Association between Appendicitis and Incident Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
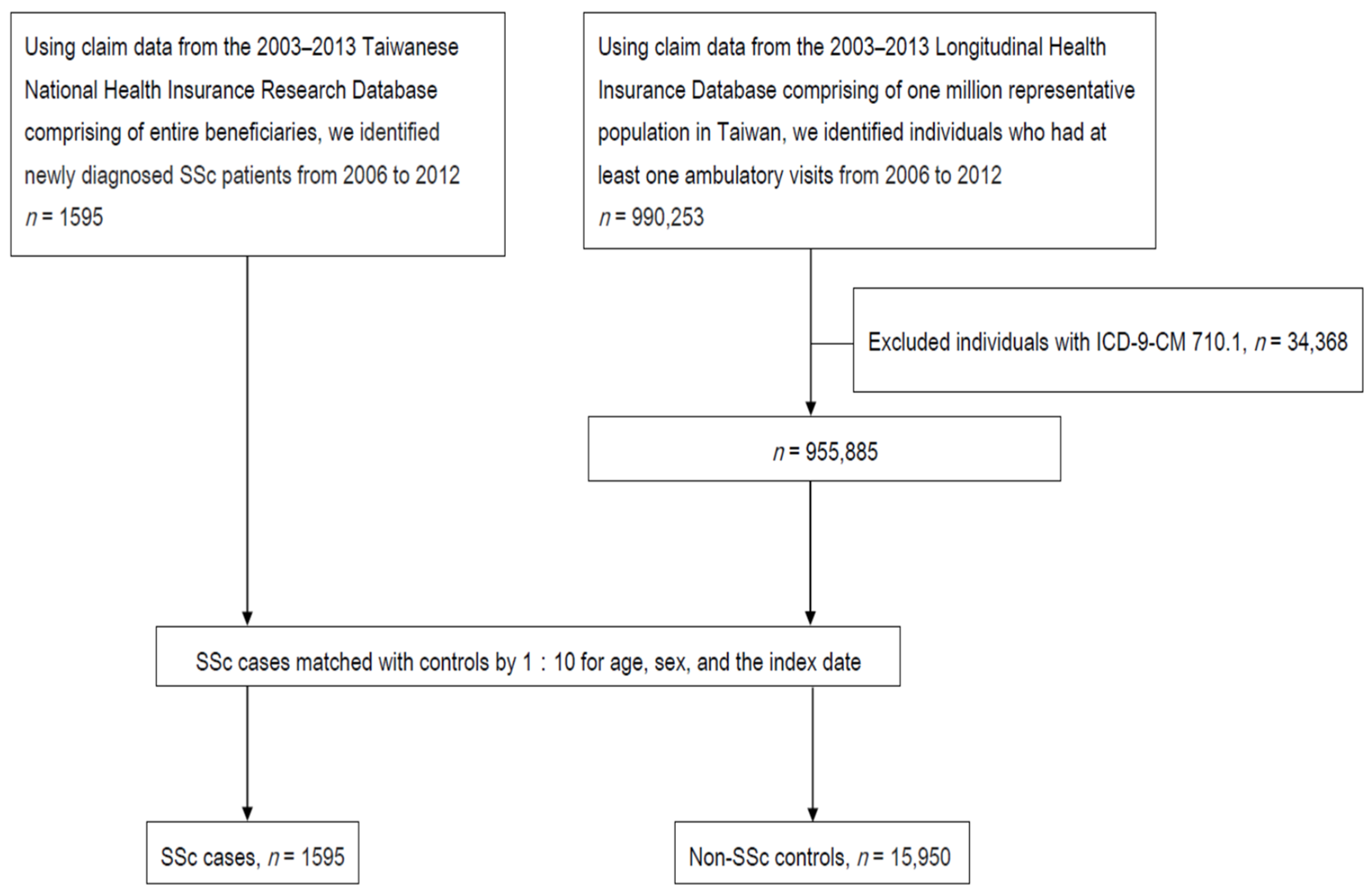
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Definition of a History of Appendicitis
2.5. Potential Confounders
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sobolewski, P.; Maślińska, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Łagun, Z.; Malewska, A.; Roszkiewicz, M.; Nitskovich, R.; Szymańska, E.; Walecka, I. Systemic sclerosis—Multidisciplinary disease: Clinical features and treatment. Reumatologia 2019, 57, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, E.P.; Denton, C.P. The Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 41, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, S.; Stagnaro, C.; Della Rossa, A. Systemic sclerosis: A critical digest of the recent literature. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Ingegnoli, F.; Ughi, N.; Mihai, C. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors, and disease outcomes of systemic sclerosis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokeerbux, M.R.; Giovannelli, J.; Dauchet, L.; Mouthon, L.; Agard, C.; Lega, J.C.; Allanore, Y.; Jego, P.; Bienvenu, B.; Berthier, S.; et al. Survival and prognosis factors in systemic sclerosis: Data of a French multicenter cohort, systematic review, and meta-analysis of the literature. Arthritis Res. 2019, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korman, B.D.; Criswell, L.A. Recent advances in the genetics of systemic sclerosis: Toward biological and clinical significance. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2015, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.; Rivera, A.; Sopeña, B.; Vilella, C.T.; Guillén-Del-Castillo, A.; Argüelles, D.C.; Rubio, J.L.C.; Rivas, M.R.; Martínez, L.T.; Parra, J.A.T.; et al. Clinical and epidemiological differences between men and women with systemic sclerosis: A study in a Spanish systemic sclerosis cohort and literature review. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio-Rivas, M.; Moreno, R.; Corbella, X. Occupational and environmental scleroderma. Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, I.; Gehanno, J.-F.; Bubenheim, M.; Duval-Modeste, A.-B.; Joly, P.; Dominique, S.; Bravard, P.; Noël, D.; Cailleux, A.-F.; Benichou, J.; et al. Systemic sclerosis and exposure to heavy metals: A case control study of 100 patients and 300 controls. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, A. The vermiform appendix: Not a useless organ. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2004, 14, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kooij, I.A.; Sahami, S.; Meijer, S.L.; Buskens, C.J.; Velde, A.A.T. The immunology of the vermiform appendix: A review of the literature. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenfels, A.B.; Maisonneuve, P. Appendectomy and protection against ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, R.E.; Olaison, G.; Tysk, C.; Ekbom, A. Appendectomy is followed by increased risk of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caserta, L.; De Filippo, F.R.; Riegler, G. Relationship between anamnestic evidence of appendectomy and onset and clinical course of Crohn’s disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, E.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Stokholm, M.G.; Sørensen, H.T.; Henderson, V.W.; Borghammer, P. Appendectomy and risk of Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide cohort study with more than 10 years of follow-up. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1918–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of National Health Insurance D, Executive Yuan, Taiwan: Database IttNHIR, (NHIRD). Available online: https://nhird.nhri.org.tw/ (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Leung, W.K.; Chu, C.H.; Mok, M.Y.; Yeung, K.W.; Ng, S.K. Periodontal status of adults with systemic sclerosis: Case-control study. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-F.; Chen, P.-L.; Liu, M.-F.; Lee, C.-C.; Lee, N.-Y.; Chang, C.-M.; Lee, H.-C.; Wu, C.-J.; Ko, W.-C. Nontyphoidal Salmonella bacteremia in patients with connective tissue diseases. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2012, 45, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.E.; Franks, J.M.; Cai, G.; Mehta, B.K.; Wood, T.A.; Archambault, K.; Pioli, P.A.; Simms, R.W.; Orzechowski, N.; Arron, S.; et al. Microbiome dysbiosis is associated with disease duration and increased inflammatory gene expression in systemic sclerosis skin. Arthritis Res. 2019, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyo, R.A.; Cherkin, D.C.; Ciol, M.A. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1992, 45, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticherling, M. Systemic sclerosis—the dermatological perspective. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Chang, Y.-L.; Barroso, N.; Furst, D.E.; Clements, P.J.; Gorn, A.H.; Roth, B.E.; Conklin, J.L.; Getzug, T.; Borneman, J.; et al. Association of Systemic Sclerosis With a Unique Colonic Microbial Consortium. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, G.L. Fusobacterial infections: An underestimated threat. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2000, 57, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, O.; Spor, A.; Felin, J.; Fak, F.; Stombaugh, J.; Tremaroli, V.; Behre, C.J.; Knight, R.; Fagerberg, B.; Ley, R.E.; et al. Human oral, gut, and plaque microbiota in patients with atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4592–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.; Kaplan, G.G.; Beck, P.L.; Rioux, K.; Panaccione, R.; DeVinney, R.; Lynch, T.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Invasive potential of gut mucosa-derived fusobacterium nucleatum positively correlates with IBD status of the host. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, J.L.; Hedin, C.R.; Koutsoumpas, A.; Ng, S.C.; McCarthy, N.E.; Prescott, N.J.; Pessoa-Lopes, P.; Mathew, C.G.; Sanderson, J.; Hart, A.L.; et al. Smokers with active Crohn’s disease have a clinically relevant dysbiosis of the gastrointestinal microbiota. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U.; Sczesnak, A.; Longman, R.S.; Segata, N.; Ubeda, C.; Bielski, C.; Rostron, T.; Cerundolo, V.; Pamer, E.G.; Abramson, S.B.; et al. Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. Elife 2013, 2, e01202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vester-Andersen, M.K.; Mirsepasi, H.C.; Prosberg, M.V.; Mortensen, C.O.; Träger, C.; Skovsen, K.; Thorkilgaard, T.; Nøjgaard, C.; Vind, I.; Krogfelt, K.A.; et al. Increased abundance of proteobacteria in aggressive Crohn’s disease seven years after diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walujkar, S.A.; Dhotre, D.P.; Marathe, N.P.; Lawate, P.S.; Bharadwaj, R.S.; Shouche, Y.S. Characterization of bacterial community shift in human Ulcerative Colitis patients revealed by Illumina based 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Gut Pathog. 2014, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinane, C.M.; Tadrous, A.; Fouhy, F.; Ryan, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; Murphy, B.; Andrews, E.; Cotter, P.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. Microbial Composition of Human Appendices from Patients following Appendectomy. mBio 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.B.; Brower-Sinning, R.; Firek, B.; Zhong, D.; Morowitz, M.J. Acute appendicitis in children is associated with a local expansion of Fusobacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlén, G. Black-pigmented Gram-negative anaerobes in periodontitis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1993, 6, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezow, A.B.; Darveau, R.P. Microbial shift and periodontitis. Periodontol. 2000 2011, 55, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cekici, A.; Kantarci, A.; Hasturk, H.; Van Dyke, T.E. Inflammatory and immune pathways in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Periodontol. 2000 2014, 64, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Aquino, S.G.; Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Koenders, M.I.; van de Loo, F.A.J.; Pruijn, G.J.M.; Marijnissen, R.J.; Walgreen, B.; Helsen, M.M.; van den Bersselaar, L.A.; de Molon, R.S.; et al. Periodontal pathogens directly promote autoimmune experimental arthritis by inducing a TLR2- and IL-1-driven Th17 response. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 4103–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chizzolini, C.; Dufour, A.M.; Brembilla, N.C. Is there a role for IL-17 in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis? Immunol. Lett. 2018, 195, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bălănescu, P.; Lădaru, A.; Bălănescu, E.; Nicolau, A.; Băicuş, C.; Dan, G.A. IL-17, IL-6 and IFN-γ in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 53, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X.-L.; Duan, Y.; Yang, L.-J.; Wang, J. Association between cigarette smoking and impaired clinical symptoms in systemic sclerosis: A review. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 318, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Control | Case | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 15,950) | (n = 1595) | p-Value | |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 51 ± 15 | 51 ± 15 | 1 |
| Gender | 1 | ||
| Female | 12,360 (77.5) | 1236 (77.5) | |
| Male | 3590 (22.5) | 359 (22.5) | |
| Appendicitis | 81 (0.5) | 17 (1.1) | 0.004 |
| Primary appendectomy | 74 (0.5) | 15 (0.9) | 0.011 |
| Appendicitis and primary appendectomy | 73 (0.5) | 15 (0.9) | 0.009 |
| Appendicitis or primary appendectomy | 82 (0.5) | 17 (1.1) | 0.005 |
| Salmonella | 65 (0.4) | 8 (0.5) | 0.578 |
| Ill-defined intestinal infections | 2020 (12.7) | 230 (14.4) | 0.047 |
| Periodontal disease | 5936 (37.2) | 774 (48.5) | <0.001 |
| CCI group | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 12,888 (80.8) | 645 (40.4) | |
| ≥1 | 3062 (19.2) | 950 (59.6) | |
| Myocardial infarction | 24 (0.2) | 8 (0.5) | 0.002 |
| Congestive heart failure | 109 (0.7) | 55 (3.4) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 36 (0.2) | 50 (3.1) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 439 (2.8) | 52 (3.3) | 0.241 |
| Dementia | 75 (0.5) | 5 (0.3) | 0.376 |
| COPD | 485 (3.0) | 156 (9.8) | <0.001 |
| Connective tissue disease | 53 (0.3) | 631 (39.6) | <0.001 |
| Peptic ulcer disease | 700 (4.4) | 175 (11) | <0.001 |
| Mild liver disease | 332 (2.1) | 82 (5.1) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1158 (7.3) | 113 (7.1) | 0.797 |
| Diabetes mellitus with end-organ damage | 246 (1.5) | 37 (2.3) | 0.019 |
| Hemiplegia | 35 (0.2) | 10 (0.6) | 0.002 |
| Moderate to severe renal disease | 181 (1.1) | 87 (5.5) | <0.001 |
| Tumor | 341 (2.1) | 105 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Moderate or severe liver disease | 13 (0.1) | 3 (0.2) | 0.179 |
| Metastatic solid tumor | 34 (0.2) | 16 (1.0) | <0.001 |
| AIDS | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.752 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Diagnosed with appendicitis | 2.11 (1.25–3.57) | 2.03 (1.14–3.60) |
| CCI ≥ 1 | 8.64 (7.64–9.76) | 8.48 (7.50–9.58) |
| Periodontal disease | 1.64 (1.48–1.83) | 1.55 (1.39–1.74) |
| Salmonella | 1.23 (0.59–2.58) | 0.97 (0.43–2.18) |
| Ill-defined intestinal infections | 1.17 (1.004–1.35) | 1.00 (0.85–1.17) |
| Control (n = 15,950) | Case (n = 1595) | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event (%) | Duration (Year) (Mean ± SD) | Event (%) | Duration (Year) (Mean ± SD) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Appendicitis | 81 (0.5) | 3.7 ± 2.2 | 17 (1.1) | 3.7 ± 2.1 | 2.03 (1.14–3.60) |
| Primary appendectomy | 74 (0.5) | 3.6 ± 2.1 | 15 (0.9) | 3.7 ± 2.1 | 1.93 (1.06–3.54) |
| Appendicitis and Primary appendectomy | 73 (0.5) | 3.6 ± 2.1 | 15 (0.9) | 3.7 ± 2.1 | 1.97 (1.07–3.61) |
| Appendicitis or Primary appendectomy | 82 (0.5) | 3.7 ± 2.2 | 17 (1.1) | 3.7 ± 2.1 | 1.99 (1.13–3.53) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.-T.; Wei, J.C.-C.; Chang, R.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, H.-H. Association between Appendicitis and Incident Systemic Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112337
Yang K-T, Wei JC-C, Chang R, Lin C-C, Chen H-H. Association between Appendicitis and Incident Systemic Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(11):2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112337
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kuang-Tsu, James Cheng-Chung Wei, Renin Chang, Chi-Chien Lin, and Hsin-Hua Chen. 2021. "Association between Appendicitis and Incident Systemic Sclerosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 11: 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112337
APA StyleYang, K.-T., Wei, J. C.-C., Chang, R., Lin, C.-C., & Chen, H.-H. (2021). Association between Appendicitis and Incident Systemic Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(11), 2337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112337







