Association between Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Esophageal Cancer: An Asian Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
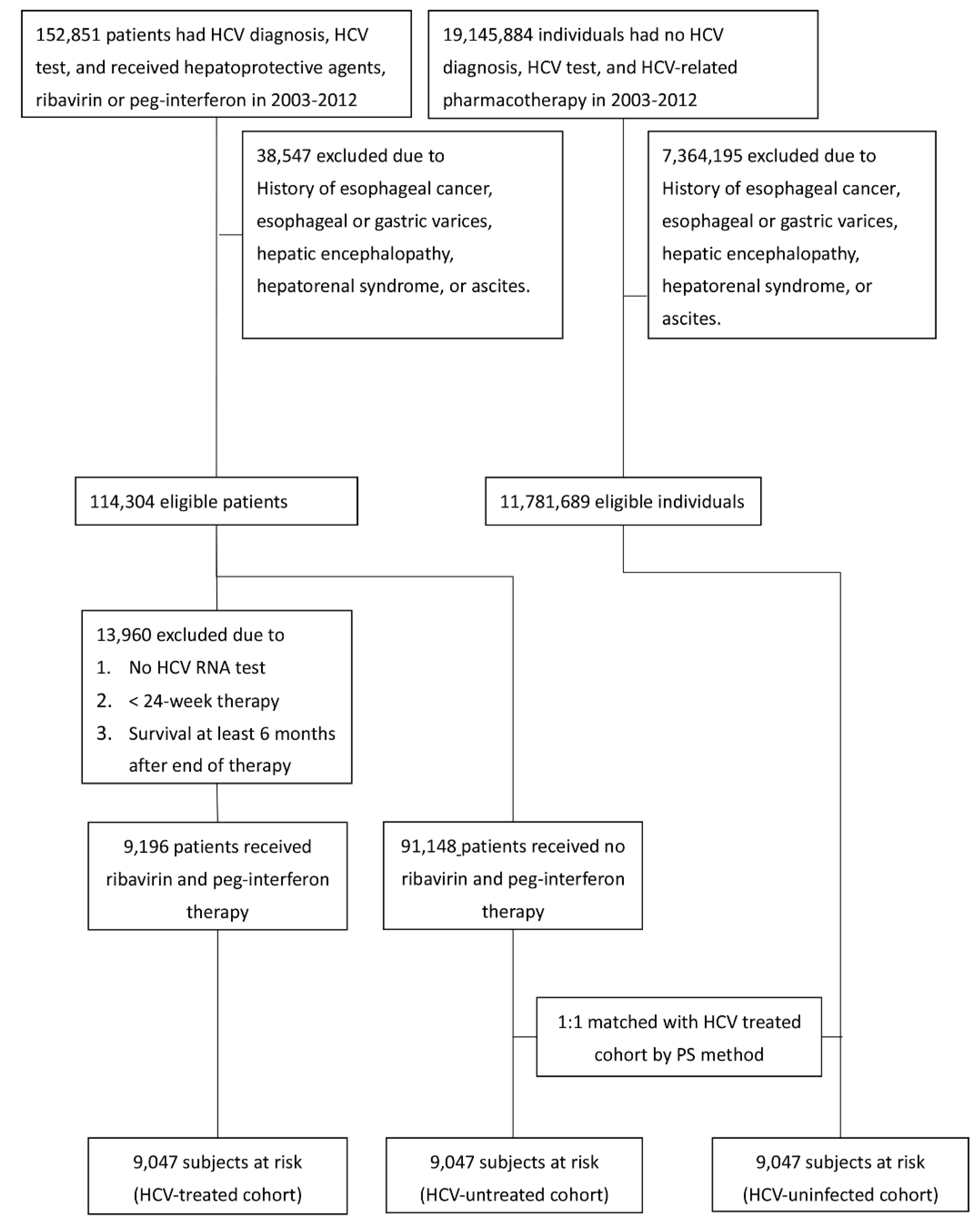
2.1. Samples and Measurements
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Informed Consent
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
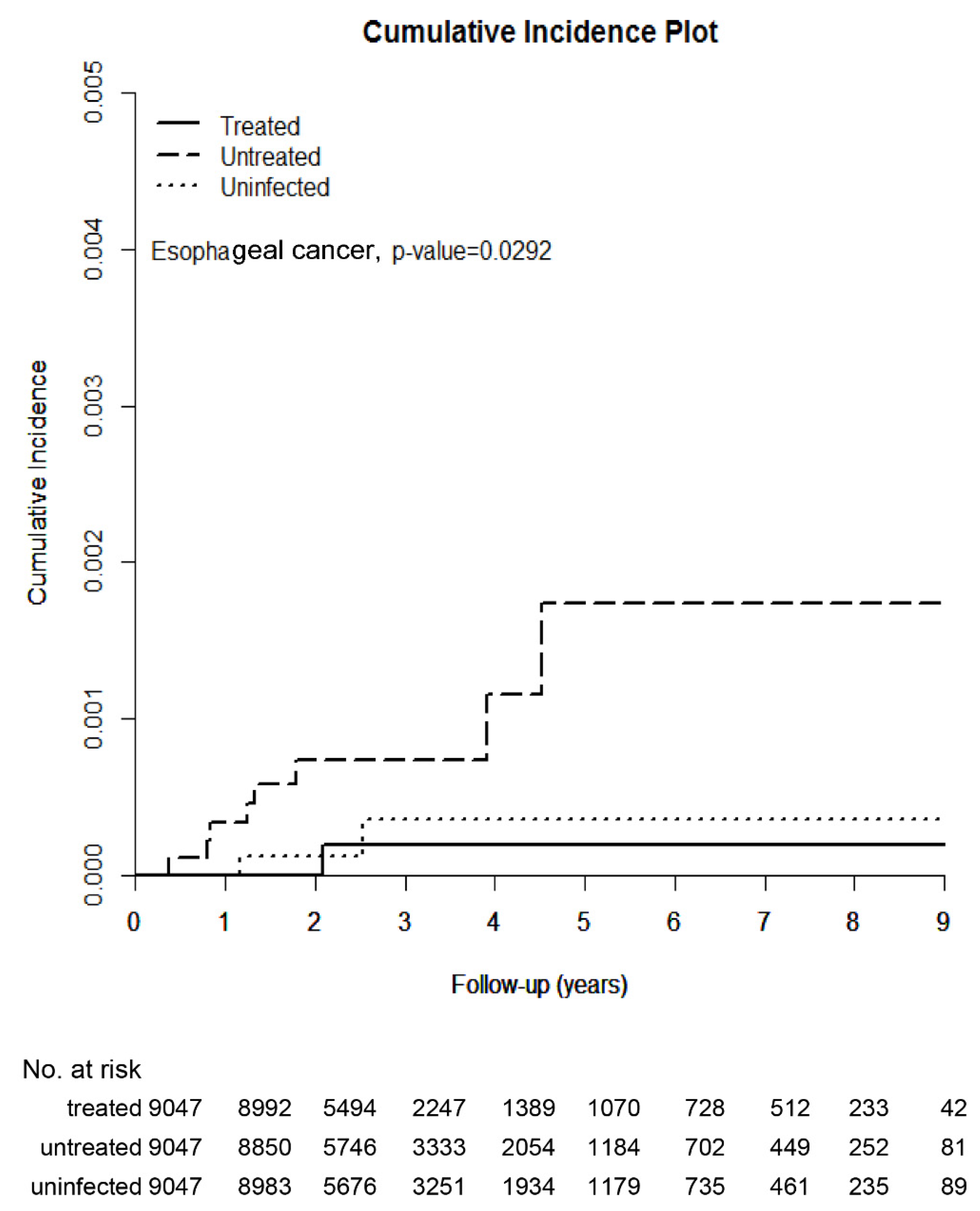
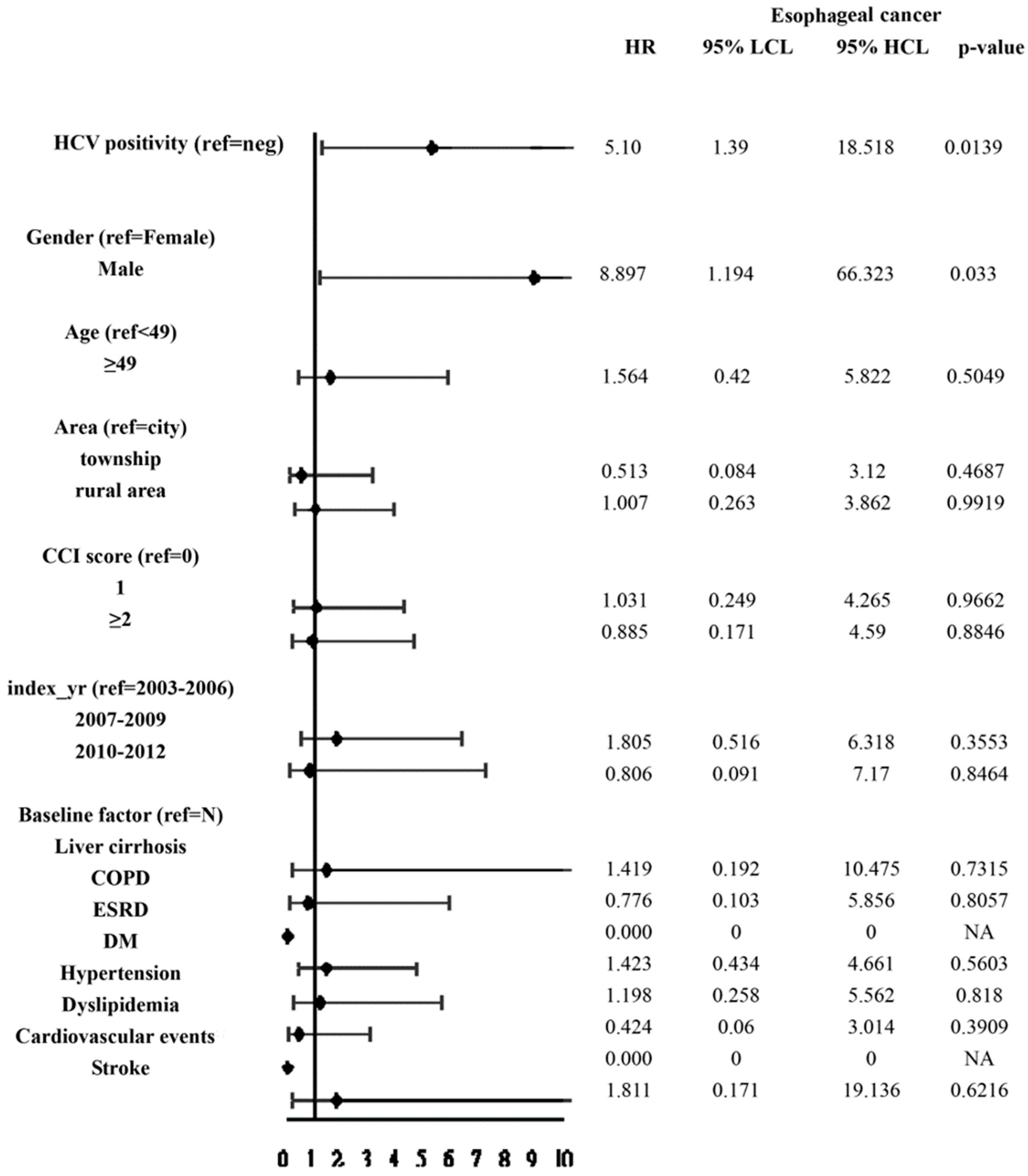
3.2. Cumulative Incidences and Associated Factors of Esophageal Cancer
3.3. Mortality
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Mph, K.D.M.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Esophageal Cancer: Genomic and Molecular Characterization, Stem Cell Compartment and Clonal Evolution. Medicines 2017, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Lee, J.-M.; Wu, D.-C.; Hsu, H.-K.; Kao, E.-L.; Huang, H.-L.; Wang, T.-N.; Huang, M.-C.; Wu, M.-T. Independent and combined effects of alcohol intake, tobacco smoking and betel quid chewing on the risk of esophageal cancer in Taiwan. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 113, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.-L.; Yu, S.-J. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J. Surg. 2018, 41, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, R. Metabolic syndrome and esophageal cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, S.-S. Roles of Adipokines in Digestive Diseases: Markers of Inflammation, Metabolic Alteration and Disease Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-L. Metabolic alterations and hepatitis C: From bench to bedside. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 1461–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Cheng, J.S.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, T.-H.; Lee, K.-C.; Chang, M.-L. Rheumatoid factor and immunoglobulin M mark hepatitis C-associated mixed cryo-globulinaemia: An 8-year prospective study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-L.; Chen, W.-T.; Hu, J.-H.; Chen, S.-C.; Gu, P.-W.; Chien, R.-N. Altering retinol binding protein 4 levels in hepatitis C: Inflammation and steatosis matter. Virulence 2020, 11, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-L.; Lin, Y.-S.; Hsu, C.-L.; Chien, R.-N.; Fann, C.S. Accelerated cardiovascular risk after viral clearance in hepatitis C patients with the NAMPT-rs61330082 TT genotype: An 8-year prospective cohort study. Virulence 2021, 12, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negro, F.; Forton, D.; Craxì, A.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Feld, J.J.; Manns, M.P. Extrahepatic Morbidity and Mortality of Chronic Hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, R.D.; Tong, X.; Moorman, A.C.; Ly, K.N.; Rupp, L.; Xu, F.; Gordon, S.C.; Holmberg, S.D. Increased incidence of cancer and cancer-related mortality among persons with chronic hepatitis C infection, 2006–2010. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, P.; Sturgis, E.M.; Tweardy, D.J.; Ariza-Heredia, E.J.; Torres, H.A. Association Between Hepatitis C Virus and Head and Neck Cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-H.; Yang, H.-I.; Lu, S.-N.; Jen, C.-L.; You, S.-L.; Wang, L.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, C.-J.; Reveal-HCV Study Group. Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection Increases Mortality from Hepatic and Extrahepatic Diseases: A Community-Based Long-Term Prospective Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-W.; Cheng, J.-S.; Chen, T.-D.; Le, P.-H.; Ku, H.-P.; Chang, M.-L. The irreversible HCV-associated risk of gastric cancer following interferon-based therapy: A joint study of hospital-based cases and nationwide population-based cohorts. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorino, S.; Bacchi-Reggiani, L.; De Biase, D.; Fornelli, A.; Masetti, M.; Tura, A.; Grizzi, F.; Zanello, M.; Mastrangelo, L.; Lombardi, R.; et al. Possible association between hepatitis C virus and malignancies different from hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12896–12953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermehren, J.; Park, J.; Jacobson, I.M.; Zeuzem, S. Challenges and perspectives of direct antivirals for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Kumada, T.; Tada, T.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Kitabatake, S.; Ito, T. Risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma development in non-cirrhotic patients with sustained virologic response for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzakis, E.; Gunnarsdottir, S.A.; Josefsson, A.; Björnsson, E. Increased Risk for Malignant Neoplasms Among Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-H.; Chen, M.-Y.; Yeh, C.-T.; Lin, S.-H.; Lin, M.-S.; Huang, T.-J.; Chang, M.-L. Sexual Dimorphic Metabolic Alterations in Hepatitis C Virus-infected Patients: A Community-Based Study in a Hepatitis B/Hepatitis C Virus Hyperendemic Area. Medicine 2016, 95, e3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyo, R.A.; Cherkin, D.C.; Ciol, M.A. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1992, 45, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.J. A Class of K-Sample Tests for Comparing the Cumulative Incidence of a Competing Risk. Ann. Stat. 1988, 16, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, J.P.; Gray, R.J. A Proportional Hazards Model for the Subdistribution of a Competing Risk. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.nhi.gov.tw/Content_List.aspx?n=A4EFF6CD1C4891CA&topn=3FC7D09599D25979 (accessed on 3 April 2021).
- Lu, C.-L.; Lang, H.-C.; Luo, J.-C.; Liu, C.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Chang, F.-Y.; Lee, S.-D. Increasing trend of the incidence of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, but not adenocarcinoma, in Taiwan. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 21, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunjal, S.; Pateel, D.G.S.; Yang, Y.-H.; Doss, J.G.; Bilal, S.; Maling, T.H.; Mehrotra, R.; Cheong, S.C.; Zain, R.B.M. An Overview on Betel Quid and Areca Nut Practice and Control in Selected Asian and South East Asian Countries. Subst. Use Misuse 2020, 55, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Lin, C.C.; Liu, C.S. Betel nut chewing as a risk factor for hepatitis C infection in Taiwan—A community-based study. Ann. Saudi Med. 2011, 31, 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Peng, F.; Hu, D.; Lin, X.; Chen, G.; Liang, B.; Zhang, H.; Dong, X.; Lin, J.; Zheng, X.; Niu, W. Analysis of Preoperative Metabolic Risk Factors Affecting the Prognosis of Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: The Fujian Prospective Investigation of Cancer (FIESTA) Study. EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, O.; Thakur, M.; Genova, A. Increased Risk of Esophageal Cancers Among Men in Taiwan. Cureus 2020, 12, e6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.-L.; Dai, C.-Y.; Huang, J.-F.; Hou, N.-J.; Lee, L.-P.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Chiu, C.-F.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Wang, L.-Y.; et al. A randomised study of peginterferon and ribavirin for 16 versus 24 weeks in patients with genotype 2 chronic hepatitis C. Gut 2007, 56, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.-L.; Huang, C.-F.; Huang, J.-F.; Chang, N.-C.; Yang, J.-F.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chang, W.-Y.; et al. Role of interleukin-28B polymorphisms in the treatment of hepatitis C virus genotype 2 infection in Asian patients. Hepatology 2010, 53, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Lan, K.H.; Huo, T.-L.; Huang, Y.-H.; Su, C.-W.; Lin, H.-C.; Lee, F.-Y.; Wu, J.-C.; Lee, S.-D. Anti-hepatitis C virus seropositivity is not associated with metabolic syndrome irrespective of age, gender and fibrosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2015, 14, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polaris Observatory HCV Collaborators. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Park, C.S.; Han, K.-D.; Joo, Y.-H. Hypertension is associated with oral, laryngeal, and esophageal cancer: A nationwide population-based study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| (1) | (2) | (3) | p-Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCV-Treated | HCV-Untreated | HCV-Uninfected | (1),(2) | (1),(3) | (2),(3) | |
| n | 9047 | 9047 | 9047 | |||
| Gender | ||||||
| Female, n, (%) | 4182 (46.23) | 4182 (46.23) | 4182 (46.23) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Age range (years), n, (%) | ||||||
| 20–39 | 1569 (17.34) | 1569 (17.34) | 1569 (17.34) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 40–49 | 2515 (27.80) | 2515 (27.80) | 2515 (27.80) | |||
| 50–59 | 3260 (36.03) | 3260 (36.03) | 3260 (36.03) | |||
| ≥60 | 1703 (18.82) | 1703 (18.82) | 1703 (18.82) | |||
| Area, n, (%) | ||||||
| city | 2205 (24.37) | 2205 (24.37) | 2205 (24.37) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| township | 2785 (30.78) | 2785 (30.78) | 2785 (30.78) | |||
| rural area | 4057 (44.84) | 4057 (44.84) | 4057 (44.84) | |||
| CCI score, n, (%) | ||||||
| 0 | 4292 (47.44) | 4292 (47.44) | 4292 (47.44) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 3029 (33.48) | 3029 (33.48) | 3029 (33.48) | |||
| ≥2 | 1726 (19.08) | 1726 (19.08) | 1726 (19.08) | |||
| Index year, n, (%) | ||||||
| 2003–2006 | 4400 (48.63) | 4400 (48.63) | 4400 (48.63) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2007–2009 | 2805 (31.00) | 2805 (31.00) | 2805 (31.00) | |||
| 2010–2012 | 1842 (20.36) | 1842 (20.36) | 1842 (20.36) | |||
| Baseline factor, n, (%) | ||||||
| Liver cirrhosis | 969 (10.71) | 546 (6.04) | 6 (0.07) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| COPD | 1050 (11.61) | 1017 (11.24) | 892 (9.86) | 0.4406 | 0.0001 | 0.0025 |
| ESRD | 61 (0.67) | 253(2.80) | 23 (0.25) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| DM | 1702 (18.81) | 2051 (22.67) | 1677 (18.54) | <0.0001 | 0.6334 | <0.0001 |
| Hypertension | 2668 (29.49) | 3154 (34.86) | 2498 (27.61) | <0.0001 | 0.0051 | <0.0001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1107 (12.24) | 1781 (19.69) | 1686 (18.64) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0727 |
| Cardiovascular events | 234 (2.59) | 360 (3.98) | 255 (2.82) | <0.0001 | 0.3357 | <0.0001 |
| Stroke | 298 (3.29) | 441 (4.87) | 466 (5.15) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3944 |
| HCV-Treated | HCV-Untreated | HCV-Uninfected | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 9047 | n = 9047 | n = 9047 | ||
| Follow-up years, mean ± SD | 2.76 ± 1.75 | 2.97 ± 1.83 | 2.96 ± 1.81 | |
| Event number, n (%) | 1 (0.01) | 86 (0.56) | 40 (0.26) | |
| Competing mortality, n (%) | 209 (2.31) | 762 (4.95) | 272 (1.77) | |
| CI, % (95% CI) | 0.019 (0.002–0.109) | 0.174 (0.068–0.395) | 0.035 (0.007–0.133) | 0.0292 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, Y.-Y.; Cheng, J.-S.; Wu, T.-S.; Chen, C.-W.; Chang, M.-Y.; Ku, H.-P.; Chien, R.-N.; Chang, M.-L. Association between Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Esophageal Cancer: An Asian Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112395
Chu Y-Y, Cheng J-S, Wu T-S, Chen C-W, Chang M-Y, Ku H-P, Chien R-N, Chang M-L. Association between Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Esophageal Cancer: An Asian Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(11):2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112395
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Yin-Yi, Jur-Shan Cheng, Ting-Shu Wu, Chun-Wei Chen, Ming-Yu Chang, Hsin-Ping Ku, Rong-Nan Chien, and Ming-Ling Chang. 2021. "Association between Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Esophageal Cancer: An Asian Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 11: 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112395
APA StyleChu, Y.-Y., Cheng, J.-S., Wu, T.-S., Chen, C.-W., Chang, M.-Y., Ku, H.-P., Chien, R.-N., & Chang, M.-L. (2021). Association between Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Esophageal Cancer: An Asian Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(11), 2395. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112395






