Ultrasound Elastography in the Assessment of the Intestinal Changes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease—Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
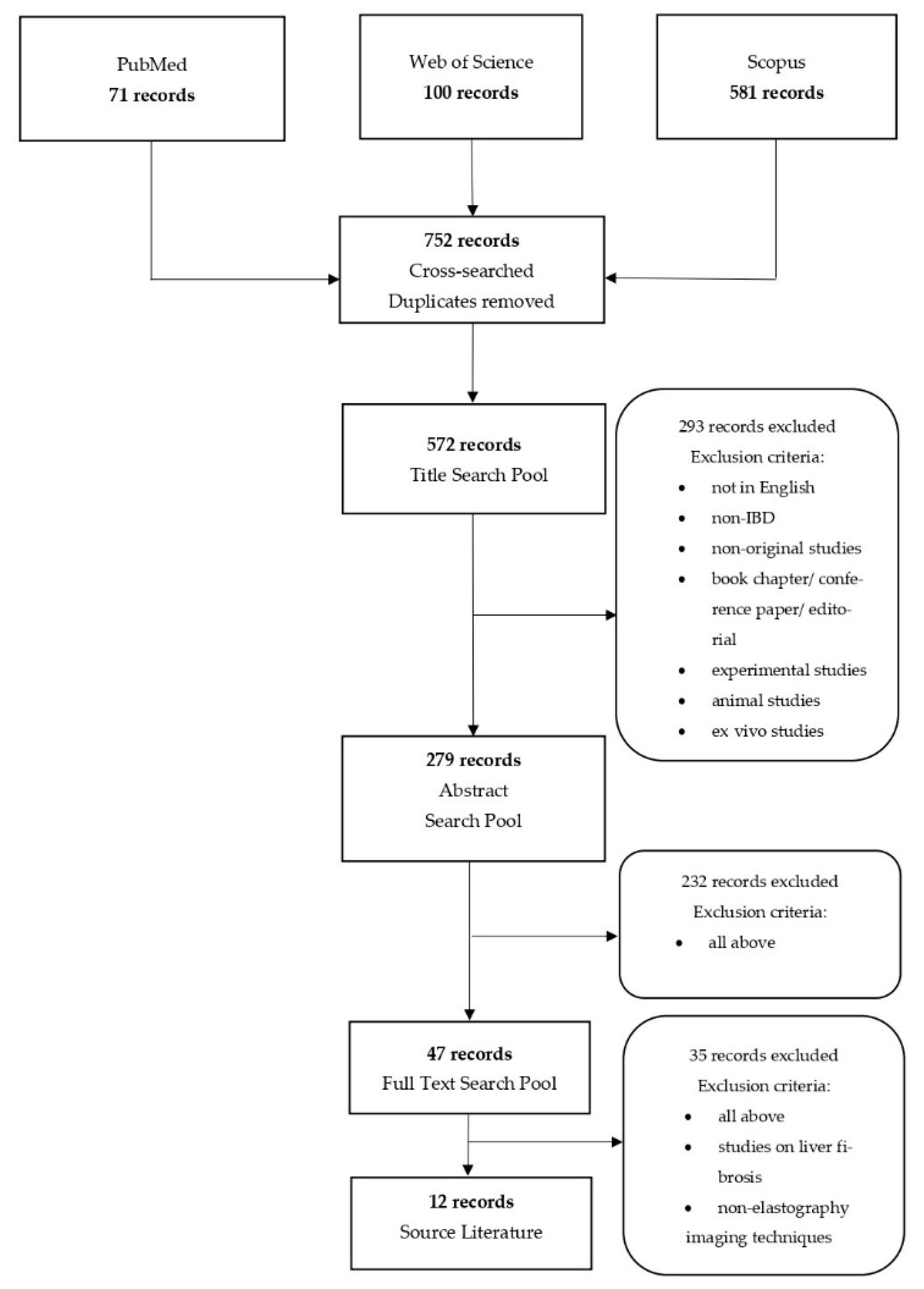
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Interpretative Synthesis of Data: Elastography in CD
3.2. Interpretative Synthesis of Data: Elastography in UC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2018, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Mehandru, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.B.; Xavier, R.J. Pathway paradigms revealed from the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2020, 578, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, F.; Langner, C.; Driessen, A.; Ensari, A.; Geboes, K.; Mantzaris, G.J.; Villanacci, V.; Becheanu, G.; Borralho Nunes, P.; Cathomas, G.; et al. European consensus on the histopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeri, N.; Pollok, R.C. Diagnostic imaging and radiation exposure in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromke, M.A.; Neubauer, K.; Kempiński, R.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M. Faecal calprotectin in assessment of mucosal healing in adults with inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garra, B.S. Elastography: History, principles, and technique comparison. Abdom. Imaging 2015, 40, 680–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich-Rust, M.; Poynard, T.; Castera, L. Critical comparison of elastography methods to assess chronic liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.R.; Suh, C.H.; Yoon, H.M.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, Y.A.; Jung, A.Y. The diagnostic performance of shear-wave elastography for liver fibrosis in children and adolescents: A systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, R.M.; Liau, J.; Kaffas, A.E.; Chammas, M.C.; Willmann, J.K. Ultrasound elastography: Review of techniques and clinical applications. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1303–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, N.; Tanaka, S. Elastography for the pancreas: Current status and future perspective. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3712–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Barr, R.G.; Farrokh, A.; Dighe, M.; Hocke, M.; Jenssen, C.; Dong, Y.; Saftoiu, A.; Havre, R.F. Strain elastography—How to do it? Ultrasound Int. Open 2017, 3, E137–E149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, D.; Piscaglia, F.; Bamber, J.; Bojunga, J.; Correas, J.M.; Gilja, O.H.; Klauser, A.S.; Sporea, I.; Calliada, F.; Cantisani, V.; et al. EFSUMB Guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography part 2: Clinical applications. Ultraschall Med. 2013, 34, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afdhal, N.H. Fibroscan (transient elastography) for the measurement of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 8, 605–607. [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale, K. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging: A review. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2011, 7, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvazyan, A.; Hall, T.J.; Urban, M.W.; Fatemi, M.; Aglyamov, S.R.; Garra, B.S. An overview of elastography—An emerging branch of medical imaging. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2011, 7, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Johnson, L.A.; Jia, C.; Joyce, J.C.; Rangwalla, S.; Higgins, P.D.; Rubin, J.M. Noninvasive ultrasound elasticity imaging (UEI) of Crohn’s disease: Animal model. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stidham, R.W.; Xu, J.; Johnson, L.A.; Kim, K.; Moons, D.S.; McKenna, B.J.; Rubin, J.M.; Higgins, P.D. Ultrasound elasticity imaging for detecting intestinal fibrosis and inflammation in rats and humans with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillman, J.R.; Stidham, R.W.; Higgins, P.D.; Moons, D.S.; Johnson, L.A.; Rubin, J.M. US elastography-derived shear wave velocity helps distinguish acutely inflamed from fibrotic bowel in a Crohn’s disease animal model. Radiology 2013, 267, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Müller, H.P.; Grittner, U.; Metzke, D.; Fischer, A.; Guckelberger, O.; Pascher, A.; Sack, I.; Vieth, M.; Rudolph, B. US-based real-time elastography for the detection of fibrotic gut tissue in patients with stricturing Crohn disease. Radiology 2015, 275, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraquelli, M.; Branchi, F.; Cribiù, F.M.; Orlando, S.; Casazza, G.; Magarotto, A.; Massironi, S.; Botti, F.; Contessini-Avesani, E.; Conte, D.; et al. The role of ultrasound elasticity imaging in predicting ileal fibrosis in Crohn’s disease patients. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fufezan, O.; Asavoaie, C.; Tamas, A.; Farcau, D.; Serban, D. Bowel elastography-a pilot study for developing an elastographic scoring system to evaluate disease activity in pediatric Crohn’s disease. Med. Ultrason. 2015, 17, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sconfienza, L.M.; Cavallaro, F.; Colombi, V.; Pastorelli, L.; Tontini, G.; Pescatori, L.; Esseridou, A.; Savarino, E.; Messina, C.; Casale, R.; et al. In-vivo axial-strain sonoelastography helps distinguish acutely-inflamed from fibrotic terminal ileum strictures in patients with Crohn’s disease: Preliminary results. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Re, G.; Picone, D.; Vernuccio, F.; Scopelliti, L.; Di Piazza, A.; Tudisca, C.; Serraino, S.; Privitera, G.; Midiri, F.; Salerno, S.; et al. Comparison of US strain elastography and entero-MRI to typify the mesenteric and bowel wall changes during Crohn’s disease: A pilot study. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4257987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.; Rizzello, F.; Pratico’, C.; Felicani, C.; Fiorini, E.; Brugnera, R.; Mazzotta, E.; Giunchi, F.; Fiorentino, M.; D’Errico, A.; et al. Real-time elastography for the detection of fibrotic and inflammatory tissue in patients with stricturing Crohn’s disease. J. Ultrasound 2017, 20, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaia, E.; Gennari, A.G.; Cova, M.A.; van Beek, E.J. Differentiation of inflammatory from fibrotic ileal strictures among patients with Crohn’s disease based on visual analysis: Feasibility study combining conventional B-mode ultrasound, contrast-enhanced ultrasound and strain elastography. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Gui, X.; Chen, W.; Fung, T.; Novak, K.; Wilson, S.R. Ultrasound shear wave elastography and contrast enhancement: Effective biomarkers in Crohn’s disease strictures. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, R.S.; Lueke, C.; Wildner, D.; Vitali, F.; Neurath, M.F.; Strobel, D. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography of the bowel wall as a possible marker of inflammatory activity in patients with Crohn’s disease. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Mao, R.; Li, X.H.; Cao, Q.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Liu, B.X.; Chen, S.L.; Chen, B.L.; He, Y.; Zeng, Z.R.; et al. Real-time shear wave ultrasound elastography differentiates fibrotic from inflammatory strictures in patients with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Kunisaki, R.; Kinoshita, H.; Kimura, H.; Kodera, T.; Nozawa, A.; Hanzawa, A.; Shibata, N.; Yonezawa, H.; Miyajima, E.; et al. Doppler ultrasound findings correlate with tissue vascularity and inflammation in surgical pathology specimens from patients with small intestinal Crohn’s disease. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.S.; Fang, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhao, C.K.; Xiang, L.H.; Liu, H.; Pu, H.; Xu, G.; Zhang, K.; Xu, X.R.; et al. Usefulness of strain elastography, ARFI imaging, and point shear wave elastography for the assessment of Crohn disease strictures. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 2861–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goertz, R.S.; Lueke, C.; Schellhaas, B.; Pfeifer, L.; Wildner, D.; Neurath, M.F.; Strobel, D. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) shear wave elastography of the bowel wall in healthy volunteers and in ulcerative colitis. Acta Radiol. Open 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, J.R.; van den Brink, G.R.; Steenkamer, J.; Buskens, C.J.; Bemelman, W.A.; Meisner, S.; Muncan, V.; te Velde, A.A.; D’Haens, G.R.; Wildenberg, M.E. Fibrostenotic phenotype of myofibroblasts in Crohn’s disease is dependent on tissue stiffness and reversed by LOX inhibition. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2018, 12, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieder, F.; Fiocchi, C.; Rogler, G. Mechanisms, management, and treatment of fibrosis in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thia, K.T.; Sandborn, W.J.; Harmsen, W.S.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Loftus, E.V. Risk factors associated with progression to intestinal complications of Crohn’s disease in a population-based cohort. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, J.W.Y.; Ng, S.C. Epidemiology of fibrostenosing inflammatory bowel disease. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulberg, J.D.; Wright, E.K.; Holt, B.A.; Wilding, H.E.; Hamilton, A.L.; Ross, A.L.; Kamm, M.A. Efficacy of drug and endoscopic treatment of Crohn’s disease strictures: A systematic review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 36, 344–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, H.M.; Coffey, J.C. Surgical treatment of intestinal stricture in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaser, C.; Sturm, A.; Vavricka, S.R.; Kucharzik, T.; Fiorino, G.; Annese, V.; Calabrese, E.; Baumgart, D.C.; Bettenworth, D.; Nunes, P.B.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for diagnostic assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, C.A.; Berinstein, J.A.; Louissaint, J.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Spence, J.R.; Shannon, C.; Lu, C.; Stidham, R.W.; Fletcher, J.G.; Bruining, D.H.; et al. Biomarkers for the Prediction and Diagnosis of Fibrostenosing Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettenworth, D.; Bokemeyer, A.; Baker, M.; Mao, R.; Parker, C.E.; Nguyen, T.; Ma, C.; Panés, J.; Rimola, J.; Fletcher, J.G.; et al. Assessment of Crohn’s disease-associated small bowel strictures and fibrosis on cross-sectional imaging: A systematic review. Gut 2019, 68, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ouali, S.; Click, B.; Holubar, S.D.; Rieder, F. Natural history, diagnosis and treatment approach to fibrostenosing Crohn’s disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, D.; Ando, T.; Watanabe, O.; Ishiguro, K.; Maeda, O.; Miyake, N.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; Ohmiya, N.; Hirooka, Y.; et al. Images of colonic real-time tissue sonoelastography correlate with those of colonoscopy and may predict response to therapy in patients with ulcerative colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustemovic, N.; Cukovic-Cavka, S.; Brinar, M.; Radić, D.; Opacic, M.; Ostojić, R.; Vucelic, B. A pilot study of transrectal endoscopic ultrasound elastography in inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Year | Total Subjects Included | Ultrasound Elastography Technique | Reference Standard | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baumgart et al. [20] | 2015 | 10 CD patients with ileocolonic CD and symptomatic stenosis that required surgery | Pre-, intra- and post-operative RTE | Histologic evaluation (morphometrics, disease activity, fibrosis); direct tensiometry strain measurement | The aggregated RTE strain mean values were significantly higher in unaffected than in affected gut segments (mean, 169.0 ± 27.9 vs. 43.0 ± 25.9; p < 0.001). There was significant association between RTE and collagen depositions. |
| Fraquelli et al. [21] | 2015 | 23 CD patients that required surgery; 20 CD patients with active non-structuring and non-penetrating disease | UEI of terminal ileum by means of color scale and quantitative strain ratio measurement | Semi-quantitative and quantitative histological image analysis: scores for fibrosis (mild/moderate versus severe) and acute/chronic inflammation (AIS, CIS) | The ileal strain ratio of inflammatory CD patients was significantly lower than in operated CD patients with severe fibrosis and was significantly correlated with the severity of bowel fibrosis at histological analysis; it was characterized by an excellent discriminatory ability for severe bowel fibrosis (AUC: 0.917). |
| Fufezan et al. [22] | 2015 | 48 bowel segments (30 ileum and 18 colon) in 14 pediatric CD patients | SE | Hydrosonography, clinical data, MRI (6 patients) | SE and SR correlated with disease activity markers (ESR, CRP) and hydrosonography findings. |
| Sconfienza et al. [23] | 2016 | 16 | SE of terminal ileum by means of color map and semi-quantitative scale | MRI enterography | RTS of the terminal ileum in CD may differentiate between fibrotic and inflammatory strictures. |
| Lu et al. [27] | 2017 | 95 patients; 15 patients had ileal resection | SWE | Histology (scores for inflammation, fibrosis, and muscular hypertrophy); CEUS | SWE mean value was significantly higher in a patient with surgery rather than without it (p < 0.01). There was a moderate correlation between SWE and muscular hypertrophy and no association between SWE and fibrosis score. |
| Serra et al. [25] | 2017 | 26 patients with symptomatic stricturing ileocolonic CD that required resection (29 bowel segments) | SE | Histopathology evaluation of CD (scoring system for inflammatory and fibrostenotic features) | No significant correlation was found between mean strain ratio and fibrosis score (p = 0.877). |
| Lo Re et al. [24] | 2017 | 35 (41 affected bowel segments and 35 unaffected) | SE | MRI | There was a correlation between US-SE color scale and T2 signal intensity, and between the US-SE color scale and ADC maps. |
| Quaia et al. [26] | 2018 | 20 | SE | Mucosal deep biopsy | Combination of the conventional B-mode ultrasound, CEUS and RTSE may support distinguishing of fibrotic strictures. |
| Goertz et al. [28] | 2018 | 77 retrospectively 21 prospectively | ARFI | Ultrasound parameters (bowel wall thickness and intramural semi-quantitative vascularization grade) | Retrospectively, the ARFI values correlated with the bowel wall thickness and Limberg vascularization score. Prospectively, there was no correlation between ARFI and bowel wall thickness, Limberg score, clinical activity, and CRP. A cut-off analysis of 105 ileal ARFI measurements showed a cut-off value of 1.92 m/s for the diagnosis of ileal inflammation with 75.3% sensitivity and 87.5% specificity. |
| Chen et al. [29] | 2018 | 35 with ileal/ileocolonic symptomatic strictures that required surgical resection | SWE | Histology (score for fibrotic and inflammatory CD) | The mean SWE value of stenotic bowel wall was significantly higher in severe fibrosis (23.0 ± 6.3 Kpa) than that in moderate (17.4 ± 3.8 Kpa) and mild fibrosis (14.4 ± 2.1 Kpa) (p = 0.008). Using 22.55 KPa as the cut-off value in discriminating between mild/moderate and severe fibrosis, the sensitivity and specificity was 69.6% and 91.7% (AUC 0.822, p = 0.002). |
| Ding et al. [31] | 2019 | 25 | SE, ARFI, p-SWE | histology | For SE, the optimal cut-off value was a score of 4 or greater (sensitivity, 75%; specificity, 66.7%; accuracy, 68%; PPV, 30%; NPV, 93.3%; AUROC, 0.708; however, p > 0.05). For ARFI, the optimal cut-off value was a score of 4 or greater (sensitivity, 50%; specificity, 81%; accuracy, 76%; PPV, 33.3%; NPV, 89.4%; AUROC, 0.669; p < 0.05). For p-SWE, the optimal cut-off value was reached when the shear wave velocity exceeded 2.73 m/s (sensitivity, 75%; specificity, 100%; accuracy, 96%; PPV, 100%; NPV, 95.5%; AUROC, 0.833; p < 0.05). |
| Author | Year | Total Subjects Included | Ultrasound Elastography Technique | Reference Standard | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goertz et al. [32] | 2019 | 20 UC 13 non-IBD | ARFI | ultrasound | ARFI values were higher in UC than in control group |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ślósarz, D.; Poniewierka, E.; Neubauer, K.; Kempiński, R. Ultrasound Elastography in the Assessment of the Intestinal Changes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease—Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184044
Ślósarz D, Poniewierka E, Neubauer K, Kempiński R. Ultrasound Elastography in the Assessment of the Intestinal Changes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease—Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(18):4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184044
Chicago/Turabian StyleŚlósarz, Dominika, Elżbieta Poniewierka, Katarzyna Neubauer, and Radosław Kempiński. 2021. "Ultrasound Elastography in the Assessment of the Intestinal Changes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease—Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 18: 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184044
APA StyleŚlósarz, D., Poniewierka, E., Neubauer, K., & Kempiński, R. (2021). Ultrasound Elastography in the Assessment of the Intestinal Changes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease—Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(18), 4044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184044






