Foot Revascularization Avoids Major Amputation in Persons with Diabetes and Ischaemic Foot Ulcers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
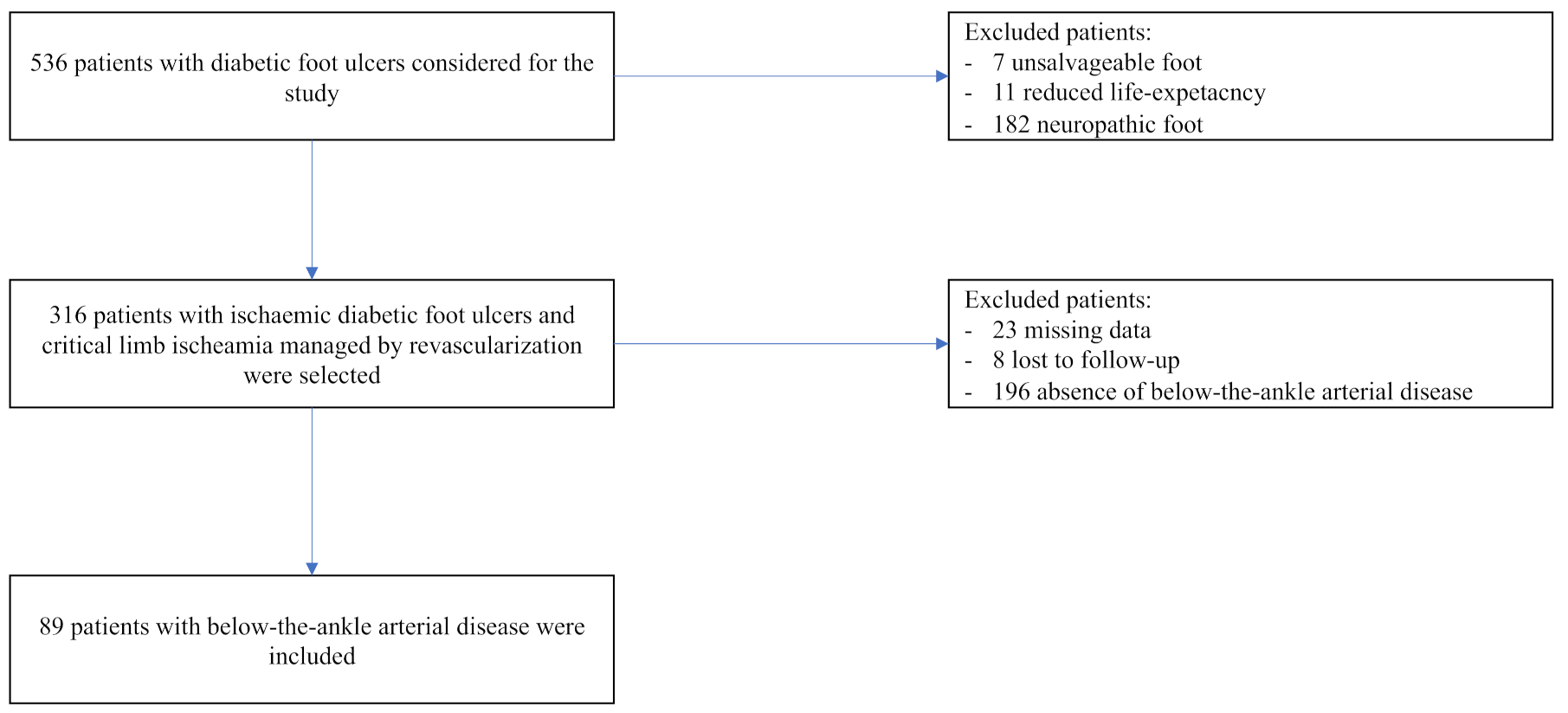
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Clinical Assessment
2.3. Ulcer Characteristics
2.4. Vascular Assessment
2.5. Clinical Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
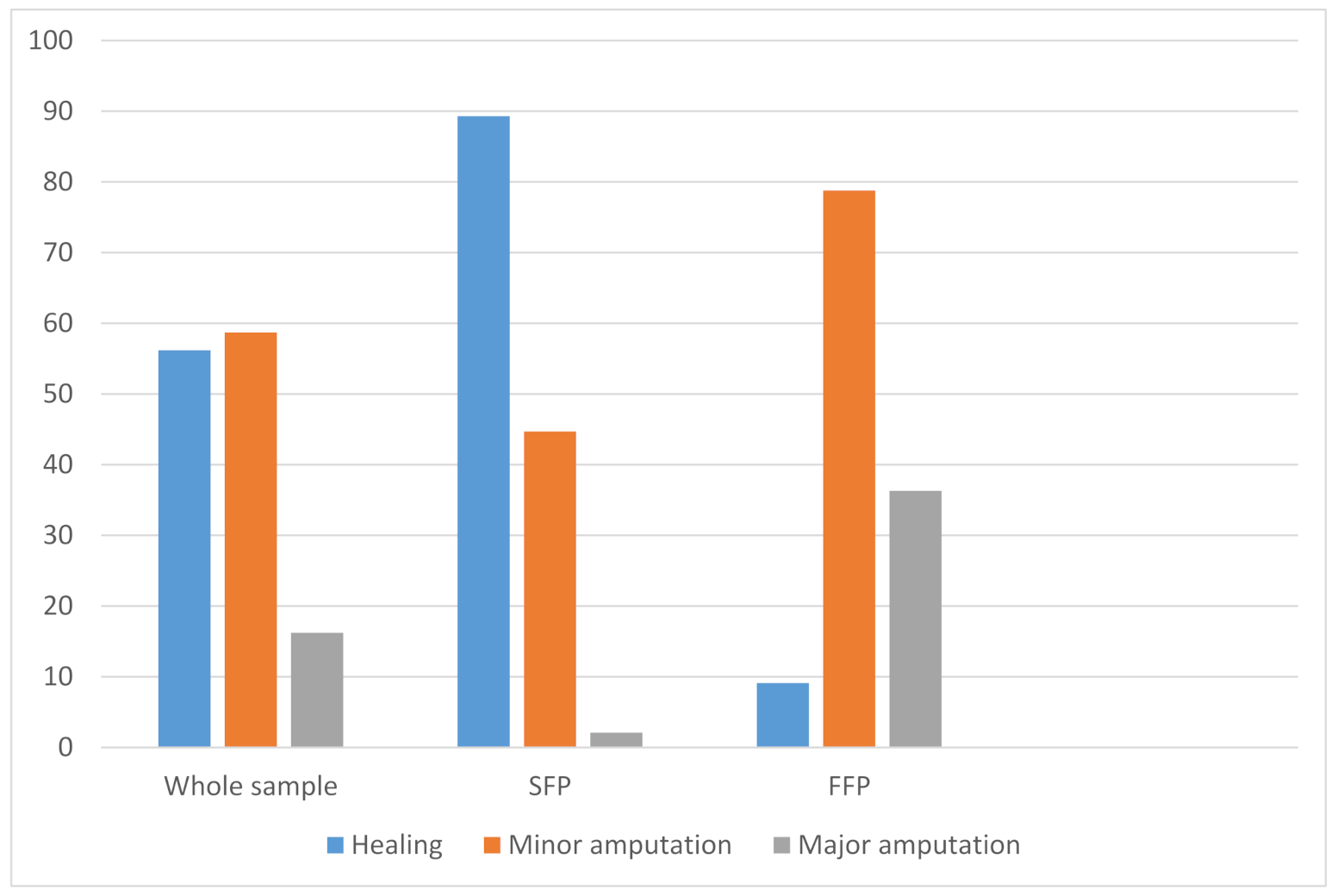
Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faglia, E.; Caravaggi, C.; Marchetti, R.; Mingardi, R.; Morabito, A.; Piaggesi, A.; Uccioli, L.; Ceriello, A.; SCAR (SCreening for ARteriopathy) Study Group. Screening for peripheral arterial disease by means of the ankle-brachial index in newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet. Med. 2005, 22, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompers, L.; Schaper, N.; Apelqvist, J.; Edmonds, M.; Jude, E.; Didac, M.; Uccioli, L.; Urbancic, V.; Bakker, K.; Holstein, P.; et al. Prediction of outcome in individuals with diabetic foot ulcers: Focus on the differences between individuals with and without peripheral arterial disease EURODIALE Study. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckman, J.A.; Creager, M.A.; Libby, P. Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and management. JAMA 2002, 15, 2570–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, L.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Ledet, T. Diabetic macroangiopathy and atherosclerosis. Diabetes 1996, 45 (Suppl. 3), S91–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meloni, M.; Izzo, V.; Giurato, L.; Del Giudice, C.; Da Ros, V.; Cervelli, V.; Gandini, R.; Uccioli, L. Recurrence of Critical Limb Ischemia after Endovascular Intervention in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Adv. Wound Care 2018, 7, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammedi, K.; Woodward, M.; Hirakawa, Y.; Zoungas, S.; Williams, B.; Lisheng, L.; Rodgers, A.; Mancia, G.; Neal, B.; Harrap, S.; et al. Microvascular and Macrovascular Disease and Risk for Major Peripheral Arterial Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jude, E.B.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Tentolouris, N. Peripheral arterial disease in diabetes—A review. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faglia, E.; Clerici, G.; Clerissi, J.; Mantero, M.; Caminiti, M.; Quarantiello, A.; Curci, V.; Lupattelli, T.; Morabito, A. When is a technically successful peripheral angioplasty effective in preventing above-the-ankle amputation in diabetic patients with critical limb ischaemia? Diabet. Med. 2007, 24, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peregrin, J.H.; Koznar, B.; Kovác, J.; Lastovicková, J.; Novotný, J.; Vedlich, D.; Skibová, J. PTA of infrapopliteal arteries: Long-term clinical follow-up and analysis of factors influencing clinical outcome. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Armstrong, E.J.; Sherif, W.; Alvandi, B.; Westin, G.G.; Singh, G.D.; Amsterdam, E.A.; Laird, J.R. Association of elevated fasting glucose with lower patency and increased major adverse limb events among patients with diabetes undergoing infrapopliteal balloon angioplasty. Vasc. Med. 2014, 19, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraresi, R.; Palena, L.M.; Mauri, G.; Manzi, M. Interventional Treatment of the Below the Ankle Peripheral Artery Disease. In PanVascular Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 3205–3226. [Google Scholar]
- Meloni, M.; Izzo, V.; Giurato, L.; Gandini, R.; Uccioli, L. Below-the-ankle arterial disease severely impairs the outcomes of diabetic patients with ischemic foot ulcers. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 152, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, S.A.; Van Netten, J.J.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Apelqvist, J.; Lipsky, B.A.; Schaper, N.C.; IWGDF Editorial Board. Standards for the development and methodology of the 2019 International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot guidelines. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36 (Suppl. 1), e3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2016, 69, 1167, English, Spanish. Erratum in: Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 70, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norgren, L.; Hiatt, W.R.; Dormandy, J.A.; Nehler, M.R.; Harris, K.A.; Fowkes, F.G.; TASC II Working Group; Bell, K.; Caporusso, J.; Durand-Zaleski, I.; et al. Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease (TASC II). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2007, 33 (Suppl. 1), S5–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, A.; Anichini, R.; Brocco, E.; Caravaggi, C.; Chiavetta, A.; Cioni, R.; Da Ros, R.; De Feo, M.E.; Ferraresi, R.; Florio, F.; et al. Treatment of peripheral arterial disease in diabetes: A consensus of the Italian Societies of Diabetes (SID, AMD), Radiology (SIRM) and Vascular Endovascular Surgery (SICVE). Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, M.; Izzo, V.; Giurato, L.; Cervelli, V.; Gandini, R.; Uccioli, L. Impact of heart failure and dialysis in the prognosis of diabetic patients with ischemic foot ulcers. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2018, 11, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meloni, M.; Giurato, L.; Izzo, V.; Stefanini, M.; Pampana, E.; Gandini, R.; Uccioli, L. Long term outcomes of diabetic haemodialysis patients with critical limb ischemia and foot ulcer. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 116, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutluoglu, M.; Sivrioglu, A.K.; Eroglu, M.; Uzun, G.; Turhan, V.; Ay, H.; Lipsky, B.A. The implications of the presence of osteomyelitis on outcomes of infected diabetic foot wounds. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 45, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón-Sánchez, F.J.; Cabrera-Galván, J.J.; Quintana-Marrero, Y.; Hernández-Herrero, M.J.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.L.; García-Morales, E.; Beneit-Montesinos, J.V.; Armstrong, D.G. Outcomes of surgical treatment of diabetic foot osteomyelitis: A series of 185 patients with histopathological confirmation of bone involvement. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro Martínez, J.L.; García Álvarez, Y.; Tardáguila-García, A.; García Morales, E. Optimal management of diabetic foot osteomyelitis: Challenges and solutions. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Paola, L.; Cimaglia, P.; Carone, A.; Scavone, G.; Boscarino, G.; Bernucci, D.; Sbarzaglia, P.; Censi, S.; Ferrari, R.; Campo, G. Limb salvage in diabetic patients with no-option critical limb ischemia: Outcomes of a specialized center experience. Diabet. Foot Ankle 2019, 10, 1696012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, M.; Izzo, V.; Da Ros, V.; Morosetti, D.; Stefanini, M.; Brocco, E.; Giurato, L.; Gandini, R.; Uccioli, L. Characteristics and Outcome for Persons with Diabetic Foot Ulcer and No-Option Critical Limb Ischemia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, M.; Izzo, V.; Giurato, L.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.L.; Uccioli, L. Prevalence, Clinical Aspects and Outcomes in a Large Cohort of Persons with Diabetic Foot Disease: Comparison between Neuropathic and Ischemic Ulcers. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faglia, E.; Clerici, G.; Clerissi, J.; Gabrielli, L.; Losa, S.; Mantero, M.; Caminiti, M.; Curci, V.; Quarantiello, A.; Luppattelli, T.; et al. Long-term prognosis of diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia: A population-based cohort study [published correction appears in Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1355. Luppattelli, Tommaso [corrected to Lupattelli, Tommaso]. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizing, E.; Schreve, M.A.; de Vries, J.P.M.; Ferraresi, R.; Kum, S.; Ünlü, Ç. Below-the-Ankle Angioplasty in Patients With Critical Limb Ischemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1361–1368.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, M.; Palena, L.M. Treating Calf and Pedal Vessel Disease: The Extremes of Intervention. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 31, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakama, T.; Watanabe, N.; Haraguchi, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Kamoi, D.; Tsubakimoto, Y.; Ogata, K.; Satoh, K.; Urasawa, K.; Andoh, H.; et al. Clinical outcomes of pedal artery angioplasty for patients with ischemic wounds: Results from the multicenter RENDEZVOUS registry. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2017, 10, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palena, L.M.; Brocco, E.; Manzi, M. The clinical utility of below-the-ankle angioplasty using “transmetatarsal artery access” in complex cases of CLI. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 83, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, K.; Diamantopoulos, A.; Spiliopoulos, S.; Karnabatidis, D.; Siablis, D. Below-the-ankle angioplasty and stenting for limb salvage: Anatomical considerations and long-term outcomes. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2015, 36, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, M.; Agostoni, P.; Biondi-Zoccai, G. “Trans-collateral” angioplasty for a challenging chronic total occlusion of the tibial vessels: A novel approach to percutaneous revascularization in critical lower limb ischemia. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2008, 71, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, M.; Palena, L.M. Retrograde percutaneous transmetatarsal artery access: New approach for extreme revascularization in challenging cases of critical limb ischemia. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, R.K.; Dattilo, P.B.; Garcia, J.A.; Tsai, T.; Casserly, I.P. Retrograde approach to recanalization of complex tibial disease. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2011, 77, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzi, M.; Fusaro, M.; Ceccacci, T.; Erente, G.; Dalla Paola, L.; Brocco, E. Clinical results of below-the knee intervention using pedal-plantar loop technique for the revascularization of foot arteries. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 50, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Karnabatidis, D.; Katsanos, K.; Spiliopoulos, S.; Diamantopoulos, A.; Kagadis, G.C.; Siablis, D. Incidence, anatomical location, and clinical significance of compressions and fractures in infrapopliteal balloon-expandable metal stents. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2009, 16, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Giudice, C.; Van Den Heuvel, D.; Wille, J.; Mirault, T.; Messas, E.; Ferraresi, R.; Kum, S.; Sapoval, M. Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization for Severe Critical Limb Ischemia in Patients With No Option of Revascularization: Early Experience From Two European Centers. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2018, 41, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Schreve, M.A.; Huizing, E.; Del Giudice, C.; Branzan, D.; Ünlü, Ç.; Varcoe, R.L.; Ferraresi, R.; Kum, S. Midterm Outcomes of Percutaneous Deep Venous Arterialization with a Dedicated System for Patients With No-Option Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia: The ALPS Multicenter Study. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2020, 27, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kum, S.; Huizing, E.; Schreve, M.A.; Ünlü, Ç.; Ferraresi, R.; Samarakoon, L.B.; van den Heuvel, D.A. Percutaneous deep venous arterialization in patients with critical limb ischemia. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 59, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, R.; Merolla, S.; Scaggiante, J.; Meloni, M.; Giurato, L.; Uccioli, L.; Konda, D. Endovascular Distal Plantar Vein Arterialization in Dialysis Patients With No-Option Critical Limb Ischemia and Posterior Tibial Artery Occlusion: A Technique for Limb Salvage in a Challenging Patient Subset. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2018, 25, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengua, F.; La Madrid, A.; Acosta, C.; Barriga, H.; Maliqui, C.; Arauco, R.; Arauco, R.; Lengua, A. Arterialization of the distal veins of the foot for limb salvage in arteritis: Techniques and results. Ann. Chir. 2001, 126, 629–638. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Whole Sample N = 89 | SFP (n = 47) | FFP (n = 33) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 70.5 ± 10.9 | 71.5 ± 10.3 | 69.3 ± 11.8 | 0.4 |
| Sex (man) | 55 (68.7%) | (30) 63.8% | (25) 75.7% | 0.2 |
| Diabetes (type 2) | 72 (90%) | 44 (93.6%) | 28 (84.5%) | 0.2 |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 22.7 ± 11.3 | 22.8 ± 10.7 | 22.6 ± 12.3 | 0.9 |
| HbA1c % (mmol/mol) | 7.8 ± 4.1 (62 ± 21) | 7.9 ± 4.2 (63 ± 22) | 7.8 ± 4 (62 ± 20) | 0.1 |
| Insulin therapy | 65 (81.2) | 39 (83%) | 26 (78.8%) | 0.5 |
| Hypertension | 68 (85%) | 43 (91.5%) | 25 (76.8%) | 0.09 |
| Dyslipidemia | 62 (77.5%) | 38 (80.8%) | 24 (72.7%) | 0.4 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 90 ± 22 | 96 ± 25 | 81 ± 18 | 0.2 |
| TAG (mg/dL) | 165 ± 55 | 173 ± 65 | 154 ± 42 | 0.4 |
| Smoke | 11 (13.7%) | 7 (14.9%) | 4 (12.1%) | 0.7 |
| Ischaemic heart disease | 61 (76.2%) | 34 (72.3%) | 27 (81.2%) | 0.3 |
| Heart failure | 29 (36.2%) | 12 (25.3%) | 17 (51.2%) | 0.01 |
| Dialysis | 30 (37.5%) | 12 (25.3%) | 18 (54.5%) | 0.008 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 35 (43.7%) | 20 (42.5%) | 15 (45.4%) | 0.7 |
| Ulcer size (>5 cm2) | 58 (72.5%) | 33 (70.2%) | 25 (75.7%) | 0.6 |
| Previous lower limb revascularization | 10 (12.5%) | 6 (12.7%) | 4 (12.1%) | 0.9 |
| Infection | 65 (81.2%) | 39 (82.9%) | 26 (78.9%) | 0.6 |
| Gangrene | 68 (85%) | 38 (80.5%) | 30 (90.1%) | 0.2 |
| Osteomyelitis | 48 (60%) | 28 (59.6%) | 20 (60.1%) | 0.9 |
| C-Reactive Protein mg/dL) | 66 ± 47 | 63 ± 50 | 72 ± 43 | 0.4 |
| Baseline TcPO2 (mmHg) | 16 ± 7 | 17 ± 8 | 14 ± 6 | 0.2 |
| 1-month post-procedure TcPO2 (mmHg) | 40 ± 13 | 48 ± 9 | 29 ± 10 | <0.0001 |
| Variables | Non-Healing | Minor Amputation | Major Amputation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Failed foot revascularization | 8.5 | 1.8–15.8 | 0.0001 | 2.1 | 1.3–7.1 | 0.001 | 9.8 | 1.2–16.6 | 0.0001 |
| Heart failure | 0.8 | 0.4–1.2 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 0.7–1.3 | 0.09 | |||
| Dialysis | 0.9 | 0.5–2.1 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.4–1.1 | 0.8 | |||
| TcPO2 < 25 mmHg | 1.3 | 0.7–1.5 | 0.09 | 1.5 | 0.9–2.3 | 0.06 | 2.3 | 1.2–5.7 | 0.03 |
| Osteomyelitis | 2.2 | 1.3–4.5. | 0.02 | ||||||
| Gangrene | 1.9 | 1.1–3.7 | 0.03 | ||||||
| Size (>5 cm2) | 1.2 | 0.8–2.0 | 0.6 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meloni, M.; Morosetti, D.; Giurato, L.; Stefanini, M.; Loreni, G.; Doddi, M.; Panunzi, A.; Bellia, A.; Gandini, R.; Brocco, E.; et al. Foot Revascularization Avoids Major Amputation in Persons with Diabetes and Ischaemic Foot Ulcers. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173977
Meloni M, Morosetti D, Giurato L, Stefanini M, Loreni G, Doddi M, Panunzi A, Bellia A, Gandini R, Brocco E, et al. Foot Revascularization Avoids Major Amputation in Persons with Diabetes and Ischaemic Foot Ulcers. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173977
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeloni, Marco, Daniele Morosetti, Laura Giurato, Matteo Stefanini, Giorgio Loreni, Marco Doddi, Andrea Panunzi, Alfonso Bellia, Roberto Gandini, Enrico Brocco, and et al. 2021. "Foot Revascularization Avoids Major Amputation in Persons with Diabetes and Ischaemic Foot Ulcers" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173977
APA StyleMeloni, M., Morosetti, D., Giurato, L., Stefanini, M., Loreni, G., Doddi, M., Panunzi, A., Bellia, A., Gandini, R., Brocco, E., Lazaro-Martinez, J. L., Lauro, D., & Uccioli, L. (2021). Foot Revascularization Avoids Major Amputation in Persons with Diabetes and Ischaemic Foot Ulcers. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 3977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173977










