Silicon Carbide-Coated Ceramic Membrane Bioreactor for Sustainable Water Purification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Silicon Carbide (SiC) Membrane Coating
2.3. Artificial Fermentation Feed
2.4. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
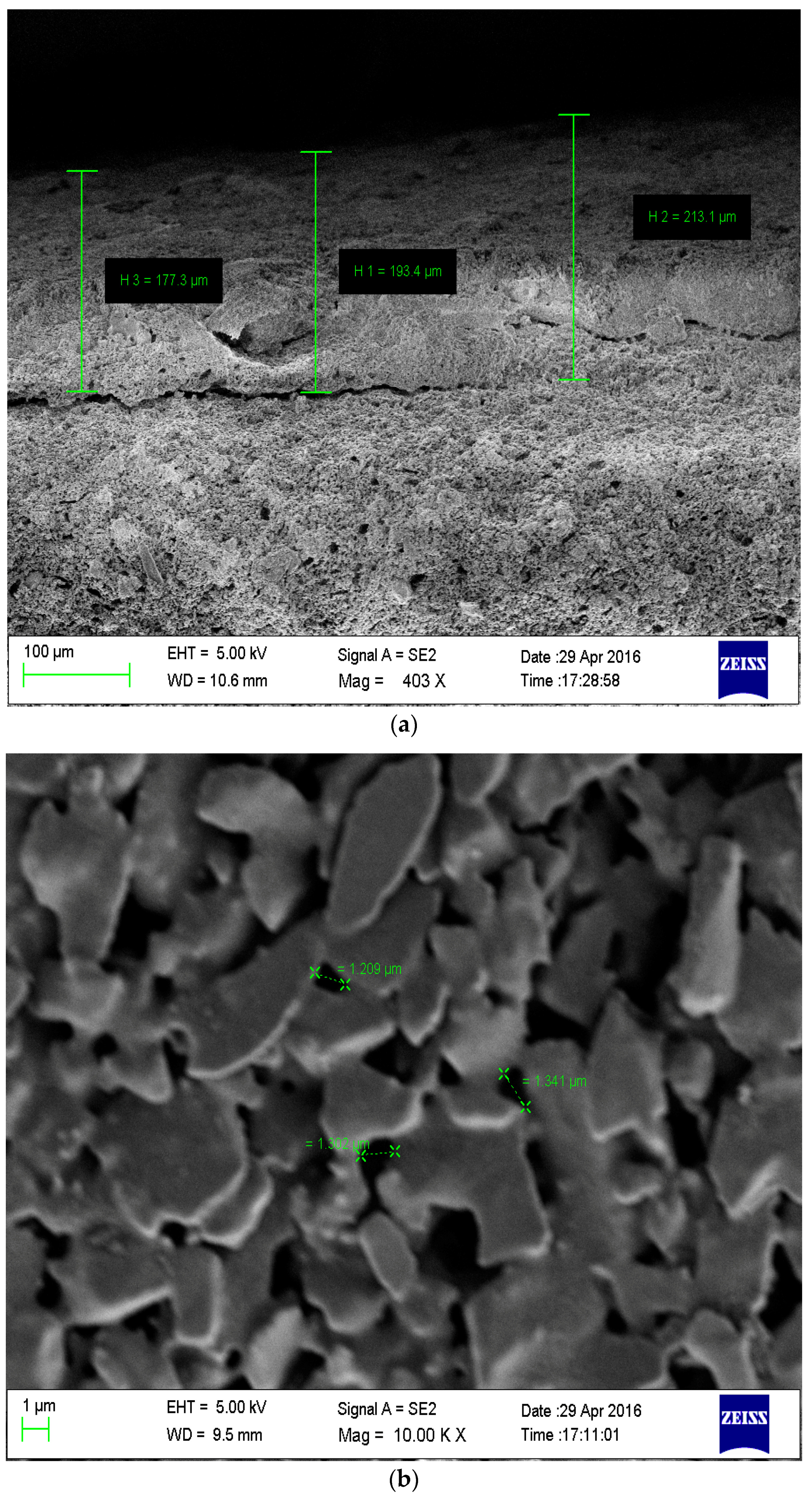
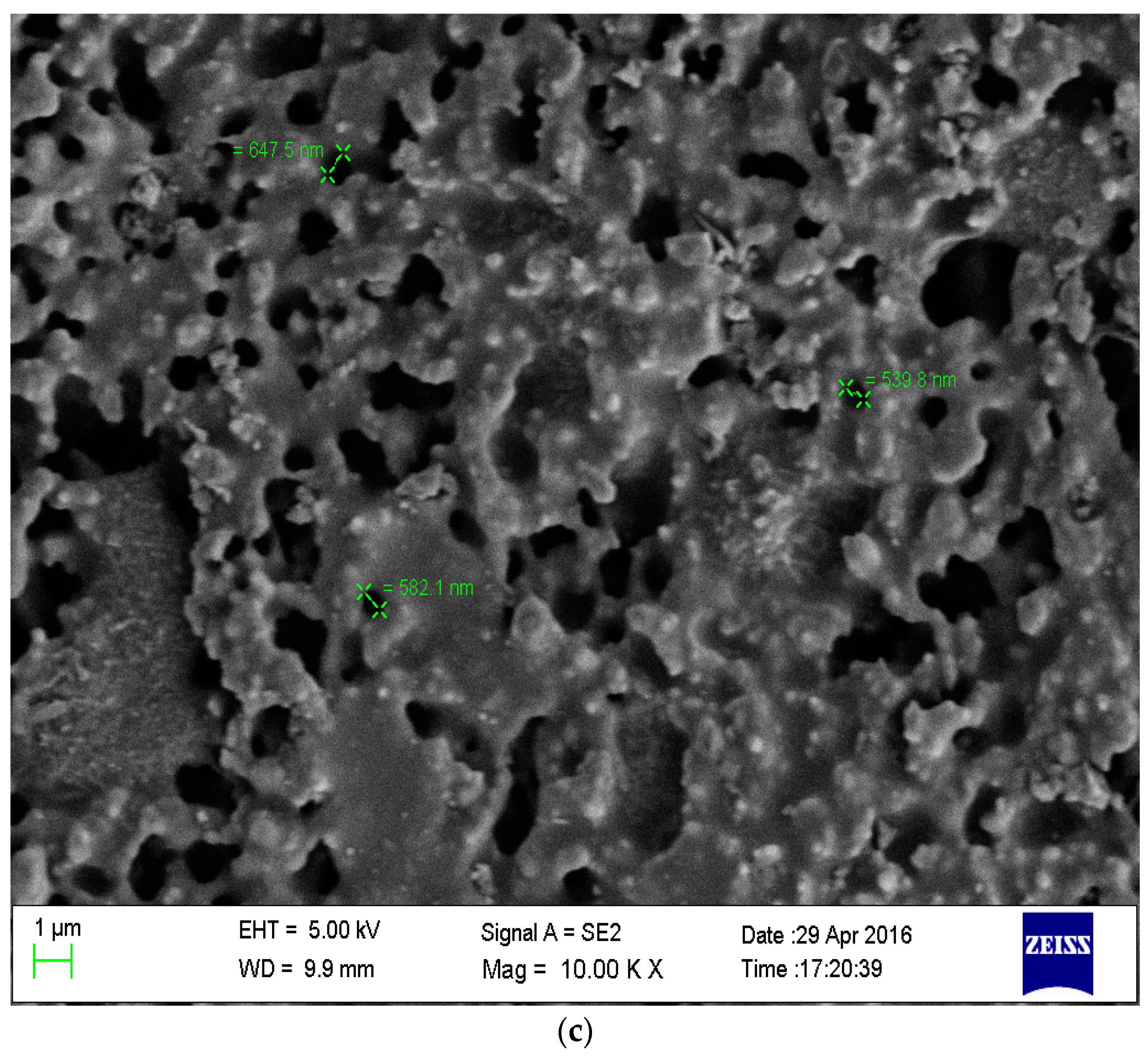
3.1. Membrane Characterization
3.2. Clean Water Flux Analysis
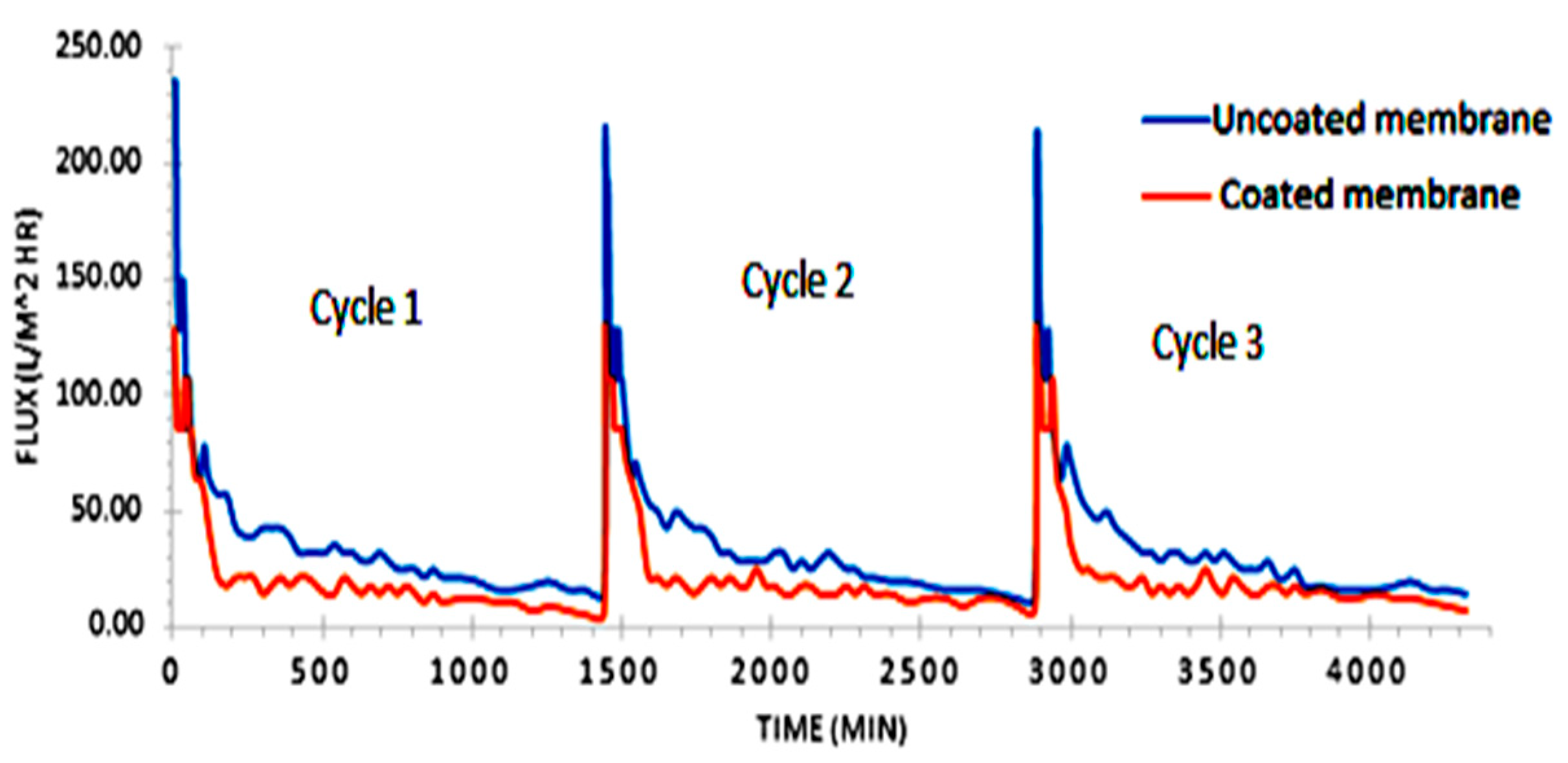
3.3. Permeate Flux Analysis
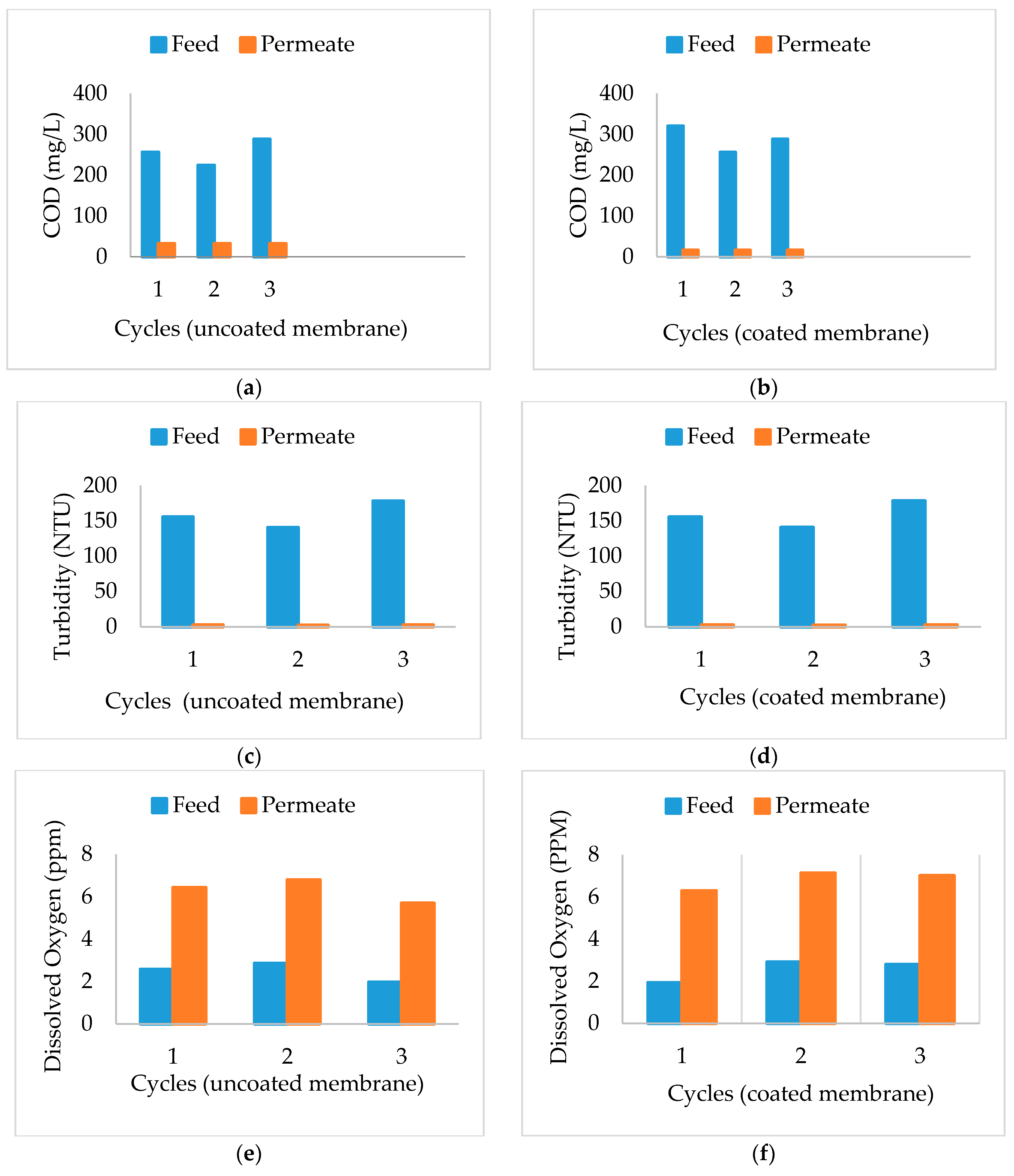
3.4. Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
3.5. Turbidity
3.6. Dissolved Oxygen
3.7. Fouling Mechanism
3.8. Analysis of Total Nitrogen, Total Phosphate, BOD5 and Total Suspended Solids
3.8.1. Water Effluent and Influent Quality for Uncoated Membranes
3.8.2. Water Effluent and Influent Quality for Coated Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Bidhendi, G.N.; Torabian, A.; Mehrdadi, N. Evaluation of membrane bioreactor for advanced treatment of industrial wastewater and reverse osmosis pretreatment. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2013, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesapillai, M.; Singh, A.; Simha, P. Separation processes and technologies as the mainstay in chemical, biochemical, petroleum and environmental engineering: A special issue. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2016, 5, S1–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Cho, J.; Lim, B.R.; Song, K.G.; Ahn, K.H. Effects of sludge retention time on membrane fouling and microbial community structure in a membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.H.; Tardieu, E.; Qian, Y.; Wen, X.H. Ultrafiltration membrane bioreactor for urban wastewater reclamation. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 177, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gander, M.; Jefferson, B.; Judd, S. Aerobic MBRs for domestic wastewater treatment: A review with cost considerations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2000, 18, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Mai, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; An, Y.; Zhou, Z. Research and applications of membrane bioreactors in China: Progress and prospect. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Hara, H.; Watanabe, Y. Removal of pharmaceutical compounds by submerged membrane bioreactors (MBRs). Desalination 2005, 178, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gui, P.; Qian, Y. Effect of sludge retention time on microbial behavior in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem. 2001, 36, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Okuno, Y.I.; Uryu, K.; Ohtsubo, S.; Watanabe, A. Filtration characteristics of hollow fiber microfiltration membranes used in membrane bioreactor for domestic wastewater treatment. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Kang, S.T. Characteristics and fates of soluble microbial products in ceramic membrane bioreactor at various sludge retention times. Water Res. 2003, 37, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, I.J.; Cho, M.H.; Park, P.K.; Lee, C.H. Potential and limitations of alum or zeolite addition to improve the performance of a submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.D.; Hay, C.T.; Khor, S.L. Effects of hydraulic retention time on behavior of start-up submerged membrane bioreactor with prolonged sludge retention time. Desalination 2006, 195, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Hiasa, M.; Mahmood, T.; Matsuo, T. Direct solid-liquid separation using hollow fiber membrane in an activated sludge aeration tank. In Proceedings of the Water Pollution Research and Control Brighton, Brighton, UK, 18–21 July 1988; pp. 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lesjean, B.; Rosenberger, S.; Schrotter, J.C.; Recherche, A. Membrane-aided biological wastewater treatment—An overview of applied systems. Membr. Technol. 2004, 8, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.L.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Characterization of membrane fouling in submerged ceramic membrane photobioreactors fed with effluent from membrane bioreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yu, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z. Relationship between sludge characteristics and membrane flux determination in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, S.; Krüger, U.; Witzig, R.; Manz, W.; Szewzyk, U.; Kraume, M. Performance of a bioreactor with submerged membranes for aerobic treatment of municipal waste water. Water Res. 2002, 36, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cicek, N.; Ilg, J. State-of-the-art of membrane bioreactors: Worldwide research and commercial applications in North America. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, L.S.; Tang, T.W.; Lau, G.N.; Sharma, K.R.; Chen, G.H. A pilot study for wastewater reclamation and reuse with MBR/RO and MF/RO systems. Desalination 2007, 202, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.; Melin, T. Wastewater reclamation by the PAC-NF process. Desalination 2005, 178, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerton, A.M.; Andrews, R.C.; Bagley, D.M. Evaluation of an MBR–RO system to produce high quality reuse water: Microbial control, DBP formation and nitrate. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3982–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Ng, H.Y. Effect of membrane type and material on performance of a submerged membrane bioreactor. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintgens, T.; Melin, T.; Schäfer, A.; Khan, S.; Muston, M.; Bixio, D.; Thoeye, C. The role of membrane processes in municipal wastewater reclamation and reuse. Desalination 2005, 178, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagana, A.E.; Sklari, S.D.; Kikkinides, E.S.; Zaspalis, V.T. Microporous ceramic membrane technology for the removal of arsenic and chromium ions from contaminated water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 110, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiemchaisri, C.; Yamamoto, K.; Vigneswaran, S. Household membrane bioreactor in domestic wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Hermanowicz, S.W.; Park, C. Treatment of food waste recycling wastewater using anaerobic ceramic membrane bioreactor for biogas production in mainstream treatment process of domestic wastewater. Water Res. 2017, 123, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Shang, W.; Dong, W.; Zhao, L.; Li, M.; Wang, R.; Sun, F. Suppression of membrane fouling in the ceramic membrane bioreactor (CMBR) by minute electric field. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Koh, Y.K.K.; Ng, H.Y. Effects of dissolved organic matters (DOMs) on membrane fouling in anaerobic ceramic membrane bioreactors (AnCMBRs) treating domestic wastewater. Water Res. 2015, 86, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R. Microfiltration. In Membrane Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 303–324. [Google Scholar]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Fane, A.G.; Wiley, D.E. Factors influencing critical flux in membrane filtration of activated sludge. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 1999, 74, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenovic, J.; Matosic, M.; Mijatovic, I.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelo, D. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) as an advanced wastewater treatment technology. In Emerging Contaminants from Industrial and Municipal Waste; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 37–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Kang, S.; Shin, H. Sludge characteristics and their contribution to microfiltration in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 216, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.A.; Chua, H.C.; Arnot, T.C. In situ manipulation of critical flux in a submerged membrane bioreactor using variable aeration rates, and effects of membrane history. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 242, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, F.I.; Yamamoto, K.; Fukushi, K. Different fouling modes of submerged hollow-fiber and flat-sheet membranes induced by high strength wastewater with concurrent biofouling. Desalination 2005, 180, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.E.; Ahring, B.K. Granular sludge formation in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1996, 49, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, P.L.; Bae, J. Model to couple anaerobic process kinetics with biological growth equilibrium thermodynamics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6838–6844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trussell, R.S.; Merlo, R.P.; Hermanowicz, S.W.; Jenkins, D. The effect of organic loading on process performance and membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor treating municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2675–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, T.; Hata, K. Domestic wastewater treatment by a submerged membrane bioreactor with gravitational filtration. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2888–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Fouling control mechanism by suspended biofilm carriers addition in submerged ceramic membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Bi, X.; Ng, H.Y. Effects of bio-carriers on membrane fouling mitigation in moving bed membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.W.; Kang, L.S. Application of combined coagulation-ultrafiltration membrane process for water treatment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Identification of activated sludge properties affecting membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chua, H.C.; Zhou, J.; Fane, A.G. Factors affecting the membrane performance in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z. Dip-Coating Method for Ceramic Membrane Preparation. In Encyclopedia of Membranes; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Huang, X.; Chen, L.; Wen, X.; Qian, Y. Operational performance of a submerged membrane bioreactor for reclamation of bath wastewater. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Maghami, M.; Mohammadi, T. High loaded synthetic hazardous wastewater treatment using lab-scale submerged ceramic membrane bioreactor. Period. Chem. Eng. 2018, 62, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, D.L. Dissolved oxygen and fish behavior. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1987, 18, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulinger, S. Coagulation Pre-Treatment for Microfiltration with. Desalination 2007, 161, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, G.; LaCasse, D.; Kuriyel, R. Combined models of membrane fouling: Development and application to microfiltration and ultrafiltration of biological fluids. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 277, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.M.; Madhu, G.M.; Roy, S. Fouling behaviour, regeneration options and on-line control of biomass-based power plant effluents using microporous ceramic membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, R.; Lebrun, R.E.; Lavallee, H.C. Comparative-study on Fluxes and performances during Paper-mill waste-water treatment with membrane bioreactor. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1997, 75, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
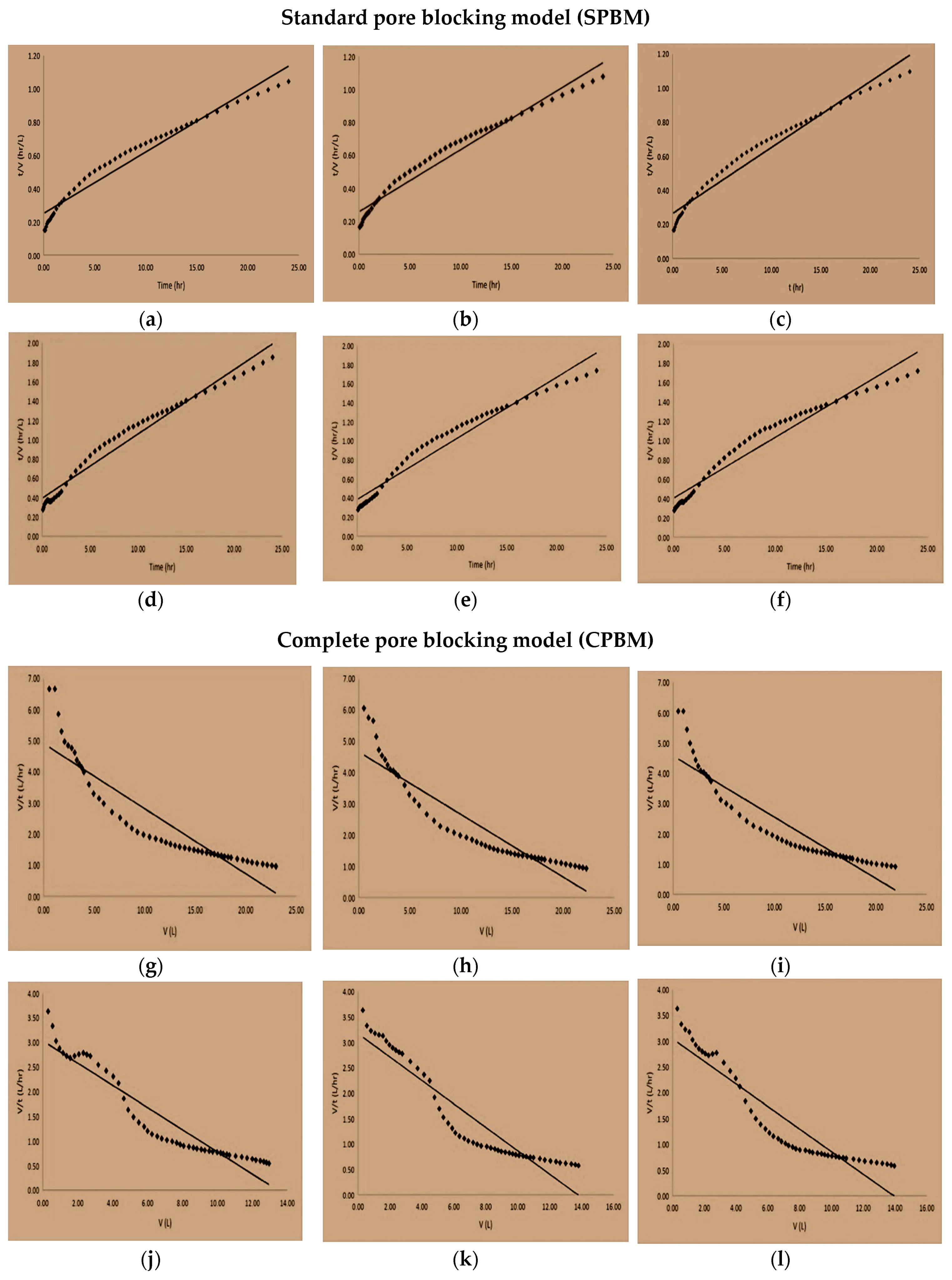
| Cycle | Uncoated Membranes | Coated Membranes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | Intercept | R2 | Slope | Intercept | R2 | |
| 1 | 0.0369 | 0.2511 | 0.9574 | 0.0666 | 0.3935 | 0.9669 |
| 2 | 0.0377 | 0.2576 | 0.9637 | 0.0641 | 0.3853 | 0.9553 |
| 3 | 0.0387 | 0.2633 | 0.9641 | 0.063 | 0.4024 | 0.947 |
| Cycle | Uncoated Membranes | Coated Membranes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | Intercept | R2 | Slope | Intercept | R2 | |
| 1 | −0.2088 | 4.8967 | 0.8204 | −0.2251 | 3.0248 | 0.8966 |
| 2 | −0.1999 | 4.6516 | 0.8543 | −0.2301 | 3.1684 | 0.8825 |
| 3 | −0.2021 | 4.5684 | 0.8449 | −0.2187 | 3.0434 | 0.8678 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Surappanahalli Rajanna, S.; Madhu, G.M.; Madhusoodana, C.D.; Govindarajan, A. Silicon Carbide-Coated Ceramic Membrane Bioreactor for Sustainable Water Purification. Membranes 2019, 9, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9040047
Surappanahalli Rajanna S, Madhu GM, Madhusoodana CD, Govindarajan A. Silicon Carbide-Coated Ceramic Membrane Bioreactor for Sustainable Water Purification. Membranes. 2019; 9(4):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9040047
Chicago/Turabian StyleSurappanahalli Rajanna, Sowmya, Gattumane Motappa Madhu, Chengala Damodara Madhusoodana, and Adithya Govindarajan. 2019. "Silicon Carbide-Coated Ceramic Membrane Bioreactor for Sustainable Water Purification" Membranes 9, no. 4: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9040047
APA StyleSurappanahalli Rajanna, S., Madhu, G. M., Madhusoodana, C. D., & Govindarajan, A. (2019). Silicon Carbide-Coated Ceramic Membrane Bioreactor for Sustainable Water Purification. Membranes, 9(4), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9040047





