Plasma Neurofilament Light (NfL) in Patients Affected by Niemann–Pick Type C Disease (NPCD)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Neurofilament Light (NfL)
2.3. Plasma Cholestane-3β,5α,6β-triol Concentration
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
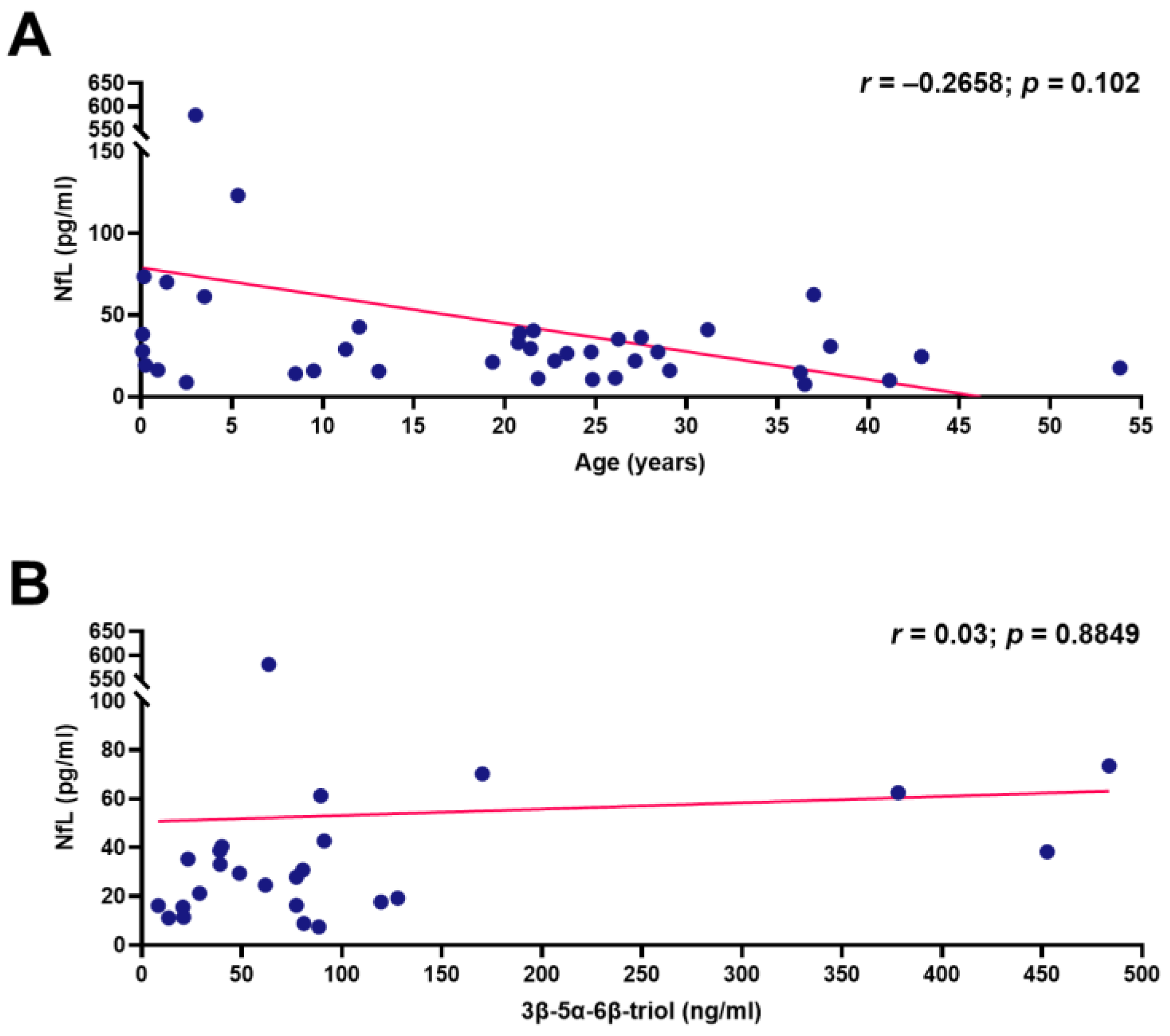
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanier, M.T. Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walterfang, M.; Fietz, M.; Fahey, M.; Sullivan, D.; Leane, P.; Lubman, D.I.; Velakoulis, D. The Neuropsychiatry of Niemann-Pick Type C Disease in Adulthood. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 18, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, M.C.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Walterfang, M.; Sedel, F.; Vanier, M.T.; Wijburg, F. Recommendations for the Diagnosis and Management of Niemann–Pick Disease Type C: An Update. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 106, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengel, E.; Klünemann, H.-H.; Lourenço, C.M.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Sedel, F.; Walterfang, M.; Kolb, S.A. Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Symptomatology: An Expert-Based Clinical Description. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Bremova-Ertl, T.; Claassen, J.; Foltan, T.; Gascon-Bayarri, J.; Gissen, P.; Hahn, A.; Hassan, A.; Hennig, A.; Jones, S.A.; Kolnikova, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of N-Acetyl-l-Leucine in Niemann–Pick Disease Type C. J. Neurol. 2021, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Sidhu, R.; Porter, F.D.; Yanjanin, N.M.; Speak, A.O.; te Vruchte, D.T.; Platt, F.M.; Fujiwara, H.; Scherrer, D.E.; Zhang, J.; et al. A Sensitive and Specific LC-MS/MS Method for Rapid Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick C1 Disease from Human Plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maekawa, M.; Misawa, Y.; Sotoura, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Togawa, M.; Ohno, K.; Nittono, H.; Kakiyama, G.; Iida, T.; Hofmann, A.F.; et al. LC/ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Urinary 3β-Sulfooxy-7β-N-Acetylglucosaminyl-5-Cholen-24-Oic Acid and Its Amides: New Biomarkers for the Detection of Niemann–Pick Type C Disease. Steroids 2013, 78, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Tengstrand, E.A.; Chourb, L.; Hsieh, F.Y. Di-22:6-Bis(Monoacylglycerol)Phosphate: A Clinical Biomarker of Drug-Induced Phospholipidosis for Drug Development and Safety Assessment. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 279, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, A.-K.; Mascher, H.; Grittner, U.; Eichler, S.; Kramp, G.; Lukas, J.; te Vruchte, D.; al Eisa, N.; Cortina-Borja, M.; Porter, F.D.; et al. A Novel, Highly Sensitive and Specific Biomarker for Niemann-Pick Type C1 Disease. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2015, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazzacuva, F.; Mills, P.; Mills, K.; Camuzeaux, S.; Gissen, P.; Nicoli, E.; Wassif, C.; Vruchte, D.; Porter, F.D.; Maekawa, M.; et al. Identification of Novel Bile Acids as Biomarkers for the Early Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick C Disease. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marques, A.R.A.; Gabriel, T.L.; Aten, J.; Roomen, C.P.A.A.; van Ottenhoff, R.; Claessen, N.; Alfonso, P.; Irún, P.; Giraldo, P.; Aerts, J.M.F.G.; et al. Gpnmb Is a Potential Marker for the Visceral Pathology in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0147208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porter, F.D.; Scherrer, D.E.; Lanier, M.H.; Langmade, S.J.; Molugu, V.; Gale, S.E.; Olzeski, D.; Sidhu, R.; Dietzen, D.J.; Fu, R.; et al. Cholesterol Oxidation Products Are Sensitive and Specific Blood-Based Biomarkers for Niemann-Pick C1 Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 56ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boenzi, S.; Deodato, F.; Taurisano, R.; Martinelli, D.; Verrigni, D.; Carrozzo, R.; Bertini, E.; Pastore, A.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Johnson, D.W. A New Simple and Rapid LC–ESI-MS/MS Method for Quantification of Plasma Oxysterols as Dimethylaminobutyrate Esters. Its Successful Use for the Diagnosis of Niemann–Pick Type C Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 437, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reunert, J.; Fobker, M.; Kannenberg, F.; du Chesne, I.; Plate, M.; Wellhausen, J.; Rust, S.; Marquardt, T. Rapid Diagnosis of 83 Patients with Niemann Pick Type C Disease and Related Cholesterol Transport Disorders by Cholestantriol Screening. EBioMedicine 2016, 4, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romanello, M.; Zampieri, S.; Bortolotti, N.; Deroma, L.; Sechi, A.; Fiumara, A.; Parini, R.; Borroni, B.; Brancati, F.; Bruni, A.; et al. Comprehensive Evaluation of Plasma 7-Ketocholesterol and Cholestan-3β,5α,6β-Triol in an Italian Cohort of Patients Affected by Niemann-Pick Disease Due to NPC1 and SMPD1 Mutations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 455, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, G.; Burlina, A.P.; Kolamunnage, T.B.; Zampieri, M.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Strisciuglio, P.; Zaninotto, M.; Plebani, M.; Burlina, A.B. Diagnosis of Sphingolipidoses: A New Simultaneous Measurement of Lysosphingolipids by LC-MS/MS. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettazzoni, M.; Froissart, R.; Pagan, C.; Vanier, M.T.; Ruet, S.; Latour, P.; Guffon, N.; Fouilhoux, A.; Germain, D.P.; Levade, T.; et al. LC-MS/MS Multiplex Analysis of Lysosphingolipids in Plasma and Amniotic Fluid: A Novel Tool for the Screening of Sphingolipidoses and Niemann-Pick Type C Disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Iwamoto, T.; Hossain, M.A.; Akiyama, K.; Igarashi, J.; Miyajima, T.; Eto, Y. A Combination of 7-Ketocholesterol, Lysosphingomyelin and Bile Acid-408 to Diagnose Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Using LC-MS/MS. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, S.; Arias, A.; García-Villoria, J.; MacÍas-Vidal, J.; Ros, E.; de Las Heras, J.; Girós, M.; Coll, M.J.; Ribes, A. Cholestane-3β,5α,6β-Triol: High Levels in Niemann-Pick Type C, Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis, and Lysosomal Acid Lipase Deficiency. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Cleveland, D. Neuronal Intermediate Filaments. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 1996, 19, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A. Neurofilament Phosphoforms: Surrogate Markers for Axonal Injury, Degeneration and Loss. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 233, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petzold, A.; Eikelenboom, M.J.; Keir, G.; Grant, D.; Lazeron, R.H.C.; Polman, C.H.; Uitdehaag, B.M.J.; Thompson, E.J.; Giovannoni, G. Axonal Damage Accumulates in the Progressive Phase of Multiple Sclerosis: Three Year Follow up Study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.-H.; Macdonald-Wallis, C.; Gray, E.; Pearce, N.; Petzold, A.; Norgren, N.; Giovannoni, G.; Fratta, P.; Sidle, K.; Fish, M.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain: A Prognostic Biomarker in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurology 2015, 84, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zetterberg, H.; Skillbäck, T.; Mattsson, N.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Portelius, E.; Shaw, L.M.; Weiner, M.W.; Blennow, K.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Concentration With Alzheimer Disease Progression. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeter, L.H.; Dopper, E.G.; Jiskoot, L.C.; Sanchez-Valle, R.; Graff, C.; Benussi, L.; Ghidoni, R.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.; Borroni, B.; Galimberti, D.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain: A Biomarker for Genetic Frontotemporal Dementia. Ann. Clin. Tansl. Neurol. 2016, 3, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.C.; Bang, J.; Lobach, I.V.; Tsai, R.M.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Miller, B.L.; Boxer, A.L. CSF Neurofilament Light Chain and Phosphorylated Tau 181 Predict Disease Progression in PSP. Neurology 2018, 90, e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.-J.; McGlasson, S.; Hunt, D.; Overell, J. Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Chain in Multiple Sclerosis and Its Subtypes: A Meta-Analysis of Case–Control Studies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eratne, D.; Loi, S.M.; Li, Q.-X.; Varghese, S.; McGlade, A.; Collins, S.; Masters, C.L.; Velakoulis, D.; Walterfang, M. Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Chain Is Elevated in Niemann–Pick Type C Compared to Psychiatric Disorders and Healthy Controls and May Be a Marker of Treatment Response. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2019, 54, 648–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bountouvi, E.; Giorgi, M.; Papadopoulou, A.; Blennow, K.; Björkhem, I.; Tsirouda, M.; Kanellakis, S.; Fryganas, A.; Spanou, M.; Georgaki, I.; et al. Longitudinal Data in Patients with Niemann-Pick Type C Disease Under Combined High Intrathecal and Low Intravenous Dose of 2-Hydroxylpropyl-β-Cyclodextrin. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaiottino, J.; Norgren, N.; Dobson, R.; Topping, J.; Nissim, A.; Malaspina, A.; Bestwick, J.P.; Monsch, A.U.; Regeniter, A.; Lindberg, R.L.; et al. Increased Neurofilament Light Chain Blood Levels in Neurodegenerative Neurological Diseases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 75091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, C.; Preische, O.; Deuschle, C.; Roeben, B.; Apel, A.; Barro, C.; Maia, L.; Maetzler, W.; Kuhle, J.; Synofzik, M. Neurofilament Light Chain in FTD Is Elevated Not Only in Cerebrospinal Fluid, but Also in Serum. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 1270–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Barro, C.; Disanto, G.; Mathias, A.; Soneson, C.; Bonnier, G.; Yaldizli, Ö.; Regeniter, A.; Derfuss, T.; Canales, M.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain in Early Relapsing Remitting MS Is Increased and Correlates with CSF Levels and with MRI Measures of Disease Severity. Mult. Scler. 2016, 22, 1550–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakova, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Sundström, P.; Axelsson, M.; Khademi, M.; Gunnarsson, M.; Malmeström, C.; Svenningsson, A.; Olsson, T.; Piehl, F.; et al. Monitoring Disease Activity in Multiple Sclerosis Using Serum Neurofilament Light Protein. Neurology 2017, 89, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Disanto, G.; Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Naegelin, Y.; Schädelin, S.; Giardiello, A.; Zecca, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Leppert, D.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light: A Biomarker of Neuronal Damage in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piehl, F.; Kockum, I.; Khademi, M.; Blennow, K.; Lycke, J.; Zetterberg, H.; Olsson, T. Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain Levels in Patients with MS Switching from Injectable Therapies to Fingolimod. Mult. Scler. 2017, 24, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, N.; Andreasson, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Association of Plasma Neurofilament Light With Neurodegeneration in Patients With Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, E.; Janelidze, S.; Lampinen, B.; Nilsson, M.; Leuzy, A.; Stomrud, E.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Differentially Detect Neurodegeneration in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 95, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Corado, C.; Soon, R.K.J.; Melton, A.C.; Harris, A.; Yu, G.K.; Pryer, N.; Sinclair, J.R.; Katz, M.L.; Ajayi, T.; et al. Neurofilament Light Is a Treatment-responsive Biomarker in CLN2 Disease. Ann. Clin. Tansl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhalla, A.; Ravi, R.; Fang, M.; Arguello, A.; Davis, S.S.; Chiu, C.-L.; Blumenfeld, J.R.; Nguyen, H.N.; Earr, T.K.; Wang, J.; et al. Characterization of Fluid Biomarkers Reveals Lysosome Dysfunction and Neurodegeneration in Neuronopathic MPS II Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geberhiwot, T.; Moro, A.; Dardis, A.; Ramaswami, U.; Sirrs, S.; Marfa, M.P.; Vanier, M.T.; Walterfang, M.; Bolton, S.; Dawson, C.; et al. Consensus Clinical Management Guidelines for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dardis, A.; Zampieri, S.; Gellera, C.; Carrozzo, R.; Cattarossi, S.; Peruzzo, P.; Dariol, R.; Sechi, A.; Deodato, F.; Caccia, C.; et al. Molecular Genetics of Niemann–Pick Type C Disease in Italy: An Update on 105 Patients and Description of 18 NPC1 Novel Variants. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gauthier, A.; Viel, S.; Perret, M.; Brocard, G.; Casey, R.; Lombard, C.; Laurent-Chabalier, S.; Debouverie, M.; Edan, G.; Vukusic, S.; et al. Comparison of Simoa TM and Ella TM to Assess Serum Neurofilament-Light Chain in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Tansl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Rocco, M.; Barone, R.; Madeo, A.; Fiumara, A. Miglustat Does Not Prevent Neurological Involvement in Niemann Pick C Disease. Pediatr. Neurol. 2015, 53, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, M.; Walterfang, M.; Patterson, M.C. Miglustat in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Patients: A Review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rego, T.; Farrand, S.; Goh, A.M.Y.; Eratne, D.; Kelso, W.; Mangelsdorf, S.; Velakoulis, D.; Walterfang, M. Psychiatric and Cognitive Symptoms Associated with Niemann-Pick Type C Disease: Neurobiology and Management. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, M.C.; Mengel, E.; Vanier, M.T.; Moneuse, P.; Rosenberg, D.; Pineda, M. Treatment Outcomes Following Continuous Miglustat Therapy in Patients with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C: A Final Report of the NPC Registry. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serum Neurofilament-Light Chain and GFAP Levels in Patients From the OFSEP Cohort at Different Landmarks of Multiple Sclerosis—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03981003 (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Yamada, N.; Inui, A.; Sanada, Y.; Ihara, Y.; Urahashi, T.; Fukuda, A.; Sakamoto, S.; Kasahara, M.; Yoshizawa, A.; Okamoto, S.; et al. Pediatric Liver Transplantation for Neonatal-Onset Niemann-Pick Disease Type C: Japanese Multicenter Experience. Pediatr. Transplant. 2019, 23, e13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pediatric NPCD Patients (n = 12) | Adult NPCD Patients (n = 14) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 6 | 5 |
| Female | 6 | 9 |
| Clinical phenotype | ||
| EISL | 2 * | 0 |
| EI | 2 (1+) | 0 |
| LI | 4 | 0 |
| J | 2 | 4 |
| A | 0 | 6 |
| NC | 2 | 4 |
| Number of analyzed samples | ||
| 15 | 24 | |
| Age at sampling (years) | ||
| Mean | 4.8 | 29.4 |
| Range | 0.08–13.08 | 21.58–53.08 |
| Presence of Neurological involvement at sampling | ||
| 6 | 14 | |
| Pediatric | Adults | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Controls (n = 39) | NPCD (n = 15) | Healthy Controls (n = 36) | NPCD (n = 24) | |
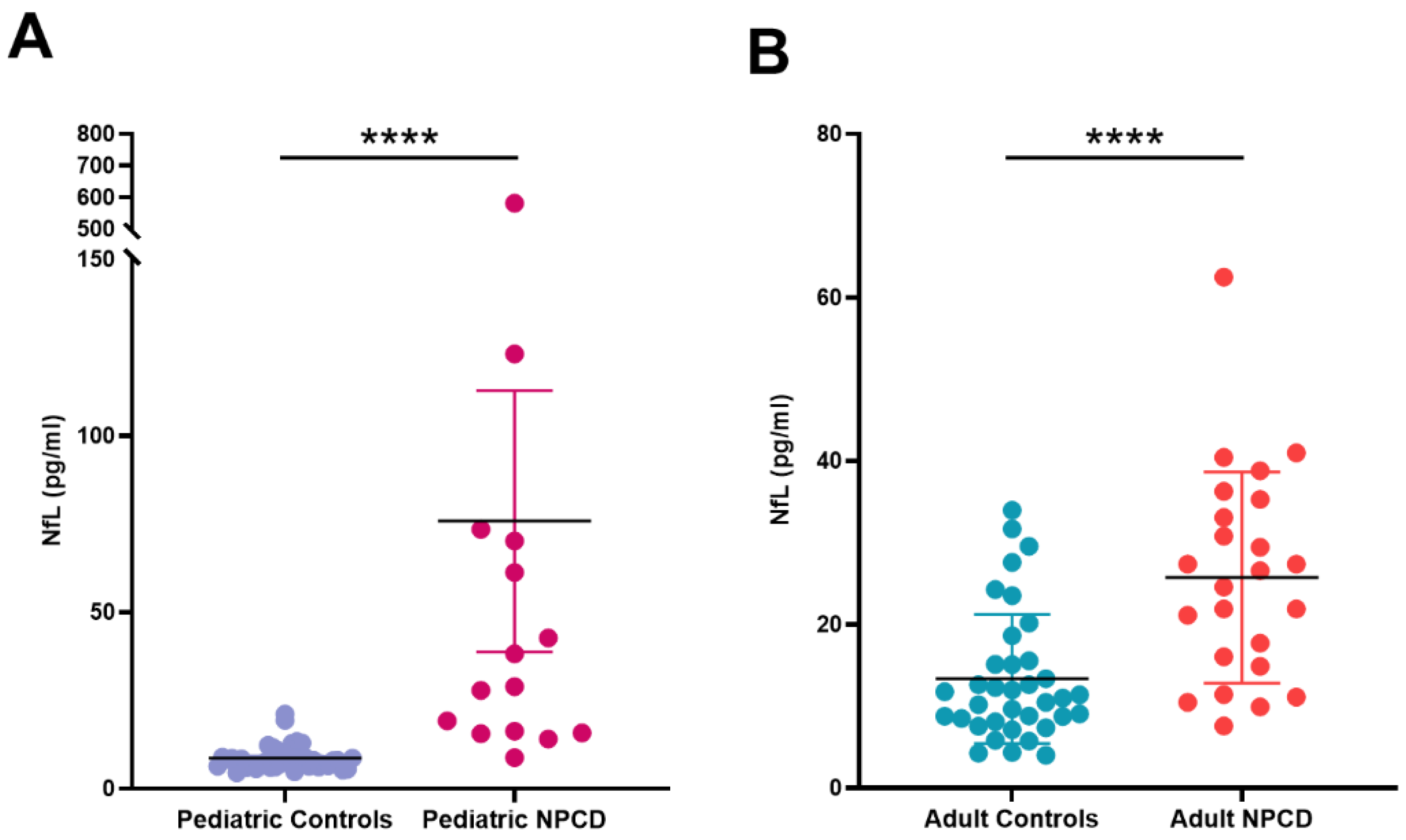
| Median | 7.94 | 28.97 **** | 11.2 | 25.6 **** |
| IQ range | 6.38–9.75 | 15.83–70.21 | 8.265–15.26 | 15.9–34.75 |
| Range | 4.56–21.2 | 8.82–581.4 | 4.01–33.97 | 7.59–62.5 |
| Pediatric | Adults | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Controls (n = 39) | NPCD (n = 12) | NPCD Neuro (n = 4) | NPCD Non Neuro (n = 7) | Healthy Controls (n = 36) | NPCD (n = 14) | NPCD Neuro (n = 9) | NPCD Non Neuro (n = 5) | |
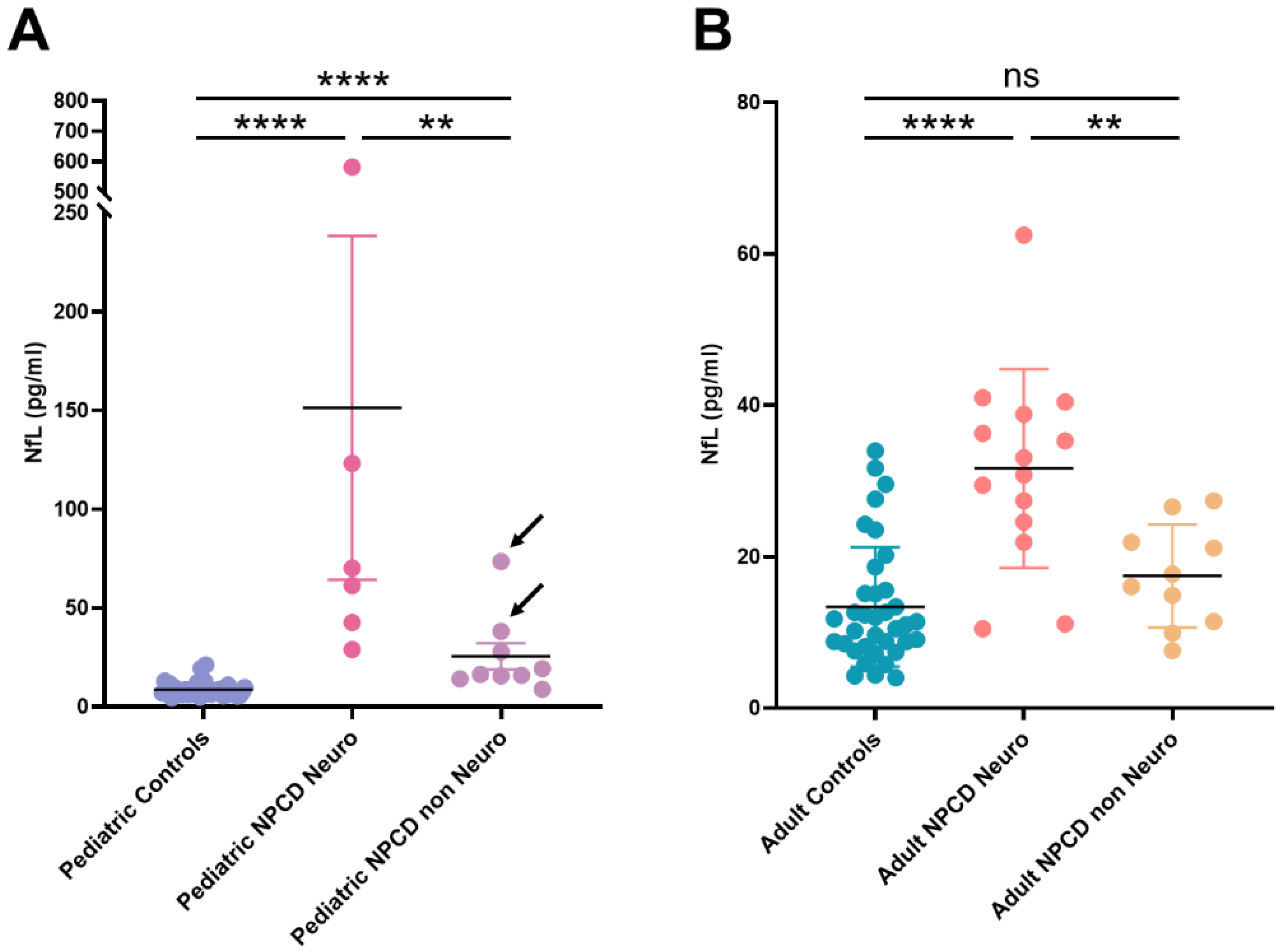
| Median | 7.94 | 33.07 **** | 65.75 | 19.26 * | 11.20 | 27.02 *** | 33.10 | 16.07 * |
| IQ range | 6.38–9.75 | 15.78–67.98 | 47.35–453.60 | 14.12–38.24 | 8.20–15.47 | 14.91–36.18 | 27.02–39.63 | 9.51–19.43 |
| Range | 4.56–21.20 | 8.82–581.40 | 42.70–581.40 | 8.82–73.50 | 4.01–33.97 | 7.59–62.50 | 11.12–62.50 | 7.59–21.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dardis, A.; Pavan, E.; Fabris, M.; Da Riol, R.M.; Sechi, A.; Fiumara, A.; Santoro, L.; Ormazabal, M.; Milanic, R.; Zampieri, S.; et al. Plasma Neurofilament Light (NfL) in Patients Affected by Niemann–Pick Type C Disease (NPCD). J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10204796
Dardis A, Pavan E, Fabris M, Da Riol RM, Sechi A, Fiumara A, Santoro L, Ormazabal M, Milanic R, Zampieri S, et al. Plasma Neurofilament Light (NfL) in Patients Affected by Niemann–Pick Type C Disease (NPCD). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(20):4796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10204796
Chicago/Turabian StyleDardis, Andrea, Eleonora Pavan, Martina Fabris, Rosalia Maria Da Riol, Annalisa Sechi, Agata Fiumara, Lucia Santoro, Maximiliano Ormazabal, Romina Milanic, Stefania Zampieri, and et al. 2021. "Plasma Neurofilament Light (NfL) in Patients Affected by Niemann–Pick Type C Disease (NPCD)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 20: 4796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10204796
APA StyleDardis, A., Pavan, E., Fabris, M., Da Riol, R. M., Sechi, A., Fiumara, A., Santoro, L., Ormazabal, M., Milanic, R., Zampieri, S., Biasizzo, J., & Scarpa, M. (2021). Plasma Neurofilament Light (NfL) in Patients Affected by Niemann–Pick Type C Disease (NPCD). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(20), 4796. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10204796







