Fecal Zonulin as a Noninvasive Biomarker of Intestinal Permeability in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases—Correlation with Disease Activity and Fecal Calprotectin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Fecal Samples
2.2. Statistical Analysis
- − The assessment of ZRP, known for reflecting intestinal permeability, as a potential noninvasive marker of IBD and its activity
- − The correlation between fecal ZRP and FCP
- − The correlation between fecal ZRP concentration and IBD clinical activity
- − Whether there is a difference in the fecal ZRP value between CD and UC
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michielan, A.; D’Incà, R. Intestinal Permeability in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenesis, Clinical Evaluation, and Therapy of Leaky Gut. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 628157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Intestinal Permeability and Its Regulation by Zonulin: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Intestinal zonulin: Open sesame! Gut 2001, 49, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- HP Gene Haptoglobin. Available online: https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=HP&keywords=Zonulin (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Fasano, A.; Not, T.; Wang, W. Zonulin, a newly discovered modulator of intestinal permeability, and its expression in coeliac disease. Lancet 2000, 29, 1518–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kort, S.; Keszthelyi, D.; Masclee, A.A. Leaky gut and diabetes mellitus: What is the link? Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küme, T.; Acar, S.; Tuhan, H.A. The relationship between serum zonulin level and clinical and laboratory parameters of childhood obesity. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Dughera, F.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Rosso, C.; Abate, M.L.; Pellicano, R.; Bresso, F.; Smedile, A.; Saracco, G.M.; Astegiano, M. Serum zonulin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A pilot study. Minerva Med. 2019, 110, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malíčková, K.; Francová, I.; Lukáš, M.; Kolar, M.; Kralikova, E.; Bortlik, M.; Duricova, D.; Stepankova, L.; Zvolska, K.; Pankova, A.; et al. Fecal zonulin is elevated in Crohn’s disease and in cigarette smokers. Pract. Lab. Med. 2017, 9, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Bonovas, S.; Doherty, G.; Kucharzik, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Raine, T.; Adamina, M.; Armuzzi, A.; Bachmann, O.; Bager, P.; et al. ECCO Working Group. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Medical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernia, F.; Di Ruscio, M.; Stefanelli, G.; Viscido, A.; Frieri, G.; Latella, G. Is fecal calprotectin an accurate marker in the management of Crohn’s disease? J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Levine, A.; Walters, T.D.; Focht, G.; Otley, A.; López, V.N.; Koletzko, S.; Baldassano, R.; Mack, D.; Hyams, J.; et al. Which PCDAI Version Best Reflects Intestinal Inflammation in Pediatric Crohn Disease? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatucu-Babet, O.A.; Forsyth, A.; Owen, E.; Navarro-Perez, D.; Radcliffe, J.; Benheim, D.; Mendis, H.; Jois, M.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Tierney, A.C. Serum zonulin measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay may not be a reliable marker of small intestinal permeability in healthy adults. Nutr. Res. 2020, 78, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: Role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Research 2020, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, J.A.; Finlay, B.B. Tight junctions as targets of infectious agents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegh, C.A.M.; de Roos, N.M.; Hovenier, R.; Meijerink, J.; Besseling-van derr Vaart, I.; van Hemert, S.; Wittemen, B.J.M. Intestinal Permeability Measured by Urinary Sucrose Excretion Correlates with Serum Zonulin and Faecal Calprotectin Concentrations in UC Patients in Remission. J. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 2019, 2472754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Zonulin and Its Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function: The Biological Door to Inflammation, Autoimmunity, and Cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajamian, M.; Steer, D.; Rosella, G.; Gibson, P.R. Serum zonulin as a marker of intestinal mucosal barrier function: May not be what it seems. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffler, L.; Crane, A.; Heyne, H.; Tönjes, A.; Schleinitz, D.; Ihling, C.H.; Stumvoll, M.; Freire, R.; Fiorentino, M.; Fasano, A.; et al. Widely Used Commercial ELISA Does Not Detect Precursor of Haptoglobin2, but Recognizes Properdin as a Potential Second Member of the Zonulin Family. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
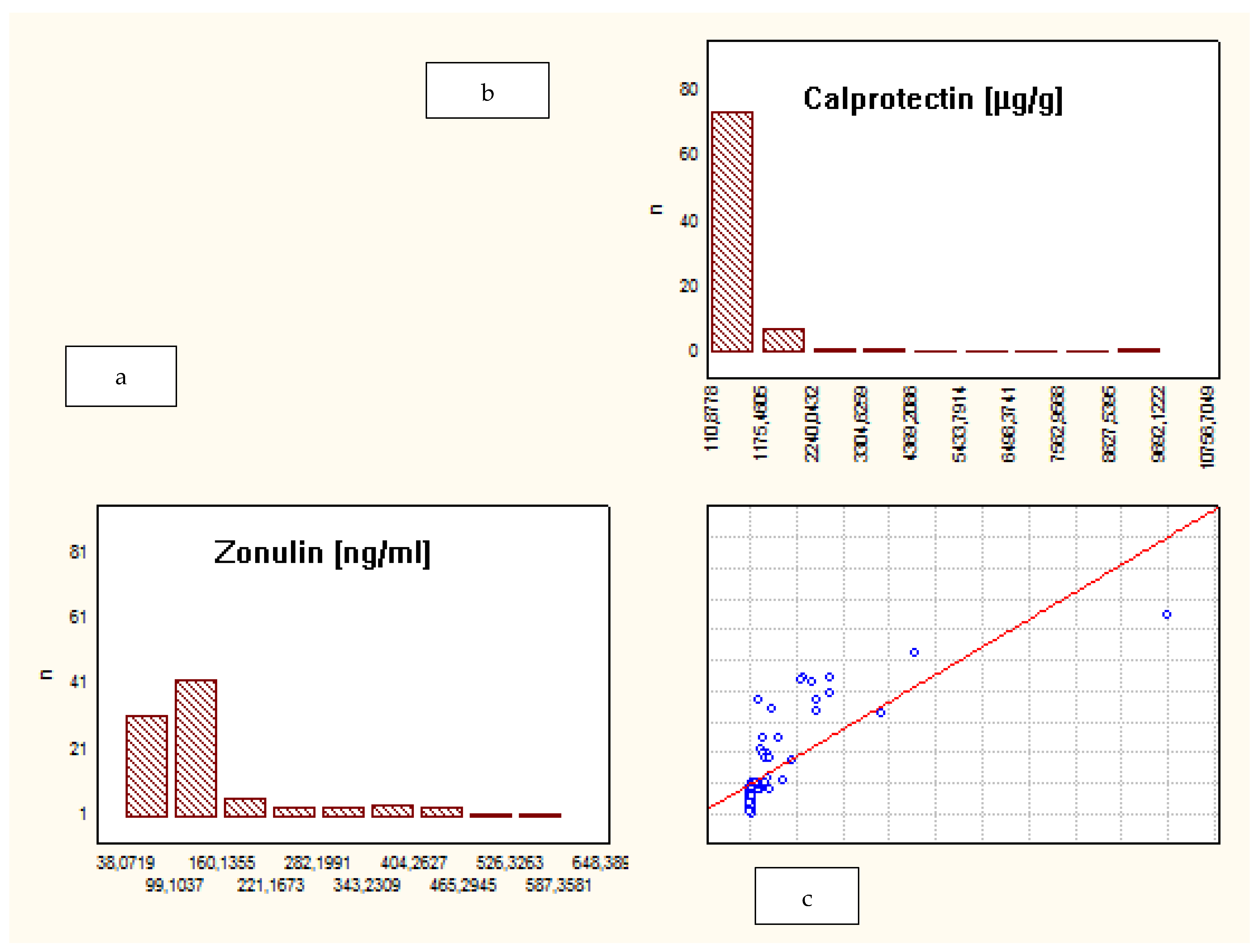
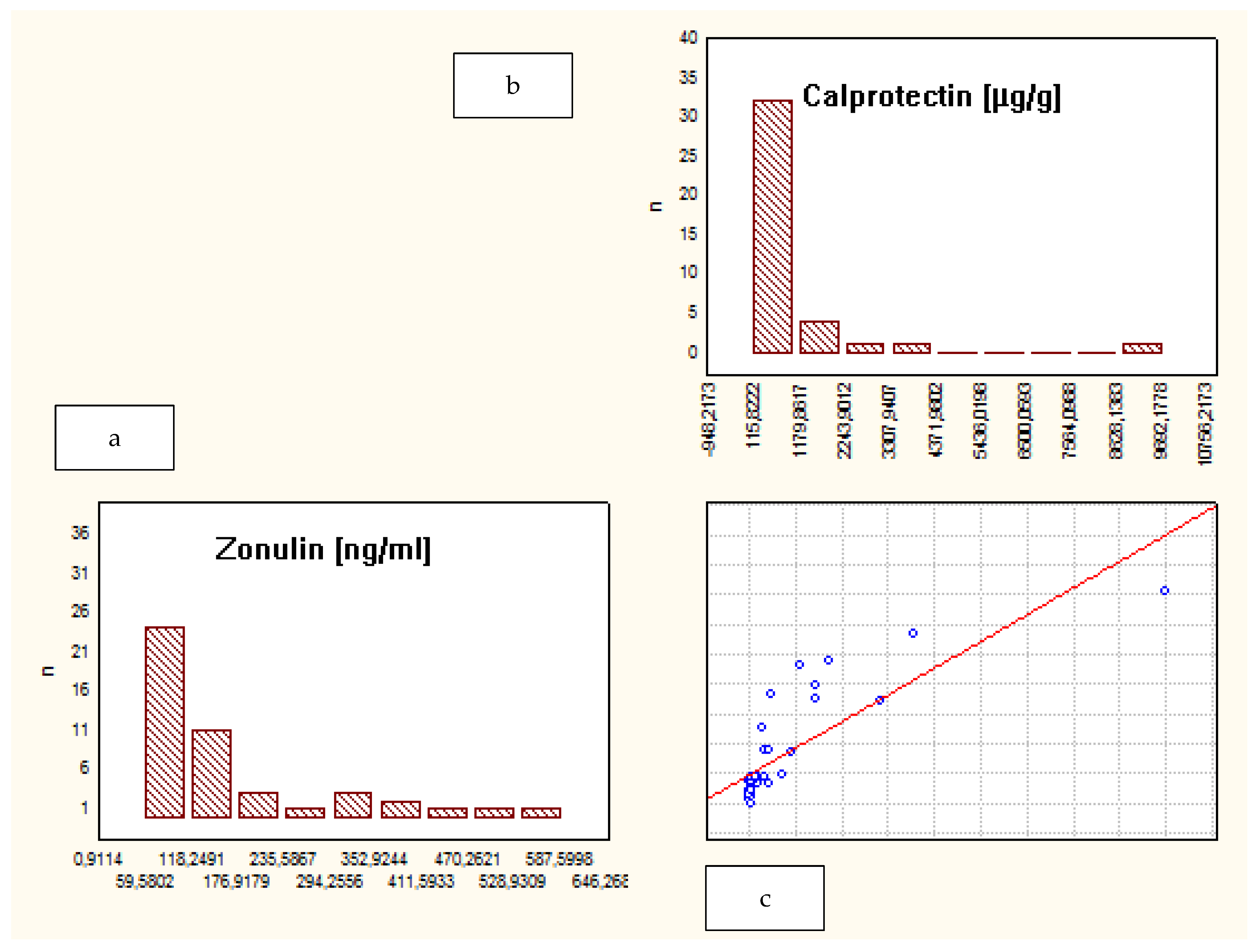
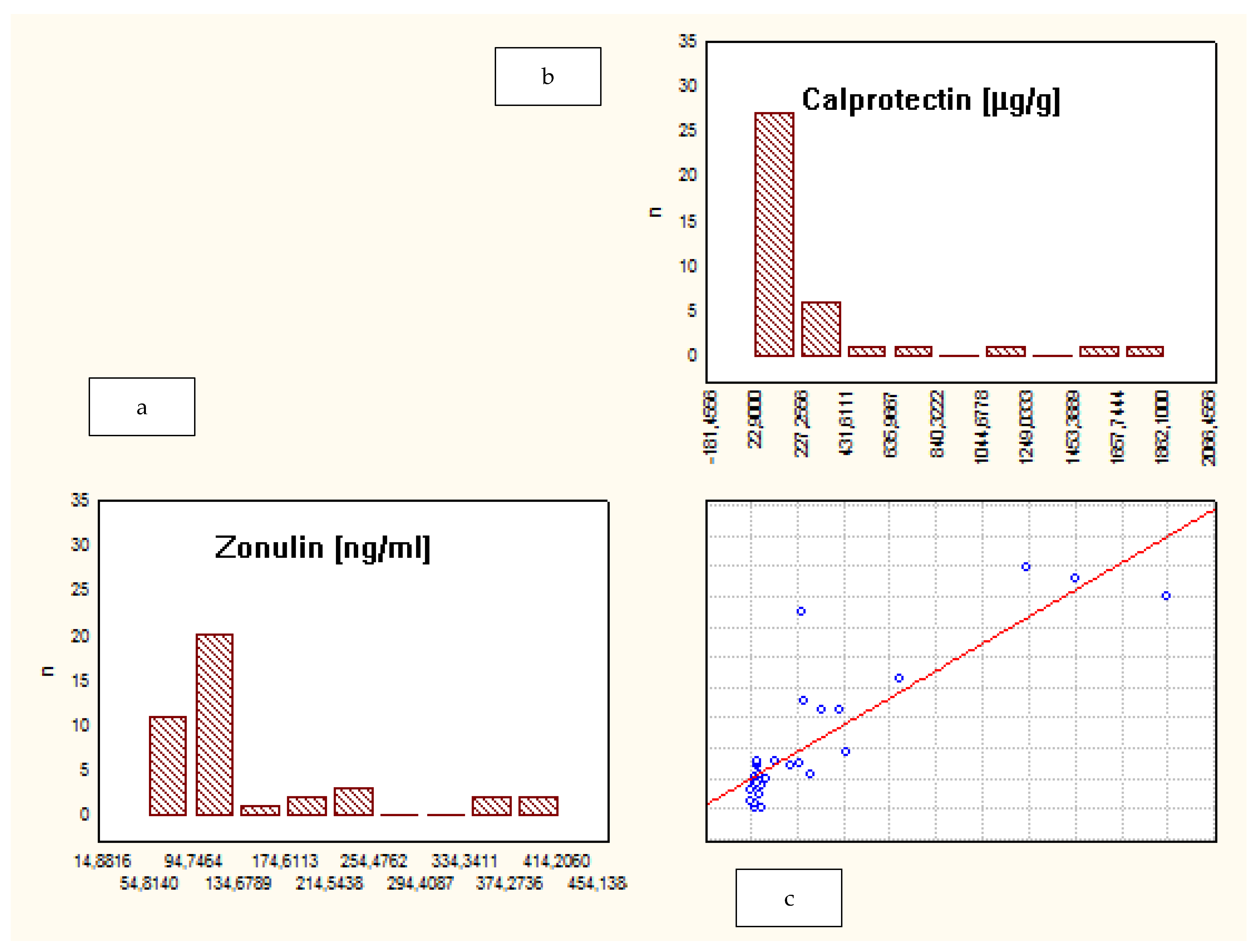
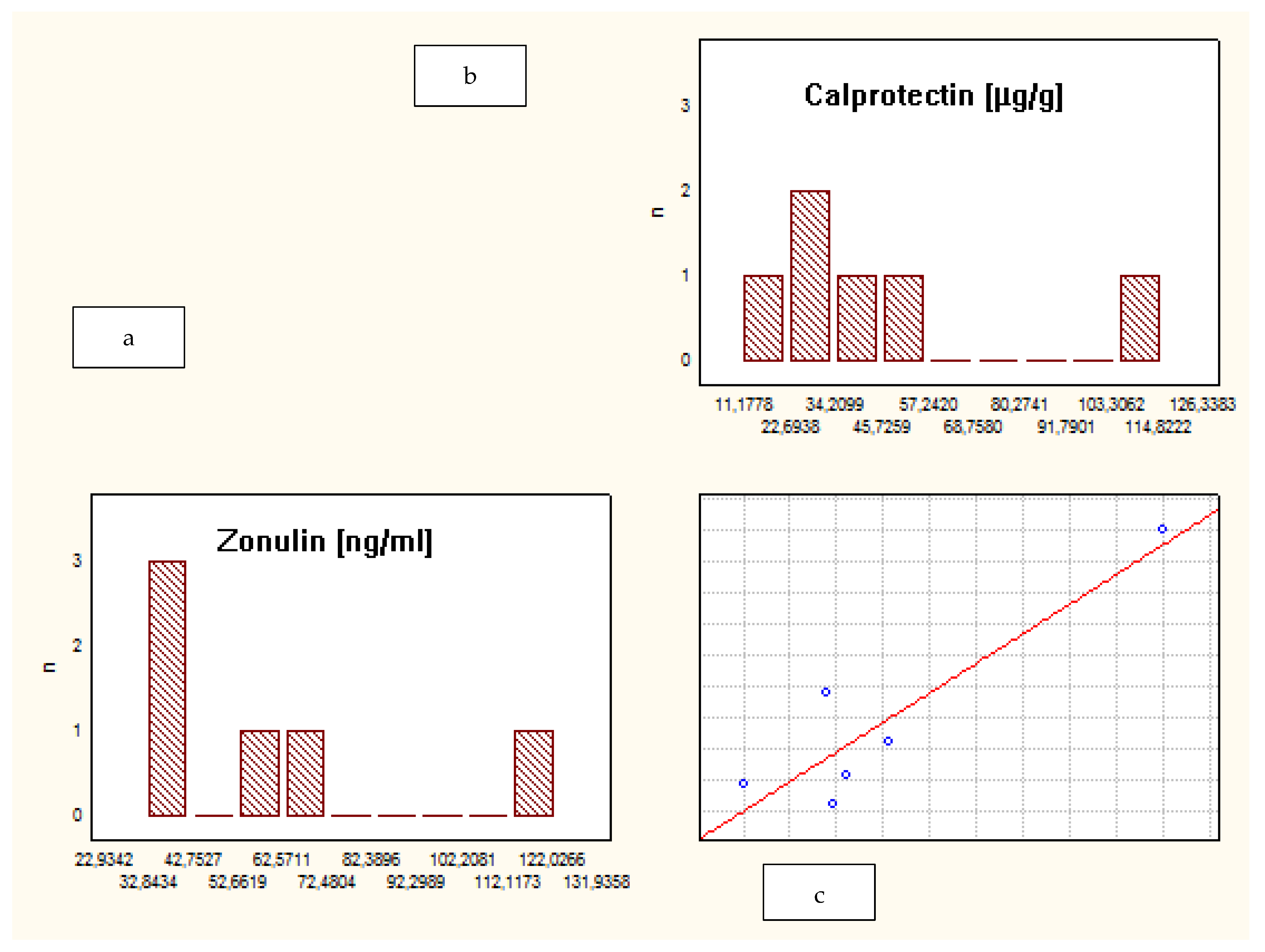
| Characteristic | Crohn’s Disease | Ulcerative Colitis | Control Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 47 (50%) | 41 (43.6%) | 6 (6.4%) |
| Median age, range (yrs) | 14 (5.5–18.0) | 14 (4.0–18.0) | 8.5 (3.0–10.0) |
| Median FCP level, range (μg/g) | 151.0 (71.0–9801.0) | 39.0 (2.0–1883.0) | 34.5 (10.0–116.0) |
| Median FZRP, range (ng/mL) | 113.3 (53.6–593.6) | 103.6 (50.7–418.3) | 46.9 (31.8–123.0) |
| Median PCDAI, range | 2.5 (0.0–52.5) | N/A | N/A |
| Median PUCAI, range | N/A | 5.0 (0.0–40.0) | N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szymanska, E.; Wierzbicka, A.; Dadalski, M.; Kierkus, J. Fecal Zonulin as a Noninvasive Biomarker of Intestinal Permeability in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases—Correlation with Disease Activity and Fecal Calprotectin. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173905
Szymanska E, Wierzbicka A, Dadalski M, Kierkus J. Fecal Zonulin as a Noninvasive Biomarker of Intestinal Permeability in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases—Correlation with Disease Activity and Fecal Calprotectin. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173905
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzymanska, Edyta, Aldona Wierzbicka, Maciej Dadalski, and Jaroslaw Kierkus. 2021. "Fecal Zonulin as a Noninvasive Biomarker of Intestinal Permeability in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases—Correlation with Disease Activity and Fecal Calprotectin" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173905
APA StyleSzymanska, E., Wierzbicka, A., Dadalski, M., & Kierkus, J. (2021). Fecal Zonulin as a Noninvasive Biomarker of Intestinal Permeability in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases—Correlation with Disease Activity and Fecal Calprotectin. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173905






