Ceramic-Based Composite Membrane with a Porous Network Surface Featuring a Highly Stable Flux for Drinking Water Purification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Mullite-CNT Composite Membrane
2.2. Membrane Separation of Bacteria-Contaminated Drinking Water
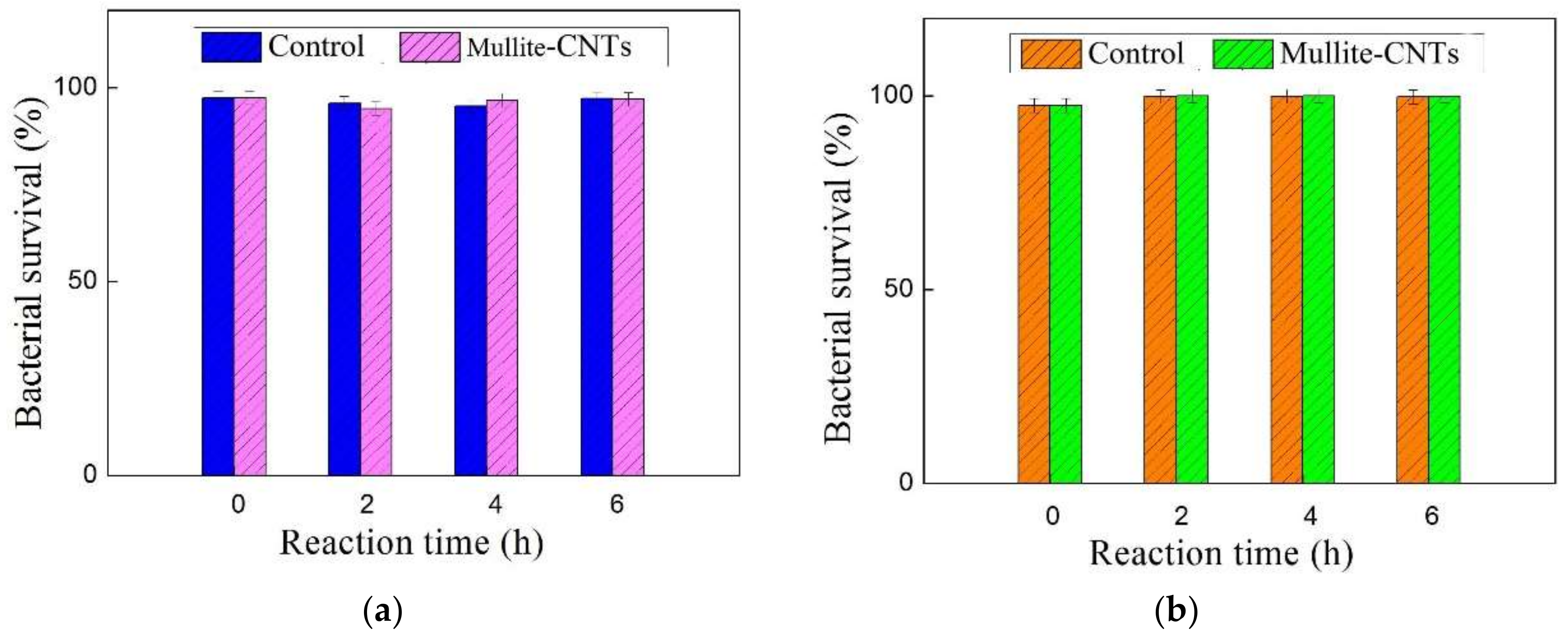
2.3. Bacterial Inactivation Assay
3. Characterizations
4. Results and Discussion
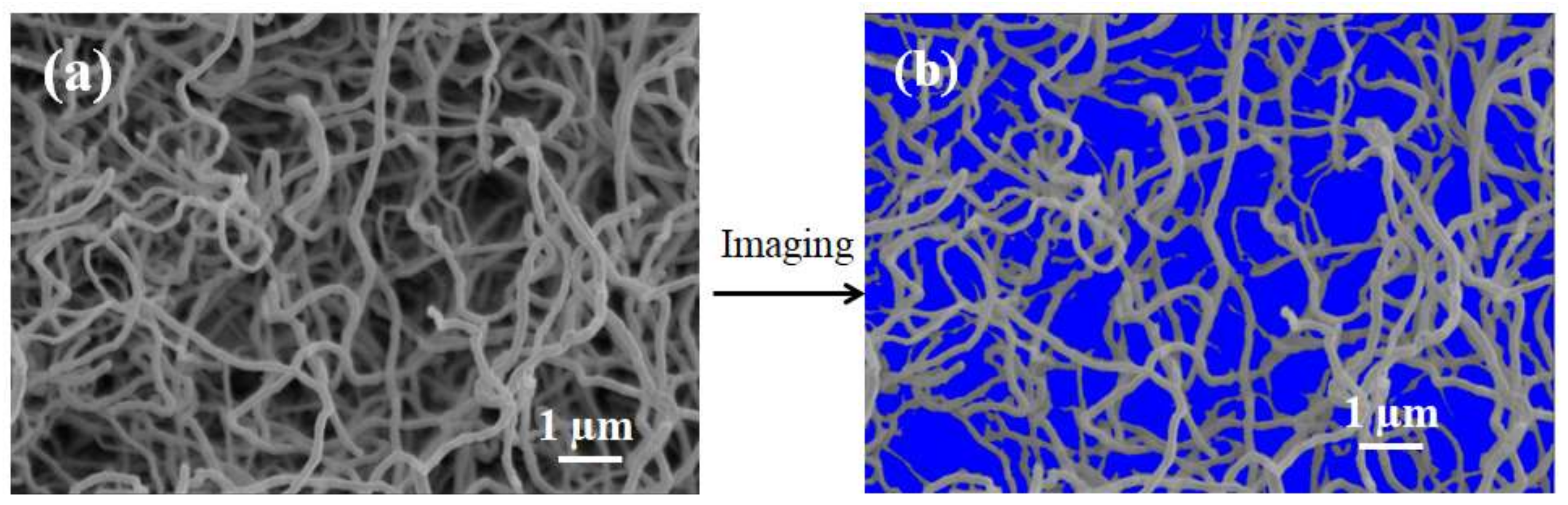
4.1. Construction of the CNTs Network on the Mullite Ceramic Substrate
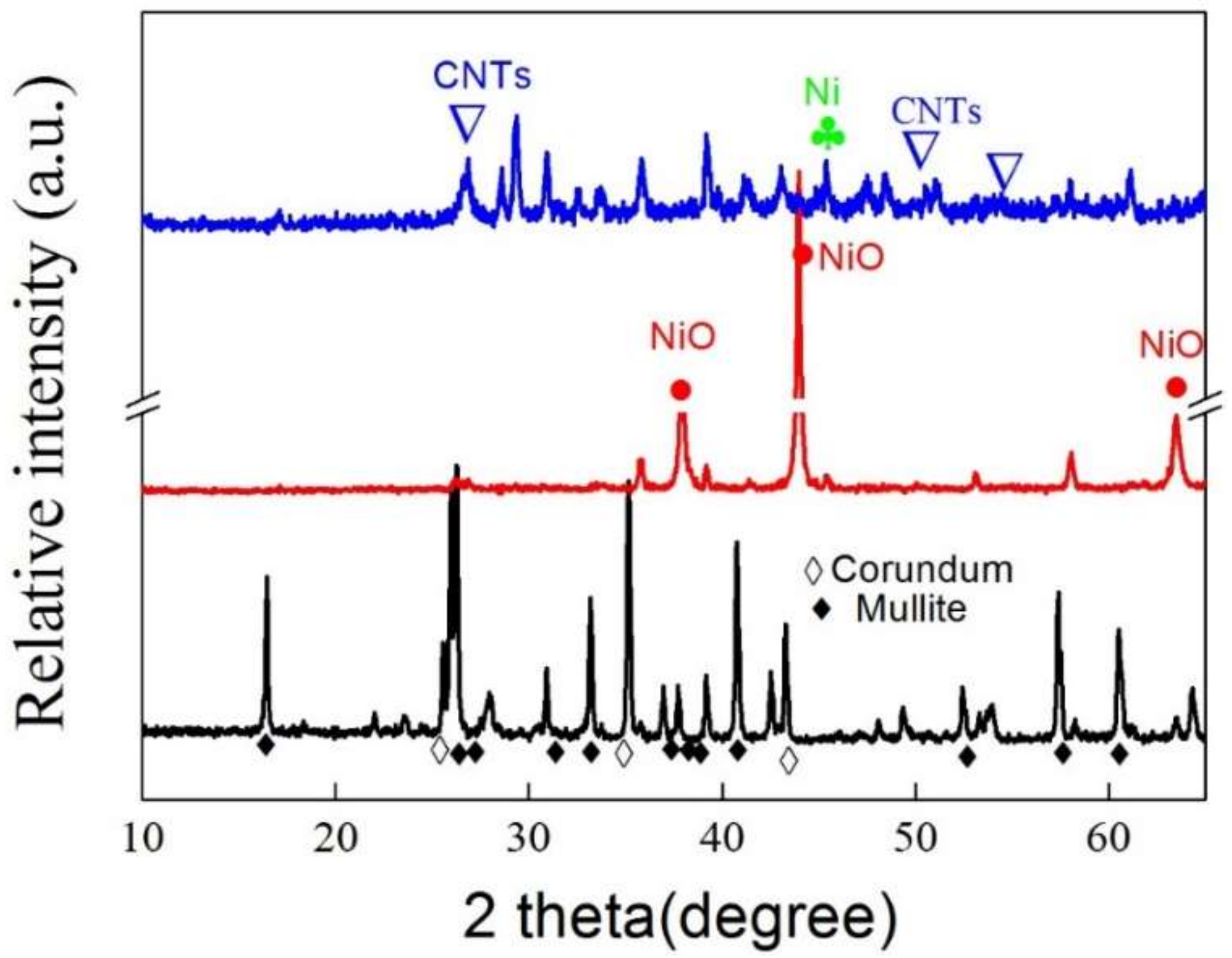
4.2. XRD Analysis
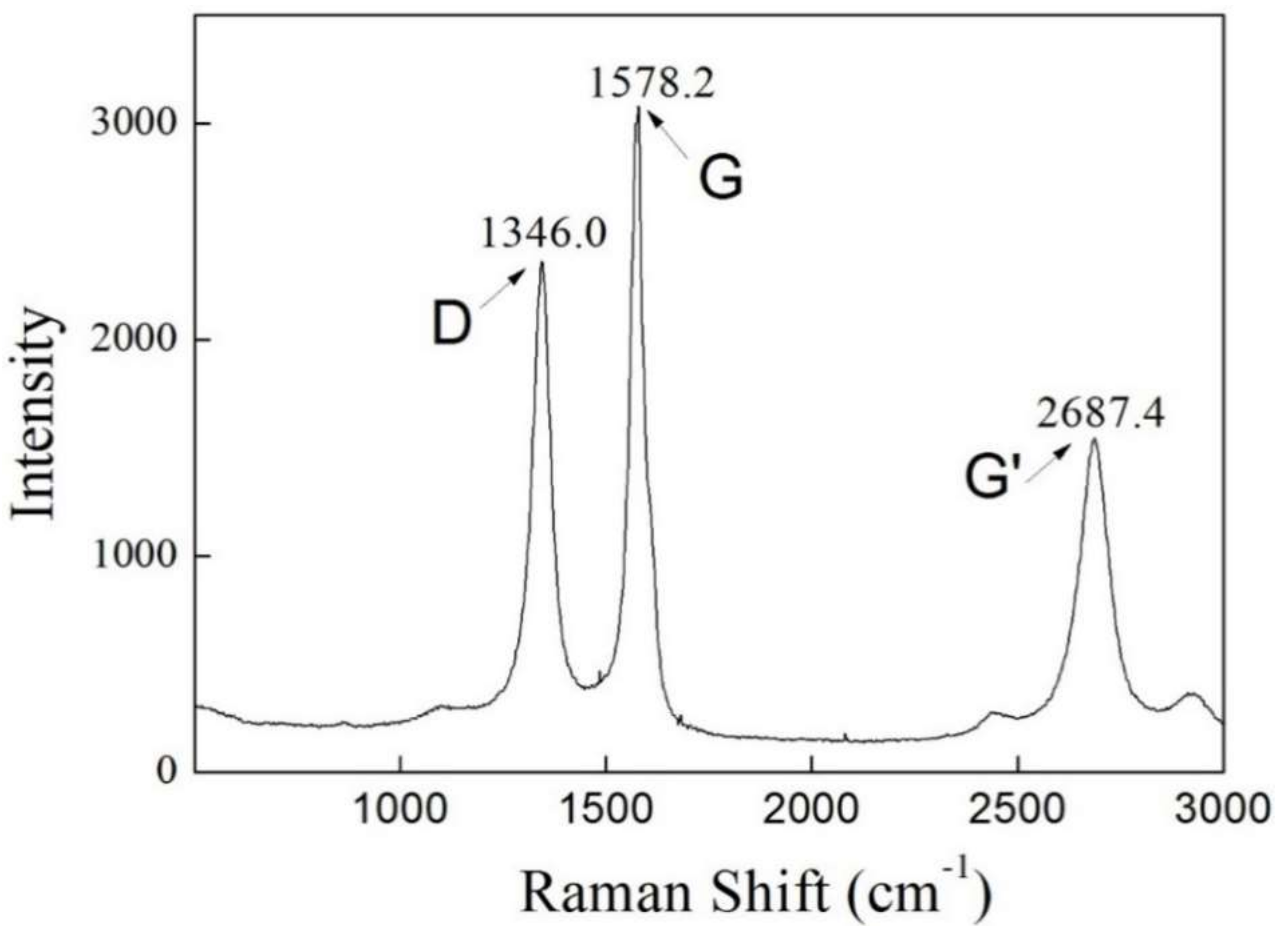
4.3. Raman Spectroscopy
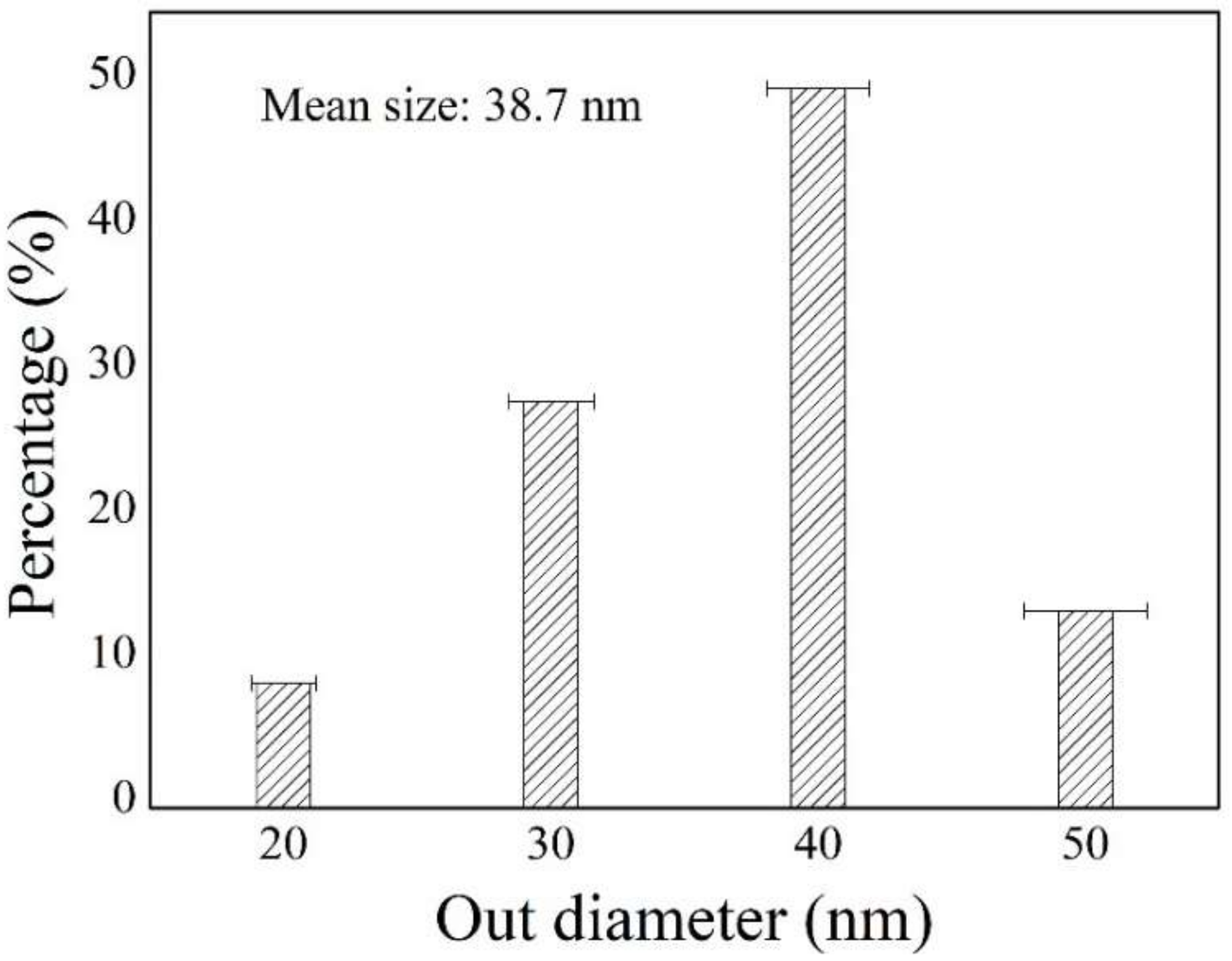
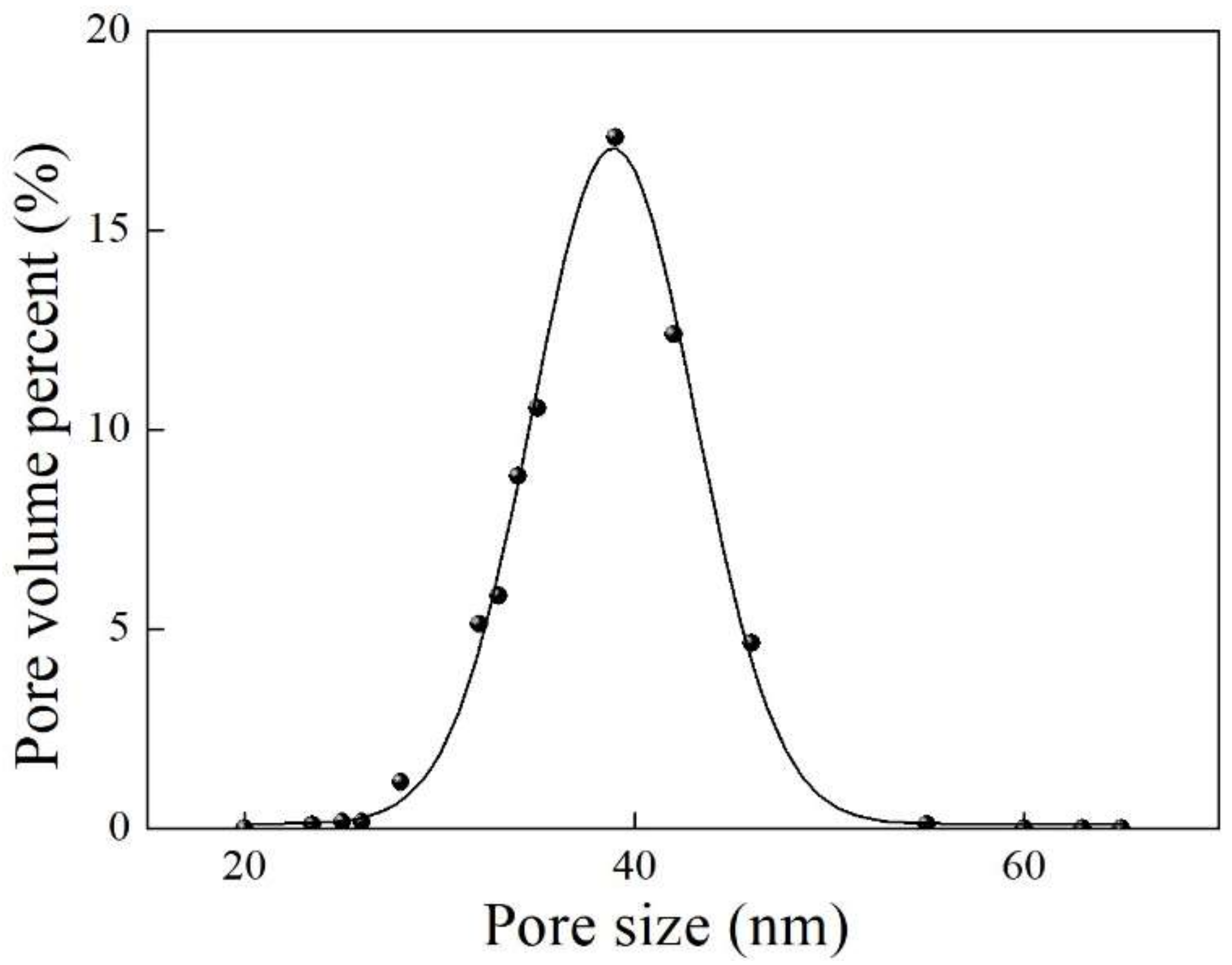
4.4. Pore Structure
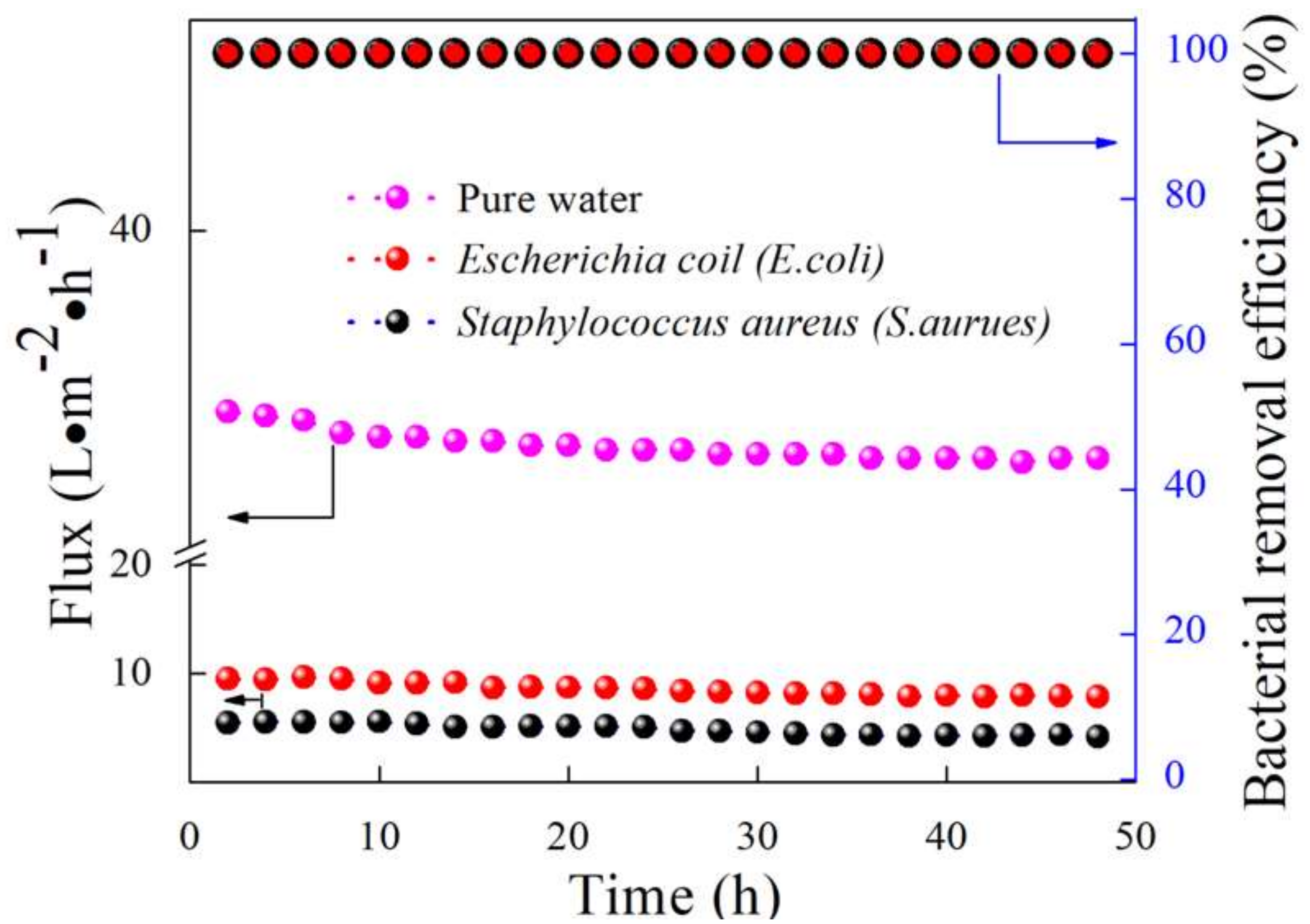
4.5. Highly Stable Flux for Bacterial Removal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Engel, M.; Hadar, Y.; Belkin, S.; Lu, X.; Elimelech, M.; Chefetz, B. Bacterial inactivation by a carbon nanotube–iron oxide nanocomposite: A mechanistic study using E. coli mutants. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, P.J.J.; Chan, C.K.; Elimelech, M.; Halas, N.J.; Villagrán, D. Emerging opportunities for nanotechnology to enhance water security. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Ali, M.E.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chowdhury, Z.Z. Carbon nanotube membranes for water purification: A bright future in water desalination. Desalination 2014, 336, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. In situ immobilization of silver nanoparticles for improving permeability, antifouling and anti-bacterial properties of ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Cao, B.; Tang, C.Y. A novel gravity-driven nanofibrous membrane for point-of-use water disinfection: Polydopamine-induced in situ silver incorporation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.K.; Erickson, M.; Oyanedel-Craver, V.A. Understanding the microbiological, organic and inorganic contaminant removal capacity of ceramic water filters doped with different silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Sasson, M.; Lu, X.; Bar-Zeev, E.; Zodrow, K.R.; Nejati, S.; Qi, G.; Giannelis, E.P.; Elimelech, M. In situ formation of silver nanoparticles on thin-film composite reverse osmosis membranes for biofouling mitigation. Water Res. 2014, 62, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-R.; Chen, K.-S.; Tsai, J.-C.; Tseng, C.-C.; Lin, S.-F. The antibacterial activities of hydrophilic-modified nonwoven PET. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 20, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror-Ehre, A.; Adin, A.; Markovich, G.; Mamane, H. Control of biofilm formation in water using molecularly capped silver nanoparticles. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2601–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blel, W.; Limousy, L.; Dutournié, P.; Ponche, A.; Boucher, A.; Le Fellic, M. Study of the antimicrobial and antifouling properties of different oxide surfaces. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9847–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergast, M.M.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1946–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musico, Y.L.F.; Santos, C.M.; Dalida, M.L.P.; Rodrigues, D.F. Surface Modification of Membrane Filters Using Graphene and Graphene Oxide-Based Nanomaterials for Bacterial Inactivation and Removal. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Pendergast, M.T.M.; Ghosh, A.K. Chapter 9—Nanotechnology-Based Membranes for Water Purification. In Nanotechnology Applications for Clean Water, 2nd ed.; Street, A., Sustich, R., Duncan, J., Savage, N., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 133–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Dong, X.; Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Dong, Y. Fabrication and Water Treatment Application of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)-Based Composite Membranes: A Review. Membranes 2017, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Schnoor, M.H.; Rahaman, M.S.; Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M. Electrochemical Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Filter for Viral and Bacterial Removal and Inactivation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3672–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Ma, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Yang, F.; Quan, X.; Jassby, D.; Zaworotko, M.J.; Guiver, M.D. Stable Superhydrophobic Ceramic-Based Carbon Nanotube Composite Desalination Membranes. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5514–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Hong, L.; Xu, Y.; Ong, Z.W. Ceramic pore channels with inducted carbon nanotubes for removing oil from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2012, 4, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functionalized electrospun nanofibrous microfiltration membranes for removal of bacteria and viruses. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; You, S.-J. Coal fly ash industrial waste recycling for fabrication of mullite-whisker-structured porous ceramic membrane supports. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11163–11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Dong, X.; Hampshire, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L. Feasible recycling of industrial waste coal fly ash for preparation of anorthite-cordierite based porous ceramic membrane supports with addition of dolomite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Diwu, J.; Feng, X.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Meng, G. Phase evolution and sintering characteristics of porous mullite ceramics produced from the flyash-Al(OH)3 coating powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 460, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lin, B.; Xie, K.; Wang, S.; Ding, H.; Fang, D.; Liu, X.; Meng, G. Cost-effective macro-porous mullite-corundum ceramic membrane supports derived from the industrial grade powder. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 477, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Waste-to-resource strategy to fabricate highly porous whisker-structured mullite ceramic membrane for simulated oil-in-water emulsion wastewater treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Hampshire, S.; Cerneaux, S.; Winnubst, L. Waste-to-resource preparation of a porous ceramic membrane support featuring elongated mullite whiskers with enhanced porosity and permeance. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady-Estévez, A.S.; Kang, S.; Elimelech, M. A Single-Walled-Carbon-Nanotube Filter for Removal of Viral and Bacterial Pathogens. Small 2008, 4, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, M.; Dong, Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Huang, A.; Li, L. A low-cost mullite-titania composite ceramic hollow fiber microfiltration membrane for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsion. Water Res. 2016, 90, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Srivastava, O.; Talapatra, S.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P. Carbon nanotube filters. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, H.; Bates, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y. A highly efficient and versatile carbon nanotube/ceramic composite filter. Carbon 2013, 54, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Dong, X.; Dong, Y.; Hao, X.; Hampshire, S. Dual-production of nickel foam supported carbon nanotubes and hydrogen by methane catalytic decomposition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 12307–12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Low, Z.-X.; Feng, S.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Z. Multifunctional hybrid porous filters with hierarchical structures for simultaneous removal of indoor VOCs, dusts and microorganisms. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 5433–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, F. Modeling the effects of material chemistry on water flow enhancement in nanotube membranes. MRS Bull. 2017, 42, 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Herzberg, M.; Rodrigues, D.F.; Elimelech, M. Antibacterial effects of carbon nanotubes: Size does matter! Langmuir 2008, 24, 6409–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady-Estévez, A.S.; Schnoor, M.H.; Vecitis, C.D.; Saleh, N.B.; Elimelech, M. Multiwalled carbon nanotube filter: Improving viral removal at low pressure. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14975–14982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Pei, R.; Yan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X. Cytotoxicity of carbon nanomaterials: Single-wall nanotube, multi-wall nanotube, and fullerene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Concentration (mg·L−1) | Al | Ni |
|---|---|---|
| CNTs membrane | 0.07 | nd |
| Drinking water criterion (WHO) | 0.2 | 0.07 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Rakesh, K.P.; Xu, M.; Dong, Y. Ceramic-Based Composite Membrane with a Porous Network Surface Featuring a Highly Stable Flux for Drinking Water Purification. Membranes 2019, 9, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010005
Zhu L, Rakesh KP, Xu M, Dong Y. Ceramic-Based Composite Membrane with a Porous Network Surface Featuring a Highly Stable Flux for Drinking Water Purification. Membranes. 2019; 9(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Li, Kadalipura Puttaswamy Rakesh, Man Xu, and Yingchao Dong. 2019. "Ceramic-Based Composite Membrane with a Porous Network Surface Featuring a Highly Stable Flux for Drinking Water Purification" Membranes 9, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010005
APA StyleZhu, L., Rakesh, K. P., Xu, M., & Dong, Y. (2019). Ceramic-Based Composite Membrane with a Porous Network Surface Featuring a Highly Stable Flux for Drinking Water Purification. Membranes, 9(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010005






