Engineering Sub-Nanometer Channels in Two-Dimensional Materials for Membrane Gas Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Graphene-Based Membranes
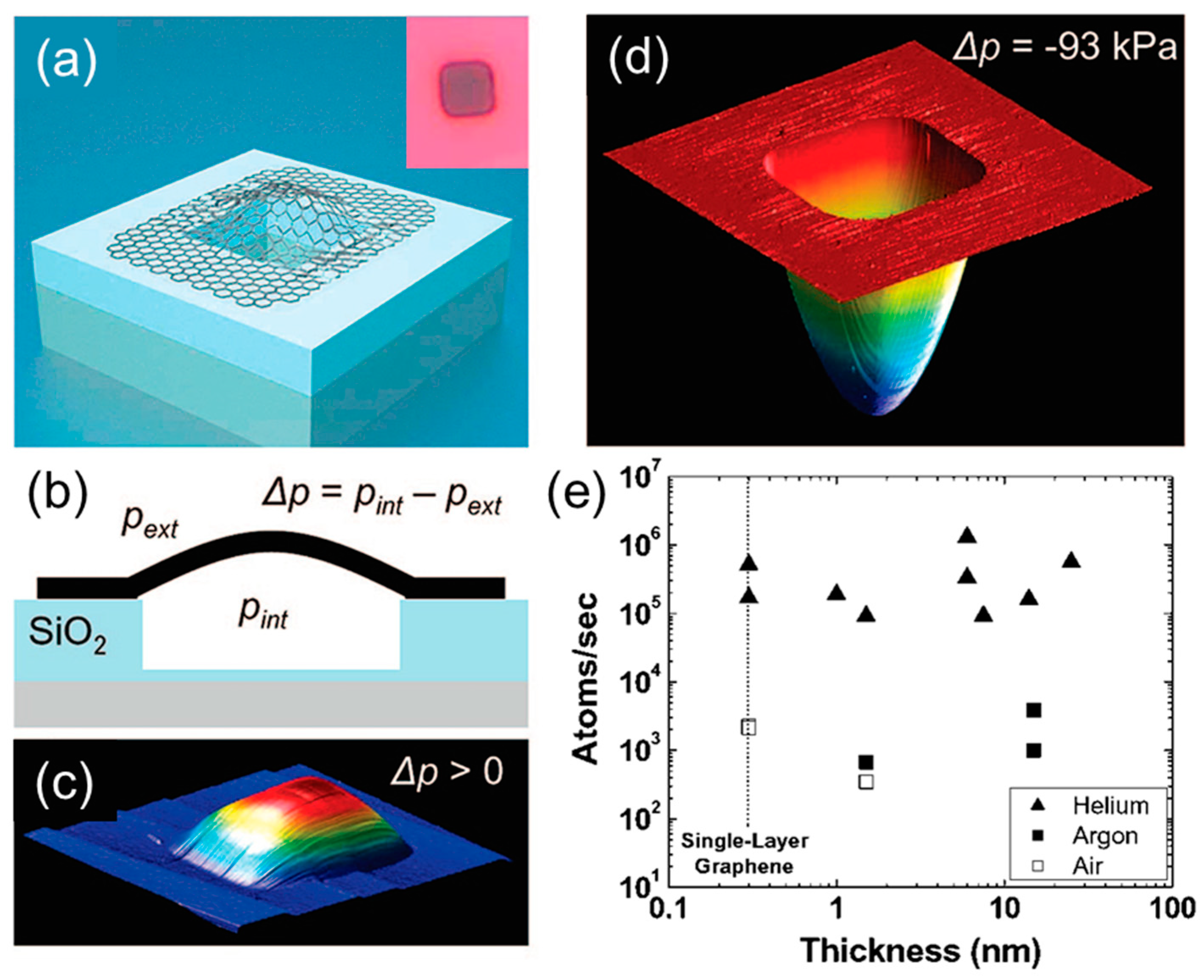
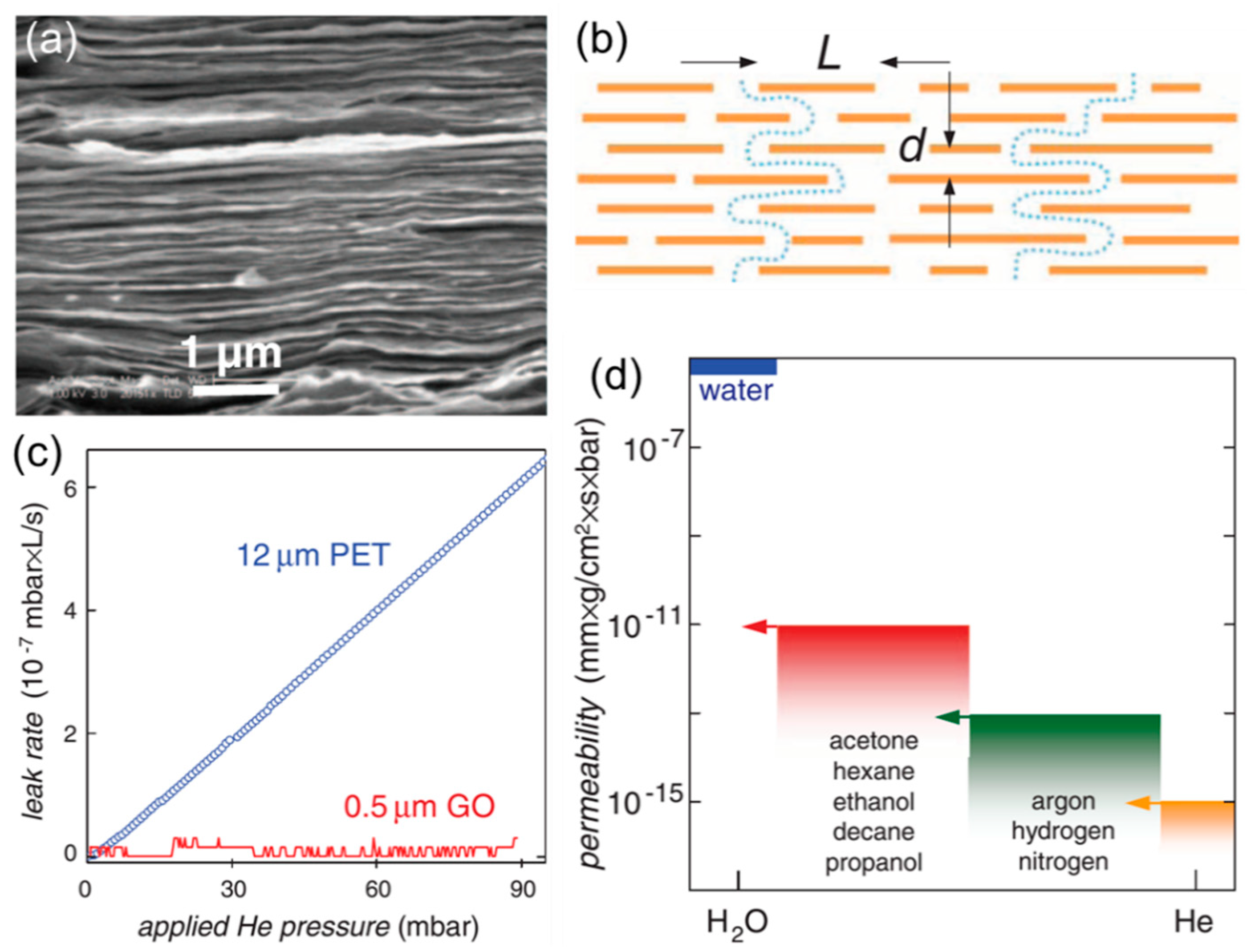
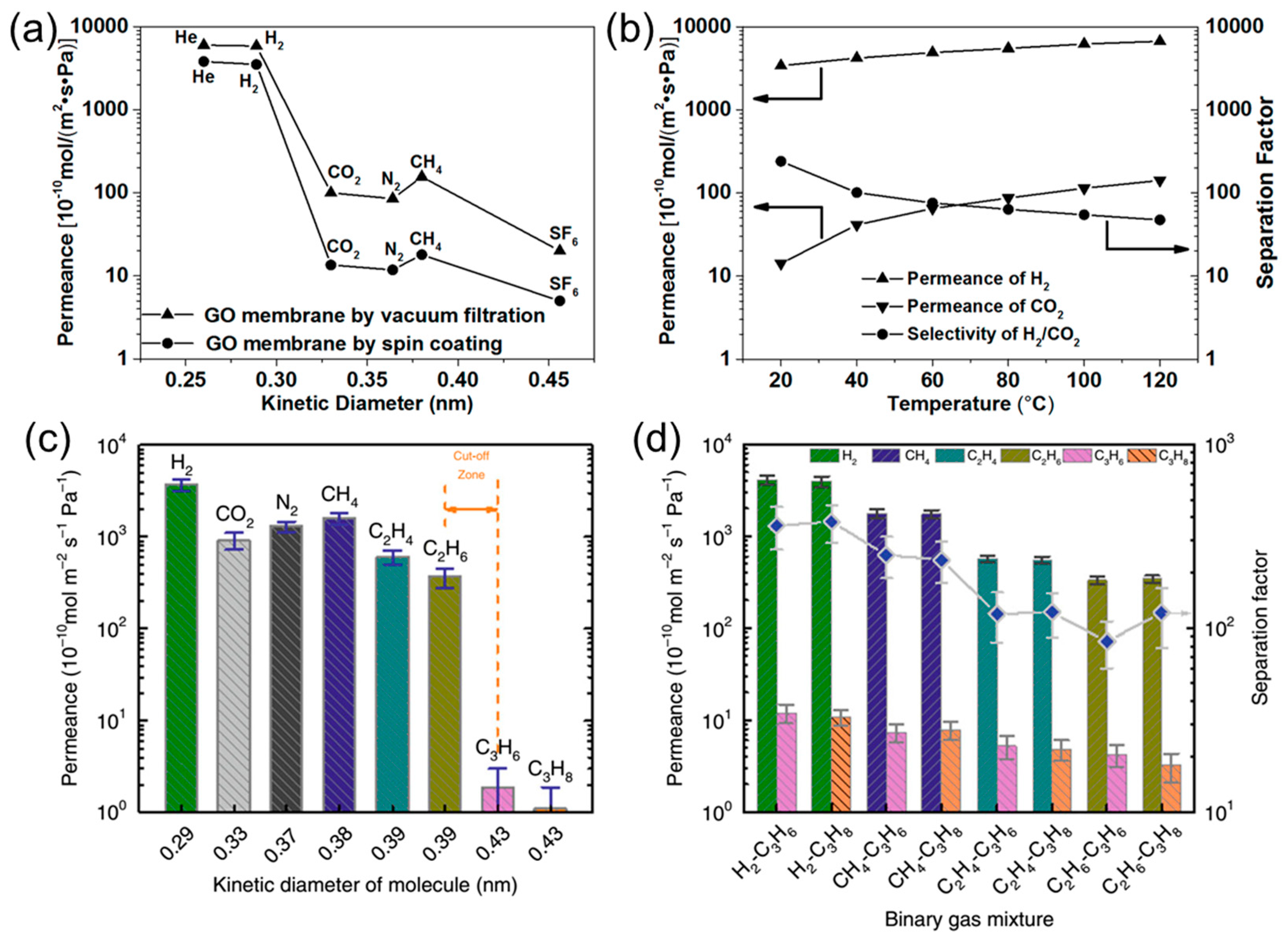
2.1. Gas Permeability of Graphene and GO Nanosheets
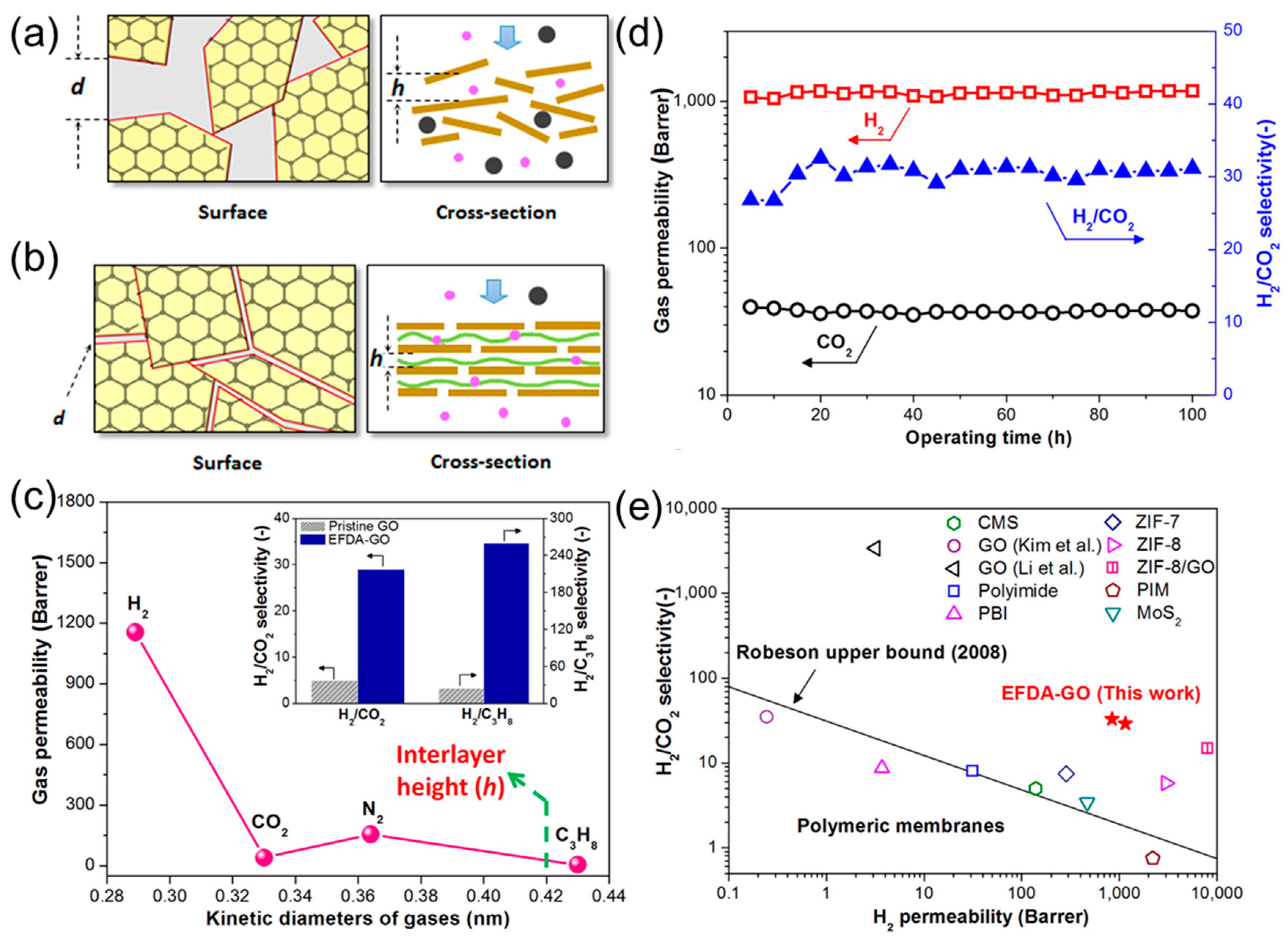
2.2. Engineering the Nanochannels between GO Nanosheets
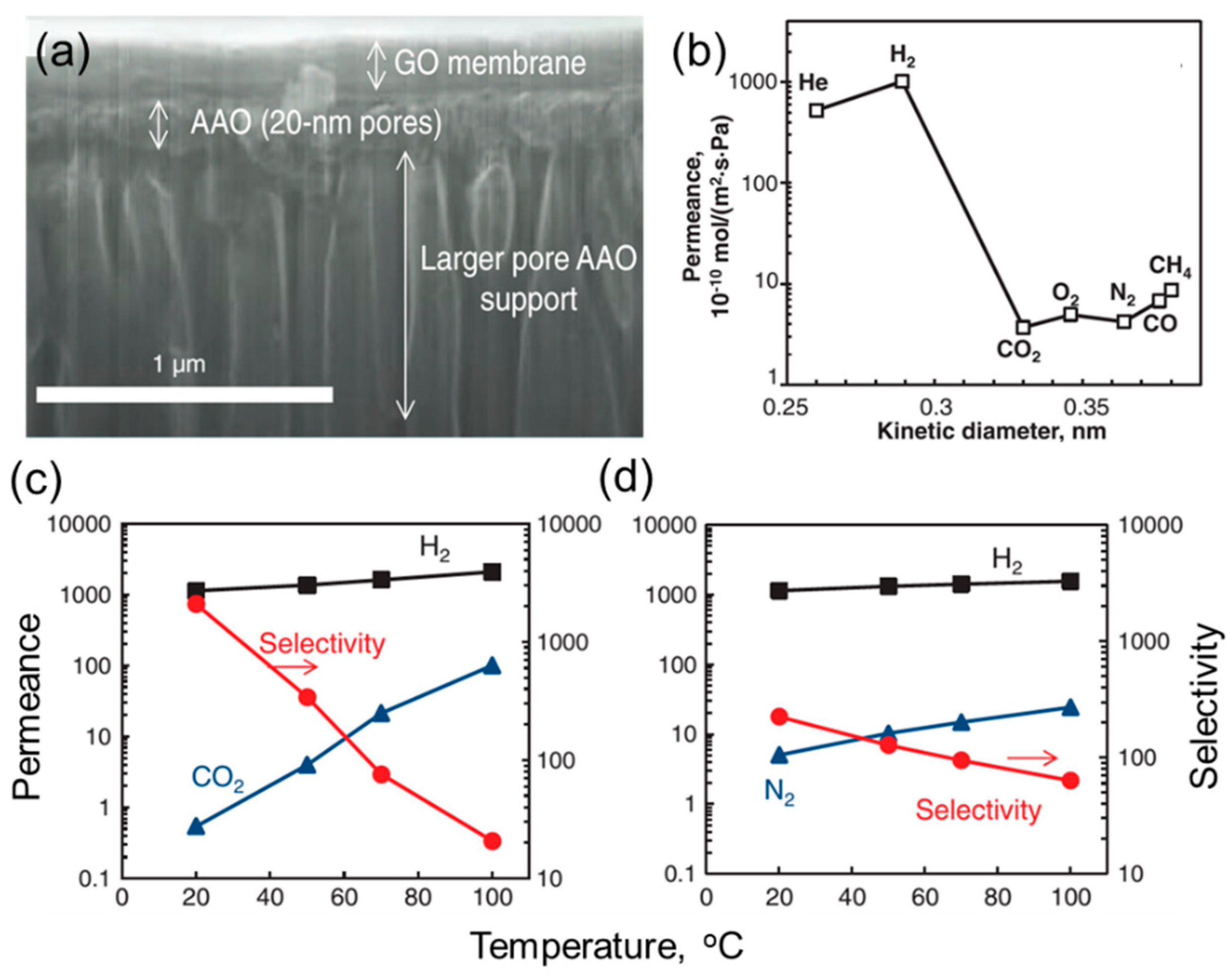
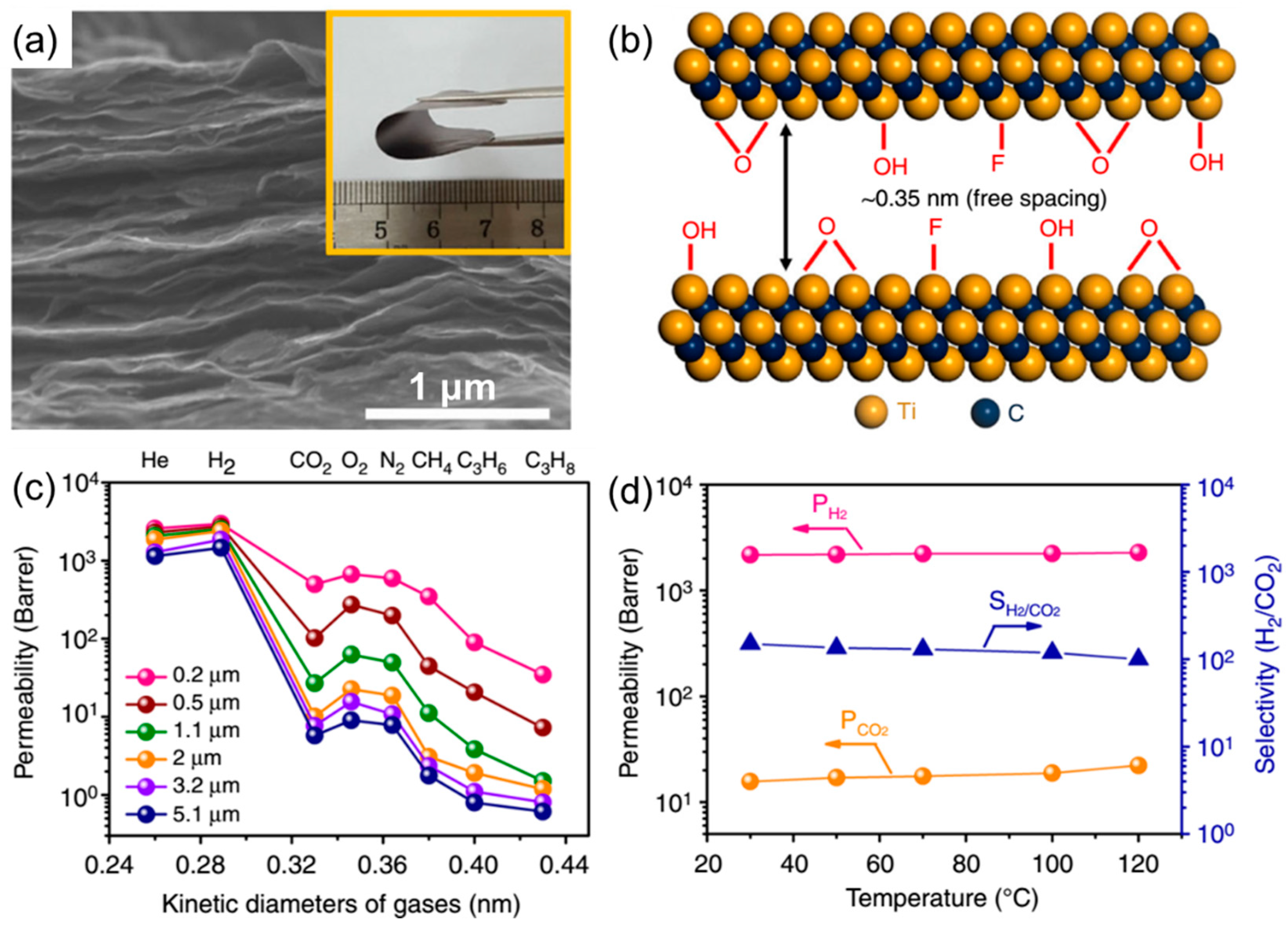
3. Gas Separation Membranes Based on Other 2D Materials
4. MMMs Containing 2D Nanochannels for Gas Separation
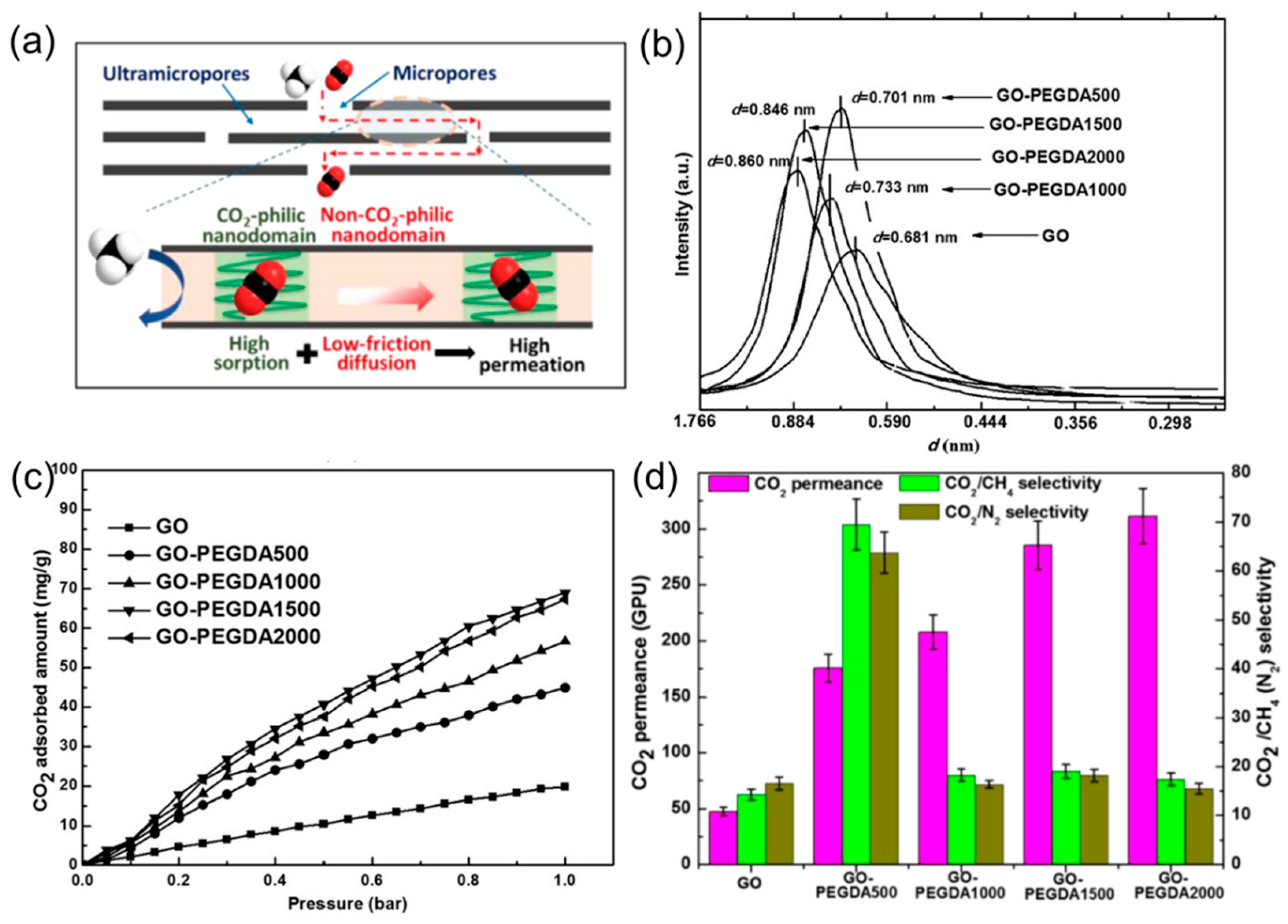
4.1. 2D Layers Intercalated with CO2-Philic Materials
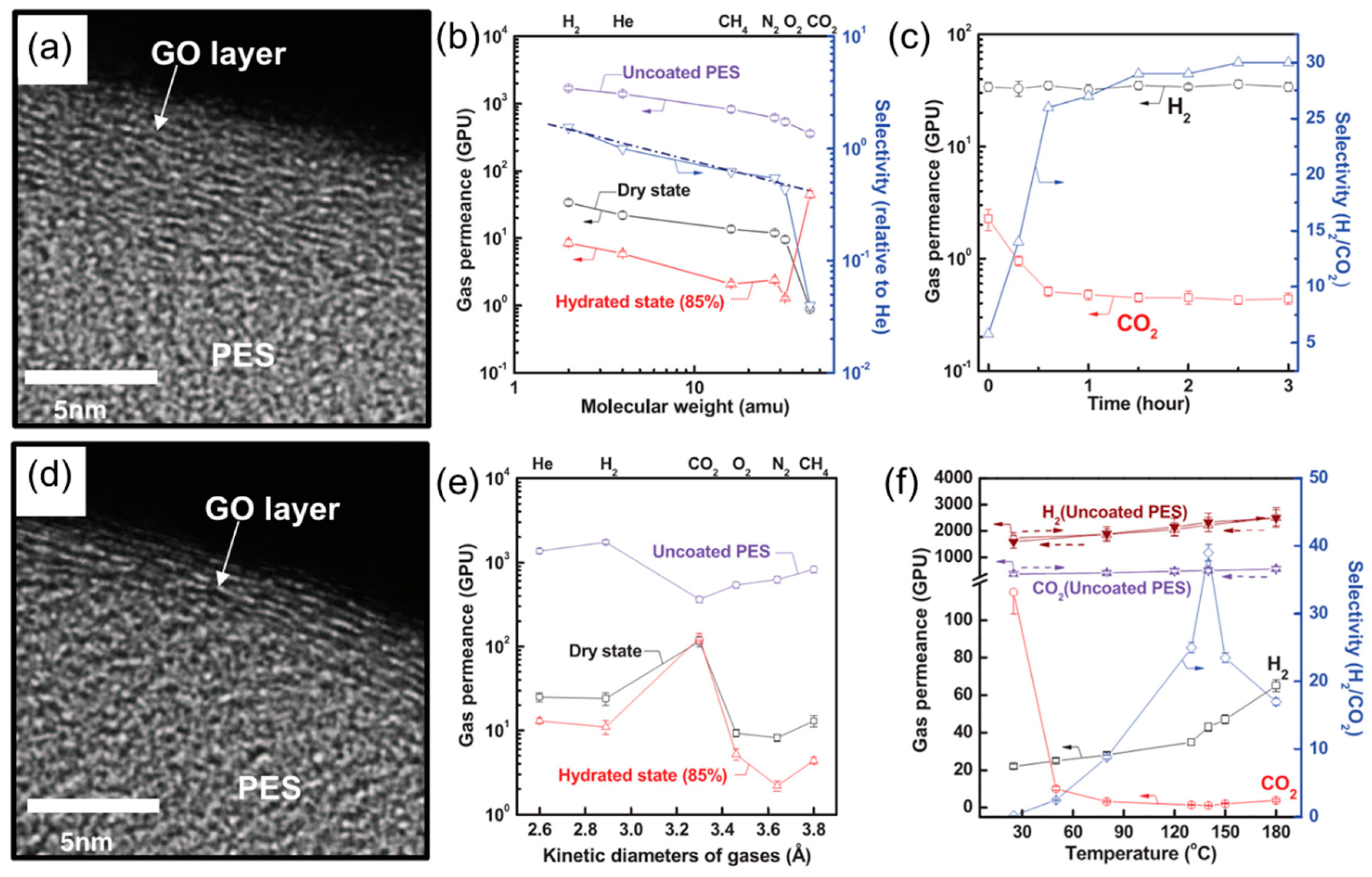
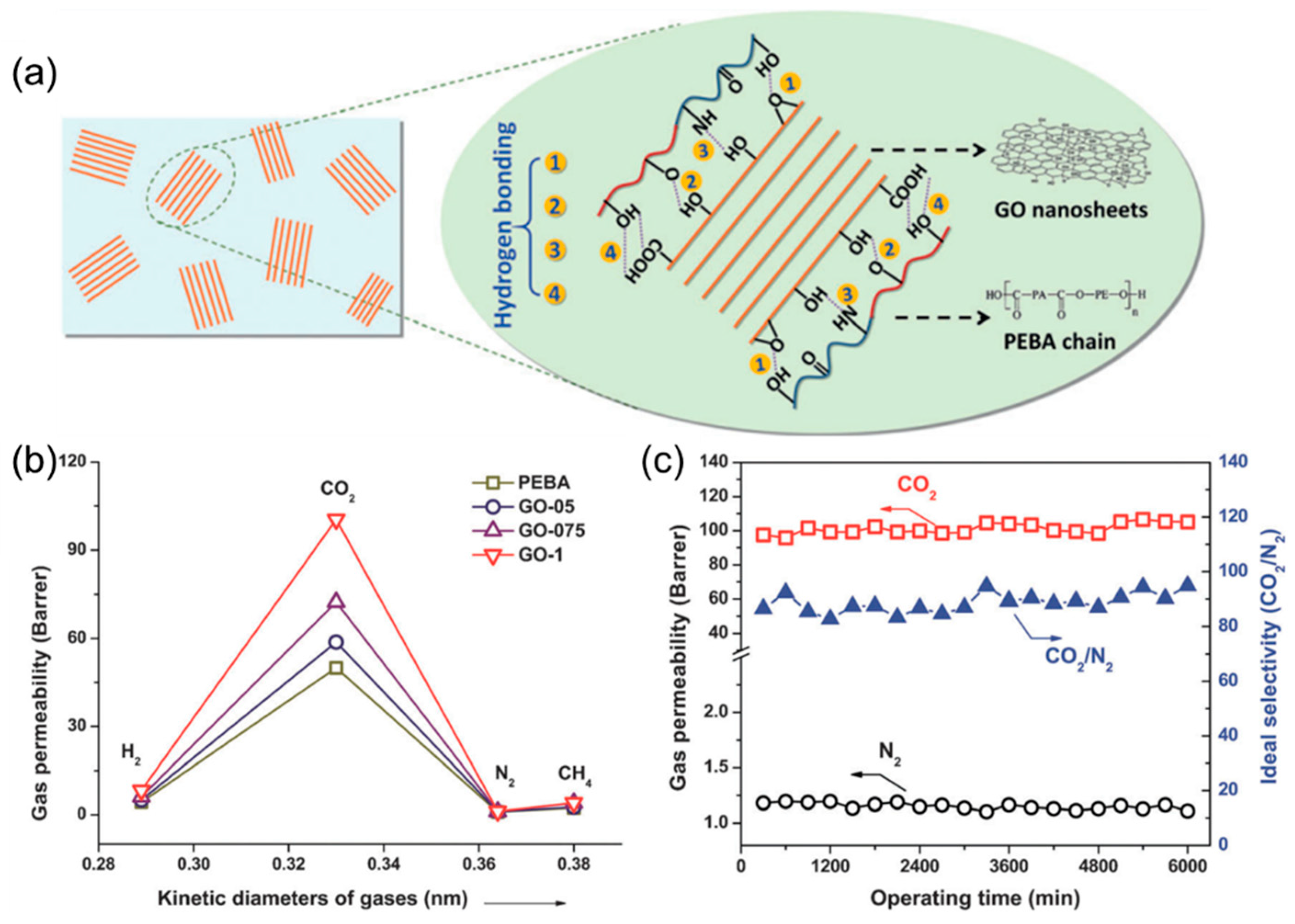
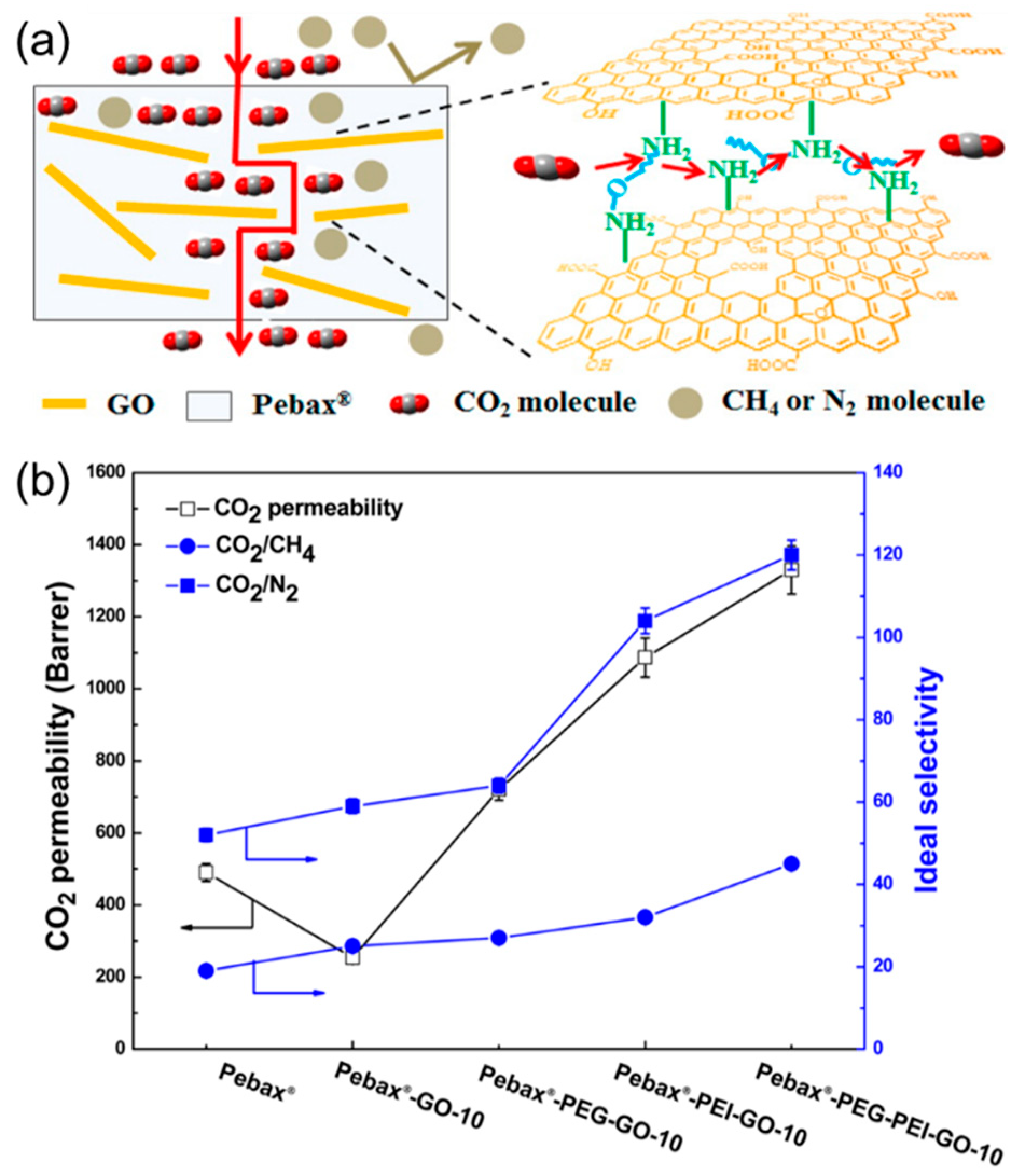
4.2. MMMs Containing GO in Polymers for Gas Separation
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.W.; Yoon, H.W.; Yoon, S.M.; Yoo, B.M.; Ahn, B.K.; Cho, Y.H.; Shin, H.J.; Yang, H.; Paik, U.; Kwon, S.; et al. Selective gas transport through few-layered graphene and graphene oxide membranes. Science 2013, 342, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizia, M.; Chi, W.S.; Smith, Z.P.; Merkel, T.C.; Baker, R.W.; Freeman, B.D. Polymers and mixed matrix membranes for gas and vapor separation: A review and prospective opportunities. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7809–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. Correlation of separation factor versus permeability for polymeric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 62, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, eaab0530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, B.D. Basis of permeability/selectivity tradeoff relations in polymeric gas separation membranes. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yavari, M. Upper bound of polymeric membranes for mixed-gas CO2/CH4 separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.P.; Freeman, B.D. Graphene oxide: A new platform for high-performance gas- and liquid-separation membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10286–10288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, B.M.; Shin, J.E.; Lee, H.D.; Park, H.B. Graphene and graphene oxide membranes for gas separation applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2017, 16, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Shi, G.Q. Graphene-based membranes for molecular separation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 2806–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.R.; Wu, H.A.; Jayaram, P.N.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Geim, A.K. Unimpeded permeation of water through helium-leak-tight graphene-based membranes. Science 2012, 335, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Song, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Mao, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Bao, Y.; Yu, M. Ultrathin, molecular-sieving graphene oxide membranes for selective hydrogen separation. Science 2013, 342, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, J.S.; Verbridge, S.S.; Alden, J.S.; Van Der Zande, A.M.; Parpia, J.M.; Craighead, H.G.; McEuen, P.L. Impermeable atomic membranes from graphene Sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, S.P.; Wang, L.; Pellegrino, J.; Bunch, J.S. Selective molecular sieving through porous graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebi, K.; Buchheim, J.; Wyss, R.M.; Droudian, A.; Gasser, P.; Shorubalko, I.; Kye, J.I.; Lee, C.; Park, H.G. Ultimate permeation across atomically thin porous graphene. Science 2014, 344, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.E.; Cooper, V.R.; Dai, S. Porous graphene as the ultimate membrane for gas separation. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4019–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ruoff, R.S. Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- William, S.; Hummers, J.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, K.; Erni, R.; Lee, Z.; Alem, N.; Gannett, W.; Zettl, A. Determination of the local chemical structure of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4467–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Li, C.; Wang, X.L.; Shi, G.Q. On the gelation of graphene oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 5545–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikin, D.A.; Stankovich, S.; Zimney, E.J.; Piner, R.D.; Dommett, G.H.; Evmenenko, G.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide paper. Nature 2007, 448, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Liu, G.; Huang, K.; Chu, Z.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Subnanometer two-dimensional graphene oxide channels for ultrafast gas sieving. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3398–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Qian, Y.; Hu, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhao, D. Facile preparation of graphene oxide membranes for gas separation. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2921–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; He, X.; Zeng, G.; Pan, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, Y. Strict molecular sieving over electrodeposited 2D-interspacing-narrowed graphene oxide membranes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Gong, D.; Li, G.; Zeng, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Wu, P.; Vovk, E.; Peng, Z.; et al. Self-assembly of thiourea-crosslinked graphene oxide framework membranes toward separation of small molecules. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.G.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Jin, J. Ultrathin membranes of single-layered MoS2 nanosheets for high-permeance hydrogen separation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17649–17652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Liu, G.; Ji, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Guan, K.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Xiong, J.; Yang, J.; et al. 2D MXene nanofilms with tunable gas transport channels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Xue, J.; Ding, L.X.; Wang, S.; Caro, J.; Gogotsi, Y. MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janakiram, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Dai, Z.; Ansaloni, L.; Deng, L. Performance of Nanocomposite Membranes Containing 0D to 2D Nanofillers for CO2 Separation: A Review. Membranes 2018, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.F.; Wu, Y.Z.; Zhang, N.; He, G.W.; Xin, Q.P.; Wu, X.Y.; Wu, H.; Cao, X.Z.; Guiver, M.D.; Jiang, Z.Y. A highly permeable graphene oxide membrane with fast and selective transport nanochannels for efficient carbon capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; He, G.; Xin, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guiver, M.D.; et al. Graphene oxide membranes with heterogeneous nanodomains for efficient CO2 separations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14246–14251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, W.; Cai, J.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Ying, Y.; Guo, Y.; Kong, X.; Xu, Z.; Peng, X. Ionic liquid selectively facilitates CO2 transport through graphene oxide membrane. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5385–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Tien, H.N.; Xu, W.L.; Chen, J.T.; Liu, Q.; Hicks, E.; Fathizadeh, M.; Li, S.; Yu, M. Ultrathin graphene oxide-based hollow fiber membranes with brush-like CO2-philic agent for highly efficient CO2 capture. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.; Park, J.; Ando, S.; Bin Kim, C.; Nagai, K.; Freeman, B.D.; Ellison, C.J. Gas permeation and selectivity of poly(dimethylsiloxane)/graphene oxide composite elastomer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 518, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.E.; Kim, H.W.; Yoo, B.M.; Park, H.B. Graphene oxide nanosheet-embedded crosslinked poly(ethylene oxide) hydrogel. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, G.; Huang, K.; Jin, W.; Lee, K.R.; Xu, N. Membranes with fast and selective gas-transport channels of laminar graphene oxide for efficient CO2 capture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 127, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, R.; Wu, H. Efficient CO2 capture by functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets as fillers to fabricate multi-permselective mixed matrix membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5528–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Jia, P.; Xu, L.L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Xiao, L.H.; Sun, J.H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Bielawski, C.W.; Geng, J.X. Tuning the surface properties of graphene oxide by surface-initiated polymerization of epoxides: An efficient method for enhancing gas separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4998–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakaran, M.; Shevate, R.; Kumar, M.; Peinemann, K.V. CO2-selective PEO-PBT (PolyActive)/graphene oxide composite membranes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14187–14190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Hou, J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Ou, R.W.; Simon, G.P.; Seong, J.G.; Lee, Y.M.; Wang, H.T. Highly permeable thermally rearranged polymer composite membranes with a graphene oxide scaffold for gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 7668–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Hou, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, V.; Liu, J. Enhanced CO2/N2 separation by porous reduced graphene oxide/Pebax mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berean, K.J.; Ou, J.Z.; Nour, M.; Field, M.R.; Alsaif, M.M.Y.A.; Wang, Y.; Ramanathan, R.; Bansal, V.; Kentish, S.; Doherty, C.M.; et al. Enhanced gas permeation through graphene nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 13700–13712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Lin, H. Engineering Sub-Nanometer Channels in Two-Dimensional Materials for Membrane Gas Separation. Membranes 2018, 8, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040100
Huang L, Lin H. Engineering Sub-Nanometer Channels in Two-Dimensional Materials for Membrane Gas Separation. Membranes. 2018; 8(4):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040100
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Liang, and Haiqing Lin. 2018. "Engineering Sub-Nanometer Channels in Two-Dimensional Materials for Membrane Gas Separation" Membranes 8, no. 4: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040100
APA StyleHuang, L., & Lin, H. (2018). Engineering Sub-Nanometer Channels in Two-Dimensional Materials for Membrane Gas Separation. Membranes, 8(4), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040100





