Genetic Susceptibility to Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Acute Kidney Injury
1.2. Controversy among Polymorphism Association Articles
2. Associated Genes
2.1. Polymorphisms
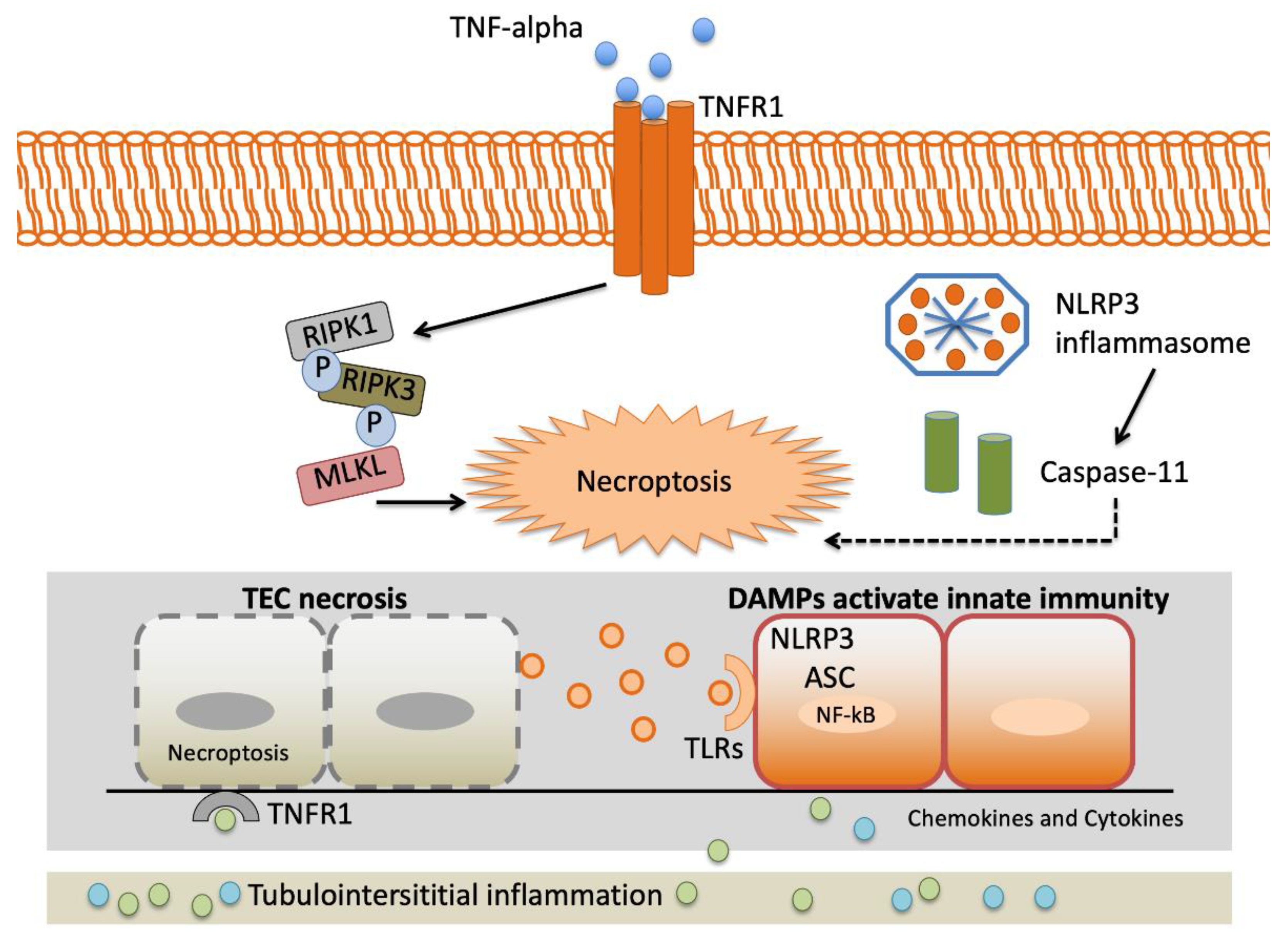
2.2. Systemic Inflammatory Response
2.2.1. Interleukin 6 (IL6)
2.2.2. Interleukin 10 (IL 10)
2.2.3. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α)
2.2.4. Lymphotoxin α (LT-α) or Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β) and Interferon γ (IFN-γ)
2.2.5. Human Leukocyte Antigen–Major Histocompatibility Complex, DR, B1 (HLA-DRB1)
2.2.6. Nuclear Factor Kappa Beta 1 (NFKB1)
2.2.7. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF)
2.2.8. Interleukin-18 (IL-18)
2.3. Vascular Hemodynamic Response
2.3.1. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
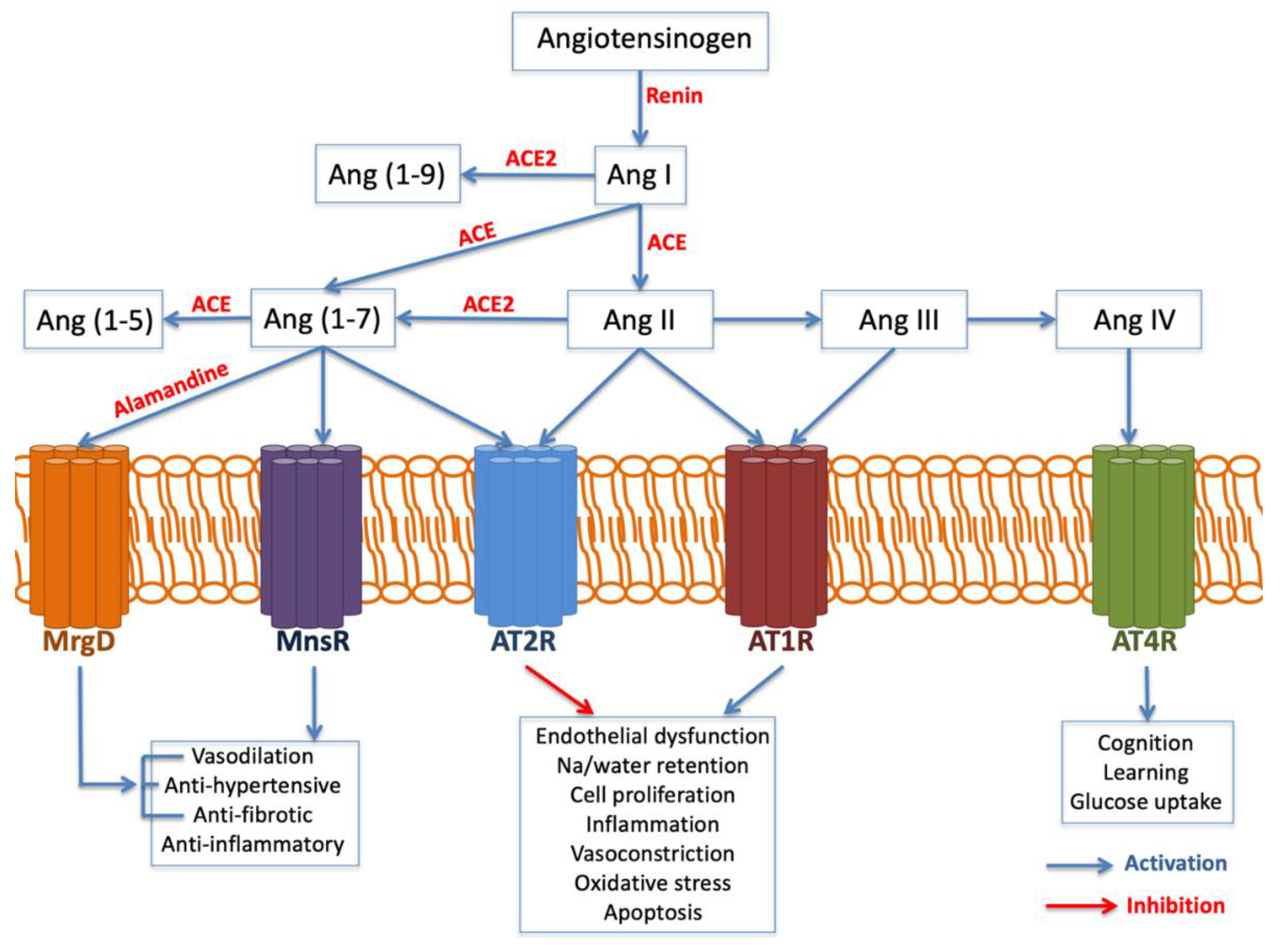
2.3.2. Angiotensinogen (AGT) and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)
2.3.3. Endothelial No Synthase (eNOS)
2.4. Cellular Metabolic Homeostasis
2.4.1. Cytochrome b245
2.4.2. Kallikrein-1 (KLK1)
2.4.3. Nicotinamide Adenosine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADPH)
2.4.4. PH Domain and Leucine-Rich Repeat Protein Phosphatase 2 (PHLPP2)
2.5. Adrenergic Response
2.5.1. Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Gene (COMT)
2.5.2. Phenylethanolamine N-Methyltransferase (PNMT)
2.6. Cell Proliferation and Differentiation
2.6.1. Glutamate Receptor Metabotropic 7 (GRM7) and LMCD1 Antisense RNA 1 (LMCD1-AS1)
2.6.2. Salt-Inducible Kinase 3 (SIK3)
2.6.3. Suppressor of Fused Homolog (SUFU)
2.6.4. Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3
2.6.5. Erythropoietin (EPO)
2.6.6. Surfactant Protein-D (SP-D)
2.7. Lipid Metabolism
2.7.1. Adiponectin
2.7.2. Apolipoprotein E (APOE)
2.7.3. Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1)
2.8. Noxious Stimuli
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1-α
2.9. Oxidative Stress
2.9.1. Myeloperoxidase (MPO)
2.9.2. Catalase
2.10. Cell Survival and Apoptosis
2.10.1. B-Cell CLL/Lymphoma 2 (BCL2)
2.10.2. Serpin Peptidase Inhibitor (SERPIN)
2.11. Cytoskeleton
Bardet–Biedl Syndrome 9 BBS9
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kruzel-Davila, E.; Wasser, W.G.; Aviram, S.; Skorecki, K. APOL1 nephropathy: From gene to mechanisms of kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.J.; Foley, R.N.; Chavers, B.; Gilbertson, D.; Herzog, C.; Johansen, K.; Kasiske, B.; Kutner, N.; Liu, J.; St Peter, W.; et al. United States Renal Data System 2011 Annual Data Report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease & end-stage renal disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 59, e1–e420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, M.E.; Chow, E.K.; Segev, D.L.; Coresh, J. Lifetime incidence of CKD stages 3-5 in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2013, 62, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartin-Ceba, R.; Haugen, E.N.; Iscimen, R.; Trillo-Alvarez, C.; Juncos, L.; Gajic, O. Evaluation of “Loss” and “End stage renal disease” after acute kidney injury defined by the Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss and ESRD classification in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Loubon, C.; Fernandez-Molina, M.; Fierro, I.; Jorge-Monjas, P.; Carrascal, Y.; Gomez-Herreras, J.I.; Tamayo, E. Postoperative kidney oxygen saturation as a novel marker for acute kidney injury after adult cardiac surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 157, 2340–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monedero, P.; García-Fernández, N.; Pérez-Valdivieso, J.R.; Vives, M.; Lavilla, J. Insuficiencia renal aguda. Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Reanim. 2011, 58, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado-Fraile, E.; Ramos, E.; Conde, E.; Rodriguez, M.; Martin-Gomez, L.; Lietor, A.; Candela, A.; Ponte, B.; Liano, F.; Garcia-Bermejo, M.L. A Pilot Study Identifying a Set of microRNAs As Precise Diagnostic Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Loubon, C.; Fernandez-Molina, M.; Carrascal-Hinojal, Y.; Fulquet-Carreras, E. Cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2016, 19, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, E.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D.; et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larach, D.B.; Engoren, M.C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Heung, M. Genetic variants and acute kidney injury: A review of the literature. J. Crit. Care 2018, 44, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.F.; Zhang, W. Role of microRNA in the detection, progression, and intervention of acute kidney injury. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.E.; Muntner, P.; Chertow, G.M.; Warnock, D.G. Acute kidney injury and mortality in hospitalized patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 35, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.; Leslie, G. Acute kidney injury and the critically ill patient. Dimens. Crit. Care Nurs. 2012, 31, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafrance, J.P.; Miller, D.R. Acute kidney injury associates with increased long-term mortality. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilander, L.M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; Pettila, V. Genetic predisposition to acute kidney injury—A systematic review. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, S.; Kellum, J.A.; Bellomo, R.; Doig, G.S.; Morimatsu, H.; Morgera, S.; Schetz, M.; Tan, I.; Bouman, C.; Macedo, E.; et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: A multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 2005, 294, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, S.; Yang, L.; Mei, C.; Consortium, I.A.b.C. Acute kidney injury burden in different clinical units: Data from nationwide survey in China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbert, S.D.; Kork, F.; Jackson, M.L.; Vanga, N.; Ghebremichael, S.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Eltzschig, H.K. Perioperative Acute Kidney Injury. Anesthesiology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2019, 394, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xie, G.; Wu, H.; Xu, S.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X. Association between inflammatory-response gene polymorphisms and risk of acute kidney injury in children. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.C.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Chu, P.H. MicroRNAs in acute kidney injury. Hum. Genomics. 2016, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, B.A.; Koyner, J.L.; Murray, P.T. Urinary glutathione S-transferases in the pathogenesis and diagnostic evaluation of acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery: A critical review. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2010, 16, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejovic, M.; Valesova, L.; Benes, J.; Sykora, R.; Hrstka, R.; Chvojka, J. Molecular differences in susceptibility of the kidney to sepsis-induced kidney injury. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Yang, L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsey, G.R.; Li, L.; Okusa, M.D. Inflammation in acute kidney injury. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2008, 109, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Murugan, R.; Peng, Z.; Kellum, J.A. Pathophysiology of acute kidney injury: A new perspective. Contrib. Nephrol. 2010, 165, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharfuddin, A.A.; Molitoris, B.A. Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, B.L.; Liangos, O.; Pereira, B.J.; Balakrishnan, V.S. Polymorphism of immunomodulatory cytokine genes: Implications in acute renal failure. Blood Purif. 2004, 22, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Jing, Y.; Hao, J.; Frankfort, N.C.; Zhou, X.; Shen, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, R. MicroRNA-21 in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcay, A.; Nguyen, Q.; Edelstein, C.L. Mediators of inflammation in acute kidney injury. Mediat. Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 137072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Kong, Y.; Yin, J.; Liang, R.; Lu, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, F.; et al. Antithrombin is a Novel Predictor for Contrast Induced Nephropathy After Coronary Angiography. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018, 43, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Yin, J.; Cheng, D.; Lu, Z.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; Liang, M. Antithrombin III Attenuates AKI Following Acute Severe Pancreatitis. Shock 2018, 49, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Z.; Geurts, A.M.; Usa, K.; Jacob, H.J.; Cowley, A.W.; Wang, N.; Liang, M. Antithrombin III/SerpinC1 insufficiency exacerbates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzotto, F.; Piccinni, P.; Cruz, D.; Gramaticopolo, S.; Dal Santo, M.; Aneloni, G.; Kim, J.C.; Rocco, M.; Alessandri, E.; Giunta, F.; et al. RIFLE-based data collection/management system applied to a prospective cohort multicenter Italian study on the epidemiology of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit. Blood Purif. 2011, 31, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Weinberg, J.M. Recent advances in the pathophysiology of ischemic acute renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.C.; Coca, S.G.; Patel, U.D.; Cantley, L.; Parikh, C.R. Translational Research Investigating, Biomarkers, Endpoints for Acute Kidney Injury Consortium: Searching for genes that matter in acute kidney injury: A systematic review. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1020–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehar, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, M.J.; Edelman, E.J.; Heidorn, S.J.; Greenman, C.D.; Dastur, A.; Lau, K.W.; Greninger, P.; Thompson, I.R.; Luo, X.; Soares, J.; et al. Systematic identification of genomic markers of drug sensitivity in cancer cells. Nature 2012, 483, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibar, L.; Wagner, J.; Pavlinic, D.; Galic, J.; Pasini, J.; Juras, K.; Barbic, J. The relationship between interferon-gamma gene polymorphism and acute kidney allograft rejection. Scand. J. Immunol. 2011, 73, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.H.; Daneshmandi, S.; Pourfathollah, A.A.; Geramizadeh, B.; Yaghobi, R.; Rais-Jalali, G.A.; Roozbeh, J.; Bolandparvaz, S. A study of the impact of cytokine gene polymorphism in acute rejection of renal transplant recipients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, A.; Georgescu, A.M.; Vitin, A.; Azamfirei, L. Precision Medicine and its Role in the Treatment of Sepsis: A Personalised View. J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 5, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinal-Fernandez, P.; Ferruelo, A.; Martin-Pellicer, A.; Nin, N.; Esteban, A.; Lorente, J.A. Genetic determinants of acute renal damage risk and prognosis: A systematic review. Med. Intensiva 2012, 36, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase-Fielitz, A.; Haase, M.; Bellomo, R.; Dragun, D. Genetic polymorphisms in sepsis- and cardiopulmonary bypass-associated acute kidney injury. Contrib. Nephrol. 2007, 156, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabel, E.G. Cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmueller, K.E.; Pearce, C.L.; Pike, M.; Lander, E.S.; Hirschhorn, J.N. Meta-analysis of genetic association studies supports a contribution of common variants to susceptibility to common disease. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilander, L.M.; Vaara, S.T.; Kaunisto, M.A.; Pettila, V.; Study Group, T.F. Common Inflammation-Related Candidate Gene Variants and Acute Kidney Injury in 2647 Critically Ill Finnish Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.; Patel, N.; Turcotte, M.; Bosse, Y.; Pare, G.; Meyre, D. Benefits and limitations of genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, A.; Farlow, A. The advantages and limitations of trait analysis with GWAS: A review. Plant Methods 2013, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, N.A.; Huang, L.; Jewett, E.M.; Szpiech, Z.A.; Jankovic, I.; Boehnke, M. Genome-wide association studies in diverse populations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, P.; Zeggini, E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Replication in genome-wide association studies. Stat. Sci. 2009, 24, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.F.; Lu, T.M.; Yang, W.C.; Lin, S.J.; Lin, C.C.; Chung, M.Y. Gene polymorphisms of interleukin-10 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha are associated with contrast-induced nephropathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 37, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A.; Stacul, F.; Becker, C.R.; Adam, A.; Lameire, N.; Tumlin, J.A.; Davidson, C.J.; CIN Consensus Working Panel. Contrast-Induced Nephropathy (CIN) Consensus Working Panel: Executive summary. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 7, 177–197. [Google Scholar]
- Caspi, A.; Sugden, K.; Moffitt, T.E.; Taylor, A.; Craig, I.W.; Harrington, H.; McClay, J.; Mill, J.; Martin, J.; Braithwaite, A.; et al. Influence of life stress on depression: Moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 2003, 301, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, P.; Aichberger, S.; Thurner, S. Disentangling genetic and environmental risk factors for individual diseases from multiplex comorbidity networks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S. Variance components models for gene-environment interaction in twin analysis. Twin Res. 2002, 5, 554–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruss-Ustun, A.; Wolf, J.; Corvalan, C.; Neville, T.; Bos, R.; Neira, M. Diseases due to unhealthy environments: An updated estimate of the global burden of disease attributable to environmental determinants of health. J. Public Health 2017, 39, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, S.M.; Smith, M.T. Epidemiology. Environment and disease risks. Science 2010, 330, 460–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, J.C.; Adams, M.D.; Myers, E.W.; Li, P.W.; Mural, R.J.; Sutton, G.G.; Smith, H.O.; Yandell, M.; Evans, C.A.; Holt, R.A.; et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science 2001, 291, 1304–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabangin, M.E.; Woo, J.G.; Martin, L.J. The effect of minor allele frequency on the likelihood of obtaining false positives. BMC Proc. 2009, 3, S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lei, C.T.; Zhang, C. Interleukin-6 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Kidney Disease: An Update. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalboni, M.A.; Quinto, B.M.; Grabulosa, C.C.; Narciso, R.; Monte, J.C.; Durao, M., Jr.; Rizzo, L.; Cendoroglo, M.; Santos, O.P.; Batista, M.C. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha plus interleukin-10 low producer phenotype predicts acute kidney injury and death in intensive care unit patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 173, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechemia-Arbely, Y.; Barkan, D.; Pizov, G.; Shriki, A.; Rose-John, S.; Galun, E.; Axelrod, J.H. IL-6/IL-6R axis plays a critical role in acute kidney injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Gurguis, C.I.; Zhou, J.J.; Zhu, Y.; Ko, E.A.; Ko, J.H.; Wang, T.; Zhou, T. Functional and Structural Consequence of Rare Exonic Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms: One Story, Two Tales. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2929–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudino, M.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Zamparelli, R.; Andreotti, F.; Burzotta, F.; Iacoviello, L.; Glieca, F.; Alessandrini, F.; Nasso, G.; Donati, M.B.; et al. Genetic control of postoperative systemic inflammatory reaction and pulmonary and renal complications after coronary artery surgery. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 126, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarainen, O.P.; Solovieva, S.; Vehmas, T.; Luoma, K.; Riihimaki, H.; Ala-Kokko, L.; Mannikko, M.; Leino-Arjas, P. Common interleukin-6 promoter variants associate with the more severe forms of distal interphalangeal osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford-Smith, M.; Podgoreanu, M.; Swaminathan, M.; Phillips-Bute, B.; Mathew, J.P.; Hauser, E.H.; Winn, M.P.; Milano, C.; Nielsen, D.M.; Smith, M.; et al. Association of genetic polymorphisms with risk of renal injury after coronary bypass graft surgery. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoyinmi, E.; Forabosco, P.; Hamaoui, R.; Bryant, A.; Hinks, A.; Ursu, S.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Thomson, W.; Lewis, C.M.; Woo, P.; et al. Association of the IL-10 gene family locus on chromosome 1 with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.R.; Garg, A.X.; Coca, S.G.; Devereaux, P.J.; Eikelboom, J.; Kavsak, P.; McArthur, E.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Shortt, C.; Shlipak, M.; et al. Plasma IL-6 and IL-10 Concentrations Predict AKI and Long-Term Mortality in Adults after Cardiac Surgery. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 3123–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J.H.; Whitlock, R.; Zhang, W.R.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.R.; Zappitelli, M.; Devarajan, P.; Eikelboom, J.; Kavsak, P.A.; Devereaux, P.J.; Shortt, C.; et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 as acute kidney injury biomarkers in pediatric cardiac surgery. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashad, D.I.; Elsayed, E.T.; Helmy, T.A.; Elawady, S.M. Study of the role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (-308 G/A) and interleukin-10 (-1082 G/A) polymorphisms as potential risk factors to acute kidney injury in patients with severe sepsis using high-resolution melting curve analysis. Ren. Fail. 2017, 39, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susantitaphong, P.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Tighiouart, H.; Liangos, O.; Bonventre, J.V.; Jaber, B.L. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter polymorphism and severity of acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2013, 123, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinal-Fernandez, P.; Ferruelo, A.; El-Assar, M.; Santiago, C.; Gomez-Gallego, F.; Martin-Pellicer, A.; Frutos-Vivar, F.; Penuelas, O.; Nin, N.; Esteban, A.; et al. Genetic predisposition to acute kidney injury induced by severe sepsis. J. Crit. Care 2013, 28, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouan, J.; Golmard, L.; Benhamouda, N.; Durrleman, N.; Golmard, J.L.; Ceccaldi, R.; Trinquart, L.; Fabiani, J.N.; Tartour, E.; Jeunemaitre, X.; et al. Gene polymorphisms and cytokine plasma levels as predictive factors of complications after cardiopulmonary bypass. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 144, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, J.; Eichhorn, S.; Kornek, M.; Hauner, K.; Prinzing, A.; Grammer, J.; Lahm, H.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Lange, R. Apolipoprotein E genotype, TNF-alpha 308G/A and risk for cardiac surgery associated-acute kidney injury in Caucasians. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchanda, P.K.; Kumar, A.; Kaul, A.; Mittal, R.D. Correlation between a gene polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (G/A) and end-stage renal disease: A pilot study from north India. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 370, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatani, S.H.; Al Refai, A.A.; Al-Amodi, H.S.; Kamel, H.F.; Al-Khatieb, K.; Bader, H. Assessment of tumor necrosis factor alpha polymorphism TNF-alpha-238 (rs 361525) as a risk factor for development of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedder, S.; Kimura, N.; Okamura, H.; Hsieh, S.C.; Gong, Y.; Sarwal, M.M. Significance and suppression of redundant IL17 responses in acute allograft rejection by bioinformatics based drug repositioning of fenofibrate. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keithi-Reddy, S.R.; Addabbo, F.; Patel, T.V.; Mittal, B.V.; Goligorsky, M.S.; Singh, A.K. Association of anemia and erythropoiesis stimulating agents with inflammatory biomarkers in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabulosa, C.C.; Batista, M.C.; Cendoroglo, M.; Quinto, B.M.; Narciso, R.; Monte, J.C.; Durao, M.; Rizzo, L.V.; Santos, O.F.; Dalboni, M.A. Frequency of TGF- beta and IFN- gamma genotype as risk factors for acute kidney injury and death in intensive care unit patients. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 904730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Shao, Y.; Fu, R. Current research status of HLA in immune-related diseases. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muczynski, K.A.; Cotner, T.; Anderson, S.K. Unusual expression of human lymphocyte antigen class II in normal renal microvascular endothelium. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payen, D.; Lukaszewicz, A.C.; Legrand, M.; Gayat, E.; Faivre, V.; Megarbane, B.; Azoulay, E.; Fieux, F.; Charron, D.; Loiseau, P.; et al. A multicentre study of acute kidney injury in severe sepsis and septic shock: Association with inflammatory phenotype and HLA genotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Sanz, A.B.; Carrasco, S.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Cannata-Ortiz, P.; Sanchez-Nino, M.D.; Ortiz, A. Bcl3: A regulator of NF-kappaB inducible by TWEAK in acute kidney injury with anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic properties in tubular cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB in inflammation and renal diseases. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Thaiss, F.; Guo, L. NFkappaB and Kidney Injury. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, F.L.; Patel, N.S.A.; Purvis, G.S.D.; Chiazza, F.; Chen, J.; Sordi, R.; Hache, G.; Merezhko, V.V.; Collino, M.; Yaqoob, M.M.; et al. Inhibition of IkappaB Kinase at 24 Hours After Acute Kidney Injury Improves Recovery of Renal Function and Attenuates Fibrosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.C.; Suzairi, M.S.; Aizat, A.A.; Aminudin, M.M.; Nurfatimah, M.S.; Bhavaraju, V.M.; Biswal, B.M.; Ankathil, R. Gender-specific association of NFKBIA promoter polymorphisms with the risk of sporadic colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppe, C.; Averdunk, L.; Goetzenich, A.; Soppert, J.; Marlier, A.; Kraemer, S.; Vieten, J.; Coburn, M.; Kowark, A.; Kim, B.S.; et al. The protective role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averdunk, L.; Bernhagen, J.; Fehnle, K.; Surowy, H.; Ludecke, H.J.; Mucha, S.; Meybohm, P.; Wieczorek, D.; Leng, L.; Marx, G.; et al. The Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) Promoter Polymorphisms (rs3063368, rs755622) Predict Acute Kidney Injury and Death after Cardiac Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Tang, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, X.H.; Yang, H.; Tang, P.M.K.; Huang, X.R.; He, Z.J.; Zhou, Z.J.; Huang, Q.Y.; et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes renal injury induced by ischemic reperfusion. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3867–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.S.; El-Sharif, A.A. Curcumin immune-mediated and anti-apoptotic mechanisms protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion and distant organ induced injuries. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zha, Y. Urine interleukin-18 in prediction of acute kidney injury: A systemic review and meta-analysis. J. Nephrol. 2015, 28, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.O. Vascular endothelial growth factors and vascular permeability. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbir, S.C.; Tekeli, A.; Ergen, A.; Yilmaz, H.; Ak, K.; Civelek, A.; Zeybek, U.; Arsan, S. Genetic polymorphisms contribute to acute kidney injury after coronary artery bypass grafting. Heart Surg. Forum 2007, 10, E439–E444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.F.; Baudouin, S.V. A systematic review of the quality of genetic association studies in human sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedroso, J.A.; Paskulin, D.d.; Dias, F.S.; de França, E.; Alho, C.S. Temporal trends in acute renal dysfunction among critically ill patients according to I/D and -262A > T ACE polymorphisms. J. Bras. Nefrol. 2010, 32, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Cheyron, D.; Fradin, S.; Ramakers, M.; Terzi, N.; Guillotin, D.; Bouchet, B.; Daubin, C.; Charbonneau, P. Angiotensin converting enzyme insertion/deletion genetic polymorphism: Its impact on renal function in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 3178–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, W.T.; Prasad, P.S.; Armstrong, M.; Patterson, C.; Gilliland, H.; Drain, A.; Vuylsteke, A.; Latimer, R.; Khalil, N.; Evans, A.; et al. Cytokine phenotype, genotype, and renal outcomes at cardiac surgery. Cytokine 2013, 61, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.F.; Hinz, J.; Schulz, E.G.; Schmitto, J.D.; Wiese, C.H.; Quintel, M.; Seipelt, R.; Schoendube, F.A. The eNOS 786C/T polymorphism in cardiac surgical patients with cardiopulmonary bypass is associated with renal dysfunction. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2009, 36, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianayagam, M.C.; Tighiouart, H.; Nievergelt, C.M.; O’Connor, D.T.; Liangos, O.; Jaber, B.L. CYBA Gene Polymorphisms and Adverse Outcomes in Acute Kidney Injury: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nephron Extra 2011, 1, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susantitaphong, P.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Kang, S.W.; Zhang, W.; Rao, F.; O’Connor, D.T.; Jaber, B.L. Association of functional kallikrein-1 promoter polymorphisms and acute kidney injury: A case-control and longitudinal cohort study. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 122, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Chen, G.J.; Liu, K.P.; Lai, Y.C.; Juang, H.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Significance of the tissue kallikrein promoter and transforming growth factor-beta1 polymorphisms with renal progression in children with vesicoureteral reflux. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Song, Q.; Freedman, B.I.; Chao, J.; Chao, L.; Rich, S.S.; Bowden, D.W. Association of the tissue kallikrein gene promoter with ESRD and hypertension. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianayagam, M.C.; Liangos, O.; Kolyada, A.Y.; Wald, R.; MacKinnon, R.W.; Li, L.; Rao, M.; Balakrishnan, V.S.; Bonventre, J.V.; Pereira, B.J.; et al. NADPH oxidase p22phox and catalase gene variants are associated with biomarkers of oxidative stress and adverse outcomes in acute renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Fang, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, B.; Wu, J.; Li, M. miR-205 targets PTEN and PHLPP2 to augment AKT signaling and drive malignant phenotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hua, X.; Xu, J.; Tian, Z.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Wu, X.R.; Huang, C. Inhibition of PHLPP2/cyclin D1 protein translation contributes to the tumor suppressive effect of NFkappaB2 (p100). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34112–34130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, S.; Stoppe, C.; Gruenewald, M.; Bein, B.; Renner, J.; Cremer, J.; Coburn, M.; Schaelte, G.; Boening, A.; Niemann, B.; et al. Genome-wide association study of myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, acute stroke, acute kidney injury and delirium after cardiac surgery—A sub-analysis of the RIPHeart-Study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase-Fielitz, A.; Haase, M.; Bellomo, R.; Lambert, G.; Matalanis, G.; Story, D.; Doolan, L.; Buxton, B.; Gutteridge, G.; Luft, F.C.; et al. Decreased catecholamine degradation associates with shock and kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, C.; Kube, J.; Haase-Fielitz, A.; Dittrich, A.; Schanze, D.; Zenker, M.; Kuppe, H.; Hetzer, R.; Bellomo, R.; Mertens, P.R.; et al. Pilot study of association of catechol-O-methyl transferase rs4680 genotypes with acute kidney injury and tubular stress after open heart surgery. Biomark. Med. 2014, 8, 1227–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornek, M.; Deutsch, M.A.; Eichhorn, S.; Lahm, H.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Krane, M.; Lange, R.; Boehm, J. COMT-Val158Met-polymorphism is not a risk factor for acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Dis. Markers 2013, 35, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; O’Connor, D.T.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Kolyada, A.Y.; Chen, Y.; Rao, F.; Mahata, M.; Mahata, S.; Liangos, O.; Jaber, B.L. Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase gene polymorphisms and adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2010, 114, c253–c259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford-Smith, M.; Li, Y.J.; Mathew, J.P.; Li, Y.W.; Ji, Y.; Phillips-Bute, B.G.; Milano, C.A.; Newman, M.F.; Kraus, W.E.; Kertai, M.D.; et al. Genome-wide association study of acute kidney injury after coronary bypass graft surgery identifies susceptibility loci. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Li, J.; Guo, J. The potent roles of salt-inducible kinases (SIKs) in metabolic homeostasis and tumorigenesis. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, M.; Springate, J.E.; Cutuli, F. Targeting of renal proximal tubule Na,K-ATPase by salt-inducible kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Frank, A.J.; Sheu, C.C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Su, L.; Gong, M.N.; Bajwa, E.; Thompson, B.T.; Christiani, D.C. BCL2 genetic variants are associated with acute kidney injury in septic shock*. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Martinez, A.F.; Agler, A.H.; LaFlamme, D.; Schwartz, D.A.; Yang, I.V. Polymorphisms in the SUFU gene are associated with organ injury protection and sepsis severity in patients with Enterobacteriacea bacteremia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 16, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghakhani Chegeni, S.; Rahimzadeh, M.; Montazerghaem, H.; Khayatian, M.; Dasturian, F.; Naderi, N. Preliminary Report on the Association Between STAT3 Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Acute Kidney Injury After Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Biochem. Genet 2018, 56, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.F.; Schulz, E.G.; Schmitto, J.D.; Coskun, K.O.; Tzvetkov, M.V.; Kazmaier, S.; Zimmermann, J.; Schondube, F.A.; Quintel, M.; Hinz, J. Relation between renal dysfunction requiring renal replacement therapy and promoter polymorphism of the erythropoietin gene in cardiac surgery. Artif. Organs 2010, 34, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Angelo, S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, G.; Phillips, S.; Ramet, M.; Luo, J.; Floros, J. Novel, non-radioactive, simple and multiplex PCR-cRFLP methods for genotyping human SP-A and SP-D marker alleles. Dis. Markers 1999, 15, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Z.; Gatto, L.A.; Hawgood, S.; Poulain, F.R.; Cooney, R.N.; Wang, G. Innate immunity of surfactant proteins A and D in urinary tract infection with uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Innate Immun. 2016, 22, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, G.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Chen, D. Surfactant protein-D (SP-D) gene polymorphisms and serum level as predictors of susceptibility and prognosis of acute kidney injury in the Chinese population. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbowska, J.; Kochan, Z. Role of adiponectin in the regulation of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, L.J.; Peake, R.; Price, S.; Morris, T.C.; Irvine, A.E. Adiponectin is produced by lymphocytes and is a negative regulator of granulopoiesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Cho, J.Y.; Pham, A.; Ramsdell, J.; Broide, D.H. Adiponectin and functional adiponectin receptor 1 are expressed by airway epithelial cells in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorsal, A.; Tarnow, L.; Frystyk, J.; Lajer, M.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Parving, H.H.; Vionnet, N.; Rossing, P. Serum adiponectin predicts all-cause mortality and end stage renal disease in patients with type I diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jin, X.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Chan, L.; Wang, Y. Genetic deficiency of adiponectin protects against acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKensen, G.B.; Swaminathan, M.; Ti, L.K.; Grocott, H.P.; Phillips-Bute, B.G.; Mathew, J.P.; Newman, M.F.; Milano, C.A.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Perioperative Outcomes Research, G.; et al. Preliminary report on the interaction of apolipoprotein E polymorphism with aortic atherosclerosis and acute nephropathy after CABG. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 78, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, S.T.; Newman, M.F.; White, W.D.; Conlon, P.J.; Saunders, A.M.; Strittmatter, W.J.; Landolfo, K.; Grocott, H.P.; Stafford-Smith, M. Preliminary report on the association of apolipoprotein E polymorphisms, with postoperative peak serum creatinine concentrations in cardiac surgical patients. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipkowitz, M.S.; Freedman, B.I.; Langefeld, C.D.; Comeau, M.E.; Bowden, D.W.; Kao, W.H.; Astor, B.C.; Bottinger, E.P.; Iyengar, S.K.; Klotman, P.E.; et al. Apolipoprotein L1 gene variants associate with hypertension-attributed nephropathy and the rate of kidney function decline in African Americans. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsa, A.; Kao, W.H.; Xie, D.; Astor, B.C.; Li, M.; Hsu, C.Y.; Feldman, H.I.; Parekh, R.S.; Kusek, J.W.; Greene, T.H.; et al. APOL1 risk variants, race, and progression of chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2183–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Lu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Belcher, J.M.; Siew, E.D.; Leaf, D.E.; Body, S.C.; Fox, A.A.; Waikar, S.S.; Collard, C.D.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study to Identify Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Acute Kidney Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Li-Ling, J.; Qiu, G.; Niu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Sun, K. Increased Tbx1 expression may play a role via TGFβ-Smad2/3 signaling pathway in acute kidney injury induced by gentamicin. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolyada, A.Y.; Tighiouart, H.; Perianayagam, M.C.; Liangos, O.; Madias, N.E.; Jaber, B.L. A genetic variant of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is associated with adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 1322–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianayagam, M.C.; Tighiouart, H.; Liangos, O.; Kouznetsov, D.; Wald, R.; Rao, F.; O’Connor, D.T.; Jaber, B.L. Polymorphisms in the myeloperoxidase gene locus are associated with acute kidney injury-related outcomes. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidir, V.; Uz, E.; Yigit, A.; Altuntas, A.; Yigit, B.; Inal, S.; Uz, E.; Sezer, M.T.; Yilmaz, H.R. Manganese superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and catalase gene polymorphisms and clinical outcomes in acute kidney injury. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Havasi, A.; Borkan, S.C. Apoptosis and acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Gao, L.; Shen, B.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Kallistatin inhibits vascular inflammation by antagonizing tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced nuclear factor kappaB activation. Hypertension 2010, 56, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Gao, L.; Hsu, Y.T.; Bledsoe, G.; Hagiwara, M.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Kallistatin attenuates endothelial apoptosis through inhibition of oxidative stress and activation of Akt-eNOS signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H1419–H1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Hernandez, V.; Pravincumar, P.; Diaz-Font, A.; May-Simera, H.; Jenkins, D.; Knight, M.; Beales, P.L. Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins control the cilia length through regulation of actin polymerization. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 3858–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

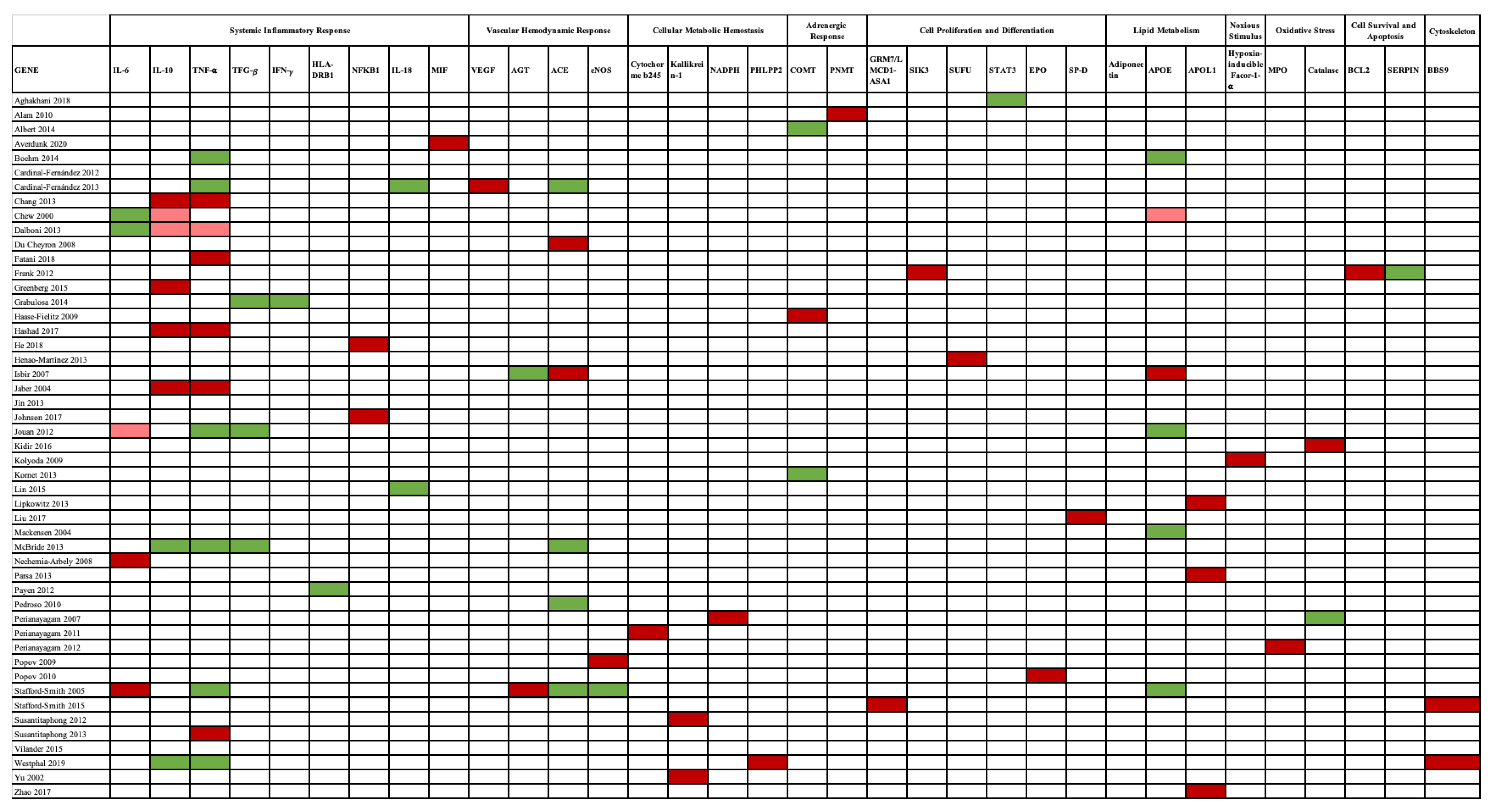
| Study | Design | Clinical Settings | Participants/Population Characteristics | Patients with AKI | Studied Polymorphisms | Outcomes | AKI Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chew, et al., 2000 | Prospective, Observational Cohort Study | CSA-AKI | 564 patients undergoing CABG Irish population | --- | Apolipoprotein E (APOE) | APO4 ε4 allele is associated with reduced postoperative increase in serum Cr after cardiac surgery, compared with the ε3 or ε2 allele | By comparisons of preoperative (CrPre), peak in-hospital postoperative (CrMax) and perioperative change (∆Cr) in serum Cr values |
| Yu, et al., 2002 | Case/Control Study | End-stage renal disease (ESRD) in African Americans | 85 control subjects, 92 type 2 diabetes ESRD patients, and 76 non-diabetic ESRD families. US population | 199 Patients | KLK1 promoter | KLK1 is associated with hypertension ESRD | |
| Jaber, et al., 2004 | Prospective Study | In-hospital patients requiring dialysis | Hospitalized patients who required intermittent hemodialysis England population | 61 Patients | TNF-α and IL-10 | TNF-α and IL-10 gene polymorphisms are related to increased mortality among patients with AKI requiring dialysis | Renal failure requiring dialysis |
| Mackensen, et al., 2004 | Prospective, Observational Cohort Study | Elective CABG patients | 130 coronary patients US population | --- | Apolipoprotein E (APOE) | Non-APOE4 patients are more vulnerable to AKI after cardiac operation APO4 ε4 allele is associated with a nephroprotective effect | Perioperative difference in serum Cr (∆Cr = Crmax Post – Cr Pre) |
| Stafford-Smith, et al., 2005 | Prospective, longitudinal study | CSA-AKI | 3149 patients undergoing CABG US population | More than half the patients |
Interleukin 6 -572C, AGT 842C, APO E 448C [ε4], AGTR1 A1166C, and [eNOS] 894T ACE I/D |
AGT 842C and IL-6 ---572C, a variant pattern that occurs in 6% of Caucasians) was associated with major postoperative renal injury, with an average peak serum Cr increase of 121% | Difference between preoperative and peak postoperative Cr values |
| Isbir, et al., 2007 | Prospective, Observational Cohort Study | CSA-AKI | 248 elective CABG patients Turkish population | 54 Patients | ACE II, ID, and DD, APO E, and AGTR1 A1166C genotype | ACE I/D and APO E gene polymorphisms may play a role in the development of AKI after cardiac surgery. AGTR1 does not have a unique association with postoperative AKI | RIFLE |
| Perianayagam, et al., 2007 | Prospective Cohort Study | Hospitalized patients with AKI | US population Hospitalized patients with established AKI of mixed cause and severity | 200 patients | Coding region (C to T substitution at position +242) NADPH oxidase p22phox subunit gene and promoter region (C to T substitution at position -262) of the catalase gene | NADPH oxidase p22phox subunit at position +242 is associated with dialysis requirement or hospital death among patients with AKI | An increase in Cr by 0.5, 1.0, or 1.5 mg/dL from a baseline level of ≤1.9, 2.0 to 4.9, and ≥5.0 mg/dL |
| Nechemia- Arbely, et al., 2008 | Animal Basic Research | Experimental mice model | IL-6–deficient mice were compared with wild-type mice | --- | IL-6/sIL-6R | IL-6 promotes a renal inflammatory response | Nephrotoxic-induced AKI |
| Du Cheyron, et al., 2008 | Prospective Cohort Study | AKI in ICU admitted patients | 180 ICU patients France population | 73 patients | ACE I/D polymorphism | ACE II genotype was independently associated with increased risk of AKI | RIFLE |
| Haase-Fielitz, et al., 2009 | Prospective, observational, cohort study | CSA-AKI | 260 patients undergoing cardiac surgery Australian population | 53 patients | Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) | COMT LL homozygosity is an independent risk factor for AKI | RIFLE |
| Popov, et al., 2009 | Prospective Study | CSA-AKI | 497 patients undergoing cardiac surgery German population | 287 patients | T-786C endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) | T-786C eNOS polymorphism is associated with AKI and increase the occurrence of RRT following cardiac surgery | RIFLE |
| Kolyada, et al., 2009 | Prospective Cohort Study | Hospitalized patients with AKI | Adult patients with AKI US population | 241 patients | Hypoxia-inducible factor-1a (HIF-1α) | HIF-1 α gene polymorphism predicts adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients with AKI | AKIN |
| Alam, et al., 2010 | Case/Control Study | Hospitalized patients with AKI | 961 Caucasian subjects US population | 194 Patients |
Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) PNMT promoter G–161A (rs876493) and coding A + 1543G (rs5638) | In Caucasians, PNMT SNPs are associated with the development of AKI, disease severity, and in-hospital mortality | AKIN |
| Popov, et al., 2010 | Prospective Cohort Study | CSA-AKI | 481 Patients undergoing Cardiac Surgery German population | 274 Patients | SNP rs1617640 in the promoter of the EPO gene | EPO rs1617460 TT allele is associated with more acute RRT | RIFLE |
| Perianayagam, et al., 2011 | Prospective, Observational Cohort Study | Hospitalized adults with AKI | 256 hospitalized patients US population | 256 Patients | CYBA gene polymorphisms (rs8854, rs3794624, rs4673, rs4782390, and rs1049255) | CYBA rs4782390, rs4673, rs3794624, and rs8854 polymorphisms were associated with dialysis requirement | A rise in serum Cr by 0.5, 1.0, or 1.5 mg/dL from a baseline level ≤1.9, 2.0–4.9, or ≥5.0 mg/dL |
| Jouan, et al., 2012 | Prospective Cohort Study | CSA-AKI | 126 Patients undergoing CABG France population | 8 Patients | LTA (Cys13Arg,þ252A > G), TNF-α (-308G > A), IL6 (-597G > A, -572G > C, -174G > C), IL10 (-592C > A, c.*117C > T), and APOE (Cys112Arg, Arg158Cys). | IL6-572GCþCC/IL10-592CC were associated with AKI | As Cr levels > 200 mmol/L or, particularly for patients having a baseline plasma Cr level > 150 mmol/L, the requirement for dialysis at any time after surgery. |
| Cardinal-Fernandez, et al., 2012 | Systematic Review | Genetic Predisposition to AKI | 4.835 patients included | 12 References | ACE, eNOS, FNMT y COMT, TNF-α, IL10, IL6, HIP-1A, EPO, NAPH oxidase, and APOE | AKI susceptibility and severity is related to genetic factors that are involved in different physiopathological mechanisms | AKI term search |
| Susantitaphong, et al., 2012 | Case/Control Study | Hospitalized cases with AKI of multiple etiology from two acute care facilities | 481 subjects (214 hospitalized patients with AKI of mixed causes and 267 healthy subjects) | 214 Patients | Multiallelic KLK1 promoter gene | KLK1 promoter polymorphisms are associated with development of AKI and adverse outcomes | AKIN |
| Perianayagam, et al., 2012 | Prospective Cohort Study | Hospitalized patients with AKI | 262 adults hospitalized with acute kidney injury | 262 Patients | MPO polymorphisms rs2243828, rs7208693, rs2071409, and rs2759 | MPO polymorphisms rs2243828, rs7208693, rs2071409, and rs2759 were associated with lower urine output, more dialysis requirement and higher in-hospital mortality. | AKIN |
| Payen, et al., 2012 | Prospective multicenter observational study | Critical ill patients with severe sepsis and septic shock | 221 Patients France population | 129 Patients | HLA-DRB1 | HLA-DRB alleles were found to be associated with less requirement of RRT | AKIN |
| Frank, et al., 2012 | Retrospective Study | AKI in Patients with septic shock | 1,264 patients with septic shock | 637 Patients | BCL2 Genetic Variants SERPINA4 SNP rs2093266 | BCL2 SNPs rs8094315 and rs12457893 were associated with a decreased risk of developing AKI SERPINA4 SNP rs2093266 was linked to a decreased risk to develop AKI | AKIN |
| Jin, et al., 2013 | Animal Basic Research | Mouse Model of Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury | Wild-type mice, compared to adiponectin knockout mice | --- | Adiponection | Adiponectin wild-type mice had less kidney dysfunction and tubular damage. There was more inhibition of NF-κB activation and reduced expression of the proinflammatory molecules IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, and MIP-2 | Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury |
| Cardinal-Fernández, et al., 2013 | Prospective, observational, cohort study | Patients admitted to the ICU with severe sepsis | 139 Patients with severe sepsis | 65 patients | Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion; tumor necrosis factor α−376, −308, and −238; interleukin-8 − 251; vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) +405 and +936; and pre–B-cell colony-enhancing factor −1001 | VEGF + 936 CC genotype increased the risk to develop AKI in patients with severe sepsis. | RIFLE |
| McBride, et al., 2013 | Prospective, observational, cohort study | CSA-AKI | 408 elective cardiac surgery patients Irish population | 69 Patients | TNF/G-308A, TGF-β 1-509 C/T, IL10/G-1082A and ACE I/D. | TNF/G-308A, TGF-β 1-509 C/T, IL10/G-1082A and ACE I/D. genotype were not associated with AKI | Drop from baseline eGFR of greater than 25% (as calculated by the method of MDRD. |
| Susantitaphong, et al., 2013 | Cohort Study | Hospitalized patients with AKI were recruited from two acute care hospitals | 262 hospitalized German population | 262 Patients | Promoter region of TNF-α | The TNF-α rs1800629 gene polymorphism is associated with markers of kidney disease severity and distant organ dysfunction among patients with AKI | A rise in serum Cr by 0.5, 1.0, or 1.5 mg/dL from a baseline level of ≤1.9, 2.0–4.9, or ≥5.0 mg/dL |
| Chang, et al., 2013 | Prospective Case/Control Study | Patients who underwent coronary artery intervention | 53 contrast induced-AKI patients compared to 455 control subjects. | 53 contrast induced-AKI patients | Four IL-10 tag SNPs (rs1554286, rs3021094, rs3790622, rs1800896) and three TNF-α tag SNPs (rs1799964, rs1800630, rs1800629) | Gene polymorphisms of IL-10 and TNF-α are associated with Contrast induced-AKI | A rise in Cr of ≥0.5 mg/dL (44 mmol/L) or a 25% increase from baseline value, assessed within 48 h after a radiological procedure |
| Kornet, et al., 2013 | Prospective, Observational Cohort Study | CSA-AKI | 1741 patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery German population | 398 Patients | COMT-Val158Met-(G/A) polymorphism (rs4680) | COMT-Val158Met-(G/A) polymorphism (rs4680) was not associated with CSA-AKI | RIFLE |
| Dalboni, et al., 2013 | Prospective nested case–control | ICU Setting | 303 ICU patients and 244 healthy individuals | 139 Patients | -308 G < A (TNF)- α, -174 G > C IL-6 and -1082 G > A IL-10 | Both low TNF-α and low IL-10 producer phenotypes were an independent risk factor of AKI and/or death and RRT and/or death in ICU patients. | AKIN, and RIFLE |
| Lipkowitz, et al., 2013 | Case/Control Study | Hypertension-attributed nephropathy who developed severe CKD | 675 Cases compared to 618 Controls African Americans | 675 Patients | APOL1 and MYH9 genes | APOL1 risk variants were consistently associated with renal disease progression | (1) Developing ESRD or Cr > 2 mg/mL; (2) developing ESKD or Cr > 3 mg/dL |
| Parsa, et al., 2013 | AASK and CRIC Study Cohort Study | Black patients in the United States with chronic kidney disease US Population | AASK: 693 black patients with chronic kidney disease attributed to hypertension CRIC: 2955 white patients and black patients with chronic kidney disease | 492 Patients in the AASK Study | APOL1 | APOL1 were associated with the higher rates of end-stage renal disease and progression of CKD that were observed in black patients as compared with white patients | A doubling of the Cr (equivalent to a reduction of 50% in the GFR) from baseline or incident ESRD |
| Henao-Martínez, et al., 2013 | Prospective, Observational Cohort Study | AKI in sepsis | 250 hospitalized patients | 159 Patients | SUFU | rs10786691 (p = 0.03), rs12414407 (p = 0.026), rs10748825 (p = 0.01), and rs7078511 correlated to AKI | Based on Serum Cr |
| Boehm, et al., 2014 | Prospective, Observational Cohort Study | CSA-AKI | 1415 elective cardiac surgery patients German population | 318 Patients | Apolipoprotein E (ApoE ε2, ε3, ε4) (rs429358 and rs7412) and TNF-α-308 G > A (rs1800629). | ApoE (ε2, ε3, ε4) polymorphism and the TNF-α-308 G > A polymorphism are not associated with CSA-AKI | RIFLE |
| Grabulosa, et al., 2014 | Prospective nested case-control study | ICU patients | 139 ICU AKI patients, 164 ICU patients without AKI, compared to 244 healthy individuals. | 139 Patients | rs1800470 (codon 10 T/C), rs1800471 (codon 25 C/G) from the TGF-β, and rs2430561 (+874 T/A) from IFN-γ | Genetic polymorphism of the TGF-β and IFN-γ was not associated as a risk factor for AKI | AKIN, RIFLE |
| Albert, et al., 2014 | Prospective, Observational Cohort Study | CSA-AKI | 195 patients German Cohort | 22 Patients | COMT-Val158Met | COMT genotype may associate with different patterns of renal functional changes and tubular stress biomarker response after cardiac surgery. | RIFLE |
| Lin, et al., 2015 | Systematic Review | AKI | 11 References from 3 countries 2796 patients | 538 patients | IL-18 | IL-18 could be used as a biomarker in the prediction of AKI | RIFLE, AKIN, pRIFLE |
| Stafford-Smith, 2015 | GWAS | AKI following CAGB | 873 non-emergent CABG patients (discovery) 380 cardiac surgery patients (replication) US population | 294 in Discovery Cohort 119 in Replication Cohort | The rs13317787 in GRM7|LMCD1-AS1 intergenic region (3p21.6) and rs10262995 in BBS9 (7p14.3) | GRM7|LMCD1-AS1 and BBS9 were associated with post-CABG AKI | KDIGO, AKIN, RIFLE |
| Greenberg, et al., 2015 | Prospective Study | Pediatric Cardiac Surgery | Cohort, including 106 children ranging in age from 1 month to 18 years undergoing CPB | 24 Patients | IL-6 and IL-10 | Preoperative plasma IL-6 levels are associated with AKI | At least a doubling of the baseline Cr concentration or dialysis |
| Vilander, et al., 2015 | Systematic Review | Genetic predisposition to AKI | 4027 References | 28 References | ACE; AGTR1; AGT; APOE; BCL-2; COMT; CYBA; eNOS; EPO; FCGR2A; FCGR3A; FCGR3B; GLI1; HHIP; HIF-1- α; HLA-DRB1; IL-6; IL-8; IL-10; LTA; MPO; NADPH; PBEF; PNMT; PTCH1; PTCH2; SERPINA4; SERPINA5; SIK3; SMO; SUFU; TGF-β; TNF-α; VEGF. | Articles quite heterogeneous and of moderate quality | KDIGO, AKIN, RIFLE |
| Kidir, et al., 2016 | Cross-sectional Study | Case (AKI)/Control Hospitalized patients | Turkish population 90 AKI patients compared to 101 healthy volunteers | 90 AKI patients | MnSOD rs4880, GPX1 rs10500450 and CAT rs769217 | T allele of CAT rs769217 was associated with increased morbidity and mortality | KDIGO |
| Zhao, et al., 2017 | GWAS | Cases and controls for the discovery population were derived from two independent populations of critically ill patients. The second population enrolled patients who underwent cardiac surgery | Discovery population: 760 acute kidney injury cases and 669 controls. Replication population: 206 cases and 1406 Controls | 760 patients (Discovery) and 206 (Replication) | APOL1-regulator IRF2 and AKI–related TBX1 genes | rs62341639 and rs62341657 on chromosome 4 near APOL1-regulator IRF2, and rs9617814 and rs10854554 on chromosome 22 near acute kidney injury–related gene TBX1 are associated with AKI | At least 0.3-mg/dL or 50% increase in Cr from baseline |
| Johnson, et al., 2017 | Animal Basic Research | Experimental mice model | 74 male Wistar rats | 74 mice | Nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) | Inhibition IκB kinase improves kidney recovery and decreases fibrosis | AKI caused by unilateral nephrectomy plus contralateral ischemia and reperfusion injury |
| Hashad, et al., 2017 | Prospective Cohort Study | Critical ill patients with severe sepsis | 150 patients with severe sepsis | 66 patients | -398 G/C of TNF-α and -1082G/A of IL-10 | Genotypes of both TNF-α and IL-10 were associated with AKI | --- |
| Liu, et al., 2017 | Case/Control Study | AKI in ICU Chinese population | 159 AKI patients (88 female and 71 male) admitted in ICU compared to 120 age-matched healthy volunteers (50 female and 70 male) | 159 patients | SP-D polymorphism Thr11Met and Thr160Ala | SP-D-Thr11Met genotype was more susceptible to AKI | KDIGO |
| Fatani, et al., 2018 | Prospective Study | Critical ill patients Severe sepsis induced AKI | 200 critically-ill patients (112 had severe sepsis and septic shock and 88 were septic) | 127 patients | TNF-α rs 361525 | TNF-α rs 361525 was significantly associated with AKI | RIFLE |
| He, et al., 2018 | Retrospective Case/Control Study | Children with AKI | 1138 children with AKI and 1382 non-AKI controls. | 1138 Children | TNF-α, IL6, IL10, IL18, NFKB1 and NFKBIA | NFKB1 rs28362491, NFKBIA rs2233406 and NFKBIA rs696 were associated with AKI in Children | pRIFLE |
| Aghakhani Chegeni, et al., 2018 | Prospective Cohort Study | Iraninan patients undergoing Cardiac surgery | 123 Patients undergoing CABG | 63 Patients | STAT3 polymorphism | Rs1053004 GG genotype significantly decreased CSA-AKI risk | AKIN |
| Westphal, et al., 2019 | Prospective, double-blind, multicenter, randomized trial (RIPHeart) GWAS. | Myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, acute stroke, acute kidney injury and delirium after cardiac surgery | 1170 patients of both genders (871 males, 299 females) undergoing elective cardiac surgery | 52 Patients | 547,644 variants | PHLPP2, BBS9, RyR2, DUSP4 and HSPA8, associated with new onset of atrial fibrillation, delirium, myocardial infarction, AKI and stroke after cardiac surgery. | --- |
| Vilander, et al., 2019 | Prospective, observational Finnish Acute Kidney Injury (FINNAKI) study | Cohort of Finnish critically ill patients | 2647 Critical ill patients without chronic kidney disease | 625 patients | TNF-α (rs1800629), IL6 (rs1800796, rs1800795, rs10499563, rs1474347, rs13306435, rs2069842 and rs2069830), IL-8 (rs4073), IL10 (rs1800896), NOS3 (rs2070744), NFKB1A (rs1050851), AGT (rs699 and rs2493133), VEGFA (rs2010963 and rs3025039), EPO (rs1617640), SUFU (rs10748825), HIF1-α (rs11549465), PNMT (rs876493), MPO (rs7208693), COMT (rs4680), HSPB1 (rs2868371), SP-D (rs2243639 and rs721917), HAMP (rs10421768) and BBS9 (rs10262995) genes | rs1800629 in TNF-α; and rs1800896 in IL-10 were not associated to AKI | KDIGO |
| Averdunk, et al., 2020 | Prospective, double-blind, multicenter, randomized trial RIPHeart Study | CSA-AKI | 1116 patients undergoing cardiac surgery | 170 Patients | MIF CATT5–7 (rs5844572/rs3063368, “-794”) and G > C single-nucleotide polymorphism (rs755622,-173) | The MIF CATT7 allele associates with a higher risk of AKI and death after cardiac surgery | KDIGO |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortega-Loubon, C.; Martínez-Paz, P.; García-Morán, E.; Tamayo-Velasco, Á.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Jorge-Monjas, P.; Tamayo, E. Genetic Susceptibility to Acute Kidney Injury. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143039
Ortega-Loubon C, Martínez-Paz P, García-Morán E, Tamayo-Velasco Á, López-Hernández FJ, Jorge-Monjas P, Tamayo E. Genetic Susceptibility to Acute Kidney Injury. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(14):3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143039
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtega-Loubon, Christian, Pedro Martínez-Paz, Emilio García-Morán, Álvaro Tamayo-Velasco, Francisco J. López-Hernández, Pablo Jorge-Monjas, and Eduardo Tamayo. 2021. "Genetic Susceptibility to Acute Kidney Injury" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 14: 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143039
APA StyleOrtega-Loubon, C., Martínez-Paz, P., García-Morán, E., Tamayo-Velasco, Á., López-Hernández, F. J., Jorge-Monjas, P., & Tamayo, E. (2021). Genetic Susceptibility to Acute Kidney Injury. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(14), 3039. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10143039






