Prenatal Anxiety and Exercise. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Comparison
2.4. Outcomes
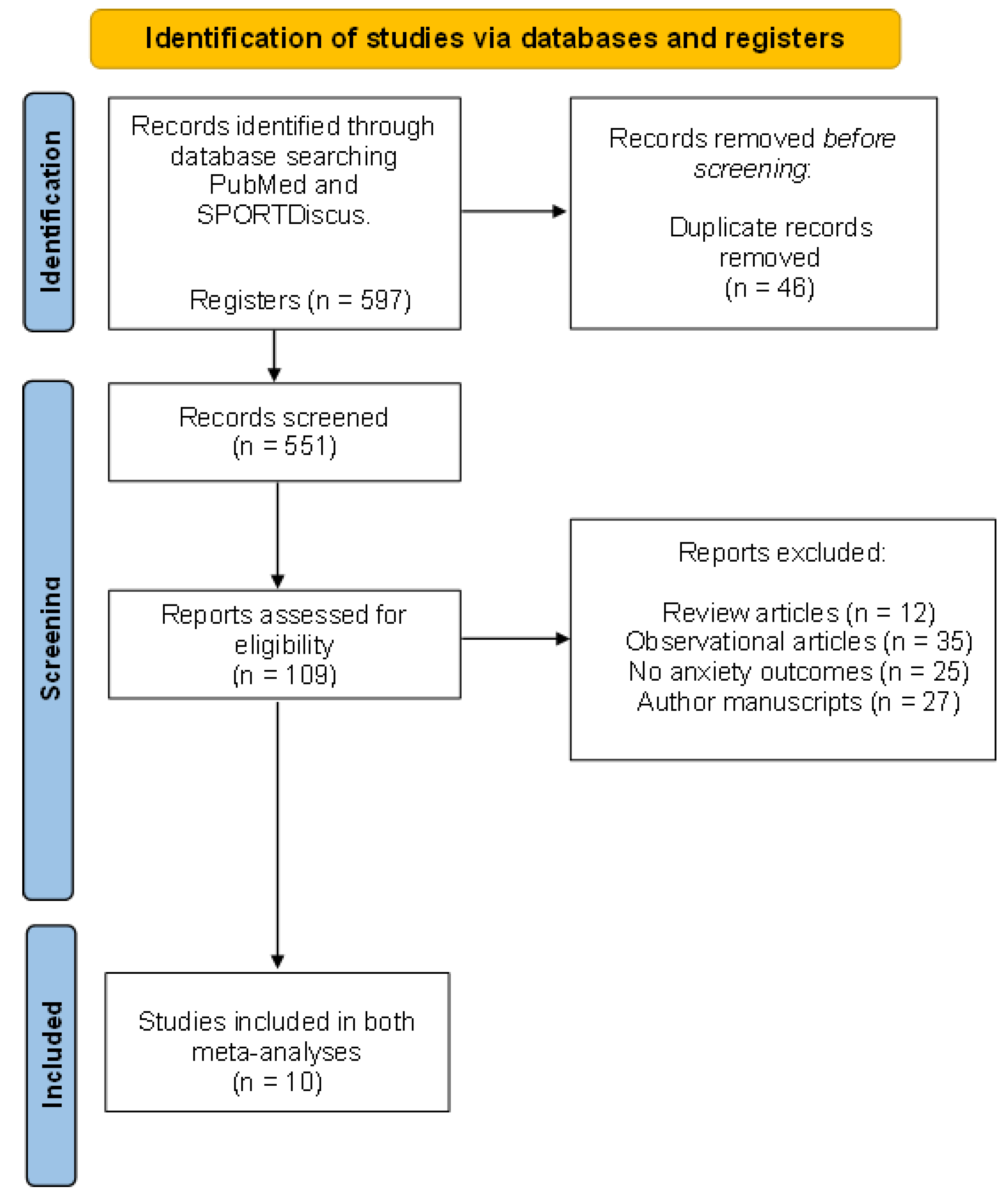
2.5. Study Design and Selection Process
- English: physical activity OR exercise OR sport OR fitness AND pregnant population OR pregnancy OR prenatal anxiety OR anxiety OR emotional OR emotional factors OR mental disorders.
- Spanish: actividad física O ejercicio O ejercicio físico O deportes Y población gestante O embarazo O ansiedad prenatal O ansiedad O emocional O factores emocionales O desórdenes mentales.
| Author, Year and Country | N; IG; CG | Intervention. Physical Activity Program | Main Variables Analysed | Secondary Variables Analysed | Co-Intervention | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W Freq. | Int. | Time | Type | Sup. | Duration | |||||
| Rong et al., 2021. China [17] | 64; 32; 32 | 3 | Mod | 22–34 * | Yoga | Yes | 60 min | Physiological discomforts, prenatal depression and anxiety | Childbirth self-efficacy and delivery outcomes | No |
| Gallagher et al., 2020. United States [18] | 79; 48; 31 | 2 | Mod | 2–32 * | Yoga | Yes | 30 min | Prenatal anxiety and depression | Demographic data | No |
| Mohyadin et al., 2020. Iran [19] | 84; 42; 42 | 3 | Mod | 26–36 | Yoga | Yes | 20–60 min | Prenatal anxiety, labour pain, and length of labour stages | Neonatal apgar score, mode of delivery, and demographic data | No |
| Davis et al., 2015. United States [20] | 46; 23; 23 | 1 | Mod | 20–28 * | Yoga | Yes | 75 min | Prenatal anxiety and depression | Maternal outcomes | No |
| Guszkowska et al., 2015. Poland [21] | 109; 62; 47 | 2 | - | 27–35 * | Pilates, Yoga, body ball, muscle strength, stretching and joint mobility exercises | Yes | 50 min | Mental health (somatic symptoms, anxiety and insomnia, social dysfunctions severe depression | Sociodemographic variables | Traditional prenatal classes |
| Field et al., 2013. United States [22] | 79; 40; 39 | 1 | Mod | 22–34 | Yoga | No | 20 min | Prenatal and postnatal anxiety and depression | Different hormone levels | No |
| Field et al., 2013. United States [23] | 75; 37; 38 | 1 | Mod | 22–34 * | Tai-chi/Yoga | Yes | 20 min | Prenatal anxiety and depression | Psychotic and somatic disorders in pregnancy | No |
| Satyapriya et al., 2013. India [24] | 96; 51; 45 | 7 | Mod | 18/20–34/ | Yoga | Yes | 60 min | Prenatal anxiety and depression | Sociodemographic data | Yoga sessions at home |
| Field et al., 2012. United States [25] | 84; 28; 28–28 | 2 | Mod | 20–32 * | Yoga | Yes | 20 min | Prenatal anxiety and depression | Back and legs pain | No |
| Ji et al., 2010. Korea [26] | 70; 33; 37 | 2 | Mod | 23–35 * | Qi exercises (yoga, breathing and meditation exercises) | Yes | 90 min | Maternal/foetal interaction, prenatal depression and anxiety, and physical well-being | Sociodemographic data | No |
2.6. Statistical Analysis, Quality of Evidence Assessment, and Risk of Bias
3. Results
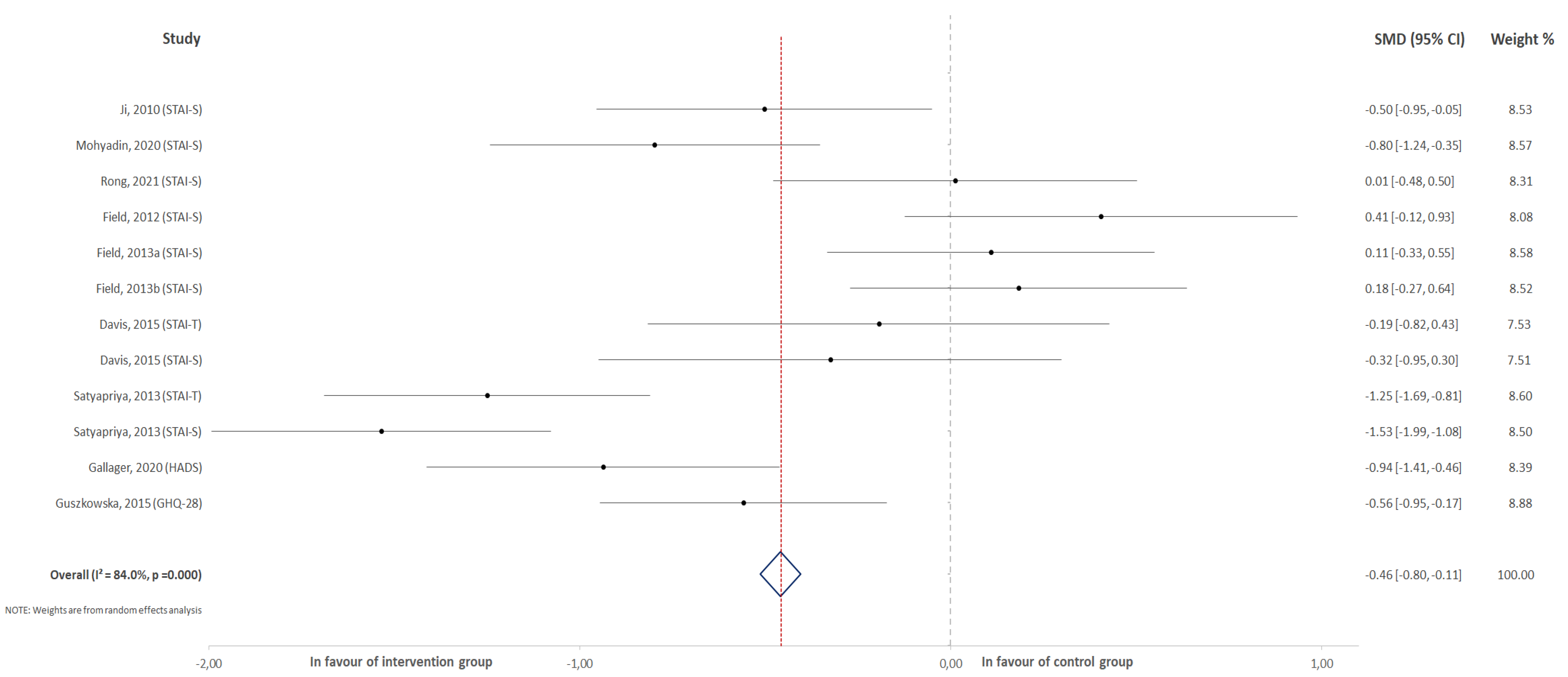
3.1. Effect of Physical Activity on the Overall Score for Anxiety
3.2. Effect of Physical Activity on the Score Change for Overall Anxiety
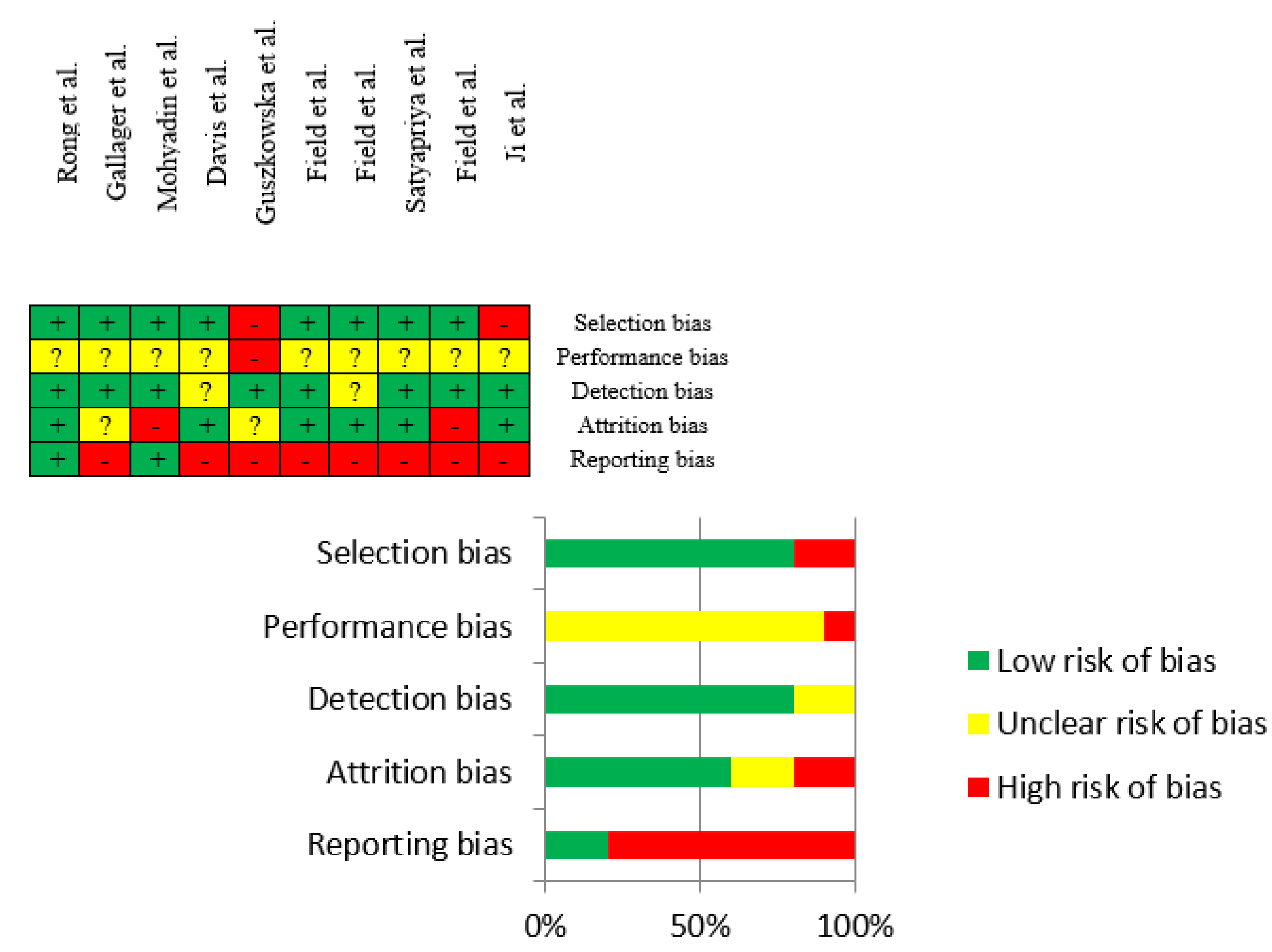
3.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santomauro, D.F.; Mantilla Herrera, A.M.; Shadid, J.; Zheng, P.; Ashbaugh, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Abbafati, C.; Adolph, C.; Amlag, J.O.; Aravkin, A.Y.; et al. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagg, P.R.; Spielberger, C.D.; O’Hearn, T.P. Is the state-trait anxiety inventory multidimensional? Personal. Individ. Differ. 1980, 1, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.L.; Schwab, J.J.; Morris, R.L.; Beldia, G. Assessment of state and trait anxiety in subjects with anxiety and depressive disorders. Psychiatr. Q. 2001, 72, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, C.D.; Gorsuch, R.L.; Lushene, R.E. Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (“Self-Evaluation Questionnaire”); California Consulting Psychologists Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Leal, P.C.; Goes, T.C.; da Silva, L.C.F.; Teixeira-Silva, F. Trait vs. state anxiety in different threatening situations. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2017, 39, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, C.; MacKinnon, A.; Bagshawe, M.; Tomfohr-Madsen, L.; Giesbrecht, G. Elevated depression and anxiety symptoms among pregnant individuals during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagne, D.M. The obstetrician and depression during pregnancy. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2004, 116, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogaerts, A.; Devlieger, R.; Nuyts, E.; Witters, I.; Gyselaers, W.; Bergh, B.R.V.D. Effects of lifestyle intervention in obese pregnant women on gestational weight gain and mental health: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 37, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niles, A.N.; O’Donovan, A. Comparing anxiety and depression to obesity and smoking as predictors of major medical illnesses and somatic symptoms. Health Psychol. 2019, 38, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, M.; Refoyo, I.; Coteron, J.; Bacchi, M.; Barakat, R. Exercise During Pregnancy Attenuates Prenatal Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Eval. Health Prof. 2014, 38, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vargas-Terrones, M.; Barakat, R.; Santacruz, B.; Buihgas, I.F.; Mottola, M.F. Physical exercise programme during pregnancy decreases perinatal depression risk: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 53, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandola, A.; Stubbs, B. Exercise and Anxiety. Phys. Exerc. Hum. Health 2020, 1228, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, M.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Luaces, M.; Pareja-Galeano, H.; Garatachea, N.; Barakat, R.; Lucia, A. Maternal Cardiac Adaptations to a Physical Exercise Program during Pregnancy. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Polán, M.; Franco, E.; Silva-José, C.; Gil-Ares, J.; Pérez-Tejero, J.; Barakat, R.; Refoyo, I. Exercise During Pregnancy and Prenatal Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Wang, R.; Ouyang, Y.Q.; Redding, S.R. Efficacy of Yoga on Physiological and Psychological Discomforts and Delivery Outcomes in Chinese Primiparas. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 44, 101434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, A.; Kring, D.; Whitley, T. Effects of Yoga on Anxiety and Depression for High Risk Mothers on Hospital Bedrest. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2020, 38, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohyadin, E.; Ghorashi, Z.; Molamomanaei, Z. The Effect of Practicing Yoga during Pregnancy on Labor Stages Length, Anxiety and Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2021, 18, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Goodman, S.H.; Leiferman, J.; Taylor, M.; Dimidjian, S. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Yoga for Pregnant Women with Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2015, 21, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guszkowska, M.; Langwald, M.; Sempolska, K. Does Physical Exercise Help Maintain Mental Health during Pregnancy? A Comparison of Changes in Mental Health in Participants of Physical Exercise Classes and Childbirth Classes. J. Phys. Act. Health 2015, 12, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, T.; Diego, M.; Delgado, J.; Medina, L. Yoga and Social Support Reduce Prenatal Depression, Anxiety and Cortisol. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2013, 17, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, T.; Diego, M.; Delgado, J.; Medina, L. Tai Chi/Yoga Reduces Prenatal Depression, Anxiety and Sleep Disturbances. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2013, 19, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satyapriya, M.; Nagarathna, R.; Padmalatha, V.; Nagendra, H.R. Effect of Integrated Yoga on Anxiety, Depression & Well Being in Normal Pregnancy. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2013, 19, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, T.; Diego, M.; Hernandez-Reif, M.; Medina, L.; Delgado, J.; Hernandez, A. Yoga and Massage Therapy Reduce Prenatal Depression and Prematurity. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2012, 16, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, E.S.; Han, H.R. The Effects of Qi Exercise on Maternal/Fetal Interaction and Maternal Well-Being During Pregnancy. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Neonatal Nurs. 2010, 39, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Tipton, E.; Johnson, M.C. Robust variance estimation in meta-regression with dependent effect size estimates. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, A.; Riaz, M.; Lewis, S.; Aveyard, P.; Coleman, T.; Manyonda, I.; West, R.; Lewis, B.; Marcus, B.; Taylor, A.; et al. Physical activity for antenatal and postnatal depression in women attempting to quit smoking: Randomised controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira González, I.; Urrútia, G.; Alonso-Coello, P. Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis: Scientific Rationale and Interpretation. Rev. Española Cardiol. 2011, 64, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.; Vist, G.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE an Emerging Consensus on Rating Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. Br. Med. J. 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Sterne, J.A.C. Assessing Risk of Bias in a Randomized Trial. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Version 6.1; Higgins, J.P., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1539–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Davenport, M.H.; McCurdy, A.P.; Mottola, M.F.; Skow, R.J.; Meah, V.L.; Poitras, V.J.; Jaramillo Garcia, A.; Gray, C.E.; Barrowman, N.; Riske, L.; et al. Impact of Prenatal Exercise on Both Prenatal and Postnatal Anxiety and Depressive Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.M.; Andrade, A.; Nunes, I. Physical Exercise in Pregnancy: Benefits, Risks and Prescription. J. Perinat. Med. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadholta, P.; Bali, P.; Singh, A.; Anand, A. Potential Benefits of Yoga in Pregnancy-Related Complications during the COVID-19 Pandemic and Implications for Working Women. Work 2020, 67, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Polán, M.; Silva-Jose, C.; Franco, E.; Nagpal, T.S.; Gil-Ares, J.; Lili, Q.; Barakat, R.; Refoyo, I. Prenatal Anxiety and Exercise. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235501
Sánchez-Polán M, Silva-Jose C, Franco E, Nagpal TS, Gil-Ares J, Lili Q, Barakat R, Refoyo I. Prenatal Anxiety and Exercise. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(23):5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235501
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Polán, Miguel, Cristina Silva-Jose, Evelia Franco, Taniya S. Nagpal, Javier Gil-Ares, Qin Lili, Rubén Barakat, and Ignacio Refoyo. 2021. "Prenatal Anxiety and Exercise. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 23: 5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235501
APA StyleSánchez-Polán, M., Silva-Jose, C., Franco, E., Nagpal, T. S., Gil-Ares, J., Lili, Q., Barakat, R., & Refoyo, I. (2021). Prenatal Anxiety and Exercise. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(23), 5501. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10235501










