Attenuative Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on 30 kDa Fibronectin Fragment-Induced MMP-13 Expression Associated with TLR2 Signaling in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Antibodies
2.2. Patients
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Human Chondrocyte Cell-Line Culture
2.5. Experimental Protocol
2.6. Extraction of RNA and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.7. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
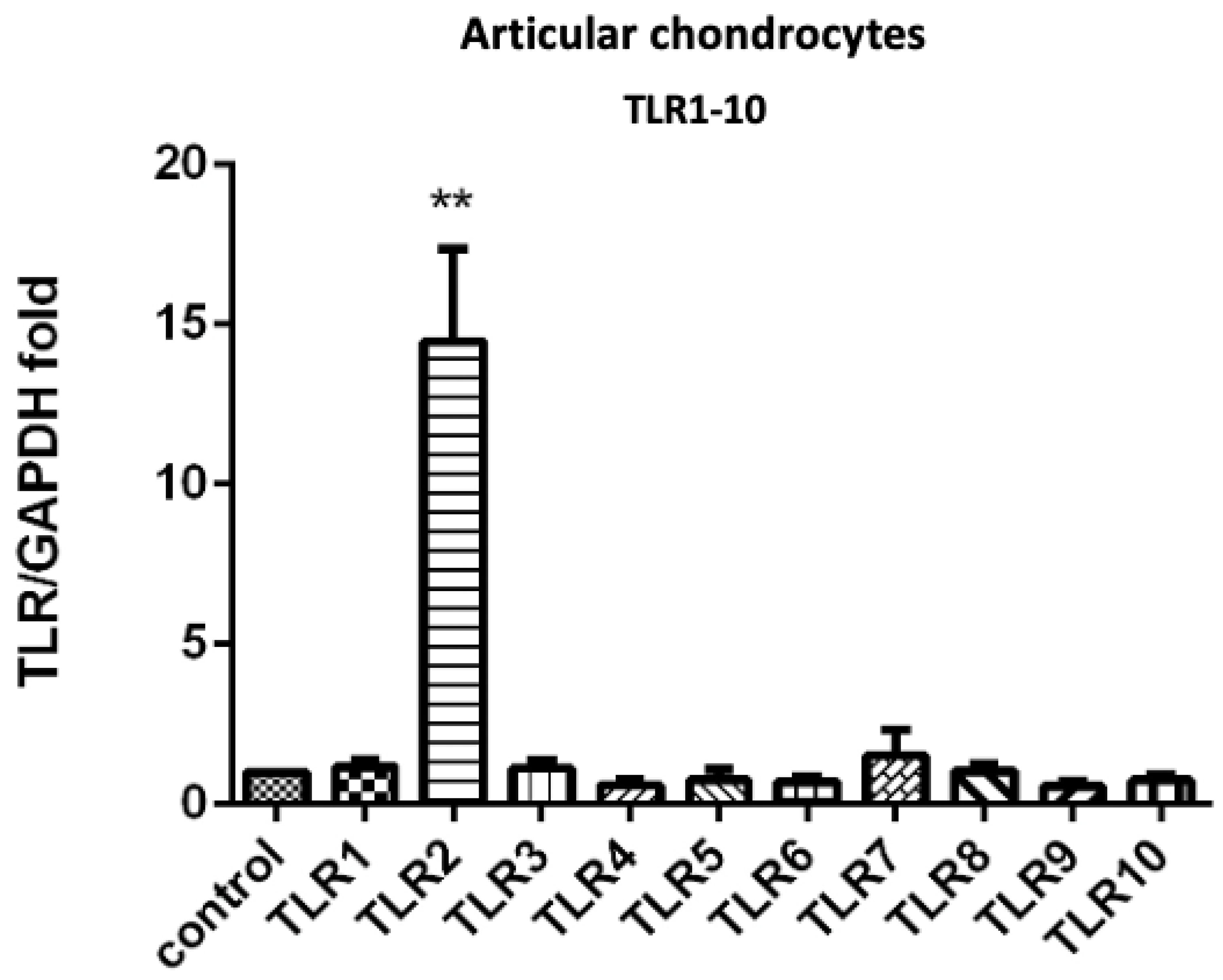
3.1. PRP-Attenuated FN-f-Induced TLR Gene Expression in Articular Chondrocytes, Meniscal Fibrochondrocytes, and Synovial Fibroblasts from the Primary Cultures
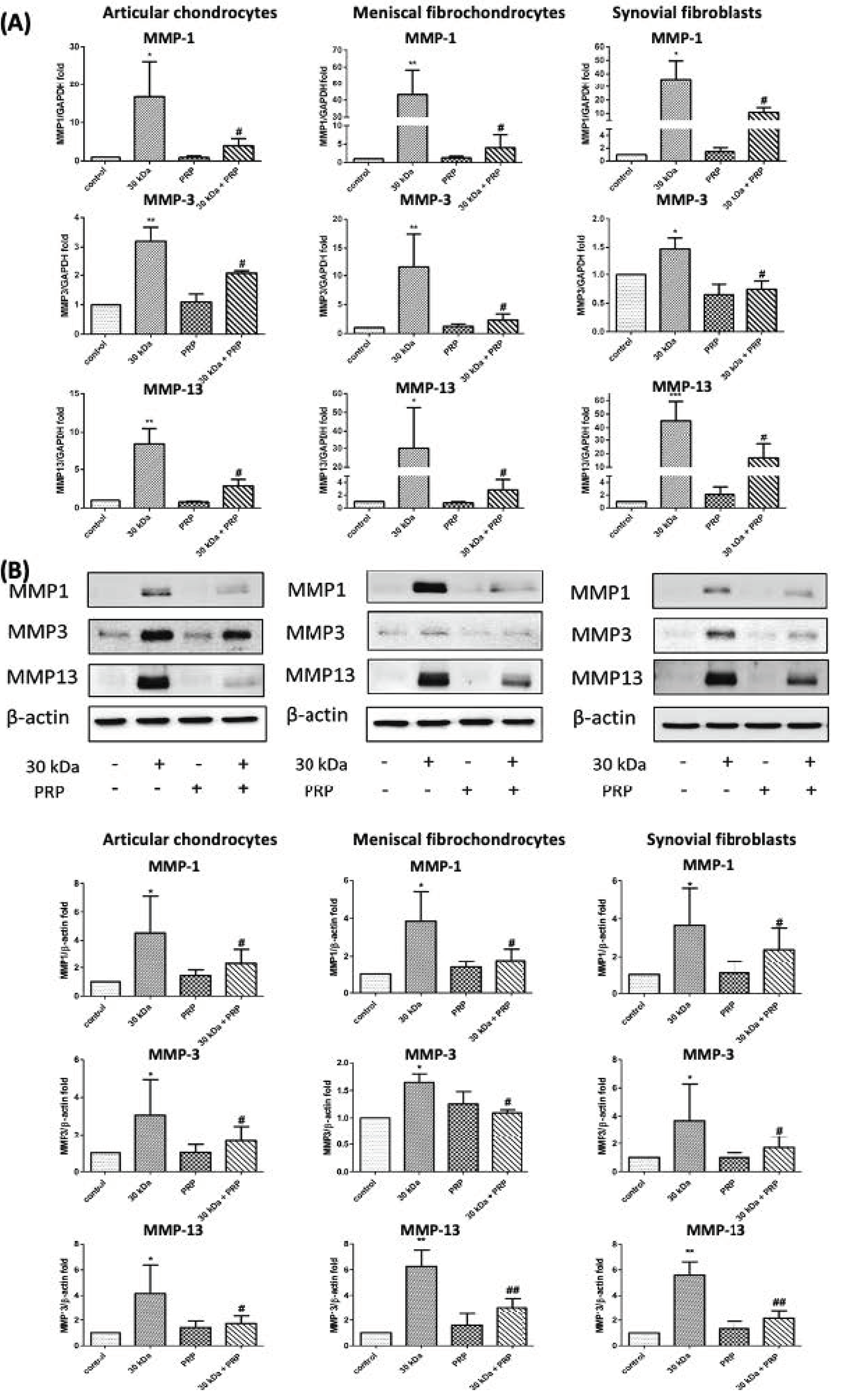
3.2. PRP-Attenuated FN-f-Induced MMPs Expression in Articular Chondrocytes, Meniscal Fibrochondrocytes, and Synovial Fibroblasts
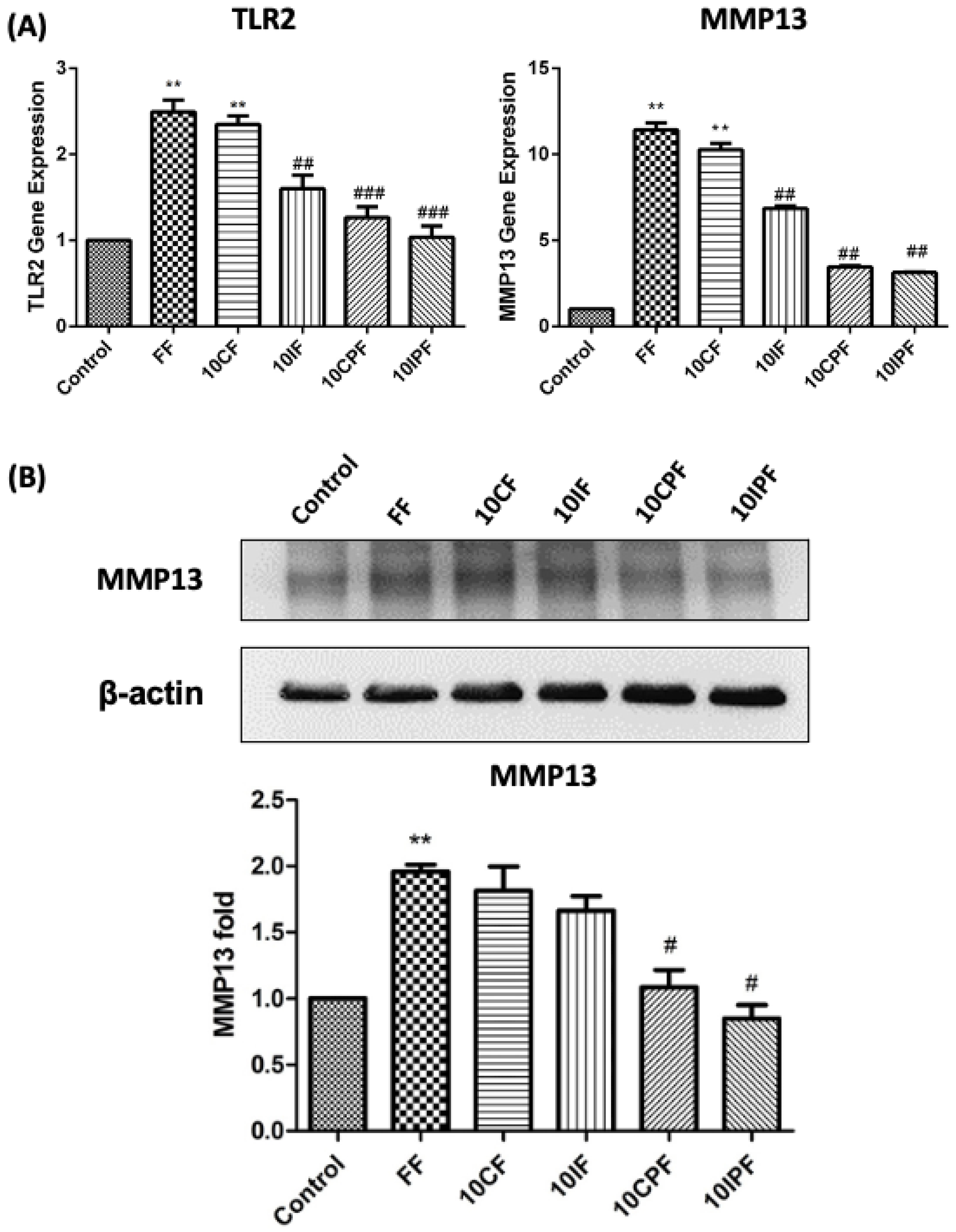
3.3. Expression of TLR2 and MMP-13 under FN-f Insult in Chondrocyte Cell Line
3.4. FN-f-Induced MMP-13 Protein Expression in Chondrocyte Cells Was Attenuated by Cotreatment with PRP
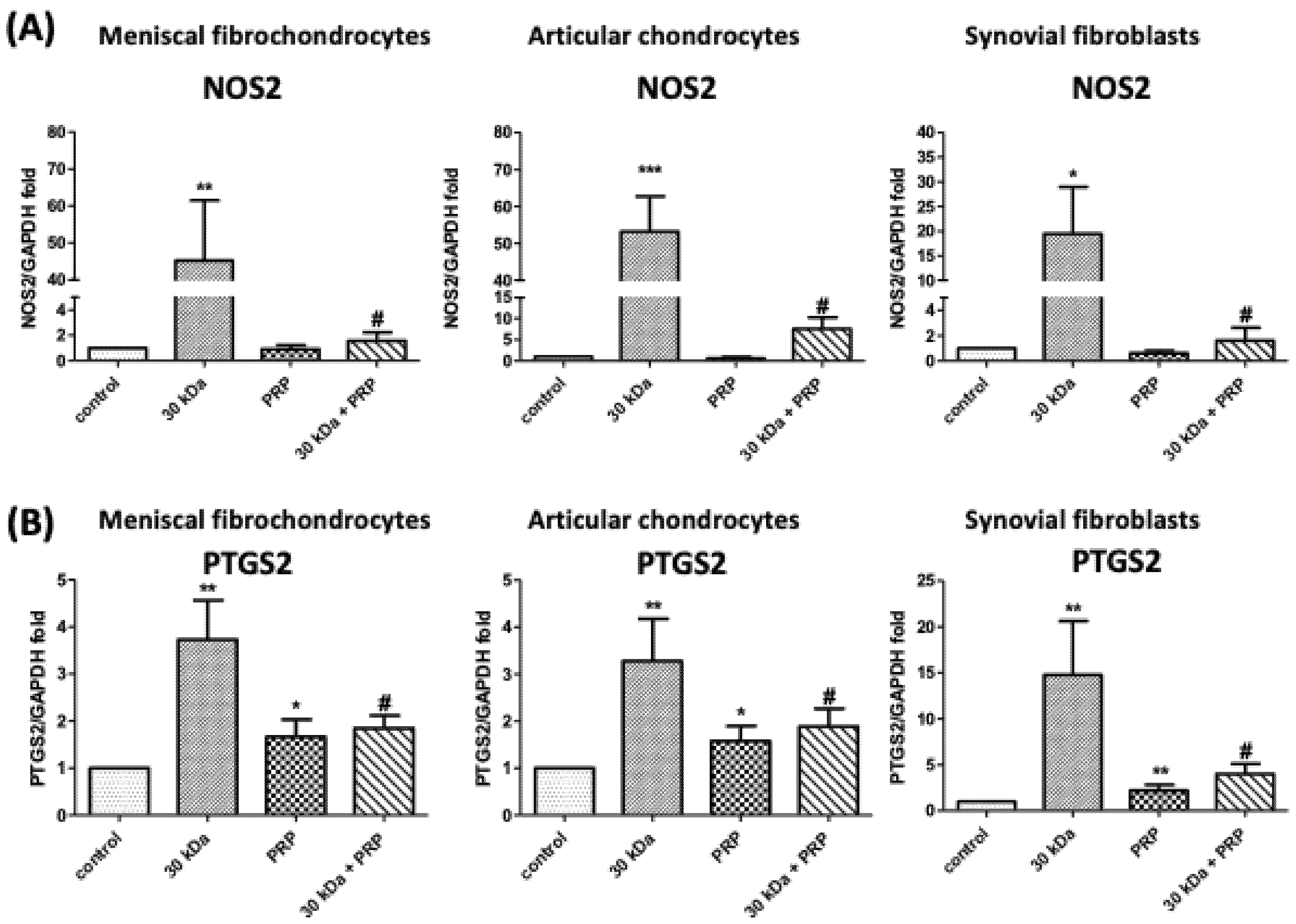
3.5. PRP Attenuates FN-f-Induced Catabolism Gene Expression in Meniscal Fibrochondrocytes, Articular Chondrocytes, and Synovial Fibroblasts
3.6. FN-f-Induced NOS2 and COX-2 Protein Levels by Meniscal fibrochondrocytes, Articular Chondrocytes, and Synovial Fibroblasts Are Inhibited by PRP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. TLR signaling pathways. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillat, T.; Barreto, G.; Clarijs, P.; Soininen, A.; Ainola, M.; Pajarinen, J.; Korhonen, M.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Sakalyte, R.; Hukkanen, M.; et al. Toll-like receptors in human chondrocytes and osteoarthritic cartilage. Acta Orthop. 2013, 84, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.L.; Tsai, C.D.; Lee, C.H.; Salter, D.M.; Lee, H.S. Expression and regulation of Toll-like receptor 2 by IL-1beta and fibronectin fragments in human articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2005, 13, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burton-Wurster, N.; Butler, M.; Harter, S.; Colombo, C.; Quintavalla, J.; Swartzendurber, D.; Arsenis, C.; Lust, G. Presence of fibronectin in articular cartilage in two animal models of osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1986, 13, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavietes, B.B.; Carsons, S.; Diamond, H.S.; Laskin, R.S. Synthesis, secretion, and deposition of fibronectin in cultured human synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1985, 28, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homandberg, G.A.; Meyers, R.; Williams, J.M. Intraarticular injection of fibronectin fragments causes severe depletion of cartilage proteoglycans in vivo. J. Rheumatol. 1993, 20, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Homandberg, G.A.; Hui, F. Association of proteoglycan degradation with catabolic cytokine and stromelysin release from cartilage cultured with fibronectin fragments. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 334, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, H.; Ung, L.; Fosang, A.J. The 45 kDa collagen-binding fragment of fibronectin induces matrix metalloproteinase-13 synthesis by chondrocytes and aggrecan degradation by aggrecanases. Biochem. J. 2002, 364, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Cole, A.A.; Homandberg, G.A. Comparison of the catabolic effects of fibronectin fragments in human knee and ankle cartilages. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weibrich, G.; Kleis, W.K.; Hafner, G.; Hitzler, W.E. Growth factor levels in platelet-rich plasma and correlations with donor age, sex, and platelet count. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2002, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrione, P.; Gianfrancesco, A.D.; Pereira, M.T.; Pigozzi, F. Platelet-rich plasma in muscle healing. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 89, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andia, I.; Maffulli, N. Platelet-rich plasma for managing pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Nat. Reviews. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundman, E.A.; Cole, B.J.; Karas, V.; Della Valle, C.; Tetreault, M.W.; Mohammed, H.O.; Fortier, L.A. The anti-inflammatory and matrix restorative mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma in osteoarthritis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2014, 42, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudy, A.B.; Bakker, E.W.; Rekers, M.; Moen, M.H. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma injections in osteoarthritis of the knee: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.C.; Lee, C.H.; Peng, Y.J.; Salter, D.M.; Lee, H.S. Platelet-Rich Plasma Attenuates 30-kDa Fibronectin Fragment-Induced Chemokine and Matrix Metalloproteinase Expression by Meniscocytes and Articular Chondrocytes. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulai, J.I.; Chen, H.; Im, H.J.; Kumar, S.; Hanning, C.; Hegde, P.S.; Loeser, R.F. NF-kappa B mediates the stimulation of cytokine and chemokine expression by human articular chondrocytes in response to fibronectin fragments. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5781–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sofat, N.; Robertson, S.D.; Wait, R. Fibronectin III 13-14 domains induce joint damage via Toll-like receptor 4 activation and synergize with interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Guo, D.; Homandberg, G.A. The cartilage chondrolytic mechanism of fibronectin fragments involves MAP kinases: Comparison of three fragments and native fibronectin. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez-Garcia, S.; Carrion, M.; Gutierrez-Canas, I.; Villanueva-Romero, R.; Castro, D.; Martinez, C.; Gonzalez-Alvaro, I.; Blanco, F.J.; Juarranz, Y.; Gomariz, R.P. Profile of Matrix-Remodeling Proteinases in Osteoarthritis: Impact of Fibronectin. Cells 2019, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, T.T.; Schulz, R.M.; Rai, S.S.; Thuemmler, C.B.; Wuestneck, N.; Bader, A.; Homandberg, G.A. Biomechanical modulation of collagen fragment-induced anabolic and catabolic activities in chondrocyte/agarose constructs. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2015, 109, 14.12.1–14.12.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobacz, K.; Sunk, I.G.; Hofstaetter, J.G.; Amoyo, L.; Toma, C.D.; Akira, S.; Weichhart, T.; Saemann, M.; Smolen, J.S. Toll-like receptors and chondrocytes: The lipopolysaccharide-induced decrease in cartilage matrix synthesis is dependent on the presence of toll-like receptor 4 and antagonized by bone morphogenetic protein 7. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 1880–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Lee, S.M.; Li, J.; Tran, G.; Jabri, B.; Chatila, T.A.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Toll-like receptor 2 pathway establishes colonization by a commensal of the human microbiota. Science 2011, 332, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barton, G.M.; Kagan, J.C. A cell biological view of Toll-like receptor function: Regulation through compartmentalization. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, C.; Gregan, S.M.; Navin, T.J.; Foxwell, B.M.; Davies, A.H.; Feldmann, M. Toll-like receptor-2 mediates inflammation and matrix degradation in human atherosclerosis. Circulation 2009, 120, 2462–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salomao, R.; Brunialti, M.K.; Gomes, N.E.; Mendes, M.E.; Diaz, R.S.; Komninakis, S.; Machado, F.R.; da Silva, I.D.; Rigato, O. Toll-like receptor pathway signaling is differently regulated in neutrophils and peripheral mononuclear cells of patients with sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijmerink, N.E.; Bottema, R.W.; Kerkhof, M.; Gerritsen, J.; Stelma, F.F.; Thijs, C.; van Schayck, C.P.; Smit, H.A.; Brunekreef, B.; Koppelman, G.H.; et al. TLR-related pathway analysis: Novel gene-gene interactions in the development of asthma and atopy. Allergy 2010, 65, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.M.; Pappu, B.P.; Peng, J.; Martinez, G.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, X.O.; Nurieva, R.I.; Tian, Q.; et al. Toll-like receptor 2 signaling in CD4(+) T lymphocytes promotes T helper 17 responses and regulates the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Immunity 2010, 32, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyburz, D.; Rethage, J.; Seibl, R.; Lauener, R.; Gay, R.E.; Carson, D.A.; Gay, S. Bacterial peptidoglycans but not CpG oligodeoxynucleotides activate synovial fibroblasts by toll-like receptor signaling. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, I.; Malizos, K.N.; Poultsides, L.; Karachalios, T.; Oikonomou, P.; Tsezou, A. The catabolic role of toll-like receptor 2 (TLR-2) mediated by the NF-kappaB pathway in septic arthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.A.; Cho, M.L.; Choi, H.Y.; Yoon, C.S.; Jhun, J.Y.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, H.Y. The catabolic pathway mediated by Toll-like receptors in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2152–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Bryan, R.; Terkeltaub, R. Chondrocyte innate immune myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent signaling drives procatabolic effects of the endogenous Toll-like receptor 2/Toll-like receptor 4 ligands low molecular weight hyaluronan and high mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar]
- Campo, G.M.; Avenoso, A.; D’Ascola, A.; Scuruchi, M.; Prestipino, V.; Nastasi, G.; Calatroni, A.; Campo, S. Adenosine A2A receptor activation and hyaluronan fragment inhibition reduce inflammation in mouse articular chondrocytes stimulated with interleukin-1beta. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2120–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramono, D.S.; Richmond, J.C.; Weitzel, P.P.; Chernoff, H.; Martin, I.; Volloch, V.; Jakuba, C.M.; Diaz, F.; Gandhi, J.S.; Kaplan, D.L.; et al. Characterization of transcript levels for matrix molecules and proteases in ruptured human anterior cruciate ligaments. Connect. Tissue Res. 2005, 46, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magra, M.; Maffulli, N. Matrix metalloproteases: A role in overuse tendinopathies. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, G.N., Jr.; Yu, L.P., Jr.; Brandt, K.D.; Capello, W.N. Oral administration of doxycycline reduces collagenase and gelatinase activities in extracts of human osteoarthritic cartilage. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Billinghurst, R.C.; O’Brien, K.; Poole, A.R.; McIlwraith, C.W. Inhibition of articular cartilage degradation in culture by a novel nonpeptidic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 878, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, S.; Carrion, M.; Jimeno, R.; Ortiz, A.M.; Gonzalez-Alvaro, I.; Fernandez, J.; Gomariz, R.P.; Juarranz, Y. Urokinase plasminogen activator system in synovial fibroblasts from osteoarthritis patients: Modulation by inflammatory mediators and neuropeptides. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 52, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, J.P.; Hondke, S.; Endres, M.; Pruss, A.; Siclari, A.; Kaps, C. Human platelet-rich plasma stimulates migration and chondrogenic differentiation of human subchondral progenitor cells. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.I.; Lee, H.R.; Kim, S.; Ahn, M.W.; Do, S.H. Time-sequential modulation in expression of growth factors from platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the chondrocyte cultures. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 361, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibrich, G.; Hansen, T.; Kleis, W.; Buch, R.; Hitzler, W.E. Effect of platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma on peri-implant bone regeneration. Bone 2004, 34, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziani, F.; Ivanovski, S.; Cei, S.; Ducci, F.; Tonetti, M.; Gabriele, M. The in vitro effect of different PRP concentrations on osteoblasts and fibroblasts. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourcho, A.M.; Smith, J.; Wisniewski, S.J.; Sellon, J.L. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: Review and recommendations. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 93, S108–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.R.; Goldring, M.B. The role of cytokines in cartilage matrix degeneration in osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 427, S27–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, C.; Gosset, M.; Berenbaum, F.; Gabay, C. The role of IL-1 and IL-1Ra in joint inflammation and cartilage degradation. Vitam. Horm. 2006, 74, 371–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abramson, S.B. Osteoarthritis and nitric oxide. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16 (Suppl. 2), S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tung, J.T.; Arnold, C.E.; Alexander, L.H.; Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan, V.; Venta, P.J.; Richardson, D.W.; Caron, J.P. Evaluation of the influence of prostaglandin E2 on recombinant equine interleukin-1beta-stimulated matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3, and 13 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 1 expression in equine chondrocyte cultures. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ellman, M.; Muddasani, P.; Wang, J.H.; Cs-Szabo, G.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Im, H.J. Prostaglandin E2 and its cognate EP receptors control human adult articular cartilage homeostasis and are linked to the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taskiran, D.; Stefanovic-Racic, M.; Georgescu, H.; Evans, C. Nitric oxide mediates suppression of cartilage proteoglycan synthesis by interleukin-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 200, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Hattori, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Takahashi, K.; Inoue, H.; Takigawa, M. Nitric oxide mediates interleukin-1-induced gene expression of matrix metalloproteinases and basic fibroblast growth factor in cultured rabbit articular chondrocytes. J. Biochem. 1998, 123, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneiro, E.; Lopez-Armada, M.J.; de Andres, M.C.; Carames, B.; Martin, M.A.; Bonilla, A.; Del Hoyo, P.; Galdo, F.; Arenas, J.; Blanco, F.J. Effect of nitric oxide on mitochondrial respiratory activity of human articular chondrocytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.J.; Chen, T.G.; Chang, H.C.; Chiu, W.T.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, R.M. Nitric oxide from both exogenous and endogenous sources activates mitochondria-dependent events and induces insults to human chondrocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 101, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Accession Number | Applied Biosystems Number |
|---|---|---|
| TLR1 | NM_003263 | Hs00413978_m1 |
| TLR2 | NM_003264 | Hs00610101_m1 |
| TLR3 | NM_003265 | Hs01551078_m1 |
| TLR4 | NM_003266 | Hs00152939_m1 |
| TLR5 | NM_003268 | Hs00152825_m1 |
| TLR6 | NM_006068 | Hs00271977_s1 |
| TLR7 | NM_016562 | Hs00152971_m1 |
| TLR8 | AF246971.1 | Hs00152972_m1 |
| TLR9 | NM_017442 | Hs00152973_m1 |
| TLR10 | NM_001017388 | Hs00999403_m1 |
| MMP1 | NM_002421 | Hs00233958_m1 |
| MMP3 | NM_002422 | Hs00968305_m1 |
| MMP13 | NM_002427 | Hs00233992_m1 |
| GAPDH | NM_002046 | Hs02758991_g1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, H.-T.; Lu, J.-W.; Lee, C.-H.; Peng, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Chu, Y.-H.; Ho, Y.-J.; Liu, F.-C.; Shen, P.-H.; Wang, C.-C. Attenuative Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on 30 kDa Fibronectin Fragment-Induced MMP-13 Expression Associated with TLR2 Signaling in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194496
Lu H-T, Lu J-W, Lee C-H, Peng Y-J, Lee H-S, Chu Y-H, Ho Y-J, Liu F-C, Shen P-H, Wang C-C. Attenuative Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on 30 kDa Fibronectin Fragment-Induced MMP-13 Expression Associated with TLR2 Signaling in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(19):4496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194496
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Hsien-Tsung, Jeng-Wei Lu, Chian-Her Lee, Yi-Jen Peng, Herng-Sheng Lee, You-Hsiang Chu, Yi-Jung Ho, Feng-Cheng Liu, Pei-Hung Shen, and Chih-Chien Wang. 2021. "Attenuative Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on 30 kDa Fibronectin Fragment-Induced MMP-13 Expression Associated with TLR2 Signaling in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 19: 4496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194496
APA StyleLu, H.-T., Lu, J.-W., Lee, C.-H., Peng, Y.-J., Lee, H.-S., Chu, Y.-H., Ho, Y.-J., Liu, F.-C., Shen, P.-H., & Wang, C.-C. (2021). Attenuative Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma on 30 kDa Fibronectin Fragment-Induced MMP-13 Expression Associated with TLR2 Signaling in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(19), 4496. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194496






