Compressed Sensing Real-Time Cine Reduces CMR Arrhythmia-Related Artifacts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Imaging Protocol
2.3. Cine Images Quality Assessment
2.4. Conditions of Image Analysis
2.5. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Description
3.2. Cine Acquisitions
3.3. Objective European CMR Standardized Criteria-Based Quality Score
3.4. Subjective Overall Quality Score
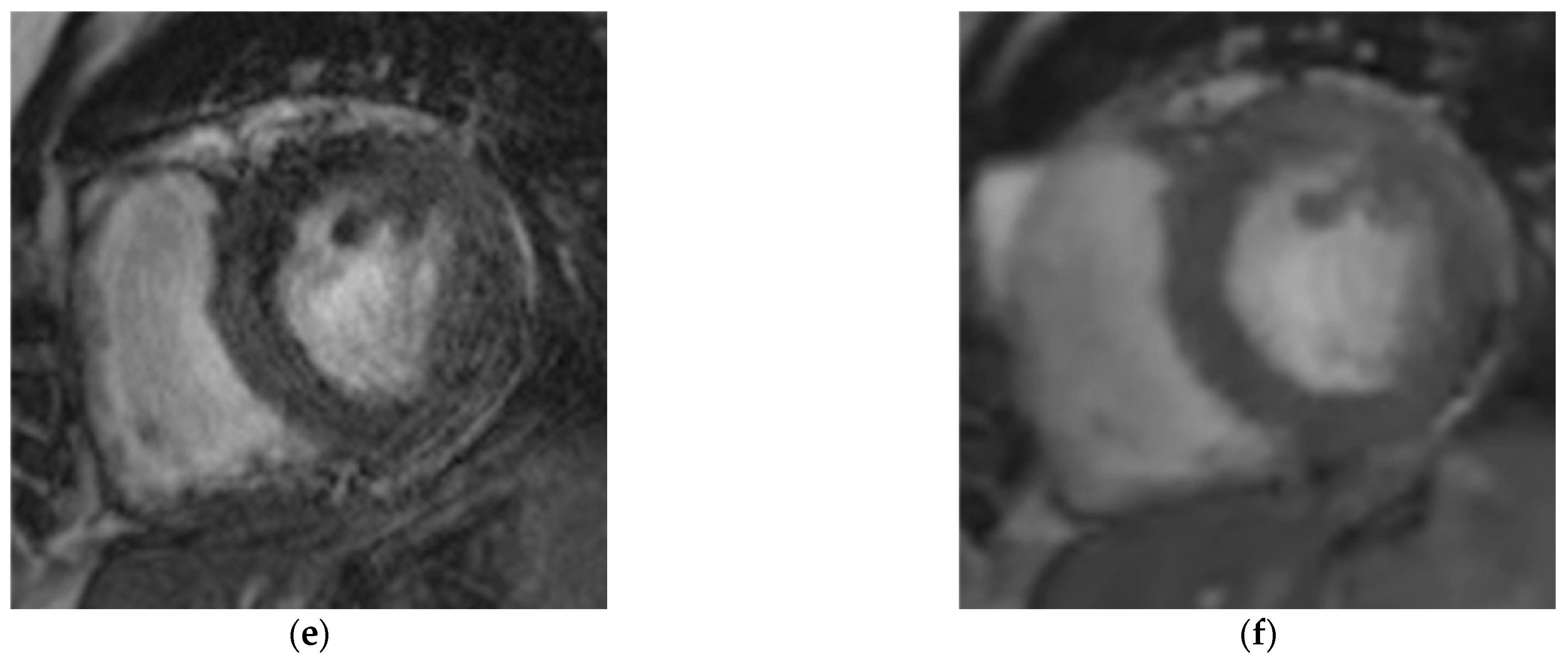
3.5. Arrhythmia-Related Artifacts Rate
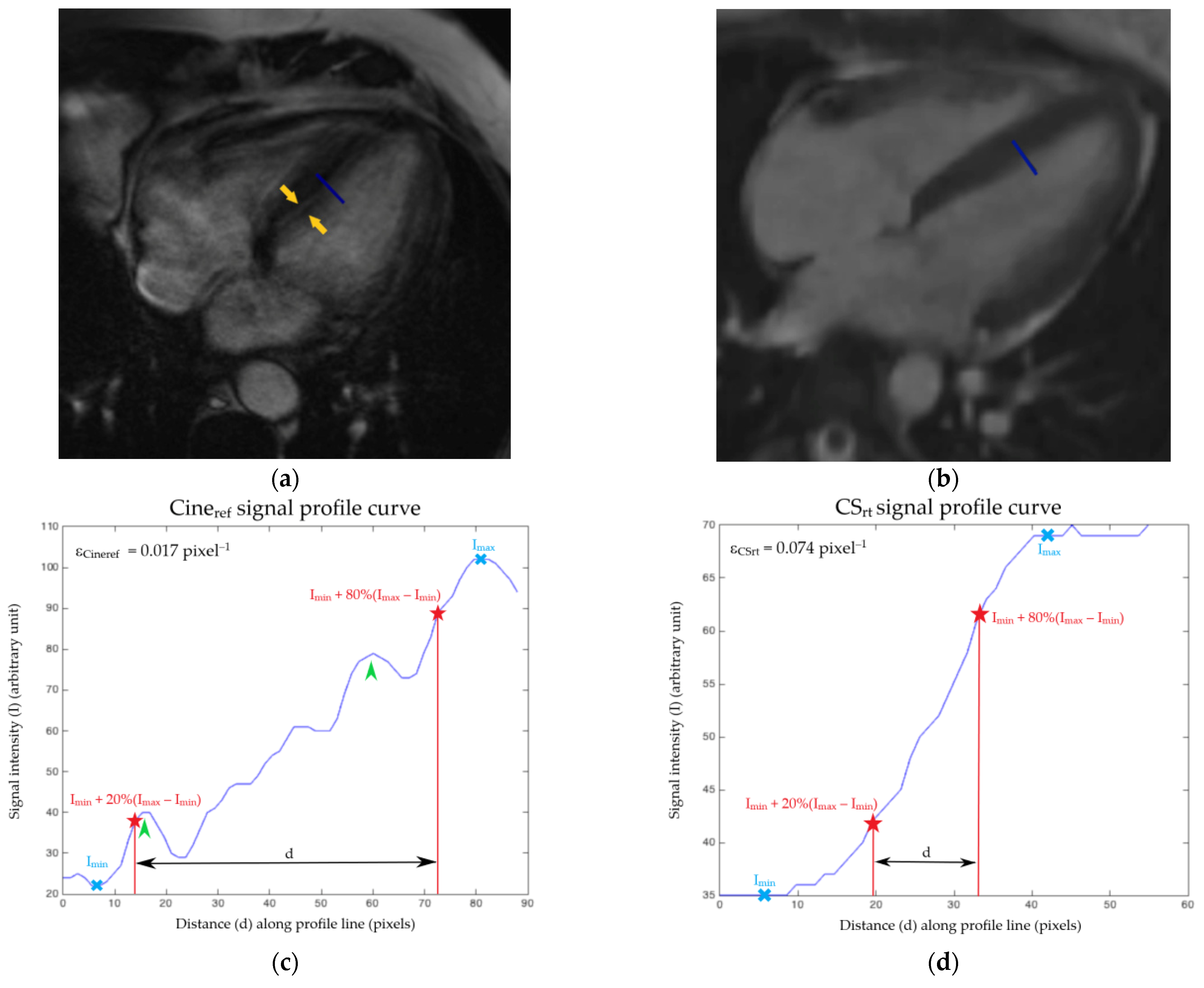
3.6. Edge Sharpness
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pennell, D.J.; Sechtem, U.P.; Higgins, C.B.; Manning, W.J.; Pohost, G.M.; Rademakers, F.E.; van Rossum, A.C.; Shaw, L.J.; Yucel, E.K.; Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance; et al. Clinical indications for cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR): Consensus Panel report. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 1940–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maceira, A.M.; Prasad, S.K.; Khan, M.; Pennell, D.J. Normalized left ventricular systolic and diastolic function by steady state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2006, 8, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceira, A.M.; Prasad, S.K.; Khan, M.; Pennell, D.J. Reference right ventricular systolic and diastolic function normalized to age, gender and body surface area from steady-state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grothues, F.; Moon, J.C.; Bellenger, N.G.; Smith, G.S.; Klein, H.U.; Pennell, D.J. Interstudy reproducibility of right ventricular volumes, function, and mass with cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Am. Heart J. 2004, 147, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plein, S.; Bloomer, T.N.; Ridgway, J.P.; Jones, T.R.; Bainbridge, G.J.; Sivananthan, M.U. Steady-state free precession magnetic resonance imaging of the heart: Comparison with segmented k-space gradient-echo imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 14, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.W.; Haacke, E.M.; White, R.D. Retrospective cardiac gating: A review of technical aspects and future directions. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1989, 7, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madore, B.; Hoge, W.S.; Chao, T.-C.; Zientara, G.P.; Chu, R. Retrospectively gated cardiac cine imaging with temporal and spatial acceleration. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 29, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nacif, M.S.; Zavodni, A.; Kawel, N.; Choi, E.-Y.; Lima, J.A.C.; Bluemke, D.A. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and its electrocardiographs (ECG): Tips and tricks. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2012, 28, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussakis, A.; Baras, P.; Seimenis, I.; Andreou, J.; Danias, P.G. Relationship of number of phases per cardiac cycle and accuracy of measurement of left ventricular volumes, ejection fraction, and mass. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. Off. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2004, 6, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.; Simonetti, O.P.; Carr, J.; Kramer, U.; Finn, J.P. MR imaging of the heart with cine true fast imaging with steady-state precession: Influence of spatial and temporal resolutions on left ventricular functional parameters. Radiology 2002, 223, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Romberg, J.K.; Tao, T. Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 2006, 59, 1207–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lustig, M.; Donoho, D.; Pauly, J.M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, M.; Santos, J.M.; Lee, J.; Donoho, D.L.; Pauly, J.M. Application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. In Proceedings of the 1st Signal Processing with Adaptive Sparse Structured Representations Workshop (SPARS 2005), Rennes, France, 16–18 November 2005; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Srichai, M.B.; Lim, R.P.; Harrison, A.; King, W.; Adluru, G.; Dibella, E.V.R.; Sodickson, D.K.; Otazo, R.; Kim, D. Highly accelerated real-time cardiac cine MRI using k-t SPARSE-SENSE. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincenti, G.; Monney, P.; Chaptinel, J.; Rutz, T.; Coppo, S.; Zenge, M.O.; Schmidt, M.; Nadar, M.S.; Piccini, D.; Chèvre, P.; et al. Compressed sensing single-breath-hold CMR for fast quantification of LV function, volumes, and mass. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goebel, J.; Nensa, F.; Schemuth, H.P.; Maderwald, S.; Gratz, M.; Quick, H.H.; Schlosser, T.; Nassenstein, K. Compressed sensing cine imaging with high spatial or high temporal resolution for analysis of left ventricular function. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubenreisser, H.; Henzler, T.; Budjan, J.; Sudarski, S.; Zenge, M.O.; Schmidt, M.; Nadar, M.S.; Borggrefe, M.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Papavassiliu, T. Right ventricular imaging in 25 seconds: Evaluating the use of sparse sampling CINE with iterative reconstruction for volumetric analysis of the right ventricle. Investig. Radiol. 2016, 51, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, T.; Kido, T.; Nakamura, M.; Watanabe, K.; Schmidt, M.; Forman, C.; Mochizuki, T. Compressed sensing real-time cine cardiovascular magnetic resonance: Accurate assessment of left ventricular function in a single-breath-hold. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2016, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vermersch, M.; Longère, B.; Coisne, A.; Schmidt, M.; Forman, C.; Monnet, A.; Pagniez, J.; Silvestri, V.; Simeone, A.; Cheasty, E.; et al. Compressed sensing real-time cine imaging for assessment of ventricular function, volumes and mass in clinical practice. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, J.; Nensa, F.; Schemuth, H.P.; Maderwald, S.; Quick, H.H.; Schlosser, T.; Nassenstein, K. Real-Time SPARSE-SENSE cine MR imaging in atrial fibrillation: A feasibility study. Acta Radiol. 2017, 58, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinke, V.; Muzzarelli, S.; Lauriers, N.; Locca, D.; Vincenti, G.; Monney, P.; Lu, C.; Nothnagel, D.; Pilz, G.; Lombardi, M.; et al. Quality assessment of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the setting of the European CMR registry: Description and validation of standardized criteria. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2013, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larson, A.C.; Kellman, P.; Arai, A.; Hirsch, G.A.; McVeigh, E.; Li, D.; Simonetti, O.P. Preliminary investigation of respiratory self-gating for free-breathing segmented cine MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetzl, J.; Schmidt, M.; Pontana, F.; Longère, B.; Lugauer, F.; Maier, A.; Hornegger, J.; Forman, C. Single-breath-hold 3-D CINE imaging of the left ventricle using cartesian sampling. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2017, 31, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, S.; Husarik, D.B.; Yadava, G.; Murphy, S.N.; Samei, E. Towards task-based assessment of CT performance: System and object MTF across different reconstruction algorithms. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benchoufi, M.; Matzner-Lober, E.; Molinari, N.; Jannot, A.-S.; Soyer, P. Interobserver agreement issues in radiology. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, C.G.; Sidky, E.Y. Compressive sensing in medical imaging. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, C23–C44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Feng, H.; Xu, Z. A New analytical edge spread function fitting model for modulation transfer function measurement. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2011, 9, 031101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurz, P.; Muthurangu, V.; Schievano, S.; Nordmeyer, J.; Bonhoeffer, P.; Taylor, A.M.; Hansen, M.S. Feasibility and reproducibility of biventricular volumetric assessment of cardiac function during exercise using real-time radial k-t SENSE magnetic resonance imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2009, 29, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voit, D.; Zhang, S.; Unterberg-Buchwald, C.; Sohns, J.M.; Lotz, J.; Frahm, J. Real-time cardiovascular magnetic resonance at 1.5 T using balanced SSFP and 40 ms resolution. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. Off. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2013, 15, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Uecker, M.; Voit, D.; Merboldt, K.-D.; Frahm, J. Real-time cardiovascular magnetic resonance at high temporal resolution: Radial FLASH with nonlinear inverse reconstruction. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. Off. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2010, 12, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraden, J. Handbook of Modern Sensors—Physics, Designs and Applications, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Cineref | CSrt |
|---|---|---|
| Repetition time—ms | 3.16 | 2.70 |
| Echo time—ms | 1.23 | 1.14 |
| Flip angle—degrees | 57 | 60 |
| Field of view—mm2 | 375 × 280 | 360 × 270 |
| Matrix—pixels2 | 288 × 216 | 224 × 168 |
| Spatial resolution—mm2 | 1.3 × 1.3 | 1.6 × 1.6 |
| Temporal resolution—ms | 41.2 | 49 |
| Slice thickness/gap—mm | 8/2 | 8/2 |
| Bandwidth—Hz/pixel | 915 | 900 |
| ECG mode | Prospective triggering | Adaptative triggering |
| Number of measured cardiac phases per cycle | 20 a | 17.0 ± 3.2 |
| Number of reconstructed cardiac frames per cycle—n | 20 a | 20 b |
| Number of views per frame—n | 13.0 ± 4.8 c | 18 a |
| Cycles of iterative reconstruction—n | NA | 40 |
| Acceleration factor | 2 | 11 |
| Items | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | Maximum Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. LV coverage | Full | - | No apex | Base or ≥1 slice missing | 5 |
| 2. Wrap around | No | 1 slice | 2 slices | ≥3 slices | 3 |
| 3. Respiratory ghost | No | 1 slice | 2 slices | ≥3 slices | |
| 4. Cardiac ghost | No | 1 slice | 2 slices | ≥3 slices | |
| 5. Blurring/ARA | No | 1 slice | 2 slices | ≥3 slices | |
| 6. Metallic artifacts | No | 1 slice | 2 slices | ≥3 slices | |
| 7. Shimming artifacts | No | 1 slice | 2 slices | ≥3 slices | |
| 8. Signal loss (coil inactive) | Activated | - | Not activated | 2 | |
| 9. Orientation of stack | Correct | - | Incorrect | - | 2 |
| 10. Slice thickness | ≤10 mm | 11–15 mm | - | >15 mm | 3 |
| 11. Gap | ≤3 mm | 3–4 mm | - | >4 mm | 3 |
| 12. Correct LV long axes | ≥2 mm | 1 | - | None | 3 |
| Score | 21 | ||||
| Modified score (items 1 to 8) | 10 |
| Mean ± SD (95% CI) | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age—years | 59.5 ± 20.1 (54.7–64.2) | 18 | 87 |
| Height—cm | 171.6 ± 9.1 (169.4–173.7) | 140 | 188 |
| Weight—kg | 79.3 ± 19.5 (74.7–83.9) | 26 | 131 |
| Body mass index—kg/m2 | 26.8 ± 6.1 (25.4–28.3) | 13.3 | 47.0 |
| Maximal heart rate—bpm | 85.9 ± 21.6 (80.8–91.0) | 50 | 139 |
| Minimal heart rate—bpm | 55.6 ± 18.7 (55.6–64.4) | 31 | 107 |
| Mean heart rate—bpm | 71.8 ± 19.0 (67.4–76.3) | 42 | 116 |
| Arrhythmia (CVRR)—% | 25.0 ± 9.4 (22.8–27.2) | 10.2 | 50.9 |
| Cineref | CSrt | Difference | PCI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVEF—% | 47.7 ± 19.0 (39.9–55.6) | 47.3 ± 18.9 (39.5–55.1) | −0.4 ± 1.9 (−1.2 to 0.4) | - | 0.30 a |
| LVEDV—mL | 193.2 ± 102.0 (151.1–235.3) | 189.6 ± 101.9 (147.6–231.6) | −3.6 ± 7.2 (−6.5 to −0.6) | - | 0.02 a |
| LVESV—mL | 114.2 ± 99.8 (73.0–155.4) | 113.3 ± 98.8 (72.5–154.1) | −0.9 ± 6.8 (−3.7 to 1.9) | - | 0.51 a |
| LVSV—mL | 79.0 ± 29.4 (66.9–91.1) | 76.3 ± 28.7 (64.5–88.2) | - | 76.7 ± 30.1 (64.3–89.1) | 0.94 b |
| LVM—g | 145.2 ± 48.0 (125.4–165.1) | 148.0 ± 50.1 (127.3–168.6) | 2.7 ± 8.8 (−0.9 to 6.3) | - | 0.13 a |
| RVEF—% | 50.9 ± 11.9 (46.0–55.8) | 51.8 ± 11.9 (46.9–56.7) | 0.9 ± 1.8 (0.1 to 1.7) | - | 0.02 a |
| RVEDV—mL | 153.7 ± 52.1 (132.2–175.2) | 148.4 ± 47.5 (128.8–168.0) | −5.3 ± 7.6 (−8.5 to −2.2) | - | 0.02 a |
| RVESV—mL | 77.5 ± 38.0 (61.8–93.1) | 73.8 ± 36.1 (58.9–88.7) | −3.7 ± 5.8 (−6.1 to −1.3) | - | 0.004 a |
| RVSV—mL | 76.2 ± 27.3 (65.0–87.5) | 74.6 ± 24.1 (64.6–84.5) | −1.7 ± 4.5 (−3.5 to 0.2) | Insufficient data | 0.08 a |
| Objective European CMR Criteria Scores | CSrt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1–3 | 4–6 | 7–10 | Total | Median (Range) | ||
| Cineref | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 (0–5) |
| 1–3 | 25 | 42 | 2 | 0 | 69 | ||
| 4–6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 7–10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Total | 26 | 43 | 2 | 0 | 71 | ||
| Median (range) | 3 (0–3) | p < 0.0001 | |||||
| Subjective Overall Quality Scores | CSrt | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Total | Median (Range) | ||
| Cineref | 1 | 5 | 3 | 15 | 0 | 23 | 3 (1–3) |
| 2 | 5 | 6 | 21 | 0 | 32 | ||
| 3 | 0 | 2 | 13 | 0 | 15 | ||
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Total | 10 | 11 | 50 | 0 | 71 | ||
| Median (range) | 2 (1–4) | p < 0.0001 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longère, B.; Allard, P.-E.; Gkizas, C.V.; Coisne, A.; Hennicaux, J.; Simeone, A.; Schmidt, M.; Forman, C.; Toupin, S.; Montaigne, D.; et al. Compressed Sensing Real-Time Cine Reduces CMR Arrhythmia-Related Artifacts. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153274
Longère B, Allard P-E, Gkizas CV, Coisne A, Hennicaux J, Simeone A, Schmidt M, Forman C, Toupin S, Montaigne D, et al. Compressed Sensing Real-Time Cine Reduces CMR Arrhythmia-Related Artifacts. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(15):3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLongère, Benjamin, Paul-Edouard Allard, Christos V Gkizas, Augustin Coisne, Justin Hennicaux, Arianna Simeone, Michaela Schmidt, Christoph Forman, Solenn Toupin, David Montaigne, and et al. 2021. "Compressed Sensing Real-Time Cine Reduces CMR Arrhythmia-Related Artifacts" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 15: 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153274
APA StyleLongère, B., Allard, P.-E., Gkizas, C. V., Coisne, A., Hennicaux, J., Simeone, A., Schmidt, M., Forman, C., Toupin, S., Montaigne, D., & Pontana, F. (2021). Compressed Sensing Real-Time Cine Reduces CMR Arrhythmia-Related Artifacts. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(15), 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153274






