Bone Cuts Accuracy of a System for Total Knee Arthroplasty including an Active Robotic Arm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
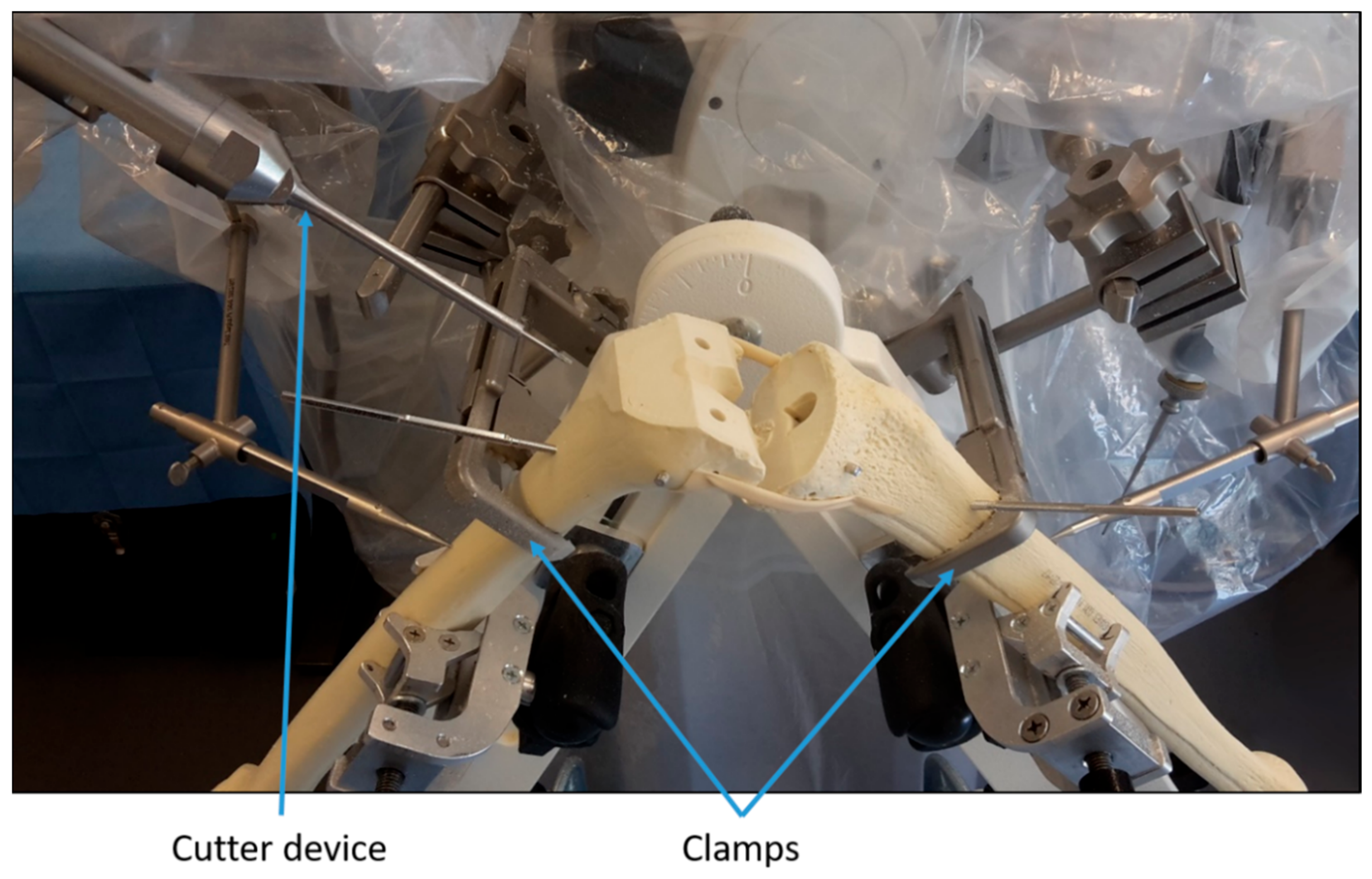
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bone Cut Accuracy Using the Robotic-Assisted System
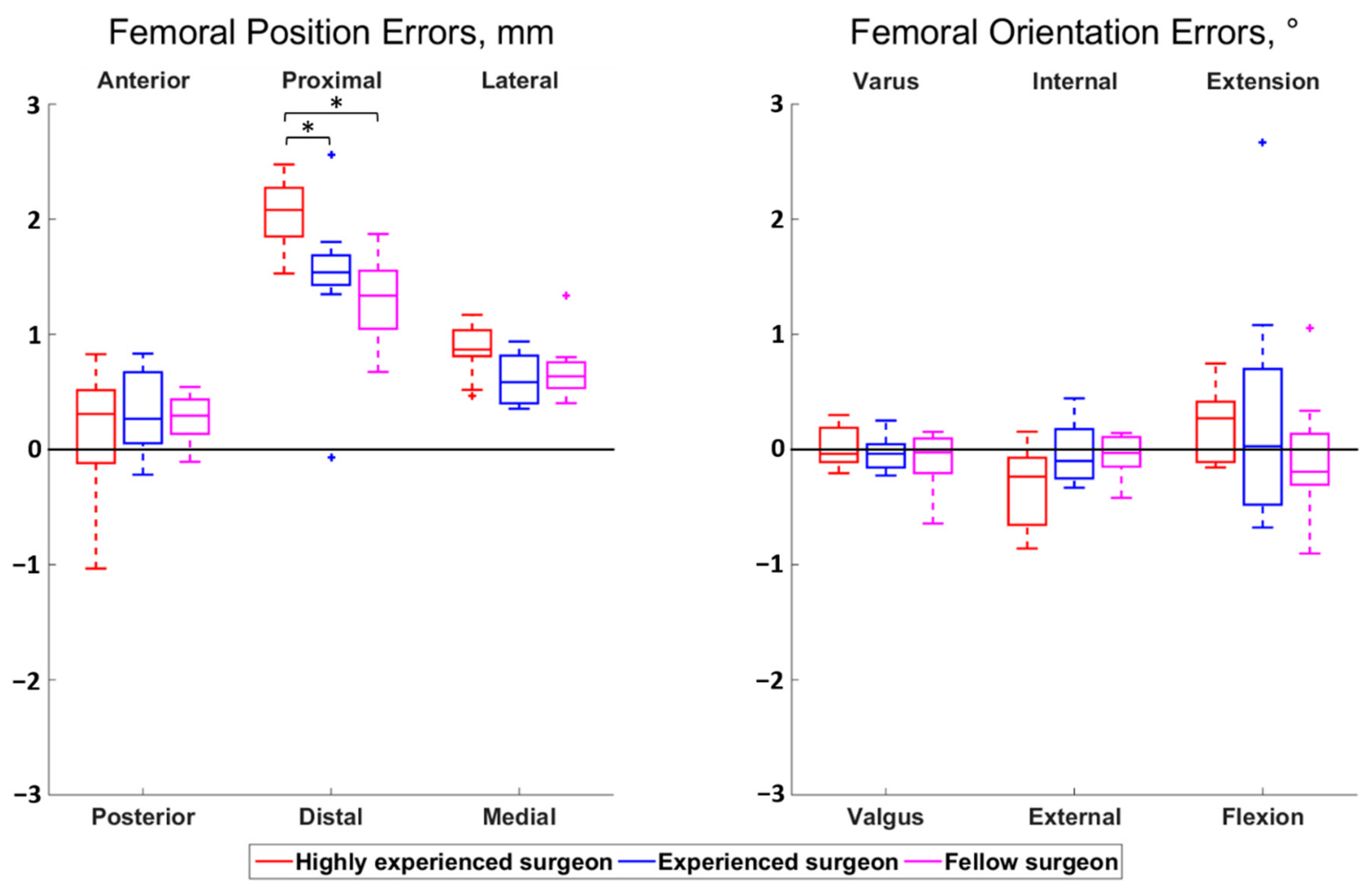
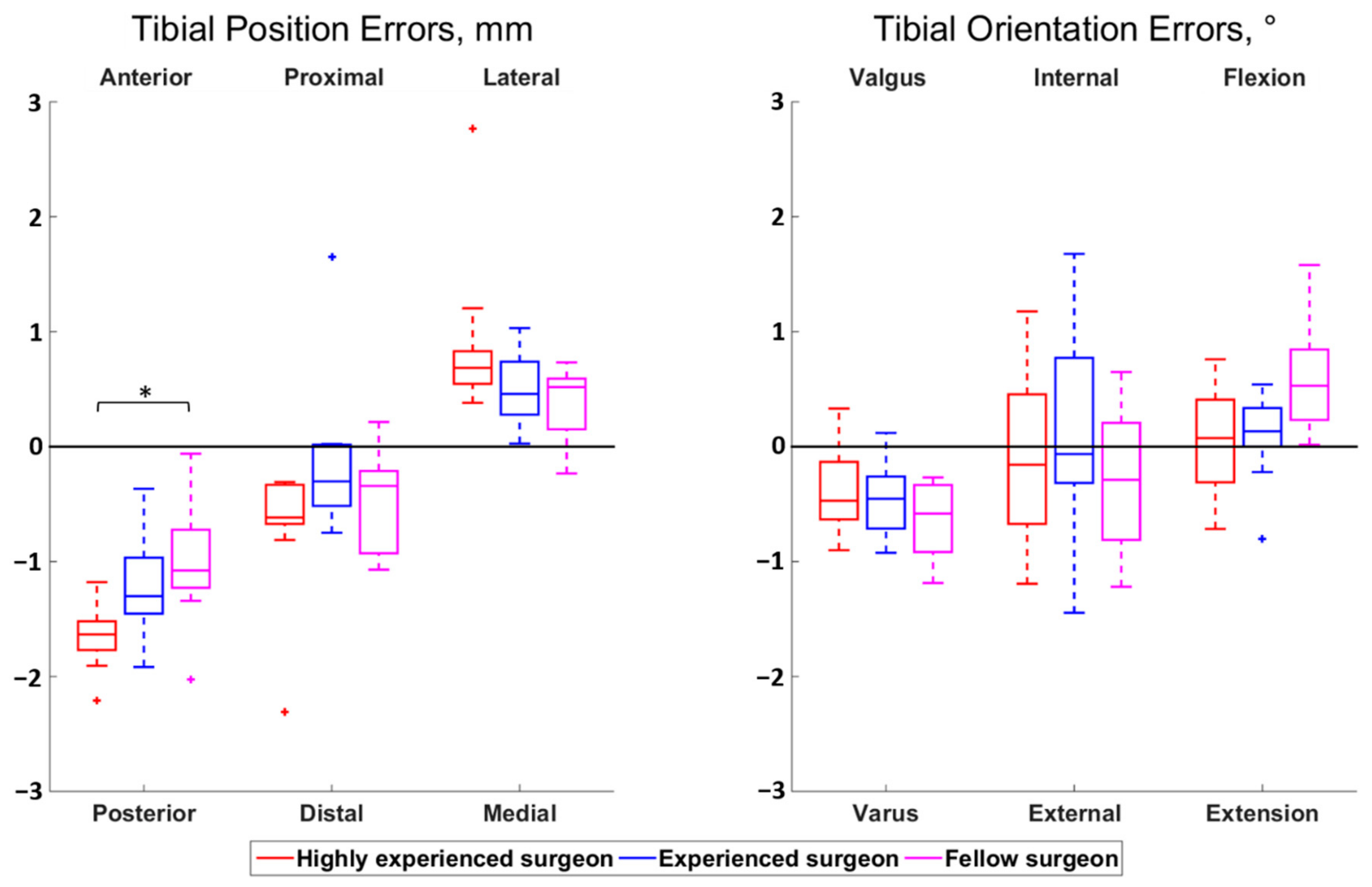
3.2. Influence of the Surgeon’s Level of Experience
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inacio, M.C.S.; Paxton, E.W.; Graves, S.E.; Namba, R.S.; Nemes, S. Projected increase in total knee arthroplasty in the United States—An alternative projection model. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, M.; Manrique, J.; Hozack, W.J. Robotics in total knee arthroplasty. J. Knee Surg. 2019, 32, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacofsky, D.J.; Allen, M. Robotics in arthroplasty: A comprehensive review. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.C.; Buehler, K.C.; Markel, D.C. Computer assisted navigation in total knee arthroplasty: Comparison with conventional methods. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, P.F.; Dowsey, M.M.; Stoney, J.D. Does Accurate Anatomical Alignment Result in Better Function and Quality of Life? Comparing Conventional and Computer-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2009, 24, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazarian, G.S.; Lawrie, C.M.; Barrack, T.N.; Donaldson, M.J.; Miller, G.M.; Haddad, F.S.; Barrack, R.L. The Impact of Surgeon Volume and Training Status on Implant Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2019, 101, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.-K.; Seon, J.-K.; Yim, J.-H.; Netravali, N.A.; Bargar, W.L. Robotic-assisted TKA reduces postoperative alignment outliers and improves gap balance compared to conventional TKA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liow, M.H.L.; Goh, G.S.H.; Wong, M.K.; Chin, P.L.; Tay, D.K.J.; Yeo, S.J. Robotic-assisted total knee arthroplasty may lead to improvement in quality-of-life measures: A 2-year follow-up of a prospective randomized trial. Knee Surg. Sport. Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 2942–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.Y.; Seon, J.K.; Shin, Y.J.; Lim, H.A.; Song, E.K. Robotic Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Cruciate-Retaining Implant: A 10-Year Follow-up Study. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 9, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, J.M. Alignment in total knee replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.M.; Pagnano, M.W. Neutral mechanical alignment. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98-B (Suppl. A), 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoumi, P.; Babel, H.; Jolles, B.M.; Favre, J. Quantitative regional and sub-regional analysis of femoral and tibial subchondral bone mineral density (sBMD) using computed tomography (CT): Comparison of non-osteoarthritic (OA) and severe OA knees. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, H.; Wägeli, L.; Sommez, B.; Thiran, J.; Omoumi, P.; Jolles, B.; Favre, J. A registration method for three-dimensional analysis of bone mineral density in the proximal tibia. J. Biomech. Eng. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldpaus, F.E.; Woltring, H.J.; Dortmans, L.J.M.G. A least-squares algorithm for the equiform transformation from spatial marker co-ordinates. J. Biomech. 1988, 21, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, J.; Van Doninck, D.; Labey, L.; Innocenti, B.; Parizel, P.M.; Bellemans, J. How precise can bony landmarks be determined on a CT scan of the knee? Knee 2009, 16, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, Y.; Miura, H.; Matsuda, S.; Okazaki, K.; Iwamoto, Y. Minimally invasive versus standard approach in total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 463, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, G.; Leong, A.; McEwen, P.; Steele, R.; Tran, T.; Trivett, A. Intra-operative reliability of ShapeMatch cutting guide placement in total knee arthroplasty. Comput. Aided Surg. 2013, 18, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, T.; Maeda, T.; Kabata, T.; Kajino, Y.; Iwai, S.; Tsuchiya, H. The Accuracy of Initial Bone Cutting in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Open J. Orthop. 2015, 5, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Antoniadis, A.; Camenzind, R.S.; Schär, M.O.; Bergadano, D.; Helmy, N. Accuracy of tibial cuts with patient-specific instrumentation is not influenced by the surgeon’s level of experience. Knee Surgery Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parratte, S.; Price, A.J.; Jeys, L.M.; Jackson, W.F.; Clarke, H.D. Accuracy of a new robotically assisted technique for total knee arthroplasty: A cadaveric study. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 2799–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampp, E.L.; Chughtai, M.; Scholl, L.Y.; Sodhi, N.; Bhowmik-Stoker, M.; Jacofsky, D.J.; Mont, M.A. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty demonstrated greater accuracy and precision to plan compared with manual techniques. J. Knee Surg. 2019, 32, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Error Type | Median {IQR} | RMS | Percentage of Outliers | Mean ± SD # | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Femur | Position | Anterior error | 0.29 {0.45} * | 0.45 | 0 | 0.25 ± 0.38 |
| Proximal error | 1.62 {0.49} * | 1.71 | 0 | 1.63 ± 0.55 | ||
| Lateral error | 0.75 {0.35} * | 0.76 | 0 | 0.72 ± 0.25 | ||
| Orientation | Varus error | −0.04 {0.24} | 0.19 | 0 | −0.03 ± 0.19 | |
| Internal rotation error | −0.13 {0.41} | 0.32 | 0 | −0.12 ± 0.30 | ||
| Extension error | 0.03 {0.61} | 0.70 | 0 | 0.14 ± 0.69 | ||
| Tibia | Position | Anterior error | −1.35 {0.58} * | 1.39 | 0 | −1.30 ± 0.50 |
| Proximal error | −0.41 {0.40} * | 0.73 | 0 | −0.43 ± 0.61 | ||
| Lateral error | 0.57 {0.38} * | 0.78 | 0 | 0.60 ± 0.52 | ||
| Orientation | Valgus error | −0.49 {0.44} * | 0.61 | 0 | −0.50 ± 0.36 | |
| Internal rotation error | −0.15 {0.99} | 0.76 | 0 | −0.12 ± 0.77 | ||
| Flexion error | 0.24 {0.51} * | 0.54 | 0 | 0.25 ± 0.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cosendey, K.; Stanovici, J.; Mahlouly, J.; Omoumi, P.; Jolles, B.M.; Favre, J. Bone Cuts Accuracy of a System for Total Knee Arthroplasty including an Active Robotic Arm. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163714
Cosendey K, Stanovici J, Mahlouly J, Omoumi P, Jolles BM, Favre J. Bone Cuts Accuracy of a System for Total Knee Arthroplasty including an Active Robotic Arm. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163714
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosendey, Killian, Julien Stanovici, Jaad Mahlouly, Patrick Omoumi, Brigitte M. Jolles, and Julien Favre. 2021. "Bone Cuts Accuracy of a System for Total Knee Arthroplasty including an Active Robotic Arm" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163714
APA StyleCosendey, K., Stanovici, J., Mahlouly, J., Omoumi, P., Jolles, B. M., & Favre, J. (2021). Bone Cuts Accuracy of a System for Total Knee Arthroplasty including an Active Robotic Arm. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163714






