Systemic Human Neutrophil Lipocalin Associates with Severe Acute Kidney Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Human Neutrophil Lipocalin Assays
2.3. Cytokine Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics, Routine Chemistry, and Organ Support Requirement
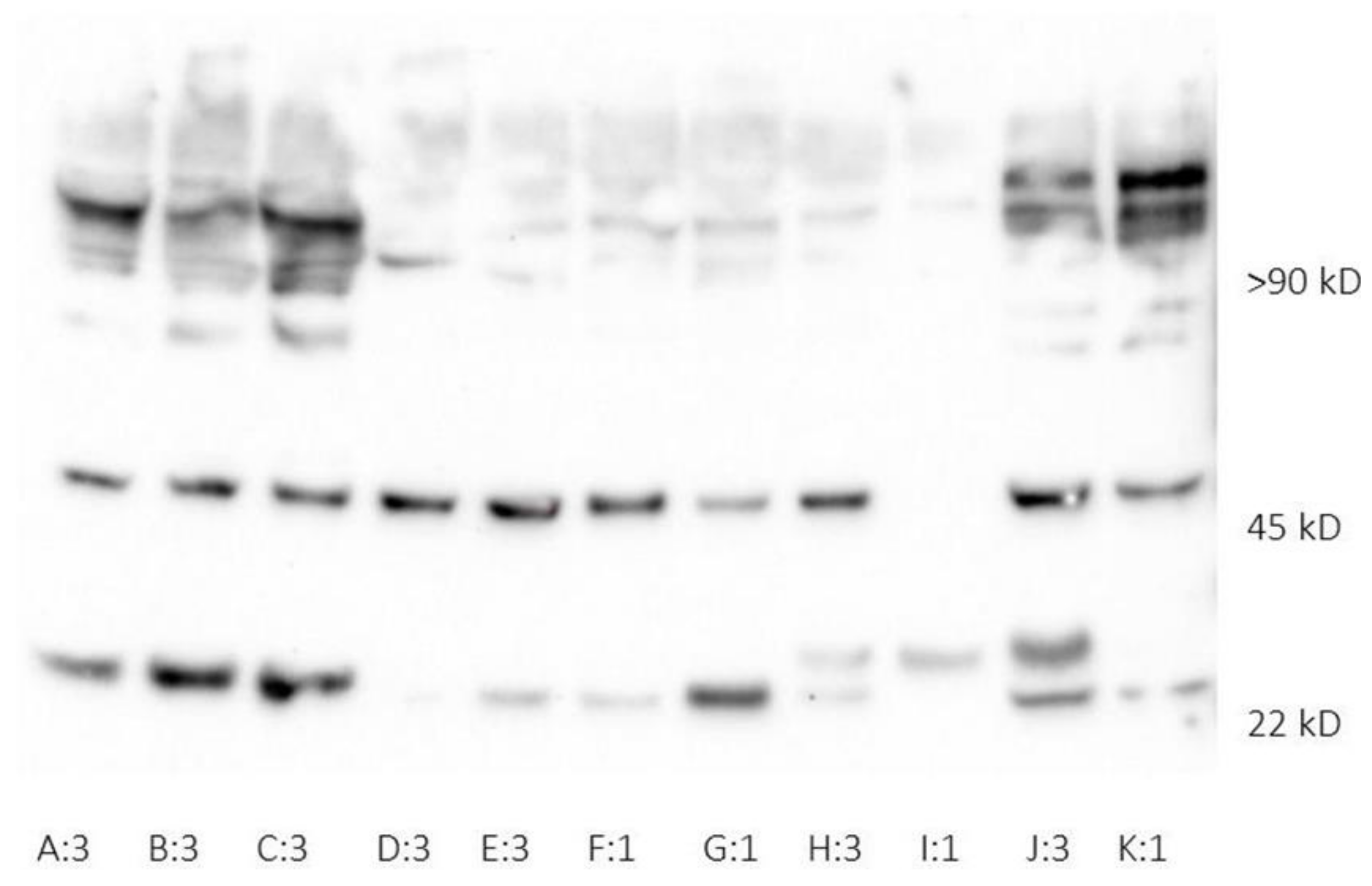
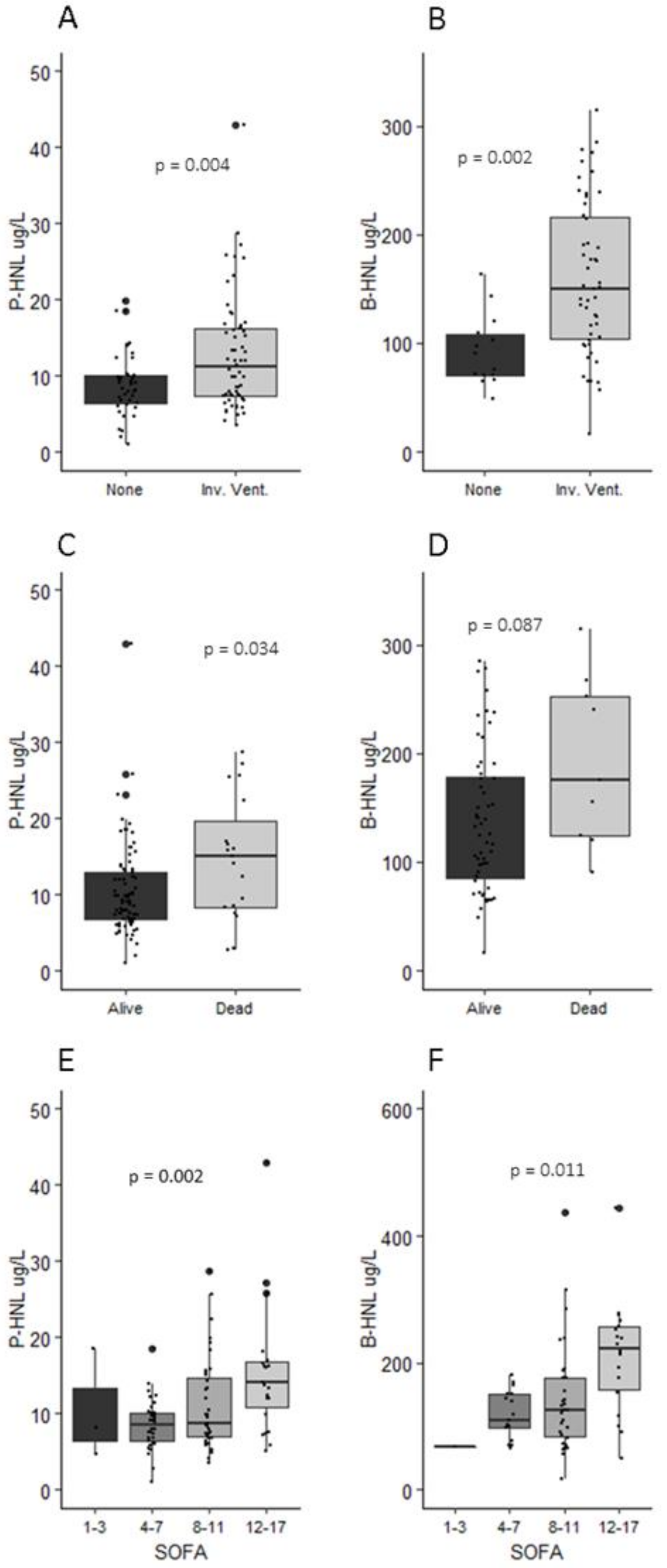
3.2. Human Neutrophil Lipocalin in Plasma and Whole Blood
3.3. Neutrophil Count, NLR, and HNL
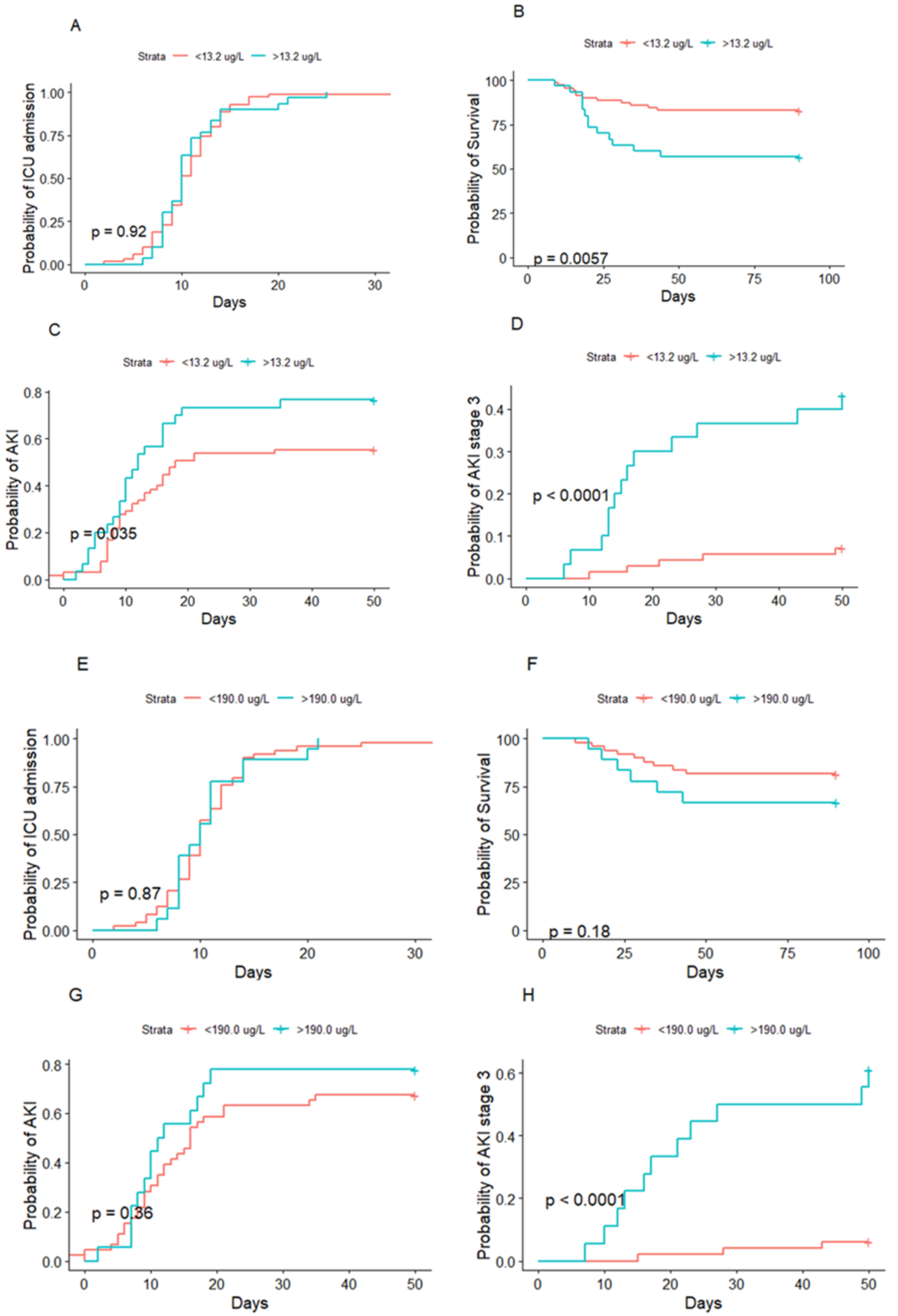
3.4. HNL and Acute Kidney Injury
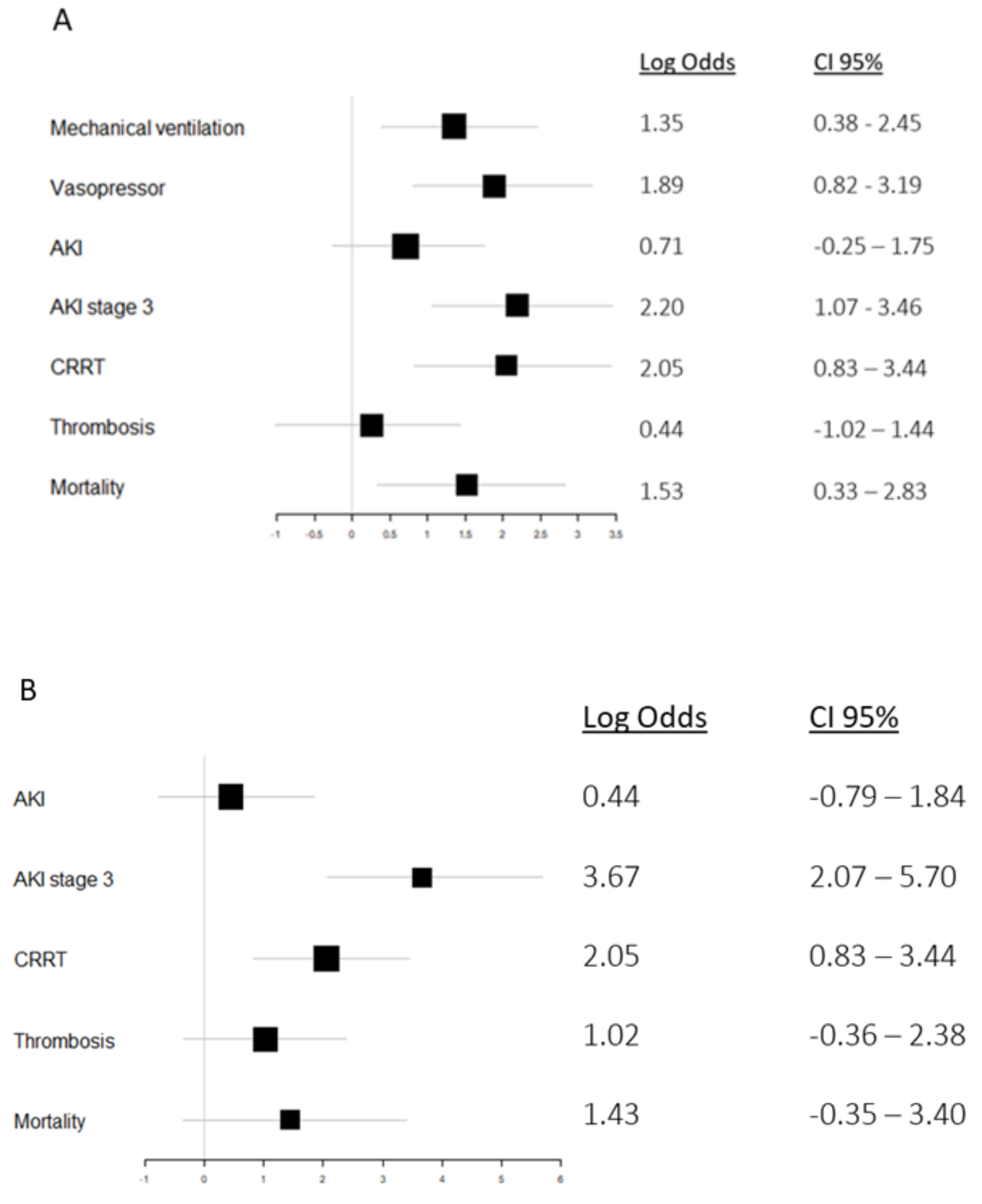
3.5. HNL and Mortality
3.6. HNL, Organ Support, and Thrombosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tyrrell, C.S.B.; Mytton, O.T.; Gentry, S.V.; Thomas-Meyer, M.; Allen, J.L.Y.; Narula, A.A.; McGrath, B.; Lupton, M.; Broadbent, J.; Ahmed, A.; et al. Managing intensive care admissions when there are not enough beds during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. Thorax 2020, 76, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.A.; Kane, A.D.; Cook, T.M. Outcomes from intensive care in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta analysis of observational studies. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadim, M.K.; Forni, L.G.; Mehta, R.L.; Connor, M.J., Jr.; Liu, K.D.; Ostermann, M.; Rimmelé, T.; Zarbock, A.; Bell, S.; Bihorac, A.; et al. COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: Consensus report of the 25th Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) Workgroup. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, T.; Bülow-Anderberg, S.; Larsson, A.; Rubertsson, S.; Lipcsey, M.; Frithiof, R.; Hultström, M. COVID-19 patients in intensive care develop predominantly oliguric acute kidney injury. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2021, 65, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 693–704.
- Horby, P.W.; Campbell, M.; Staplin, N.; Spata, E.; Emberson, J.R.; Pessoa-Amorim, G.; Peto, L.; Brightling, C.E.; Sarkar, R.; Thomas, K.; et al. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): Preliminary results of a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): A randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, C. Neutrophils at the crossroads of innate and adaptive immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadas, T.N.; Cullere, X.; Lowell, C.A. The multifaceted functions of neutrophils. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 181–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grudzinska, F.S.; Sapey, E. Friend or foe? The dual role of neutrophils in lung injury and repair . Thorax 2018, 73, 305–307. [Google Scholar]
- Hellebrekers, P.; Vrisekoop, N.; Koenderman, L. Neutrophil phenotypes in health and disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, B.; Anders, H.J.; Desai, J.; Mulay, S.R. Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Drive Necroinflammation in COVID-19. Cells 2020, 9, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponti, G.; Maccaferri, M.; Ruini, C.; Tomasi, A.; Ozben, T. Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab Sci. 2020, 57, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, P.; Pu, L.; Xiong, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Tan, J.; Xu, Y.; Song, R.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts critical illness patients with 2019 coronavirus disease in the early stage. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veras, F.P.; Pontelli, M.C.; Silva, C.M.; Toller-Kawahisa, J.E.; de Lima, M.; Nascimento, D.C.; Schneider, A.H.; Caetité, D.; Tavares, L.A.; Paiva, I.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-triggered neutrophil extracellular traps mediate COVID-19 pathology. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20201129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huckriede, J.; Anderberg, S.B.; Morales, A.; de Vries, F.; Hultström, M.; Bergqvist, A.; Ortiz-Pérez, J.T.; Sels, J.W.; Wichapong, K.; Lipcsey, M.; et al. Evolution of NETosis markers and DAMPs have prognostic value in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15701. [Google Scholar]
- Radermecker, C.; Detrembleur, N.; Guiot, J.; Cavalier, E.; Henket, M.; d’Emal, C.; Vanwinge, C.; Cataldo, D.; Oury, C.; Delvenne, P.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps infiltrate the lung airway, interstitial, and vascular compartments in severe COVID-19. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kaur, S.; Guha, S.; Batra, S.K. The multifaceted roles of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) in inflammation and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2012, 1826, 129–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogt, K.L.; Summers, C.; Chilvers, E.R.; Condliffe, A.M. Priming and de-priming of neutrophil responses in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Carlson, M.; Engström, A.; Garcia, R.; Peterson, C.G.; Venge, P. Purification and characterization of a human neutrophil lipocalin (HNL) from the secondary granules of human neutrophils. Scand. J. Clin. Lab Investig. 1994, 54, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Rubin, J.; Han, W.; Venge, P.; Xu, S. The origin of multiple molecular forms in urine of HNL/NGAL. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awad, A.S.; Rouse, M.; Huang, L.; Vergis, A.L.; Reutershan, J.; Cathro, H.P.; Linden, J.; Okusa, M.D. Compartmentalization of neutrophils in the kidney and lung following acute ischemic kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Törnblom, S.; Nisula, S.; Vaara, S.T.; Poukkanen, M.; Andersson, S.; Pettilä, V.; Pesonen, E. Neutrophil activation in septic acute kidney injury: A post hoc analysis of the FINNAKI study. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2019, 63, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, R.P.; Metnitz, P.G.; Almeida, E.; Jordan, B.; Bauer, P.; Campos, R.A.; Iapichino, G.; Edbrooke, D.; Capuzzo, M.; Le Gall, J.-R. SAPS 3--From evaluation of the patient to evaluation of the intensive care unit. Part 2: Development of a prognostic model for hospital mortality at ICU admission. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonça, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, C.K.; Suter, P.; Thijs, L.G. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venge, P.; Håkansson, L.D.; Garwicz, D.; Peterson, C.; Xu, S.; Pauksen, K. Human neutrophil lipocalin in fMLP-activated whole bloodas a diagnostic means to distinguish between acute bacterial and viral infections. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 424, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Jing, H.; Hongtao, P.; Furong, J.; Yuting, J.; Xu, S.; Venge, P. Distinction between bacterial and viral infections by serum measurementof human neutrophil lipocalin (HNL) and the impact of antibody selection. J. Immunol. Methods 2016, 432, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2019, 394, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultström, M.; von Seth, M.; Frithiof, R. Hyperreninemia and low total body water may contribute to acute kidney injury inCOVID-19 patients in intensive care. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1613–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.; Neugarten, J.; Bellin, E.; Yunes, M.; Stahl, L.; Johns, T.S.; Abramowitz, M.K.; Levy, R.; Kumar, N.; Mokrzycki, M.H.; et al. AKI in Hospitalized Patients with and without COVID-19: A Comparison Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Parikh, C.R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Liu, K.D.; Coca, S.G.; Garg, A.X.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Siew, E.D.; Wurfel, M.M.; et al. A prospective cohort study of acute kidney injury and kidney outcomes, cardiovascular events, and death. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurink, B.; Roos, E.; Radonic, T.; Barbe, E.; Bouman, C.S.C.; de Boer, H.H.; de Bree, G.J.; Bulle, E.B.; Aronica, E.M.; Florquin, S.; et al. Viral presence and immunopathology in patients with lethal COVID-19: A prospective autopsy cohort study. Lancet Microbe. 2020, 1, e290–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; González-Rivera, M.; Almansa, R.; Micheloud, D.; Tedim, A.P.; Domínguez-Gil, M.; Resino, S.; Martín-Fernández, M.; Murua, P.R.; Pérez-García, F.; et al. Viral RNA load in plasma is associated with critical illness and a dysregulated host response in COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järhult, J.D.; Hultström, M.; Bergqvist, A.; Frithiof, R.; Lipcsey, M. The impact of viremia on organ failure, biomarkers and mortality in a Swedish cohort of critically ill COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frithiof, R.; Bergqvist, A.; Järhult, J.D.; Lipcsey, M.; Hultström, M. Presence of SARS-CoV-2 in urine is rare and not associated with acute kidney injury in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, J.; Soehnlein, O. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo Marin, B.; Aghagoli, G.; Lavine, K.; Yang, L.; Siff, E.J.; Chiang, S.S.; Salazar-Mather, T.P.; Dumenco, L.; Savaria, M.C.; Aung, S.N.; et al. Predictors of COVID-19 severity: A literature review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31, 182–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Yalavarthi, S.; Shi, H.; Gockman, K.; Zuo, M.; Madison, J.A.; Blair, C.; Weber, A.; Barnes, B.J.; Egeblad, M.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e138999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arcanjo, A.; Logullo, J.; Menezes, C.C.B.; de Souza Carvalho Giangiarulo, T.C.; dos Reis, M.C.; de Castro, G.M.M.; Fontes, Y.D.S.; Todeschini, A.R.; Freire-De-Lima, L.; Decoté-Ricardo, D.; et al. The emerging role of neutrophil extracellular traps in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (COVID-19). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, C.L.; Ma, Q.; Dastrala, S.; Bennett, M.; Mitsnefes, M.M.; Barasch, J.; Devarajan, P. Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts acute kidney injury, morbidity and mortality after pediatric cardiac surgery: A prospective uncontrolled cohort study. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, A.; Hayase, N.; Doi, K. Acute Kidney Injury Induces Innate Immune Response and Neutrophil Activation in the Lung. Front. Med. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joannidis, M.; Forni, L.G.; Klein, S.J.; Honore, P.M.; Kashani, K.; Ostermann, M.; Prowle, J.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Darmon, M.; et al. Lung-kidney interactions in critically ill patients: Consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 21 Workgroup. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 654–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rewa, O.; Wald, R.; Adhikari, N.K.; Hladunewich, M.; Lapinsky, S.; Muscedere, J.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Smith, O.M.; Lebovic, G.; Kuint, R.; et al. Whole-blood neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin to predict adverse events in acute kidney injury: A prospective observational cohort study. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuartero, M.; Betbesé, A.J.; Núñez, K.; Baldirà, J.; Ordonez-Llanos, J. Does Whole-Blood Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Stratify Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients? Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 8480925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No AKI (n = 36) | AKI Stage 1 and 2 (n = 49) | AKI Stage 3 (n = 18) | All (n = 103) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 55.9 (15.8) | 59.3 (14.4) | 67.0 (9.0) | 60.5 (14.1) |
| Female, n (%) | 11 (31%) | 15 (30%) | 1 (6%) | 27 (26%) |
| BMI, mean (SD) n = 89 | 27.6 (4.5) (n = 28) | 29.5 (6.0) (n = 46) | 32.2 (11.0) (n = 15) | 29.6 (6.0) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 15 (42%) | 25 (51%) (n = 48) | 13 (72%) | 53 (52%) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 7 (19%) | 17 (35%) (n = 48) | 5 (28%) | 29 (28%) |
| Pulmonary disease n (%) | 11 (31%) | 10 (20%) (n = 48) | 4 (22%) | 25 (24%) |
| Days since symptom onset, median (IQR) n = 103 | 11 (3) | 10 (4) | 10 (5) | 10 (4) |
| SAPS3, median (IQR) n = 101 | 51 (7) (n = 34) | 53 (17) | 55 (9) | 54 (11) |
| SOFA admission, median (IQR) n = 100 | 4 (3) (n = 24) | 6 (4) (n = 47) | 6 (5) (n = 15) | 5 (4) |
| AKI, any stage, n (%) | na | na | na | 67 (65%) |
| Stage 1, n (%) | na | na | na | 33 (32%) |
| Stage 2, n (%) | na | na | na | 16 (16%) |
| Stage 3, n (%) | na | na | na | 18 (17%) |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio at admission, median (IQR) n = 99 | 93.8 (42.8) (n = 34) | 80.3 (29.3) (n = 47) | 75.0 (25.5) | 80.3 (29.3) |
| Free days | ||||
| ICU, mean (SD) | 18.2 (9.5) | 13.1 (10.7) | 4.2 (7.2) | 13.4 (10.8) |
| Invasive ventilation, mean (SD) | 23.0 (10.4) | 17.3 (12.9) | 7.8 (10.1) | 17.6 (12.6) |
| Vasopressor, mean (SD) | 24.3 (10.3) | 18.4 (12.7) | 9.7 (10.6) | 18.9 (12.5) |
| CRRT, mean (SD) | 26.7 (9.6) | 20.8 (14.0) | 9.6 (11.9) | 20.9 (13.5) |
| 30-day mortality, n (%) | 4 (11%) | 10 (20%) | 6 (33%) | 20 (19.4%) |
| At Admission | Peak | Reference Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L), median (IQR) | 168 (109) n = 99 | 286 (191) n = 101 | <5 |
| Leukocytes (109/L), median (IQR) | 7.4 (3.9) n = 100 | 13.4 (8.7) n = 101 | 3.5–9.0 |
| Neutrophils (109/L), median (IQR) | 6.0 (4.1) n = 84 | 9.2 (6.2) n = 93 | 1.3–5.4 |
| Procalcitonin (ug/L), median (IQR) | 0.46 (0.93) n = 93 | 1.50 (4.14) n = 100 | <0.05 |
| Ferritin (ug/L), median (IQR) | 1284 (2051) n = 83 | 2429 (2635) n = 101 | 25–310 |
| Interleukin-6 (pg/mL), median (IQR) | 30.0 (48.7) n = 101 | na | na |
| Interleukin-8 (pg/mL), median (IQR) | 15.1 (14.1) n = 101 | na | na |
| B-HNL (µg/L), median (IQR) | 96.6 (71.2) * n = 67 | 134 (101) n = 67 | 95.5 (55) |
| P-HNL (µg/L), median (IQR) | 9.5 (7.5) n = 100 | 11.1 (8.2) n = 103 | 3.6 (2) |
| NLR, median (IQR) | 6.7 (4.9) n = 83 | 8.1 (7.6) n = 90 | na |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bülow Anderberg, S.; Lipcsey, M.; Hultström, M.; Eriksson, A.-K.; Venge, P.; Frithiof, R.; on behalf of the Uppsala Intensive Care COVID-19 Research Group. Systemic Human Neutrophil Lipocalin Associates with Severe Acute Kidney Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184144
Bülow Anderberg S, Lipcsey M, Hultström M, Eriksson A-K, Venge P, Frithiof R, on behalf of the Uppsala Intensive Care COVID-19 Research Group. Systemic Human Neutrophil Lipocalin Associates with Severe Acute Kidney Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(18):4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184144
Chicago/Turabian StyleBülow Anderberg, Sara, Miklos Lipcsey, Michael Hultström, Ann-Katrin Eriksson, Per Venge, Robert Frithiof, and on behalf of the Uppsala Intensive Care COVID-19 Research Group. 2021. "Systemic Human Neutrophil Lipocalin Associates with Severe Acute Kidney Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 18: 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184144
APA StyleBülow Anderberg, S., Lipcsey, M., Hultström, M., Eriksson, A.-K., Venge, P., Frithiof, R., & on behalf of the Uppsala Intensive Care COVID-19 Research Group. (2021). Systemic Human Neutrophil Lipocalin Associates with Severe Acute Kidney Injury in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(18), 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184144







