Effects of Neurofeedback in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
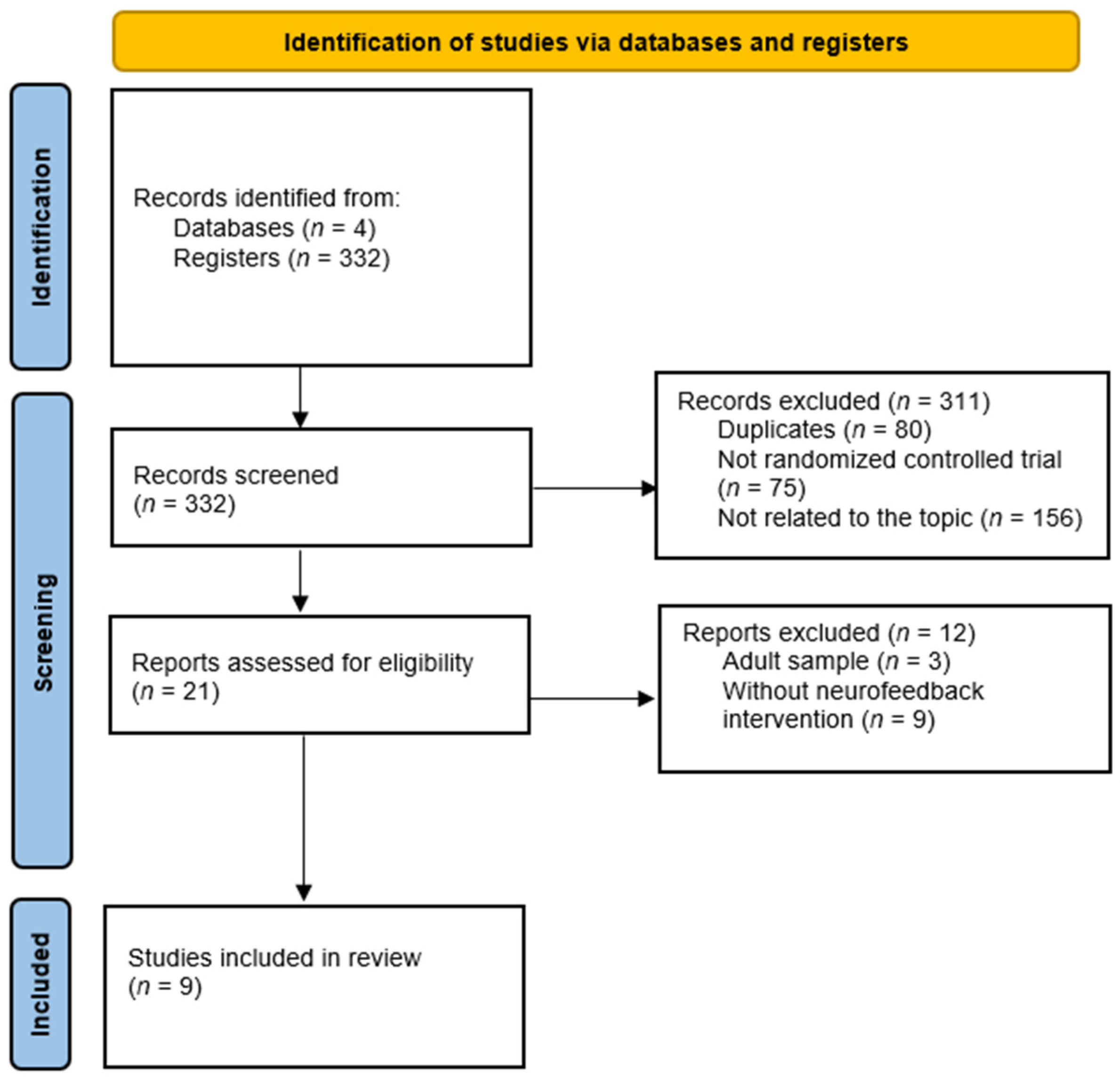
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection, Quality Appraisal, and Risk of Bias
2.4. Data Abstraction
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Training through NF: Slow Cortical Potentials (SCP), Sensory-Motor Rhythm Training (SMR), and Theta-Beta Waves
3.3. Neurofeedback vs. Drug Treatment
3.4. Neurofeedback vs. Other Interventions
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Banaschewski, T.; Becker, K.; Döpfner, M.; Holtmann, M.; Rösler, M.; Romanos, M. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder-a current overview. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2017, 114, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cueli, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Cabaleiro, P.; García, T.; González-Castro, P. Differential Efficacy of Neurofeedback in Children with ADHD Presentations. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drechsler, R.; Brem, S.; Brandeis, D.; Grünblatt, E.; Berger, G.; Walitza, S. ADHD: Current concepts and treatments in children and adolescents. Neuropediatrics 2020, 51, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caye, A.; Swanson, J.M.; Coghill, D.; Rohde, L.A. Treatment strategies for ADHD: An evidence-based guide to select optimal treatment. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 390–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loe, I.M.; Feldman, H.M. Academic and educational outcomes of children with ADHD. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2007, 32, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Operto, F.F.; Smirni, D.; Scuoppo, C.; Padovano, C.; Vivenzio, V.; Quatrosi, G.; Carotenuto, M.; Precenzano, F.; Pastorino, G.M.G. Neuropsychological profile, emotional/behavioral problems, and parental stress in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velő, S.; Keresztény, Á.; Ferenczi-Dallos, G.; Pump, L.; Móra, K.; Balázs, J. The association between prosocial behaviour and peer relationships with comorbid externalizing disorders and quality of life in treatment-naïve children and adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storebø, O.J.; Andersen, M.E.; Skoog, M.; Hansen, S.J.; Simonsen, E.; Pedersen, N.; Tendal, B.; Callesen, H.E.; Faltinsen, E.; Gluud, C. Social skills training for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children aged 5 to 18 years. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 6, CD008223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.; Döpfner, M.; Sergeant, J.; Asherson, P.; Banaschewski, T.; Buitelaar, J.; Coghill, D.; Danckaerts, M.; Rothenberger, A.; Sonuga-Barke, E.; et al. European clinical guidelines for hyperkinetic disorder—First upgrade. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2004, 13, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Jaramillo, L.; Herrera-Solís, A.; Herrera-Morales, W.V. Adhd: Reviewing the causes and evaluating solutions. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells, X.; Blanco-Silvente, L.; Cunill, R. Amphetamines for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, CD007813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolraich, M.L.; Hagan, J.F.; Allan, C.; Chan, E.; Davison, D.; Earls, M.; Evans, S.W.; Flinn, S.K.; Froehlich, T.; Frost, J.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20192528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodgson, K.; Hutchinson, A.D.; Denson, L. Nonpharmacological treatments for ADHD: A meta-analytic review. J. Atten. Disord. 2014, 18, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, H.; Gevensleben, H.; Strehl, U. Annotation: Neurofeedback—Train your brain to train behaviour. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2007, 48, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doren, J.; Arns, M.; Heinrich, H.; Vollebregt, M.A.; Strehl, U.; Loo, S.K. Sustained effects of neurofeedback in ADHD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2019, 28, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enriquez-Geppert, S.; Smit, D.; Pimenta, M.G.; Arns, M. Neurofeedback as a Treatment Intervention in ADHD: Current Evidence and Practice. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, Z.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yao, L. Dynamic functional network connectivity changes associated with fMRI neurofeedback of right premotor cortex. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagdasaryan, J.; Le Van Quyen, M. Experiencing your brain: Neurofeedback as a new bridge between neuroscience and phenomenology. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambez, B.; Harwood-Gross, A.; Golumbic, E.Z.; Rassovsky, Y. Non-pharmacological interventions for cognitive difficulties in ADHD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 120, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goode, A.P.; Coeytaux, R.R.; Maslow, G.R.; Davis, N.; Hill, S.; Namdari, B.; Allen LaPointe, N.M.; Befus, D.; Lallinger, K.R.; Bowen, S.E.; et al. Nonpharmacologic treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20180094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Razoki, B. Neurofeedback versus psychostimulants in the treatment of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 2905–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howick, J.; Chalmers, I.; Glasziou, P.; Greenhalg, T.; Heneghan, C.; Liberati, A.; Moschetti, I.; Phillips, B.; Thornton, H. The Oxford 2011 Levels of Evidence. Available online: https://www.cebm.net/2016/05/ocebm-levels-of-evidence (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0; The Cochrane Collaboration. Available online: www.cochrane-handbook.org (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Duric, N.S.; Assmus, J.; Gundersen, D.; Duric Golos, A.; Elgen, I.B. Multimodal treatment in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A 6-month follow-up. Nord. J. Psychiatry 2017, 71, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geladé, K.; Bink, M.; Janssen, T.W.P.; van Mourik, R.; Maras, A.; Oosterlaan, J. An RCT into the effects of neurofeedback on neurocognitive functioning compared to stimulant medication and physical activity in children with ADHD. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.J.; Jung, C.H. Additive effects of neurofeedback on the treatment of ADHD: A randomized controlled study. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2017, 25, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.G.; Poh, X.W.W.; Fung, S.S.D.; Guan, C.; Bautista, D.; Cheung, Y.B.; Zhang, H.; Yeo, S.N.; Krishnan, R.; Lee, T.S. A randomized controlled trial of a brain-computer interface based attention training program for ADHD. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-García, I.; Meneres-Sancho, S.; Camacho-Vara de Rey, C.; Servera, M. A randomized controlled trial to examine the posttreatment efficacy of neurofeedback, behavior therapy, and pharmacology on ADHD measures. J. Atten. Disord. 2019, 23, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, E.; Hossieni, F.; Solymani, M. Effects of neurofeedback training on performing bimanual coordination in-phase and anti-phase patterns in children with ADHD. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2018, 43, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, S.; Pakize, A.; Moradi, N.A. Effect of combined neurofeedback and game-based cognitive training on the treatment of ADHD: A randomized controlled study. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child. 2020, 9, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Kamarzard, T.S.; Razavi, M.N. The effects of neurofeedback, yoga interventions on memory and cognitive activity in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A randomized controlled trial. Ann. Appl. Sport Sci. 2018, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudnawa, K.K.; Chirdkiatgumchai, V.; Ruangdaraganon, N.; Khongkhatithum, C.; Udomsubpayakul, U.; Jirayucharoensak, S.; Israsena, P. Effectiveness of neurofeedback versus medication for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ayuso, D.; Toledano-González, A.; Rodríguez-Martínez, M.D.; Arroyo-Castillo, P.; Triviño-Juárez, J.M.; González, P.; Ariza-Vega, P.; González, A.D.; Segura-Fragoso, A. Effectiveness of virtual reality-based interventions for children and adolescents with ADHD: A systematic review and meta-Analysis. Children 2021, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leins, U.; Goth, G.; Hinterberger, T.; Klinger, C.; Rumpf, N.; Strehl, U. Neurofeedback for children with ADHD: A comparison of SCP and Theta/Beta protocols. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2007, 32, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshayesh, A.R.; Hänsch, S.; Wyschkon, A.; Rezai, M.J.; Esser, G. Neurofeedback in ADHD: A single-blind randomized controlled trial. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2011, 20, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes-Montes, R.; Delgado-Lobete, L.; Rodríguez-Seoane, S. Developmental coordination disorder, motor performance, and daily participation in children with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder. Children 2021, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokobane, M.; Pillay, B.J.; Meyer, A. Fine motor deficits and attention deficit hyperdisorder in primary school children. South Afr. J. Psychiatry 2019, 25, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, T.W.P.; Bink, M.; Weeda, W.D.; Geladé, K.; van Mourik, R.; Maras, A.; Oosterlaan, J. Learning curves of theta/beta neurofeedback in children with ADHD. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2017, 26, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duric, N.S.; Assmus, J.; Gundersen, D.; Elgen, I.B. Neurofeedback for the treatment of children and adolescents with ADHD: A randomized and controlled clinical trial using parental reports. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, Q.X.; Ho, C.Y.X.; Chan, H.W.; Yong, B.Z.J.; Yeo, W.S. Managing childhood and adolescent attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) with exercise: A systematic review. Complement. Ther. Med. 2017, 34, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyanthi, S.; Arumugam, N.; Parasher, R.K. Effect of physical exercises on attention, motor skill and physical fitness in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. ADHD Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2019, 11, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.C.; Huang, C.J. Effects of an 8-week yoga program on sustained attention and discrimination function in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. PeerJ 2017, 2017, e2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarraya, S.; Wagnr, M.; Jarraya, M.; Engel, F.A. 12 weeks of kindergarten-based yoga practice increases visual attention, visual-motor precision and decreases behavior of inattention and hyperactivity in 5-year-old children. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catalá-López, F.; Hutton, B.; Núñez-Beltrán, A.; Page, M.J.; Ridao, M.; Saint-Gerons, D.M.; Catalá, M.A.; Tabarés-Seisdedos, R.; Moher, D. The pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: A systematic review with network meta-analyses of randomised trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peñuelas-Calvo, I.; Jiang-Lin, L.K.; Girela-Serrano, B.; Delgado-Gomez, D.; Navarro-Jimenez, R.; Baca-Garcia, E.; Porras-Segovia, A. Video games for the assessment and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.G.; Lee, T.S.; Guan, C.; Fung, D.S.S.; Zhao, Y.; Teng, S.S.W.; Zhang, H.; Krishnan, K.R.R. A brain-computer interface based attention training program for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 46692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Authors, (Year), Country | Design | Sample | Aim | Measuring Duration/Follow-Up | Main Results Baseline/Follow-Up | EL/RG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duric et al., [26], 2017, Norway | RCT | n = 130 Mean age = 10.9 (3.35) years G1 medication n = 44 G2 medication + NF n = 44 G3 NF n = 42 | To explore efficacy of medication and NF | Disruptive Behaviour Disorders Rating Scale (Barkley’s Manual):
6 months | Disruptive Behaviour Disorders Rating Scale Mean (95% CI) Teacher Attention G1: 17.8 (16.3–19.3)/13.1 (11.0–15.1) G2: 19.4 (17.8–21.1)/11.6 (9.3–13.8) G3: 15.6 (14.1–17.1)/14.8 (12.7–16.8) Hyperactivity G1: 11.6 (9.1–14.1)/13.0 (10.7–15.3) G2: 8.6 (5.8–11.4)/10.5 (8.0–13.0) G3: 11.6 (9.0–14.2)/10.5 (8.2–12.8) Parents Attention G1: 17.8 (16.0–19.5)/12.1 (10.2–14.0) G2: 17.2 (15.4–19.0)/11.8 (9.8–13.7) G3: 15.3 (13.4–17.2)/13.9 (11.9–15.9) Hyperactivity G1: 18.5 (16.5–20.5)/11.4 (9.4–13.5) G2: 15.9 (13.9–17.9)/10.9 (8.8–13.0) G3: 16.8 (14.8–18.9)/10.0 (7.8–12.1) Self-report children Attention G1: 5.4 (4.5–6.3)/6.0 (5.2–6.8) G2: 5.2 (4.2–6.1)/6.9 (6.1–7.7) G3: 4.7 (3.7–5.7)/5.6 (4.8–6.5) Hyperactivity G1: 5.2 (4.2–6.1)/5.9 (5.0–6.8) G2: 6.0 (5.1–7.0)/5.9 (5.0–6.8) G3: 4.3 (3.3–5.3)/5.8 (4.8–6.7) Education G1: 5.2 (4.2–6.1)/5.9 (5.0–6.8) G2: 6.0 (5.1–7.0)/5.9 (5.0–6.8) G3: 4.3 (3.3–5.3)/5.8 (4.8–6.7) | 1b/A |
| Geladé et al. [27], 2017, Netherlands | RCT | n = 112 Age 7–13 yearsG1 NF n = 39 G2 medication n = 36 G3 PA n = 37 | To compare NF effects on neurocognitive functioning | Oddball task Stop-signal task Visual spatial working memory task 30 sessions 6–9 months | Oddball task M (SD) Mean reaction time G1: 440.72 (100.00)/433.54 (95.63) Adjusted difference [95%CI] −7.20 [−25.64, 11.30] G2: 461.56 (68.65)/404.40 (63.00) Adjusted difference [95%CI] −57.19 [−81.60, −32.80] G3: 438.01 (88.51)/447.02 (90.06) Adjusted difference [95%CI] 9.01 [−9.33, 27.35] Stop-signal task Stop-signal reaction time G1: 271.39 (76.00)/252.89 (83.60) Adjusted difference [95%CI] −19.03 [−38.42, 0.36] G2: 278.10 (91.40)/202.30 (96.20) Adjusted difference [95%CI] −94.92 [−123.90, −65.94] G3: 245.56 (84.83)/236.54 (84.06) Adjusted difference [95%CI] −9.02 [−29.79, 11.74] Mean reaction time Adjusted difference [95%CI] −32.40 [−49.51, −15.28] G1: 642.68 (123.71)/610.12 (122.39) G2: 679.78 (122.31)/629.35 (136.23) G3: 631.73 (110.42)/617.52 (123.86) Visual spatial working memory Forward Adjusted difference [95%CI] 0.71 [0.24, 1.17] G1: 12.26 (2.92)/12.67 (3.60) G2: 11.00 (2.58)/12.17 (2.72) G3: 11.16 (2.73)/11.68 (3.53) Backward Adjusted difference [95%CI] 1.32 [0.78, 1.86] G1: 10.90 (3.08)/11.67 (3.40) G2: 9.58 (2.50)/11.33 (3.60) G3: 9.95 (2.95)/11.00 (3.32) | 1b/A |
| Lee & Jung [28], 2017, Korea | RCT | n = 36 Age 7–12 yearsCG medication n = 18 IG NF n = 18 | To examine the effect of NF on cognitive functions, parental symptom reports, and brainwave activity before and after treatment | ADHD diagnostic system (ADS)ADHD Rating Scale (ARS) Conners Rating Scale Revised (CRS) Korean-Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-III (K-WISC-III) 20 twice-weekly sessions 2,5 months | ADS M(SD) Inattention CG: 107.22 (83.03)/66.00 (48.49) * IG: 78.39 (30.67)/52.67 (11.78) ** Impulsivity CG: 72.72 (27.22)/59.50 (20.70) * IG: 79.39 (36.21)/59.44 (17.87) * Response time CG: 53.61 (14.36)/51.67 (11.62) IG: 52.33 (9.25)/47.33 (11.24) Variability CG: 85.61 (38.25)/67.72 (25.67) IG: 85.61 (38.25)/67.72 (25.67) * ARS CG: 15.94 (2.24)/15.22 (2.86) IG: 14.33 (3.40)/10.78 (4.91) * CRS CG: 15.83 (6.71)/11.33 (5.03) ** IG: 13.89 (7.61)/7.61 (4.90) ** K-WISC-III Full scale intelligence CG: 100.72 (12.06)/110.72 (12.80) *** IG: 100.06 (16.60)/107.33 (16.93) *** Verbal intelligence CG: 100.44 (10.65)/105.28 (12.44) ** IG: 100.39 (16.21)/107.06 (15.39) * Performance intelligence CG: 101.06 (14.58)/114.61 (13.45) *** IG: 99.22(16.21)/107.06 (16.54) *** Verbal comprehension CG 101.94 (10.71)/105.61 (10.78) IG: 100.22 (15.89)/107.22 (15.40) *** Perceptual organization CG: 100.17 (15.51)/112.78 (15.19) *** IG: 101.67 (16.83)/109.78 (16.92) ** Freedom from distractibility CG: 93.94 (17.55)/100.39 (17.42) * IG: 95.94 (15.14)/100.39 (16.25) Perceptual speed CG: 99.61 (11.67)/105.06 (19.83) IG: 95.11 (13.56)/101.78 (12.36) ** | 1b/A |
| Lim et al. [29], 2019, Singapore | RCT | n = 172 Age 6–12 yearsCG n= 87 IG NF-BCI n = 85 | To investigate the efficacy of NF attention training program | ADHD Rating Scale (ARS) 6 sessions 8-week | ARS M (SD) Inattention score MD (95% CI) 1.6 (0.3–2.9) p = 0.017 CG: 18.6 (4.38)/16.7 (5.14) IG: 18.9 (4.25)/15.5 (4.48) | 1b/A |
| Moreno-García et al. [30], 2019, Spain | RCT | n = 57 Age 7–10 yearsG1 NF n= 19 G2 medication n= 19 G3 behavioural therapy n= 19 | To examine the efficacy of NF on the improvement of symptoms | ADHD Rating Scales (ARS) Attention Deficit Disorders Evaluation Scale (ADDES) 40 sessions 20 weeks | ARS M (SD) Parents Hyperactivity G1: 17.43 (4.98)/14.21 (6.77) G2: 12.40 (8.69)/8.80 (5.82) G3: 15.38 (6.66)/9.94 (5.42) ** Inattention G1: 17.64 (4.63)/15.86 (6.81) G2: 19.75 (5.07)/14.31 (6.41) G3: 19.30 (5.41)/14.40 (3.83) ** Teacher Hyperactivity G1: 17 (9.09)/10.86 (8.35) * G2: 9.83 (7.88)/6.83 (4.57) G3: 12.10 (7.53)/12.10 (7.53) ** Inattention G1: 20.43 (4.89) /14.14 (5.30) G2:17.50 (8.09)/15.67 (4.03) G3: 13.90 (5.19)/13.90 (5.19) ** ADDES Hyperactivity G1: 47.38 (20.86)/38.63 (19.42) * G2: 33.55 (22.22)/21.00 (20.01) * G3: 44.94 (28.38)/30.63 (24.22) ** Inattention G1 54.25 (14.90)/45.63 (16.29) * G2 50.91 (14.43)/38.09 (21.61) * G3 55.88 (20.90)/36.25 (20.29) *** | 1b/A |
| Norouzi et al., [31], 2018, Iran | RCT | n = 20 Age 6–10 years CG n =10 IG NF-SMR n= 20 | To analyse NF for improving bimanual coordination | Bimanual coordination task 6−9 sessions 4 weeks | Bimanual coordination accuracy and consistency improved from baseline to follow up in NF group *** | 1b/A |
| Rajabi et al., [32], 2020, Iran | RCT | n = 32 Mean age = 10.20 (1.03) years CG n = 16 IG NF + CogT n= 16 | To examine the effects of NF | Integrated Visual and Auditory continuous performance (IVA) Conners Parent Rating Scales-Revised (CPRS-R) Conners Teacher Rating Scales-Revised (CTRS-R) 30 sessions 3 months | IVA M (SD) CG: 65.71 (16.8)/59.71 (11.1) IG: 58.20 (24.8)/80.50 (7.6) *** CPRS-R CG: 13.00 (3.5)/13.20 (3.3) IG: 11.91 (2.5)/9.61 (2.2) *** CTRS-R CG: 9.10 (3.9)/9.40 (3.8) IG: 11.11 (2.1)/7.21 (1.6) * | 1b/A |
| Rezaei et al. [33], 2018, Iran | RCT | n = 21 Age 7–11 yearsCG n = 7 G1 NF n = 7 G2 yoga n = 7 | To examine the effects of NF | Continues Performance Test (CPT) 24 sessions 8 weeks | CPT M (SD) Correct Detection CG: 30 (10.6)/33.1 (7.9) *** IG1: 16.71 (5.55)/4.71 (3.49) *** IG2: 21.71 (21.24)/9.57 (9.10) *** Reaction time CG: 577 (45)/590 (20) IG1: 611 (79)/555 (72) IG2: 591 (129)/587 (74) Types of error Commission CG: 107.7 (17.3)/105.1 (13) *** IG1: 130.9 (6.3)/144.1 (3.5) *** IG2: 118.1 (24)/135.1 (11) *** Omission CG: 12.3 (8.5)/11.7 (5.9) *** IG1: 2.42 (2.07)/1.14 (1.34) *** IG2: 10.14 (4.05)/5 (3.55) *** | 1b/A |
| Sudnawa et al., [34], 2018, Thailand | RCT | n = 40 Mean age = 8.7 1.55) years CG medication n = 20 G1 NF n = 20 | To evaluate the effectiveness of NF | Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Rating Scales 30 sessions 12 weeks | Vanderbilt scores M (SD) Parent scores Inattentive CG: 17.1 (4.3)/10.1 (4.2) * IG: 15.3 (5.3)/11.8 (6.3) * ADHD symptoms CG: 33.1 (8.3)/20.1 (8.0) * IG: 29.1 (9.7)/22.0 (11.6) * Teacher scores Inattentive CG: 17.3 (4.2)/9.3 (6.1) * IG: 19.5 (3.1)/16.2 (6.3) * ADHD symptoms: CG: 32.9 (7.0)/16.0 (12.7) * IG: 34.0 (9.2)/27.6 (12.2) | 1b/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sampedro Baena, L.; Fuente, G.A.C.-D.l.; Martos-Cabrera, M.B.; Gómez-Urquiza, J.L.; Albendín-García, L.; Romero-Bejar, J.L.; Suleiman-Martos, N. Effects of Neurofeedback in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173797
Sampedro Baena L, Fuente GAC-Dl, Martos-Cabrera MB, Gómez-Urquiza JL, Albendín-García L, Romero-Bejar JL, Suleiman-Martos N. Effects of Neurofeedback in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(17):3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173797
Chicago/Turabian StyleSampedro Baena, Lucía, Guillermo A. Cañadas-De la Fuente, María Begoña Martos-Cabrera, José L. Gómez-Urquiza, Luis Albendín-García, José Luis Romero-Bejar, and Nora Suleiman-Martos. 2021. "Effects of Neurofeedback in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 17: 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173797
APA StyleSampedro Baena, L., Fuente, G. A. C.-D. l., Martos-Cabrera, M. B., Gómez-Urquiza, J. L., Albendín-García, L., Romero-Bejar, J. L., & Suleiman-Martos, N. (2021). Effects of Neurofeedback in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(17), 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10173797











