Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury after Acute Stroke—Insights from a German Tertiary Care Center
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
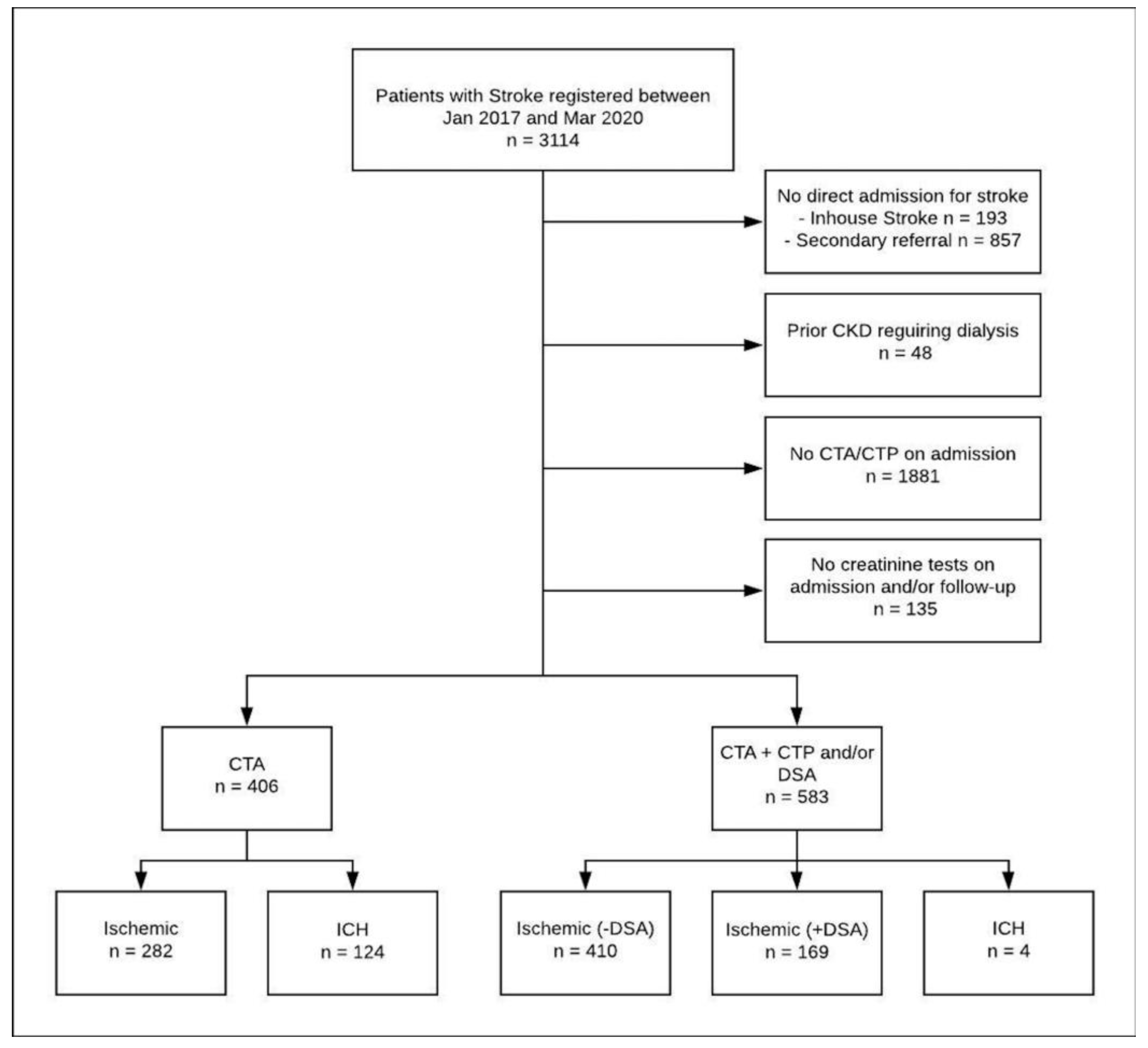
2.1. Data Source and Study Population
2.2. Imaging Protocol
2.3. Hydration Protocol
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
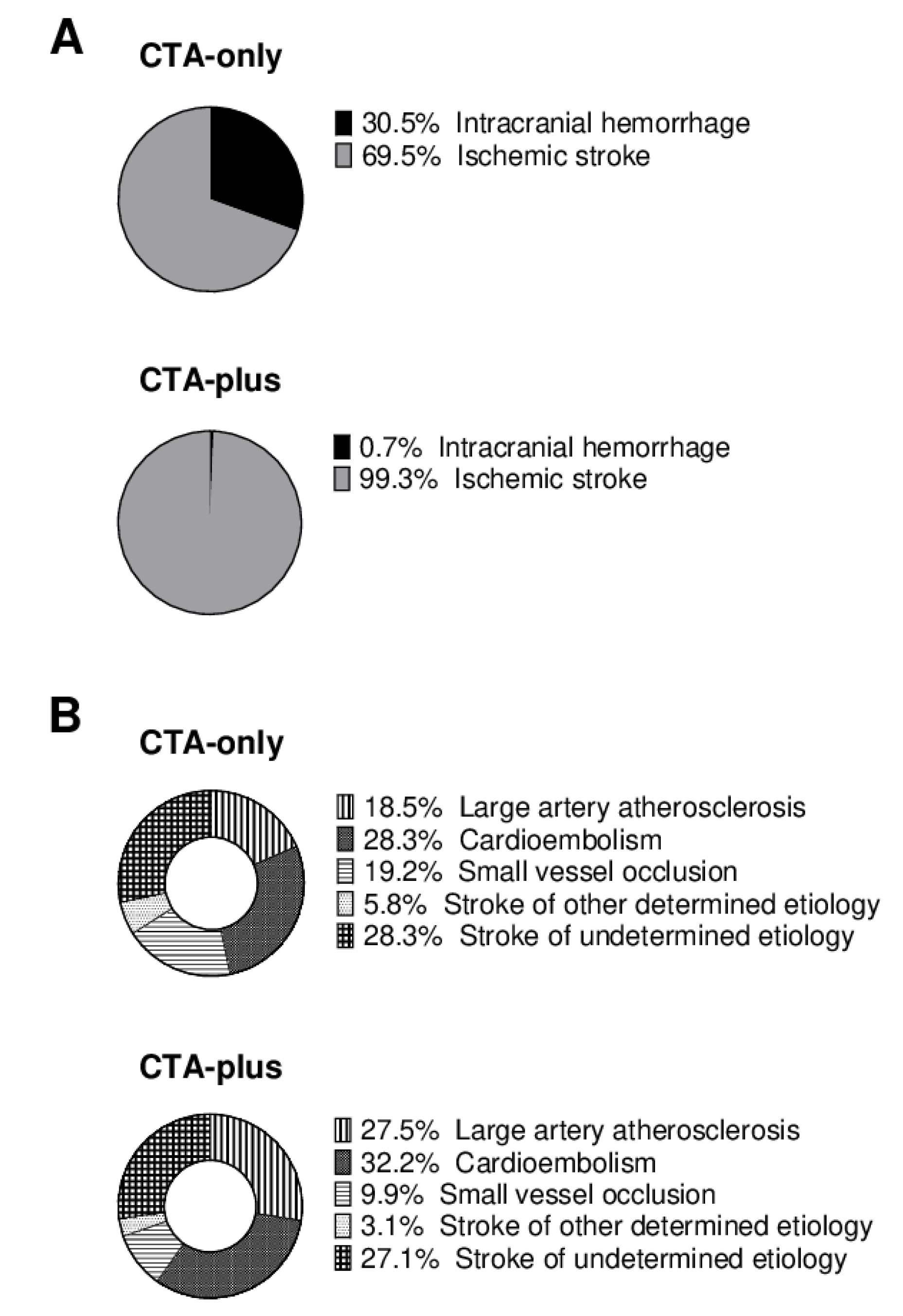
3.1. Incidence of Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury and Underlying Causes
3.2. Predictors of Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macleod, M.R.; Campbell, B.C.; Parsons, M.W.; Churilov, L.; Levi, C.; Hsu, C.; Kleinig, T.J.; Wijeratne, T.; Curtze, S.; Dewey, H.M.; et al. Thrombolysis Guided by Perfusion Imaging up to 9 Hours after Onset of Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, J.J.; Wintermark, M. Perfusion Computed Tomography for the Evaluation of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacGregor, K.; Li, I.; Dowdell, T.; Gray, B.G. Identifying Institutional Diagnostic Reference Levels for CT with Radiation Dose Index Monitoring Software. Radiology 2015, 276, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zensen, S.; Guberina, N.; Opitz, M.; Köhrmann, M.; Deuschl, C.; Forsting, M.; Wetter, A.; Bos, D. Radiation exposure of computed tomography imaging for the assessment of acute stroke. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diprose, W.K. Contrast-Associated Acute Kidney Injury in Endovascular Thrombectomy Patients with and Without Baseline Renal Impairment. Stroke 2019, 50, 3527–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laible, M.; Jenetzky, E.; Möhlenbruch, M.A.; Bendszus, M.; Ringleb, P.A.; Rizos, T. The Impact of Post-contrast Acute Kidney Injury on In-hospital Mortality After Endovascular Thrombectomy in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 665614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Molen, A.J.; Reimer, P.; Dekkers, I.A.; Bongartz, G.; Bellin, M.-F.; Bertolotto, M.; Clement, O.; Heinz-Peer, G.; Stacul, F.; Webb, J.A.W.; et al. Post-contrast acute kidney injury—Part 1: Definition, clinical features, incidence, role of contrast medium and risk factors. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brinjikji, W.; Demchuk, A.; Murad, M.H.; Rabinstein, A.A.; McDonald, R.J.; McDonald, J.S.; Kallmes, D.F. Neurons Over Nephrons. Stroke 2017, 48, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopyan, J.; Gladstone, D.; Mallia, G.; Schiff, J.; Fox, A.; Symons, S.; Buck, B.; Black, S.; Aviv, R. Renal Safety of CT Angiography and Perfusion Imaging in the Emergency Evaluation of Acute Stroke. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1826–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, R.; van Hal, R.; Stracke, P.; Hadisurya, J.; Nordmeyer, H.; Chapot, R. Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury After Computed Tomography Angiography±Computed Tomography Perfusion Followed by Thrombectomy in Patients with Stroke Using a Postprocedural Hydration Protocol. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2020, 9, e014418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereda, C.W.; Mlynash, M.; Cippà, P.E.; Kemp, S.; Heit, J.J.; Marks, M.P.; Lansberg, M.G.; Albers, G.W. Renal Safety of Multimodal Brain Imaging Followed by Endovascular Therapy. Stroke 2021, 52, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myung, J.W. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Radiologic Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke in the Emergency Setting. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorrilla-Vaca, A.; Ziai, W.; Connolly, E.S., Jr.; Geocadin, R.; Thompson, R.; Rivera-Lara, L. Acute Kidney Injury Following Acute Ischemic Stroke and Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Meta-Analysis of Prevalence Rate and Mortality Risk. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Huang, W.; Lobanova, I.; Hanley, D.F.; Hsu, C.Y.; Malhotra, K.; Steiner, T.; Suarez, J.I.; Toyoda, K.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. Systolic Blood Pressure Reduction and Acute Kidney Injury in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2020, 51, 3030–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, L.G.; Goyal, N.; Jones, G.M.; Khorchid, Y.; Kerro, A.; Chapple, K.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Alexandrov, A.V.; Chang, J.J. Evaluation of Acute Kidney Injury and Mortality After Intensive Blood Pressure Control in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | CTA-Only (n = 406) | CTA-Plus (n = 583) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 70.5 (13.6) | 72.6 (13.6) | 0.020 |
| Sex: male | 231 (56.9) | 276/583 (47.3) | 0.003 |
| Hypertension | 307 (75.6) | 461 (79.1) | 0.199 |
| Diabetes | 96 (23.6) | 193 (33.1) | 0.001 |
| Chronic Kidney Disease | 15 (3.7) | 18 (3.1) | 0.601 |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 120 (29.6) | 196 (33.6) | 0.243 |
| Coronary Artery Disease | 69 (17.0) | 110 (18.9) | 0.452 |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | 29 (7.1) | 41 (7.0) | 0.947 |
| Premorbid Dependency a | 29 (7.4) | 46 (7.9) | 0.755 |
| Tumor disease | 71 (17.5) | 90 (15.4) | 0.088 |
| Smoking | 85 (20.9) | 134 (23.0) | 0.125 |
| Pior Stroke | 106 (26.1) | 145 (24.9) | 0.765 |
| Prior TIA | 13 (3.2) | 22 (3.8) | 0.338 |
| NIHSS | 6.0 (2.0–12.0) | 7.0 (4.0–13.0) | 0.001 |
| Thrombolysis | 85 (20.9) | 332 (56.9) | <0.001 |
| Time (h) from symptom onset | 4.1 (1.2–17.1) | 2.8 (1.1–9.3) | <0.001 |
| Contrast Agent (mL) | 70.0 (70.0–70.0) | 120.0 (120.0–120.0) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 1.1 (0.9–1.3) | 0.300 |
| Covariate Effect | Group Effect | |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Sex, male vs. female | 0.73 (0.33–1.61) | 0.90 (0.39–2.05) |
| Age, per additional year | 1.00 (0.97–1.03) | 0.92 (0.40–2.08) |
| Chronic Kidney Disease, Yes vs. No | 9.25 (3.18–26.9) | 0.90 (0.39–2.07) |
| Premorbid Dependency, Yes vs. No | 1.14 (0.26–4.96) | 1.15 (0.47–2.81) |
| Diabetes, Yes vs. No | 1.22 (0.54–2.79) | 0.90 (0.40–2.06) |
| Hypertension, Yes vs. No | 1.55 (0.53–4.55) | 0.91 (0.40–2.07) |
| Coronary Artery Disease, Yes vs. No | 2.26 (0.99–5.18) | 0.93 (0.41–2.13) |
| NIHSS at Admission, per increment | 1.05 (1.01–1.09) | 0.80 (0.35–1.84) |
| Altered LOC at Admission, Yes vs. No | 1.58 (1.00–2.49) | 0.90 (0.40–2.05) |
| GFR < 30 mL/min, Yes vs. No § | 7.47 (1.88–29.7) | 1.14 (0.42–3.11) |
| Creatinine, per increment | 1.72 (1.10–2.70) | 0.96 (0.42–2.19) |
| Time from Onset to Admission, per increment | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 1.01 (0.43–2.38) |
| Atrial Fibrillation, Yes vs. No | 0.73 (0.30–1.76) | 0.92 (0.40–2.09) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frank, B.; Escolà, J.K.; Biermann-Ratjen, L.; Hüsing, A.; Li, Y.; Dammann, P.; Sure, U.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Forsting, M.; Köhrmann, M.; et al. Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury after Acute Stroke—Insights from a German Tertiary Care Center. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235684
Frank B, Escolà JK, Biermann-Ratjen L, Hüsing A, Li Y, Dammann P, Sure U, Kleinschnitz C, Forsting M, Köhrmann M, et al. Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury after Acute Stroke—Insights from a German Tertiary Care Center. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(23):5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235684
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrank, Benedikt, Jordi Kühne Escolà, Leoni Biermann-Ratjen, Anika Hüsing, Yan Li, Philipp Dammann, Ulrich Sure, Christoph Kleinschnitz, Michael Forsting, Martin Köhrmann, and et al. 2021. "Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury after Acute Stroke—Insights from a German Tertiary Care Center" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 23: 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235684
APA StyleFrank, B., Escolà, J. K., Biermann-Ratjen, L., Hüsing, A., Li, Y., Dammann, P., Sure, U., Kleinschnitz, C., Forsting, M., Köhrmann, M., & Deuschl, C. (2021). Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury after Acute Stroke—Insights from a German Tertiary Care Center. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(23), 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235684








