Serum Liberation of Fetal Fibronectin Variants in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: ED-A+ Fn as Promising Novel Biomarker of Pulmonary Vascular and Right Ventricular Myocardial Remodeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Blood Samples and Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Serum Quantification of Fetal Variants of Fibronectin by ELISA Technique
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characterization of the Study Population
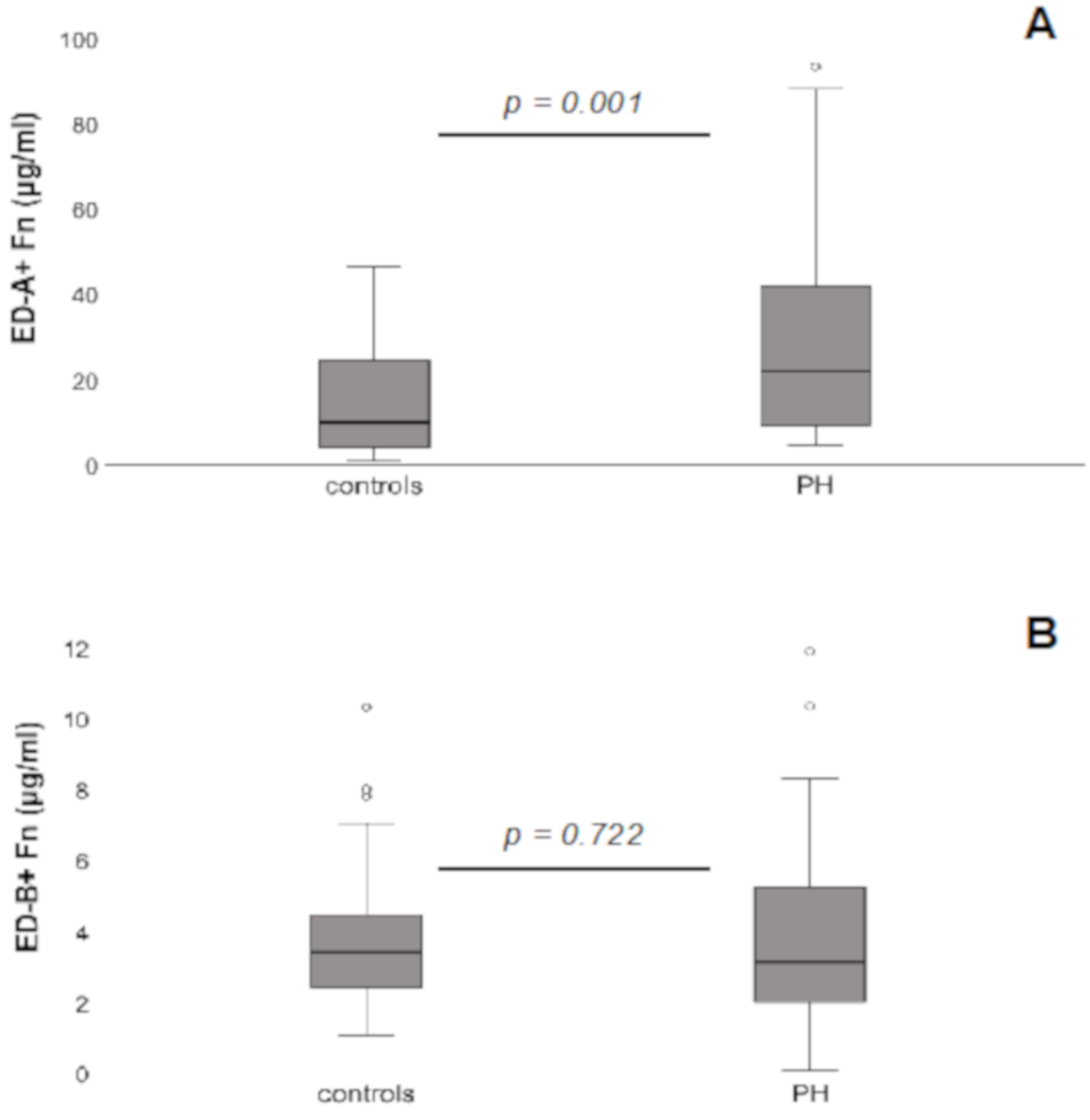
3.2. Serum Levels of ED-A+ Fn and ED-B+ Fn in PH Patients Compared to Controls
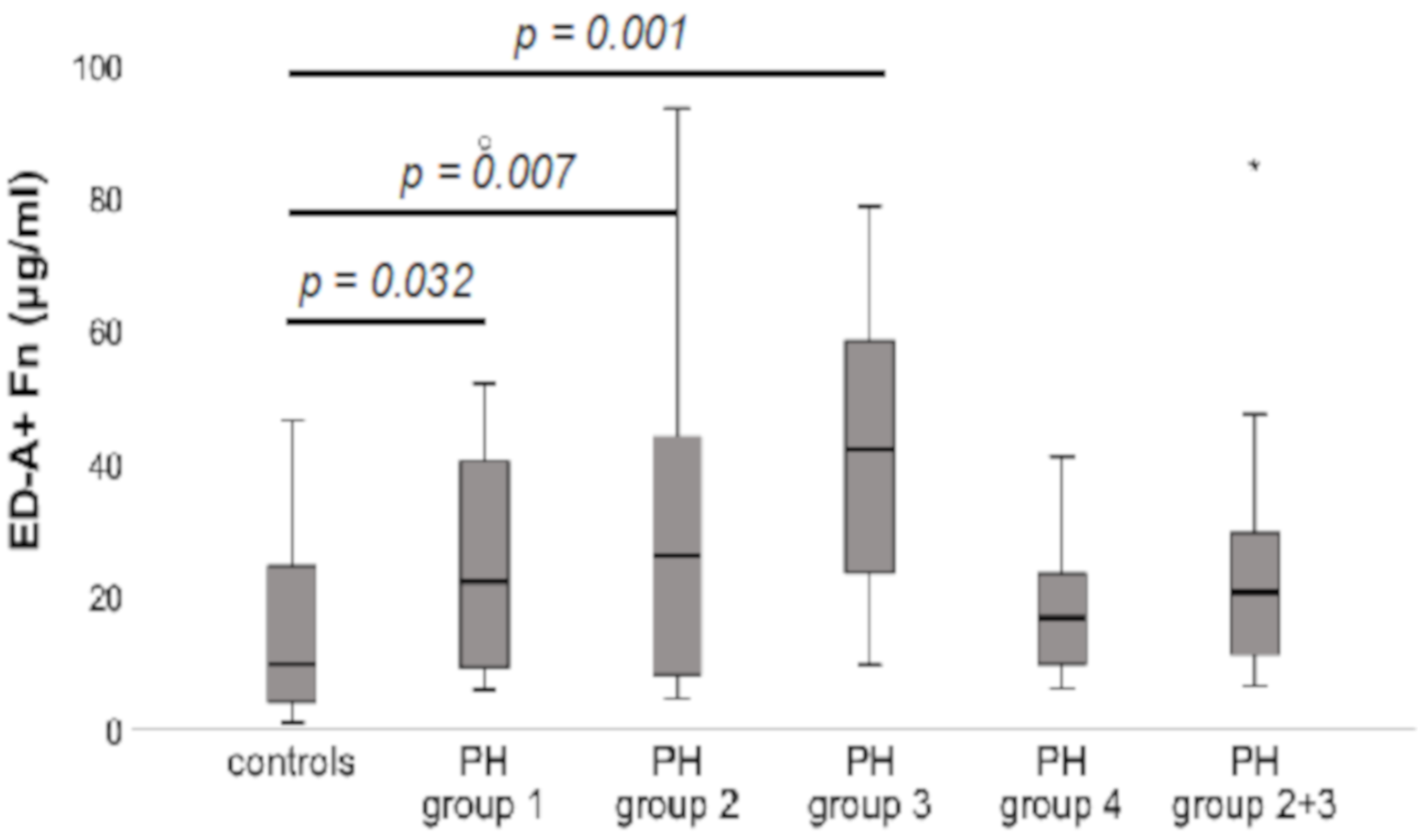
3.3. Serum Levels of ED-A+ Fn in Comparison between the Different Aetiological Groups within the PH Patients’ Collective Compared to Controls
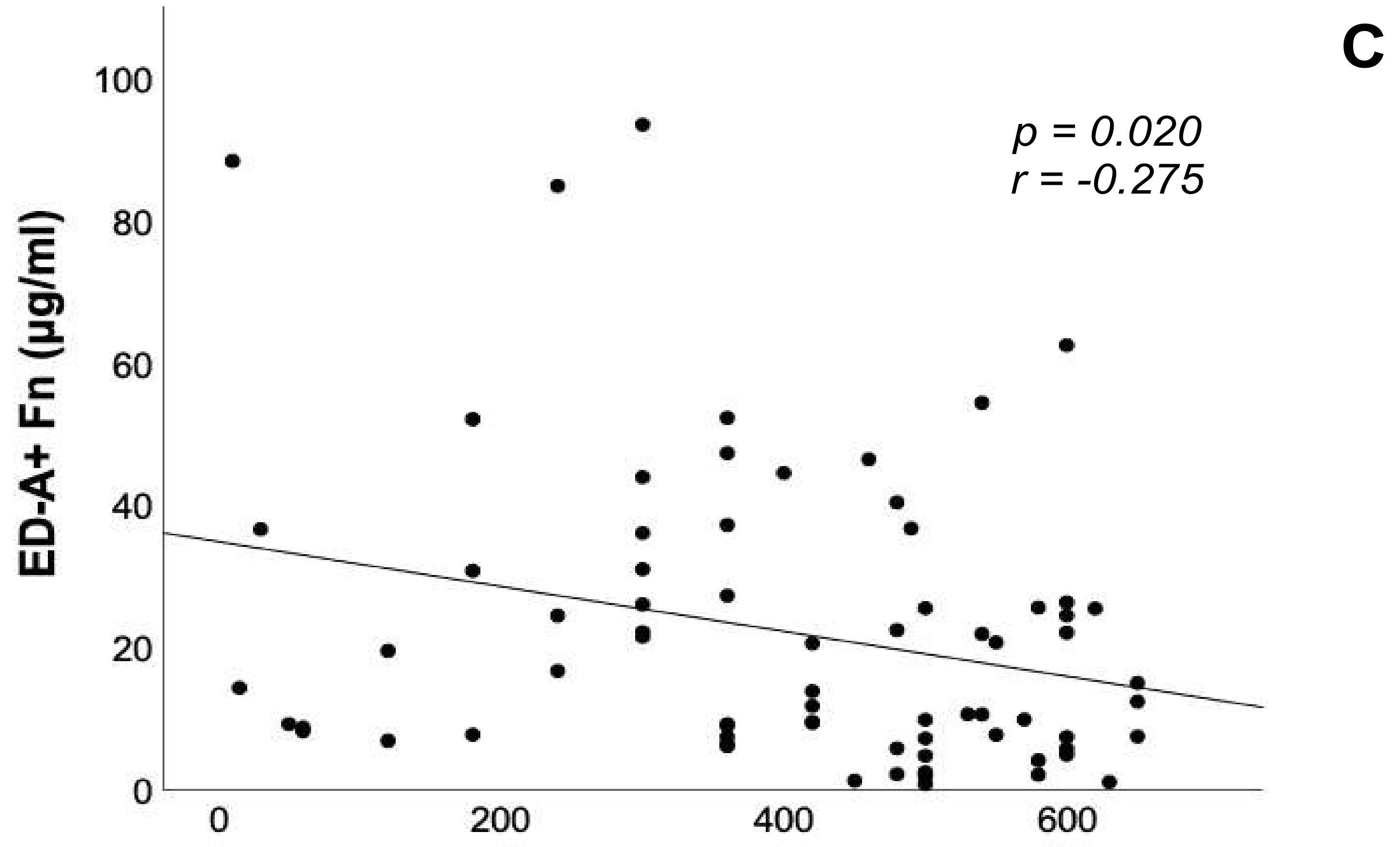
3.4. Correlation Analyses of ED-A+ Fn Serum Levels with Brain Natriuretic Peptide, 6-Minute Walk Distance and Echocardiographic Parameters
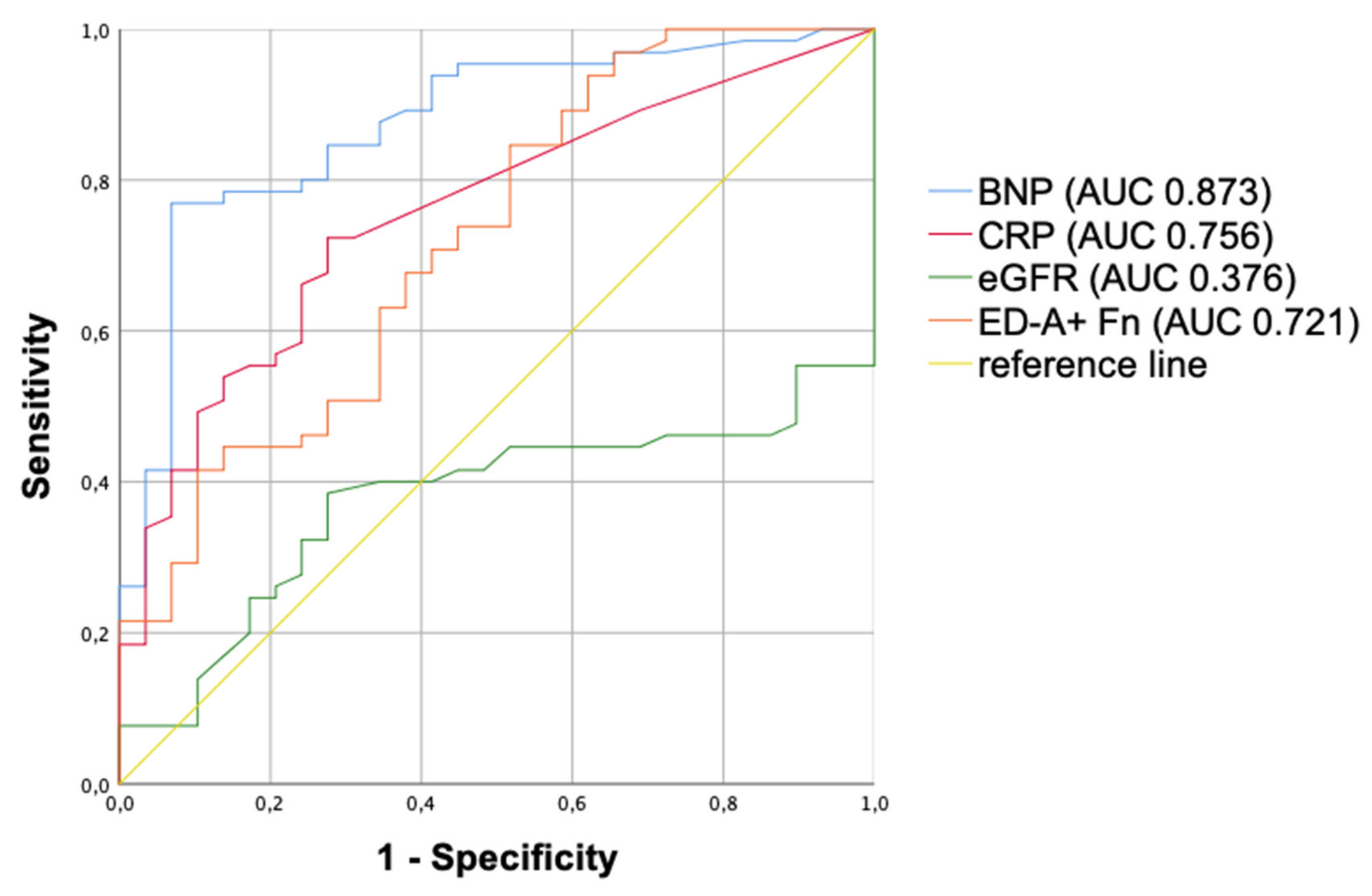
3.5. Multivariate Analysis and ROC Curves
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenkranz, S.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Grünig, E.; Klose, H.; Olschewski, H.; Hoeper, M.M. Cologne consensus conference on pulmonary hypertension—Update 2018. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 272, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiéry, J.-L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.M.; Kaminski, K.A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Noordegraaf, A.V.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benza, R.L.; Miller, D.P.; Barst, R.J.; Badesch, D.B.; Frost, A.E.; McGoon, M.D. An Evaluation of Long-term Survival From Time of Diagnosis in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension From the REVEAL Registry. Chest 2012, 142, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordegraaf, A.V.; Westerhof, B.E.; Westerhof, N. The Relationship Between the Right Ventricle and its Load in Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savale, L.; Weatherald, J.; Jaïs, X.; Vuillard, C.; Boucly, A.; Jevnikar, M.; Montani, D.; Mercier, O.; Simonneau, G.; Fadel, E.; et al. Acute decompensated pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkranz, S.; Lang, I.M.; Blindt, R.; Bonderman, D.; Bruch, L.; Diller, G.P.; Felgendreher, R.; Gerges, C.; Hohenforst-Schmidt, W.; Holt, S.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension associated with left heart disease: Updated Recommendations of the Cologne Consensus Conference 2018. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 272, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Apitz, C.; Grünig, E.; Halank, M.; Ewert, R.; Kaemmerer, H.; Kabitz, H.-J.; Kähler, C.; Klose, H.; Leuchte, H.; et al. Targeted therapy of pulmonary arterial hypertension: Updated recommendations from the Cologne Consensus Conference 2018. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 272, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, H.; Konstantinides, S.; Lang, I.M.; Bunck, A.C.; Gerges, M.; Gerhardt, F.; Grgic, A.; Grohé, C.; Guth, S.; Held, M.; et al. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH): Updated Recommendations from the Cologne Consensus Conference 2018. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 272, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Xu, Q.; McTiernan, C.; Lai, Y.-C.; Osei-Hwedieh, D.; Gladwin, M. Novel Targets of Drug Treatment for Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2015, 15, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajecki, D.; Gawrys, J.; Szahidewicz-Krupska, E.; Doroszko, A. Novel Molecular Mechanisms of Pulmonary Hypertension: A Search for Biomarkers and Novel Drug Targets—From Bench to Bed Site. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, L.C.; Bye, H.; Brock, M. The pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension—An update. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2015, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, V.V.; Shah, S.J.; Souza, R.; Humbert, M. Management of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1976–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, I.; Tura-Ceide, O.; Peinado, V.I.; Barberà, J.A. Updated Perspectives on Pulmonary Hypertension in COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2020, 15, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitling, S.; Ravindran, K.; Goldenberg, N.M.; Kuebler, W.M. The pathophysiology of pulmonary hypertension in left heart disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015, 309, L924–L941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuder, R.M. Pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrof, S.; Hynes, R.O. Fibronectins in vascular morphogenesis. Angiogenesis 2009, 12, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Jung, C.; Lauten, A.; Figulla, H.R.; Berndt, A. Tenascin-C in cardiovascular remodeling: Potential impact for diagnosis, prognosis estimation and targeted therapy. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golledge, J.; Clancy, P.; Maguire, J.; Lincz, L.; Koblar, S. The role of tenascin C in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 92, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, I.; Grün, K.; Müller, L.M.; Kretzschmar, D.; Fritzenwanger, M.; Yilmaz, A.; Lauten, A.; Jung, C.; Schulze, P.C.; Berndt, A.; et al. Increased Serum Levels of Fetal Tenascin-C Variants in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: Novel Biomarkers Reflecting Vascular Remodeling and Right Ventricular Dysfunction? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Neri, D.; Berndt, A. Chronic cardiac allograft rejection: Critical role of ED-A+fibronectin and implications for targeted therapy strategies. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, J.-N.; Trachsel, E.; Scheuermann, J.; Neri, D. Ligand-Based Vascular Targeting of Disease. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, E.S.; Baralle, F.E.; Muro, A.F. New insights into form and function of fibronectin splice variants. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zollinger, A.J.; Smith, M.L. Fibronectin, the extracellular glue. Matrix Biol. 2017, 60–61, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, K.; Junker, K.; Franz, M.; Hentschel, J.; Richter, P.; Gajda, M.; Göhlert, A.; Von Eggeling, F.; Heller, R.; Giavazzi, R.; et al. Differential vascular expression and regulation of oncofetal tenascin-C and fibronectin variants in renal cell carcinoma (RCC): Implications for an individualized angiogenesis-related targeted drug delivery. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 137, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabler, U.; Berndt, A.; Kosmehl, H.; Mandel, U.; Zardi, L.; Muller, S.; Stelzner, A.; Katenkamp, D. Matrix remodelling in dilated cardiomyopathy entails the occurrence of oncofetal fibronectin molecular variants. Heart 1996, 75, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.; Matusiak-Brückner, M.; Richter, P.; Grün, K.; Ziffels, B.; Neri, D.; Maschek, H.; Schulz, U.; Pfeil, A.; Jung, C.; et al. De novo expression of fetal ED-A+ fibronectin and B+ tenascin-C splicing variants in human cardiac allografts: Potential impact for targeted therapy of rejection. J. Mol. Histol. 2014, 45, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.; Brehm, B.R.; Richter, P.; Gruen, K.; Neri, D.; Kosmehl, H.; Hekmat, K.; Renner, A.; Gummert, J.; Figulla, H.R.; et al. Changes in extra cellular matrix remodelling and re-expression of fibronectin and tenascin-C splicing variants in human myocardial tissue of the right atrial auricle: Implications for a targeted therapy of cardiovascular diseases using human SIP format antibodies. J. Mol. Histol. 2010, 41, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Berndt, A.; Neri, D.; Galler, K.; Grün, K.; Porrmann, C.; Reinbothe, F.; Mall, G.; Schlattmann, P.; Renner, A.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1, B+ tenascin-C and ED-A+ fibronectin in dilated cardiomyopathy: Potential impact on disease progression and patients’ prognosis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.; Berndt, A.; Grün, K.; Richter, P.; Kosmehl, H.; Neri, D.; Gummert, J.; Figulla, H.R.; Brehm, B.R.; Renner, A. Expression of extra domain A containing fibronectin in chronic cardiac allograft rejection. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2011, 30, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldinger, A.; Brehm, B.R.; Richter, P.; Bossert, T.; Gruen, K.; Hekmat, K.; Kosmehl, H.; Neri, D.; Figulla, H.-R.; Berndt, A.; et al. Comparative analysis of oncofetal fibronectin and tenascin-C expression in right atrial auricular and left ventricular human cardiac tissue from patients with coronary artery disease and aortic valve stenosis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 135, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouyou, B.; Grün, K.; Kerschenmeyer, A.; Villa, A.; Matasci, M.; Schrepper, A.; Pfeil, A.; Bäz, L.; Jung, C.; Schulze, P.; et al. Therapeutic Evaluation of Antibody-Based Targeted Delivery of Interleukin 9 in Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.; Grün, K.; Betge, S.; Rohm, I.; Ndongson-Dongmo, B.; Bauer, R.; Schulze, P.C.; Lichtenauer, M.; Petersen, I.; Neri, D.; et al. Lung tissue remodelling in MCT-induced pulmonary hypertension: A proposal for a novel scoring system and changes in extracellular matrix and fibrosis associated gene expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81241–81254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziffels, B.; Ospel, J.; Grün, K.; Neri, D.; Pfeil, A.; Fritzenwanger, M.; Figulla, H.R.; Jung, C.; Berndt, A.; Franz, M. Detection of Soluble ED-A+Fibronectin and Evaluation as Novel Serum Biomarker for Cardiac Tissue Remodeling. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, E.; Cordazzo, C.; Quarto, R.; Zardi, L.; Rosano, C. C6: A Monoclonal Antibody Specific for a Fibronectin Epitope Situated at the Interface between the Oncofoetal Extra-Domain B and the Repeat III8. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnemolla, B.; Borsi, L.; Zardi, L.; Owens, R.J.; Baralle, F.E. Localization of the cellular-fibronectin-specific epitope recognized by the monoclonal antibody IST-9 using fusion proteins expressed in E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1987, 215, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäz, L.; Dannberg, G.; Grün, K.; Westphal, J.; Möbius-Winkler, S.; Jung, C.; Pfeil, A.; Schulze, P.; Franz, M. Serum Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Remodelling Reflect Extra-Valvular Cardiac Damage in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Grün, K.; Richter, P.; Brehm, B.R.; Fritzenwanger, M.; Hekmat, K.; Neri, D.; Gummert, J.; Figulla, H.R.; Kosmehl, H.; et al. Extra cellular matrix remodelling after heterotopic rat heart transplantation: Gene expression profiling and involvement of ED-A+ fibronectin, alpha-smooth muscle actin and B+ tenascin-C in chronic cardiac allograft rejection. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 134, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Généreux, P.; Pibarot, P.; Redfors, B.; Mack, M.J.; Makkar, R.R.; Jaber, W.A.; Svensson, L.G.; Kapadia, S.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Thourani, V.H.; et al. Staging classification of aortic stenosis based on the extent of cardiac damage. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 3351–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieverse, R.I.Y.; Marcus, D.; Van Der Wiel, A.M.; Van Limbergen, E.J.; Theys, J.; Yaromina, A.; Lambin, P.; Dubois, L.J. Human fibronectin extra domain B as a biomarker for targeted therapy in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menrad, A.; Menssen, H.D. ED-B fibronectin as a target for antibody-based cancer treatments. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolò, G.; Salvi, S.; Oliveri, G.; Borsi, L.; Castellani, P.; Zardi, L. Expression of tenascin and of the ED-B containing oncofetal fibronectin isoform in human cancer. Cell Differ. Dev. 1990, 32, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandrapalli, S.; Tariq, S.; Kumar, J.; Aronow, W.S.; Malekan, R.; Frishman, W.H.; Lanier, G.M. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Cardiol. Rev. 2018, 26, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Sitbon, O.; Chaouat, A.; Bertocchi, M.; Habib, G.; Gressin, V.; Yaiïci, A.; Weitzenblum, E.; Cordier, J.-F.; Chabot, F.; et al. Survival in Patients With Idiopathic, Familial, and Anorexigen-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in the Modern Management Era. Circulation 2010, 122, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Sitbon, O.; Chaouat, A.; Bertocchi, M.; Habib, G.; Gressin, V.; Yaici, A.; Weitzenblum, E.; Cordier, J.-F.; Chabot, F.; et al. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in France. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doddapattar, P.; Dev, R.; Jain, M.; Dhanesha, N.; Chauhan, A.K. Differential Roles of Endothelial Cell-Derived and Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Fibronectin Containing Extra Domain A in Early and Late Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Controls (n = 40) | PH Patients (n = 80) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Parameters | |||
| Age (years) | 66 ± 7 | 71 ± 13 | <0.001 |
| Male gender (%) | 33 | 39 | n.s. |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.9 ± 4.7 | 28.6 ± 6.0 | n.s. |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 146 ± 31 | 143 ± 25 | n.s. |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 81 ± 16 | 81 ± 14 | n.s. |
| Functional class | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 2.6 ± 0.8 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Arterial hypertension (%) | 95 | 83 | n.s. |
| Coronary artery disease/infarction (%) | 0 | 26 | 0.001 |
| Hypertensive heart disease (%) | 59 | 50 | n.s. |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 18 | 49 | 0.002 |
| Pulmonary diseases (%) | 5 | 44 | <0.001 |
| COPD (%) | 3 | 24 | 0.004 |
| Pulmonary fibrosis (%) | 0 | 11 | 0.031 |
| Chronic kidney disease (%), viz. GFR < 50 mL/min | 8 | 49 | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidaemia (%) | 85 | 57 | 0.002 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 20 | 49 | 0.002 |
| Obesity (%), viz. BMI > 30 kg/m2 | 43 | 38 | n.s. |
| Autoimmune diseases (%) | 0 | 16 | 0.009 |
| Smoking (%) | 29 | 52 | n.s. |
| Medication | |||
| ASA (%) | 25 | 19 | n.s. |
| Beta blockers (%) | 63 | 64 | n.s. |
| ACE-Inhibitors/Sartans (%) | 85 | 76 | n.s. |
| Calcium channel blockers (%) | 25 | 27 | n.s. |
| Diuretics (%) | 45 | 80 | <0.001 |
| Statins (%) | 38 | 60 | 0.022 |
| Prednisolone (%) | 0 | 12 | 0.025 |
| Inhaled Corticosteroids (%) | 5 | 23 | 0.016 |
| Laboratory | |||
| BNP (pg/mL) | 34 ± 70 | 190 ± 584 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 2.0 ± 2.6 | 5.0 ± 17.5 | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 71 ± 16 | 100 ± 50 | <0.001 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.5 ± 1,0 | 2.6 ± 1.0 | <0.001 |
| Haemoglobin (mmol/L) | 8.8 ± 0,8 | 8.0 ± 1.4 | 0.001 |
| Leukocytes (Gpt/L) | 7.0 ± 1.4 | 7.2 ± 2.2 | n.s. |
| Platelets (Gpt/L) | 237 ± 48 | 232 ± 76 | n.s. |
| Controls | PH Group 1 | PH Group 2 | PH Group 3 | PH Group 4 | PH Group 2 + 3 | p-Value between Different PH Groups | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 40 | 13 | 30 | 11 | 12 | 14 | |
| Clinical parameters | |||||||
| Age (years) | 66 ± 7 | 66 ± 12 | 76 ± 8 | 59 ± 22 | 71 ± 12 | 76 ± 8 | 0.015 |
| Male gender (%) | 33 | 15 | 37 | 45 | 50 | 50 | n.s. |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.9 ± 4.7 | 29.0 ± 8.4 | 27.9 ± 3.9 | 25.9 ± 7.5 | 30.6 ± 5.2 | 29.9 ± 6.5 | n.s. |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 146 ± 31 | 134 ± 17 | 156 ± 31 | 142 ± 22 | 143 ± 20 | 135 ± 26 | n.s. |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 81 ± 16 | 78 ± 8 | 80 ± 14 | 85 ± 9 | 83 ± 16 | 79 ± 20 | n.s. |
| Functional class | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 2.6 ± 0.8 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 2.3 ± 0.7 | 2.8 ± 0.7 | n.s. |
| Comorbidities | |||||||
| Arterial Hypertension (%) | 95 | 77 | 93 | 70 | 83 | 77 | n.s. |
| Coronary artery disease/infarction (%) | 0 | 15 | 33 | 36 | 0 | 36 | n.s. |
| Hypertensive heart disease (%) | 59 | 27 | 70 | 27 | 17 | 71 | 0.002 |
| Atrial fibrillation (%) | 18 | 8 | 73 | 45 | 17 | 64 | <0.001 |
| Pulmonary diseases (%) | 5 | 54 | 10 | 91 | 25 | 86 | <0.001 |
| COPD (%) | 3 | 8 | 10 | 50 | 17 | 57 | 0.002 |
| Pulmonary fibrosis (%) | 0 | 15 | 0 | 20 | 0 | 36 | 0.006 |
| Chronic kidney disease (%), GFR < 50 mL/min | 8 | 23 | 59 | 36 | 36 | 71 | n.s. |
| Hyperlipidaemia (%) | 85 | 36 | 57 | 60 | 75 | 54 | n.s. |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 20 | 31 | 60 | 90 | 25 | 36 | 0.009 |
| Obesity (%), BMI > 30 kg/m2 | 43 | 40 | 30 | 33 | 36 | 58 | n.s. |
| Autoimmune diseases (%) | 0 | 38 | 7 | 27 | 0 | 21 | 0.037 |
| Smoking (%) | 29 | 20 | 63 | 33 | 60 | 67 | n.s. |
| Medication | |||||||
| ASA (%) | 25 | 17 | 21 | 20 | 0 | 36 | n.s. |
| Beta blockers (%) | 63 | 38 | 90 | 40 | 42 | 73 | 0.002 |
| ACE-Inhibitors/Sartans (%) | 85 | 62 | 86 | 60 | 75 | 82 | n.s. |
| Calcium channel blockers (%) | 25 | 31 | 28 | 30 | 8 | 36 | n.s. |
| Diuretics (%) | 45 | 92 | 83 | 60 | 67 | 91 | n.s. |
| Statins (%) | 38 | 54 | 76 | 40 | 50 | 55 | n.s. |
| Prednisolone (%) | 0 | 15 | 3 | 40 | 0 | 15 | 0.022 |
| Inhaled Corticosteroids (%) | 5 | 38 | 7 | 50 | 8 | 36 | 0.013 |
| Laboratory | |||||||
| BNP (pg/ml) | 34 ± 70 | 104 ± 82 | 325 ± 678 | 326 ± 469 | 117 ± 87 | 285 ± 731 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 2.0 ± 2.6 | 3.7 ± 10.7 | 5.5 ± 21.0 | 7.6 ± 12.9 | 2.6 ± 5.8 | 8.4 ± 22.0 | n.s. |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 71 ± 16 | 70 ± 44 | 123 ± 59 | 100 ± 24 | 86 ± 40 | 103 ± 47 | 0.019 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.5 ± 1.0 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | 2.9 ± 1.0 | 2.9 ± 0.9 | 2.8 ± 1.2 | n.s. |
| Haemoglobin (mmol/L) | 8.8 ± 0.8 | 8.0 ± 1.5 | 7.3 ± 1.2 | 8.4 ±1.0 | 9.5 ± 1.4 | 7.9 ± 1.6 | 0.014 |
| Leukocytes (Gpt/L) | 7.0 ± 1.4 | 6.0 ± 2.4 | 7.6 ± 1.7 | 7.7 ±1.6 | 7.4 ± 1.8 | 6.6 ± 3.4 | n.s. |
| Platelets (Gpt/L) | 237 ± 48 | 232 ± 51 | 224 ± 82 | 303 ±63 | 297 ± 73 | 193 ± 70 | 0.012 |
| Parameter | PH Group 1 (n = 13) | IPAH (n = 7) | CTD-PAH (n = 4) | CHD-PAH/Heritable (n = 2) | PH Group 2 (n = 30) | PH Group 3 (n = 11) | PH Group 4 (n = 12) | PH Group 2 + 3 (n = 14) | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mPAP (mmHg) | 53 ± 12 | 55 ± 14 | 53 ± 12 | 45 ± 1 | 39 ± 11 | 37 ± 9 | 43 ± 16 | 45 ± 10 | 0.021 |
| PCWP (mmHg) | 12 ± 3 | 12 ± 2 | 13 ± 5 | 11 ± 5 | 23 ± 6 | 12 ± 11 | 14 ± 5 | 24 ± 8 | <0.001 |
| PVR (dyn*sec*cm−5) | 755 ± 412 | 799 ± 406 | 781 ± 541 | 548 ± 252 | 321 ± 191 | 518 ± 287 | 568 ± 447 | 352 ± 249 | 0.002 |
| mRAP (mmHg) | 9 ± 7 | 11 ± 5 | 9 ± 8 | N/A | 12 ± 5 | 6 ± 4 | 10 ± 6 | 15 ± 8 | 0.017 |
| CI ((L/min)/m2) | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 3 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 0.5 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | n.s. |
| Parameter | Controls | PH Patients | p Value * | PH Group 1 | PH Group 2 | PH Group 3 | PH Group 4 | PH Group 2 + 3 | p Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAPsys (mmHg) | 21 ± 4 | 55 ± 18 | <0,001 | 59 ± 22 | 52 ± 16 | 57 ± 22 | 50 ± 20 | 56 ± 16 | n.s. |
| RA area (cm2) | 15 ± 2 | 25 ± 10 | <0.001 | 21 ± 8 | 28 ± 10 | 20 ± 9 | 22 ± 5 | 31 ± 14 | n.s. |
| RVEDd (mm) | 35 ± 2 | 45 ± 8 | <0.001 | 41 ± 9 | 46 ± 7 | 47 ± 10 | 44 ± 7 | 49 ± 9 | n.s. |
| LVEF (%) | 68 ± 7 | 58 ± 11 | <0.001 | 63 ± 7 | 56 ± 13 | 63 ± 9 | 60 ± 6 | 52 ± 12 | 0.050 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bäz, L.; Roßberg, M.; Grün, K.; Kretzschmar, D.; Berndt, A.; Schulze, P.C.; Jung, C.; Franz, M. Serum Liberation of Fetal Fibronectin Variants in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: ED-A+ Fn as Promising Novel Biomarker of Pulmonary Vascular and Right Ventricular Myocardial Remodeling. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122559
Bäz L, Roßberg M, Grün K, Kretzschmar D, Berndt A, Schulze PC, Jung C, Franz M. Serum Liberation of Fetal Fibronectin Variants in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: ED-A+ Fn as Promising Novel Biomarker of Pulmonary Vascular and Right Ventricular Myocardial Remodeling. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(12):2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122559
Chicago/Turabian StyleBäz, Laura, Michelle Roßberg, Katja Grün, Daniel Kretzschmar, Alexander Berndt, P. Christian Schulze, Christian Jung, and Marcus Franz. 2021. "Serum Liberation of Fetal Fibronectin Variants in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: ED-A+ Fn as Promising Novel Biomarker of Pulmonary Vascular and Right Ventricular Myocardial Remodeling" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 12: 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122559
APA StyleBäz, L., Roßberg, M., Grün, K., Kretzschmar, D., Berndt, A., Schulze, P. C., Jung, C., & Franz, M. (2021). Serum Liberation of Fetal Fibronectin Variants in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension: ED-A+ Fn as Promising Novel Biomarker of Pulmonary Vascular and Right Ventricular Myocardial Remodeling. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(12), 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122559






