Membrane Binding and Modulation of the PDZ Domain of PICK1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PDZ Domain Structure and Canonical Ligand Binding
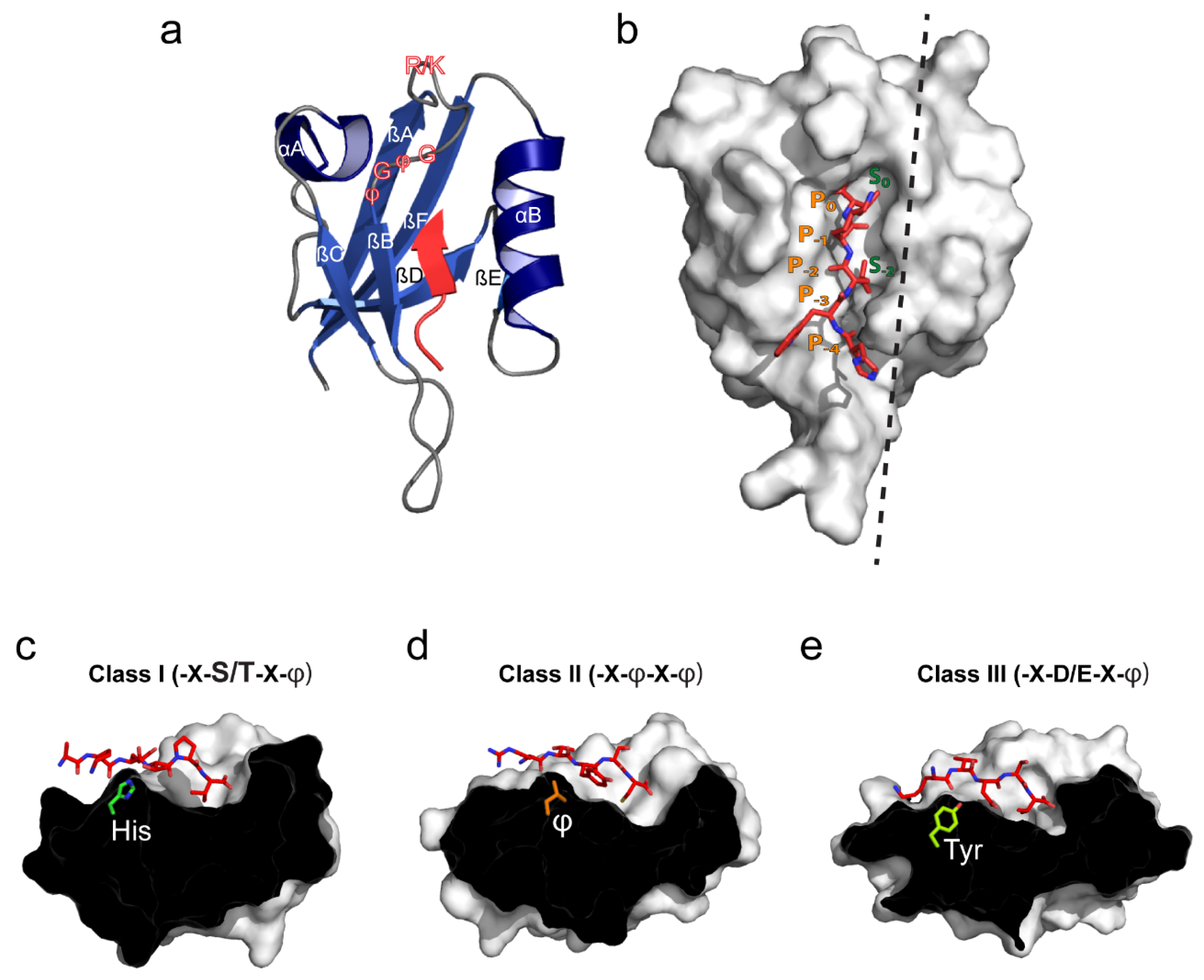
3. Membrane Lipid Binding Is a General Property of PDZ Domains
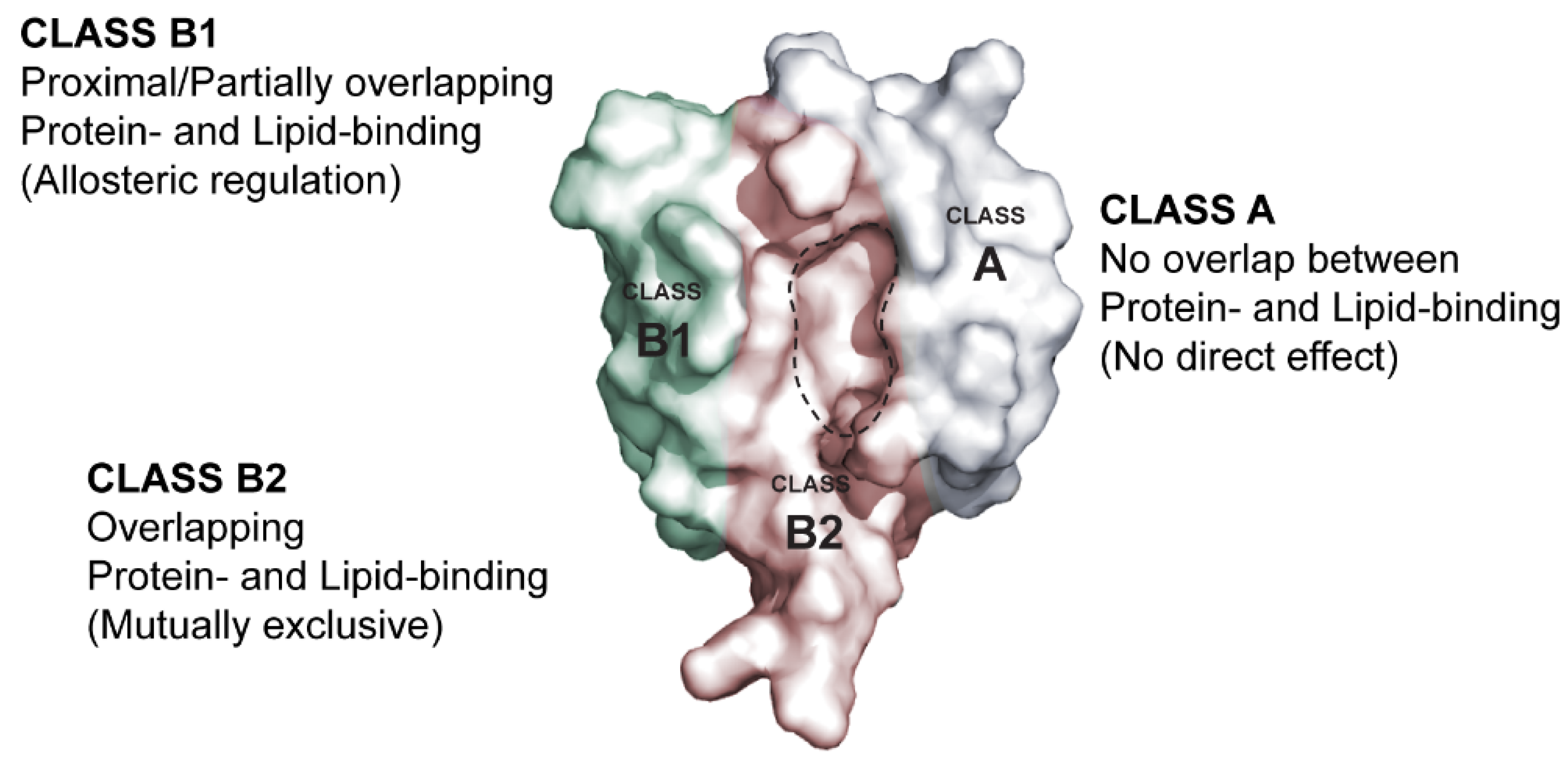
4. PICK1 Is a Flexible Membrane-Associated Scaffolding Protein
5. PICK1 Contains a Non-Canonical Promiscuous PDZ Domain
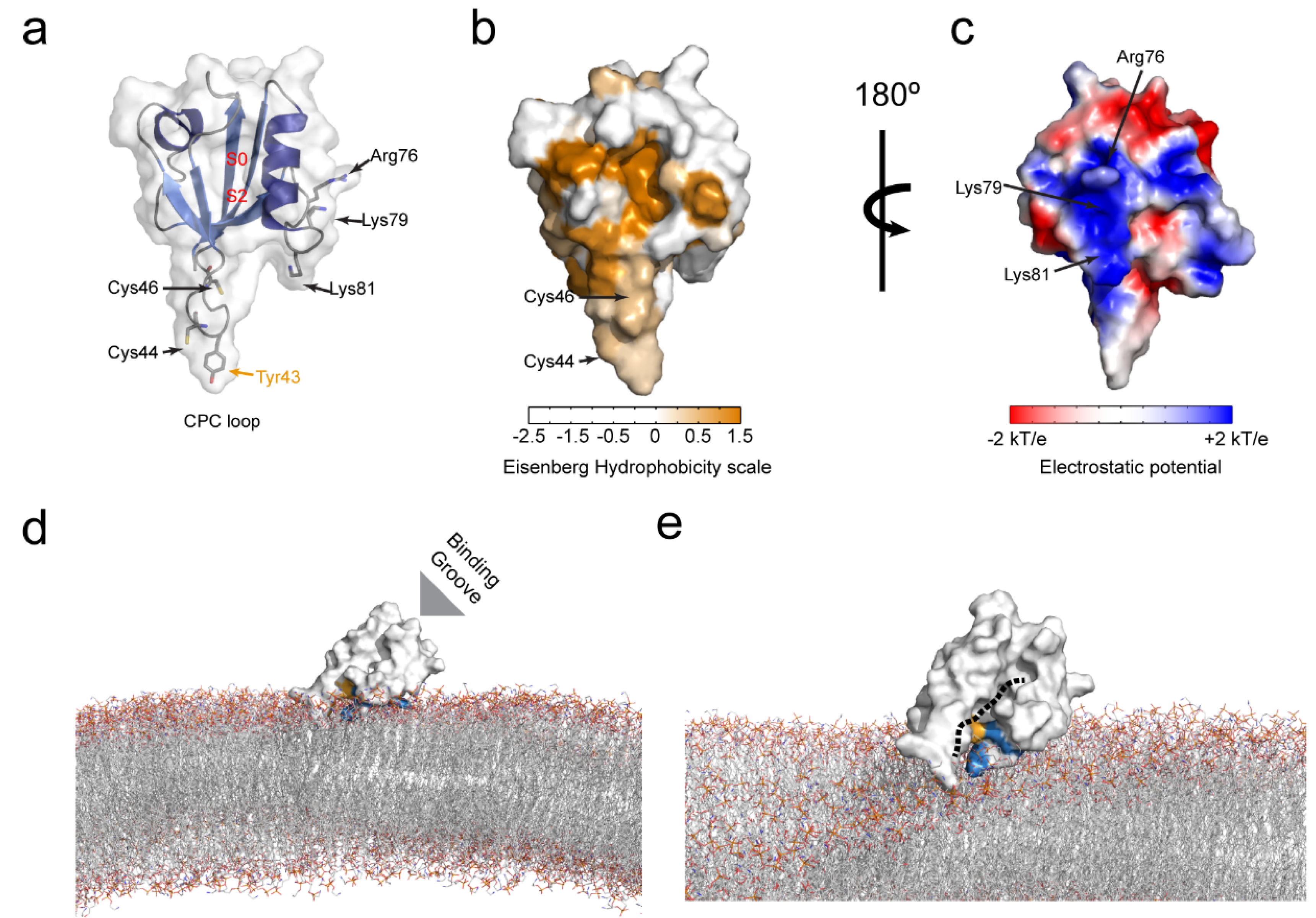
6. Membrane Lipid Binding of the PICK1 PDZ Domain
6.1. Molecular Determinants of the PICK1 PDZ Domain Membrane Lipid Binding
6.2. The CPC Loop of PICK1 PDZ Is a Proposed Zinc Binding Site
6.3. PICK1 Membrane Binding May by Redox-Regulated
6.4. Posttranslational Modifications of PICK1 PDZ Domain Can Regulate Membrane Binding

7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, L.; Warren, T.C.; King, J.; Betageri, R.; Rose, J.; Jakes, S. Crystal structures of the human p56lck SH2 domain in complex with two short phosphotyrosyl peptides at 1.0 A and 1.8 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 256, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.B.; Breed, J.; Barton, G.J. Conservation analysis and structure prediction of the SH2 family of phosphotyrosine binding domains. FEBS Lett. 1992, 304, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawson, T.; Schlessingert, J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr. Biol. 1993, 3, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.J. SH3 domains: Complexity in moderation. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macias, M.J.; Hyvönen, M.; Baraldi, E.; Schultz, J.; Sudol, M.; Saraste, M.; Oschkinat, H. Structure of the WW domain of a kinase-associated protein complexed with a proline-rich peptide. Nature 1996, 382, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eck, M.J.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Trüb, T.; Nolte, R.T.; Shoelson, S.E. Structure of the IRS-1 PTB domain bound to the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor. Cell 1996, 85, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.M.; Huang, B.; Olejniczak, E.T.; Meadows, R.P.; Shuker, S.B.; Miyazaki, M.; Trüb, T.; Shoelson, S.E.; Fesik, S.W. Structural basis for IL-4 receptor phosphopeptide recognition by the IRS-1 PTB domain. Nat. Struct Biol. 1996, 3, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Zhang, M. Organization and dynamics of PDZ-domain-related supramodules in the postsynaptic density. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, D.A.; Lee, A.; Lewis, J.; Kim, E.; Sheng, M.; MacKinnon, R. Crystal structures of a complexed and peptide-free membrane protein-binding domain: Molecular basis of peptide recognition by PDZ. Cell 1996, 85, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahelin, R.V. Lipid binding domains: More than simple lipid effectors. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S299–S304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahelin, R.V.; Scott, J.L.; Frick, C.T. Cellular and molecular interactions of phosphoinositides and peripheral proteins. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 182, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A. Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains and phosphoinositides. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 2007, 74, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzyniak, A.M.; Kashyap, R.; Zimmermann, P. Phosphoinositides and PDZ domain scaffolds. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 991, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, D.F.; Bryant, P.J. The discs-large tumor suppressor gene of Drosophila encodes a guanylate kinase homolog localized at septate junctions. Cell 1991, 66, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.O.; Hunt, C.A.; Kennedy, M.B. The rat brain postsynaptic density fraction contains a homolog of the Drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor protein. Neuron 1992, 9, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.B. Origin of PDZ (DHR, GLGF) domains. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, K.; Charbonnier, S.; Travé, G. The emerging contribution of sequence context to the specificity of protein interactions mediated by PDZ domains. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2648–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais Cabral, J.H.; Petosa, C.; Sutcliffe, M.J.; Raza, S.; Byron, O.; Poy, F.; Marfatia, S.M.; Chishti, A.H.; Liddington, R.C. Crystal structure of a PDZ domain. Nature 1996, 382, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ham, M.; Hendriks, W. PDZ domains-glue and guide. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2003, 30, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, B.Z.; Lim, W.A. Mechanism and role of PDZ domains in signaling complex assembly. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3219–3231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erlendsson, S.; Rathje, M.; Heidarsson, P.O.; Poulsen, F.M.; Madsen, K.L.; Teilum, K.; Gether, U. Protein interacting with C-kinase 1 (PICK1) binding promiscuity relies on unconventional PSD-95/discs-large/ZO-1 homology (PDZ) binding modes for nonclass II PDZ ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25327–25340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saro, D.; Martin, P.; Vickrey, J.F.; Griffin, A.; Kovari, L.C.; Spaller, M.R. Structure of the Third PDZ Domain of PSD-95 Protein Complexed with KKETPV Peptide Ligand. Available online: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1tp3 (accessed on 20 September 2005).
- Im, Y.J.; Im, Y.J.; Park, S.H.; Rho, S.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, G.B.; Sheng, M.; Kim, E.; Eom, S.H. Crystal Structure of GRIP1 PDZ6-Peptide Complex Reveals the Structural Basis for Class II PDZ Target Recognition and PDZ Domain-mediated Multimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 278, 8501–8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tochio, H.; Zhang, Q.; Mandal, P.; Li, M.; Zhang, M. Solution structure of the extended neuronal nitric oxide synthase PDZ domain complexed with an associated peptide. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hung, A.Y.; Sheng, M. PDZ domains: Structural modules for protein complex assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5699–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songyang, Z. Recognition of unique carboxyl-terminal motifs by distinct PDZ domains. Science 1997, 275, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stricker, N.L.; Christopherson, K.S.; Yi, B.A.; Schatz, P.J.; Raab, R.W.; Dawes, G.; Bassett, D.E.; Bredt, D.S.; Li, M. PDZ domain of neuronal nitric oxide synthase recognizes novel C-terminal peptide sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonikian, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sazinsky, S.L.; Currell, B.; Yeh, J.-H.; Reva, B.; Held, H.A.; Appleton, B.A.; Evangelista, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. A specificity map for the PDZ domain family. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W. Organization of signaling complexes by PDZ-domain scaffold proteins. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Sheng, M.; Sala, C.; Sala, C. PDZ domains and the organization of supramolecular complexes. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, J.; Hoffmüller, U.; Krause, G.; Ashurst, J.; Macias, M.J.; Schmieder, P.; Schneider-Mergener, J.; Oschkinat, H. Specific interactions between the syntrophin PDZ domain and voltage-gated sodium channels. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootjans, J.J.; Reekmans, G.; Ceulemans, H.; David, G. Syntenin-syndecan binding requires syndecan-synteny and the co-operation of both PDZ domains of syntenin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 19933–19941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, D.L.; Cohen, A.R.; Anderson, J.M.; Brünger, A.T. Crystal structure of the hCASK PDZ domain reveals the structural basis of class II PDZ domain target recognition. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Tomatis, D.; Rosas, M.; Grootjans, J.; Leenaerts, I.; Degeest, G.; Reekmans, G.; Coomans, C.; David, G. Characterization of syntenin, a syndecan-binding PDZ protein, as a component of cell adhesion sites and microfilaments. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Meerschaert, K.; Reekmans, G.; Leenaerts, I.; Small, J.V.; Vandekerckhove, J.; David, G.; Gettemans, J. PIP(2)-PDZ domain binding controls the association of syntenin with the plasma membrane. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 1215–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, E.; Wuytens, G.; Leenaerts, I.; Hannes, F.; Heung, M.Y.; Degeest, G.; David, G.; Zimmermann, P. Nuclear speckles and nucleoli targeting by PIP2-PDZ domain interactions. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2556–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugi, T.; Oyama, T.; Morikawa, K.; Jingami, H. Structural insights into the PIP2 recognition by syntenin-1 PDZ domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 366, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Feng, W.; Chen, J.; Chan, L.-N.; Huang, S.; Zhang, M. PDZ domains of Par-3 as potential phosphoinositide signaling integrators. Mol. Cell 2007, 28, 886–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachel, N.; Erdmann, K.S.; Kremer, W.; Wolff, P.; Gronwald, W.; Heumann, R.; Kalbitzer, H.R. Structure determination and ligand interactions of the PDZ2b domain of PTP-Bas (hPTP1E): Splicing-induced modulation of ligand specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 334, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerschaert, K.; Tun, M.P.; Remue, E.; de Ganck, A.; Boucherie, C.; Vanloo, B.; Degeest, G.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Zimmermann, P.; Bhardwaj, N.; et al. The PDZ2 domain of zonula occludens-1 and -2 is a phosphoinositide binding domain. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3951–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Wu, H.; Shen, C.; Shi, Y.; Jin, W.; Xia, J.; Zhang, M. Clustering and synaptic targeting of PICK1 requires direct interaction between the PDZ domain and lipid membranes. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4576–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, R.; Ivarsson, Y.; Schymkowitz, J.; Rousseau, F.; Zimmermann, P. Structural diversity of PDZ-lipid interactions. ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sheng, R.; Källberg, M.; Silkov, A.; Tun, M.P.; Bhardwaj, N.; Kurilova, S.; Hall, R.A.; Honig, B.; Lu, H.; Cho, W. Genome-wide functional annotation of dual-specificity protein- and lipid-binding modules that regulate protein interactions. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivarsson, Y.; Wawrzyniak, A.M.; Kashyap, R.; Polanowska, J.; Betzi, S.; Lembo, F.; Vermeiren, E.; Chiheb, D.; Lenfant, N.; Morelli, X.; et al. Prevalence, specificity and determinants of lipid-interacting PDZ domains from an in-cell screen and in vitro binding experiments. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudinger, J.; Zhou, J.; Burgess, R.; Elledge, S.J.; Olson, E.N. PICK1: A perinuclear binding protein and substrate for protein kinase C isolated by the yeast two-hybrid system. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 128, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Xu, J. Structure and Function of PICK1. Neuro Signals 2006, 15, 190–201. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.; Kam, C.; Xu, J.; Shen, C.; Huganir, R.L.; Xia, J.; Xu, J.; Shen, C.; Kam, C.; Huganir, R.L.; et al. PICK1 ICA69 Heteromeric BAR Domain Complex Regulates Synaptic Targeting and Surface Expression of AMPA Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12945–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, J.P.; Shen, Y.; Rubio, M.E.; Linden, D.J.; Huganir, R.L.; Jin, W.; Thomas, G.M.; Xia, J.; Yu, S.; Takamiya, K. Targeted In Vivo Mutations of the AMPA Receptor Subunit GluR2 and Its Interacting Protein PICK1 Eliminate Cerebellar Long-Term Depression. Neuron 2006, 49, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggono, V.; Huganir, R.L. Regulation of AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2012, 22, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, J.G. Molecular mechanisms for regulation of AMPAR trafficking by PICK1. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, K.L.; Thorsen, T.S.; Rahbek-Clemmensen, T.; Eriksen, J.; Gether, U. Protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) reduces reinsertion rates of interaction partners sorted to Rab11-dependent slow recycling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12293–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citri, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Ma, C.; Morishita, W.; Fang, S.; Rizo, J.; Malenka, R.C.; Citri, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Ma, C.; et al. Calcium Binding to PICK1 Is Essential for the Intracellular Retention of AMPA Receptors Underlying Long-Term Depression. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 16437–16452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volk, L.; Kim, C.-H.; Takamiya, K.; Yu, Y.; Huganir, R.L. Developmental regulation of protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) function in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21784–21789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focant, M.C.; Hermans, E. Protein interacting with C kinase and neurological disorders. Synapse 2013, 67, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, B.; Madsen, K.L.; Jansen, A.M.; Jin, C.; Rickhag, M.; Lund, V.K.; Jensen, M.; Bhatia, V.; Sørensen, G.; Madsen, A.N.; et al. PICK1 Deficiency Impairs Secretory Vesicle Biogenesis and Leads to Growth Retardation and Decreased Glucose Tolerance. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, A.M.; Nässel, D.R.; Madsen, K.L.; Jung, A.G.; Gether, U.; Kjaerulff, O. PICK1 expression in the Drosophila central nervous system primarily occurs in the neuroendocrine system. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 517, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Mao, Z.; Kam, C.; Xiao, N.; Cao, X.; Shen, C.; Cheng, K.K.Y.; Xu, A.; Lee, K.-M.; Jiang, L.; et al. PICK1 and ICA69 control insulin granule trafficking and their deficiencies lead to impaired glucose tolerance. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Weinstein, H.; Liwo, A.; Scheraga, H.A.; He, Y. PDZ Binding to the BAR Domain of PICK1 is Elucidated by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 405, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsen, M.L.; Thorsen, T.S.; Johner, N.; Ammendrup-Johnsen, I.; Erlendsson, S.; Tian, X.; Simonsen, J.B.; Høiberg-Nielsen, R.; Christensen, N.M.; Khelashvili, G.; et al. Structure of Dimeric and Tetrameric Complexes of the BAR Domain Protein PICK1 Determined by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. Structure 2015, 23, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madasu, Y.; Yang, C.; Boczkowska, M.; Bethoney, K.A.; Zwolak, A.; Rebowski, G.; Svitkina, T.; Dominguez, R. PICK1 is implicated in organelle motility in an Arp2/3 complex-independent manner. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, B.J.; Kent, H.M.; Mills, I.G.; Vallis, Y.; Butler, P.J. G.; Evans, P.R.; McMahon, H.T. BAR domains as sensors of membrane curvature: The amphiphysin BAR structure. Science 2004, 303, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallop, J.L.; Jao, C.C.; Kent, H.M.; Butler, P.J. G.; Evans, P.R.; Langen, R.; McMahon, H.T. Mechanism of endophilin N-BAR domain-mediated membrane curvature. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2898–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarricone, C.; Xiao, B.; Justin, N.; Walker, P.A.; Rittinger, K.; Gamblin, S.J.; Smerdon, S.J. The structural basis of Arfaptin-mediated cross-talk between Rac and Arf signalling pathways. Nature 2001, 411, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Ziff, E.B. PICK1 interacts with ABP/GRIP to regulate AMPA receptor trafficking. Neuron 2005, 47, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Ge, W.-P.; Xu, J.; Cao, M.; Peng, L.; Yung, W.; Liao, D.; Duan, S.; Zhang, M.; Xia, J. Lipid binding regulates synaptic targeting of PICK1, AMPA receptor trafficking, and synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2380–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, J.G. PICK1: A multi-talented modulator of AMPA receptor trafficking. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 118, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, K.L.; Beuming, T.; Niv, M.Y.; Chang, C.-W.; Dev, K.K.; Weinstein, H.; Gether, U. Molecular determinants for the complex binding specificity of the PDZ domain in PICK1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20539–20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dev, K.K. PDZ domain protein-protein interactions: A case study with PICK1. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, O.; Dev, K.K.; Bolia, A.; Gerek, Z.N.; Banu Ozkan, S.; Ozkan, S.B. The binding affinities of proteins interacting with the PDZ domain of PICK1. Proteins 2012, 80, 1393–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, R.C.; Peterson, F.C.; Volkman, B.F. Distal interactions within the par3-VE-cadherin complex. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkins, J.M.; Papagrigoriou, E.; Berridge, G.; Yang, X.; Phillips, C.; Gileadi, C.; Savitsky, P.; Doyle, D.A. Structure of PICK1 and other PDZ domains obtained with the help of self-binding C-terminal extensions. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, J.; Jia, Y.; Pan, L.; Shen, C.; Xia, J.; Zhang, M. Redox-regulated lipid membrane binding of the PICK1 PDZ domain. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4432–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.S.; Jansen, A.M.; de Wit, H.; Tawfik, B.; Madsen, K.L.; Verhage, M.; Gether, U.; Sørensen, J.B. The BAR domain protein PICK1 controls vesicle number and size in adrenal chromaffin cells. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10688–10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argüello, J.M.; Eren, E.; González-Guerrero, M. The structure and function of heavy metal transport P1B-ATPases. Biometals 2007, 20, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, H.; Yang, X.; Niu, L. Zinc binding site in PICK1 is dominantly located at the CPC motif of its PDZ domain. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammendrup-Johnsen, I.; Thorsen, T.S.; Gether, U.; Madsen, K.L. Serine 77 in the PDZ domain of PICK1 is a protein kinase Cα phosphorylation site regulated by lipid membrane binding. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, J.; Shen, Y.; Xia, J.; Luo, J. Threonine 82 at the PDZ domain of PICK1 is critical for AMPA receptor interaction and localization. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Valero, M.; Ferrer-Orta, C.; Querol-Audí, J.; Marin-Vicente, C.; Fita, I.; Gómez-Fernández, J.C.; Verdaguer, N.; Corbalán-García, S. Structural and mechanistic insights into the association of PKCalpha-C2 domain to PtdIns(4,5)P2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6603–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niefind, K.; Guerra, B.; Ermakowa, I.; Issinger, O.G. Crystal structure of human protein kinase CK2: Insights into basic properties of the CK2 holoenzyme. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5320–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohout, S.C.; Corbalán-García, S.; Gómez-Fernández, J.C.; Falke, J.J. C2 domain of protein kinase C alpha: Elucidation of the membrane docking surface by site-directed fluorescence and spin labeling. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, K.L.; Bhatia, V.K.; Gether, U.; Stamou, D. BAR domains, amphipathic helices and membrane-anchored proteins use the same mechanism to sense membrane curvature. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erlendsson, S.; Madsen, K.L. Membrane Binding and Modulation of the PDZ Domain of PICK1. Membranes 2015, 5, 597-615. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040597
Erlendsson S, Madsen KL. Membrane Binding and Modulation of the PDZ Domain of PICK1. Membranes. 2015; 5(4):597-615. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040597
Chicago/Turabian StyleErlendsson, Simon, and Kenneth Lindegaard Madsen. 2015. "Membrane Binding and Modulation of the PDZ Domain of PICK1" Membranes 5, no. 4: 597-615. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040597
APA StyleErlendsson, S., & Madsen, K. L. (2015). Membrane Binding and Modulation of the PDZ Domain of PICK1. Membranes, 5(4), 597-615. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5040597




