Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion: What Is Crucial to Take into Account
Abstract
1. Introduction
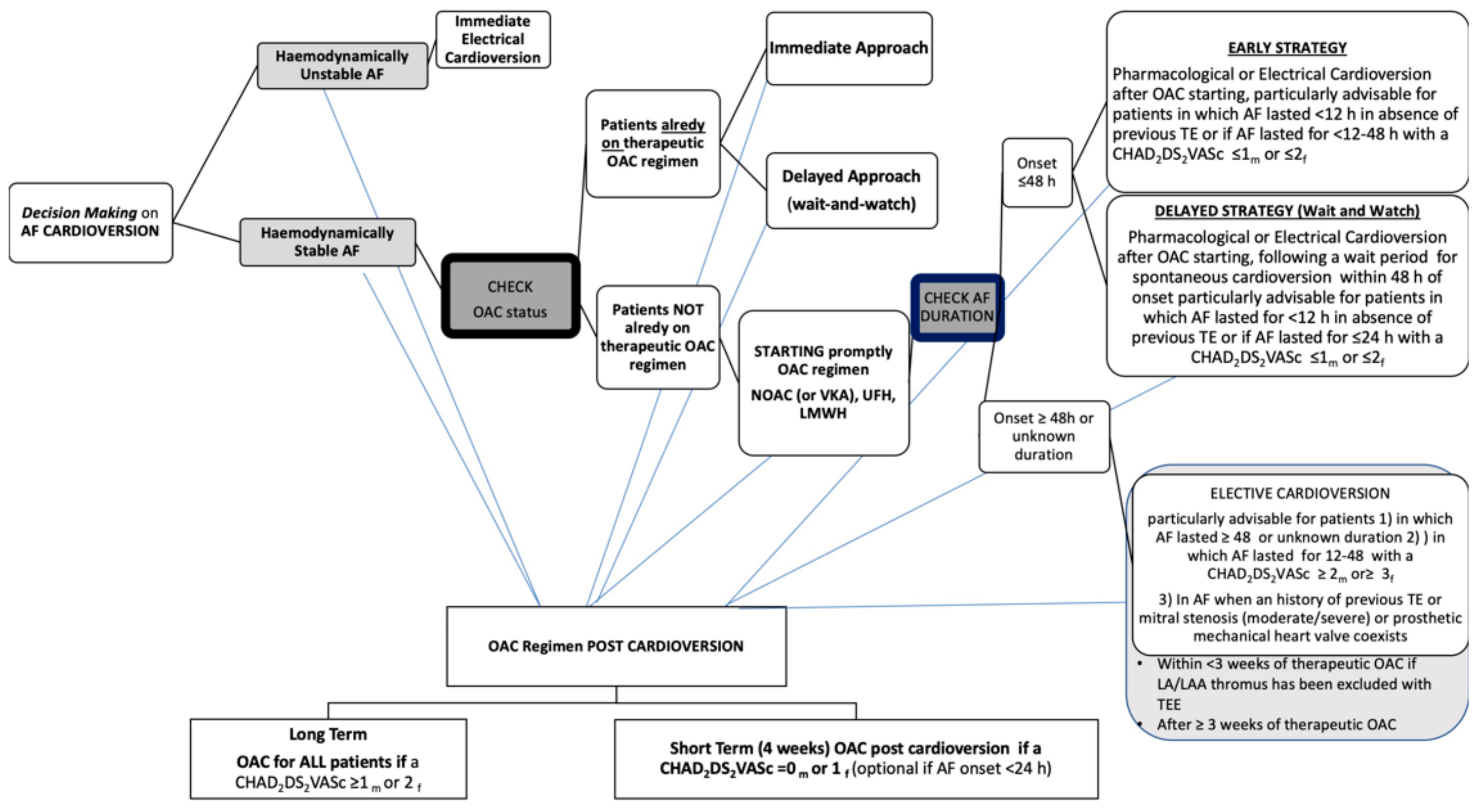
2. Acute Hemodynamic Instability
3. Electrical Cardioversion in Emergency
3.1. Electrical Cardioversion in Patients with AF Which Occurred within Less Than 48 h
3.2. Electrical Cardioversion in AF Which Lasted for Longer Than 48 h
4. TEE Guided Approach
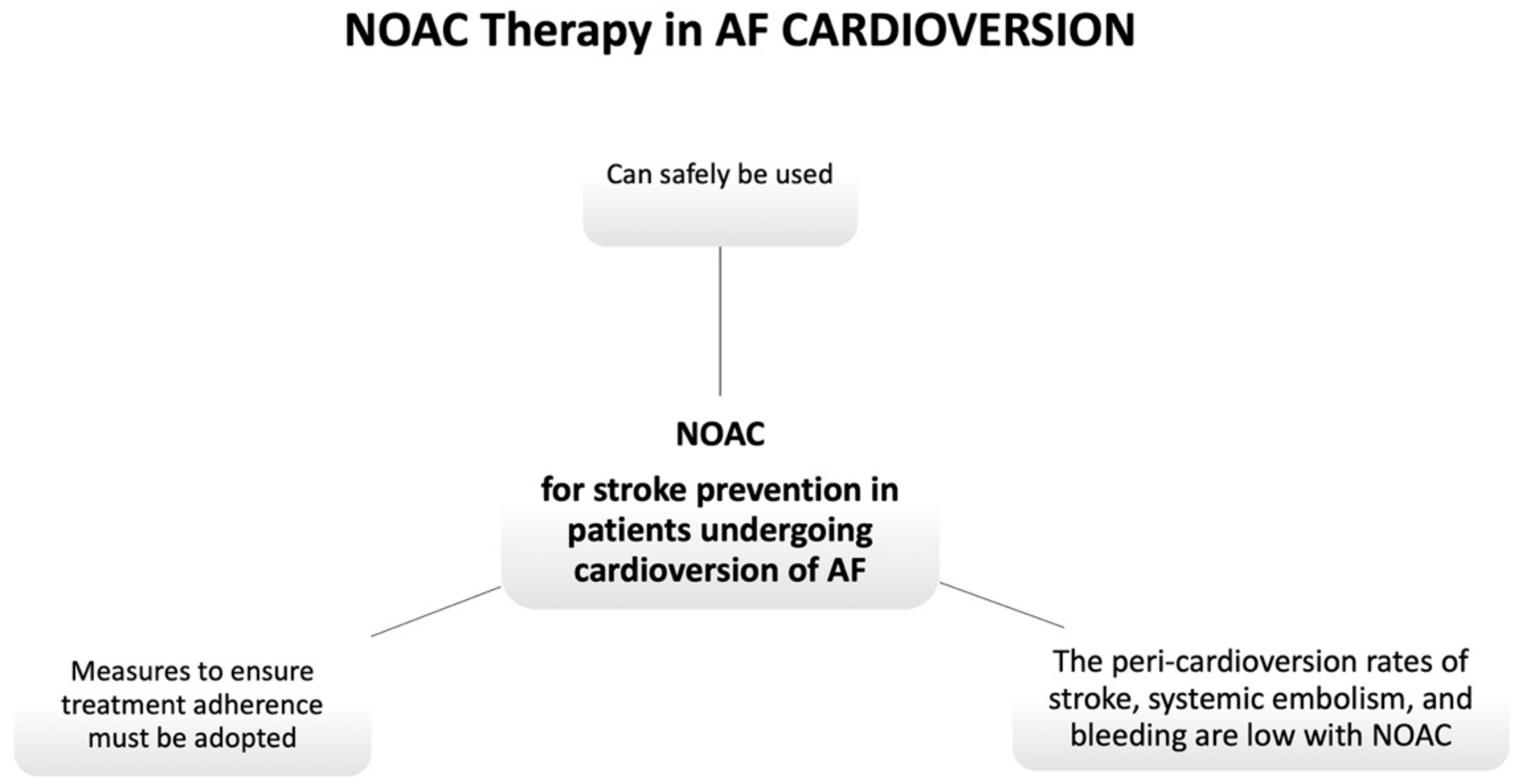
5. NOACs in the Setting of Cardioversion
6. Dabigatran
6.1. Rivaroxaban
6.2. Edoxaban
6.3. Apixaban
7. Recommendations from ESC Guidelines and Consensus Documents for the Use of NOACs in Peri-Cardioversion Setting
8. Controversial Issues
8.1. The Need of Image-Guided Strategy to Exclude Atrial Thrombi
8.2. NOACs Efficacy and Safety According to Thromboembolic Risk
8.3. Patients with Renal Dysfunction
8.4. Patients Undergoing Pharmacological Cardioversion
8.5. Early- vs. Delayed Strategy
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wyse, D.G.; Waldo, A.L.; Di Marco, J.P.; Domanski, M.J.; Rosenberg, Y.; Schron, E.B.; Kellen, J.C.; Greene, H.L.; Mickel, M.C.; Dalquist, J.; et al. A Comparison of Rate Control and Rhythm Control in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Chew, D.P.; Hartshorne, T.; Selvanayagam, J.B.; Aylward, P.; Sanders, P.; McGavigan, A.D. The impact of atrial fibrillation type on the risk of thromboembolism, mortality, and bleeding: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, B.A.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Patel, M.R.; Breithardt, G.; Hankey, G.; Becker, R.C.; Singer, D.E.; Halperin, J.L.; Hacke, W.; et al. Higher risk of death and stroke in patients with persistent vs. paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: Results from the ROCKET-AF Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collabora-tion with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.L.; Jepsen, R.M.H.G.; Olesen, J.B.; Ruwald, M.H.; Karasoy, D.; Gislason, G.; Hansen, J.; Køber, L.; Husted, S.; Torp-Pedersen, C. Thromboembolic risk in 16 274 atrial fibrillation patients undergoing direct current cardioversion with and without oral anticoagulant therapy. Europace 2015, 17, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, C.T.; Giugliano, R.; Braunwald, E.; Hoffman, E.B.; Deenadayalu, N.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Camm, A.J.; Weitz, J.; Lewis, B.S.; Parkhomenko, A.; et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 383, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, J.; Zima, E.; Bover, R.; Karaliute, R.; Rossi, A.; Szymanski, C.; Troccoli, R.; Schneider, J.; Fagerland, M.W.; Camm, A.J.; et al. Changes in oral anticoagulation for elective cardioversion: Results from a European cardioversion registry. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2017, 3, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffel, J.; Collins, R.; Ant, M.; Cornu, P.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; Rowell, N.; et al. 2021 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the Use of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Europace 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, S.; Dorian, P. Management of supraventricular tachycardia in the emergency department. Can. J. Cardiol. 1997, 13, 19A–24A. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, A.J.; Pelletier, A.J.; Ellinor, P.; Camargo, C.A. Increasing US Emergency Department Visit Rates and Subsequent Hospital Admissions for Atrial Fibrillation from 1993 to 2004. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2008, 51, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Ayati, S.; Stein, K.M.; Schwartzman, D.; Cavlovich, D.; Tchou, P.J.; Markowitz, S.M.; Slotwiner, D.J.; Scheiner, M.A.; Lerman, B.B. Transthoracic Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation: Comparison of Rectilinear Biphasic Versus Damped Sine Wave Monophasic Shocks. Circulation 2000, 101, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toso, E.; Blandino, A.; Sardi, D.; Battaglia, A.; Garberoglio, L.; Miceli, S.; Azzaro, G.; Capello, A.L.; Gaita, F. Electrical Cardioversion of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Acute and Long-Term Results Stratified According to Arrhythmia Duration. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2012, 35, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elesber, A.A.; Rosales, A.G.; Herges, R.M.; Shen, W.-K.; Moon, B.S.; Malouf, J.F.; Ammash, N.M.; Somers, V.; Hodge, D.O.; Gersh, B.J.; et al. Relapse and mortality following cardioversion of new-onset vs. recurrent atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter in the elderly. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.S.; Lauridsen, K.G.; Torp, P.; Bach, L.F.; Rickers, H.; Løfgren, B. Maximum-fixed energy shocks for cardioverting atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 41, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, M.M.; Guo, X.-H.; Poloniecki, J.D.; Yap, Y.G.; Ward, D.; Camm, A. Initial energy setting, outcome and efficiency in direct current cardioversion of atrial fibrillation and flutter. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 38, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, T.; Hiraki, T.; Ikeda, H.; Kubara, I.; Yoshida, T.; Ohga, M.; Imaizumi, T. Mechanisms for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2002, 13, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Hagens, V.E.; Bosker, H.A.; Kingma, J.H.; Kamp, O.; Kingma, T.; Said, S.A.; Darmanata, J.I.; Timmermans, A.J.M.; Tijssen, J.G.P.; et al. A Comparison of Rate Control and Rhythm Control in Patients with Recurrent Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankner, R.; Shahar, A.; Novikov, I.; Agmon, U.; Ziv, A.; Hod, H. Treatment of Stable Atrial Fibrillation in the Emergency Department: A Population-Based Comparison of Electrical Direct-Current versus Pharmacological Cardioversion or Conservative Management. Cardiology 2009, 112, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluymaekers, N.A.; Dudink, E.A.; Luermans, J.G.; Meeder, J.G.; Lenderink, T.; Widdershoven, J.; Bucx, J.J.; Rienstra, M.; Kamp, O.; Van Opstal, J.M.; et al. Early or Delayed Cardioversion in Recent-Onset Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-J.; Wolf, P.A.; Kelly-Hayes, M.; Beiser, A.; Kase, C.S.; Benjamin, E.; D’Agostino, R.B. Stroke Severity in Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 1996, 27, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowicki, B.; Matusik, P.T.; Plens, K.; Undas, A. Prothrombotic State in Atrial Fibrillation Patients With One Additional Risk Factor of the CHA2DS2-VASc Score (Beyond Sex). Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.L.; Grimm, R.A.; Murray, R.D.; Apperson-Hansen, C.; Asinger, R.W.; Black, I.W.; Davidoff, R.; Erbel, R.; Halperin, J.L.; Orsinelli, D.; et al. Use of Transesophageal Echocardiography to Guide Cardioversion in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.B.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Hansen, M.L.; Hansen, P.R.; Tolstrup, J.S.; Lindhardsen, J.; Selmer, C.; Ahlehoff, O.; Olsen, A.-M.S.; Gislason, G.; et al. Validation of risk stratification schemes for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in patients with atrial fibrillation: Nationwide cohort study. BMJ 2011, 342, d124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, L.; Skeppholm, M.; Terént, A. Benefit of Anticoagulation Unlikely in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and a CHA2DS2-VASc Score of 1. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuotio, I.; Hartikainen, J.E.K.; Grönberg, T.; Biancari, F.; Airaksinen, J. Time to Cardioversion for Acute Atrial Fibrillation and Thromboembolic Complications. JAMA 2014, 312, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Hemels, M.E. The progressive nature of atrial fibrillation: A rationale for early restoration and maintenance of sinus rhythm. Europace 2006, 8, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airaksinen, K.E.J.; Grönberg, T.; Nuotio, I.; Nikkinen, M.; Ylitalo, A.; Biancari, F.; Hartikainen, J.E.K. Thromboembolic Complications after Cardioversion of Acute Atrial Fibrillation: The FinCV (Finnish CardioVersion) Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Alpert, J.S.; Calkins, H.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C.; Conti, J.B.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: Executive summary: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation 2014, 130, 2071–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, D.I.; Manning, W.J. Role of Echocardiography in Patients Undergoing Elective Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 1998, 98, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sardar, P.; Lichstein, E.; Mukherjee, D.; Aikat, S. Pharmacologic Rate versus Rhythm-Control Strategies in Atrial Fibrillation: An Updated Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2013, 36, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Denus, S.; Sanoski, C.A.; Carlsson, J.; Opolski, G.; Spinler, S.A. Rate vs Rhythm Control in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toufan, M.; Kazemi, B.; Molazadeh, N. The significance of the left atrial volume index in prediction of atrial fibrillation recurrence after electrical cardioversion. J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res. 2017, 9, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremidis, M.; Alexanian, I.P.; Oikonomou, D.; Manolatos, D.; Letsas, K.P.; Pappas, L.K.; Gavrielatos, G.; Vadiaka, M.; Mihas, C.C.; Filippatos, G.S.; et al. Predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence in patients with long-lasting atrial fibrillation. Can. J. Cardiol. 2009, 25, e119–e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baranchuk, A.; Yeung, C. Advanced interatrial block predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence across different populations: Learning Bayés syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 272, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhof, P.; Andresen, D.; Bosch, R.; Borggrefe, M.; Meinertz, T.; Parade, U.; Ravens, U.; Samol, A.; Steinbeck, G.; Treszl, A.; et al. Short-term versus long-term antiarrhythmic drug treatment after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation (Flec-SL): A prospective, randomised, open-label, blinded endpoint assessment trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Singh, S.N.; Reda, D.J.; Tang, X.C.; Lopez, B.; Harris, C.L.; Fletcher, R.D.; Sharma, S.C.; Atwood, J.E.; Jacobson, A.K.; et al. Amiodarone versus Sotalol for Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wazni, O.M.; Tsao, H.; Chen, S.; Chuang, H.; Saliba, W.; Natale, A.; Klein, A.L. Cardiovascular Imaging in the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, V.; Di Biase, L.; Leung, M.; Romero, J.; Tops, L.F.; Casadei, B.; Marrouche, N.; Bax, J.J. Structure and function of the left atrium and left atrial appendage: AF and stroke implications. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 3157–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollick, C.; Taylor, D. Assessment of left atrial appendage function by transesophageal echocardiography. Implications for the development of thrombus. Circulation 1991, 84, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonielli, E.; Pizzuti, A.; Pálinkás, A.; Tanga, M.; Gruber, N.; Michelassi, C.; Varga, A.; Bonzano, A.; Gandolfo, N.; Halmai, L.; et al. Clinical value of left atrial appendage flow for prediction of long-term sinus rhythm maintenance in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, C.R.; Klein, A.L. Transesophageal Echocardiography to Guide Cardioversion in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: ACUTE Trial Update. Card. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2003, 7, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, M.; Hennessy, B.; Edvardsson, N. Embolic complications of direct current cardioversion of atrial arrhythmias: Association with low intensity of anticoagulation at the time of cardioversion. ACC Curr. J. Rev. 2003, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.K.; Lollback, N.; Slater, L.; Hill, J.; Gould, P.A.; Kaye, G.C. Elective Cardioversion in the Era of Novel Oral Anticoagulants—Does a Nurse Administered Verbal Questionnaire for Compliance Negate the Need for Routine Transoesophageal Echocardiography? Heart Lung Circ. 2018, 27, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellbrink, C.; Nixdorff, U.; Hofmann, T.; Lehmacher, W.; Daniel, W.G.; Hanrath, P.; Geller, C.; Mügge, A.; Sehnert, W.; Schmidt-Lucke, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Enoxaparin Compared With Unfractionated Heparin and Oral Anticoagulants for Prevention of Thromboembolic Complications in Cardioversion of Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2004, 109, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarakanti, R.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Oldgren, J.; Yang, S.; Chernick, M.; Aikens, T.H.; Flaker, G.; Brugada, J.; Kamenský, G.; Parekh, A.; et al. Dabigatran Versus Warfarin in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2011, 123, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, J.P.; Stevens, S.R.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Patel, M.R.; Halperin, J.L.; Singer, D.E.; Hankey, G.J.; Hacke, W.; Becker, R.C.; Nessel, C.C.; et al. Outcomes after cardioversion and atrial fibrillation ablation in patients treated with rivaroxaban and warfarin in the ROCKET AF trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 61, 1998–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaker, G.; Lopes, R.D.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; Hermosillo, A.G.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Tinga, B.; Zhu, J.; Mohan, P.; Garcia, D.; Bartunek, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Apixaban in Patients After Cardioversion for Atrial Fibrillation: Insights From the ARISTOTLE Trial (Apixaban for Reduction in Stroke and Other Thromboembolic Events in Atrial Fibrillation). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plitt, A.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; De Caterina, R.; Nordio, F.; Peterson, N.; Giugliano, R.P.; on behalf of the ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48. Investigators Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation in ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48. Clin. Cardiol. 2016, 39, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappato, R.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Klein, A.L.; Camm, A.J.; Ma, C.-S.; Le Heuzey, J.-Y.; Talajic, M.; Scanavacca, M.; Vardas, P.E.; Kirchhof, P.; et al. Rivaroxaban vs. vitamin K antagonists for cardioversion in atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 3346–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goette, A.; Merino, J.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Zamoryakhin, D.; Melino, M.; Jin, J.; Mercuri, M.F.; Grosso, M.; Fernandez, V.; Al-Saady, N.; et al. Edoxaban versus enoxaparin–warfarin in patients undergoing cardioversion of atrial fibrillation (ENSURE-AF): A randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 1995–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezekowitz, M.D.; Pollack, C.V.; Halperin, J.L.; England, R.D.; Nguyen, S.V.; Spahr, J.; Sudworth, M.; Cater, N.B.; Breazna, A.; Oldgren, J.; et al. Apixaban compared to heparin/vitamin K antagonist in patients with atrial fibrillation scheduled for cardioversion: The EMANATE trial. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2959–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grönberg, T.; Hartikainen, J.E.; Nuotio, I.; Biancari, F.; Ylitalo, A.; Airaksinen, K.J. Anticoagulation, CHA2DS2VASc Score, and Thromboembolic Risk of Cardioversion of Acute Atrial Fibrillation (from the FinCV Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fusco, S.A.; Colivicchi, F.; Aspromonte, N.; Tubaro, M.; Aiello, A.; Santini, M. Direct oral anticoagulants in patients undergoing cardioversion: Insight from randomized clinical trials. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2017, 87, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCready, J.W.; Nunn, L.; Lambiase, P.; Ahsan, S.Y.; Segal, O.R.; Rowland, E.; Lowe, M.D.; Chow, A.W. Incidence of left atrial thrombus prior to atrial fibrillation ablation: Is pre-procedural transoesophageal echocardiography mandatory? Europace 2010, 12, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puwanant, S.; Varr, B.C.; Shrestha, K.; Hussain, S.K.; Tang, W.W.; Gabriel, R.S.; Wazni, O.M.; Bhargava, M.; Saliba, W.I.; Thomas, J.D.; et al. Role of the CHADS2Score in the Evaluation of Thromboembolic Risk in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Transesophageal Echocardiography Before Pulmonary Vein Isolation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, D.; Dalal, D.; Chilukuri, K.; Dong, J.; Spragg, D.; Henrikson, C.A.; Nazarian, S.; Cheng, A.; Berger, R.D.; Abraham, T.P.; et al. Incidence and Predictors of Left Atrial Thrombus Prior to Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2009, 20, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusik, P.; Heleniak, Z.; Papuga-Szela, E.; Plens, K.; Lelakowski, J.; Undas, A. Chronic Kidney Disease and Its Impact on a Prothrombotic State in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RELY [37] | ROCKET-AF [38] | ARISTOTLE [39] | ENGAGE AF TIMI [40] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOAC | Dabigatran | Rivaroxaban | Apixaban | Edoxaban |
| Patients | 1270 | 285 | 540 | 365 |
| CV | 1983 | 375 | 743 | 632 |
| Comparator | Warfarin | Warfarin | Warfarin | Warfarin |
| TEE-guided CV | 21% | NA | 27% | NA |
| Follow-up | 30 days | 30 days | 30 days | 30 days |
| Stroke Or Systemic Embolism | 11 (0.6%) | 2 (0.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| NOAC vs. VKA | 7 (0.5%) vs. 4 (0.6%) | NA | - | - |
| Major bleeding | 19 (1.0%) | NA | 2 (0.2%) | 0 (0%) |
| NOAC vs. VKA | 15 (1.1%) vs. 4 (0.6%) | NA | 1 (0.3%) vs. 1 (0.2%) | - |
| X-VeRT [41] | ENSURE AF [42] | EMANATE [43] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOAC | Rivaroxaban | Edoxaban | Apixaban |
| Study design | Open-label, randomized 2:1 | Open-label, randomized 1:1 | Open-label, randomized 1:1 |
| Patients | 1504 | 2199 | 1500 |
| AF duration | ≥48 h | ≥48 h | <48 h and ≥48 h |
| Comparator | VKA | LMWH/VKA | Heparin/VKA |
| Treatment strategy | TEE vs. no TEE | TEE vs. no TEE | Imaging vs. no Imaging |
| TEE-guided CV | Riva 67%, VKA 65% | 100% | 100% |
| Early strategy | Adeguate anticoagulant or TEE + Rivarovaban at least 4 h before CV | Adeguate anticoagulant or TEE+ Edoxaban at least 2 h before CV | Imaging + Loading dose Apixaban at least 2 h before CV or after five doses |
| Post-procedural anticoagulation | 42 days | 28 days | 30 days |
| Primary efficacy endpoint | Composite of stroke, TIA, SE, MI and CV death | Composite of stroke, TIA, SE, MI and CV death | Stroke, SE, Death |
| NOAC vs. VKA | 5 (0.5%) vs. 5 (1.0%) | 5 (0.5%) vs. 11 (1.0%) | 0 (0%) vs. 6 (0.8%) |
| Primary safety end point | ISTH Major bleeding | ISTH Major or CRNM bleeding | ISTH Major or CRNM bleeding |
| NOAC vs. VKA | 6 (0.6%) vs. 4 (0.8%) | 16 (1.5%) vs. 11 (1.0%) | 14 (1.9%) vs. 19 (2.5%) |
| Difference in time to CV | Yes | No | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucà, F.; Giubilato, S.; Di Fusco, S.A.; Piccioni, L.; Rao, C.M.; Iorio, A.; Cipolletta, L.; D’Elia, E.; Gelsomino, S.; Rossini, R.; et al. Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion: What Is Crucial to Take into Account. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153212
Lucà F, Giubilato S, Di Fusco SA, Piccioni L, Rao CM, Iorio A, Cipolletta L, D’Elia E, Gelsomino S, Rossini R, et al. Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion: What Is Crucial to Take into Account. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(15):3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153212
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucà, Fabiana, Simona Giubilato, Stefania Angela Di Fusco, Laura Piccioni, Carmelo Massimiliano Rao, Annamaria Iorio, Laura Cipolletta, Emilia D’Elia, Sandro Gelsomino, Roberta Rossini, and et al. 2021. "Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion: What Is Crucial to Take into Account" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 15: 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153212
APA StyleLucà, F., Giubilato, S., Di Fusco, S. A., Piccioni, L., Rao, C. M., Iorio, A., Cipolletta, L., D’Elia, E., Gelsomino, S., Rossini, R., Colivicchi, F., & Gulizia, M. M. (2021). Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Cardioversion: What Is Crucial to Take into Account. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(15), 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153212







