Diabetic Retinopathy and Hearing Loss: Results from the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Ophthalmic Examinations and Grading of DR
2.2.2. Assessment of Hearing Loss
2.3. Subgroup Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Enrolled Participants
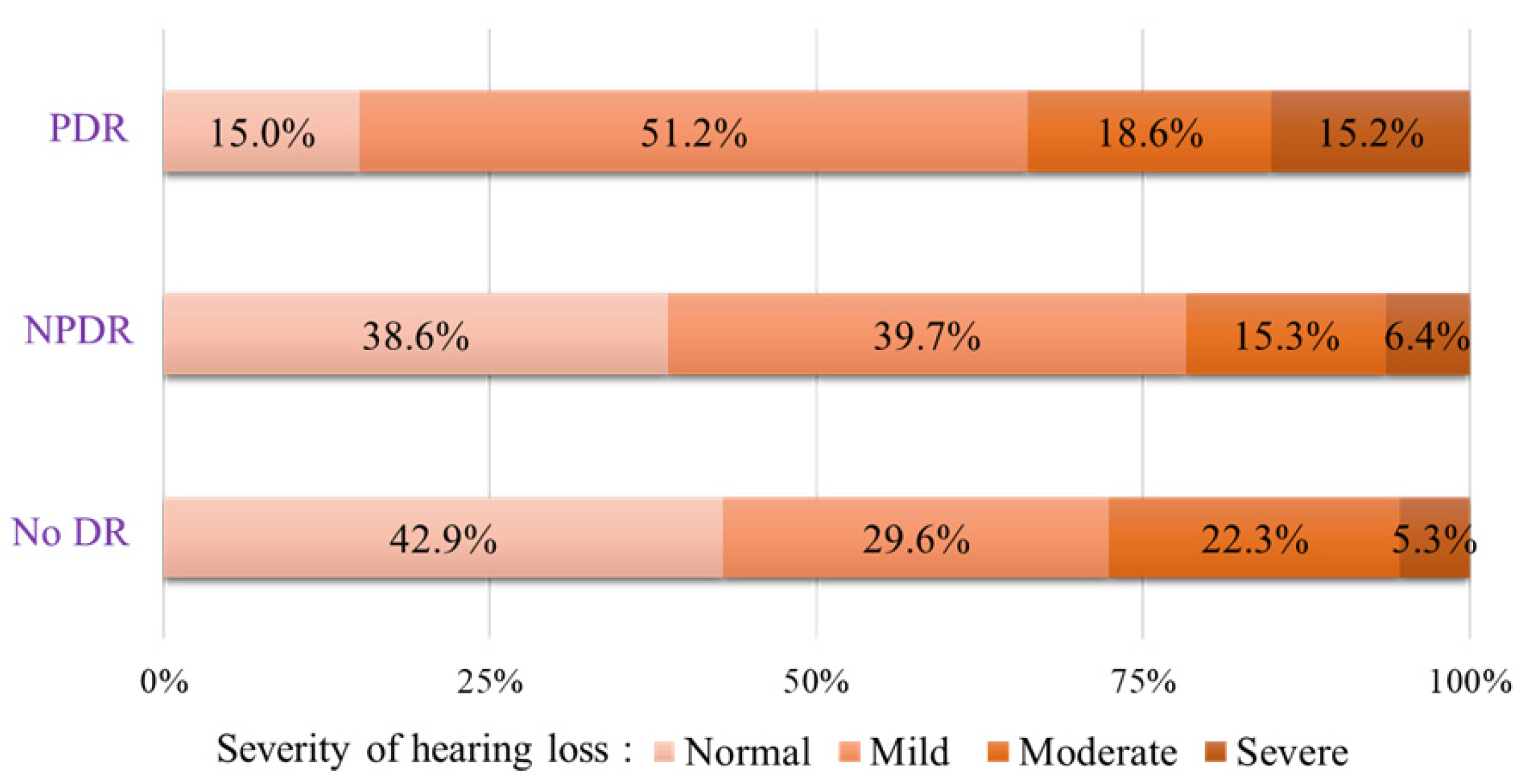
3.2. Association of Diabetic Retinopathy with Hearing Loss
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gates, G.A.; Cobb, J.L.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Wolf, P.A. The relation of hearing in the elderly to the presence of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk factors. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1993, 119, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, M.; Hildesheimer, M.; Zohar, S.; Chilarovitz, T. Chronic cardiovascular pathology and hearing loss in the aged. Gerontology 1977, 23, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidman, M.D.; Quirk, W.S.; Shirwany, N.A. Mechanisms of alterations in the microcirculation of the cochlea. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 884, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, L.D.; Brothers, R.J.; King, W.N.; Clegg, L.X.; Klein, R.; Cooper, L.S.; Sharrett, A.R.; Davis, M.D.; Cai, J. Methods for evaluation of retinal microvascular abnormalities associated with hypertension/sclerosis in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Ophthalmology 1999, 106, 2269–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Klein, R.; Sharrett, A.R.; Schmidt, M.I.; Pankow, J.S.; Couper, D.J.; Klein, B.E.; Hubbard, L.D.; Duncan, B.B. Retinal arteriolar narrowing and risk of diabetes mellitus in middle-aged persons. JAMA 2002, 287, 2528–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, T.Y.; Mitchell, P. Hypertensive retinopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2310–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Rochtchina, E.; Liew, G.; Tan, A.G.; Wong, T.Y.; Leeder, S.R.; Smith, W.; Shankar, A.; Mitchell, P. The long-term relation among retinal arteriolar narrowing, blood pressure, and incident severe hypertension. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Classification of diabetic retinopathy from fluorescein angiograms. ETDRS report number 11. Ophthalmology 1991, 98, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.; Moss, S.E.; Cruickshanks, K.J. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy: XVII. The 14-year incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy and associated risk factors in type 1 diabetes. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 1801–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, D.; Lee, W.K.; Kang, S. Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2011. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 6827–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, N.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy and systemic vascular complications. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dabdoub, A.; Smallwood, P.M.; Williams, J.; Woods, C.; Kelley, M.W.; Jiang, L.; Tasman, W.; Zhang, K.; et al. Vascular development in the retina and inner ear: Control by Norrin and Frizzled-4, a high-affinity ligand-receptor pair. Cell 2004, 116, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helzner, E.P.; Contrera, K.J. Type 2 Diabetes and Hearing Impairment. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Mishra, A.; Jagade, M.; Kasbekar, V.; Nagle, S.K. Effects of hypertension on hearing. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 65, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V); Ministry of Health and Welfare: Sejong, Korea, 2012.
- Kweon, S.; Kim, Y.; Jang, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.; Chun, C.; Khang, Y.H.; Oh, K. Data resource profile: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.J.; Sobrin, L.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, M.H.; Seong, M.; Cho, H. The Relationship between Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Nephropathy in a Population-Based Study in Korea (KNHANES V-2, 3). Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6547–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Grading Diabetic Retinopathy from Stereoscopic Color Fundus Photographs--An Extension of the Modified Airlie House Classification. ETDRS report number 10. Ophthalmology 1991, 98, 786–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.C.; Choi, W.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, C.Y.; Park, K.H.; Park, Y.J.; Baek, S.H.; Song, S.J.; et al. An Overview of Ophthalmologic Survey Methodology in the 2008-2015 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Korean J. Ophthalmol. KJO 2015, 29, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.J.; Beck, L.; Davis, A.; Jones, D.E.; Thomas, A.B. Hearing loss in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1983, 4, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt, E.; Öztürk, F.; Günen, A.; Sadikoglu, Y.; Sari, R.A.; Yoldas, T.K.; Avsar, A.; Inan, Ü.Ü. Relationship of retinopathy and hearing loss in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. Ophthalmol. 2002, 34, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, G.; Wong, T.Y.; Mitchell, P.; Newall, P.; Smith, W.; Wang, J.J. Retinal microvascular abnormalities and age-related hearing loss: The Blue Mountains hearing study. Ear Hear. 2007, 28, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkezari, S.J.; Namiranian, N.; Rahmanian, M.; Atighechi, S.; Mohajeri-Tehrani, M.-R.; Gholami, S. Is hearing impairment in diabetic patients correlated to other complications? In. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2018, 17, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Chin, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, N.R. Epidemiologic Survey Committee Of The Korean Ophthalmological Society, O. Relationships between Hearing Loss and the Prevalences of Cataract, Glaucoma, Diabetic Retinopathy, and Age-Related Macular Degeneration in Korea. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, Y.U.; Lim, H.W.; Hong, E.H.; Kang, M.H.; Seong, M.; Nam, E.; Cho, H. The association between periodontal disease and age-related macular degeneration in the Korea National health and nutrition examination survey: A cross-sectional observational study. Medicine 2017, 96, e6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, M.B.; Buch, N.H. Studies on inner-ear function and cranial nerves in diabetics. Acta Otolaryngol. 1961, 53, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.A.; Schulman, R.H.; Weiss, S. Hearing and diabetic neuropathy. Arch. Intern. Med. 1975, 135, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooley, C.; Jun, W.; Le, K.; Kim, A.; Rock, N.; Cardenal, M.; Kline, R.; Aldrich, D.; Hayes, J. Correlational Study of Diabetic Retinopathy and Hearing Loss. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2017, 94, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helzner, E.P.; Cauley, J.A.; Pratt, S.R.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Zmuda, J.M.; Talbott, E.O.; de Rekeneire, N.; Harris, T.B.; Rubin, S.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; et al. Race and Sex Differences in Age-Related Hearing Loss: The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Park, J.M.; Han, J.S.; Seo, J.H.; Han, K.-D.; Joo, Y.H.; Park, K.H. Age-related hearing loss in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ikram, M.K.; Cotch, M.F.; Klein, B.; Varma, R.; Shaw, J.E.; Klein, R.; Mitchell, P.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Wong, T.Y. Association of Diabetic Macular Edema and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy With Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Lee, Y.-K.; Cho, A.; Han, C.H.; Noh, J.-W.; Shin, Y.J.; Bae, S.H.; Kim, H. Diabetic retinopathy is a prognostic factor for progression of chronic kidney disease in the patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Associated Factors | Middle Age (40–64 years) (n = 411) | Old Age (≥65 years) (n = 634) | All Participants (n = 1045) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 53.3 ± 0.3 | 71.9 ± 0.3 | 59.2 ± 0.4 |
| Sex, female, % | 38.5 ± 2.3 | 57.7 ± 2.6 | 44.6 ± 1.8 |
| Education level (greater than high school), % | 52.7 ± 2.6 | 18.8 ± 2.1 | 42.0 ± 2.1 |
| Household income (top 1/2), % | 54.2 ± 2.7 | 25.7 ± 2.7 | 45.1 ± 2.0 |
| Smoking, % | 55.4 ± 2.6 | 44.1 ± 2.7 | 51.9 ± 1.9 |
| Alcohol consumption, % | 72.3 ± 2.1 | 64.5 ± 2.7 | 69.9 ± 1.7 |
| Noise exposure, % | 34.2 ± 2.5 | 31.9 ± 2.7 | 33.5 ± 2.0 |
| Hypertension, % | 53.6 ± 2.7 | 74.8 ± 2.4 | 60.4 ± 2.0 |
| Chronic kidney disease, % | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 13.2 ± 1.9 | 6.0 ± 0.8 |
| Previous angina or MI, % | 5.8 ± 1.2 | 14.2 ± 2.0 | 8.4 ± 1.0 |
| Previous stroke, % | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 6.8 ± 1.4 | 3.3 ± 0.6 |
| Fasting blood glucose, mg/dL | 149.6 ± 2.6 | 131.9 ± 2.1 | 144.3 ± 1.9 |
| HbA1c, % | 7.4 ± 0.1 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 7.3 ± 0.1 |
| Serum total cholesterol, mg/dl | 188.9 ± 2.5 | 184.2 ± 2.4 | 187.5 ± 1.8 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 25.7 ± 0.2 | 24.9 ± 0.2 | 25.4 ± 0.2 |
| Serum triglyceride, mg/dl | 199.8 ± 13.0 | 163.0 ± 8.1 | 188.6 ± 9.1 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 15.4 ± 0.3 | 16.4 ± 0.3 | 15.7 ± 0.2 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.0 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 93.1 ± 1.0 | 78.7 ± 0.9 | 88.7 ± 0.8 |
| Hearing loss, % | 44.4 ± 2.5 | 86.7 ± 1.6 | 57.9 ± 1.9 |
| Diabetic retinopathy, % | 8.4 ± 1.4 | 10.5 ± 1.7 | 9.1 ± 1.1 |
| No | 91.6 ± 1.4 | 89.5 ± 1.7 | 90.9 ± 1.1 |
| NPDR | 7.3 ± 1.4 | 8.4 ± 1.6 | 7.7 ± 1.1 |
| PDR | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.3 |
| Associated Factors | Hearing Loss (n = 678) | No Hearing Loss (n = 367) | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle Age (40–64 Years) | Old Age (≥ 65 Years) | p-Value | All Participants | Middle Age (40–64 Years) | Old Age (≥65 Years) | p-Value | All Participants | ||
| Age, years | 55.2 ± 0.5 | 72.3 ± 0.3 | <0.001 | 63.4 ± 0.5 | 51.7 ± 0.4 | 68.8 ± 0.5 | <0.001 | 53.4 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| Sex, female % | 26.3 ± 3.1 | 55.3 ± 2.9 | <0.001 | 40.2 ± 2.2 | 48.1 ± 3.3 | 73.4 ± 6.2 | 0.002 | 50.7 ± 3.1 | 0.007 |
| Education level, % | |||||||||
| High school or lower | 54.3 ± 3.7 | 82.0 ± 2.3 | <0.001 | 67.4 ± 2.4 | 41.6 ± 3.5 | 76.3 ± 5.9 | <0.001 | 54.8 ± 3.3 | <0.001 |
| Greater than high school | 45.7 ± 3.7 | 18.0 ± 2.3 | <0.001 | 32.6 ± 2.4 | 58.4 ± 3.5 | 23.7 ± 5.9 | <0.001 | 45.2 ± 3.3 | <0.001 |
| Household income, % | |||||||||
| Top 1/2 | 48.4 ± 3.8 | 24.2 ± 3.0 | <0.001 | 36.8 ± 2.5 | 58.9 ± 3.3 | 35.3 ± 6.9 | 0.003 | 56.5 ± 3.1 | <0.001 |
| Lower 1/2 | 51.6 ± 3.8 | 75.8 ± 3.0 | <0.001 | 63.2 ± 2.5 | 41.1 ± 3.3 | 64.7 ± 6.9 | 0.003 | 43.5 ± 3.1 | <0.001 |
| Smoking, % | 64.3 ± 3.8 | 47.0 ± 2.9 | 0.001 | 56.2 ± 2.3 | 48.3 ± 3.6 | 25.8 ± 6.3 | 0.005 | 46.0 ± 3.3 | 0.013 |
| Alcohol consumption, % | 75.3 ± 3.0 | 65.7 ± 2.9 | 0.020 | 70.8 ± 2.1 | 69.9 ± 3.0 | 56.7 ± 7.0 | 0.084 | 68.6 ± 2.7 | 0.515 |
| Noise exposure, % | 45.3 ± 3.9 | 32.1 ± 3.1 | 0.007 | 39.0 ± 2.6 | 25.4 ± 2.9 | 30.8 ± 6.6 | 0.432 | 25.9 ± 2.7 | 0.001 |
| Hypertension, % | 53.3 ± 3.7 | 75.2 ± 2.7 | <0.001 | 63.8 ± 2.3 | 53.9 ± 3.5 | 72.7 ± 6.2 | 0.014 | 55.8 ± 3.2 | 0.028 |
| Chronic kidney disease, % | 4.4 ± 1.5 | 14.1 ± 2.2 | 0.001 | 8.9 ± 1.3 | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 7.8 ± 4.1 | 0.02 | 2.3 ± 0.8 | <0.001 |
| Previous angina or MI, % | 7.2 ± 2.0 | 13.7 ± 2.2 | 0.039 | 10.3 ± 1.5 | 4.6 ± 1.5 | 17.2 ± 5.5 | 0.003 | 5.9 ± 1.4 | 0.053 |
| Previous stroke, % | 2.8 ± 1.3 | 7.2 ± 1.6 | 0.051 | 4.9 ± 1.0 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 4.1 ± 2.7 | 0.027 | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 0.001 |
| Fasting blood glucose, mg/dL | 147.0 ± 3.6 | 132.4 ± 2.3 | 0.001 | 140.3 ± 2.2 | 151.7 ± 4.0 | 129.1 ± 4.3 | <0.001 | 149.4 ± 3.7 | 0.039 |
| HbA1c, % | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 0.193 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 7.1 ± 0.1 | 0.048 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 0.172 |
| Serum total cholesterol, mg/dL | 183.4 ± 3.1 | 184.7 ± 2.8 | 0.745 | 184.0 ± 2.1 | 193.2 ± 3.5 | 181.2 ± 5.1 | 0.054 | 192.0 ± 3.2 | 0.040 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.2 ± 0.3 | 24.7 ± 0.2 | 0.862 | 25.0 ± 0.2 | 26.1 ± 0.3 | 26.1 ± 0.5 | 0.973 | 26.1 ± 0.3 | 0.001 |
| Serum triglycerides, mg/dL | 190.5 ± 9.0 | 165.2 ± 8.8 | 0.057 | 178.9 ± 6.0 | 207.1 ± 22.0 | 149.6 ± 14.0 | 0.029 | 201.3 ± 19.8 | 0.283 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 15.6 ± 0.3 | 16.6 ± 0.3 | 0.025 | 16.1 ± 0.2 | 15.2 ± 0.4 | 15.6 ± 0.8 | 0.641 | 15.2 ± 0.4 | 0.050 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.189 | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 0.797 | 0.8 ± 0.0 | 0.003 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 92.9 ± 1.6 | 78.2 ± 1.1 | <0.001 | 86.1 ± 1.1 | 93.3 ± 1.1 | 82.0 ± 2.4 | <0.001 | 92.2 ± 1.1 | <0.001 |
| Diabetic retinopathy, % | 9.5 ± 2.1 | 10.9 ± 1.9 | 0.600 | 10.2 ± 1.5 | 7.5 ± 2.0 | 7.4 ± 4.0 | 0.973 | 7.5 ± 1.8 | 0.277 |
| No | 90.5 ± 2.1 | 89.1 ± 1.9 | 0.848 | 89.8 ± 1.5 | 92.5 ± 2.0 | 92.6 ± 4.0 | 0.285 | 92.5 ± 1.8 | 0.143 |
| NPDR | 7.5 ± 2.0 | 8.8 ± 1.8 | 8.1 ± 1.4 | 7.2 ± 1.9 | 5.4 ± 3.9 | 7.0 ± 1.8 | |||
| PDR | 2.0 ± 0.8 | 2.1 ± 0.7 | 2.1 ± 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 1.2 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | |||
| Associated Factors | Middle Age (40–64 Years) | Old Age (≥65 Years) | All Participants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (per 1-year increase) | 1.09 (1.06–1.13) | <0.001 | 1.24 (1.13–1.36) | <0.001 | 1.12 (1.10–1.14) | <0.001 |
| Sex, (male vs. female) | 2.56 (1.70–4.00) | <0.001 | 2.22 (1.14–4.35) | 0.019 | 1.53 (1.12–2.09) | 0.008 |
| Education (high school or less vs. greater than high school) | 1.67 (1.11–2.50) | 0.014 | 1.41 (0.71–2.86) | 0.327 | 2.51 (1.79–3.50) | <0.001 |
| Household income (lower 1/2 vs. top 1/2) | 1.51 (1.03–2.27) | 0.033 | 1.72 (0.85–3.45) | 0.134 | 2.23 (1.61–3.07) | <0.001 |
| Smoking, % | 1.93 (1.24–3.01) | 0.004 | 2.55 (1.31–4.94) | 0.006 | 1.50 (1.09–2.08) | 0.013 |
| Alcohol consumption, % | 1.32 (0.86–2.01) | 0.206 | 1.46 (0.81–2.64) | 0.206 | 1.11 (0.81–1.53) | 0.515 |
| Noise exposure, % | 2.44 (1.58–3.79) | <0.001 | 1.06 (0.53–2.11) | 0.866 | 1.83 (1.29–2.59) | 0.001 |
| Hypertension, % | 0.98 (0.67–1.43) | 0.914 | 1.14 (0.57–2.28) | 0.712 | 1.40 (1.04–1.88) | 0.028 |
| Chronic kidney disease, % | 2.73 (0.83–9.06) | 0.100 | 1.94 (0.59–6.33) | 0.272 | 4.19 (1.86–9.45) | 0.001 |
| Previous angina or MI, % | 1.60 (0.66–3.90) | 0.299 | 0.77 (0.32–1.86) | 0.558 | 1.83 (0.99–3.40) | 0.056 |
| Previous stroke, % | 4.02 (0.91–17.70) | 0.066 | 1.78 (0.44–7.31) | 0.421 | 4.73 (1.77–12.66) | 0.002 |
| Fasting blood glucose, mg/dL | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.389 | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 0.516 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.030 |
| HbA1c, % | 0.94 (0.81–1.09) | 0.400 | 1.04 (0.82–1.30) | 0.768 | 0.91 (0.81–1.03) | 0.148 |
| Serum total cholesterol, mg/dL | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.030 | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 0.561 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.030 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 0.94 (0.90–0.99) | 0.020 | 0.88 (0.80–0.97) | 0.009 | 0.92 (0.88–0.96) | <0.001 |
| Serum triglyceride, mg/dL | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.370 | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 0.408 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.125 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 1.02 (0.97–1.07) | 0.451 | 1.05 (0.95–1.15) | 0.332 | 1.04 (0.99–1.09) | 0.116 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 2.30 (0.77–6.84) | 0.134 | 6.08 (1.09–33.87) | 0.039 | 3.19 (1.14–8.95) | 0.028 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 0.834 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 0.166 | 0.98 (0.97–0.99) | 0.001 |
| Diabetic retinopathy, % | 1.29 (0.62–2.70) | 0.496 | 1.55 (0.45–5.30) | 0.487 | 1.40 (0.76–2.57) | 0.279 |
| No | Reference | 0.052 | Reference | 0.796 | Reference | 0.019 |
| NPDR | 1.07 (0.48–2.38) | 1.69 (0.35–8.03) | 1.20 (0.62–2.31) | |||
| PDR | 6.00 (1.42–25.43) | 1.15 (0.29–4.68) | 4.24 (1.54–11.79) | |||
| Diabetic Retinopathy | Age Stratification † | All Participants * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle Age (40–64 Years) | Old Age (≥65 Years) | |||||
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Presence of DR | 0.97 (0.43–2.20) | 0.944 | 1.61 (0.40–6.48) | 0.502 | 1.01 (0.51–2.00) | 0.976 |
| Severity of DR | 0.008 | 0.709 | 0.195 | |||
| No | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
| NPDR | 0.77 (0.32–1.85) | 1.96 (0.33–11.72) | 0.88 (0.42–1.82) | |||
| PDR | 7.74 (2.08–28.82) | 0.73 (0.17–3.09) | 2.99 (0.87–10.29) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, Y.U.; Park, S.H.; Chung, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, H. Diabetic Retinopathy and Hearing Loss: Results from the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112398
Shin YU, Park SH, Chung JH, Lee SH, Cho H. Diabetic Retinopathy and Hearing Loss: Results from the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(11):2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112398
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Yong Un, Seung Hun Park, Jae Ho Chung, Seung Hwan Lee, and Heeyoon Cho. 2021. "Diabetic Retinopathy and Hearing Loss: Results from the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 11: 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112398
APA StyleShin, Y. U., Park, S. H., Chung, J. H., Lee, S. H., & Cho, H. (2021). Diabetic Retinopathy and Hearing Loss: Results from the Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(11), 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112398






