Preliminary Study of Emulsion Liquid Membrane Formulation on Acetaminophen Removal from the Aqueous Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
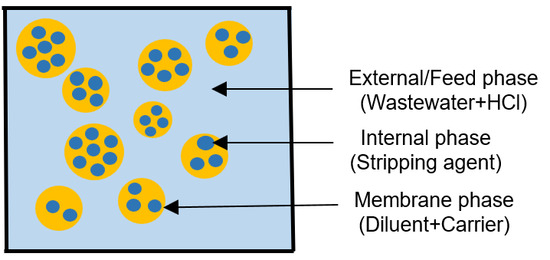
2.2. Determination of ELM Components
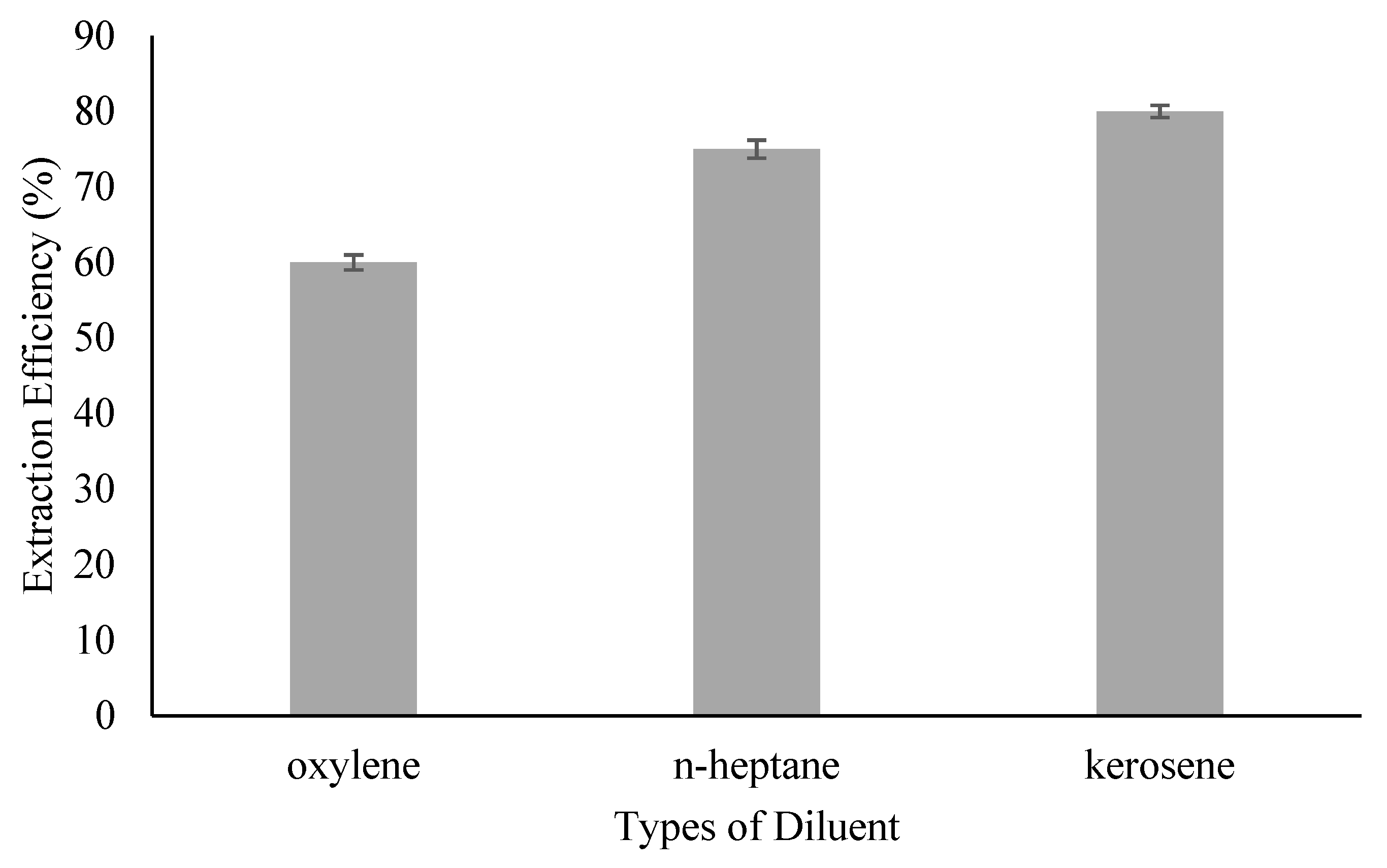
2.3. Diluent Screening
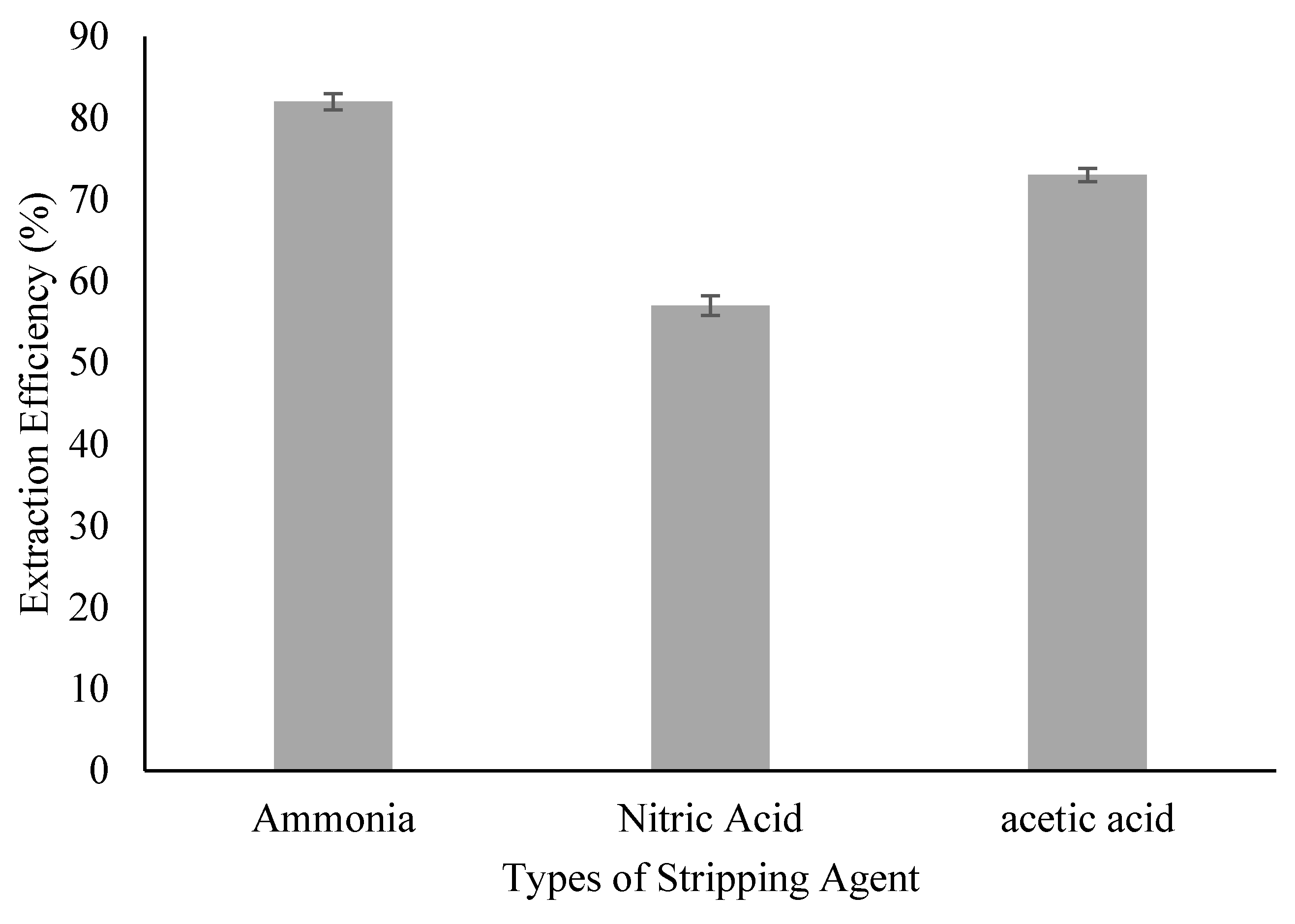
2.4. Stripping Agent Screening
2.5. Emulsion Preparation
2.6. Extraction Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Diluent’s Type
3.2. Effect of Stripping Agent’s Type
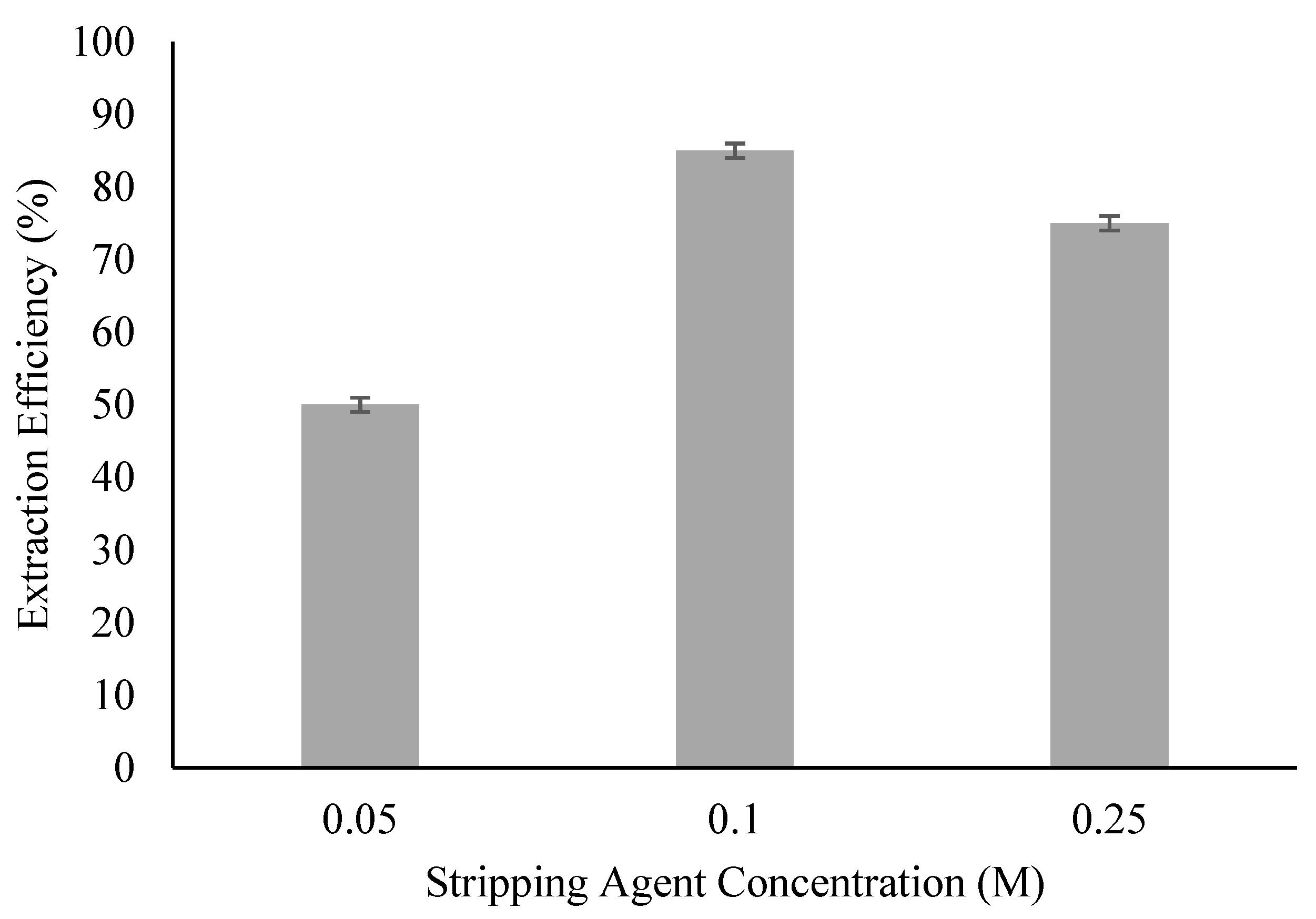
3.3. Effect of Stripping Agent Concentration
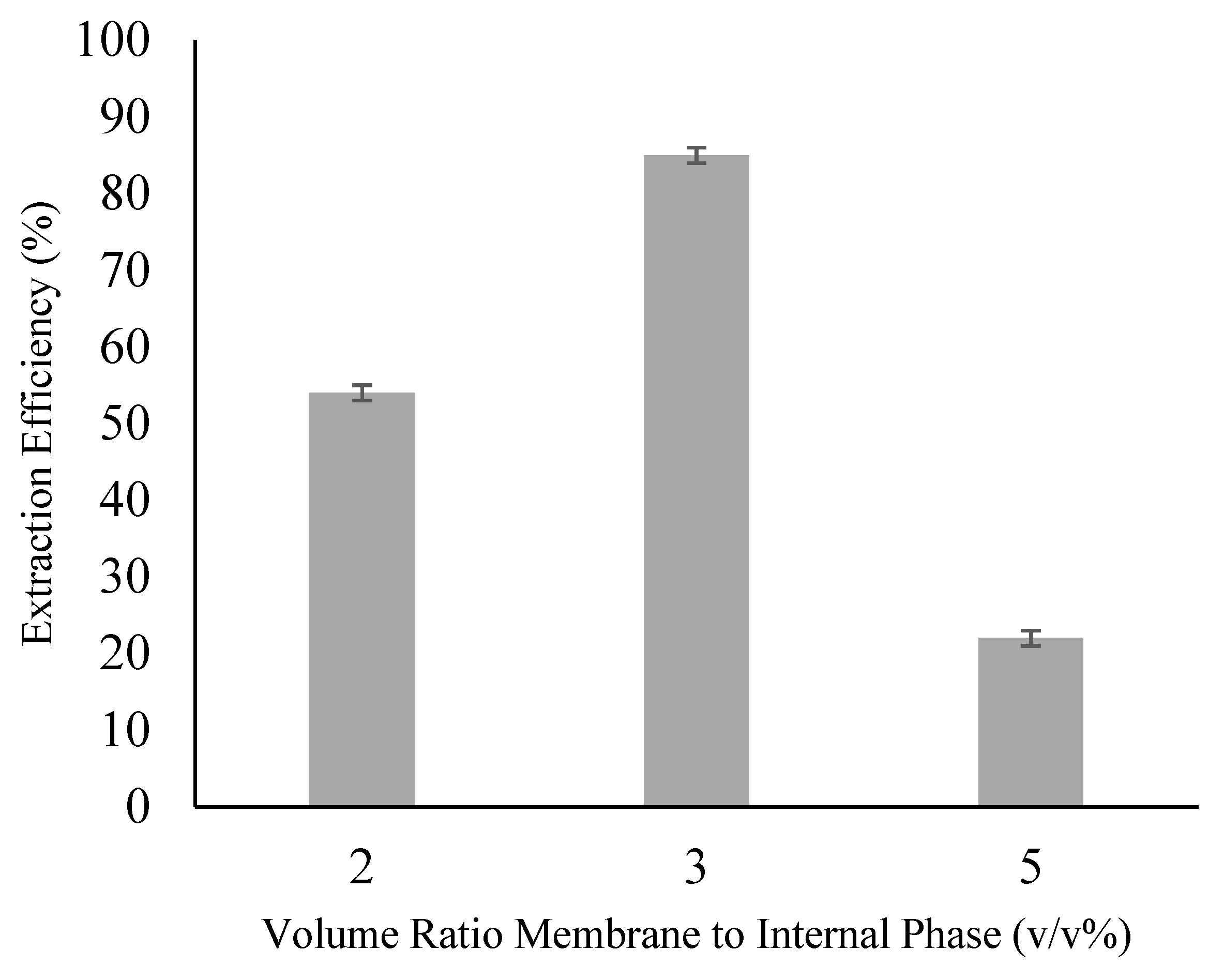
3.4. Effect of the Membrane to Internal Phase Volume Ratio
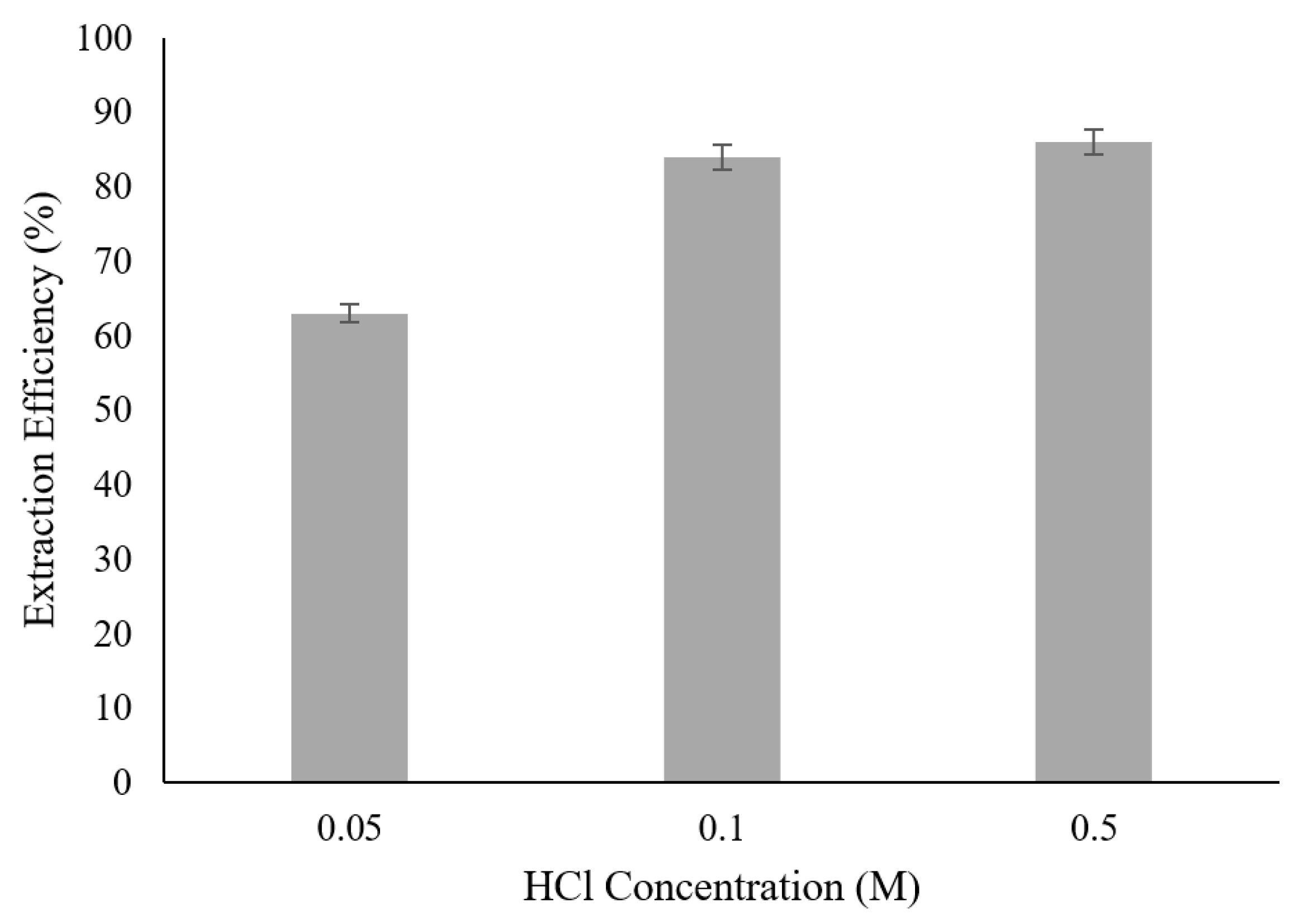
3.5. Effect of HCl Concentration in Initial Feed Solution
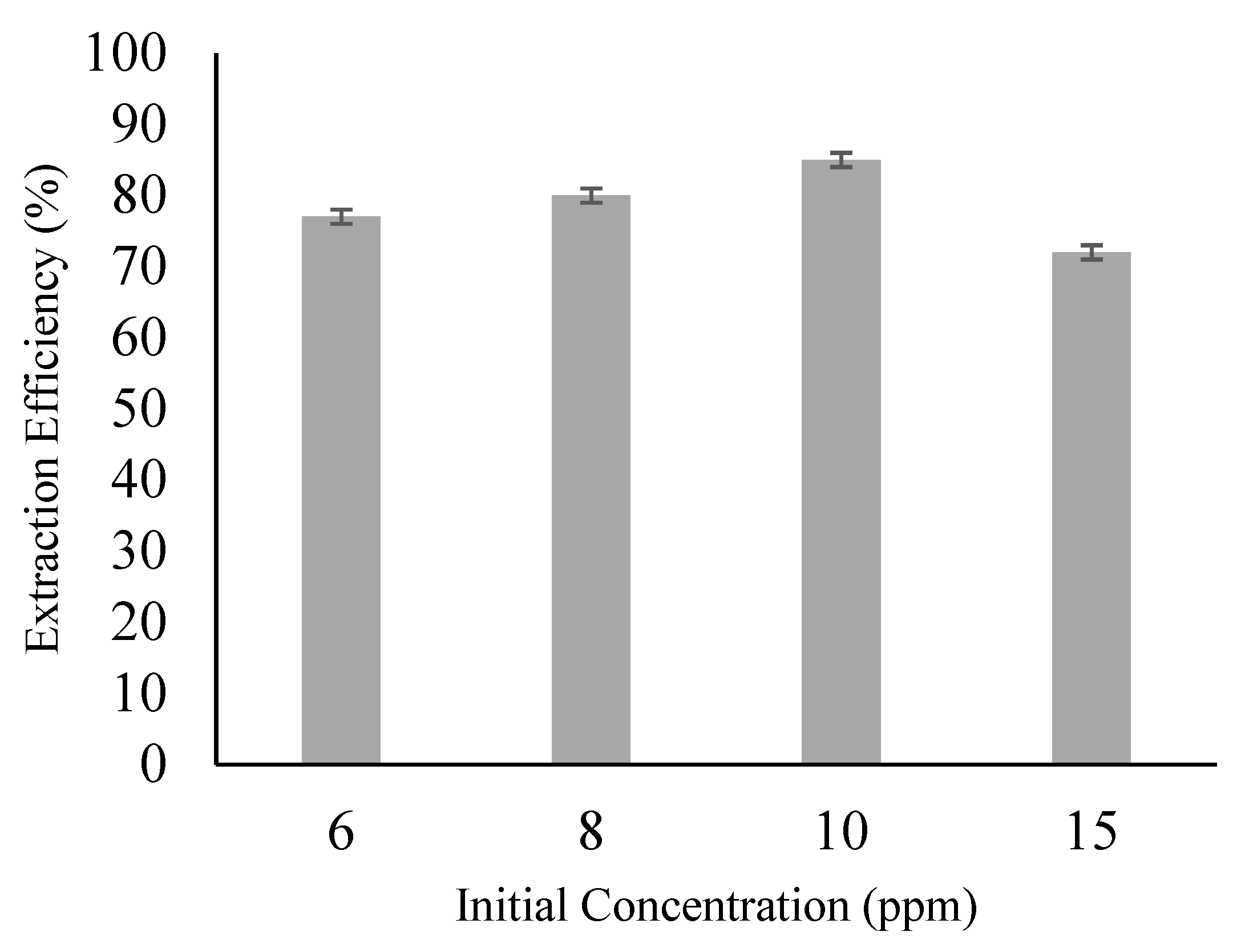
3.6. Effect of Initial Feed Concentration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, S.D.; Kimura, S.Y. Emerging environmental contaminants: Challenges facing our next generation and potential engineering solutions. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2017, 8, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.E.; Ward, R.S. Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: A review of sources, fate and occurrence. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguera-Oviedo, K.; Aga, D.S. Lessons learned from more than two decades of research on emerging contaminants in the environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawell, J.; Ong, C.N. Emerging Contaminants and the Implications for Drinking Water. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2012, 28, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Odaini, N.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Yaziz, M.I.; Surif, S.; Abdul, M. The occurrence of human pharmaceuticals in wastewater effluents and surface water of Langat River and its tributaries, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2013, 93, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouchi, S.; Hamdaoui, O. Acetaminophen extraction by emulsion liquid membrane using Aliquat 336 as extractant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 129, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, A. Pharmaceutical Disposal and Water Quality; PennState Extension: State College, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ooi, Z.-Y.; Harruddin, N.; Othman, N. Recovery of Kraft Lignin From Pulping Wastewater via Emulsion Liquid Membrane Process. Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Fu, J.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Matis, K.A. New approaches on the removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewaters with adsorbent materials. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, M.; Kaykioglu, G.; Belgiorno, V.; Lofrano, G. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water and Wastewater by Adsorption Process. In Emerging Compounds Removal from Wastewater; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 15–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kislik, V.S. Introduction, General Description, Definitions, and Classification. Overview. In Liquid Membranes; Kislik, V.S., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Fei, D.; Dang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, J. Studies on the extraction of chromium(III) by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaguraj, M.; Palanivelu, K.; Velan, M. Removal Of Cu (II) Using Emulsion Liquid Membrane. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2009, 1, 722–726. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Kusumastuti, A.; Derek, C.J.C.; Ooi, B.S. Emulsion Liquid Membranes For Cadmium Removal: Studies Of Extraction Efficiency. Membr. Water Treat. 2013, 4, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.S.; Jayakumar, N.S.; Hashim, M.A. Performance Evaluation of Organic Emulsion Liquid Membrane on Phenol Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C. Extraction of succinic acid from simulated media by emulsion liquid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichang, Z.; Qinlin, C.; Chao, K.; Xin, M.; Zunliang, Y. Rare earth extraction from wet process phosphoric acid by emulsion liquid membrane. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 717–723. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, N.; Mat, H.; Goto, M. Separation of Silver from Photographic Wastes by Emulsion Liquid Membrane System. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaulkiflee, N.D.; Buddin, M.M.H.S.; Ahmad, A.L. Extraction of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solution by Emulsion Liquid Membrane Using Taylor-Couette Column. Int. J. Eng. 2018, 31, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Yuxin, L.; Yundong, W.; Youyuan, D. Effect of Diluents on the Extraction of Oxalic Acid by Trialkylphosphine Oxide. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2004, 12, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Mat, H.; Othman, N.; Chan, K.H.; Chiong, T.; Hii, K.H.; Ng, K.S. Selective Emulsion Liquid Membrane Extraction of Silver from Liquid Photographic Waste Industries. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor, Malaysia, 2006; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Canselier, J.P.; Delmas, H.; Wilhelm, A.M.; Abismaïl, B. Ultrasound Emulsification—An Overview. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2002, 23, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Noah, N.F.M.; Poh, K.W.; Yi, O.Z. High Performance of Chromium Recovery from Aqueous Waste Solution Using Mixture of Palm-oil in Emulsion Liquid Membrane. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.; Palanivelu, K. Recovery of Acetic Acid by Supported Liquid Membrane using vegetable oil as liquid membrane. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2008, 15, 266–270. [Google Scholar]
- Chiha, M.; Hamdaoui, O.; Ahmedchekkat, F.; Pétrier, C. Study On Ultrasonically Assisted Emulsification And Recovery Of Copper(II) From Wastewater Using An Emulsion Liquid Membrane Process. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2010, 17, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Shah, B.M.M.H.; Ooi, B.S.; Kusumastuti, A. Cadmium Removal Using Vegetable Oil Based Emulsion Liquid Membrane (ELM): Membrane Breakage. J. Teknol. 2015, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.K.; Natesan, J.; Hashim, M.A. Chromium removal by emulsion liquid membrane using [BMIM] +[NTf 2] − as stabilizer and TOMAC as extractant. Desalination 2011, 278, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Zailani, S.; Mili, N. Recovery of synthetic dye from simulated wastewater using emulsion liquid membrane process containing tri-dodecyl amine as a mobile carrier. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 198, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.; Selim, Y.T.; Mohamed, K.M. Removal of chromium from aqueous waste solution using liquid emulsion membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Kusumastuti, A.; Derek, C.J.C.; Ooi, B.S. Emulsion Liquid Membrane For Cadmium Removal: Studies On Emulsion Diameter And Stability. Desalination 2012, 287, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Zaulkiflee, N.D.; Kusumastuti, A.; Buddin, M.M.H.S. Removal of Acetaminophen from Aqueous Solution by Emulsion Liquid Membrane: Emulsion Stability Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 58, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.H.; Zhang, X.J. Swelling Determination Of W/O/W Emulsion Liquid Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 196, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Buddin, M.M.H.S.; Ooi, B.S.; Kusumastutic, A. Utilization of environmentally benign emulsion liquid membrane(ELM) for cadmium extraction from aqueous solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 15, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbasar, R.A. Selective Separation of Chromium (VI) from Acidic Solutions Containing Various Metal Ions Through Emulsion Liquid Membrane Using Trioctylamine as Extractant. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 64, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C. Removal of acetic acid from simulated hemicellulosic hydrolysates byemulsion liquid membrane with organophosphorus extractants. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Component | Extraction | Stripping |
|---|---|---|
| Type of carrier | TOA | TOA |
| Type of diluent | Kerosene, n-heptane, oxylene | Kerosene |
| Type of internal phase | - | Ammonia, nitric acid, acetic acid |
| Initial feed solution and concentration (external phase) | 10 ppm of ACTP in 0.1M HCl | ACTP-loaded organic solution |
| Treat ratio (v/v) | 1:1 | 1:1 |
| Diluent | KD |
|---|---|
| Oxylene | 1.50 |
| n-heptane | 2.70 |
| Kerosene | 4.55 |
| Stripping Phase Solution | KD |
|---|---|
| Ammonia | 4.55 |
| Nitric Acid | 1.32 |
| Acetic Acid | 2.70 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, A.L.; Shafie, Z.M.H.M.; Zaulkiflee, N.D.; Pang, W.Y. Preliminary Study of Emulsion Liquid Membrane Formulation on Acetaminophen Removal from the Aqueous Phase. Membranes 2019, 9, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9100133
Ahmad AL, Shafie ZMHM, Zaulkiflee ND, Pang WY. Preliminary Study of Emulsion Liquid Membrane Formulation on Acetaminophen Removal from the Aqueous Phase. Membranes. 2019; 9(10):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9100133
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Abdul Latif, Zulfida Mohamad Hafis Mohd Shafie, Nur Dina Zaulkiflee, and Wen Yu Pang. 2019. "Preliminary Study of Emulsion Liquid Membrane Formulation on Acetaminophen Removal from the Aqueous Phase" Membranes 9, no. 10: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9100133
APA StyleAhmad, A. L., Shafie, Z. M. H. M., Zaulkiflee, N. D., & Pang, W. Y. (2019). Preliminary Study of Emulsion Liquid Membrane Formulation on Acetaminophen Removal from the Aqueous Phase. Membranes, 9(10), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9100133