Electrowinning of Iron from Spent Leaching Solutions Using Novel Anion Exchange Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
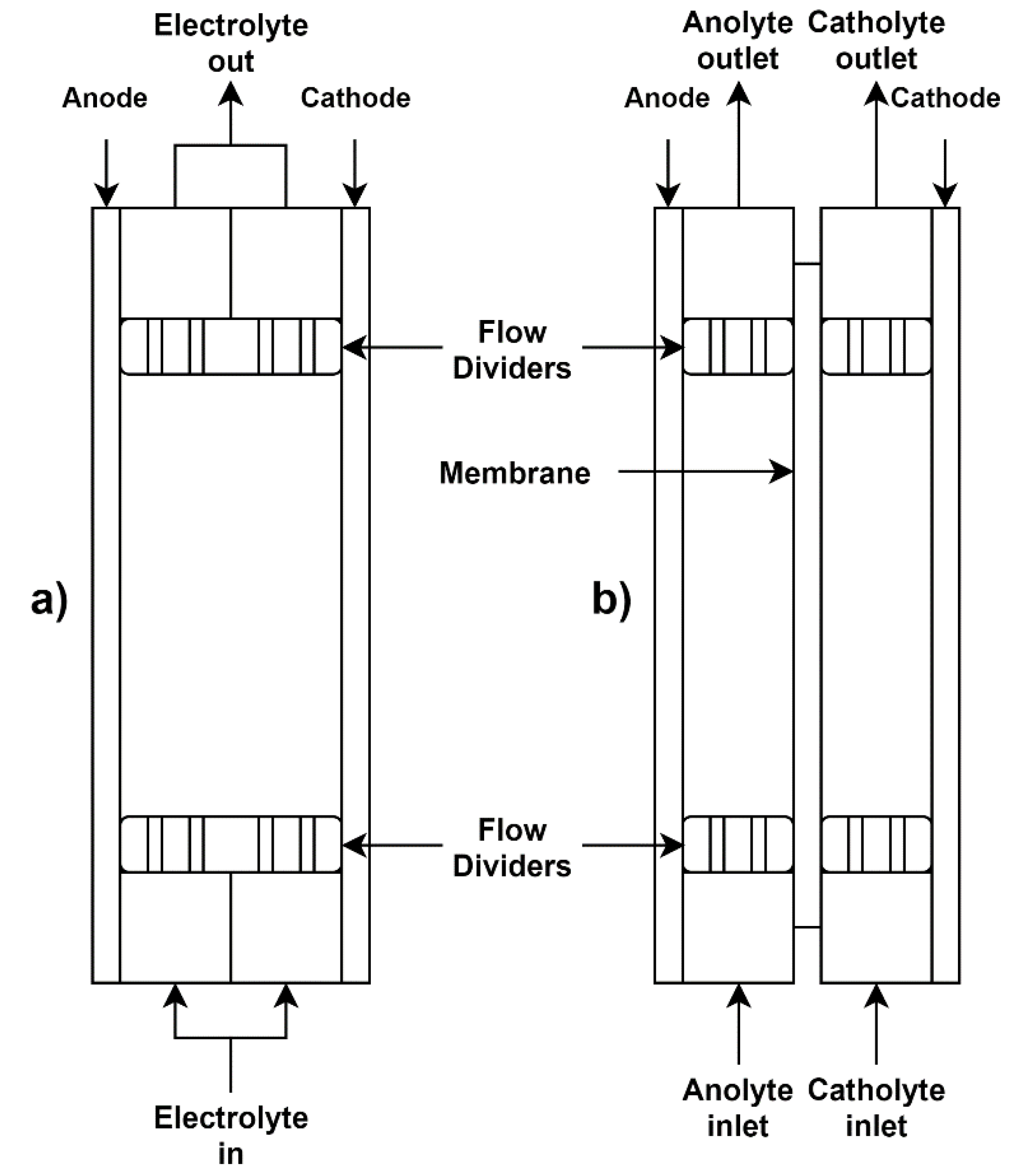
2.1. Flow Cell
2.2. EW Cell Configuration
2.2.1. Undivided
2.2.2. Porous Membrane
2.2.3. Anion Exchange Membrane
2.3. AEM Synthesis, Characterisation, and Screening
2.3.1. Membrane Synthesis
2.3.2. Membrane Characterisation
2.3.3. EW Screening of Novel AEMs
3. Results
3.1. EW Cell Configuration
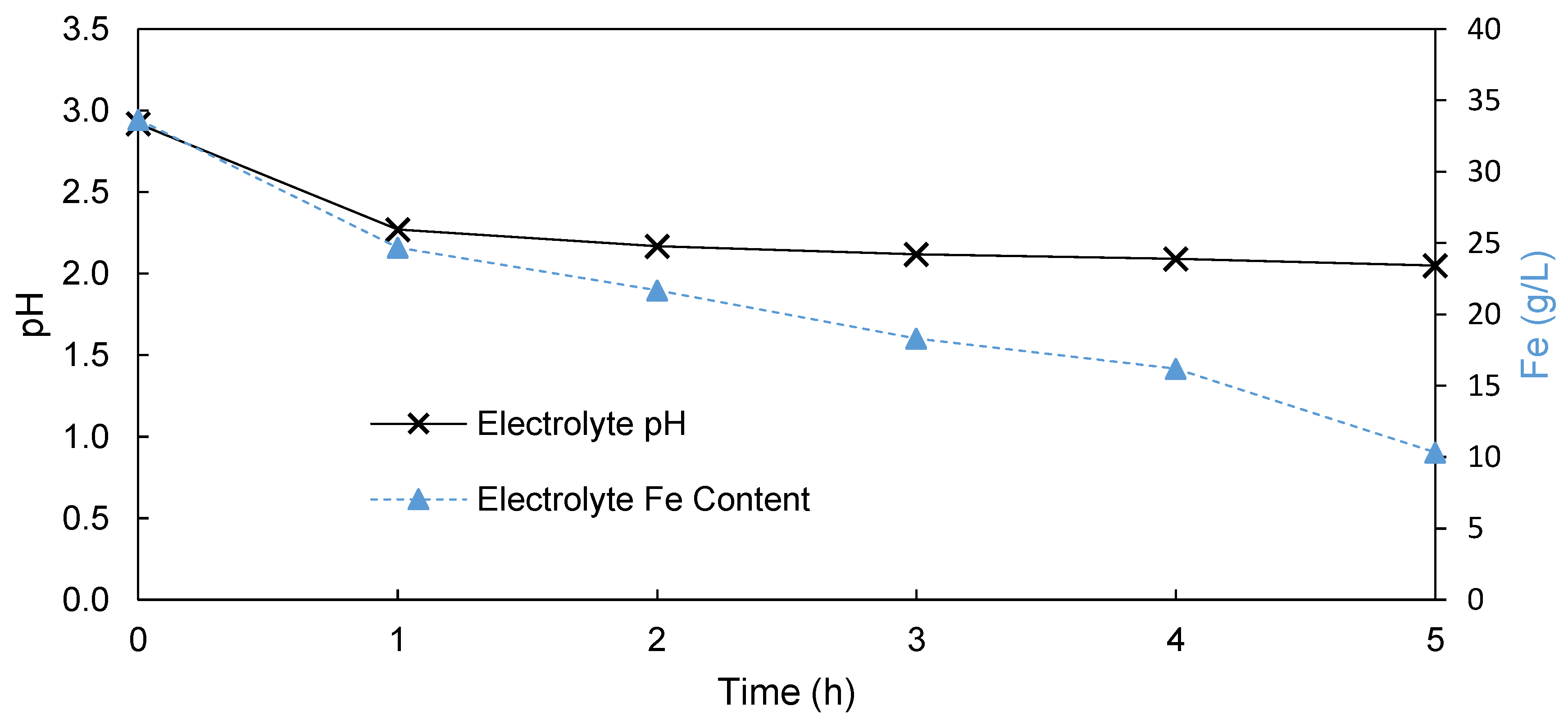
3.1.1. Undivided
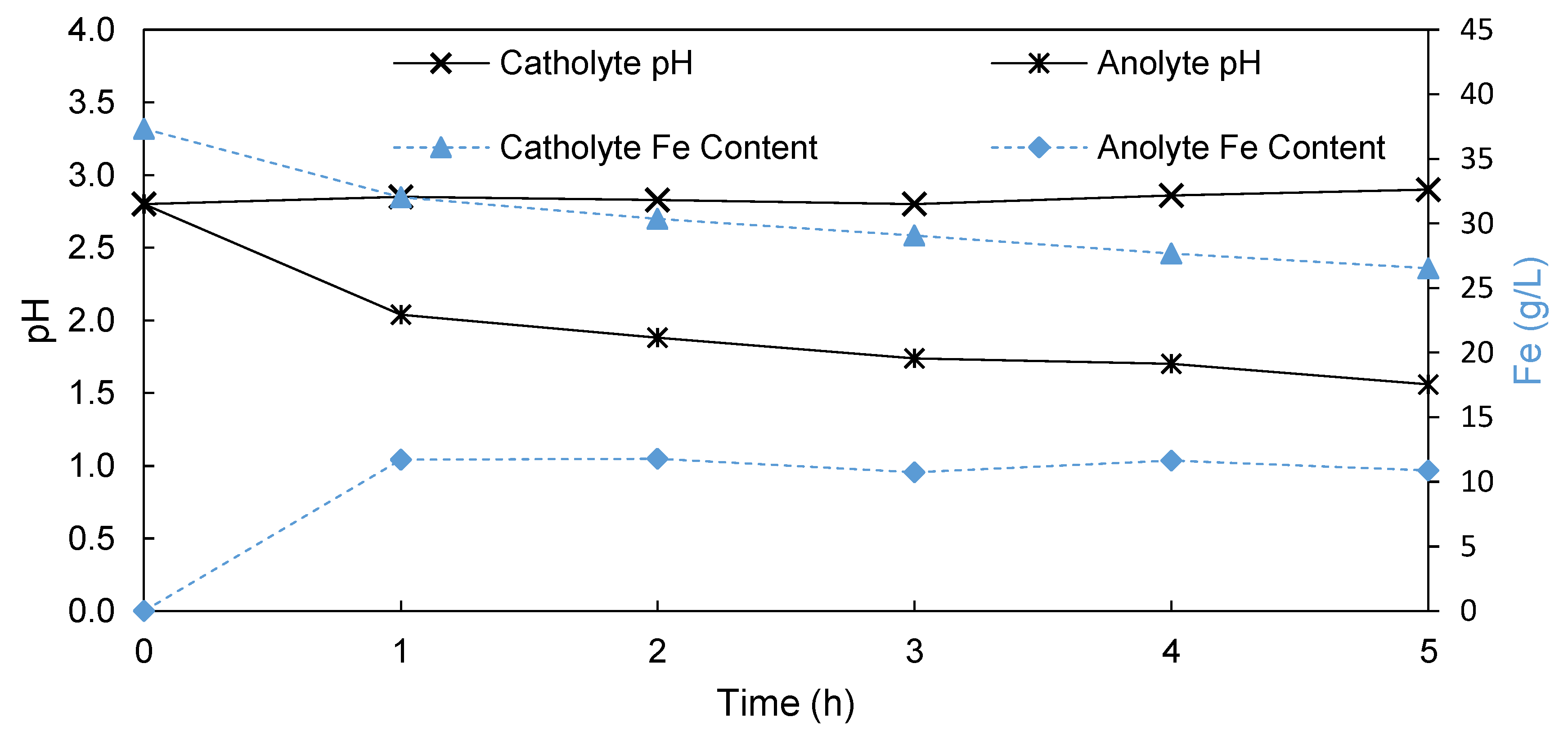
3.1.2. Porous Membrane
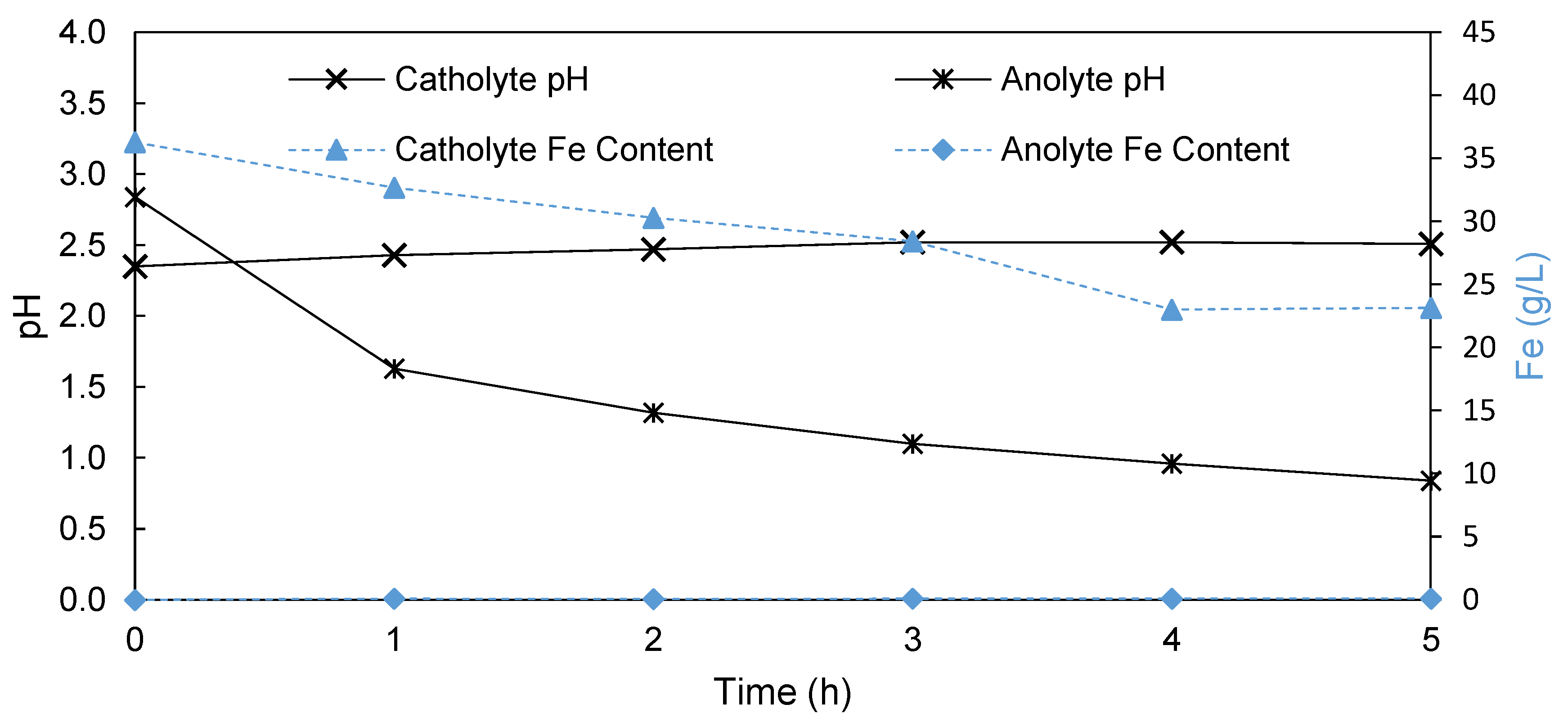
3.1.3. Anion Exchange Membrane
3.2. AEM Synthesis, Characterisation, and Ccreening
3.2.1. Characterisation
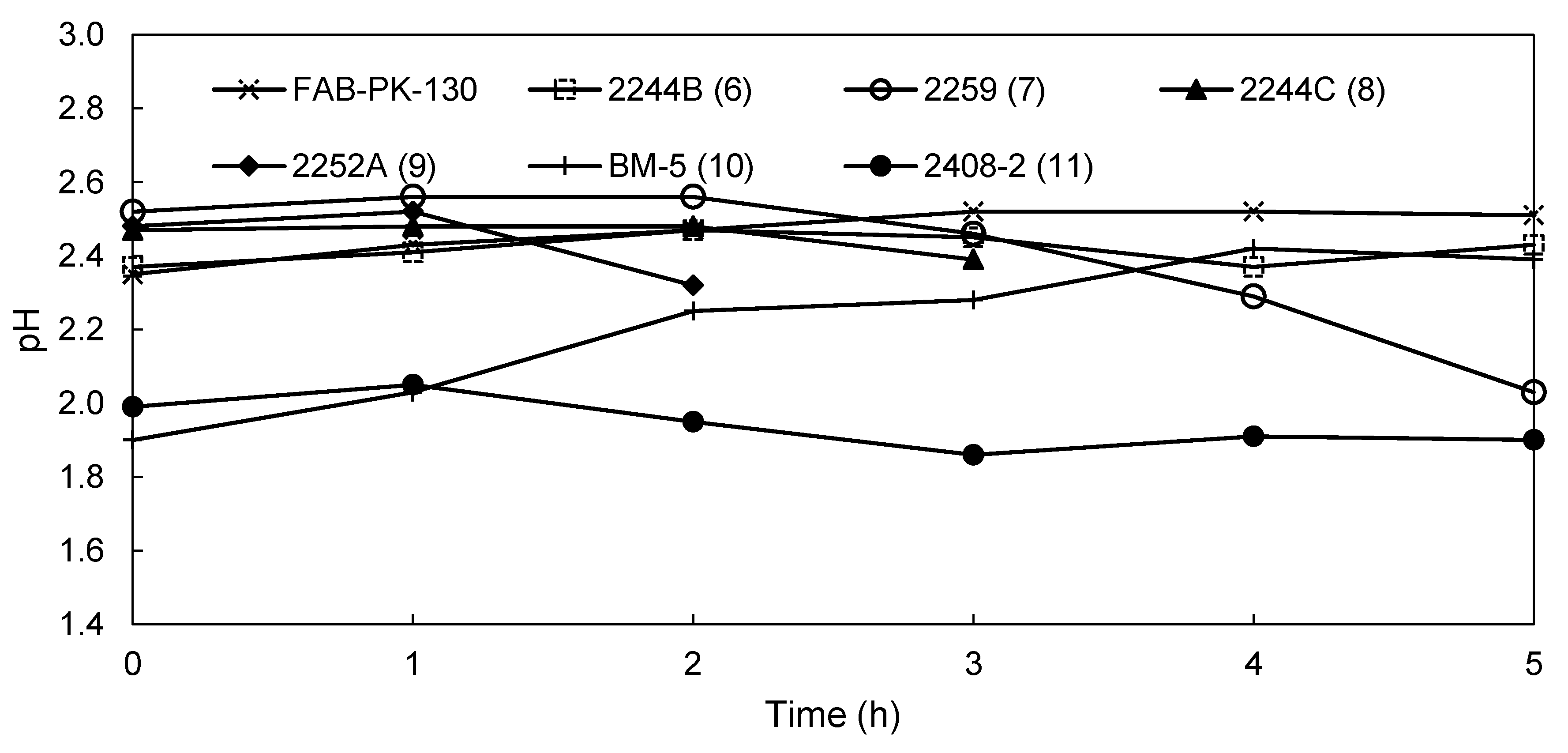
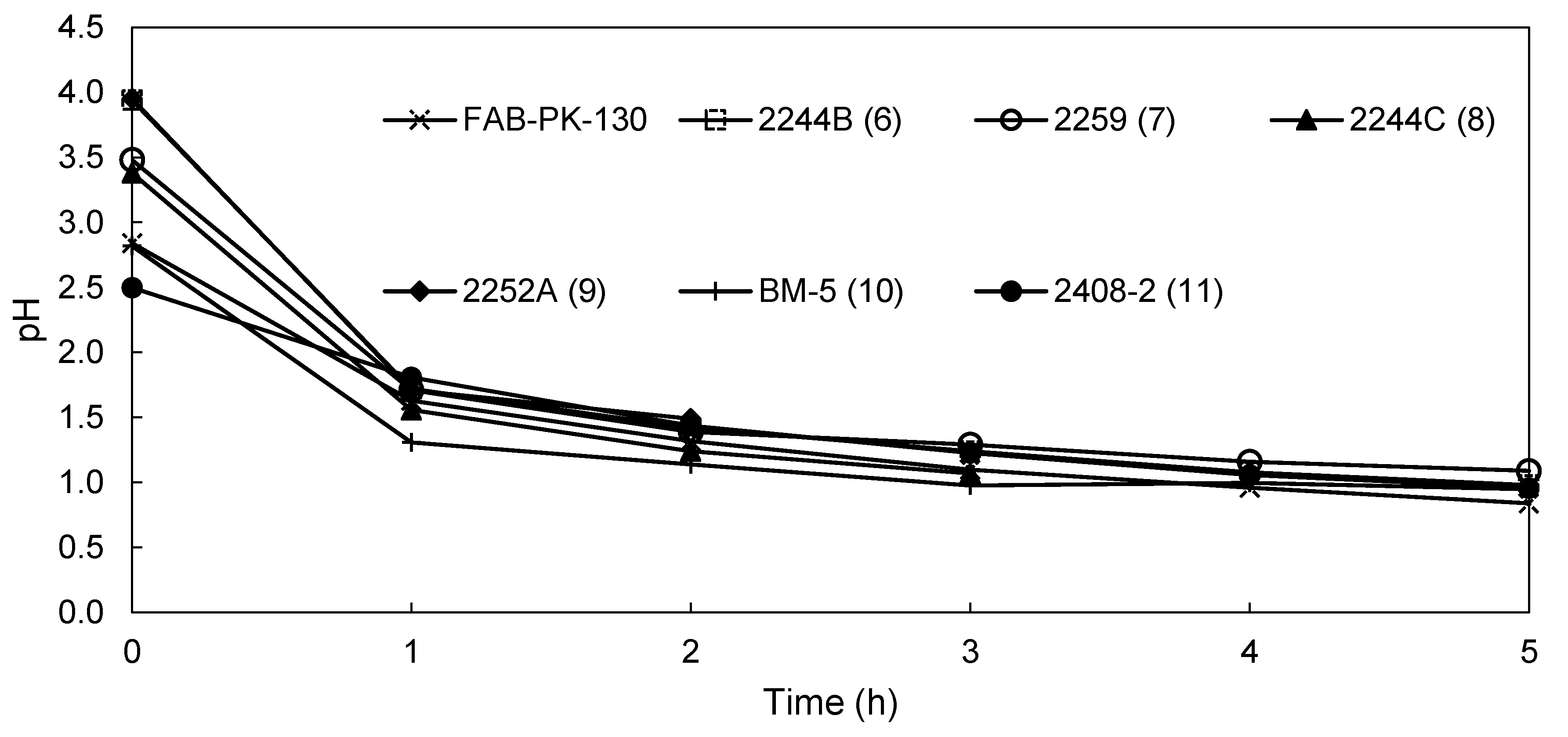
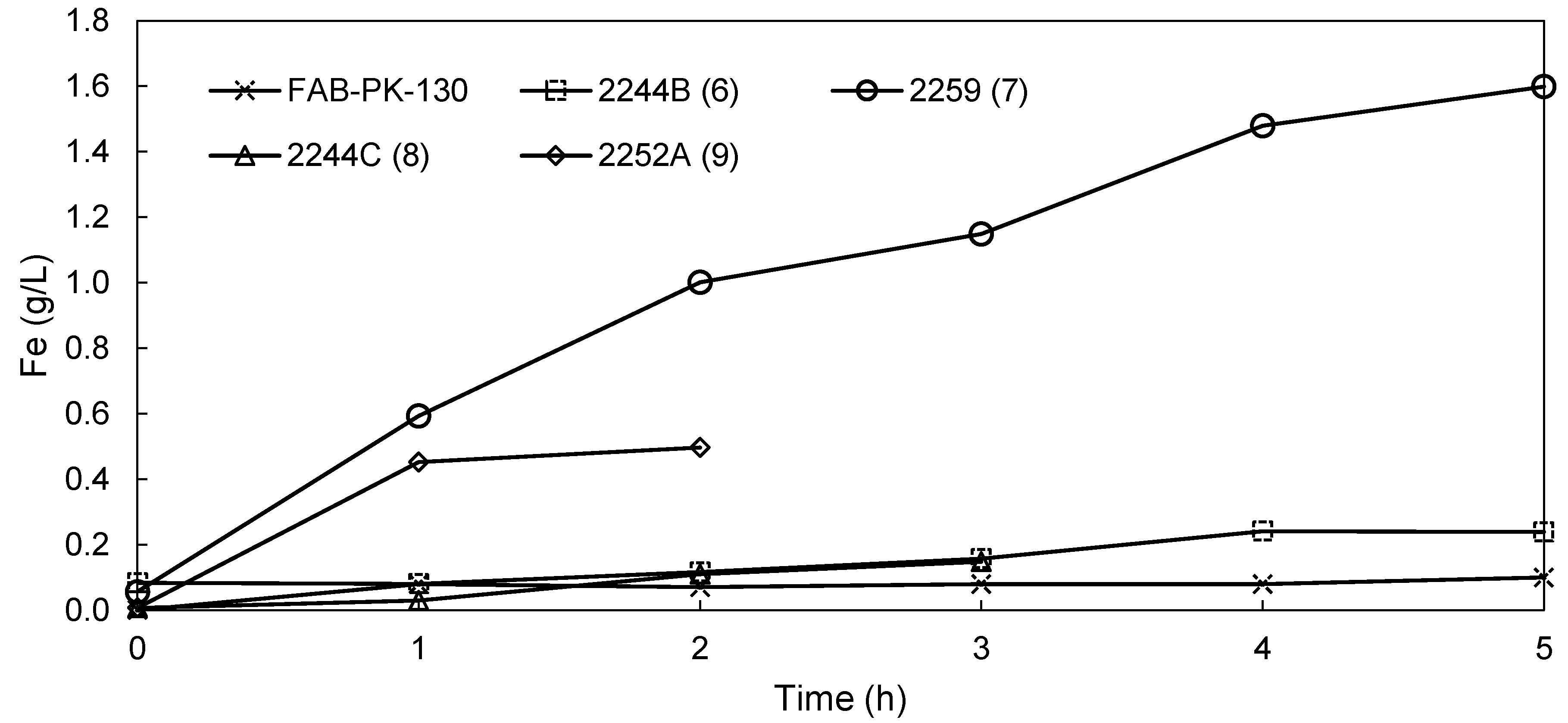
3.2.2. EW Screening of Novel AEMs
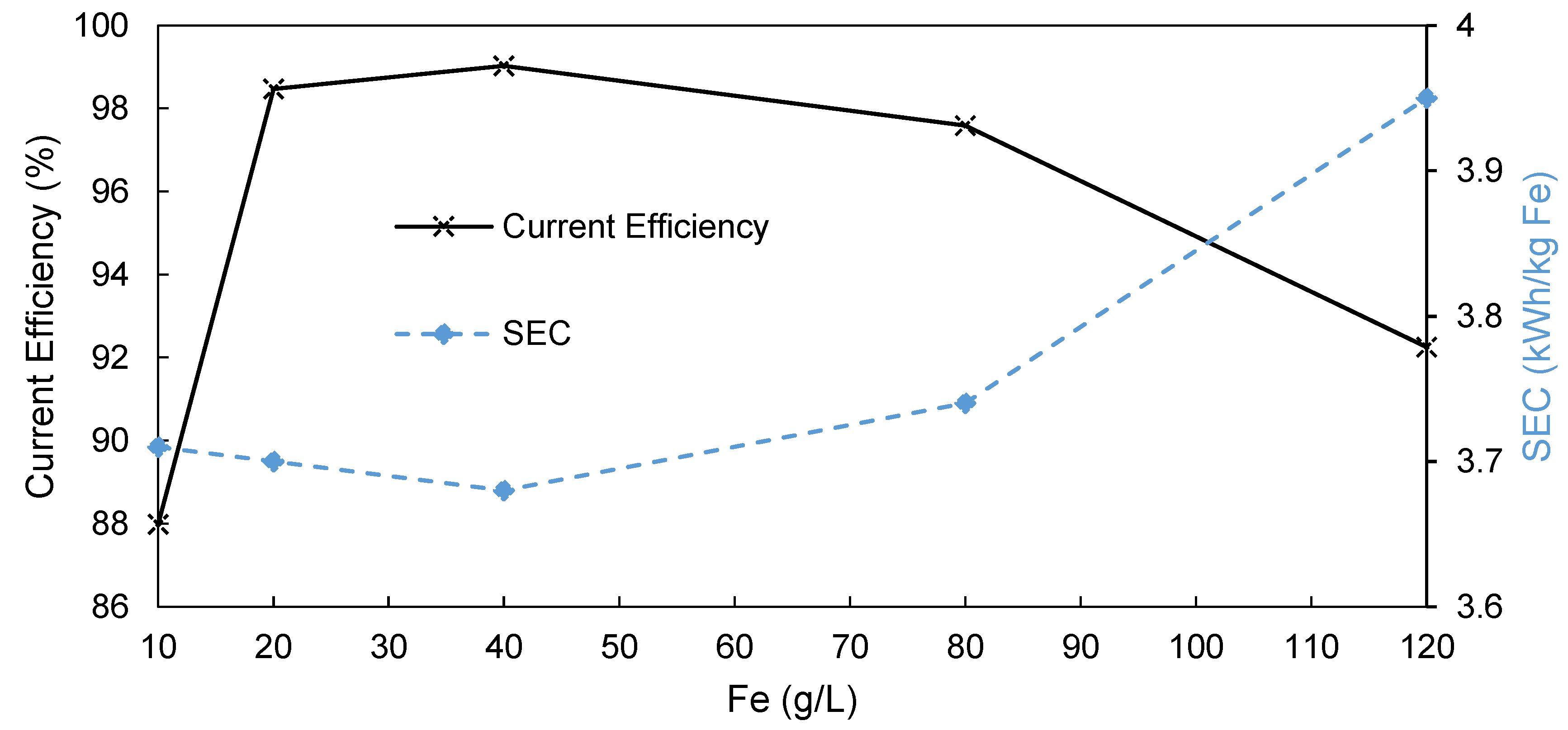
3.3. Influence of Fe Content on AEM-EW Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Hallberg, K.B. Acid mine drainage remediation options: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, C.W.; Maddin, C.M. Method for Preventing the Precipitation of Ferric Compounds during the Acid Treatment of Wells. U.S. Patent 4,574,050, 4 March 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, H.J. Method of Preventing Precipitation of Iron Compounds from an Aqueous Solution. U.S. Patent 3,150,081, 22 September 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, I.G.; Alex, P.; Bidaye, A.C.; Suri, A.K. Electrowinning of cobalt from sulphate solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 80, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, M.I.; Choo, W.L.; Breuer, P.L. The effect of additives and impurities on the cobalt electrowinning process. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, C.; Pasquali, M. Electrolytic nickel recovery from lithium-ion batteries. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostad, E.; Rolseth, S.; Thonstad, J. Electrowinning of iron from sulphate solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 90, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varcoe, J.R.; Slade, R.C. Prospects for alkaline anion-exchange membranes in low temperature fuel cells. Fuel Cells 2005, 5, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varcoe, J.R.; Atanassov, P.; Dekel, D.R.; Herring, A.M.; Hickner, M.A.; Kohl, P.A.; Kucernak, A.R.; Mustain, W.E.; Nijmeijer, K.; Scott, K.; et al. Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3135–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arges, C.G.; Ramani, V. Investigation of Cation Degradation in Anion Exchange Membranes Using Multi-Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, F1006–F1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.Y.; Wu, C.M.; Xu, T.W.; Wu, Y.H. Diffusion dialysis-concept, principle and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regel-Rosocka, M. A review on methods of regeneration of spent pickling solutions from steel processing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K.K. An overview of the recovery of acid from spent acidic solutions from steel and electroplating industries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasuraman, A.; Lim, T.M.; Menictas, C.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Review of material research and development for vanadium redox flow battery applications. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 101, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkar, T.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M. Membrane stability studies for vanadium redox cell applications. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2004, 34, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hickner, M.A.; Agar, E.; Kumbur, E.C. Optimized anion exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7559–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hickner, M.A. V 5+ degradation of sulfonated Radel membranes for vanadium redox flow batteries. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11299–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Moon, S.-H.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Xu, T. Ion-exchange membranes. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 2012, 906952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Abad, J.; Garcia-Gabaldon, M.; Ortiz-Gandara, I.; Bringas, E.; Urtiaga, A.M.; Ortiz, I.; Perez-Herranz, V. Selective recovery of zinc from spent pickling, baths by the combination of membrane-based solvent extraction and electrowinning technologies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 151, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Abad, J.; Garcia-Gabaldon, M.; Perez-Herranz, V. Study of the zinc recovery from spent pickling baths by means of an electrochemical membrane reactor using a cation-exchange membrane under galvanostatic control. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, C.G.; Peach, R.; Krieg, H.M.; Kerres, J. Novel morpholinium-functionalized anion-exchange PBI–polymer blends. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, C.G.; Peach, R.; Krieg, H.M.; Kerres, J. Novel imidazolium-functionalized anion-exchange polymer PBI blend membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.A.; Krieg, H.M. Poly(vinylbenzylchloride) Based Anion-Exchange Blend Membranes (AEBMs): Influence of PEG Additive on Conductivity and Stability. Membranes 2017, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Krieg, H.M.; Kerres, J.A. Application of Novel Anion-Exchange Blend Membranes (AEBMs) to Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries. Membranes 2018, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, A.; Burr, M.; Ellis, T.; Evans, D.; Kakengela, D.; Webb, L.; Gagnon, J.; Leclercq, F.; Johnston, A. Corrosion of lead anodes in base metals electrowinning. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2016, 116, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.C.; Singh, P.; Muir, D.M. Effect of manganese(II) and boric acid on the electrowinning of cobalt from acidic sulfate solutions. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2001, 32, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Yang, Q.-H.; Zhang, Z. Effects of additives on nickel electrowinning from sulfate system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, s97–s101. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J.; Keeler, J. Atkins’ Physical Chemistry; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane/electrode area (A) | cm2 | 100 (10 × 10) |
| Anode cathode distance (ACD) | cm | 2 |
| Cell constant (ACD/A) | cm | 50 |
| Electrolyte volume (Va = Vc) | L | 1/2 |
| Superficial flow velocity (vsup) | cm/s | 1 |
| FeSO4 concentration in catholyte | g Fe/L as FeSO4 | 0–80 |
| Na2SO4 concentration in catholyte and anolyte | g Na2SO4/L | 60 |
| H3BO3 concentration in catholyte and anolyte | g H3BO3/L | 10 |
| Current density (i) | A/m2 | 300 |
| Current (I) | A | 3 |
| Plating rate at 100% current efficiency | g Fe/h | 3.13 |
| Run time | h | 5 |
| No. | Name | Halogenated Polymer (g) | Tertiary Amine (g) | Polybenzimidazole (PBI) (g) | Sulfonated Polymer (g) | PEG-Diepoxide (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2243A | PVBCl (0.75) | TMIm (1.22) | F6PBI (0.70) | SFS001 (0.18) | PEG500 * (0.10) |
| 2 | MHC4-C | PPOBr (1.20) | TMIm (**) | PBIOO (0.80) | SAC098 (0.30) | - |
| 3 | 2258 | PVBCl (2.00) | TMIm (1.30) | F6PBI (1.30) | SFS001 (0.35) | PEG500 * (0.30) |
| 4 | 2281A | PVBCl (2.25) | TMIm (3.66) | PBIOO (2.40) | SFS001 (0.55) | - |
| 5 | 2285A | PVBCl (2.25) | TMIm (3.66) | PBIOO (2.40) | sPEEKNa (0.62) | - |
| 6 | 2244B | PVBCl (2.25) | TMIm (3.66) | F6PBI (2.40) | SFS001 (0.53) | - |
| 7 | 2259 | PVBCl (2.75) | TMIm (4.50) | F6PBI (1.30) | SFS001 (0.35) | PEG500 * (0.30) |
| 8 | 2244C | PVBCl (1.50) | TMIm (2.44) | F6PBI (1.60) | SFS001 (0.35) | - |
| 9 | 2252A | PVBCl (1.50) | TMIm (2.44) | PBIOO (1.60) | SAC098 (0.43) | - |
| 10 | BM-5 | PPOBr (0.80) | TMIm (0.65) | PBIOO (1.2) | SAC096 (0.2) | - |
| 11 | 2408-2 | PVBCl (1.50) | TMIm (1.3) | F6PBI (2.35) | - | - |
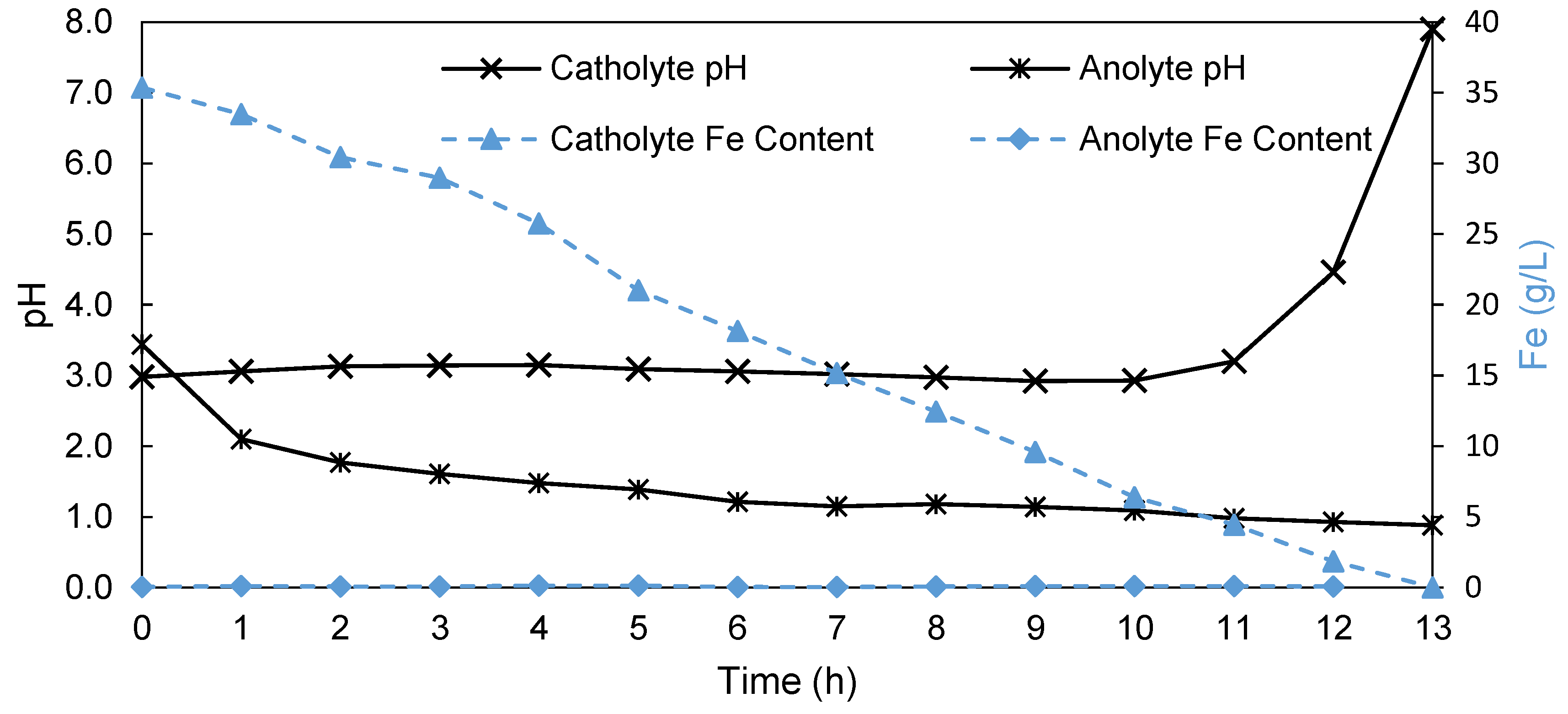
| Halogenated Polymers | Tertiary Amine | |
|---|---|---|
| PVBCl | PPOBr | TMIm |
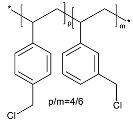 | 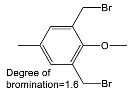 | 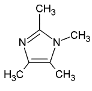 |
| PBI polymers | ||
| F6PBI | PBIOO | |
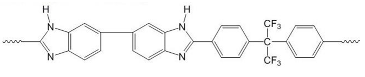 | 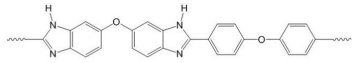 | |
| Sulfonated polymers | ||
| SFS | SAC | |
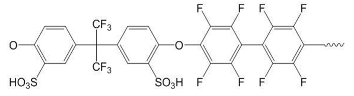 | 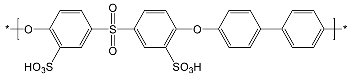 | |
| sPEEKNa | ||
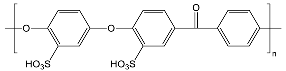 | ||
| Poly(ethylene glycol diepoxide) | ||
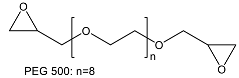 | ||
| Variable | Undivided | Terylene Membrane | FAB-PK-130 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH catholyte | 2.05 | 2.90 | 2.51 |
| pH anolyte | 2.05 | 1.56 | 0.84 |
| Fe plated (g) | 3.30 | 12.1 | 15.5 |
| Current efficiency (%) | 21 | 77 | 99 |
| Specific energy consumption (SEC) (kWh/kg Fe) | 17.7 | 9.50 | 3.75 |
| [H2SO4] (g/L) | 0.45 | 1.4 | 7.2 |
| Membrane | IECtotal (meq/g) | (mS/cm) | Water Uptake 25 °C/90 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) 2243A | 2.45 | 10.5 | 40/50 |
| (2) MHC4-C | - | - | - |
| (3) 2258 | 2.42 | 26.5 | 77/91 |
| (4) 2281A | 2.91 | 45.5 | 34/39 |
| (5) 2285A | 2.89 | 4.30 | 34/39 |
| (6) 2244B | 2.50 | 5.20 | 37/41 |
| (7) 2259 | 2.41 | 22.0 | 157/258 |
| (8) 2244C | 2.50 | 1.60 | 27/27 |
| (9) 2252A | 2.90 | 4.60 | 37/44 |
| (10) BM-5 | 0.28 | 0.09 | 10/4 |
| (11) 2408-2 | 0.45 | 0.31 | 7/5 |
| Name (No.) | FAB-PK-130 | 2244B (6) | 2259 (7) | 2244C (8) * | 2252A (9) ** | BM-5 (10) | 2408-2 (11) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH catholyte | 2.51 | 2.43 | 2.03 | 1.89 | 1.82 | 2.39 | 1.9 |
| pH anolyte | 0.84 | 0.98 | 1.09 | 0.57 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.96 |
| Fe plated (g) | 15.5 | 11.0 | 11.1 | 7.8 | 4.20 | 14.8 | 13.8 |
| Efficiency % | 99 | 70 | 71 | 83 | 99 | 95 | 88 |
| SEC (kWh/kg Fe) | 3.75 | 5.16 | 5.13 | 4.61 | 3.55 | 3.53 | 4.18 |
| Lifetime (h) | >5 | >5 | >5 | 3 | 2 | >5 | >5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badenhorst, W.D.; Rossouw, C.; Cho, H.; Kerres, J.; Bruinsma, D.; Krieg, H. Electrowinning of Iron from Spent Leaching Solutions Using Novel Anion Exchange Membranes. Membranes 2019, 9, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110137
Badenhorst WD, Rossouw C, Cho H, Kerres J, Bruinsma D, Krieg H. Electrowinning of Iron from Spent Leaching Solutions Using Novel Anion Exchange Membranes. Membranes. 2019; 9(11):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110137
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadenhorst, Wouter Dirk, Cloete Rossouw, Hyeongrae Cho, Jochen Kerres, Dolf Bruinsma, and Henning Krieg. 2019. "Electrowinning of Iron from Spent Leaching Solutions Using Novel Anion Exchange Membranes" Membranes 9, no. 11: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110137
APA StyleBadenhorst, W. D., Rossouw, C., Cho, H., Kerres, J., Bruinsma, D., & Krieg, H. (2019). Electrowinning of Iron from Spent Leaching Solutions Using Novel Anion Exchange Membranes. Membranes, 9(11), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110137





