Multiple Comorbidity Profile of Psychiatric Disorders in Epilepsy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Evaluation
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kessler, R.C.; Chiu, W.T.; Demler, O.; Walters, E.E. Prevalence, Severity, and Comorbidity of 12-Month DSM-IV Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, A.J.; Sharpe, L.; Hunt, C.; Gandy, M. Anxiety and depressive disorders in people with epilepsy: A meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellez-Zenteno, J.F.; Patten, S.B.; Jetté, N.; Williams, J.; Wiebe, S. Psychiatric Comorbidity in Epilepsy: A Population-Based Analysis. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 2336–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmagro, C.L.; Velasco, T.R.; Bianchin, M.M.; Martins, A.P.P.; Guarnieri, R.; Cescato, M.P.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr.; Assirati, J.A., Jr.; Araújo, D., Jr.; Santos, A.C.; et al. Psychiatric comorbidity in refractory focal epilepsy: A study of 490 patients. Epilepsy Behav. 2012, 25, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.E.; Hermann, B.P.; Barry, J.J.; Gilliam, F.; Kanner, A.M.; Meador, K.J. Clinical Assessment of Axis I Psychiatric Morbidity in Chronic Epilepsy: A Multicenter Investigation. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineka, S.; Watson, D.; Clark, L.A. Comorbidity of anxiety and unipolar mood disorders. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1998, 49, 377–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, T.A.; Campbell, L.A.; Lehman, C.L.; Grisham, J.R.; Mancill, R.B. Current and lifetime comorbidity of the DSM-IV anxiety and mood disorders in a large clinical sample. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2001, 110, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, M.; Rankin, M.A.; Wright, E.C.; Alpert, J.E.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Pava, J.; Rosenbaum, J.F. Anxiety disorders in major depression. Compr. Psychiatry 2000, 41, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, F.; Van Oppen, P.; Comijs, H.C.; Smit, J.H.; Spinhoven, P.; Van Balkom, A.J.L.M.; Nolen, W.A.; Zitman, F.G.; Beekman, A.T.F.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Comorbidity patterns of anxiety and depressive disorders in a large cohort study: The Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety (NESDA). J. Clin. Psychiatry 2011, 72, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfield, R.M.A. The Comorbidity of Major Depression and Anxiety Disorders: Recognition and Management in Primary Care. Prim. Care Companion J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 3, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, J. Depression and anxiety: Implications for nosology, course, and treatment. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1997, 58 (Suppl. 8), 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, R.C. The global burden of anxiety and mood disorders: Putting the European Study of the Epidemiology of Mental Disorders (ESEMeD) findings into perspective. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2007, 68 (Suppl. 2), 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, R.C.; Dupont, R.L.; Berglund, P.; Wittchen, H.U. Impairment in pure and comorbid generalized anxiety disorder and major depression at 12 months in two national surveys. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ording, A.; Sørensen, H.H.T. Concepts of comorbidities, multiple morbidities, complications, and their clinical epidemiologic analogs. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 5, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Josephson, C.B.; Jetté, N. Psychiatric comorbidities in epilepsy. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2017, 29, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiglusz, M.S.; Landowski, J.; Michalak, L.; Cubała, W.J. Reevaluating the prevalence and diagnostic subtypes of depressive disorders in epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 53, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiglusz, M.S.; Landowski, J.; Cubała, W.J. Prevalence of anxiety disorders in epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 79, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proposal for Revised Classification of Epilepsies and Epileptic Syndromes. Epilepsia 1989, 30, 389–399. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- First, M.B.; Spitzer, R.L.; Gibbon, M.; Williams, J. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders, Research Version; Biometrics Research, New York State Psychiatric Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein-Piekarski, A.N.; Williams, L.M.; Humphreys, K. A trans-diagnostic review of anxiety disorder comorbidity and the impact of multiple exclusion criteria on studying clinical outcomes in anxiety disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Berglund, P.A.; Chiu, W.T.; Demler, O.; Heeringa, S.; Hiripi, E.; Jin, R.; Pennell, B.-E.; Walters, E.E.; Zaslavsky, A.; et al. The US National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R): Design and field procedures. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2004, 13, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kessler, R.C.; Merikangas, K.R. The National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R): Background and aims. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2004, 13, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; McLeish, A.C.; Shear, P.K.; Privitera, M. Panic and epilepsy in adults: A systematic review. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 85, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.; McLeish, A.C.; Alsaid-Habia, T.; Shear, P.K.; Privitera, M. Anxiety Sensitivity as a Predictor of Epilepsy-Related Quality of Life and Illness Severity Among Adult Epilepsy. Cogn. Ther. Res. 2019, 43, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandy, M.; Sharpe, L.; Perry, K.N.; Miller, L.; Thayer, Z.; Boserio, J.; Mohamed, A. Anxiety in epilepsy: A neglected disorder. J. Psychosom. Res. 2015, 78, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandy, M.; Sharpe, L.; Perry, K.N.; Miller, L.; Thayer, Z.; Boserio, J.; Mohamed, A. Rates of DSM-IV mood, anxiety disorders, and suicidality in Australian adult epilepsy outpatients: A comparison of well-controlled versus refractory epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2013, 26, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, A.M.; Barry, J.J.; Gilliam, F.; Hermann, B.; Meador, K.J. Anxiety disorders, subsyndromic depressive episodes, and major depressive episodes: Do they differ on their impact on the quality of life of patients with epilepsy? Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuladee, S.; Prachason, T.; Srisopit, P.; Trakulchang, D.; Boongird, A.; Wisajan, P.; Jullagate, S. Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in Thai patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 90, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mintzer, S.; Lopez, F. Comorbidity of ictal fear and panic disorder. Epilepsy Behav. 2002, 3, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, D. Comorbidity of ictal fear and panic disorder. Epilepsy Behav. 2002, 3, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, D.; Montouris, G.; Davies, K. The interictal dysphoric disorder: Recognition, pathogenesis, and treatment of the major psychiatric disorder of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2004, 5, 826–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mula, M.; Jauch, R.; Cavanna, A.; Gaus, V.; Kretz, R.; Collimedaglia, L.; Barbagli, D.; Cantello, R.; Monaco, F.; Schmitz, B. Interictal Dysphoric Disorder and Periictal Dysphoric Symptoms in Patients with Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanner, A.M.; Soto, A.; Gross-Kanner, H. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Postictal Psychiatric Symptoms in Partial Epilepsy. Neurology 2004, 62, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, L.; A Scuffham, P.; Hilton, M.F.; Muspratt, A.; Ng, S.-K.; A Whiteford, H. Patterns of multimorbidity in working Australians. Popul. Health Metrics 2011, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schäfer, I.; Von Leitner, E.-C.; Schön, G.; Koller, D.; Hansen, H.; Kolonko, T.; Kaduszkiewicz, H.; Wegscheider, K.; Glaeske, G.; Bussche, H.V.D. Multimorbidity Patterns in the Elderly: A New Approach of Disease Clustering Identifies Complex Interrelations between Chronic Conditions. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitson, H.E.; Duan-Porter, W.; Schmader, K.E.; Morey, M.C.; Cohen, H.J.; Colón-Emeric, C.S. Physical Resilience in Older Adults: Systematic Review and Development of an Emerging Construct. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med Sci. 2016, 71, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, J.; Jacoby, A.; Baker, G.A.; Marson, A.; Ring, A.; Whitehead, M. Factors predictive of resilience and vulnerability in new-onset epilepsy. Epilepsia 2010, 52, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No Affective Disorders (n = 56) | MDD (n = 21) | Other Depressive Disorders (n = 19) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy-related characteristics | ||||
| Age of seizure onset: mean (SD) | 16.8 (10.3) | 27.4 (13.5) * | 18.5 (8.8) | 0.001 # |
| Duration of epilepsy: mean (SD) | 18.5 (11.1) | 16.8 (12.6) | 12.9 (9.1) | |
| Number of seizures/last month-median (IQR) | 4 (2, 5) | 3 (2, 6) | 2 (2, 8) | |
| Seizure type (%) | 3 (5.4) | 1 (4.8) | 3(15.8) | |
| simple partial | 16 (28.6) | 5 (23.8) | 6 (31.6) | |
| complex partial | 26 (46.4) | 13 (61.9) | 8 (42.1) | |
| partial evolving to general | 8 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (10.5) | |
| tonic–clonic | 2 (3.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| absence | 0(0.0) | 1(4.8) | 0 (0.0) | |
| myoclonic atonic | 1 (1.8) | 1 (4.8) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Number of AEDs (IQR) | 1.5 (1, 2) | 1 (1, 2) | 2 (1, 2) | |
| Receiving AEDs with negative psychotropic effects (%) | 16 (28.6) | 5 (23.8) | 8 (42.1) | |
| Drug resistant (%) | 43 (76.8) | 14 (66.7) | 13 (68.4) | |
| Polytherapy (%) | 26 (46.4) | 8 (38.1) | 12 (63.2) |
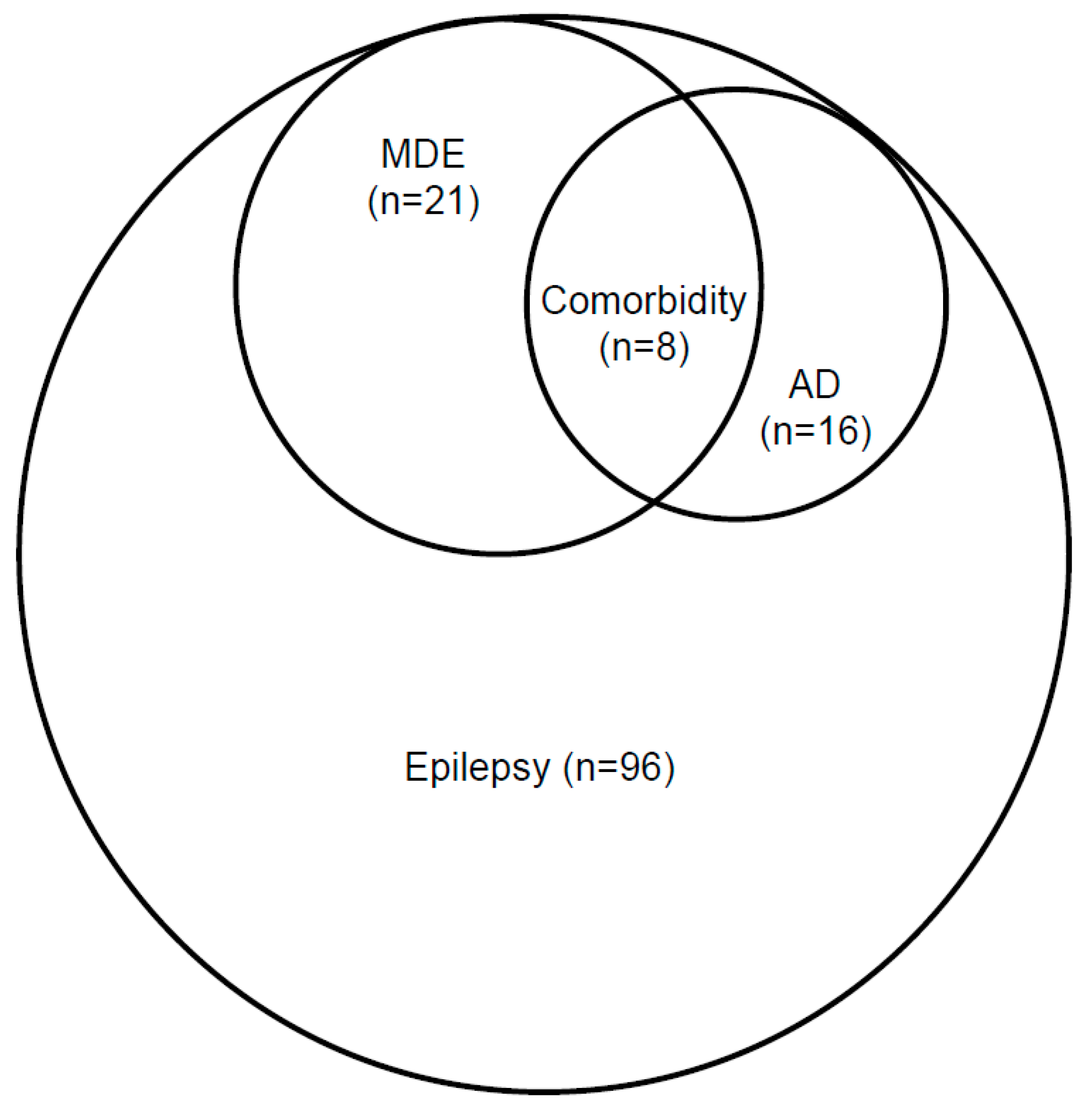
| Anxiety Disorders: | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD (+) | AD (−) | SUM | ||||||||
| Major depressive episode (MDE): | N | N | N | |||||||
| column% | column% | column% | ||||||||
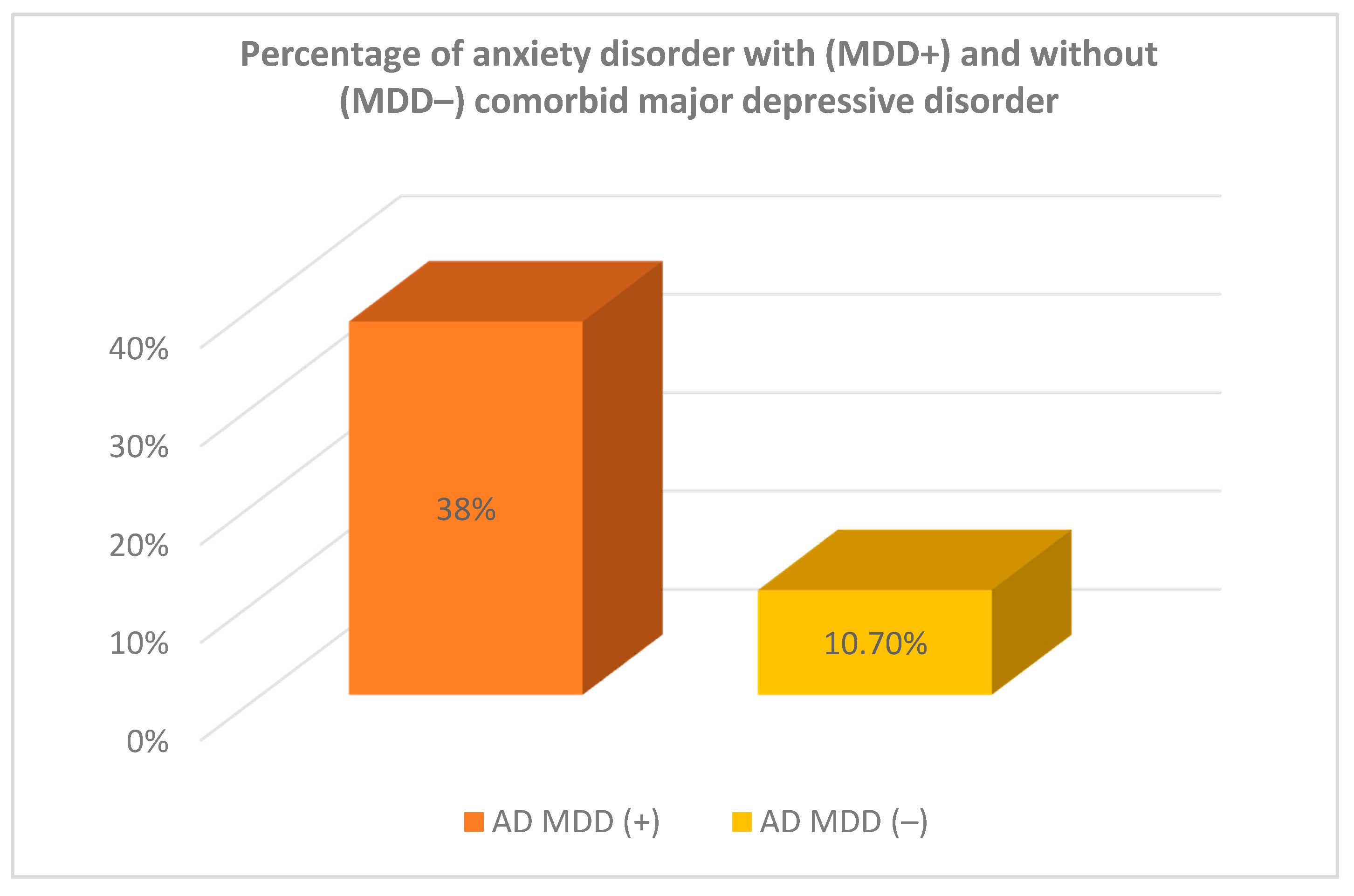
| MDE (−) | N | 8 | 67 | 75 | ||||||
| row% | 10.7% | 89.3% | 100% | |||||||
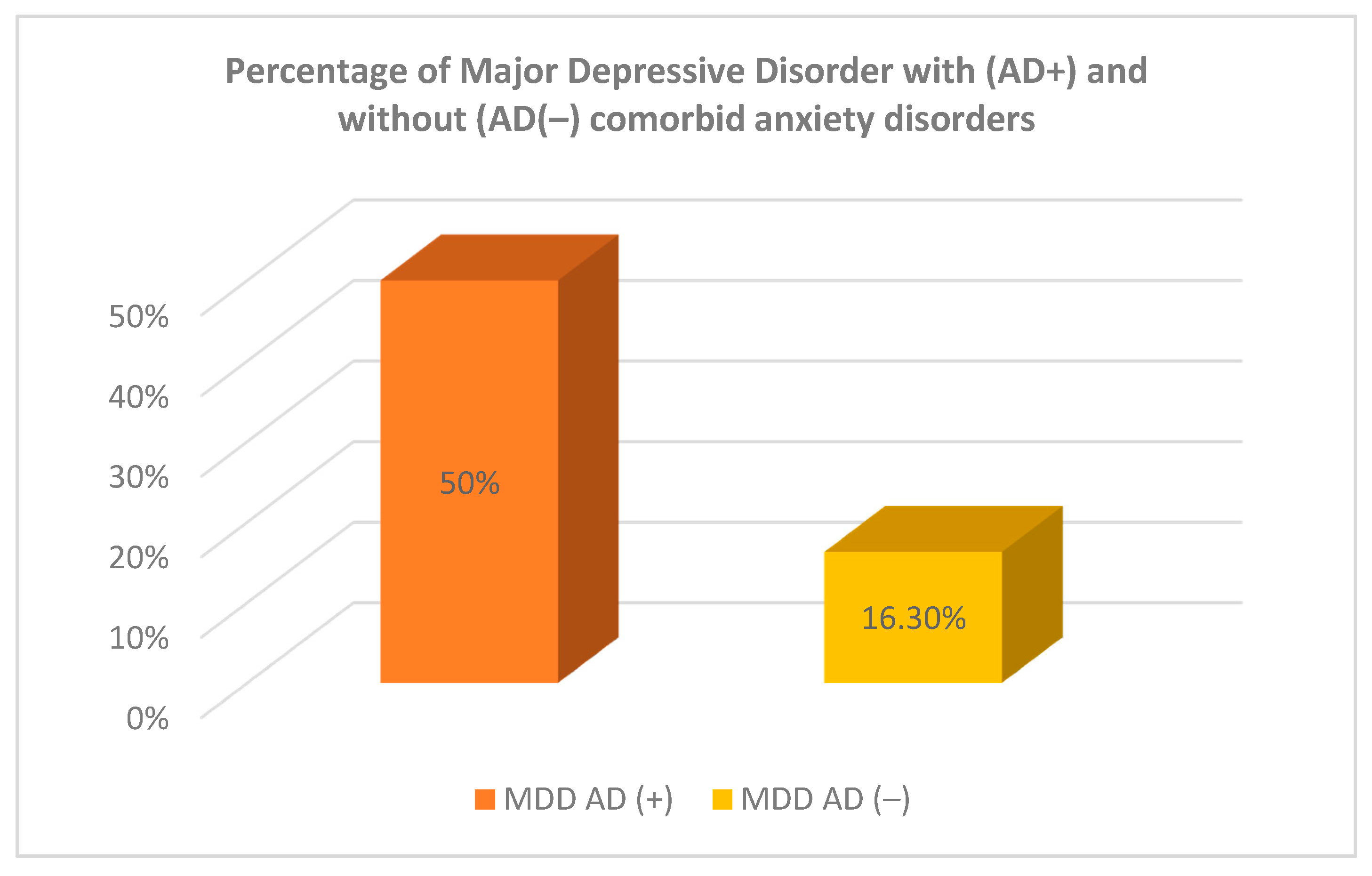
| 50% | 83.7% | 78.1% | ||||||||
| MDE (+) | N | 8 | 13 | 21 | ||||||
| row% | 38.1% | 61.9% | 100% | |||||||
| 50% | 16.3% | 11.9% | ||||||||
| SUM | N | 16 | 80 | 96 | ||||||
| row% | 16.7% | 83.3% | 100% | |||||||
| 100% | 100% | 100% | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzegorzewska, A.M.; Wiglusz, M.S.; Landowski, J.; Jakuszkowiak-Wojten, K.; Cubała, W.J.; Włodarczyk, A.; Szarmach, J. Multiple Comorbidity Profile of Psychiatric Disorders in Epilepsy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184104
Grzegorzewska AM, Wiglusz MS, Landowski J, Jakuszkowiak-Wojten K, Cubała WJ, Włodarczyk A, Szarmach J. Multiple Comorbidity Profile of Psychiatric Disorders in Epilepsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(18):4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184104
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzegorzewska, Agata M., Mariusz S. Wiglusz, Jerzy Landowski, Katarzyna Jakuszkowiak-Wojten, Wiesław J. Cubała, Adam Włodarczyk, and Joanna Szarmach. 2021. "Multiple Comorbidity Profile of Psychiatric Disorders in Epilepsy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 18: 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184104
APA StyleGrzegorzewska, A. M., Wiglusz, M. S., Landowski, J., Jakuszkowiak-Wojten, K., Cubała, W. J., Włodarczyk, A., & Szarmach, J. (2021). Multiple Comorbidity Profile of Psychiatric Disorders in Epilepsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(18), 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184104






