Comparison of Respiratory Effects between Dexmedetomidine and Propofol Sedation for Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Neoplasm: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
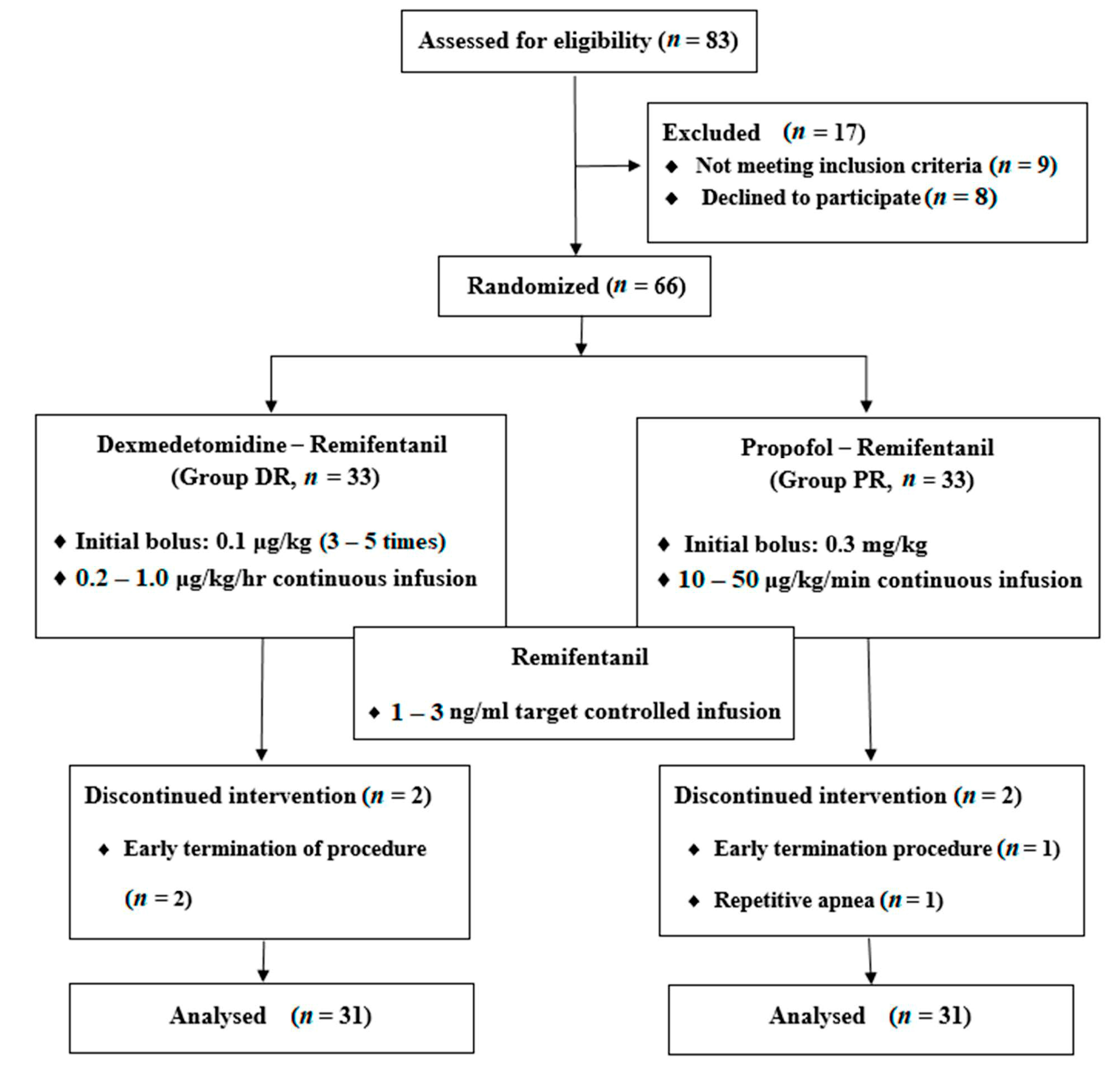
2. Materials and Methods
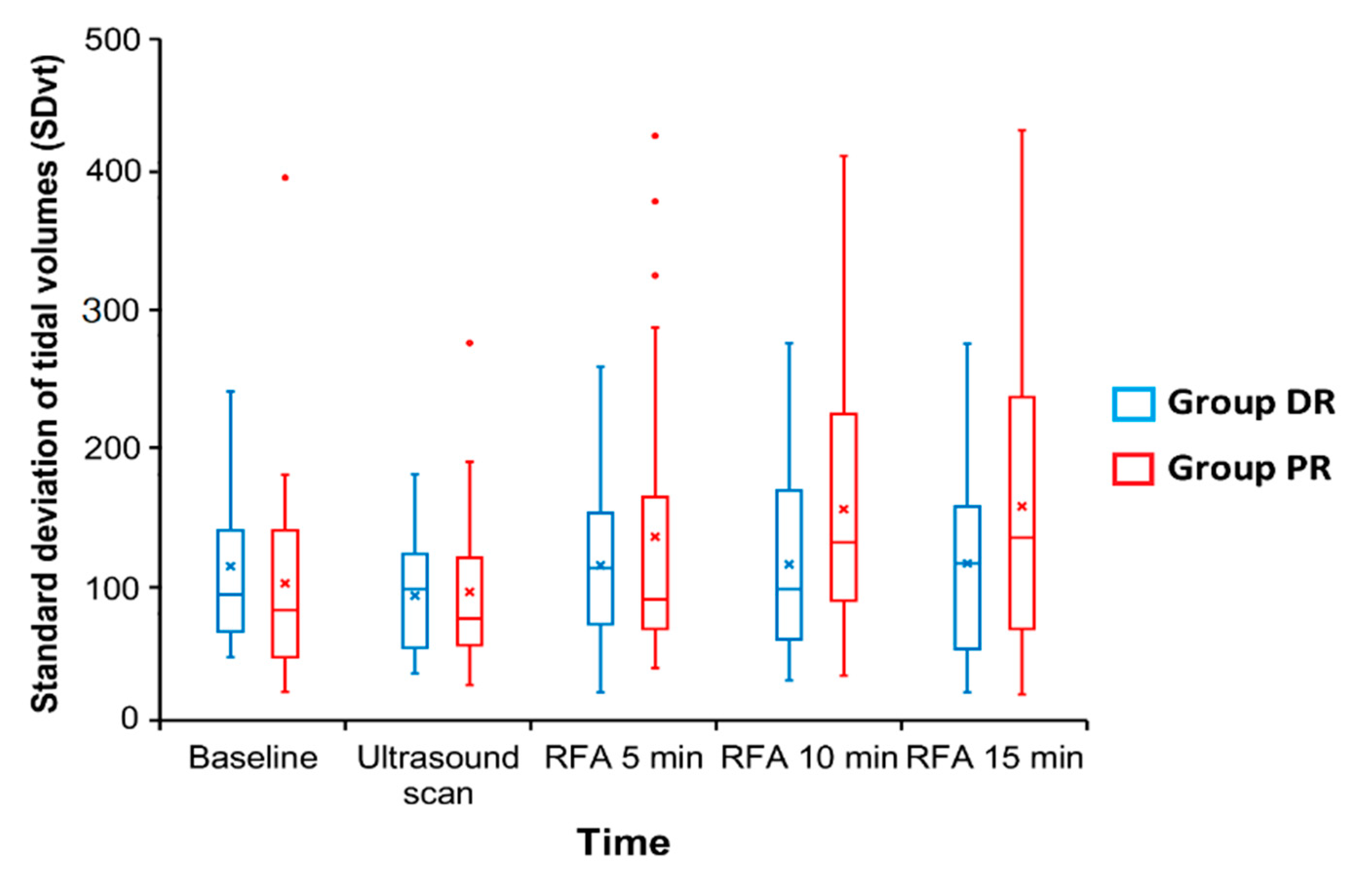
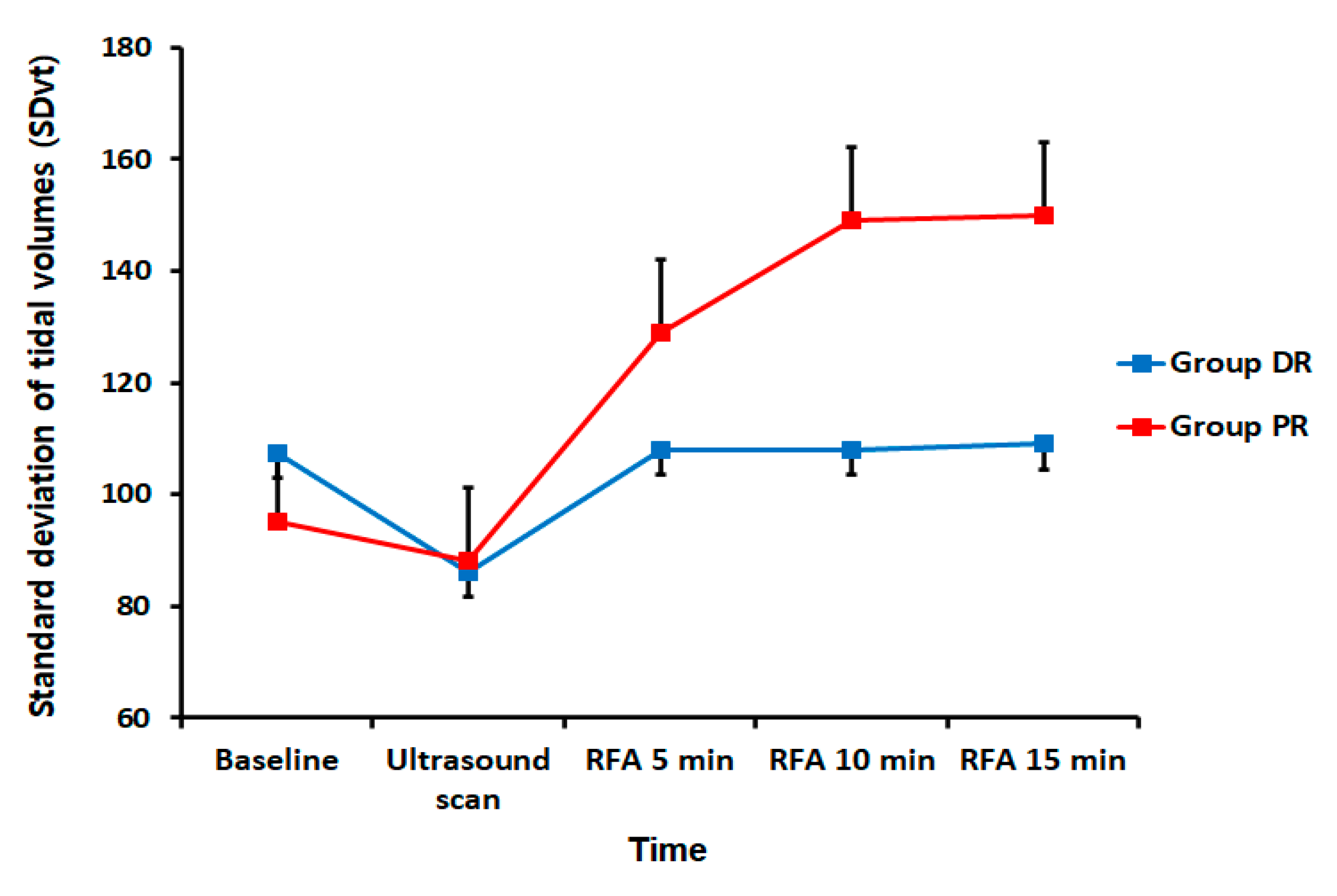
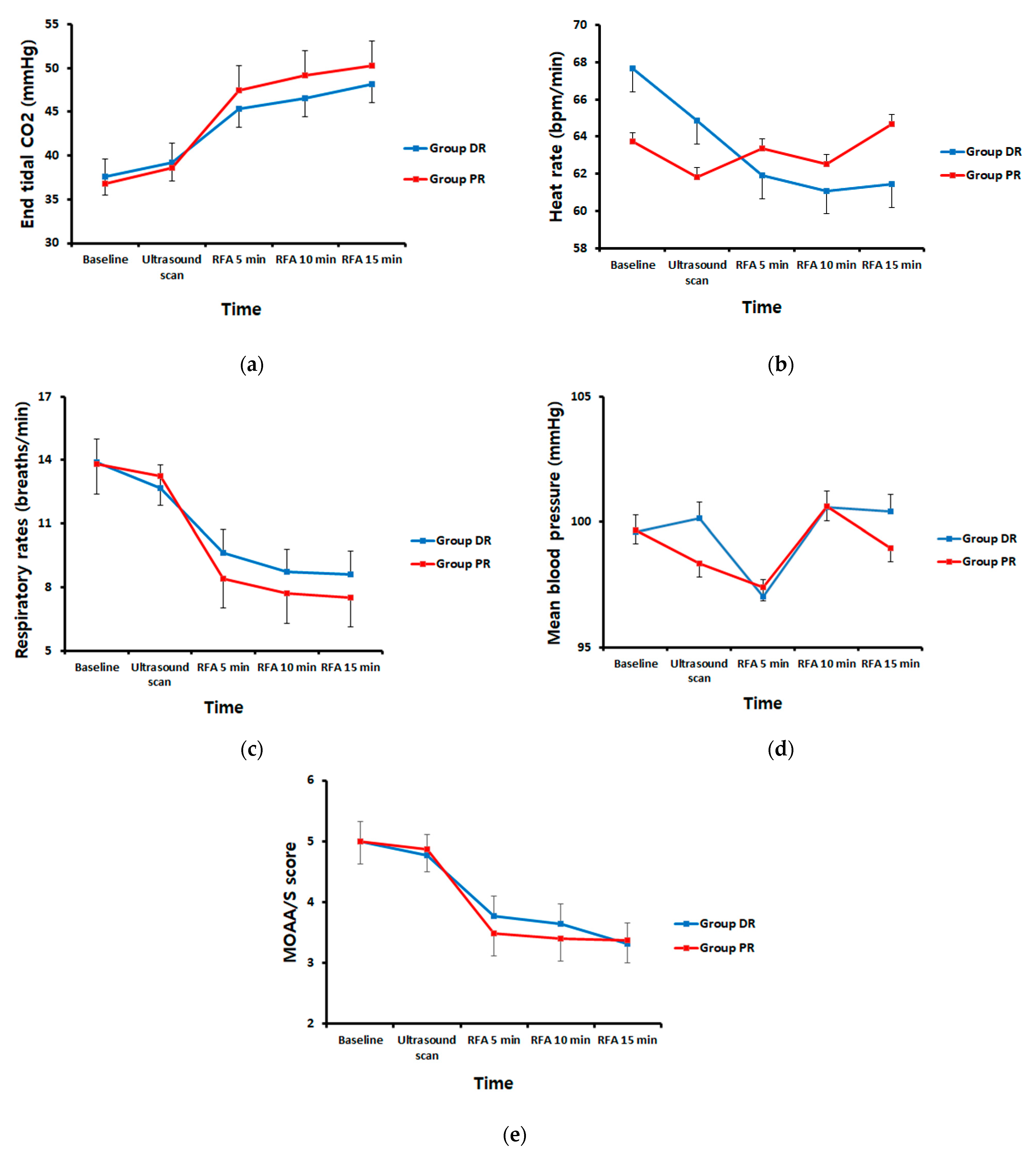
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanaka, T.; Ikeda, K.; Sorin, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Kumada, H. Three-Dimensional Imaging Using Contrast-Enhanced and Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Techniques in the Ablative Zone Treated with a Multipolar Radiofrequency Ablation System for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncology 2016, 90, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.A.; Allgaier, H.P.; Cioni, D.; Olschewski, M.; Deibert, P.; Crocetti, L.; Frings, H.; Laubenberger, J.; Zuber, I.; Blum, H.E.; et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 2003, 228, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, R.T.; Fan, S.T.; Tsang, F.H.; Wong, J. Locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: A critical review from the surgeon’s perspective. Ann. Surg. 2002, 235, 466–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, K.; Ikeda, O.; Kawanaka, K.; Nakasone, Y.; Inoue, S.; Tamura, Y.; Yamashita, Y. Pain control in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated by percutaneous radiofrequency ablation: Comparison of the efficacy of one-shot and continuous intravenous fentanyl delivery. Acta Radiol. 2014, 55, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, R.; Rosa, T.; Tsou, D.Y.; Nekhendzy, V.; Drover, D.; Collins, J.; Zaghi, S.; Camacho, M. Variable Findings for Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Propofol versus Dexmedetomidine. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 154, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Mason, K.P. Dexmedetomidine: Review, update, and future considerations of paediatric perioperative and periprocedural applications and limitations. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joung, K.W.; Choi, S.S.; Jang, D.M.; Kong, Y.G.; Lee, H.M.; Shim, J.H.; Won, H.J.; Shin, Y.M.; Kim, P.N.; Song, M.H. Comparative Effects of Dexmedetomidine and Propofol on US-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Neoplasm Under Monitored Anesthesia Care: A Randomized Controlled Study. Medicine 2015, 94, e1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewertsen, C.; Hansen, K.L.; Henriksen, B.M.; Nielsen, M.B. Improving Accuracy for Image Fusion in Abdominal Ultrasonography. Diagnostics 2012, 2, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.S.; Shim, J.K.; Na, S.; Park, I.; Kwak, Y.L. Improved sedation with dexmedetomidine—Remifentanil compared with midazolam—Remifentanil during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: A randomized, controlled trial. EP Eur. 2014, 16, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothineni, N.V.; Hayes, K.; Deshmukh, A.; Paydak, H. Propofol-related infusion syndrome: Rare and fatal. Am. J. Ther. 2015, 22, e33–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwuemeka, A.; Ko, R.; Ralph-Edwards, A. Short-term low-dose propofol anaesthesia associated with severe metabolic acidosis. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2006, 34, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coté, G.A.; Hovis, R.M.; Ansstas, M.A.; Waldbaum, L.; Azar, R.R.; Early, D.S.; Edmundowicz, S.A.; Mullady, D.K.; Jonnalagadda, S.S. Incidence of sedation-related complications with propofol use during advanced endoscopic procedures. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.W.; Hong, J.M.; Hong, S.L.; Koo, S.K.; Roh, H.J.; Cho, K.S. A comparison of dexmedetomidine versus propofol during drug-induced sleep endoscopy in sleep apnea patients. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Yoo, Y.C.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.; Ju, H.M.; Min, K.T. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of sedation between dexmedetomidine-remifentanil and propofol-remifentanil during endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3671–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Thoracic Society Bronchoscopy Guidelines Committee, British Thoracic Society guidelines on diagnostic flexible bronchoscopy. Thorax 2001, 56 (Suppl. S1), i1–i21. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andjelković, L.; Novak-Jankovič, V.; Požar-Lukanovič, N.; Bosnić, Z.; Spindler-Vesel, A. Influence of dexmedetomidine and lidocaine on perioperative opioid consumption in laparoscopic intestine resection: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 5143–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira Neto, F.J.; Carregaro, A.B.; Mannarino, R.; Cruz, M.L.; Luna, S.P. Comparison of a sidestream capnograph and a mainstream capnograph in mechanically ventilated dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 221, 1582–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, Y.; Sakamoto, O.; Kiyofuji, C.; Ito, K. A comparison of the end-tidal CO2 measured by portable capnometer and the arterial PCO2 in spontaneously breathing patients. Respir. Med. 2003, 97, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, J.H.; Williams, G.W., 2nd; Harvey, B.C.; Grewal, N.K.; George, E.E. The relationship between minute ventilation and end tidal CO2 in intubated and spontaneously breathing patients undergoing procedural sedation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, G.W., 2nd; George, C.A.; Harvey, B.C.; Freeman, J.E. A Comparison of Measurements of Change in Respiratory Status in Spontaneously Breathing Volunteers by the ExSpiron Noninvasive Respiratory Volume Monitor Versus the Capnostream Capnometer. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 124, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, R.D.; Nuccio, P.; Spratt, G.; Waugh, J. Current applications of capnography in non-intubated patients. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2014, 8, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokelainen, J.; Mustonen, H.; Kylänpää, L.; Udd, M.; Lindström, O.; Pöyhiä, R. Assessment of sedation level for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography—A prospective validation study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, F.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X. Activation of opioid mu receptors in caudal medullary raphe region inhibits the ventilatory response to hypercapnia in anesthetized rats. Anesthesiology 2007, 107, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glass, P.S.; Iselin-Chaves, I.A.; Goodman, D.; Delong, E.; Hermann, D.J. Determination of the potency of remifentanil compared with alfentanil using ventilatory depression as the measure of opioid effect. Anesthesiology 1999, 90, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, J.A.; Pallett, E.J.; Duthie, D.J. Breath interval as a measure of dynamic opioid effect. Br. J. Anaesth. 2000, 84, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Group DR (n = 31) | Group PR (n = 31) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male/female | 21/10 | 17/14 | 0.435 |
| Age, years | 60.94 ± 10.71 | 61.94 ± 12.07 | 0.406 |
| Height, m | 1.64 ± 0.09 | 1.61 ± 0.10 | 0.291 |
| Weight, kg | 67.36 ± 15.27 | 61.74 ± 11.26 | 0.080 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 24.84 ± 4.24 | 23.79 ± 2.90 | 0.285 |
| ASA physical status, II/III | 30/1 | 27/4 | 0.354 |
| Snoring history | 13 (42) | 11 (36) | 0.795 |
| Cause of tumor | 0.388 | ||
| Hepatitis B | 25 (81) | 19 (61) | |
| Hepatitis C | 2 (7) | 5 (16) | |
| Metastasis | 3 (10) | 4 (13) | |
| Others | 1 (3) | 3 (10) | |
| Child-Pugh classification, A/B | 31/0 | 29/2 | 0.492 |
| Platelet count, 103/μL | 131.68 ± 88.04 | 140.03 ± 87.29 | 0.526 |
| Previous treatment a | 0.173 | ||
| Liver surgery | 6 | 8 | |
| RFA | 18 | 13 | |
| TACE | 13 | 17 | |
| Tumor size, mm | 17.03 ± 7.76 | 14.45 ± 5.89 | 0.193 |
| Tumor location | 0.320 | ||
| Liver surface | 7 (23) | 3 (10) | |
| Liver parenchyma | 21 (68) | 23 (74) | |
| Vascular structures | 3 (10) | 3 (10) | |
| Parietal peritoneum | 0 (0) | 2 (6) | |
| Distance to diaphragm, mm | 30.19 ± 24.06 | 28.95 ± 22.15 | 0.855 |
| Operator, 1/2/3/4/5/6 | 23/2/4/1/0/1 | 22/3/1/1/2/2 | 0.655 |
| Anesthesiologist, 1/2 | 16/15 | 14/17 | 0.799 |
| Outcome | Group DR (n = 31) | Group PR (n = 31) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sedation time, min | 56.06 ± 27.19 | 52.00 ± 14.64 | 0.827 |
| Ablation time, min | 22.18 ± 10.41 | 20.50 ± 6.82 | 0.989 |
| Total dose of remifentanil, μg/kg | 3.82 ± 1.63 | 3.58 ± 1.42 | 0.564 |
| Ce of remifentanil, ng/mL | |||
| At RFA 5 min | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.4 | 0.575 |
| At RFA 10 min | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 0.521 |
| At RFA 15 min | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 0.710 |
| Patient movement | 0.064 | ||
| none/mild/gross | 22/9/0 | 14/15/2 | |
| MOAA/S score | |||
| At RFA 5 min | 3.77 ± 0.56 | 3.48 ± 0.77 | 0.095 |
| At RFA 10 min | 3.65 ± 0.66 | 3.42 ± 0.76 | 0.218 |
| At RFA 15 min | 3.39 ± 0.99 | 3.42 ± 0.67 | 0.881 |
| After procedure | 4.58 ± 0.62 | 4.42 ± 0.67 | 0.311 |
| VAS score at PACU (0–10) | 0.87 ± 1.34 | 1.71 ± 1.88 | 0.053 |
| Operator satisfaction (0–4) a | 3.47 ± 0.66 | 2.93 ± 0.88 | 0.010 |
| Patient satisfaction (0–4) a | 3.29 ± 0.69 | 3.29 ± 0.82 | 0.812 |
| Variables | Group DR (n = 31) | Group PR (n = 31) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apnea (>20 s) | 7 (23) | 18 (58) | 0.009 |
| Desaturation (SpO2 < 90%) | 0 (0) | 1 (3.2) | 1.000 |
| Bradycardia (HR < 45 bpm) | 4 (13) | 3 (10) | 0.255 |
| Nausea or vomiting | 2 (7) | 2 (7) | 1.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.K.; Chung, I.S.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, K.; Kim, M.; Choi, J.W. Comparison of Respiratory Effects between Dexmedetomidine and Propofol Sedation for Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Neoplasm: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143040
Jeong H, Kim D, Kim DK, Chung IS, Bang YJ, Kim K, Kim M, Choi JW. Comparison of Respiratory Effects between Dexmedetomidine and Propofol Sedation for Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Neoplasm: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(14):3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143040
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Heejoon, Doyeon Kim, Duk Kyung Kim, In Sun Chung, Yu Jeong Bang, Keoungah Kim, Myungsuk Kim, and Ji Won Choi. 2021. "Comparison of Respiratory Effects between Dexmedetomidine and Propofol Sedation for Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Neoplasm: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 14: 3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143040
APA StyleJeong, H., Kim, D., Kim, D. K., Chung, I. S., Bang, Y. J., Kim, K., Kim, M., & Choi, J. W. (2021). Comparison of Respiratory Effects between Dexmedetomidine and Propofol Sedation for Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Neoplasm: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(14), 3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143040






