Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Resveratrol and HE
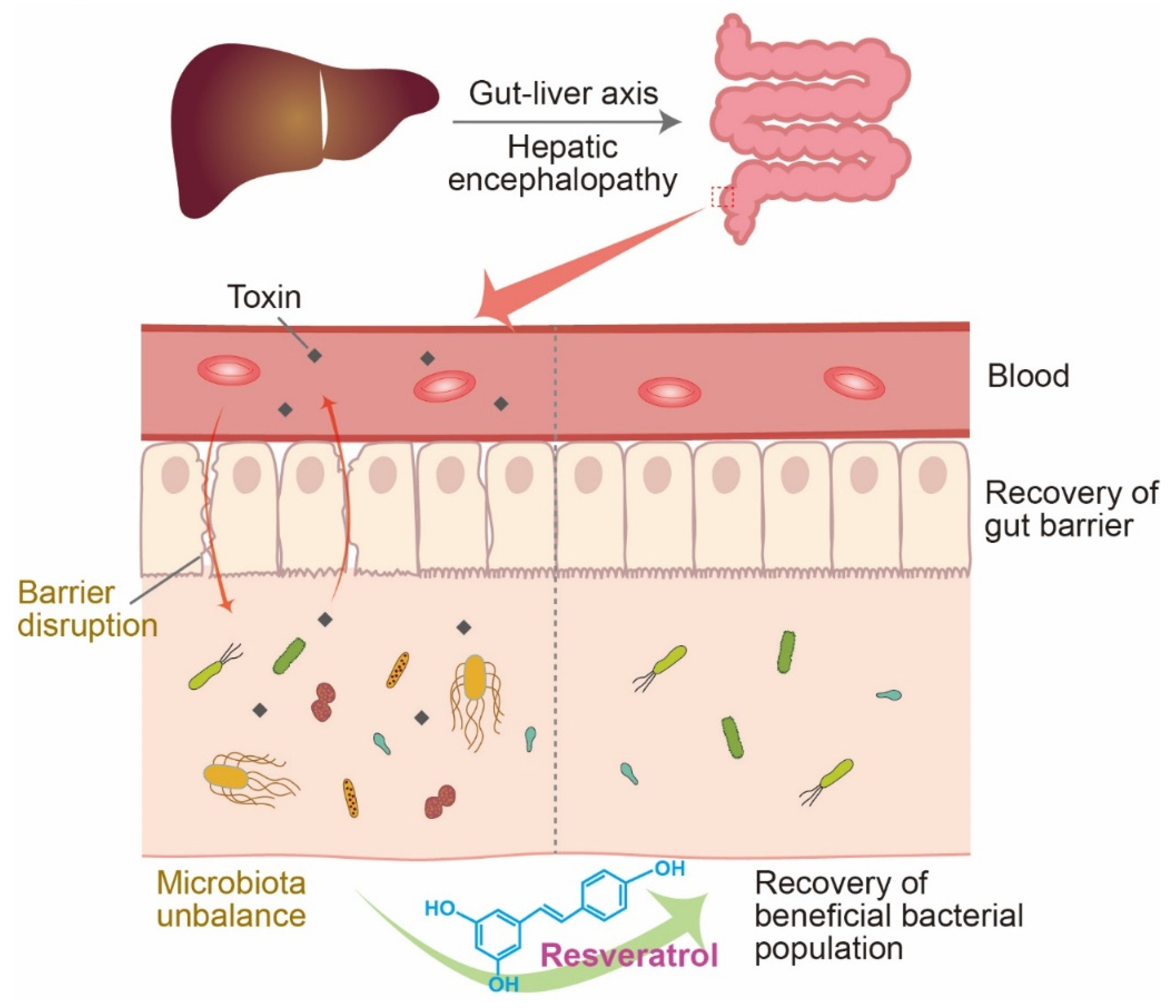
3. Resveratrol and the Microbiome in HE
4. Resveratrol and Brain Edema in HE
5. Resveratrol and Ammonia-Induced Neuroinflammation in HE
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajaj, J.S. Hepatic encephalopathy: Classification and treatment. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 838–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patidar, K.R.; Bajaj, J.S. Covert and Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy: Diagnosis and Management. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 2048–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsaid, M.I.; Rustgi, V.K. Epidemiology of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 24, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnese, S.; Russo, F.P.; Amodio, P.; Burra, P.; Gasbarrini, A.; Loguercio, C.; Marchesini, G.; Merli, M.; Ponziani, F.R.; Riggio, O.; et al. Hepatic encephalopathy 2018: A clinical practice guideline by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF). Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanny, B.; Winters, A.; Boutros, S.; Saab, S. Hepatic Encephalopathy Challenges, Burden, and Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approach. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kircheis, G.; Wettstein, M.; Timmermann, L.; Schnitzler, A.; Häussinger, D. Critical flicker frequency for quantification of low-grade hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2002, 35, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M.; Butz, M.; Baumgarten, T.J.; Füllenbach, N.-D.; Jördens, M.S.; Häussinger, D.; Schnitzler, A.; Lange, J. Impaired Tactile Temporal Discrimination in Patients With Hepatic Encephalopathy. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobermin, L.D.; Wartchow, K.M.; Flores, M.P.; Leite, M.C.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; Gonçalves, C.-A. Ammonia-induced oxidative damage in neurons is prevented by resveratrol and lipoic acid with participation of heme oxygenase 1. NeuroToxicology 2015, 49, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häussinger, D.; Butz, M.; Schnitzler, A.; Görg, B. Pathomechanisms in hepatic encephalopathy. Biol. Chem. 2021, 402, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S. Review article: The modern management of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, O.; Ridola, L.; Pasquale, C.; Pentassuglio, I.; Nardelli, S.; Moscucci, F.; Merli, M.; Montagnese, S.; Amodio, P.; Merkel, C. A Simplified Psychometric Evaluation for the Diagnosis of Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 613–616.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.; Sinclair, D. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizzo, A.; Forte, M.; Damato, A.; Trimarco, V.; Salzano, F.; Bartolo, M.; Maciag, A.; Puca, A.A.; Vecchione, C. Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in cardiovascular, cerebral and metabolic diseases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 61, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Švajger, U.; Jeras, M. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Resveratrol and Its Potential Use in Therapy of Immune-mediated Diseases. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 31, 202–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Bertino, G.; Gagliano, C.; Malaguarnera, M.; Bella, R.; Borzì, A.M.; Madeddu, R.; Drago, F.; Malaguarnera, G. Resveratrol in Hepatitis C Patients Treated with Pegylated-Interferon-α-2b and Ribavirin Reduces Sleep Disturbance. Nutrients 2017, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Resveratrol: A Double-Edged Sword in Health Benefits. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.-L.; Jun, M.; Jeong, W.-S. Role of resveratrol in regulation of cellular defense systems against oxidative stress. BioFactors 2017, 44, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borra, M.T.; Smith, B.; Denu, J.M. Mechanism of Human SIRT1 Activation by Resveratrol. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 17187–17195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, V.; Nestler, E.J. The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature 2008, 455, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Gan, L.; Vosler, P.S.; Gao, Y.; Zigmond, M.J.; Chen, J. Protective effects and mechanisms of sirtuins in the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 95, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denissova, N.G.; Nasello, C.M.; Yeung, P.L.; Tischfield, J.; Brenneman, M.A. Resveratrol protects mouse embryonic stem cells from ionizing radiation by accelerating recovery from DNA strand breakage. Carcinogenesis 2011, 33, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbele, A.T.; Fasoro, O.J.; Fabamise, O.M.; Oluyide, O.O.; Idolor, O.R.; Bamise, E.A. Protection Against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Normal Tissue Damage by Resveratrol: A Systematic Review. Eurasian J. Med. 2020, 52, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Pinzon, M.A.; Koronowski, K. Sirt1 in cerebral ischemia. Brain Circ. 2015, 1, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadori, G.; Lee, C.E.; Bookout, A.L.; Lee, S.; Williams, K.; Anderson, J.; Elmquist, J.K.; Coppari, R. Brain SIRT1: Anatomical Distribution and Regulation by Energy Availability. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9989–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, G.; Gatfield, D.; Stratmann, M.; Reinke, H.; Dibner, C.; Kreppel, F.; Mostoslavsky, R.; Alt, F.W.; Schibler, U. SIRT1 Regulates Circadian Clock Gene Expression through PER2 Deacetylation. Cell 2008, 134, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Anamika; Chakraborty, S.; Tripathi, S.J.; Acharjee, A.; Bs, S.R.; Trigun, S.K. SIRT1 activation by resveratrol reverses atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons and neurobehavioral impairments in moderate grade hepatic encephalopathy rats. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2020, 106, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.W.; Li, S. Resveratrol, pterostilbene, and dementia. Biofactors 2018, 44, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Beidler, J.; Hong, M.Y. Resveratrol and Depression in Animal Models: A Systematic Review of the Biological Mechanisms. Molecules 2018, 23, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgili, M.; Contestabile, A. Partial neuroprotection of in vivo excitotoxic brain damage by chronic administration of the red wine antioxidant agent, trans-resveratrol in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 281, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Simonyi, A.; Lubahn, D.; Sun, G.Y.; Sun, A.Y. Resveratrol protects against global cerebral ischemic injury in gerbils. Brain Res. 2002, 958, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Han, H.; Cao, P.; Yu, W.; Yang, C.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, W. Resveratrol improves neuron protection and functional recovery through enhancement of autophagy after spinal cord injury in mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 4607–4616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michán, S.; Li, Y.; Chou, M.M.-H.; Parrella, E.; Ge, H.; Long, J.M.; Allard, J.S.; Lewis, K.; Miller, M.; Xu, W.; et al. SIRT1 Is Essential for Normal Cognitive Function and Synaptic Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9695–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, T.; Wang, G. SIRT1 Regulates Cognitive Performance and Ability of Learning and Memory in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Models. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Rahimi, R.; Nikfar, S.; Abdollahi, M. Effect of resveratrol on cognitive and memory performance and mood: A meta-analysis of 225 patients. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, W.; Kelly, J.; Marshall, S.; Cutajar, J.; Annois, B.; Pipingas, A.; Tierney, A.; Itsiopoulos, C. Effect of resveratrol supplementation on cognitive performance and mood in adults: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidi, F.; Poljak, A.; Liu, Y.; Lo, J.W.; Crawford, J.D.; Sachdev, P.S. Resveratrol: A “miracle” drug in neuropsychiatry or a cognitive enhancer for mice only? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 65, 101199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P. Hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 5, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijdicks, E.F. Hepatic Encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.; Jalan, R.; Thabut, M. Understanding hepatic encephalopathy. Intensiv. Care Med. 2017, 44, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poordad, F.F. Review article: The burden of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.Y.; Bajaj, J.S. Advances in the Evaluation and Management of Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 13, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felipo, V.; Urios, A.; Montesinos, E.; Molina, I.; Garcia-Torres, M.L.; Civera, M.; Olmo, J.A.D.; Ortega, J.; Martinez-Valls, J.; Serra, M.A.; et al. Contribution of hyperammonemia and inflammatory factors to cognitive impairment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2011, 27, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawcross, D.L.; Shabbir, S.S.; Taylor, N.J.; Hughes, R.D. Ammonia and the neutrophil in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawhney, R.; Holland-Fischer, P.; Rosselli, M.; Mookerjee, R.; Agarwal, B.; Jalan, R. Role of ammonia, inflammation, and cerebral oxygenation in brain dysfunction of acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Liver Transplant. 2016, 22, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Jones, E. Hepatic encephalopathy: Molecular mechanisms underlying the clinical syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 170, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limón, I.D.; Angulo-Cruz, I.; Sánchez-Abdon, L.; Patricio-Martínez, A. Disturbance of the Glutamate-Glutamine Cycle, Secondary to Hepatic Damage, Compromises Memory Function. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 578922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.G.; Córdoba, J. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: The brain. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2011, 17, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Faff, L. Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions in Hyperammonemia and Hepatic Encephalopathy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1994, 368, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E. Neuron-Astrocyte Interactions: Partnership for Normal Function and Disease in the Central Nervous System. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005, 80, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.H.; Yamamoto, S.; Steers, J.; Sevlever, D.; Lin, W.; Shimojima, N.; Castanedes-Casey, M.; Genco, P.; Golde, T.; Richelson, E.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to brain extravasation and edema in fulminant hepatic failure mice. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauli, O.; López–Larrubia, P.; Rodrigo, R.; Agusti, A.; Boix, J.; Nieto–Charques, L.; Cerdán, S.; Felipo, V. Brain Region-Selective Mechanisms Contribute to the Progression of Cerebral Alterations in Acute Liver Failure in Rats. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Song, H.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.-X.; Cui, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, P. Tumour necrosis factor-α affects blood-brain barrier permeability and tight junction-associated occludin in acute liver failure. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godichaud, S.; Krisa, S.; Couronné, B.; Dubuisson, L.; Mérillon, J.-M.; Desmoulière, A.; Rosenbaum, J. Deactivation of cultured human liver myofibroblasts byTrans-resveratrol, a grapevine-derived polyphenol. Hepatology 2000, 31, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Chen, L.-L.; Xiao, F.-X.; Sun, H.; Ding, H.-C.; Xiao, H. Resveratrol improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, I.C.; Martins, L.A.M.; Coelho, B.P.; Grivicich, I.; Guaragna, R.M.; Gottfried, C.; Borojevic, R.; Guma, F.C.R. Resveratrol inhibits cell growth by inducing cell cycle arrest in activated hepatic stellate cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 315, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.Y.; Chong, S.A.; Nam, M.J. Resveratrol induces apoptosis in human SK-HEP-1 hepatic cancer cells. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2009, 6, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.-H.; Ootsuki, Y.; Fujita, H.; Miyazaki, M.; Yie, Q.; Tsutsui, K.; Sano, K.; Masuoka, N.; Ogino, K. Resveratrol Inhibited Hydroquinone-Induced Cytotoxicity in Mouse Primary Hepatocytes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubiolo, J.A.; Mithieux, G.; Vega, F.V. Resveratrol protects primary rat hepatocytes against oxidative stress damage: Activation of the Nrf2 transcription factor and augmented activities of antioxidant enzymes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallis, J.-L.; Serhan, N.; Gin, H.; Couzigou, P.; Beauvieux, M.-C. Resveratrol plus ethanol counteract the ethanol-induced impairment of energy metabolism: 31P NMR study of ATP and sn-glycerol-3-phosphate on isolated and perfused rat liver. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-L.; Yu, L.; Pan, C.-E.; Jiao, X.-Y.; Lv, Y.; Fu, J.; Meng, K.-W. Apoptosis of lymphocytes in allograft in a rat liver transplantation model induced by resveratrol. Pharmacol. Res. 2006, 54, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, T.A.; Robich, M.P.; Chu, L.M.; Bianchi, C.; Sellke, F.W. Improving glucose metabolism with resveratrol in a swine model of metabolic syndrome through alteration of signaling pathways in the liver and skeletal muscle. Arch. Surg. 2011, 146, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, H.; Černý, D.; Kameníková, L.; Martínek, J.; Horinek, A.; Kmoníčková, E.; Zídek, Z. Resveratrol attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatitis in d-galactosamine sensitized rats: Role of nitric oxide synthase 2 and heme oxygenase-1. Nitric Oxide 2009, 21, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.-C.; Cheng, L.-Y.; Lin, C.-L.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Lee, F.-Y. The protective role of natural phytoalexin resveratrol on inflammation, fibrosis and regeneration in cholestatic liver injury. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebai, H.; Sani, M.; Yacoubi, M.T.; Aouani, E.; Ghanem-Boughanmi, N.; Ben-Attia, M. Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in rat liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacPherson, A.J.; Geuking, M.B.; McCoy, K.D. Immune responses that adapt the intestinal mucosa to commensal intestinal bacteria. Immunology 2005, 115, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Are We Really Vastly Outnumbered? Revisiting the Ratio of Bacterial to Host Cells in Humans. Cell 2016, 164, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, K.T.; Kim, D.J. Gut microbiota: Novel therapeutic target for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C.; Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; et al. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Wu, E. The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeda, C.; Djukovic, A.; Isaac, S. Roles of the intestinal microbiota in pathogen protection. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. The gut–liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yin, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, W. The Molecular and Mechanistic Insights Based on Gut–Liver Axis: Nutritional Target for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Improvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, N.; Guo, J.; Qian, G.; Fang, D.; Shi, D.; Xu, M.; Yang, F.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; et al. Functional gene arrays-based analysis of fecal microbiomes in patients with liver cirrhosis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fukui, H. Gut-liver axis in liver cirrhosis: How to manage leaky gut and endotoxemia. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Martin-Mateos, R.; Shah, V.H. Gut–liver axis, cirrhosis and portal hypertension: The chicken and the egg. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 12, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, R.; Ye, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Berberine protects acute liver failure in mice through inhibiting inflammation and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 819, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, M.J.; Plummer, N.T. Part 1: The Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. Integr. Med. Encinitas Calif. 2014, 13, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fukui, H. Role of Gut Dysbiosis in Liver Diseases: What Have We Learned So Far? Diseases 2019, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, E.M.; Stanton, C.; Murphy, E.F. The gut microbiota and the liver. Pathophysiological and clinical implications. J. Hepatol. 2012, 58, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Bacterial Infections, Sepsis, and Multiorgan Failure in Cirrhosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2008, 28, 026–042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Hylemon, P.B.; Ridlon, J.M.; Heuman, D.M.; Daita, K.; White, M.B.; Monteith, P.; Noble, N.A.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Colonic mucosal microbiome differs from stool microbiome in cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy and is linked to cognition and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G675–G685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Lu, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Lei, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, L. Characterization of fecal microbial communities in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Salzman, N.H.; Acharya, C.; Sterling, R.K.; White, M.B.; Gavis, E.A.; Fagan, A.; Hayward, M.; Holtz, M.L.; Matherly, S.; et al. Fecal Microbial Transplant Capsules Are Safe in Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Phase 1, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Yang, F.; Li, A.; Prifti, E.; Chen, Y.; Shao, L.; Guo, J.; Le Chatelier, E.; Yao, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in liver cirrhosis. Nature 2014, 513, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessione, E. Lactic acid bacteria contribution to gut microbiota complexity: Lights and shadows. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, R.K.; Rana, B.; Agrawal, S.; Garg, A.; Chopra, M.; Thumburu, K.K.; Khattri, A.; Malhotra, S.; Duseja, A.; Chawla, Y.K. Probiotic VSL#3 Reduces Liver Disease Severity and Hospitalization in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1327–1337.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Heuman, D.M.; Hylemon, P.B.; Sanyal, A.J.; Puri, P.; Sterling, R.K.; Luketic, V.; Stravitz, R.T.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Fuchs, M.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Lactobacillus GG modulates gut microbiome, metabolome and endotoxemia in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Chen, J.; Xia, J.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ling, Z. Role of probiotics in the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with HBV-induced liver cirrhosis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 3596–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davani-Davari, D.; Negahdaripour, M.; Karimzadeh, I.; Seifan, M.; Mohkam, M.; Masoumi, S.J.; Berenjian, A.; Ghasemi, Y. Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidot, H.; Cvejic, E.; Finegan, L.J.; Shores, E.A.; Bowen, D.G.; Strasser, S.I.; McCaughan, G.W.; Carey, S.; Allman-Farinelli, M.; Shackel, N.A. Supplementation with Synbiotics and/or Branched Chain Amino Acids in Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Pilot Randomised Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, Z.; Chang, P.E. A Current Review of the Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, V.; Wade, J.B.; Heuman, D.M.; Hammeke, T.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sterling, R.K.; Stravitz, R.T.; Luketic, V.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Puri, P.; et al. Enhancement of functional connectivity, working memory and inhibitory control on multi-modal brain MR imaging with Rifaximin in Cirrhosis: Implications for the gut-liver-brain axis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Duan, Z.P.; Ha, D.K.; Bengmark, S.; Kurtovic, J.; Riordan, S.M. Synbiotic modulation of gut flora: Effect on minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.-T.; Ye, X.-L.; Li, R.-R.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Yong, H.-J.; Pan, M.-L.; Lu, W.; Tang, Y.; Miao, H.; et al. Resveratrol Modulates the Gut Microbiota and Inflammation to Protect Against Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Ke, W.; Chen, F.; Hu, X. Targeting the gut microbiota with resveratrol: A demonstration of novel evidence for the management of hepatic steatosis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 81, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, H.; Shu, L.; Xing, H.; Wang, C.; Lu, C.; Song, G. Effect of resveratrol on intestinal tight junction proteins and the gut microbiome in high-fat diet-fed insulin resistant mice. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hou, P.; Zhou, M.; Ren, Q.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Hui, S.; Yi, L.; Mi, M. Resveratrol attenuates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by maintaining gut barrier integrity and inhibiting gut inflammation through regulation of the endocannabinoid system. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 39, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, D.; Ke, W.; Liang, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, F. Resveratrol-induced gut microbiota reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 44, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bémeur, C.; Cudalbu, C.; Dam, G.; Thrane, A.S.; Cooper, A.J.L.; Rose, C.F. Brain edema: A valid endpoint for measuring hepatic encephalopathy? Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosoi, C.R.; Rose, C. Brain edema in acute liver failure and chronic liver disease: Similarities and differences. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norenberg, M.D.; Rao, K.V.R.; Jayakumar, A.R. Mechanisms of Ammonia-Induced Astrocyte Swelling. Metab. Brain Dis. 2005, 20, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francesca, B.; Rezzani, R. Aquaporin and Blood Brain Barrier. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin water channels in the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrane, A.S.; Thrane, V.R.; Nedergaard, M. Drowning stars: Reassessing the role of astrocytes in brain edema. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.V.R.; Norenberg, M.D. Aquaporin-4 in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2007, 22, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Rao, K.R.; Murthy, C.; Norenberg, M. Glutamine in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solenov, E.; Watanabe, H.; Manley, G.T.; Verkman, A.S. Sevenfold-reduced osmotic water permeability in primary astrocyte cultures from AQP-4-deficient mice, measured by a fluorescence quenching method. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2004, 286, C426–C432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 Gene Disruption in Mice Reduces Brain Swelling and Mortality in Pneumococcal Meningitis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13906–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.R.; Kronsten, V.T.; Hughes, R.D.; Shawcross, D.L. Pathophysiology of cerebral oedema in acute liver failure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 9240–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.R.; Jayakumar, A.R.; Norenberg, M.D. Brain edema in acute liver failure: Mechanisms and concepts. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.R.; Verkman, A.; Curtis, K.; Norenberg, M.D. Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces encephalopathy and brain edema in experimental acute liver failure. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 63, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Bethea, J.; Tong, X.; Gomez, J.; Norenberg, M. NF-κB in the mechanism of brain edema in acute liver failure: Studies in transgenic mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 41, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changlin, H.; Tan, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Gui, Y.; Qin, L.; Deng, F.; Yuejiang, G.; Hu, C.; et al. Resveratrol ameliorates oxidative stress and inhibits aquaporin 4 expression following rat cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7756–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, I.M.A.; Ortiz-Plata, A.; Franco-Pérez, J.; Millán, A.; Aguilera, P. Resveratrol reduces cerebral edema through inhibition of de novo SUR1 expression induced after focal ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 330, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Jin, J.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Mo, H.; Chen, G. SIRT1 activation by resveratrol reduces brain edema and neuronal apoptosis in an experimental rat subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 9627–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Dong, J.; Zheng, D.; Li, X.; Ding, D.; Xu, H. Reperfusion combined with intraarterial administration of resveratrol-loaded nanoparticles improved cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 28, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherian, M.; Norenberg, M.D.; Panickar, K.S.; Shamaladevi, N.; Ahmad, A.; Rahman, P.; Jayakumar, A.R. Additive Effect of Resveratrol on Astrocyte Swelling Post-exposure to Ammonia, Ischemia and Trauma In Vitro. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamann, G.F.; Liebetrau, M.; Martens, H.; Burggraf, D.; Kloss, C.U.A.; Bültemeier, G.; Wunderlich, N.; Jäger, G.; Pfefferkorn, T. Microvascular Basal Lamina Injury after Experimental Focal Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion in the Rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 22, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka, I.; Hirota, S. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in neutrophils in glycogen-induced peritoneal inflammation of guinea pigs. Inflamm. Res. 2000, 49, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Patnaik, R.; Bhattacharya, P.; Shukla, S.C.; Paul, S. Resveratrol inhibits matrix metalloproteinases to attenuate neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia: A molecular docking study exploring possible neuroprotection. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, S.; Zhen, L.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Lei, X.; Lv, J.; Xiong, L.; Xue, R. Resveratrol Attenuates the Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Regulation of the MMP-9/TIMP-1 Balance after Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion in Rats. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 55, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Z.; Rong, X.; Zhao, E.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Y. Neuroprotection of Resveratrol Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice Through a Mechanism Targeting Gut-Brain Axis. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Gao, D.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Li, F. New insights into mechanism for the effect of resveratrol preconditioning against cerebral ischemic stroke: Possible role of matrix metalloprotease-9. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Peng, Y.; Huang, W.; Cheng, G.; Song, L. Resveratrol reduces the elevated level of MMP-9 induced by cerebral ischemia–reperfusion in mice. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2564–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.; Yan, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, J.; Tong, F.; Ma, Q. Combined Ischemic Preconditioning and Resveratrol Improved Bloodbrain Barrier Breakdown via Hippo/YAP/TAZ Signaling Pathway. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 18, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, T. Resveratrol decreases the insoluble Aβ1–42 level in hippocampus and protects the integrity of the blood–brain barrier in AD rats. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairappan, B.; Sundhar, M.; Srinivas, B.H. Resveratrol Restores Neuronal Tight Junction Proteins Through Correction of Ammonia and Inflammation in CCl4-Induced Cirrhotic Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 56, 4718–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.S.; Norenberg, M.D. Effect of ammonia on GABA uptake and release in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2000, 36, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Rao, K.R.; Murthy, C.; Panickar, K.; Jayakumar, A.; Norenberg, M. Ammonia induces the mitochondrial permeability transition in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 66, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.M.; Rao, K.V.R.; Brahmbhatt, M.; Norenberg, M.D. Interaction between cytokines and ammonia in the mitochondrial permeability transition in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 89, 2028–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.; Kafitz, K.W.; Roderigo, C.; Rose, C.R. Ammonium-evoked alterations in intracellular sodium and pH reduce glial glutamate transport activity. Glia 2009, 57, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobermin, L.D.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; Guerra, M.C.; Leite, M.C.; Souza, D.O.; Gonçalves, C.-A.; Gottfried, C. Resveratrol Prevents Ammonia Toxicity in Astroglial Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skowrońska, M.; Albrecht, J. Oxidative and nitrosative stress in ammonia neurotoxicity. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosoi, C.R.; Rose, C.F. Identifying the direct effects of ammonia on the brain. Metab. Brain Dis. 2008, 24, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northrop, N.A.; Halpin, L.E.; Yamamoto, B.K. Peripheral ammonia and blood brain barrier structure and function after methamphetamine. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hao, D.; Jin, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, T.; Su, Y. Internal ammonium excess induces ROS-mediated reactions and causes carbon scarcity in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klejman, A.; Węgrzynowicz, M.; Szatmari, E.M.; Mioduszewska, B.; Hetman, M.; Albrecht, J. Mechanisms of ammonia-induced cell death in rat cortical neurons: Roles of NMDA receptors and glutathione. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 47, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schousboe, A.; Waagepetersen, H.; Leke, R.; Bak, L.K. Effects of hyperammonemia on brain energy metabolism: Controversial findings in vivo and in vitro. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, K.; Aoyama, M.; Fujita, M.; Sobue, K.; Asai, K. Prolonged exposure to ammonia increases extracellular glutamate in cultured rat astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 462, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görg, B.; Qvartskhava, N.; Keitel, V.; Bidmon, H.J.; Selbach, O.; Schliess, F.; Häussinger, D. Ammonia induces RNA oxidation in cultured astrocytes and brainin vivo. Hepatology 2008, 48, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, R.; Cauli, O.; Gomez–Pinedo, U.; Agusti, A.; Hernandez–Rabaza, V.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Felipo, V. Hyperammonemia Induces Neuroinflammation That Contributes to Cognitive Impairment in Rats With Hepatic Encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenko, E.; Venediktova, N.; Kaminsky, Y.; Montoliu, C.; Felipo, V. Sources of oxygen radicals in brain in acute ammonia intoxication in vivo. Brain Res. 2003, 981, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RamaRao, K.; Jayakumar, A.; Norenberg, M.; Rao, K.R. Role of oxidative stress in the ammonia-induced mitochondrial permeability transition in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 47, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, R.F. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cirrhosis: Pathology and Pathophysiology. Drugs 2019, 79, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitbaev, K.A.; Murkamilov, I.T.; Fomin, V.V. Liver diseases: The pathogenetic role of the gut microbiome and the potential of treatment for its modulation. Terapevticheskii 2017, 89, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedik, E.; Girgin, S.; Ozturk, H.; Obay, B.D.; Ozturk, H.; Buyukbayram, H. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress and histological alterations induced by liver ischemia/reperfusion in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 7101–7106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan-Khabbar, S.; Vamy, M.; Cottart, C.-H.; Wendum, D.; Vibert, F.; Savouret, J.-F.; Thérond, P.; Clot, J.-P.; Waligora, A.-J.; Nivet-Antoine, V. Protective effect of post-ischemic treatment with trans-resveratrol on cytokine production and neutrophil recruitment by rat liver. Biochimie 2010, 92, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobermin, L.D.; Souza, D.; Gonçalves, C.-A.; Quincozes-Santos, A. Resveratrol prevents ammonia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular redox imbalance in C6 astroglial cells. Nutr. Neurosci. 2017, 21, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobermin, L.D.; Hansel, G.; Scherer, E.B.; Wyse, A.T.; Souza, D.; Quincozes-Santos, A.; Gonçalves, C.-A. Ammonia impairs glutamatergic communication in astroglial cells: Protective role of resveratrol. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 2022–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quincozes-Santos, A.; Andreazza, A.C.; Nardin, P.; Funchal, C.; Gonçalves, C.-A.; Gottfried, C. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative-induced DNA damage in C6 Glioma cells. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, X. Regulators in the DNA damage response. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 594, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaky, A.; Mohammad, B.; Moftah, M.; Kandeel, K.M.; Bassiouny, A.R. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 is a key modulator of aluminum-induced neuroinflammation. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, N.; Gomes, A.P.; Ling, A.J.; Duarte, F.V.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; North, B.J.; Agarwal, B.; Ye, L.; Ramadori, G.; Teodoro, J.; et al. SIRT1 Is Required for AMPK Activation and the Beneficial Effects of Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Function. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriel, P.; Espinoza, Y.R. Beneficial drugs for liver diseases. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, L.; Zahn, D.; Gieseler, R.K.; Fingas, C.D.; Marquitan, G.; Jochum, C.; Gerken, G.; Friedman, S.L.; Canbay, A. Resveratrol amplifies profibrogenic effects of free fatty acids on human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodotou, M.; Fokianos, K.; Moniatis, D.; Kadlenic, R.; Chrysikou, A.; Aristotelous, A.; Mouzouridou, A.; Diakides, J.; Stavrou, E. Effect of resveratrol on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaguarnera, G.; Pennisi, M.; Bertino, G.; Motta, M.; Borzì, A.M.; Vicari, E.; Bella, R.; Drago, F.; Malaguarnera, M. Resveratrol in Patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. Nutrients 2018, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.P.; Gupta, G.; Dahiya, R.; Jain, D.A.; Mishra, A.; Dua, K. Current Update on Preclinical and Clinical Studies of Resveratrol, a Naturally Occurring Phenolic Compound. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2019, 29, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-K.; Song, J. Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173819
Kim Y-K, Song J. Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173819
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young-Kook, and Juhyun Song. 2021. "Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173819
APA StyleKim, Y.-K., & Song, J. (2021). Therapeutic Applications of Resveratrol in Hepatic Encephalopathy through Its Regulation of the Microbiota, Brain Edema, and Inflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173819






