Gene Expression in Pancreatic Cancer-Like Cells and Induced Pancreatic Stem Cells Generated by Transient Overexpression of Reprogramming Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice and Cell Culture
2.2. Plasmid Construction and Transfection
2.3. Teratoma/Tumor Formation
2.4. Hematoxylin–Eosin Staining
2.5. Microarray Analysis
2.6. qRT-PCR
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Generation of iPS, iTS-P and iF Cells from Mouse Pancreatic Tissue
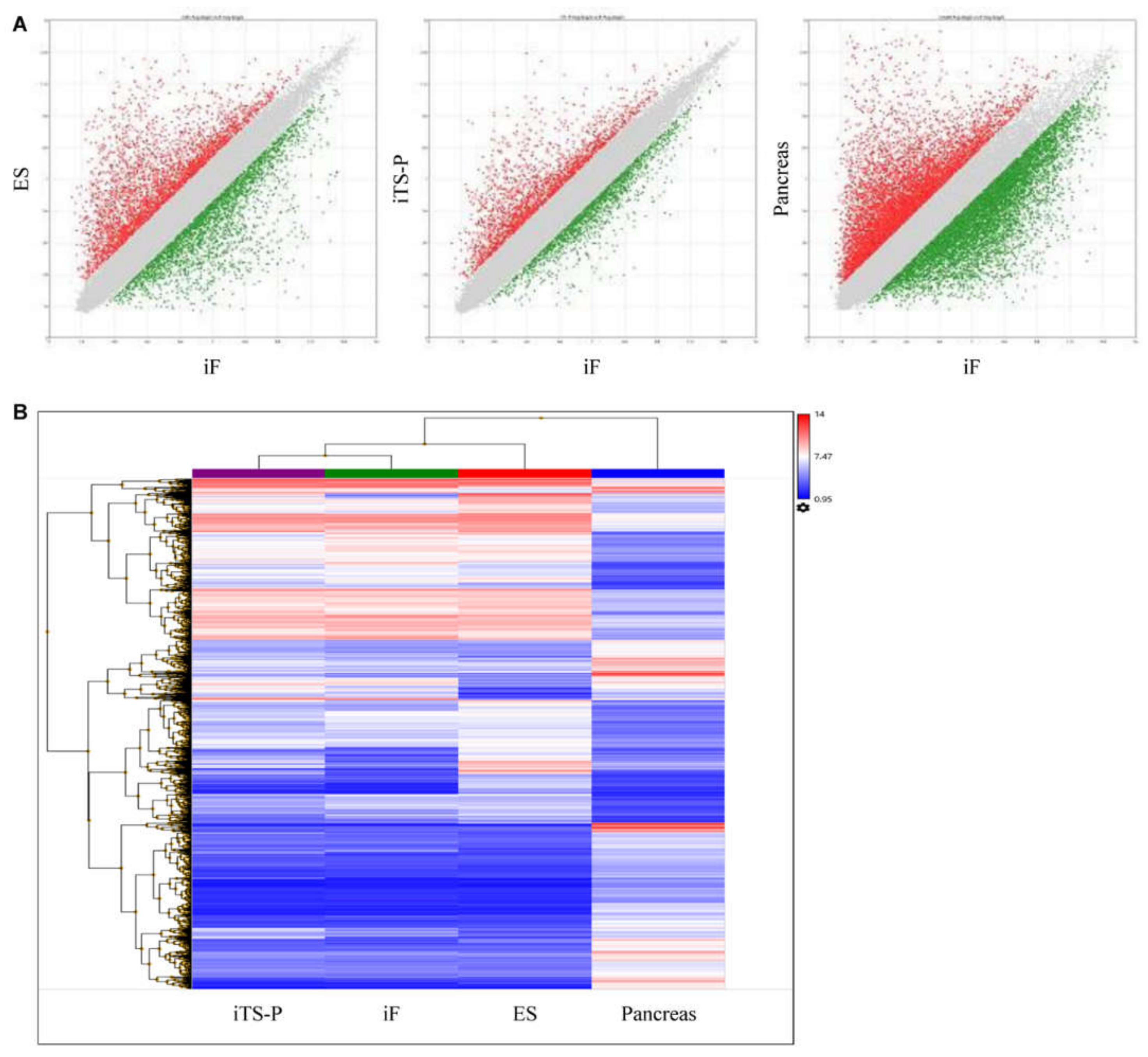
3.2. Microarray Analysis
3.3. Expression of ES Cell Markers and Endoderm/Pancreatic Markers in iF Cells and iTS-P Cells
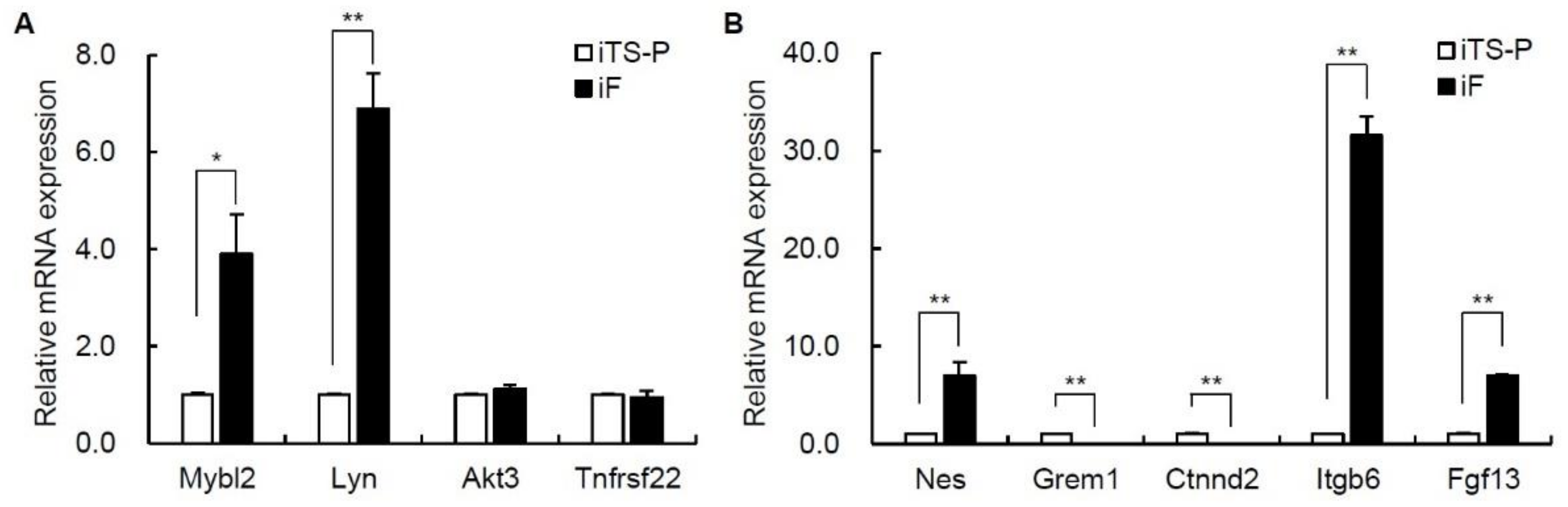
3.4. Expression of Oncogenes and Intercellular Adhesion Markers in iF Cells and iTS-P Cells
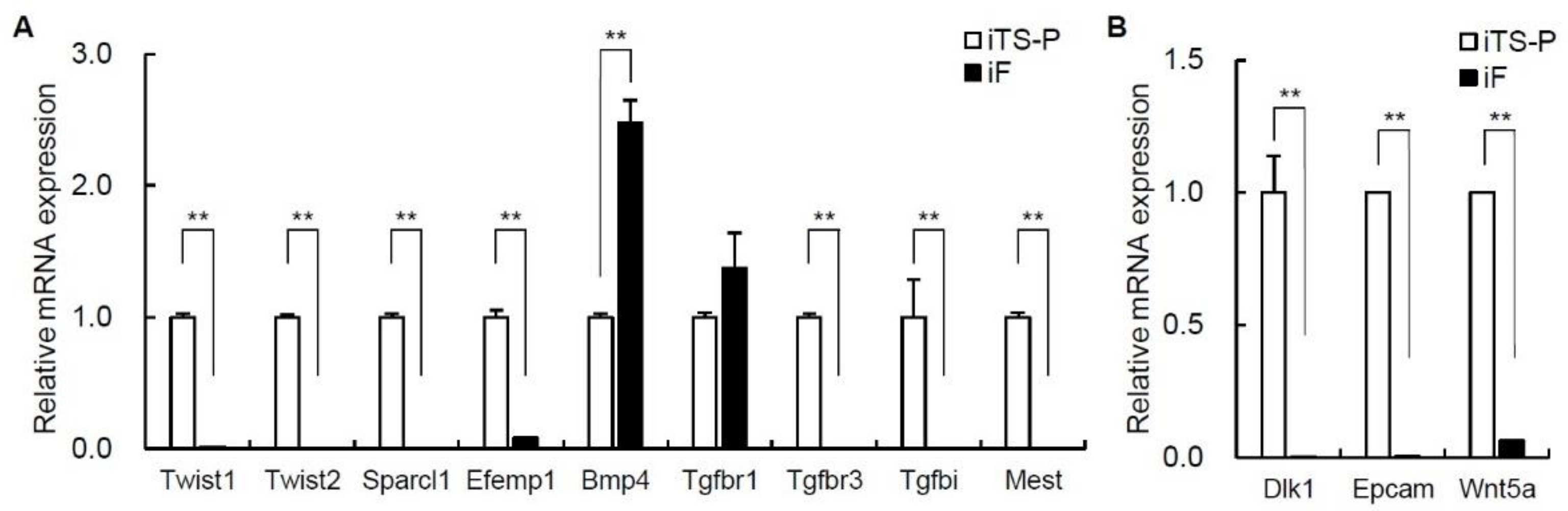
3.5. Expression of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Markers and Cell Growth Markers in iF Cells and iTS-P Cells
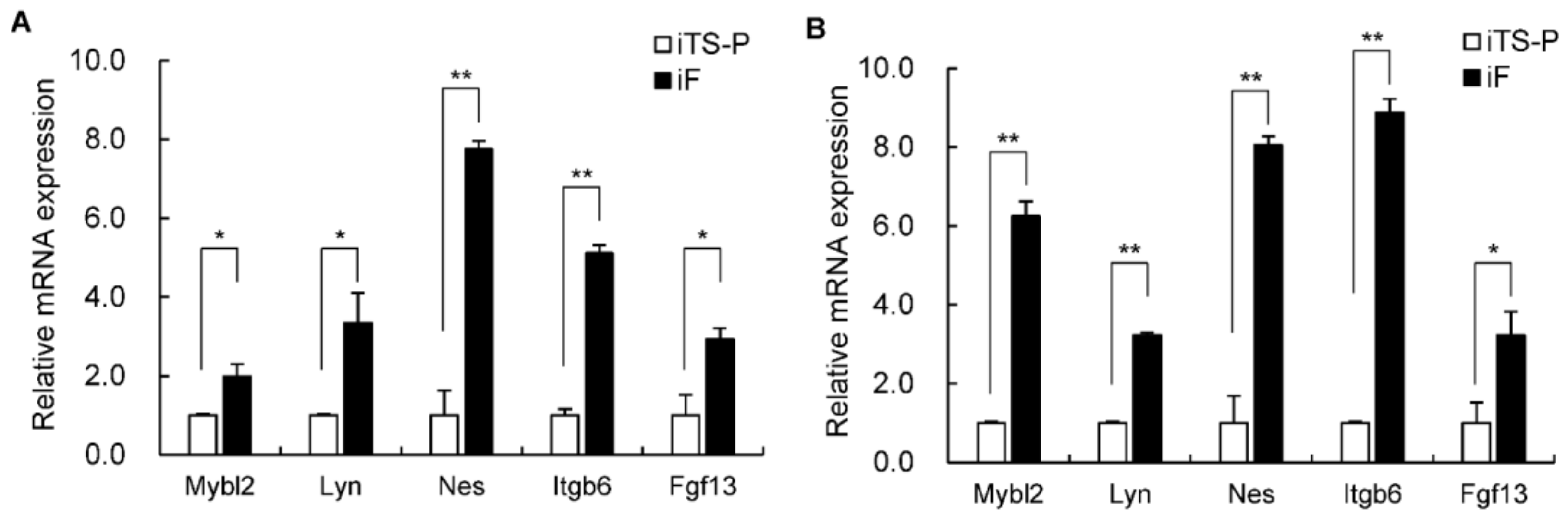
3.6. Expression of the Mybl2, Lyn, Nestin, Itgb6, and Fgf13 Genes in iF Cells and iTS-P Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Vodyanik, M.A.; Smuga-Otto, K.; Antosiewicz-Bourget, J.; Frane, J.L.; Tian, S.; Nie, J.; Jonsdottir, G.A.; Ruotti, V.; Stewart, R.; et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 2007, 318, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.H.; Zhao, R.; West, J.A.; Yabuuchi, A.; Huo, H.; Ince, T.A.; Lerou, P.H.; Lensch, M.W.; Daley, G.Q. Reprogramming of human somatic cells to pluripotency with defined factors. Nature 2008, 451, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maherali, N.; Sridharan, R.; Xie, W.; Utikal, J.; Eminli, S.; Arnold, K.; Stadtfeld, M.; Yachechko, R.; Tchieu, J.; Jaenisch, R.; et al. Directly reprogrammed fibroblasts show global epigenetic remodeling and widespread tissue contribution. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okita, K.; Ichisaka, T.; Yamanaka, S. Generation of germline-competent induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2007, 448, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernig, M.; Meissner, A.; Foreman, R.; Brambrink, T.; Ku, M.; Hochedlinger, K.; Bernstein, B.E.; Jaenisch, R. In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. Nature 2007, 448, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okita, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Hyenjong, H.; Ichisaka, T.; Yamanaka, S. Generation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells without viral vectors. Science 2008, 322, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okita, K.; Matsumura, Y.; Sato, Y.; Okada, A.; Morizane, A.; Okamoto, S.; Hong, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Tanabe, K.; Tezuka, K.; et al. A more efficient method to generate integration-free human iPS cells. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hu, K.; Smuga-Otto, K.; Tian, S.; Stewart, R.; Slukvin, I.I.; Thomson, J.A. Human induced pluripotent stem cells free of vector and transgene sequences. Science 2009, 324, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtfeld, M.; Nagaya, M.; Utikal, J.; Weir, G.; Hochedlinger, K. Induced pluripotent stem cells generated without viral integration. Science 2008, 322, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, N. Effcient generation of human iPSCs by a synthetic self-replicative RNA. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Okada, Y.; Aoi, T.; Okada, A.; Takahashi, K.; Okita, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Koyanagi, M.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; et al. Variation in the safety of induced pluripotent stem cell lines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, U.; Benvenisty, N. The tumorigenicity of human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Lee, A.S.; Volkmer, J.P.; Sahoo, D.; Nag, D.; Mosley, A.R.; Inlay, M.A.; Ardehali, R.; Chavez, S.L.; Pera, R.R.; et al. An antibody against SSEA-5 glycan on human pluripotent stem cells enables removal of teratoma-forming cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriebl, K.; Satianegara, G.; Hwang, A.; Tan, H.L.; Fong, W.J.; Yang, H.H.; Jungbauer, A.; Choo, A. Selective removal of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells using magnetic activated cell sorting followed by a cytotoxic antibody. Tissue Eng. Part A 2012, 18, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, A.B.; Tan, H.L.; Ang, S.N.; Fong, W.J.; Chin, A.; Lo, J.; Zheng, L.; Hentze, H.; Philp, R.J.; Oh, S.K.; et al. Selection against undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells by a cytotoxic antibody recognizing podocalyxin-like protein-1. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Saitoh, I.; Tsugata, T.; Kataoka, H.; Watanabe, M.; Noguchi, Y. Induction of tissue-specific stem cells by reprogramming factors, and tissue-specific selection. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, I.; Sato, M.; Soda, M.; Inada, E.; Iwase, Y.; Murakami, T.; Ohshima, H.; Hayasaki, H.; Noguchi, H. Tissue-Specific Stem Cells Obtained by Reprogramming of Non-Obese Diabetic (NOD) Mouse-Derived Pancreatic Cells Confer Insulin Production in Response to Glucose. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi-Shiohira, C.; Nakashima, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Saitoh, I.; Watanabe, M.; Noguchi, H. Characterization of induced tissue-specific stem cells from pancreas by a synthetic self-replicative RNA. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi-Shiohira, C.; Saitoh, I.; Watanabe, M.; Noguchi, H. Kyoto probe-1 reveals phenotypic differences between mouse ES cells and iTS-P cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi-Shiohira, C.; Nakashima, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Kitamura, S.; Saitoh, I.; Watanabe, M.; Noguchi, H. Induction of Expandable Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Aged Mesenchymal Stem Cells by a Synthetic Self-Replicating RNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, H.; Miyagi-Shiohira, C.; Nakashima, Y.; Kinjo, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Saitoh, I.; Watanabe, M.; Shapiro, A.M.J.; Kin, T. Induction of Expandable Tissue-Specific Progenitor Cells from Human Pancreatic Tissue through Transient Expression of Defined Factors. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2019, 13, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panciera, T.; Azzolin, L.; Fujimura, A.; Di Biagio, D.; Frasson, C.; Bresolin, S.; Soligo, S.; Basso, G.; Bicciato, S.; Rosato, A.; et al. Induction of Expandable Tissue-Specific Stem/Progenitor Cells through Transient Expression of YAP/TAZ. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, F.; Chang, M.; Liu, X.; et al. Conversion of Human Gastric Epithelial Cells to Multipotent Endodermal Progenitors using Defined Small Molecules. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Doi, A.; Wen, B.; Ng, K.; Zhao, R.; Cahan, P.; Kim, J.; Aryee, M.J.; Ji, H.; Ehrlich, L.I.; et al. Epigenetic memory in induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2010, 467, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, J.M.; Liu, S.; Figueroa, M.E.; Kulalert, W.; Eminli, S.; Tan, K.Y.; Apostolou, E.; Stadtfeld, M.; Li, Y.; Shioda, T.; et al. Cell type of origin influences the molecular and functional properties of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, A.; Park, I.H.; Wen, B.; Murakami, P.; Aryee, M.J.; Irizarry, R.; Herb, B.; Ladd-Acosta, C.; Rho, J.; Loewer, S.; et al. Differential methylation of tissue- and cancer-specific CpG island shores distinguishes human induced pluripotent stem cells, embryonic stem cells and fibroblasts. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, R.; Pelizzola, M.; Kida, Y.S.; Hawkins, R.D.; Nery, J.R.; Hon, G.; Antosiewicz-Bourget, J.; O’Malley, R.; Castanon, R.; Klugman, S.; et al. Hotspots of aberrant epigenomic reprogramming in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2011, 471, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohi, Y.; Qin, H.; Hong, C.; Blouin, L.; Polo, J.M.; Guo, T.; Qi, Z.; Downey, S.L.; Manos, P.D.; Rossi, D.J.; et al. Incomplete DNA methylation underlies a transcriptional memory of somatic cells in human iPS cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Nur, O.; Russ, H.A.; Efrat, S.; Benvenisty, N. Epigenetic memory and preferential lineage-specific differentiation in induced pluripotent stem cells derived from human pancreatic islet beta cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi-Shiohira, C.; Nakashima, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Saitoh, I.; Watanabe, M.; Noguchi, Y.; Kinjo, T.; Noguchi, H. The Development of Cancer through the Transient Overexpression of Reprogramming Factors. Cell Med. 2018, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Porath, I.; Thomson, M.W.; Carey, V.J.; Ge, R.; Bell, G.W.; Regev, A.; Weinberg, R.A. An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, H.; Komura, S.; Yamada, Y.; Sankoda, N.; Tanaka, A.; Ukai, T.; Kabata, M.; Sakurai, S.; Kuze, B.; Woltjen, K.; et al. In vivo reprogramming drives Kras-induced cancer development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastushenko, I.; Brisebarre, A.; Sifrim, A.; Fioramonti, M.; Revenco, T.; Boumahdi, S.; Van Keymeulen, A.; Brown, D.; Moers, V.; Lemaire, S.; et al. Identification of the tumour transition states occurring during EMT. Nature 2018, 556, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, K.; Semi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Shimizu, M.; Tanaka, A.; Mitsunaga, K.; Okita, K.; Osafune, K.; Arioka, Y.; Maeda, T.; et al. Premature termination of reprogramming in vivo leads to cancer development through altered epigenetic regulation. Cell 2014, 156, 663–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, J.; Aynaud, M.M.; Mirabeau, O.; Delattre, O.; Grünewald, T.G. MYBL2 (B-Myb): A central regulator of cell proliferation, cell survival and differentiation involved in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Zhang, J. Oncogenic role of LYN in human gastric cancer via the Wnt/β-catenin and AKT/mTOR pathways. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.J.; Hua, K.; Singh, A. Molecular Pathogenesis of Pancreatic Cancer. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2016, 144, 241–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kure, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Hagio, M.; Ueda, J.; Naito, Z.; Ishiwata, T. Expression of cancer stem cell markers in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamahatsu, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Ishiwata, T.; Uchida, E.; Naito, Z. Nestin as a novel therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer via tumor angiogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meecham, A.; Marshall, J.F. The ITGB6 gene: Its role in experimental and clinical biology. Gene X 2019, 5, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missiaglia, E.; Dalai, I.; Barbi, S.; Beghelli, S.; Falconi, M.; della Peruta, M.; Piemonti, L.; Capurso, G.; Di Florio, A.; delle Fave, G.; et al. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: Expression profiling evidences a role for AKT-mTOR pathway. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Murata, K.; Hirose, R.; Matsuda, C.; Komatsu, T.; Ikekita, M.; Nakawatari, M.; Nakayama, F.; Wakatsuki, M.; Ohno, T.; et al. Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Kang, S.G.; Jin, W. MEST induces Twist-1-mediated EMT through STAT3 activation in breast cancers. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2594–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, S.; Satoh, K.; Hirota, M.; Kimura, K.; Kanno, A.; Masamune, A.; Shimosegawa, T. Bone morphogenetic protein 4 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through MSX2 induction on pancreatic cancer cell line. J. Cell Physiol. 2007, 213, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M.; Derynck, R.; Miyazono, K. TGF-β and the TGF-β Family: Context-Dependent Roles in Cell and Tissue Physiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazono, K.; Ehata, S.; Koinuma, D. Tumor-promoting functions of transforming growth factor-β in progression of cancer. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2012, 117, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.J.; Yang, M.H. The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2011, 2, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traustadóttir, G.Á.; Lagoni, L.V.; Ankerstjerne, L.B.S.; Bisgaard, H.C.; Jensen, C.H.; Andersen, D.C. The imprinted gene Delta like non-canonical Notch ligand 1 (Dlk1) is conserved in mammals, and serves a growth modulatory role during tissue development and regeneration through Notch dependent and independent mechanisms. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 46, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Nakamura, K.; Hijioka, S.; Kamei, A.; Ikari, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Shinozaki, E.; Mizunuma, N.; Hatake, K.; Miyajima, A. Dlk-1, a cell surface antigen on foetal hepatic stem/progenitor cells, is expressed in hepatocellular, colon, pancreas and breast carcinomas at a high frequency. J. Biochem. 2010, 148, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Schleiffarth, J.R.; Jessurun, J.; Sumanas, S.; Petryk, A.; Lin, S.; Ekker, S.C. Wnt5 signaling in vertebrate pancreas development. BMC Biol. 2005, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, H.; Gao, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, M. Upregulation of the expression of Wnt5a promotes the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in a nude mouse model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| iTS-P Ave (log2) | iF Ave (log2) | Fold Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ES marker | |||
| Sox2 | 5.39 | 3.67 | 3.3 |
| Oct3/4 | 6.98 | 4.76 | 4.66 |
| Myc-n | 5.68 | 2.92 | 6.8 |
| Endoderm/Pancreatic marker | |||
| Reg3b | 12.56 | 4.16 | 337.13 |
| Reg1 | 11.69 | 4.52 | 143.91 |
| Reg3g | 10.1 | 4.41 | 51.61 |
| Mafa | 5.39 | 3.67 | 3.3 |
| Sox9 | 7.11 | 5.26 | 3.63 |
| Oncogene | |||
| Mybl2 | 5.18 | 7.21 | −4.09 |
| Lyn | 5.28 | 7.29 | −4.03 |
| Akt3 | 3.88 | 5.73 | −3.62 |
| Tnfrsf22 | 4.58 | 6.82 | −4.75 |
| Intercellular adhesion marker | |||
| Nes | 2.08 | 6.49 | −21.27 |
| Grem1 | 9.72 | 4.55 | 35.85 |
| Ctnnd2 | 4.64 | 2.5 | 4.42 |
| Itgb6 | 3.65 | 6.76 | −8.61 |
| Fgf13 | 3.42 | 6.42 | −7.98 |
| EMT marker | |||
| Twist1 | 6.48 | 3.77 | 6.53 |
| Twist2 | 6.18 | 4.2 | 3.93 |
| Sparcl1 | 4.39 | 2.38 | 4.03 |
| Efemp1 | 10.76 | 6.65 | 17.32 |
| Bmp4 | 5.47 | 7.09 | −3.08 |
| Tgfbr1 | 3.99 | 7.34 | −10.15 |
| Tgfbr3 | 8.53 | 4.22 | 19.82 |
| Tgfbi | 4.97 | 2.06 | 7.51 |
| Mest | 6.66 | 4.23 | 5.41 |
| Cell growth regulation factor | |||
| Dlk1 | 8.83 | 4.26 | 23.66 |
| Epcam | 10.63 | 4.14 | 90.04 |
| Wnt5a | 5.87 | 2.3 | 11.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyagi-Shiohira, C.; Saitoh, I.; Watanabe, M.; Noguchi, H. Gene Expression in Pancreatic Cancer-Like Cells and Induced Pancreatic Stem Cells Generated by Transient Overexpression of Reprogramming Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10030454
Miyagi-Shiohira C, Saitoh I, Watanabe M, Noguchi H. Gene Expression in Pancreatic Cancer-Like Cells and Induced Pancreatic Stem Cells Generated by Transient Overexpression of Reprogramming Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(3):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10030454
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyagi-Shiohira, Chika, Issei Saitoh, Masami Watanabe, and Hirofumi Noguchi. 2021. "Gene Expression in Pancreatic Cancer-Like Cells and Induced Pancreatic Stem Cells Generated by Transient Overexpression of Reprogramming Factors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 3: 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10030454
APA StyleMiyagi-Shiohira, C., Saitoh, I., Watanabe, M., & Noguchi, H. (2021). Gene Expression in Pancreatic Cancer-Like Cells and Induced Pancreatic Stem Cells Generated by Transient Overexpression of Reprogramming Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(3), 454. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10030454






