Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Replacement Dosing in Morbidly Obese Hypothyroid Patients after Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Parameters Analyzed
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.4. Calculations
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preoperative Characteristics
3.2. Evolution over Time of the Clinical and Analytical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Fisac, J.L.; Guallar-Castillon, P.; León-Muñoz, L.M.; Graciani, A.; Banegas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Prevalence of general and abdominal obesity in the adult population of Spain, 2008-2010: The ENRICA study. Obes. Rev. 2011, 13, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquali, R.; Casanueva, F.; Haluzik, M.; Van Hulsteijn, L.; LeDoux, S.; Monteiro, M.; Salvador, J.; Santini, F.; Toplak, H.; Dekkers, O.M. European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Endocrine work-up in obesity. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 182, G1–G32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, Z.J.; Bleich, S.N.; Cradock, A.L.; Barrett, J.L.; Giles, C.M.; Flax, C.; Long, M.W.; Gortmaker, S.L. Projected U.S. State-Level Prevalence of Adult Obesity and Severe Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magkos, F.; Fraterrigo, G.; Yoshino, J.; Luecking, C.; Kirbach, K.; Kelly, S.C.; Fuentes, L.D.L.; He, S.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Effects of Moderate and Subsequent Progressive Weight Loss on Metabolic Function and Adipose Tissue Biology in Humans with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varela-Rodríguez, B.M.; Juiz-Valiña, P.; Varela, L.; Outeiriño-Blanco, E.; Bravo, S.B.; García-Brao, M.J.; Mena, E.; Noguera, J.F.; Valero-Gasalla, J.; Cordido, F.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Bariatric Surgery-Induced by Weight Loss on the Proteome of Abdominal Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reges, O.; Greenland, P.; Dicker, D.; Leibowitz, M.; Hoshen, M.; Gofer, I.; Rasmussen-Torvik, L.; Balicer, R. Association of Bariatric Surgery Using Laparoscopic Banding, Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass, or Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs Usual Care Obesity Management With All-Cause Mortality. JAMA 2018, 319, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlsson, L.M.; Sjöholm, K.; Jacobson, P.; Andersson-Assarsson, J.C.; Svensson, P.-A.; Taube, M.; Carlsson, B.; Peltonen, M. Life Expectancy after Bariatric Surgery in the Swedish Obese Subjects Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuero, C.; Valenti, V.; Rotellar, F.; Landecho, M.F.; Cienfuegos, J.A.; Frühbeck, G. Revisiting the Ghrelin Changes Following Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 2763–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, M.; Kayser, B.D.; Yoshino, J.; Stein, R.I.; Reeds, D.; Eagon, J.C.; Eckhouse, S.R.; Watrous, J.D.; Jain, M.; Knight, R.; et al. Effects of Diet versus Gastric Bypass on Metabolic Function in Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, B.; Cappola, A.R.; Cooper, D.S. Subclinical Hypothyroidism. JAMA 2019, 322, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena-Bello, L.; Seoane-Pillado, T.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Outeiriño-Blanco, E.; Varela-Rodriguez, B.; Juiz-Valiña, P.; Cordido, M.; Cordido, F. Oral glucose-stimulated growth hormone (GH) test in adult GH deficiency patients and controls: Potential utility of a novel test. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 44, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena-Bello, L.; Pértega-Díaz, S.; Outeiriño-Blanco, E.; Garcia-Buela, J.; Tovar, S.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Diéguez, C.; Cordido, F. Effect of Oral Glucose Administration on Rebound Growth Hormone Release in Normal and Obese Women: The Role of Adiposity, Insulin Sensitivity and Ghrelin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Castro, P.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Brandón-Sandá, I.; Cordido, F. Función endocrina en la obesidad. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2011, 58, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juiz-Valiña, P.; Pena-Bello, L.; Cordido, M.; Outeiriño-Blanco, E.; Pértega, S.; Varela-Rodriguez, B.; Garcia-Brao, M.J.; Mena, E.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Cordido, F. Altered GH-IGF-1 Axis in Severe Obese Subjects is Reversed after Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss and Related with Low-Grade Chronic Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, B. Thyroid and Obesity: An Intriguing Relationship. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3614–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojomo, K.A.; Schneider, D.F.; Reiher, A.E.; Lai, N.; Schaefer, S.; Chen, H.; Sippel, R.S. Using Body Mass Index to Predict Optimal Thyroid Dosing after Thyroidectomy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2013, 216, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubio, I.G.; Galrao, A.L.; Santo, M.A.; Zanini, A.C.; Medeiros-Neto, G. Levothyroxine Absorption in Morbidly Obese Patients Before and After Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalaki, M.A.; Gkotsina, M.I.; Mamali, I.; Markantes, G.; Faltaka, A.; Kalfarentzos, F.; Vagenakis, A.G.; Markou, K.B. Impaired Pharmacokinetics of Levothyroxine in Severely Obese Volunteers. Thyroid 2011, 21, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.F.; Singla, V.; Aggarwal, S.; Gupta, Y. Outcome of bariatric surgery on hypothyroidism: Experience from a tertiary care center in India. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2020, 16, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richou, M.; Gilly, O.; Taillard, V.; De Brauwere, D.P.; Donici, I.; Guedj, A.M. Levothyroxine dose adjustment in hypothyroid patients following gastric sleeve surgery. Ann. d’Endocrinol. 2020, 81, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotsina, M.; Michalaki, M.; Mamali, I.; Markantes, G.; Sakellaropoulos, G.C.; Kalfarentzos, F.; Vagenakis, A.G.; Markou, K.B. Improved Levothyroxine Pharmacokinetics After Bariatric Surgery. Thyroid 2013, 23, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadiraju, S.; Lee, C.J.; Cooper, D.S. Levothyroxine Dosing Following Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2538–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, J.; Cunha, F.; Souteiro, P.; Neves, J.S.; Guerreiro, V.; Magalhães, D.; Bettencourt-Silva, R.; Oliveira, S.C.; Costa, M.M.; Queirós, J.; et al. The Effect of the Bariatric Surgery Type on the Levothyroxine Dose of Morbidly Obese Hypothyroid Patients. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 3538–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoian, V.; Ylli, D.; Felger, E.A.; Wartofsky, L.; Rosen, J.E. Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Replacement Dosing in Overweight and Obese Patients After a Thyroidectomy. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, F.; Pinchera, A.; Marsili, A.; Ceccarini, G.; Castagna, M.G.; Valeriano, R.; Giannetti, M.; Taddei, D.; Centoni, R.; Scartabelli, G.; et al. Lean Body Mass Is a Major Determinant of Levothyroxine Dosage in the Treatment of Thyroid Diseases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juiz-Valiña, P.; Cordido, M.; Outeiriño-Blanco, E.; Pértega, S.; Varela-Rodríguez, B.M.; García-Brao, M.J.; Mena, E.; Pena-Bello, L.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Cordido, F.; et al. Central Resistance to Thyroid Hormones in Morbidly Obese Subjects Is Reversed after Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juiz-Valiña, P.; Outeiriño-Blanco, E.; Pértega, S.; Varela-Rodríguez, B.M.; García-Brao, M.J.; Mena, E.; Pena-Bello, L.; Cordido, M.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Cordido, F. Effect of Weight Loss after Bariatric Surgery on Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Levels in Euthyroid Patients with Morbid Obesity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devine, B. Gentamicin therapy. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 1974, 8, 650–655. [Google Scholar]
- Mosteller, R.D. Simplified Calculation of Body-Surface Area. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakdash, J.Z.; Marusich, L. Repeated Measures Correlation. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawaya, R.A.; Jaffe, J.; Friedenberg, L.; Friedenberg, F.K. Vitamin, Mineral, and Drug Absorption Following Bariatric Surgery. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Henriksen, B.; Cohen, A. Pharmacokinetic considerations in Roux-en-Y gastric bypass patients. Am. J. Heal. Pharm. 2011, 68, 2241–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwanpo, L.; Hershman, J.M. Conditions and drugs interfering with thyroxine absorption. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, R.; Brocks, D.; Sharma, A.M. A systematic review of drug absorption following bariatric surgery and its theoretical implications. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, F.; Belur, R.; Albano, J. Malabsorption of Thyroid Hormones After Jejunoileal Bypass for Obesity. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 90, 941–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan, J.S.; Munro, J.F. Thyroxine malabsorption following intestinal bypass surgery. Int. J. Obes. 1986, 10, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Topliss, D.; A Wright, J.; Volpé, R. Increased requirement for thyroid hormone after a jejunoileal bypass operation. Can. Med Assoc. J. 1980, 123, 765–766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stone, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lambert, J.R.; Silverberg, J.D.H.; Jeejeebhoy, K.N.; Burrow, G.N. L-Thyroxine Absorption in Patients with Short Bowel. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1984, 59, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Camastra, S.; Politti, U.; Ruffilli, I.; Vita, R.; Navarra, G.; Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A. TSH Normalization in Bariatric Surgery Patients After the Switch from l-Thyroxine in Tablet to an Oral Liquid Formulation. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Modi, S.; Jose, T. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Leads to Reduction in Thyroxine Requirement in Morbidly Obese Patients With Hypothyroidism. World J. Surg. 2014, 38, 2628–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnicki, Y.; Slavin, M.; Keidar, A.; Kent, I.; Berkovich, L.; Tiomkin, V.; Inbar, R.; Avital, S. The effect of bariatric surgery on hypothyroidism: Sleeve gastrectomy versus gastric bypass. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2018, 14, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendel, A.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Dux, J.; Mor, E.; Zippel, D.; Goitein, D. The Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Thyroid Function and Medication Use in Patients with Hypothyroidism. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 2000–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almunif, D.S.; Bamehriz, F.; Althuwaini, S.; Almigbal, T.H.; Batais, M.A. The Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy on Serum Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Levels in Obese Patients with Overt and Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A 7-Year Retrospective Study. Obes. Surg. 2019, 30, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azran, C.; Hanhan-Shamshoum, N.; Irshied, T.; Ben-Shushan, T.; Dicker, D.; Dahan, A.; Matok, I. Hypothyroidism and levothyroxine therapy following bariatric surgery: A systematic review, meta-analysis, network meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2021, 17, 1206–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierabracci, P.; Martinelli, S.; Tamberi, A.; Piaggi, P.; Basolo, A.; Pelosini, C.; Ricco, I.; Magno, S.; Querci, G.; Ceccarini, G.; et al. Weight Loss and Variation of Levothyroxine Requirements in Hypothyroid Obese Patients After Bariatric Surgery. Thyroid 2016, 26, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julià, H.; Benaiges, D.; Mollà, P.; Pedro-Botet, J.; Villatoro, M.; Fontané, L.; Ramon, J.M.; Climent, E.; Le Roux, J.A.F.; Goday, A. Changes in Thyroid Replacement Therapy after Bariatric Surgery: Differences between Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2593–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skelin, M.; Lucijanić, T.; Klarić, D.A.; Rešić, A.; Bakula, M.; Liberati-Čizmek, A.-M.; Gharib, H.; Rahelić, D. Factors Affecting Gastrointestinal Absorption of Levothyroxine: A Review. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 378–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quercia, I.; Dutia, R.; Kotler, D.; Belsley, S.; Laferrère, B. Gastrointestinal changes after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Metab. 2014, 40, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.D.; Herkes, S.B.; Behrns, K.E.; Fairbanks, V.F.; Kelly, K.A.; Sarr, M.G. Gastric Acid Secretion and Vitamin B12 Absorption After Vertical Rouxen-Y Gastric Bypass for Morbid Obesity. Ann. Surg. 1993, 218, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidro, M.L.; Penín, M.A.; Nemiña, R.; Cordido, F. Metformin reduces thyrotropin levels in obese, diabetic women with primary hypothyroidism on thyroxine replacement therapy. Endocrine 2007, 32, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virili, C.; Antonelli, A.; Santaguida, M.G.; Benvenga, S.; Centanni, M. Gastrointestinal Malabsorption of Thyroxine. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muraca, E.; Ciardullo, S.; Oltolini, A.; Zerbini, F.; Bianconi, E.; Perra, S.; Villa, M.; Cannistraci, R.; Castoldi, G.; Pizzi, P.; et al. Resting Energy Expenditure in Obese Women with Primary Hypothyroidism and Appropriate Levothyroxine Replacement Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e1741–e1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mele, C.; Tagliaferri, M.A.; Pagano, L.; Soranna, D.; Scacchi, M.; Aimaretti, G.; Biondi, B.; Marzullo, P. Levothyroxine Replacement in Obese Adults: The Role of Metabolic Variables and Aging on Thyroid Testing Abnormalities. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 6265–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Median | 25th Percentile | 75th Percentile | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) t0 | 47.1 | 42.5 | 49.4 |
| Body Fat (%) t0 | 51.2 | 49.1 | 53.3 |
| Lean Body Weight (kg) t0 | 57.4 | 53.5 | 62.4 |
| Body Surface Area (m2) t0 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.4 |
| Fasting Glucose (mg/dL) t0 | 92.0 | 78.0 | 115.0 |
| Fasting Insulin (µIU/mL) t0 | 6.4 | 3.6 | 11.5 |
| Free T4 (ng/dL) t0 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.7 |
| TSH (µU/mL) t0 | 2.6 | 1.2 | 6.9 |
| 3 Months after Surgery | 6 Months after Surgery | 12 Month safter Surgery | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | P25 | P75 | Median | P25 | P75 | Median | P25 | P75 | |
| BMI | 38.0 | 33.6 | 40.2 | 32.8 | 29.6 | 36.5 | 31.6 | 29.1 | 34.0 |
| EWL (%) | 43.3 | 34.7 | 47.4 | 58.1 | 49.8 | 63.6 | 65.6 | 60.1 | 75.2 |
| EBMIL (%) | 48.2 | 37.0 | 52.8 | 64.8 | 53.4 | 76.2 | 71.5 | 65.6 | 80.1 |
| Body Fat (%) | 43.4 | 38.2 | 48.9 | 36.8 | 35.2 | 41.0 | 36.7 | 30.3 | 41.2 |
| Body Surface Area (m2) | 2.0 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.9 |
| Fasting Glucose (mg/dL) | 84.0 | 78.0 | 89.0 | 81.0 | 74.0 | 88.0 | 82.0 | 78.0 | 88.0 |
| Fasting Insulin (µIU/mL) | 5.7 | 3.6 | 6.0 | 5.2 | 3.4 | 9.2 | 7.8 | 3.1 | 10.0 |
| Free T4 (ng/dL) | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
| TSH (µU/mL) | 2.1 | 1.1 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 2.0 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 1.7 | 5.0 |
| Before Surgery | 3 Months after Surgery | 6 Months after Surgery | 12 Months after Surgery | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | P25 | P75 | Median | P25 | P75 | Median | P25 | P75 | Median | P25 | P75 | p * | |
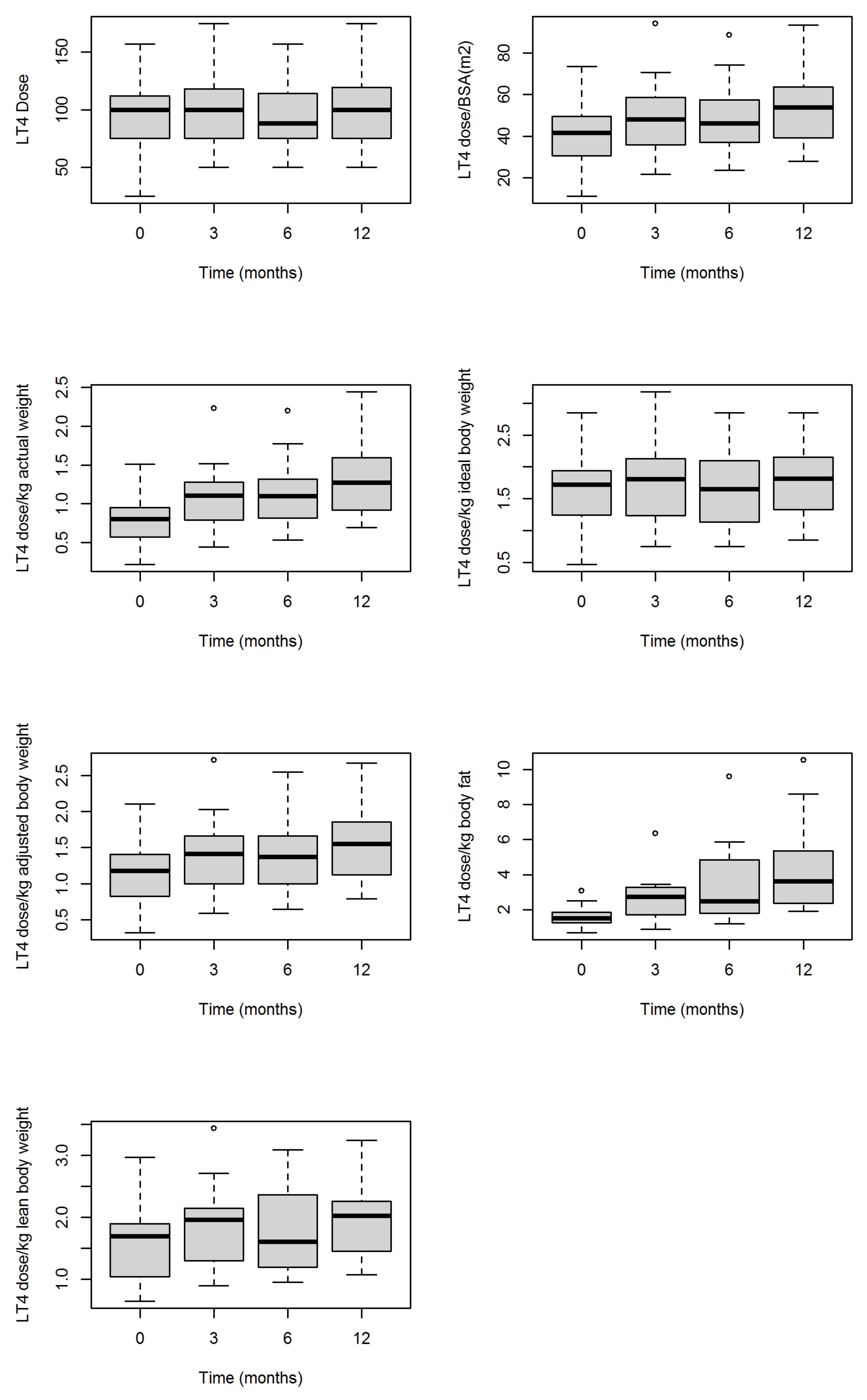
| LT4 dose | 100.0 | 75.0 | 112.0 | 100.0 | 75.0 | 122.0 | 88.0 | 75.0 | 114.0 | 100.0 | 75.0 | 119.5 | 0.058 |
| LT4 dose/BSA (m2) | 41.7 | 30.6 | 49.5 | 48.2 | 35.8 | 59.0 | 46.3 | 37.0 | 57.5 | 53.8 | 39.2 | 63.8 | <0.001 |
| LT4 dose/kg actual weight | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 1.6 | <0.001 |
| LT4 dose/kg ideal body weight | 1.72 | 1.24 | 1.94 | 1.81 | 1.13 | 2.16 | 1.65 | 1.13 | 2.10 | 1.82 | 1.33 | 2.15 | 0.058 |
| LT4 dose/kg adjusted body weight | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 1.9 | <0.001 |
| LT4 dose/kg body fat | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 1.7 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 4.8 | 3.6 | 2.4 | 5.4 | <0.001 |
| LT4 dose/kg lean body weight | 1.7 | 1.0 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 1.1 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 2.3 | <0.001 |
| Absolute Change at 12 Months | Relative Change at 12 Months (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | P25 | P75 | Median | P25 | P75 | p * | |
| LT4 dose | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.083 |
| LT4 dose/BSA (m2) | 12.05 | 6.61 | 14.85 | 25.94 | 20.23 | 30.32 | <0.001 |
| LT4 dose/kg actual weight | 0.53 | 0.29 | 0.63 | 58.62 | 44.56 | 69.84 | <0.001 |
| LT4 dose/kg ideal body weight | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.109 |
| LT4 dose/kg adjusted body weight | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.51 | 26.35 | 21.43 | 33.38 | <0.001 |
| LT4 dose/kg body fat | 2.02 | 1.59 | 3.23 | 134.86 | 113.13 | 178.67 | 0.001 |
| LT4 dose/kg lean body weight | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 17.35 | 11.83 | 18.91 | 0.001 |
| LT4 Dose | LT4 Dose/BSA (m2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | p | B | SE | p | |
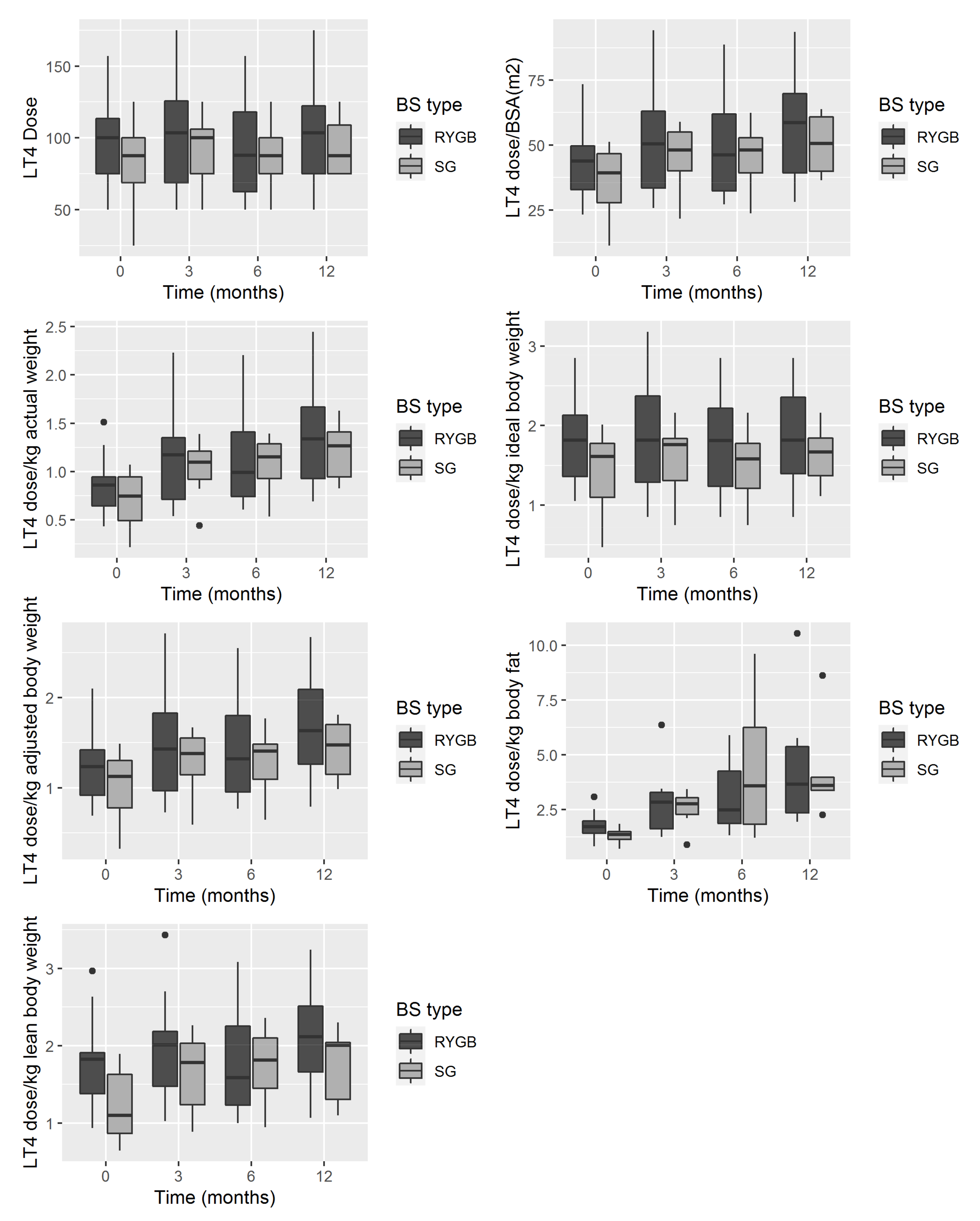
| Intercept | 100.16 | 9.06 | <0.001 | 45.41 | 4.17 | <0.001 |
| Linear time (months after surgery) | 0.65 | 0.20 | 0.142 | 0.88 | 5.13 | <0.001 |
| BS type (SG vs. RYGB) | −17.74 | 12.09 | 0.142 | −9.07 | 5.74 | 0.110 |
| LT4 dose/kg Ideal Body Weight | LT4 dose/kg Actual Weight | |||||
| B | SE | p | B | SE | p | |
| Intercept | 1.82 | 0.15 | <0.001 | 0.90 | 0.09 | <0.001 |
| Linear time (months after surgery) | 0.01 | 0.004 | 0.095 | 0.03 | 0.01 | <0.001 |
| BS type (SG vs. RYGB) | −0.40 | 0.20 | 0.051 | −0.18 | 0.13 | 0.160 |
| LT4 dose/kg Adjusted Body Weight | LT4 dose/kg Body Fat | |||||
| Intercept | 1.29 | 0.12 | <0.001 | 1.87 | 0.24 | <0.001 |
| Linear time (months after surgery) | 0.03 | 0.004 | <0.001 | 0.18 | 0.04 | <0.001 |
| BS type (SG vs. RYGB) | −0.27 | 0.16 | 0.092 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 0.950 |
| LT4 dose/kg Lean Body Weight | ||||||
| Intercept | 1.82 | 0.17 | <0.001 | |||
| Linear time (months after surgery) | 0.02 | 0.004 | <0.001 | |||
| BS type (SG vs. RYGB) | −0.47 | 0.23 | 0.041 | |||
| BMI | Body Fat (%) | Lean Body Weight (kg) | EWL (%) | EBMIL (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LT4 dose | −0.309 (−0.537; −0.040) * | −0.189 (−0.470; 0.125) | −0.232 (−0.500; 0.077) | −0.068 (−0.412; 0.294) | −0.087 (−0.428; 0.276) |
| LT4 dose/BSA (m2) | −0.855 (−0.915; −0.759) * | −0.817 (−0.899; −0.680) * | −0.784 (−0.879; −0.630) * | 0.631 (0.356; 0.805) * | 0.615 (0.333; 0.796) * |
| LT4 dose/kg actual Weight | −0.904 (−0.944; −0.838) * | −0.895 (−0.943; −0.811) * | −0.839 (−0.910; −0.718) * | 0.851 (0.712; 0.926) * | 0.841 (0.693; 0.921) * |
| LT4 dose/kg ideal body weight | −0.310 (−0.537; −0.040) * | −0.187 (−0.468; 0.128) | −0.226 (−0.496; 0.084) | −0.045 (−0.393; 0.314) | −0.062 (−0.408; 0.299) |
| LT4 dose/kg adjusted body weight | −0.863 (−0.920; −0.770) * | −0.814 (−0.897; −0.675) * | −0.783 (−0.878; −0.628) * | 0.605 (0.313; 0.792) * | 0.588 (0.289; 0.783) * |
| LT4 dose/kg body fat | −0.673 (−0.812; −0.461) * | −0.700 (−0.829; −0.500) * | −0.667 (−0.808; −0.452) * | 0.496 (0.106; 0.754) * | 0.495 (0.104; 0.753) * |
| LT4 dose/kg lean body weight | −0.730 (−0.849; −0.542) * | −0.590 (−0.762; −0.342) * | −0.647 (−0.798; −0.420) * | 0.240 (−0.191; 0.594) | 0.231 (−0.200; 0.588) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juiz-Valiña, P.; Cordido, M.; Outeiriño-Blanco, E.; Pértega, S.; Urones, P.; García-Brao, M.J.; Mena, E.; Pena-Bello, L.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Cordido, F. Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Replacement Dosing in Morbidly Obese Hypothyroid Patients after Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163685
Juiz-Valiña P, Cordido M, Outeiriño-Blanco E, Pértega S, Urones P, García-Brao MJ, Mena E, Pena-Bello L, Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Cordido F. Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Replacement Dosing in Morbidly Obese Hypothyroid Patients after Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(16):3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163685
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuiz-Valiña, Paula, María Cordido, Elena Outeiriño-Blanco, Sonia Pértega, Paula Urones, María Jesús García-Brao, Enrique Mena, Lara Pena-Bello, Susana Sangiao-Alvarellos, and Fernando Cordido. 2021. "Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Replacement Dosing in Morbidly Obese Hypothyroid Patients after Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 16: 3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163685
APA StyleJuiz-Valiña, P., Cordido, M., Outeiriño-Blanco, E., Pértega, S., Urones, P., García-Brao, M. J., Mena, E., Pena-Bello, L., Sangiao-Alvarellos, S., & Cordido, F. (2021). Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Replacement Dosing in Morbidly Obese Hypothyroid Patients after Bariatric Surgery-Induced Weight Loss. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), 3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10163685









