F. Pediatric urodynamics: A clinical comparison of surface versus needle pelvic floor/external sphincter electromyography. J. Urol. 1979, 122, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Gómez, M.; Gómez-García, A.; Padilla-Fernández, B.; García-Criado, F.; Silva-Abuín, J.; Mirón-Canelo, J.; Urrutia-Avisrror, M. Risk factors for failure after transobturator vaginal tape for urinary incontinence. Actas Urol. Esp. 2011, 35, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Jiménez, P.-S. Fisioterapia y Calidad de Vida Relacionada con la Salud en los Trastornos Inflamatorios Crónicos, Infecciosos y no Infecciosos, del Tracto Urinario Inferior Femenino; Advisor María Fernanda Lorenzo-Gómez and José Antonio Mirón Canelo, original research. Qualification excellent (A) Cum Laude; Universidad de Salamanca: Salamanca, España, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mirón-Canelo, J. Calidad de vida relacionada con la salud: Un indicador de resultados y efectividad clínica. In Suelo Pelviano; Lorenzo-Gómez, M., Ed.; Ratio Legis: Salamanca, España, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Gómez, M.-F. Cistopatía Intersticial. In Tratado de Uro ginecología. Incontinencia Urinaria; Espuña, M., Salinas, J., Eds.; Editorial Ars Médica: Barcelona, España, 2003; pp. 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Fernandes-Vale-Matos, M.-R.; Mendez-Garcia, P.; Sanchez-Jaen, M.; Cordeque-Mejia, M.-P.; Hernandez-Sanchez, T.; Garcia-Sanchez, M.-H.; Garcia-Cenador, M.-B.; Lorenzo-Gomez, M.-F. Efecto del Tratamiento con Anti-inflamatorios No Esteroideos en el Síndrome de Dolor Vesical/Cistopatia Intersticial. In Proceedings of the XV Congreso SINUG 2018, Sevilla, España, 15–17 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barroso-López, K.; Bliek-Bueno, K.; Cantero-Acedo, A.; Domínguez-García, J.; Lorenzo-Gomez, M.-F. Eficacia de la neuromodulación como trata-miento de la vejiga dolorosa o cistopatía intersticial en varones y mujeres. In Proceedings of the XIII Congreso Nacional de Investigación de Grado en cc de la Salud, Madrid, Spain, 30 March–1 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
| BFB+ | BFB− | p | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Median | Range | Mean | SD | Median | Range | ||
| Age (y.o) | 46.12 | 2.04 | 49 | 24–77 | 56.82 | 1.34 | 58 | 23–82 | 0.0535 |
| BMI | 24.16 | 0.64 | 21.78 | 19.63–35.16 | 25.47 | 0.35 | 25.95 | 18.75–29.97 | 0.04463 |
| TFU | 2321.05 | 16.47 | 2200 | 1650–4380 | 2392.97 | 10.56 | 2098 | 1247–5720 | 0.8502 |
| YPT | 3.2 | 0.17 | 2.5 | 1–6 | 6.58 | 0.49 | 5 | 1–20 | 0.0391 |
| SF-36 basal | 42.98 | 2.44 | 42.00 | 41–47 | 47.96 | 6.17 | 45.00 | 40–58 | 0.0046 |
| Concurrent diseases or conditions | |||||||||
| BFB− (n = 75) n = 48 | BFB+ (n = 48) n = 75 | p | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | ||||||
| HT | 0 | 0.00 | 5 | 6.67 | 0.1553 | ||||
| DM | 0 | 0.00 | 3 | 4.00 | 0.2803 | ||||
| Hypothyroidism | 10 | 20.83 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.0001 | ||||
| Depression | 6 | 12.50 | 6 | 8.00 | 0.5355 | ||||
| Other pathological conditions or diseases | 32 | 66.67 | 45 | 60.00 | 0.5677 | ||||
| More than 2 concurrent medical conditions | 6 | 12.50 | 1 | 1.33 | 0.0140 | ||||
| History of UTI | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1.33 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Overactive bladder | 5 | 10.42 | 2 | 2.67 | 0.1088 | ||||
| UI | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1.33 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Mild or level 1 urinary incontinence | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 5.33 | 0.1553 | ||||
| Non-repaired cystocele | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 2.67 | 0.5202 | ||||
| Non-repaired rectocele | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1.33 | 1.0000 | ||||
| Concurrent treatment with benzodiazepine | 19 | 39.58 | 9 | 12.00 | 0.0007 | ||||
| Concurrent treatment with anticholinergics | 0 | 0.00 | 9 | 12.00 | 0.0118 | ||||
| Concurrent treatment with topical oestrogens | 10 | 20.83 | 3 | 4.00 | 0.0052 | ||||
| Concurrent treatment with second-step analgesic drugs | 0 | 0.00 | 3 | 4.00 | 0.2803 | ||||
| Concurrent treatment with third-step analgesic drugs | 19 | 39.58 | 11 | 14.67 | 0.0024 | ||||
| Concurrent treatment with amitriptyline antidepressant | 14 | 29.17 | 15 | 20.00 | 0.2797 | ||||
| Treatment with intravesical instillation of GAG | 26 | 54.17 | 25 | 33.33 | 0.0256 | ||||
| Other pharmacological treatments | 24 | 50.00 | 27 | 36.00 | 0.1373 | ||||
| More than 2 concurrent treatments | 19 | 39.58 | 26 | 34.67 | 0.7014 | ||||
| Smoker | 5 | 10.42 | 10 | 13.33 | 0.7802 | ||||
| Toxic habit plus concurrent medical conditions | 5 | 10.42 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.0079 | ||||
| Surgical Background | |||||||||
| UI surgery | 10 | 20.83 | 8 | 10.67 | 0.1898 | ||||
| Repaired cystocele | 6 | 12.50 | 8 | 10.67 | 0.7771 | ||||
| Curettage | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 2.67 | 0.5202 | ||||
| Hysterectomy | 0 | 0.00 | 7 | 9.33 | 0.0419 | ||||
| Other surgical interventions | 17 | 35.42 | 17 | 22.67 | 0.1495 | ||||
| Gynecological cancer surgery | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1.33 | 1.0000 | ||||
| History of more than 2 concurrent surgical interventions | 11 | 22.92 | 11 | 14.67 | 0.3348 | ||||
| Toxic habit plus history of concurrent surgical interventions | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 2.67 | 0.5202 | ||||
| Obstetric Background | |||||||||
| Cesarean section | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 2.67 | 0.5202 | ||||
| Eutocic delivery | 0 | 0.00 | 12 | 16.00 | 0.0032 | ||||
| Dystocic delivery | 10 | 20.83 | 1 | 1.33 | 0.0003 | ||||
| SF-36 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Check Point | Media | SD | Median | Range | p |
| BFB+ | Pre-treatment | 42.98 | 2.44 | 42 | 41–47 | |
| Post-treatment 3 months | 78.27 | 13.02 | 85 | 51–92 | 0.0092 | |
| Post-treatment 6 months | 78.31 | 13.40 | 85 | 49–92 | ||
| Post-treatment 12 months | 75.72 | 12.81 | 81 | 47–90 | ||
| Post-treatment average | 77.29 | 13.20 | 84 | 51.89 | ||
| BFB+ success | Pre-treatment | 42.81 | 2.66 | 41 | 41–47 | |
| Post-treatment 3 months | 85.38 | 3.51 | 86 | 77–92 | 0.2284 | |
| Post-treatment 6 months | 85.52 | 4.16 | 86 | 76–92 | ||
| Post-treatment 12 months | 82.08 | 3.84 | 81 | 73–90 | ||
| Post-treatment average | 84.55 | 3.15 | 85 | 78–89 | ||
| BFB+ failure | Pre-treatment | 43.50 | 1.57 | 43.5 | 42–45 | |
| Post-treatment 3 months | 56.92 | 4.68 | 56.5 | 51–62 | 0.8499 | |
| Post-treatment 6 months | 56.67 | 5.50 | 57 | 49–62 | ||
| Post-treatment 12 months | 52.80 | 4.21 | 53.5 | 47–58 | ||
| Post-treatment average | 55.50 | 4.7 | 55.50 | 51–60 | ||
| BFB− | Pre-treatment | 47.96 | 6.17 | 45 | 40–58 | |
| Post-treatment 3 months | 73.92 | 15.97 | 83 | 48.95 | 0.0375 | |
| Post-treatment 6 months | 72.25 | 15.69 | 81 | 48.90 | ||
| Post-treatment 12 months | 69.76 | 16.38 | 80 | 46–87 | ||
| Post-treatment average | 71.79 | 15.79 | 82 | 50–82 | ||
| BFB− success | Pre-treatment | 48.20 | 5.78 | 45 | 40–58 | |
| Post-treatment 3 months | 86.90 | 3.58 | 87 | 80–95 | 0.1028 | |
| Post-treatment 6 months | 85 | 3.23 | 85 | 78–90 | ||
| Post-treatment 12 months | 83.27 | 2.43 | 83 | 78–87 | ||
| Post-treatment average | 84.77 | 2.44 | 85 | 80–88 | ||
| BFB− failure | Pre-treatment | 47.61 | 6.75 | 45 | 41–58 | |
| Post-treatment 3 months | 55.48 | 3.45 | 55 | 48–61 | 0.2185 | |
| Post-treatment 6 months | 54.16 | 3.91 | 53 | 48–61 | ||
| Post-treatment 12 months | 50.58 | 2.40 | 50 | 46–55 | ||
| Post-treatment average | 53.35 | 2.85 | 52 | 50–59 | ||
| Variables | RR | p Value | 95% C.I. | RR | p Value | 76% C.I. | RR | p Value | 58% C.I. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||||
| Age | 0.958 | 0.001 | 0.935 | 0.982 | 0.958 | 0.001 | 0.944 | 0.972 | 0.958 | 0.001 | 0.948 | 0.968 |
| BMI | 0.640 | 0.016 | 0.910 | 1.078 | 0.991 | 0.828 | 0.942 | 1.042 | 0.991 | 0.828 | 0.957 | 1.026 |
| SF-36 pretreatment | 0.793 | 0.0029 | 0.711 | 0.884 | 0.793 | 0.029 | 0.743 | 0.846 | 0.793 | 0.029 | 0.758 | 0.829 |
| Evolution time in years | 0.808 | 0.0011 | 0.711 | 0.918 | 0.808 | 0.001 | 0.748 | 0.872 | 0.808 | 0.001 | 0.766 | 0.852 |
| Other pathological | 0.217. | 0.010 | 0.090 | 0.524 | 0.217 | 0.001 | 0.128 | 0.368 | 0.217 | 0.001 | 0.151 | 0.312 |
| Other pharmacological treatments | 0.398 | 0.015 | 0.189 | 0.840 | 1.083 | 0.015 | 0.254 | 0.623 | 0.398 | 0.015 | 0.293 | 0.541 |
| Smoker | 0.271 | 0.025 | 0.086 | 0.852 | 2.000 | 0.025 | 0.137 | 0.539 | 0.271 | 0.025 | 0.170 | 0.435 |
| Repaired cystocele | 0.330 | 0.046 | 0.111 | 0.980 | 0.330 | 0.046 | 0.172 | 0.634 | 0.330 | 0.046 | 0.211 | 0.517 |
| Dystocic delivery | 7.231 | 0.064 | 0.895 | 58.437 | 7.231 | 0.064 | 2.066 | 25.306 | 7.231 | 0.064 | 3.061 | 17.083 |
| More 2 concurrent medical conditions | 4.087 | 0.199 | 0.476 | 35.058 | 4.087 | 0.199 | 1.127 | 14.824 | 4.087 | 0.199 | 1.688 | 9.896 |
| Overactive bladder | 1.643 | 0.563 | 0.306 | 8.828 | 1.643 | 0.563 | 0.600 | 4.502 | 1.643 | 0.563 | 0.822 | 3.281 |
| Benzodiazepine | 1.576 | 0.315 | 0.649 | 3.827 | 1.576 | 0.315 | 0.926 | 2.682 | 1.576 | 0.315 | 1.094 | 2.270 |
| Topical oestrogens | 2.308 | 0.223 | 0.601 | 8.858 | 2.308 | 0.223 | 1.030 | 5.169 | 2.308 | 0.223 | 1.327 | 4.013 |
| Amitriptyline antidepressant | 0.505 | 0.112 | 0.217 | 1.173 | 0.958 | 0.001 | 0.944 | 0.972 | 0.958 | 0.001 | 0.948 | 0.968 |
| Intravesical instillation of GAG | 0.488 | 0.057 | 0.233 | 1.023 | 0.991 | 0.828 | 0.942 | 1.042 | 0.991 | 0.828 | 0.957 | 1.026 |
| More than 2 concurrent treatments | 0.287 | 0.0014 | 0.133 | 0.620 | 0.793 | 0.029 | 0.743 | 0.846 | 0.793 | 0.029 | 0.758 | 0.829 |
| Other surgical interventions | 0.495 | 0.088 | 0.220 | 1.111 | 0.808 | 0.001 | 0.748 | 0.872 | 0.808 | 0.001 | 0.766 | 0.852 |
| More than 2 concurrent surgical interventions | 0.578 | 0.247 | 0.228 | 1.463 | 0.217 | 0.001 | 0.128 | 0.368 | 0.217 | 0.001 | 0.151 | 0.312 |
| SF-36 post-treatment | 1.026 | 0.049 | 1000 | 1053 | 1.026 | 0.049 | 1010 | 1042 | 1.026 | 0.049 | 1.015 | 1.037 |
| Multiple Regression Analysis in the General Sample | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | p Value | 95.0% Confidence Interval for B | ||
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| Age | −0.001 | −0.001 | 0.969 | −0.034 | 0.033 |
| BMI | −0.188 | −0.053 | 0.006 | −0.320 | −0.056 |
| SF-36 pretreatment | 0.065 | 0.024 | 0.247 | −0.045 | 0.175 |
| Evolution time in years | −0.020 | −0.006 | 0.751 | −0.144 | 0.105 |
| Time disease free | −0.012 | −0.008 | 0.712 | −0.074 | 0.050 |
| DM | −5.142 | −0.054 | 0.038 | −9.990 | −0.294 |
| Other pathological | −1.444 | −0.047 | 0.025 | −2.705 | −0.182 |
| Overactive bladder | 3.357 | 0.053 | 0.023 | 0.464 | 6.250 |
| Non-repaired rectocele | 3.035 | 0.018 | 0.423 | −4.447 | 10.518 |
| Benzodiazepine | 0.619 | 0.018 | 0.520 | −1.282 | 2.520 |
| Intravesical instillation of GAG | 2.113 | 0.070 | 0.028 | 0.227 | 3.998 |
| Other pharmacological treatments | −2.104 | −0.069 | 0.038 | −4.085 | −0.123 |
| Hysterectomy | −1.272 | −0.013 | 0.670 | −7.174 | 4.629 |
| Other surgical interventions | 1.124 | 0.034 | 0.330 | −1.156 | 3.404 |
| Gynecological cancer surgery | 0.869 | 0.005 | 0.767 | −4.925 | 6.663 |
| Cesarean section | 2.253 | 0.019 | 0.546 | −5.118 | 9.624 |
| Eutocic delivery | −0.930 | −0.019 | 0.492 | −3.605 | 1.745 |
| Results | −30.580 | −0.976 | 0.0005 | −32.020 | −29.139 |
| Multiple Regression Analysis in BFB+ | |||||
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | p-Value | 95.0% Confidence Interval for B | ||
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| Age | −0.042 | −0.062 | 0.186 | −0.106 | 0.022 |
| BMI | −1.013 | −0.374 | 0.00019 | −1.227 | −0.798 |
| SF-36 pretreatment | −0.777 | −0.148 | 0.003 | −1.272 | −0.282 |
| Evolution time in years | −1.325 | −0.180 | 0.000085 | −1.916 | −0.733 |
| Time disease free | −0.008 | −0.003 | 0.926 | −0.173 | 0.157 |
| DM | −0.896 | −0.017 | 0.704 | −5.677 | 3.885 |
| Other pathological | −0.623 | −0.019 | 0.555 | −2.761 | 1.515 |
| Overactive bladder | 1.312 | 0.021 | 0.720 | −6.098 | 8.723 |
| Non-repaired rectocele | 1.139 | 0.013 | 0.752 | −6.181 | 8.460 |
| Benzodiazepine | −0.475 | −0.015 | 0.821 | −4.728 | 3.778 |
| Intravesical instillation of GAG | 1.736 | 0.068 | 0.208 | −1.022 | 4.493 |
| Other pharmacological treatments | −1.645 | −0.064 | 0.322 | −4.991 | 1.701 |
| Hysterectomy | 0.836 | 0.016 | 0.704 | −3.623 | 5.294 |
| Other surgical interventions | −0.168 | −0.006 | 0.918 | −3.490 | 3.155 |
| Caesarean section | 0.627 | 0.010 | 0.856 | −6.372 | 7.625 |
| Eutocic delivery | −0.859 | −0.030 | 0.482 | −3.328 | 1.610 |
| Results | 22.524 | 0.755 | 0.00095 | 26.690 | 18.359 |
| Multiple Regression Analysis in BFB− | |||||
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | p-Value | 95.0% Confidence Interval for B | ||
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| Age | −0.016 | −0.013 | 0.452 | −0.058 | 0.026 |
| BMI | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.871 | −0.128 | 0.151 |
| SF-36 pretreatment | 0.047 | 0.018 | 0.373 | −0.058 | 0.152 |
| Evolution time in years | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | 0.998 | −0.105 | 0.104 |
| Time disease free | −0.014 | −0.005 | 0.774 | −0.108 | 0.081 |
| Other pathological | −1.839 | −0.059 | 0.003 | −3.020 | −0.659 |
| Overactive bladder | 3.559 | 0.057 | 0.007 | 1.002 | 6.116 |
| Benzodiazepine | 2.038 | 0.057 | 0.062 | −0.107 | 4.182 |
| Intravesical instillation of GAG | 2.870 | 0.087 | 0.008 | 0.780 | 4.961 |
| Other pharmacological treatments | −2.264 | −0.067 | 0.057 | −4.594 | 0.066 |
| Other surgical interventions | −0.443 | −0.012 | 0.739 | −3.088 | 2.203 |
| Gynecological cancer surgery | 0.960 | 0.007 | 0.684 | −3.738 | 5.658 |
| Results | −31.568 | −0.991 | 0.0005 | −32.842 | −30.293 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrego-Jimenez, P.-S.; Flores-Fraile, J.; Padilla-Fernández, B.-Y.; Valverde-Martinez, S.; Gómez-Prieto, A.; Márquez-Sánchez, M.T.; Mirón-Canelo, J.-A.; Lorenzo-Gómez, M.-F. Improvement in Quality of Life with Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Biofeedback in Patients with Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040862
Borrego-Jimenez P-S, Flores-Fraile J, Padilla-Fernández B-Y, Valverde-Martinez S, Gómez-Prieto A, Márquez-Sánchez MT, Mirón-Canelo J-A, Lorenzo-Gómez M-F. Improvement in Quality of Life with Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Biofeedback in Patients with Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(4):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040862
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrego-Jimenez, Pedro-Santiago, Javier Flores-Fraile, Bárbara-Yolanda Padilla-Fernández, Sebastián Valverde-Martinez, Agustín Gómez-Prieto, Magaly Teresa Márquez-Sánchez, José-Antonio Mirón-Canelo, and María-Fernanda Lorenzo-Gómez. 2021. "Improvement in Quality of Life with Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Biofeedback in Patients with Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 4: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040862
APA StyleBorrego-Jimenez, P.-S., Flores-Fraile, J., Padilla-Fernández, B.-Y., Valverde-Martinez, S., Gómez-Prieto, A., Márquez-Sánchez, M. T., Mirón-Canelo, J.-A., & Lorenzo-Gómez, M.-F. (2021). Improvement in Quality of Life with Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Biofeedback in Patients with Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(4), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040862











