Determinants of Prolonged Length of Hospital Stay of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
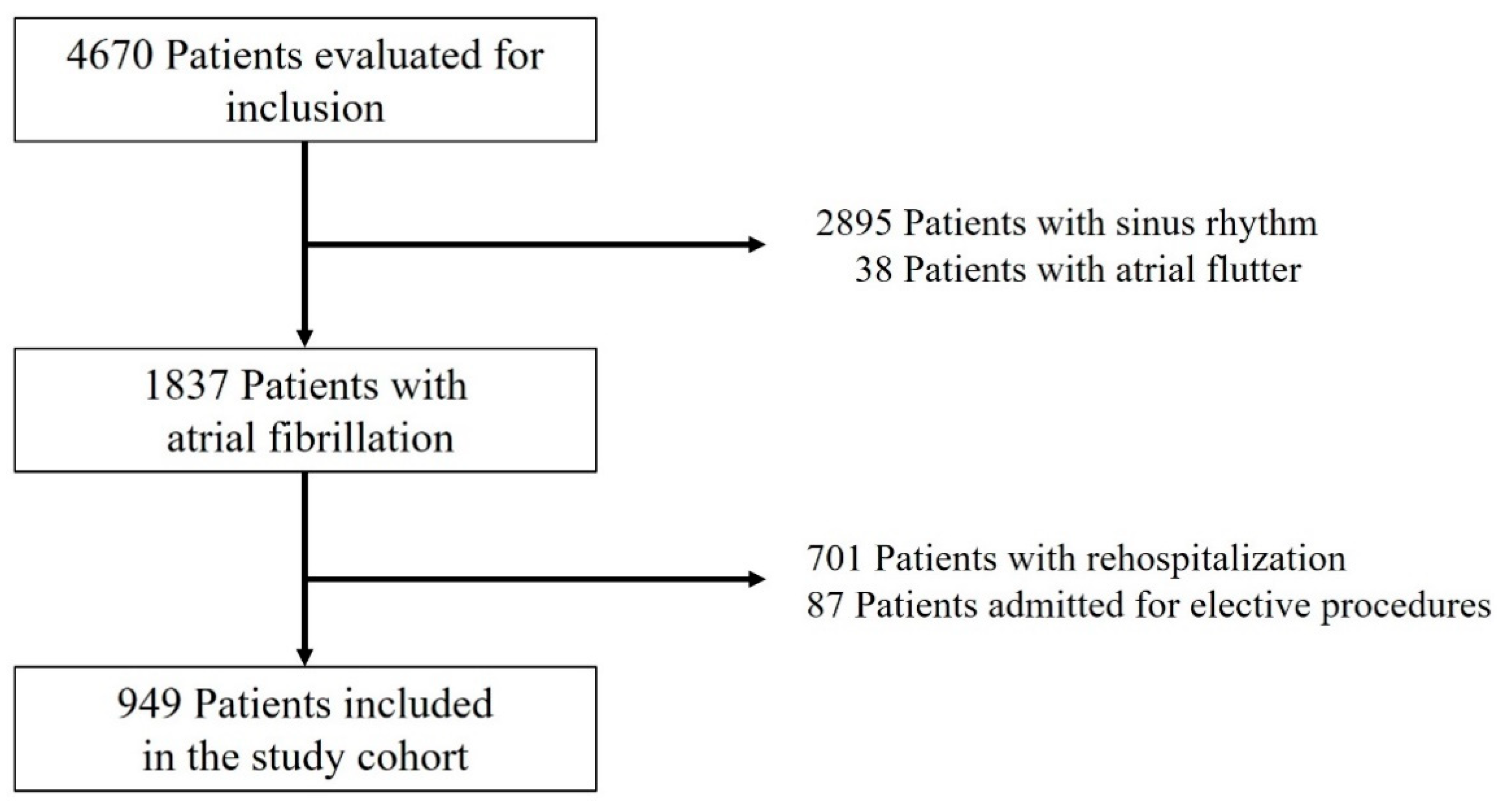
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Length of Hospital Stay
4. Discussion
4.1. Risk Scores in Atrial Fibrillation
4.2. Severity of Atrial Fibrillation Burden
4.3. Cardiac Substrate Characteristics
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruskin, J.N.; Singh, J.P. Atrial fibrillation endpoints: Hospitalization. Heart Rhythm 2004, 1, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerk, L.; Wang, B.; Preis, S.R.; Larson, M.G.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.T.; McManus, D.D.; Ko, D.; Weng, L.-C.; Lunetta, K.; et al. Lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation according to optimal, borderline, or elevated levels of risk factors: Cohort study based on longitudinal data from the Framingham Heart Study. BMJ 2018, 361, k1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnussen, C.; Niiranen, T.J.; Ojeda, F.M.; Gianfagna, F.; Blankenberg, S.; Njølstad, I.; Vartiainen, E.; Sans, S.; Pasterkamp, G.; Hughes, M.; et al. Sex differences and similarities in atrial fibrillation epidemiology, risk factors, and mortality in community cohorts: Results from the biomarcare consortium (Biomarker for cardiovascular risk assessment in Europe). Circulation 2017, 136, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, A.L.; Otto, C.M. Heartbeat: The worldwide burden of atrial fibrillation. Heart 2018, 104, 1987–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blomstrom Lundqvist, C.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Kirchhof, P. What are the costs of atrial fibrillation? Europace 2011, 13, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyre, P.; Blum, S.; Berger, S.; Aeschbacher, S.; Schoepfer, H.; Briel, M.; Osswald, S.; Conen, D. Risk of Hospital Admissions in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, B.A.; Kim, S.; Fonarow, G.C.; Thomas, L.; Ansell, J.; Kowey, P.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Gersh, B.J.; Hylek, E.; Naccarelli, G.; et al. Drivers of hospitalization for patients with atrial fibrillation: Results from the Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (ORBIT-AF). Am. Heart J. 2014, 167, 735–742.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Yin, X.; Gona, P.; Larson, M.G.; Beiser, A.S.; McManus, D.D.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Lubitz, S.A.; Magnani, J.W.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. 50 year trends in atrial fibrillation prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and mortality in the Framingham Heart Study: A cohort study. Lancet 2015, 386, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, R.M.; Michaud, G.F.; Stevenson, W.G. Atrial fibrillation hospitalization, mortality, and therapy. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3958–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, A.; Keshishian, A.; Trocio, J.; Dina, O.; Le, H.; Rosenblatt, L.; Liu, X.; Mardekian, J.; Zhang, Q.; Baser, O.; et al. A Real-World Observational Study of Hospitalization and Health Care Costs Among Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Patients Prescribed Oral Anticoagulants in the U.S. Medicare Population. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2020, 26, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anter, E.; Jessup, M.; Callans, D.J. Atrial fibrillation and heart failure: Treatment considerations for a dual epidemic. Circulation 2009, 119, 2516–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ninni, S.; Lemesle, G.; Meurice, T.; Tricot, O.; Lamblin, N.; Bauters, C. Relative Importance of Heart Failure Events Compared to Stroke and Bleeding in AF Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziewiȩcka, E.; Gliniak, M.; Winiarczyk, M.; Karapetyan, A.; Wiśniowska-Śmiałek, S.; Karabinowska, A.; Holcman, K.; Kostkiewicz, M.; Hlawaty, M.; Leśniak-Sobelga, A.; et al. The burden of atrial fibrillation and its prognostic value in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Kardiol. Pol. 2020, 78, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karnik, A.A.; Gopal, D.M.; Ko, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Helm, R.H. Epidemiology of Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure: A Growing and Important Problem. Cardiol. Clin. 2019, 37, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanakrishnan, R.; Wang, N.; Larson, M.G.; Magnani, J.W.; McManus, D.D.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.; Cheng, S.; Vasan, R.S.; Lee, D.S.; et al. Atrial fibrillation begets heart failure and vice versa: Temporal associations and differences in preserved versus reduced ejection fraction. Circulation 2016, 133, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Outes, A.; Lagunar-Ruíz, J.; Terleira-Fernández, A.I.; Calvo-Rojas, G.; Suárez-Gea, M.L.; Vargas-Castrillón, E. Causes of Death in Anticoagulated Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2508–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghistani, T.A.; Elshawi, R.; Sakr, S.; Ahmed, A.M.; Al-Thwayee, A.; Al-Mallah, M.H. Predictors of in-hospital length of stay among cardiac patients: A machine learning approach. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 288, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.F.J.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Song, H.Y.; Lin, H.M.; Lin, F.M.; Huang, Q.-P. Length of Hospital Stay Prediction at the Admission Stage for Cardiology Patients Using Artificial Neural Network. J. Healthc. Eng. 2016, 2016, 7035463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hachesu, P.R.; Ahmadi, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Sadoughi, F. Use of data mining techniques to determine and predict length of stay of cardiac patients. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2013, 19, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaprutko, J.; Michalak, M.; Nowicka, A.; Dankowski, R.; Drozdz, J.; Ponikowski, P.; Opolski, G.; Nessler, J.; Nowalany-Kozielska, E.; Szyszka, A. Hospitalisation length and prognosis in heart failure patients. Kardiol. Pol. 2017, 75, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriyama, H.; Kohno, T.; Kohsaka, S.; Shiraishi, Y.; Fukuoka, R.; Nagatomo, Y.; Goda, A.; Mizuno, A.; Fukuda, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; et al. West Tokyo Heart Failure Registry Investigators; Length of hospital stay and its impact on subsequent early readmission in patients with acute heart failure: A report from the WET-HF Registry. Heart Vessel. 2019, 34, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.-P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusselaers, N.; Lagergren, J. The charlson comorbidity index in registry-based research: Which version to use? Methods Inf. Med. 2017, 56, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whellan, D.J.; Zhao, X.; Hernandez, A.F.; Liang, L.; Peterson, E.D.; Bhatt, D.L.; Heidenreich, P.A.; Schwamm, L.H.; Fonarow, G.C. Predictors of hospital length of stay in heart failure: Findings from get with the guidelines. J. Card. Fail. 2011, 17, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcea, C.; Buzea, C.A.; Vijan, A.; Draghici, A.; Stoichitoiu, L.E.; Dan, G.A. Comparative role of hematological indices for the assessment of in-hospital outcome of heart failure patients. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2021, 55, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, A.; Patel, N.J.; Nalluri, N.; Agnihotri, K.; Spagnola, J.; Patel, A.; Asti, D.; Kanotra, R.; Khan, H.; Savani, C.; et al. Trends in Hospitalization for Atrial Fibrillation: Epidemiology, Cost, and Implications for the Future. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 58, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.J.; Deshmukh, A.; Pant, S.; Singh, V.; Patel, N.; Arora, S.; Shah, N.; Chothani, A.; Savani, G.T.; Mehta, K.; et al. Contemporary trends of hospitalization for atrial fibrillation in the united states, 2000 through 2010 implications for healthcare planning. Circulation 2014, 129, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahewala, S.; Arora, S.; Patel, P.; Kumar, V.; Patel, N.; Tripathi, B.; Patel, N.; Kallur, K.R.; Shah, H.; Syed, A.; et al. Atrial fibrillation: Utility of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores as predictors of readmission, mortality and resource utilization. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 245, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivănescu, A.C.; Buzea, C.A.; Delcea, C.; Dan, G.-A. Stroke Risk Scores as Predictors of Severe Outcomes in Atrial Fibrillation: A Comprehensive Review. Am. J. Ther. 2021, 28, e319–e334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrone, D.; Kroep, S.; Ricci, F.; Renda, G.; Patti, G.; Kirchhof, P.; Chuang, L.-H.; Van Hout, B.; De Caterina, R. Mortality Prediction of the CHA2DS2-VASc Score, the HAS-BLED Score, and Their Combination in Anticoagulated Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Sánchez, R.Á.; Lorenzo-Villalba, N.; Calvo-Elías, A.E.; Dubón-Peralta, E.E.; Chocrón-Benbunan, C.E.; Cano-De Luque, C.M.; López-García, L.; Rivas-Molinero, M.; Outón-González, C.; Marco-Martínez, J.; et al. Clinical impact of the time in therapeutic range on early hospital readmission in patients with acute heart failure treated with oral anticoagulation in internal medicine. Medicina 2021, 57, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Cumming, R.G.; Hilmer, S.N. The Impact of Frailty on Mortality, Length of Stay and Re-hospitalisation in Older Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Heart Lung Circ. 2016, 25, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laliberté, F.; Cloutier, M.; Crivera, C.; Nelson, W.W.; Olson, W.H.; Schein, J.; Vanderpoel, J.; Germain, G.; Lefebvre, P. Effects of Rivaroxaban Versus Warfarin on Hospitalization Days and Other Health Care Resource Utilization in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: An Observational Study from a Cohort of Matched Users. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farr, A.M.; Jing, Y.; Johnston, S.; Trocio, J.; Singhal, S.; Bruno, A.; Graham, J. Comparison of hospital length of stay between hospitalized non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients treated with either apixaban or warfarin. Hosp. Pract. 2015, 43, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, E.; Sander, S.D.; Hess, G.P.; Ghosh, S. Hospital admissions, costs, and 30-day readmissions among newly diagnosed nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients treated with dabigatran etexilate or warfarin. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2015, 21, 1039–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potpara, T.S.; Trendafilova, E.; Dan, G.A.; Goda, A.; Kusljugic, Z.; Manola, S.; Music, L.; Gjini, V.; Pojskic, B.; Popescu, M.I.; et al. The Patterns of Non-vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs) Use in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in Seven Balkan Countries: A Report from the BALKAN-AF Survey. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 2043–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lip, G.Y.H.; Laroche, C.; Boriani, G.; Dan, G.A.; Santini, M.; Kalarus, Z.; Rasmussen, L.H.; Oliveira, M.M.; Mairesse, G.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; et al. Regional differences in presentation and treatment of patients with atrial fibrillation in Europe: A report from the EURObservational Research Programme Atrial Fibrillation (EORP-AF) Pilot General Registry. Europace 2014, 17, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozieł, M.; Simovic, S.; Pavlovic, N.; Kocijancic, A.; Paparisto, V.; Music, L.; Trendafilova, E.; Dan, A.R.; Kusljugic, Z.; Dan, G.-A.; et al. Adherence to the ABC (Atrial fibrillation Better Care) pathway in the Balkan region: The BALKAN-AF survey. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2020, 130, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henly, S.J. Scientific letters. Nurs. Res. 2008, 57, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziff, O.J.; Carter, P.R.; McGowan, J.; Uppal, H.; Chandran, S.; Russell, S.; Bainey, K.R.; Potluri, R. The interplay between atrial fibrillation and heart failure on long-term mortality and length of stay: Insights from the, United Kingdom ACALM registry. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 252, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, C.; McDonald, K.; de Boer, R.A.; Maisel, A.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Kozhuharov, N.; Coats, A.J.S.; Metra, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Ruschitzka, F.; et al. Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology practical guidance on the use of natriuretic peptide concentrations. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biasco, L.; Radovanovic, D.; Moccetti, M.; Rickli, H.; Roffi, M.; Eberli, F.; Jeger, R.; Moccetti, T.; Erne, P.; Pedrazzini, G. New-onset or Pre-existing Atrial Fibrillation in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Two Distinct Phenomena With a Similar Prognosis. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2019, 72, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, D.H.; Huynh, L.T.; Chew, D.P.; Astley, C.M.; Soman, A.; Sanders, P. Prognostic Impact of Types of Atrial Fibrillation in Acute Coronary Syndromes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 104, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devore, A.D.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Becker, R.C.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Breithardt, G.; Hacke, W.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Nessel, C.C.; et al. Hospitalizations in patients with atrial fibrillation: An analysis from ROCKET AF. Europace 2016, 18, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total n = 949 | LOS < 7 Days n = 659 | LOS ≥ 7 Days n = 290 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||||
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 72.5 ± 10.4 | 71.87 ± 10.5 | 73.9 ± 9.6 | 0.005 |
| Female gender, n (%) | 509 (52.9%) | 350 (53.1%) | 152 (52.4%) | 0.69 |
| AF characteristics | ||||
| Type of AF | ||||
| Paroxysmal, n (%) | 295 (31.1%) | 210 (31.9%) | 85 (29.3%) | 0.433 |
| Persistent, n (%) | 229 (24.1%) | 162 (24.6%) | 67 (23.1%) | 0.249 |
| Permanent, n (%) | 425 (44.8%) | 287 (43.6%) | 138 (47.6%) | 0.624 |
| AF on admission | 724 (76.3%) | 490 (74.4%) | 234 (80.7%) | 0.04 |
| Risk scores | ||||
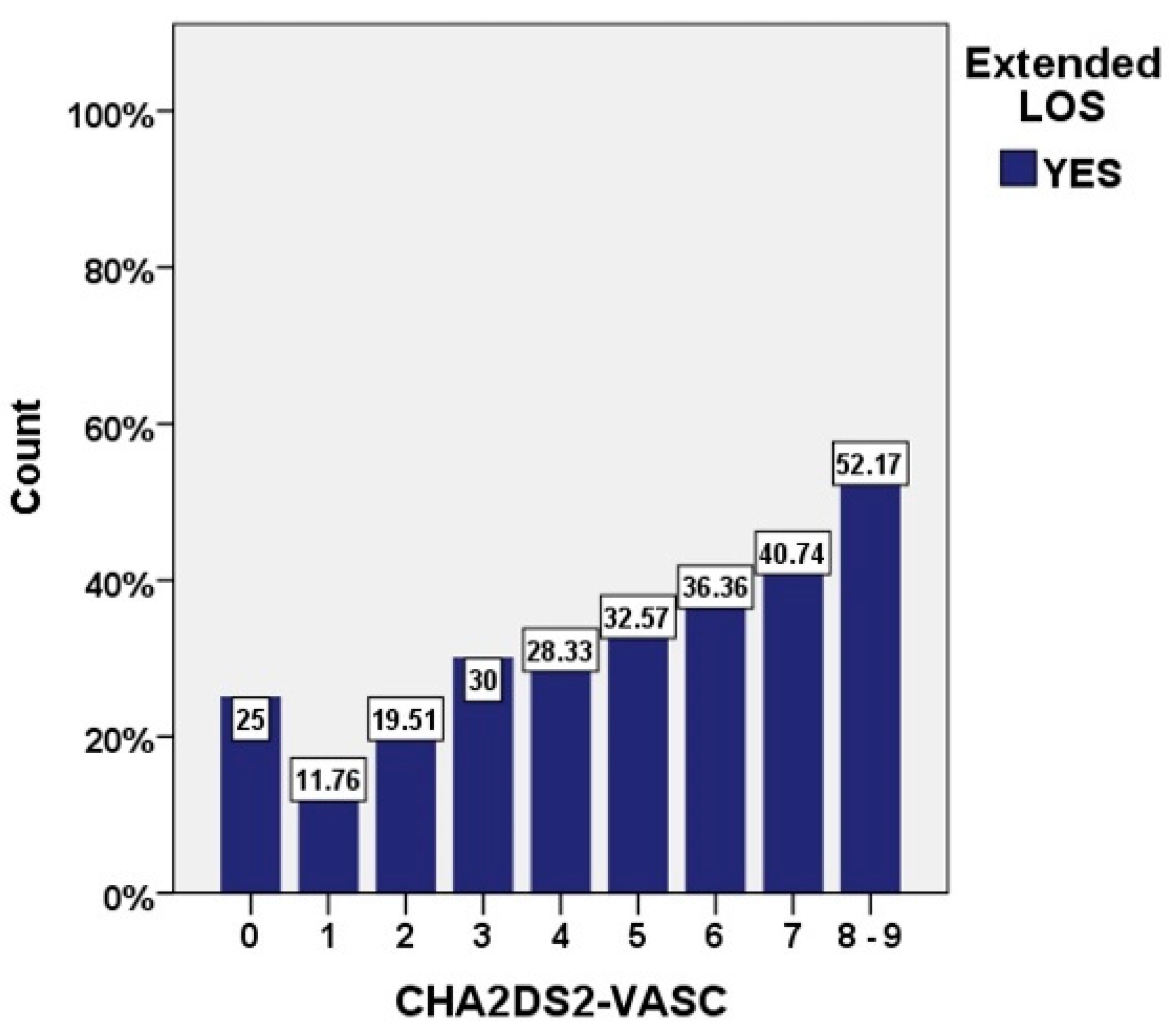
| CHA2DS2 VASc, median [IQR] | 4 [3, 5] | 4 [3, 5] | 5 [4, 6] | <0.001 |
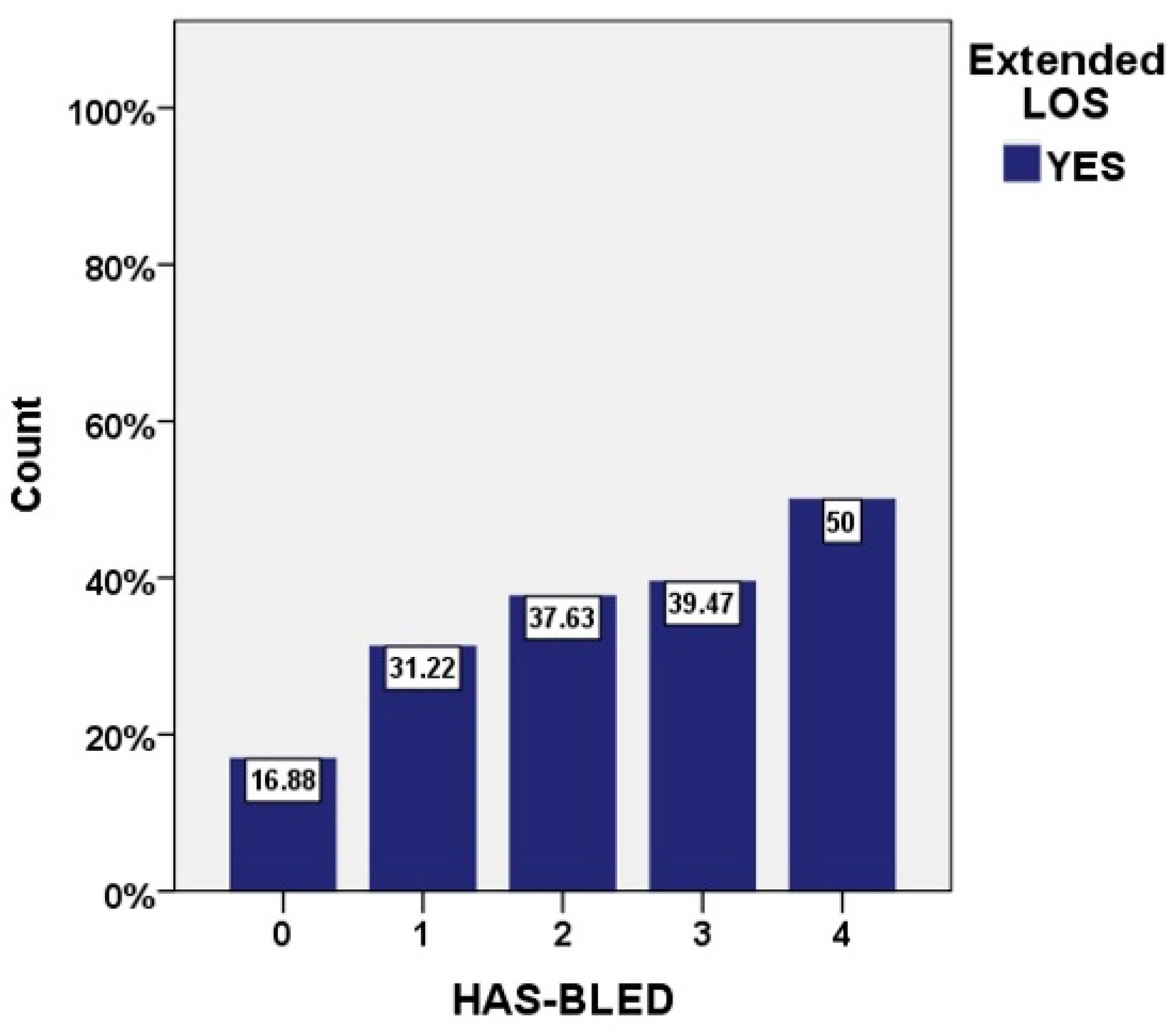
| HAS BLED, median [IQR] | 1 [1, 1] | 1 [1, 1] | 1 [1, 2] | <0.001 |
| Emergency AF Cardioversion | 60 (6.3%) | 39 (5.9%) | 21 (7.2%) | 0.53 |
| HF characteristics | ||||
| HF, n (%) | 786 (82.9%) | 528 (80.2%) | 258 (89.0%) | <0.001 |
| ADHF, n (%) | 383 (40.4%) | 210 (31.9%) | 173 (59.9%) | <0.001 |
| Type of HF | ||||
| HFpEF, n (%) | 456 (55.1%) | 341 (61.2%) | 115 (42.6%) | <0.001 |
| HFmrEF, n (%) | 157 (19.0%) | 104 (18.7%) | 53 (19.6%) | 0.742 |
| HFrEF, n (%) | 214 (25.9%) | 112 (20.1%) | 102 (37.8%) | <0.001 |
| NYHA class | ||||
| I-II, n (%) | 517 (54.5%) | 395 (59.9%) | 122 (42.1%) | <0.001 |
| III-IV, n (%) | 267 (28.1%) | 132 (20.0%) | 135 (46.6%) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities and cardiovascular risk factors | ||||
| Charlson comorbidity index | 4 [3, 5] | 4 [3, 5] | 4 [3, 4] | 0.178 |
| IHD, n (%) | 307 (32.4%) | 192 (29.2%) | 115 (39.7%) | 0.001 |
| Prior MI, n (%) | 99 (10.4%) | 56 (8.5%) | 43 (14.8%) | 0.003 |
| ACS, n (%) | 26 (2.7%) | 11 (1.7%) | 15 (5.2%) | 0.002 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 764 (80.6%) | 551 (83.7%) | 213 (73.4%) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 637 (68.0%) | 444 (68.2%) | 193 (67.5%) | 0.828 |
| Diabetes Mellitus, n (%) | 297 (31.3%) | 190 (28.8%) | 107 (36.9%) | 0.014 |
| Anemia, n (%) | 275 (29.4%) | 168 (25.9%) | 107 (37.3%) | <0.001 |
| History of Stroke/ TIA, n (%) | 137 (14.5%) | 82 (12.5%) | 55 (19.0%) | 0.009 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 295 (31.1%) | 212 (32.2%) | 83 (28.6%) | 0.27 |
| CKD, n (%) | 341 (36.0%) | 222 (33.7%) | 191 (41.0%) | 0.031 |
| Dementia, n (%) | 35 (3.7%) | 17 (2.6%) | 18 (6.2%) | 0.006 |
| Clinical data | ||||
| Chief complaints | ||||
| Dyspnea | 421 (44.3%) | 243 (36.9%) | 178 (61.4%) | <0.001 |
| Chest pain | 36 (3.8%) | 19 (2.9%) | 17 (5.9%) | 0.04 |
| Hypertensive emergency | 76 (8.0%) | 64 (9.7%) | 12 (4.1%) | 0.005 |
| Sincope/presincope | 49 (5.2%) | 36 (5.5%) | 13 (4.5%) | 0.64 |
| Fatigue | 138 (14.5) | 105 (15.9%) | 33 (11.4%) | 0.08 |
| Palpitations | 85 (8.9%) | 69 (10.5%) | 16 (5.5%) | 0.02 |
| HR, bpm, mean ± SD | 85.03 ± 27.33 | 83.01 ± 25.73 | 89.55 ± 30.17 | <0.001 |
| Biological data | ||||
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL, median [IQR] | 1771 [793.6, 3520] | 1395 [629.7, 2700] | 2905 [1429, 5597] | <0.001 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2, median [IQR] | 70.14 [52.27, 87.18] | 71.46 [54.05, 88.96] | 66.95 [46.04, 82.76] | <0.001 |
| INR *, median [IQR] | 1.51 [1.16, 2.28] | 1.53 [1.15, 2.25] | 1.47 [1.20, 2.42] | 0.27 |
| Hb, g/dL, median [IQR] | 13.4 [12.0, 14.5] | 13.5 [12.3, 14.6] | 13.1 [11.7, 14.3] | 0.001 |
| Echocardiographic parameters | ||||
| LA, mm, mean ± SD | 46.9 ± 7.86 | 46.1 ± 7.5 | 48.4 ± 8.3 | <0.001 |
| EF, %, mean ± SD | 45.8 ± 13.4 | 48.0 ± 12.1 | 41.4 ± 14.8 | <0.001 |
| Medication | ||||
| Anticoagulant therapy | ||||
| NOACs, n (%) | 479 (51.5%) | 345 (53.5%) | 134 (47.0%) | 0.07 |
| VKA, n (%) | 427 (45.9%) | 285 (44.2%) | 142 (49.8%) | 0.12 |
| All other cardiovascular medication | ||||
| Antiplatelet therapy, n (%) | 61 (6.4%) | 45 (6.8%) | 16 (5.6%) | 0.47 |
| Beta-blockers, n (%) | 705 (75.5%) | 489 (75.3%) | 216 (75.8%) | 0.85 |
| ACEI or ARB, n (%) | 756 (81.0%) | 531 (81.9%) | 225 (78.9%) | 0.28 |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 706 (76.2%) | 483 (75.2%) | 223 (78.5%) | 0.28 |
| MRA, n (%) | 273 (29.9%) | 161 (25.6%) | 112 (39.4%) | <0.001 |
| Digoxin, n (%) | 62 (6.6%) | 41 (6.3%) | 21 (7.4%) | 0.56 |
| Statins, n (%) | 557 (59.6%) | 389 (59.9%) | 168 (58.9%) | 0.776 |
| Antiarrhythmic drugs, n (%) | 103 (11.4%) | 73 (11.7%) | 30 (10.6%) | 0.07 |
| RR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.10 (1.01–1.20) | 0.02 |
| AF on admission | 1.11 (1.01–1.21) | 0.04 |
| Palpitations on admission | 0.84 (0.75–0.94) | 0.02 |
| HF | 1.19 (1.09–1.30) | <0.001 |
| ADHF | 1.44 (1.31–1.60) | <0.001 |
| Dyspnea at rest | 2.82 (1.41–5.65) | <0.001 |
| HFrEF | 1.38 (1.20–1.59) | <0.001 |
| IHD | 1.16 (1.05–1.28) | <0.001 |
| Prior MI | 1.25 (1.04–1.49) | 0.003 |
| ACS | 1.65 (1.05–2.60) | 0.002 |
| Chest pain on admission | 1.33 (0.97–1.81) | 0.04 |
| Hypertensive emergency | 0.81 (0.73–0.90) | 0.005 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.12 (1.01–1.24) | 0.01 |
| TIA/stroke | 1.18 (1.02–1.37) | 0.008 |
| CKD < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 1.10 (1.01–1.20) | 0.03 |
| Anemia | 1.19 (1.07–1.32) | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 1.44 (1.02–2.03) | 0.006 |
| Infection | 1.48 (1.26–1.73) | <0.001 |
| AUC (95% CI) | Cut-Off Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate | 0.56 (0.53–0.59) | >104 bpm | 0.005 |
| NT-proBNP | 0.69 (0.66–0.73) | >1986 pg/mL | <0.001 |
| EF | 0.63 (0.6–0.67) | <44% | <0.001 |
| CHA2DS2-VASC | 0.58 (0.55–0.61) | >4 | <0.001 |
| HAS-BLED | 0.58 (0.54–0.61) | >3 | <0.001 |
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACS a | 4.60 | 1.66–12.69 | 0.003 |
| Infections a | 2.61 | 1.44–3.23 | <0.001 |
| NT-proBNP > 2008 ng/mL a | 1.96 | 1.37–2.82 | <0.001 |
| ADHF a | 1.76 | 1.23–2.51 | 0.002 |
| HFrEF a | 1.69 | 1.15–2.47 | 0.007 |
| HAS-BLED score b | 1.42 | 1.14–1.78 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vîjan, A.E.; Daha, I.C.; Delcea, C.; Dan, G.-A. Determinants of Prolonged Length of Hospital Stay of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3715. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163715
Vîjan AE, Daha IC, Delcea C, Dan G-A. Determinants of Prolonged Length of Hospital Stay of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3715. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163715
Chicago/Turabian StyleVîjan, Ancuța Elena, Ioana Cristina Daha, Caterina Delcea, and Gheorghe-Andrei Dan. 2021. "Determinants of Prolonged Length of Hospital Stay of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3715. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163715
APA StyleVîjan, A. E., Daha, I. C., Delcea, C., & Dan, G.-A. (2021). Determinants of Prolonged Length of Hospital Stay of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3715. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163715







