Breath Figure Method for Construction of Honeycomb Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanism of Honeycomb Film Formation: Breath Figure Method
2.1. Development of the Breath Figure Method to Form Honeycomb Films
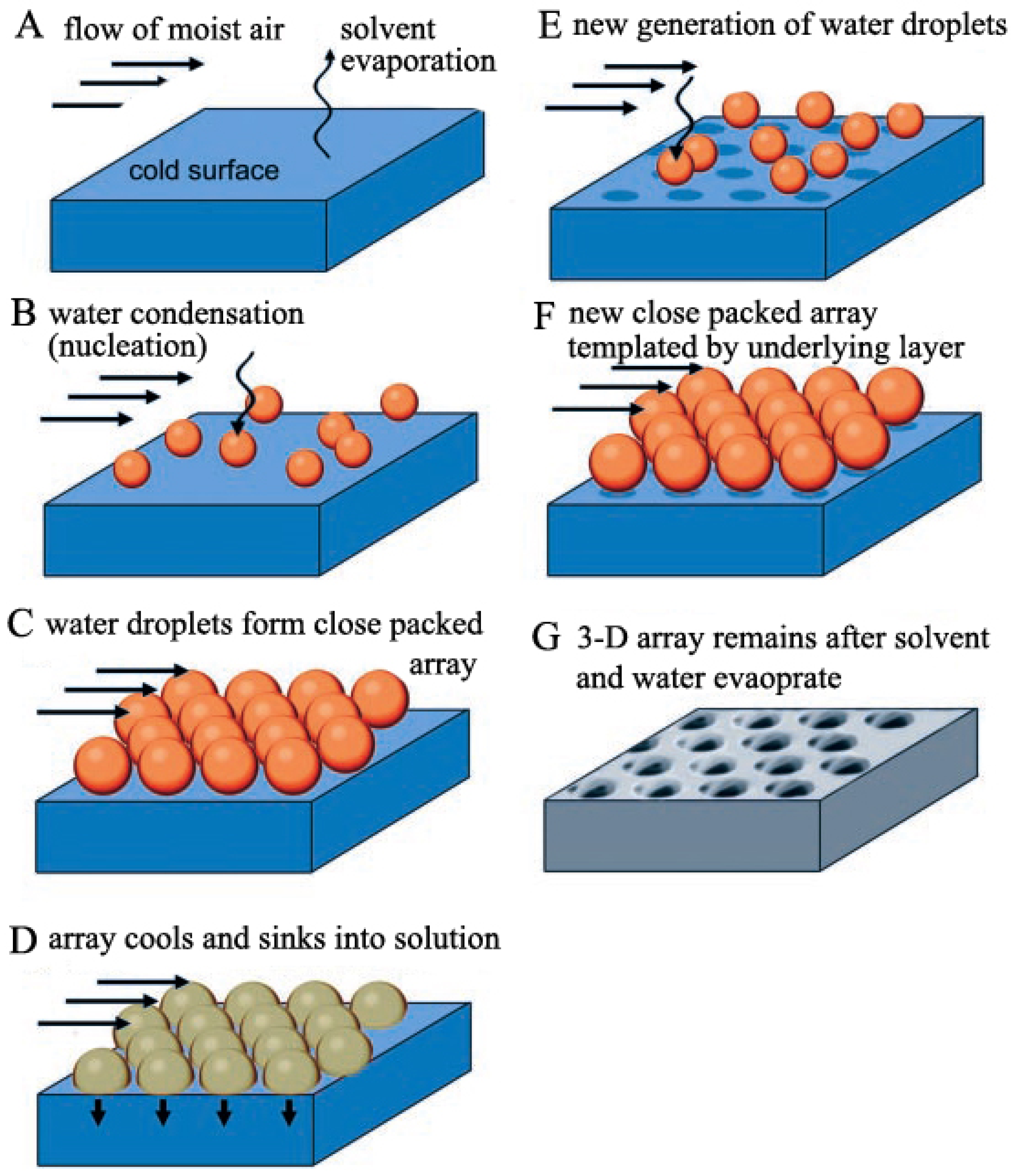
- (a)
- Phase separation with rapid solvent evaporation;
- (b)
- Polymer concentration increasing;
- (c)
- Solution surface cooling;
- (d)
- Water condensation.
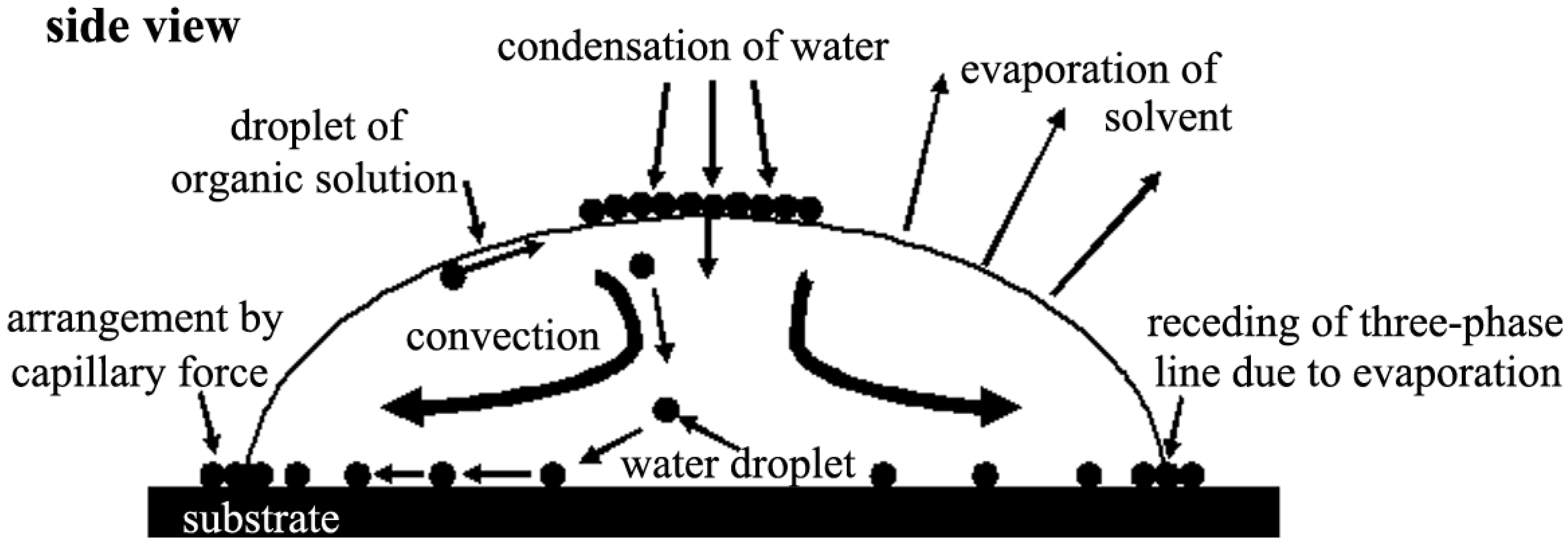
- (a)
- Liquid surface becomes cold with the solvent evaporation;
- (b)
- Water condenses on the cold surface to become water droplets, which is the nucleation process;
- (c)
- Water droplets form a close packed hexagonal array because of the convective currents of the evaporation and moist air flow;
- (d)
- Water droplet array cools and sinks into the polymer solution;
- (e)
- New nucleation and growth of the moist air induce the formation of another water droplet layer;
- (f)
- New layers of close packed hexagonal water droplet arrays are generated;
- (g)
- The solution surface cools back to room temperature after the solvent is totally evaporated, along with the honeycomb film formation after water evaporation;
- (h)
- Repeating the process from (d) to (f), another water droplet array layer forms.
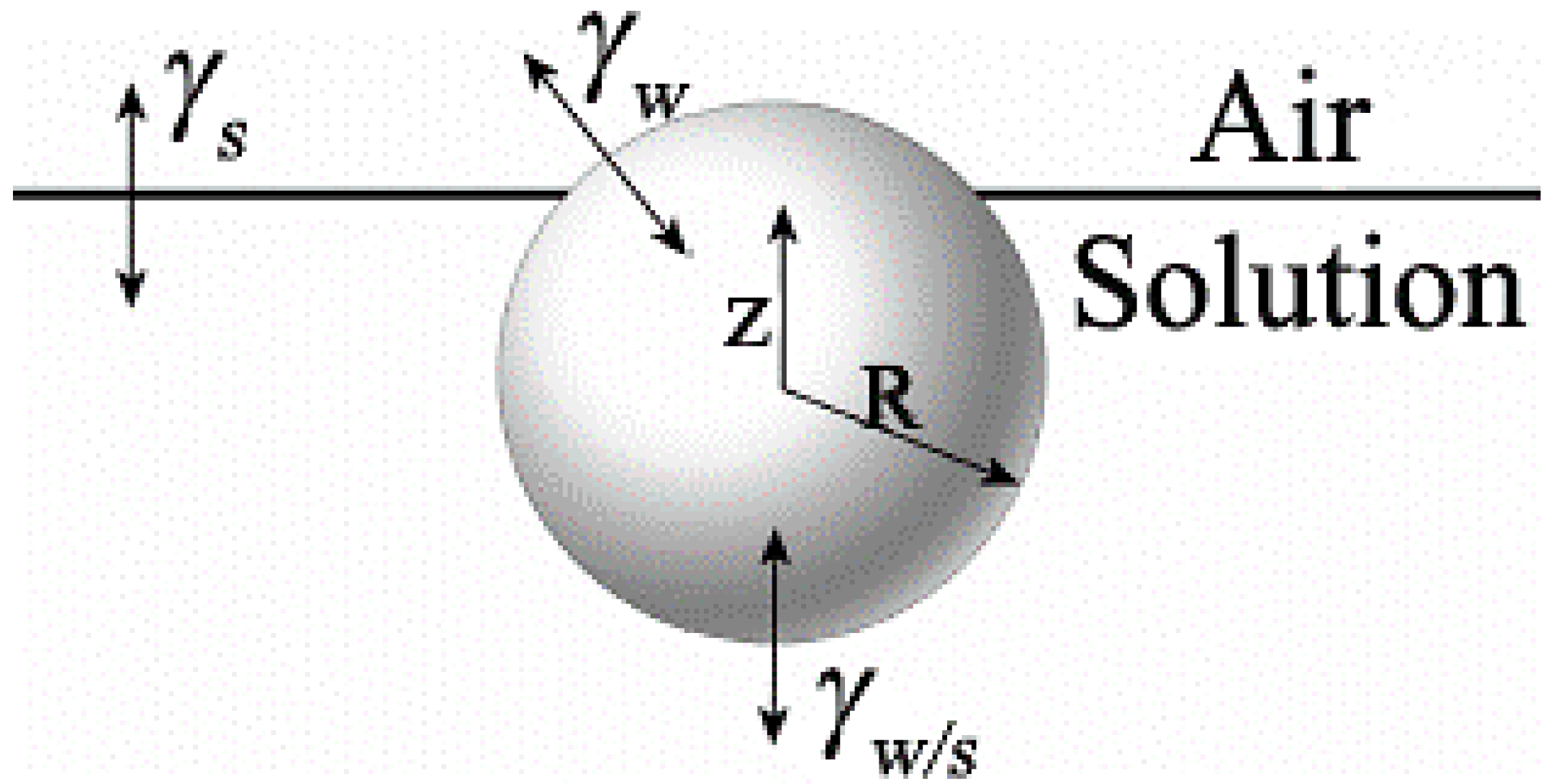
| Solvent | γ (mN/m) T = 20 °C | γH2O/solvent (mN/m) T = 20 °C | z0 | Type of Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS2 | 32.3 | 47.3 | 0.84 | monolayer |
| toluene | 27.9 | 36.1 | 1.30 | multilayer |
| benzene | 28.2 | 35 | 1.33 | multilayer |
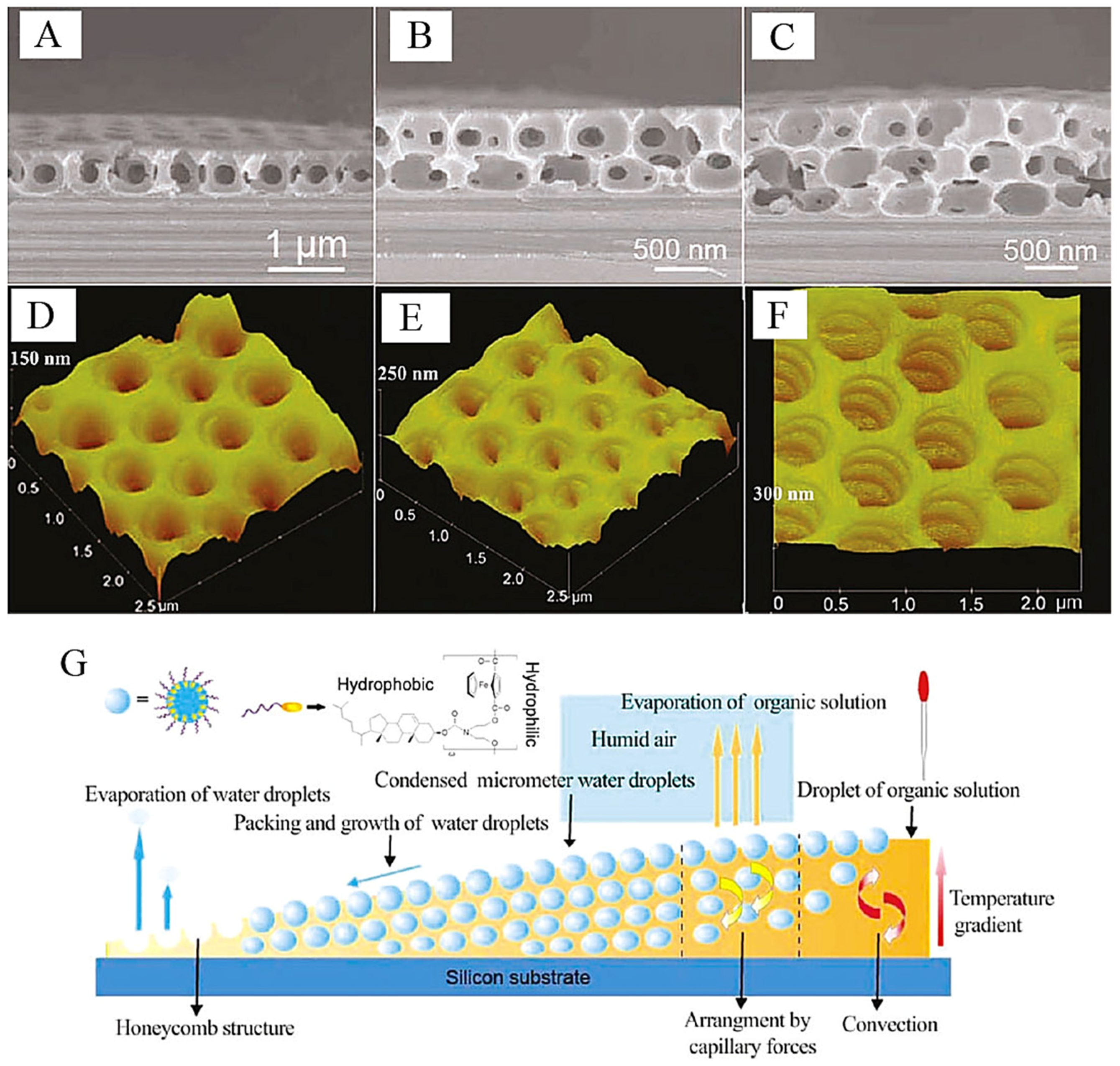
2.2. Influence Factors of the Honeycomb Film Formation by the Breath Figure Method
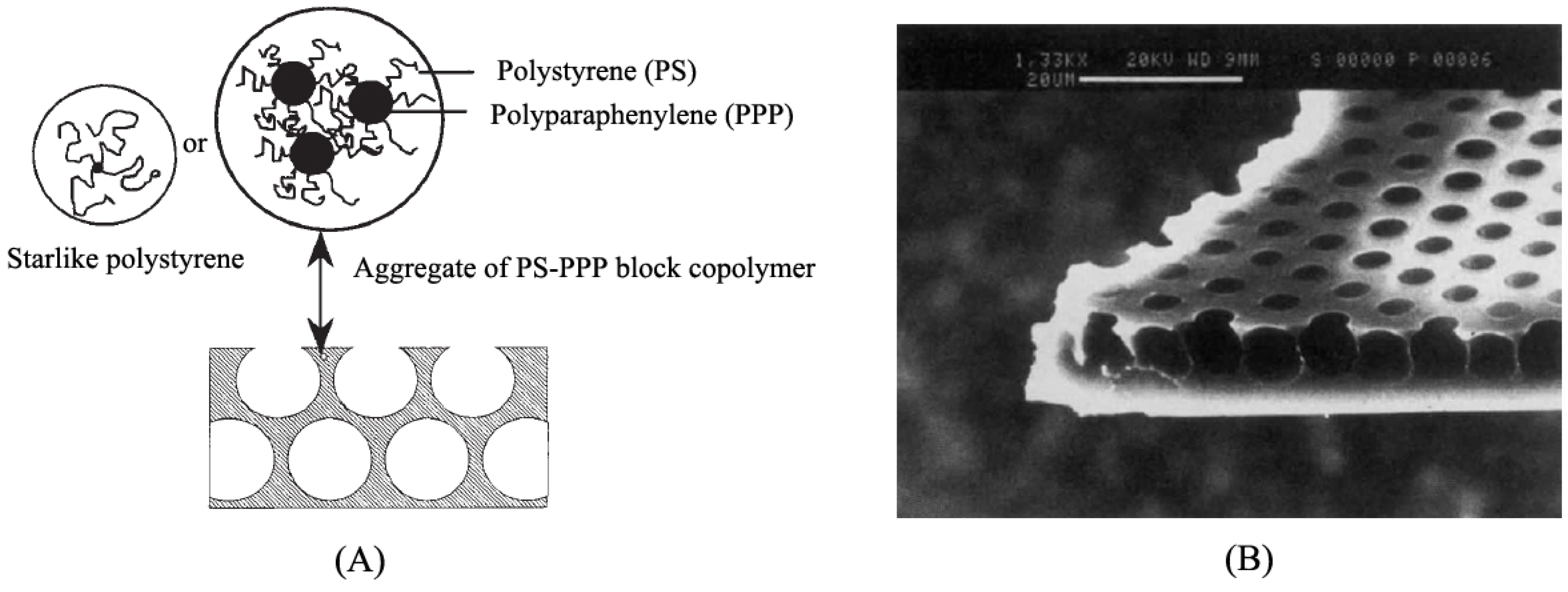
2.2.1. Building Units

2.2.2. Solvents
2.2.3. Substrates
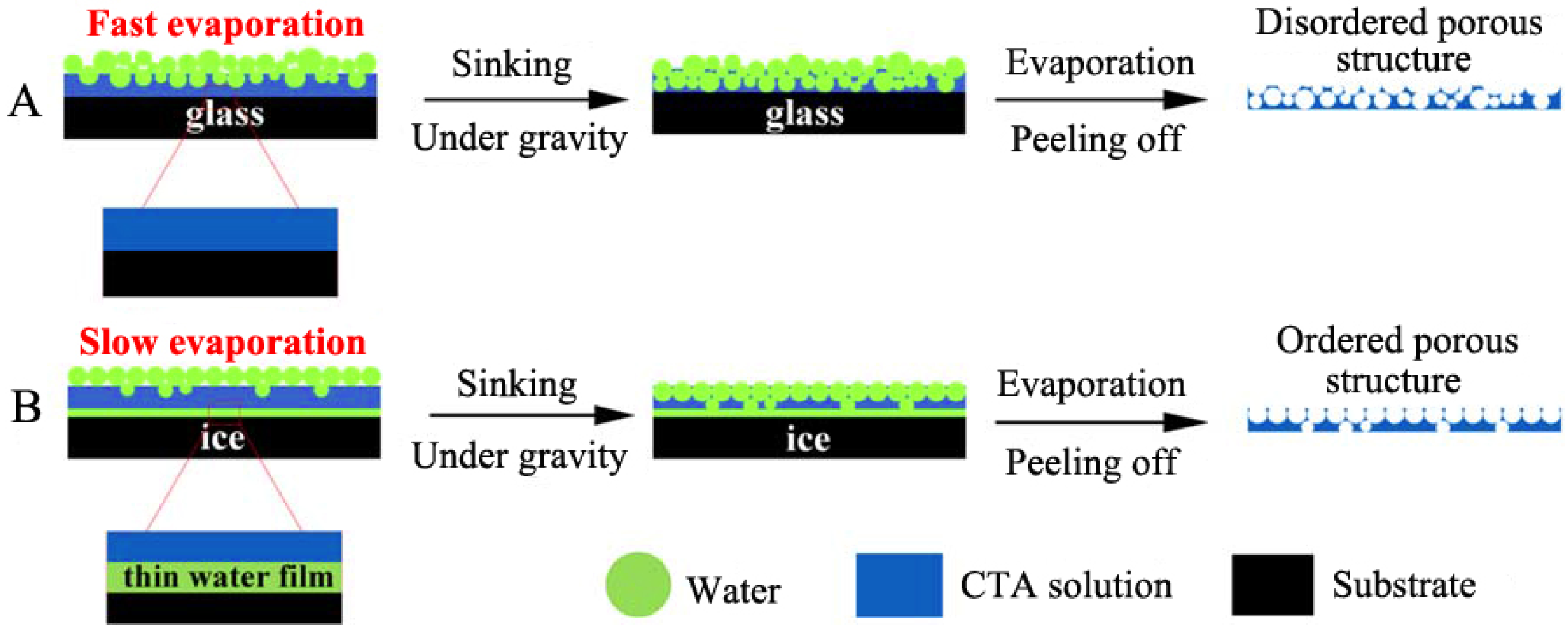
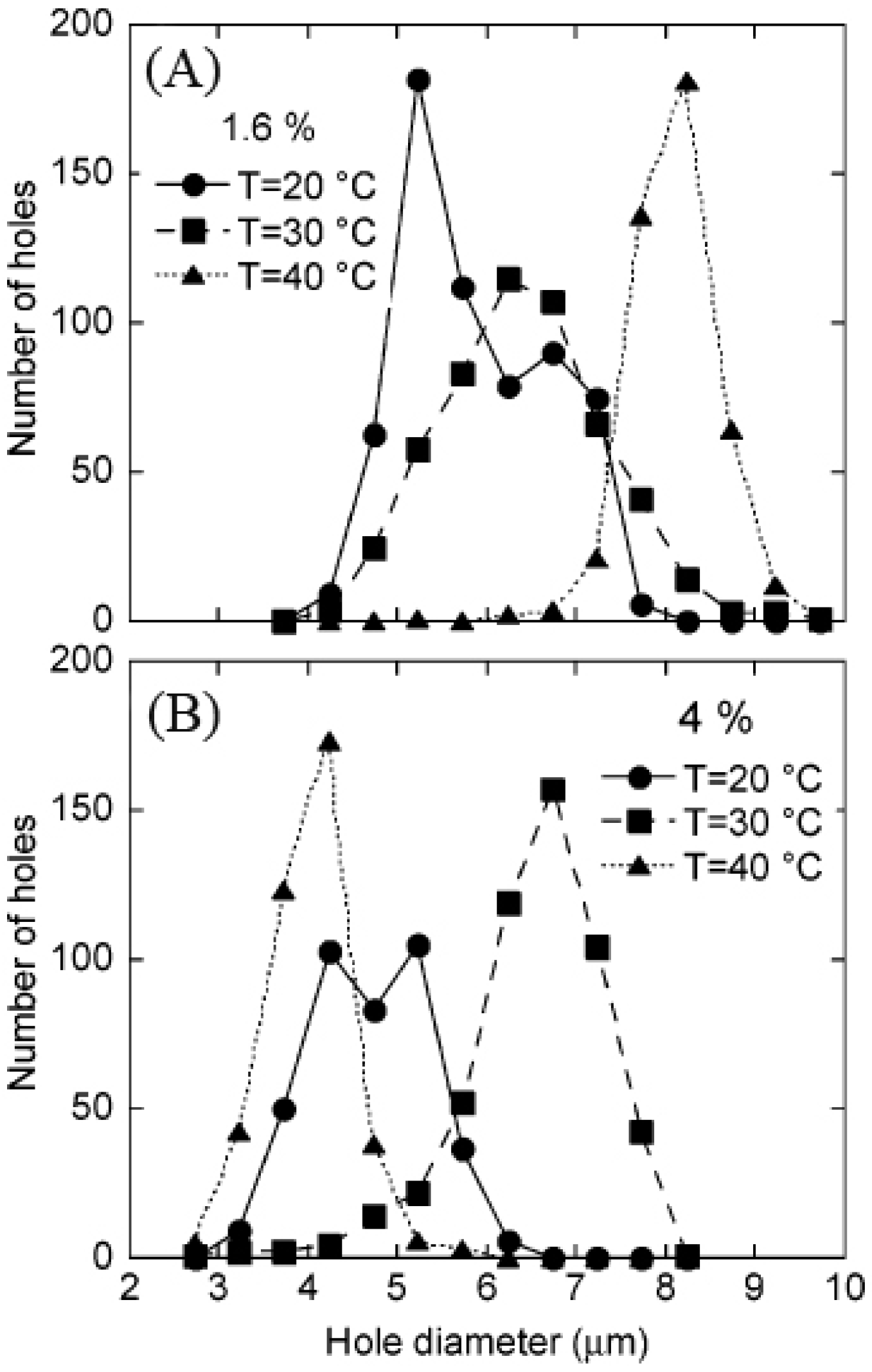
2.2.4. Temperature
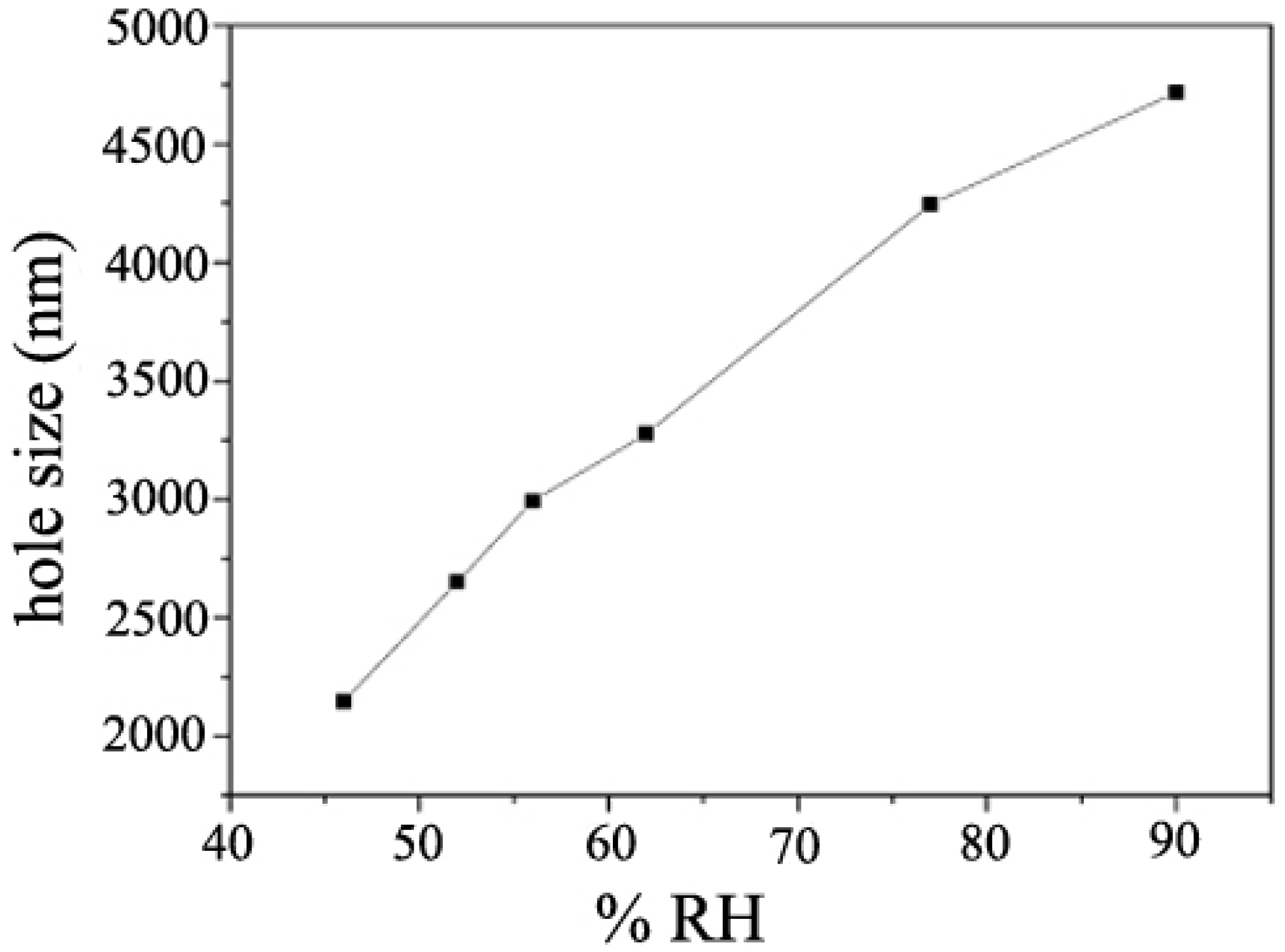
2.2.5. Humidity
2.2.6. Other Factors
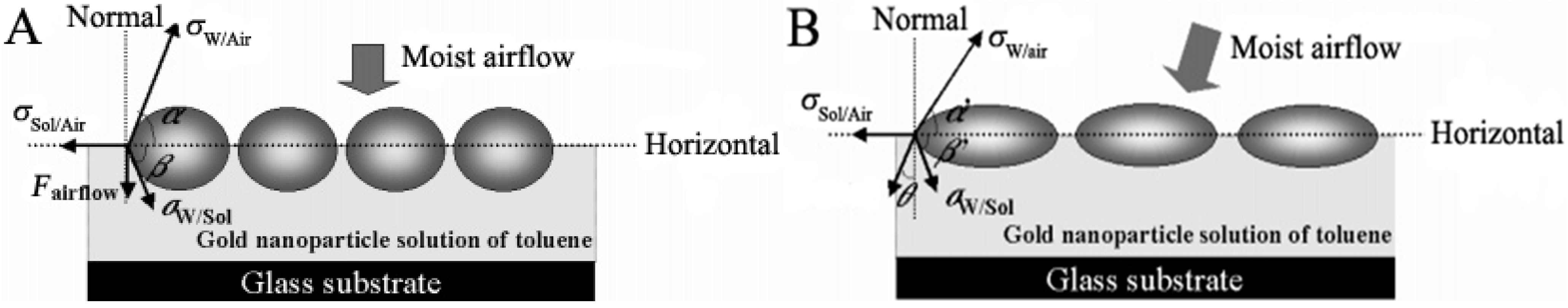
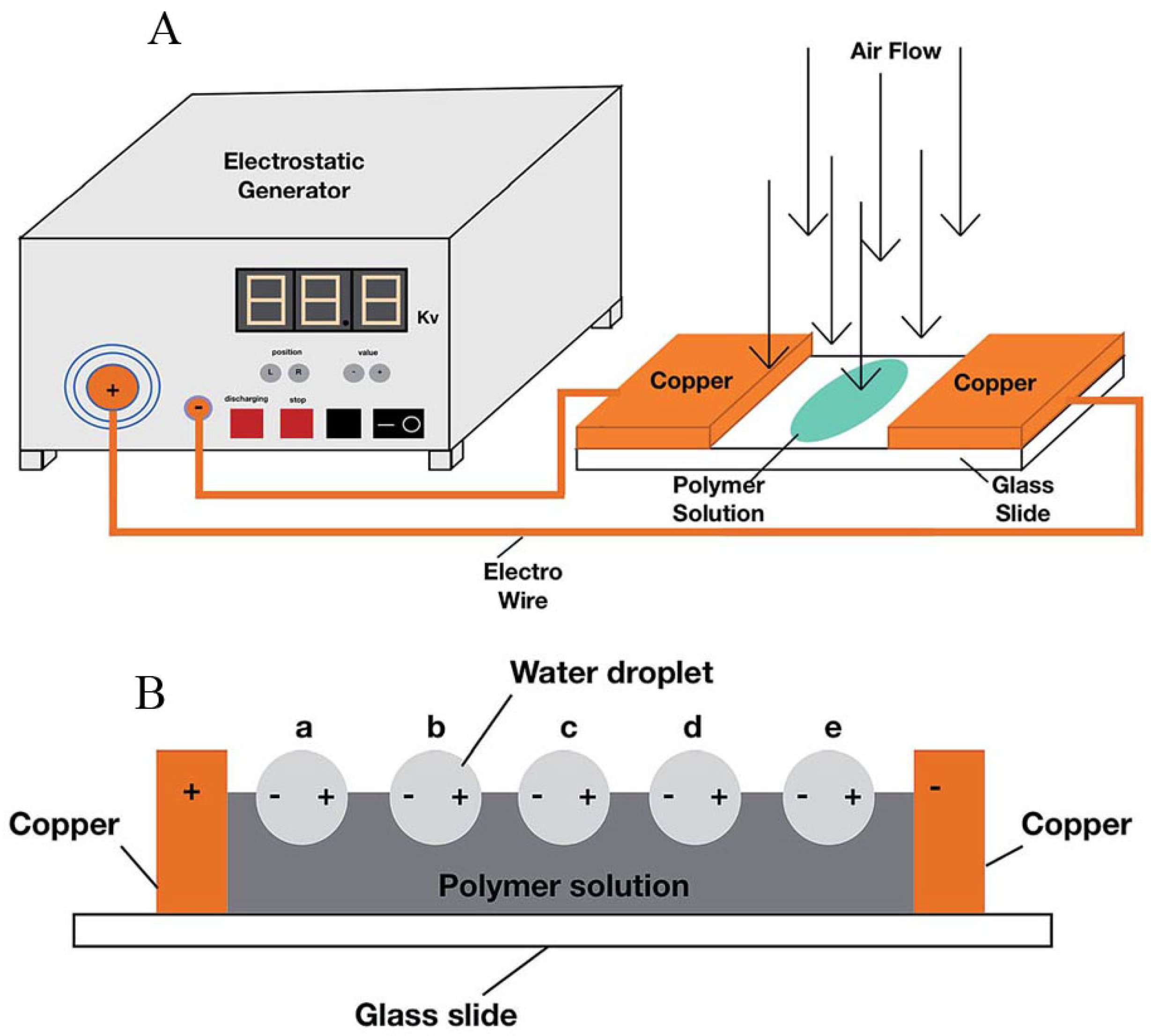
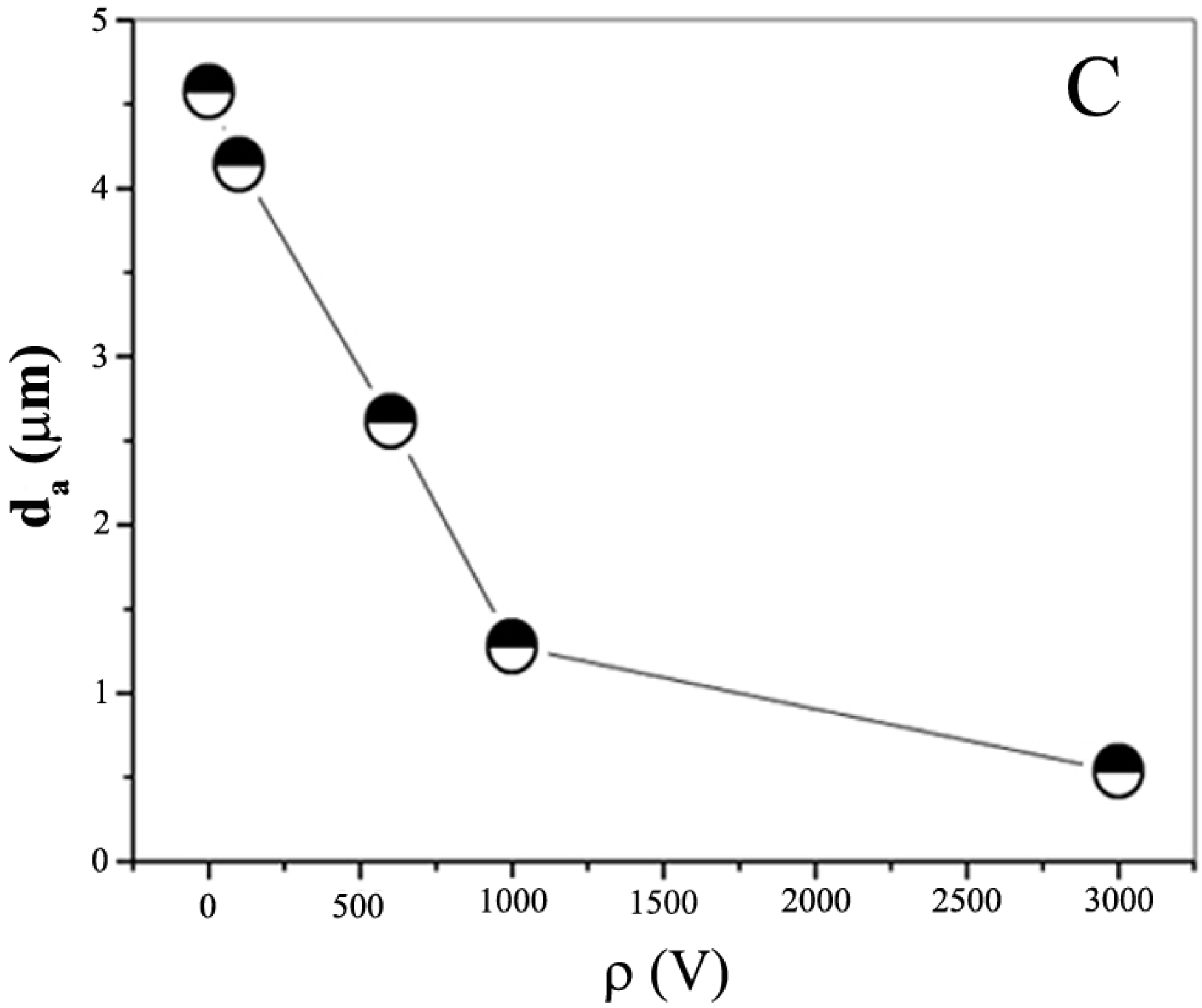
3. Organic-Inorganic Hybrids as Building Units to Form Honeycomb Films
3.1. Surfactant Modified Nanoparticles
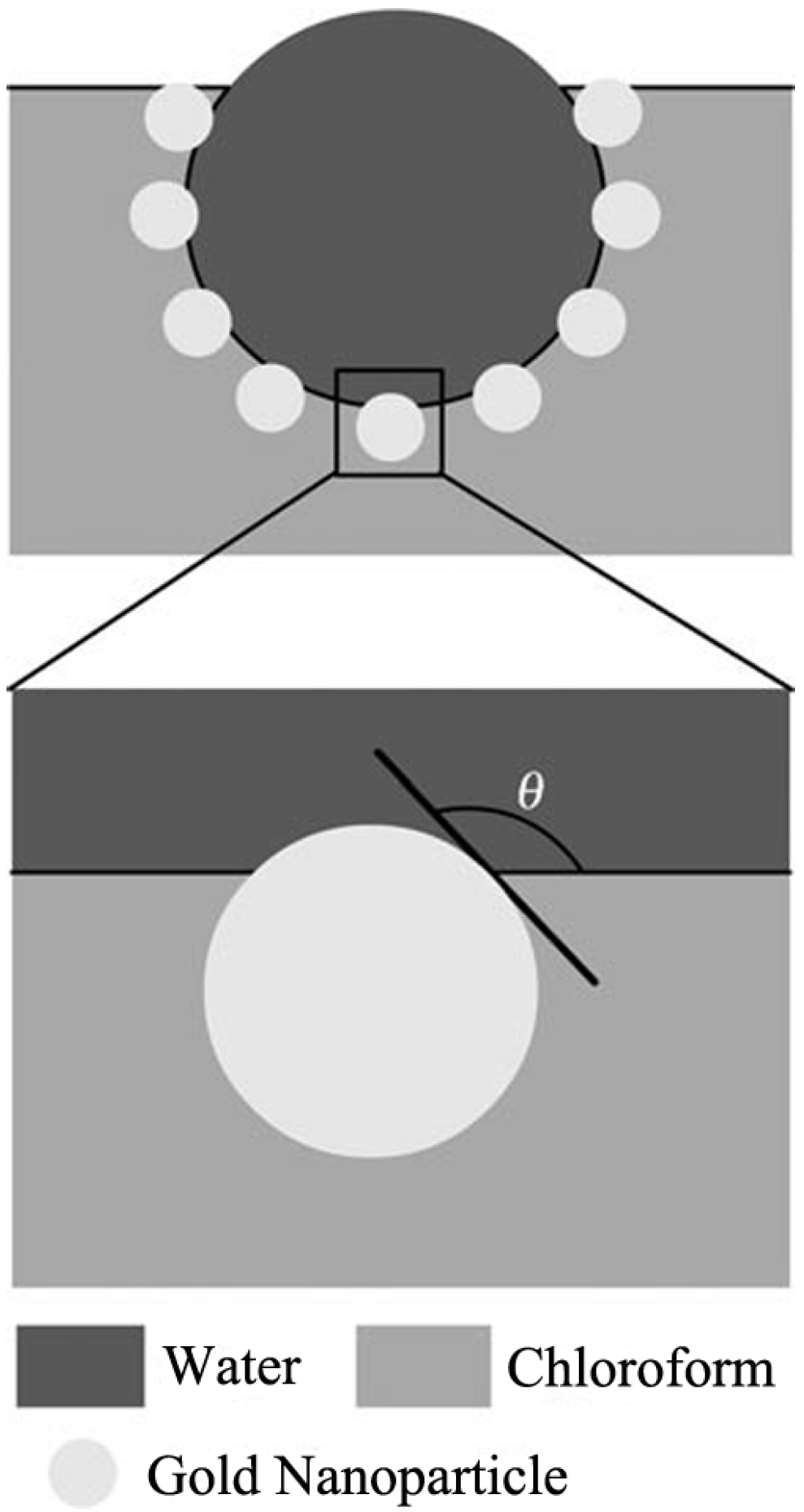

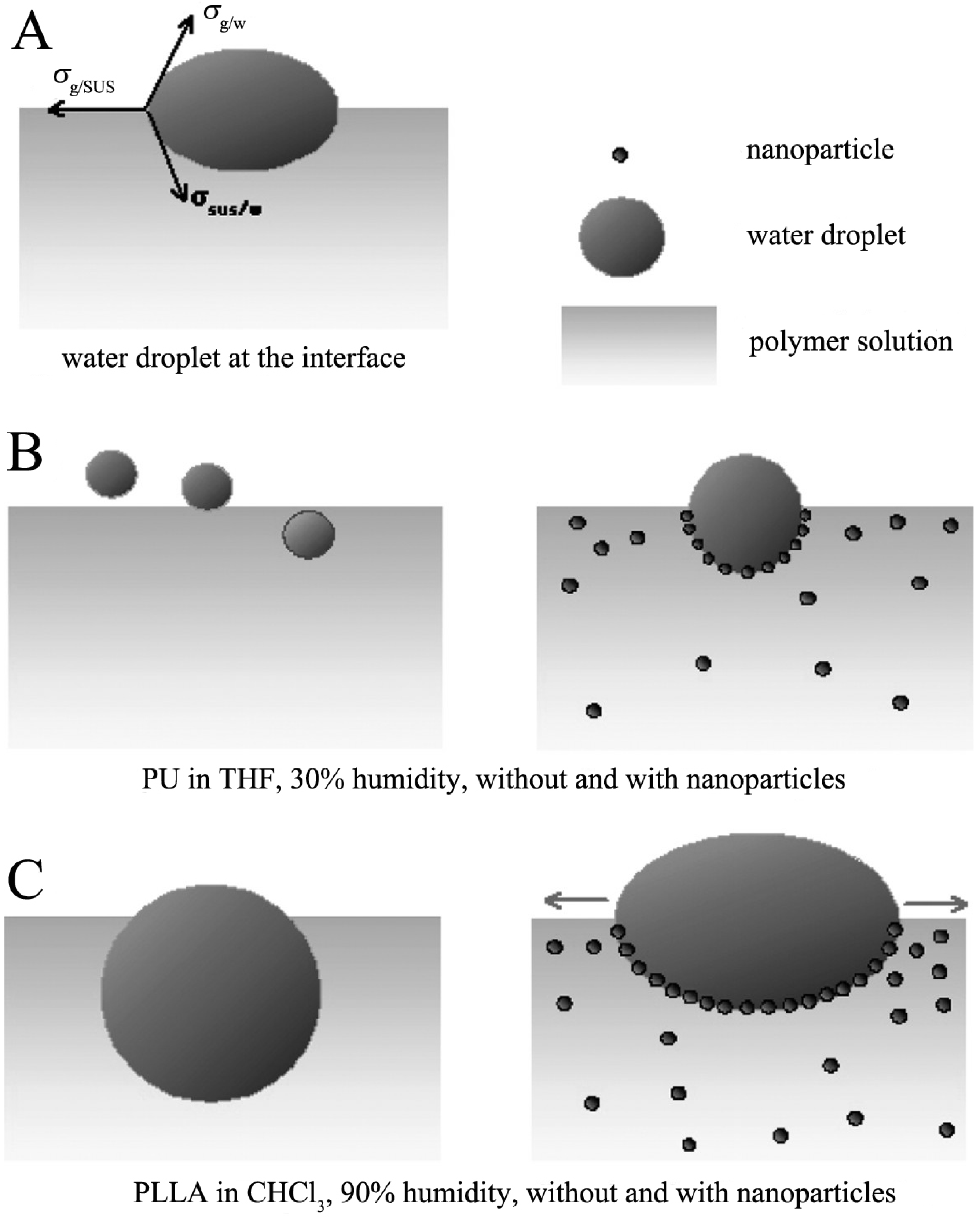
3.2. Surfactant Modified POMs

3.3. Modified QDs
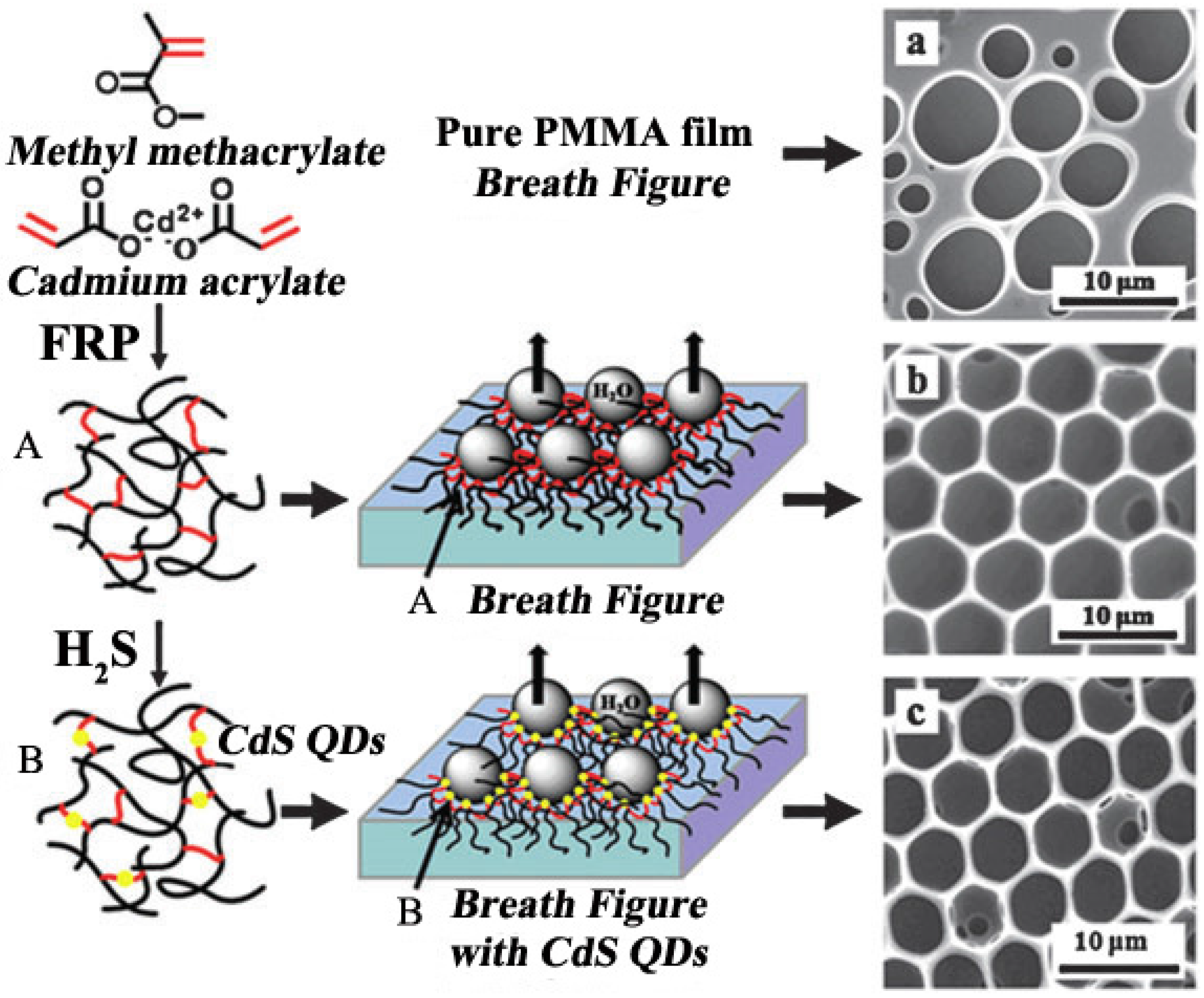
3.4. Applications of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Honeycomb Films

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varcoe, J.R.; Atanassov, P.; Dekel, D.R.; Herring, A.M.; Hickner, M.A.; Kohl, P.A.; Kucernak, A.R.; Mustain, W.E.; Nijmeijer, K.; Scott, K.; et al. Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3135–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, Z. Optimizing the performance of a membrane bio-electrochemical reactor using an anion exchange membrane for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2015, 1, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarale, R.K.; Gohil, G.S.; Shahi, V.K. Recent developments on ion-exchange membranes and electro-membrane processes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 119, 97–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: State of their development and perspective. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 263, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgort, M.G.; Hermann, M.G.; Erali, M.; Durtschi, J.D.; Voelkerding, K.V.; Smith, R.E. Extraction and amplification of genomic DNA for human blood on nanoporous aluminum oxide membranes. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1817–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sircar, S.; Rao, M.B. Nanoporous carbon membranes for separation of gas mixtures by selective surface flow. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 85, 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sircar, S.; Rao, M.B. Performance and pore characterization of nanoporous carbon membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 110, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Y.; Ryu, I.; Kim, H.Y.; Jang, S.K.; Russell, T.P. Nanoporous membranes with ultrahigh selectivity and flux for the filtration of viruses. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.C.; Choi, Y.; Horne, L.P.; Baker, L.A.; Siwy, Z.S.; Martin, C.R. Resistive-pulse DNA detection with a conical nanopore sensor. Langmuir 2006, 22, 10837–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fologea, D.; Gershow, M.; Ledden, B.; McNabb, D.S.; Golovchenko, J.A.; Li, J. Detecting single stranded DNA with a solid state nanoproe. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1905–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Felipe, A. Liquid crystal polymers and ionomers for membrane applications. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 1607–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Engel, J.; Liu, C. Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) for MEMS: Processes and applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2003, 13, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broer, D.J.; Bastiaansen, C.M.W.; Debije, M.G.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Functional organic materials based on polymerized liquid-crystal monomers: Supramolecular hydrogen-bonded systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7102–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenning, A.P.H.J.; Gonzalez-Lemus, Y.C.; Shishmanova, I.K.; Broer, D.J. Nanoporous membranes based on liquid crystalline polymers. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, D.Y.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.J.; Hong, S.; Yoon, S.S. Antibacterial and water purification activities of self-assembled honeycomb structure of aerosol deposited titania film. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12510–12518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, K.; Shang, F.; Zhang, X.; Guo, S.; Tan, Y. The biocompatible and anti-bacterial effect of the poly(L-lactic acid) film with regularly impregnated Ag nanoparticles. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 17, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, D.; Wong, K.H.; Williams, C.; Poole-Warren, L.A.; Davis, T.P.; Barner-Kowollik, C.; Stenzel, M.H. Honeycomb-structured porous films from polypyrrole-containing block copolymers prepared via RAFT polymerization as a scaffold for cell growth. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, J.B.; Davidson, M.G.; Ellis, M.J.; Jones, M.D.; Wu, X. Fabrication of honeycomb-structured poly(DL-lactide) and poly [(DL-lactide)-co-glycolide] films and their use as scaffolds for osteoblast-like cell culture. Macromol. Symp. 2008, 272, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunami, H.; Ito, E.; Tanaka, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Shimomura, M. Effect of honeycomb film on protein adsorption, cell adhesion and proliferation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 284–285, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Aso, Y.; Furuse, M.; Noishiki, Y.; Miyata, T. A honeycomb collagen carrier for cell culture as a tissue engineering scaffold. Artif. Organs 2001, 25, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisco, M.; Quero, G.; Iadicicco, A.; Giordano, M.; Galeotti, F.; Cusano, A. Lab on fiber by using the breath figure technique. In Lab-on-Fiber Technology; Cusano, A., Consales, M., Crescitelli, A., Ricciardi, A., Eds.; Springer Series in Surface Sciences: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 56, pp. 233–250. [Google Scholar]
- Bormashenko, E.; Pogreb, R.; Bormashenko, Y.; Aharoni, H.; Shulzinger, E.; Grinev, R.; Rozenman, D.; Rozenman, Z. Progress in low voltage reversible electrowetting with lubricated polymer honeycomb substrates. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32491–32496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Balter, S.; Bormashenko, Y.; Aurbach, D. Honeycomb structures obtained with breath figures self-assembly allow water/oil separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 415, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, K.M.; Wycisk, R.; Pintauro, P.N.; Mather, P.T. Nanofiber network ion-exchange membranes. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 4569–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Building from the bottom up. Materialstoday 2003, 6, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.S.; Lichtenegger, H.C.; Stucky, G.D.; McFarland, E.W. Electrochemical synthesis of nanostructured ZnO films utilizing self-assembly of surfactant molecules at solid-liquid interfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12402–12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capito, R.M.; Azevedo, H.S.; Velichko, Y.S.; Mata, A.; Stupp, S. Self-assembly of large and small molecules into hierarchically ordered sacs and membranes. Science 2008, 319, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Hong, K.; Guiochon, G.A.; Mays, J.W.; Dai, S. Synthesis of a large-scale highly ordered porous carbon film by self-assembly of block copolymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5785–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, A.; Claus, R. Molecular self-assembly of TiO2/polymer nanocomposite films. J. Phys. Chem. 1997, 101, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, Y.F.; Cronin, L.; Liu, T. Self-assembly of organic-inorganic hybrid amphiphilic surfactants with large polyoxometalates as polar head groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14408–14409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govor, L.V.; Parisi, J. Honeycomb carbon networks: Preparation, structure, and transpor. In Self-organized Morphology in Nanostructured Materials, 6th ed.; Al-Shamery, K., Parisi, J., Eds.; Springer: Verlag Berlin, Germany; GmbH & Co. K: Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 99, pp. 115–153. [Google Scholar]
- Couck, S.; Denayer, J.F.M.; Baron, G.V.; Remy, T.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. An amine-functionalized MIL-53 metal-organic framework with large separation power for CO2 and CH4. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6326–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lim, C.; Hong, S. Gas permeation properties of organic-inorganic hybrid membranes prepared from hydroxyl-terminated polyether and 3-isocyanatopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Sol. Gel. Sci. Technol. 2005, 36, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Hao, J. Ordered patterns and structures via interfacial self-assembly: Superlattices, honeycomb structures and coffee rings. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5457–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunz, U.H.F. Breath figures as a dynamic templating method for polymers and nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, M.H.; Barner-Kowollik, C.; Davis, T.P. Formation of honeycomb-structured, porous films via breath figures with different polymer architectures. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 2363–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, M.L.K.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of porous materials with ordered hole structure. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 121, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, W.; Li, H.; Sun, H.; Yin, S.; Wu, L. Polyoxometalate-based vesicle and its honeycomb architectures on solid surfaces. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8016–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitkek, J. Breath figures. Nature 1911, 86, 516–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L. Breath figures. Nature 1911, 86, 416–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L. Breath figures. Nature 1912, 90, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widawski, G.; Rawiso, M.; François, B. Self-organized honeycomb morphology of star-polymer polystyrene films. Nature 1994, 369, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitois, O.; François, B. Crystallization of condensation droplets on a liquid surface. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1999, 277, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitois, O.; François, B. Formation of ordered micro-porous membranes. Eur. Phys. J. B 1999, 8, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, M.H. Formation of regular honeycomb-patterned porous film by self-organization. Aust. J. Chem. 2002, 55, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasarao, M.; Collings, D.; Philips, A.; Patel, S. Three-dimensionally ordered array of air bubbles in apolymer film. Science 2001, 292, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, A.; Mercogliano, C.; Yunus, S.; Civardi, M.; Comoretto, D.; Turturro, A. Self-organization of polystyrenes into ordered microstructured films and their replication by soft lithography. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.; Malkin, A.; Musin, A.; Bormashenko, Y.; Whyman, G.; Litvak, N.; Barkay, Z.; Machavariani, V. Mesoscopic patterning in evaporated polymer solutions: Poly(ethylene glycol) and room-temperature-vulcanized polyorganosilanes/-siloxanes promote formation of honeycomb structures. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2008, 209, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, J.E.; Goh, G.T.W.; Huang, S.; Reithofer, M.R.; Thong, A.Z.; Chin, J.M. Non-close-packed breath figures via ion-partitioning-mediated self- assembly. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6688–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scriven, L.E.; Sternling, C.V. The Marangoni effects. Nature 1960, 187, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, N.; Koito, T.; Nishida, J.; Sawadaishi, T.; Cieren, X.; Ijiro, K.; Karthaus, O.; Shimomura, M. Mesoscopic patterns of molecular aggregates on solid substrates. Thin Solid Films 1998, 327–329, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, B. The influencing factors on the macroporous formation in polymer films by water droplet templating. Polymer 2004, 45, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y. Robust organic/inorganic hybrid porous thin films via breath-figure method and gelation process. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 2024–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, D.; Mai, Y.; He, L.; Jin, C. Honeycomb-structured microporous films made from hyperbranched polymers by the breath figure method. Langmuir 2009, 25, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Zang, D.; Shang, B.; Qiang, X.; Hong, Q.; Guan, X. Morphology and wettability control of honeycomb porous films of amphiphilic fluorinated pentablock copolymers via breath figure method. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 49655–49662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Yan, J.; Ma, H.; Fang, Y.; Hao, J. Dimensional architecture of ferrocenyl-based oligomer honeycomb-patterned films: From monolayer to multilayer. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9052–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Ma, H.; Yan, J.; Fang, Y.; Hao, J. Tunable morphology of 2D honeycomb-patterned films and the hydrophobicity of a ferrocenyl-based oligomer. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 7674–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabu, H.; Takebayashi, M.; Tanaka, M.; Shimomura, M. Superhydrophobic and lipophobic properties of self-organized honeycomb and pincushion structures. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3235–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamei, J.; Saito, Y.; Yabu, H. Biomimetic ultra-bubble-repellent surfaces based on a self-organized honeycomb film. Langmuir 2014, 30, 14118–14122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabu, H.; Shimomura, M. Mesoscale pincushions, microrings, and microdots prepared by heating and peeling of self-organized honeycomb-patterned films deposited on a solid substrate. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4992–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabu, H.; Hirai, Y.; Shimomura, M. Electroless plating of honeycomb and pincushion polymer films prepared by self-organization. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9760–9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, Y.; Yabu, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Ijiro, K.; Shimomura, M. Arrays of triangular shaped pincushions for SERS substrates prepared by using self-organization and vapor deposition. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2298–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Kawano, T.; Shimomura, M.; Yabu, H. Fabrication of mussel-inspired highly adhesive honeycomb films containing catechol groups and their applications for substrate-independent porous templates. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gao, C.; Yan, D. Honeycomb-patterned photoluminescent films fabricated by self-Assembly of hyperbranched polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4128–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escalé, P.; Rubatat, L.; Billon, L.; Save, M. Recent advances in honeycomb-structured porous polymer films prepared via breath figures. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1001–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, D.; Malmström, E.; Hult, A.; Blakey, I.; Boyer, C.; Davis, T.P.; Whittaker, M.R. Biomimetic surface modification of honeycomb films via a “Grafting From” approach. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12748–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, W.; Wu, L. Honeycomb-patterned films fabricated by self-organization of DNA-surfactant complexes. Langmuir 2009, 25, 10466–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabu, H.; Shimomura, M. Single-step fabrication of transparent superhydrophobic porous polymer films. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5231–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabu, H.; Hirai, Y.; Kojima, M.; Shimomura, M. Structured films containing thermoresponsive polymers and their surface wettability. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 1787–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Hirai, Y.; Yabu, H.; Shimomura, M. Photo-patterning of honeycomb films prepared from amphiphilic copolymer containing photochromic spiropyran. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3970–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, T.; Hirai, Y.; Kojima, M.; Yabu, H.; Shimomura, M. Patterned metallic honeycomb films prepared by photo-patterning and electroless plating. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6741–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, Y.; Hirai, Y.; Yabu, H.; Shimomura, M. Fabrication of patterned and anisotropic porous films based on photo-cross-linking of poly(1,2-butadiene) honeycomb films. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3884–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, T.; Nakamichi, Y.; Fujinami, S.; Nakajima, N.; Yabu, H.; Shimomura, M. Mechanical regulation of cellular adhesion onto honeycomb-patterned porous scaffolds by altering the elasticity of material surfaces. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabu, H.; Nakamichi, Y.; Hirai, Y.; Shimomura, M. Robust anisotropic polymer meshes prepared by stretching and photo-crosslinking of poly(1,2-butadiene) honeycomb films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4877–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabu, H.; Akagi, K.; Shimomura, M. Micropatterning of liquid crystalline polyacetylene derivative by using self-organization processes. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Xu, Y. A study on formation of regular honeycomb pattern in polysulfone film. Polymer 2005, 46, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Ohga, K.; Maki, T.; Teramoto, M. The effect of polymer molecular weight on the structure of a honeycomb patterned thin film prepared by solvent evaporation. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2004, 37, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, E.; Pogreb, R.; Stanevsky, O.; Bormashenko, Y.; Gendelman, O. Formation of honeycomb patterns in evaporated polymer solutions: Influence of the molecular weight. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3553–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Kim, J.K. Breath figure patterns prepared by spin coating in a dry environment. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5347–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.S.; Joo, W.; Kim, J.K. Porous structures of polymer films prepared by spin coating with mixed solvents under humid condition. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4594–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, E.; Fabbri, P.; Pilati, F. Solvent and substrate contributions to the formation of breath figure patterns in polystyrene films. Langmuir 2011, 27, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.X.; Tian, Y.; Shi, Y.Q.; Tang, R.P.; Xi, F. Porous polymer films and honeycomb structures based on amphiphilic dendronized block copolymers. Langmuir 2005, 21, 6576–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Sheng, R.; Luo, T.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Sun, W.; Cao, A. Honeycomb-structured films by multifunctional amphiphilic biodegradable copolymers: Surface morphology control and biomedical application as scaffolds for cell growth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.; Pogreb, R.; Stanevsky, O.; Bormashenko, Y.; Stein, T.; Gengelman, O. Mesoscopic patterning in evaporated polymer solutions: New experimental data and physical mechanisms. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9604–9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Zang, D.; Hong, Q.; Guan, X. Honeycomb porous films of pentablock copolymer on liquid substrates via breath figure method and their hydrophobic properties with static and dynamic behavior. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 21084–21089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Li, Z.; Yuan, H.; Peng, Q.; Chi, M.; Yang, S.; Yang, R.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Tang, J. Fabrication of highly ordered porous membranes of cellulose triacetate on ice substrates using breath figure method. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Ookura, R.; Nishida, J.; Arai, K.; Hayashi, J.; Kurono, N.; Sawadaishi, T.; Hara, M.; Shimomura, M. Fabrication of honeycomb film of an amphiphilic copolymer at the air-water interface. Langmuir 2002, 18, 5734–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, A.Z.; Lim, D.S.W.; Ahsan, A.; Goh, G.T.W.; Xu, J.; Chin, J.M. Non-close-packed pore arrays through one-step breath figure self-assembly and reversal. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan, M.J.; Campbell, P.A. Breath-figure polymer films with local microporosity controlled via spatio-thermal templating. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2008, 2008, 2514–2517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Birnie, D.P., III; Zeilinski, B.J.; Perry, D.L. Infrared observation of evaporative cooling during spin-coating processes. Opt. Eng. 1995, 34, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, J.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y.; Fu, J.; Cong, Y.; Xue, L.; Han, Y. Ordered honeycomb-structured gold nanoparticle films with changeable pore morphology: From circle to ellipse. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S. Integration of photo-crosslinking and breath figures to fabricate biodegradable polymer substrates with tunable pores that regulate cellular behavior. Polymer 2014, 55, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Ye, J.; Wang, N.; Jiang, L.; Shen, Q. Fabrication of porous film with controlled pore size and wettability by electric breath figure method. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 7168–7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Hu, E.; Zhi, Y.; Shen, Q. Fabrication of highly ordered porous superhydrophobic polystyrene films by electric breath figure and surface chemical modification. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 469, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D.H.; Bai, W.B.; Hu, B.H.; Xu, Y.L.; Lin, J.H. Preparation of urushiol-titanium chelate polymer/multiwall carbon nanotubes composite honeycomb films with chemical resistance by breath figures. Polym. Compos. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Cui, J.; Chen, J.; Hao, J. Self-organized polymer nanocomposite inverse opal films with combined optical properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Hao, J. Evaporation-induced ordered honeycomb structures of gold nanoparticles at the air/water interface. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Z.; Gu, N. Interfacial effects of in situ-synthesized Ag nanoparticles on breath figures. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasricha, R.; Swami, A.; Sastry, M. Transmetalation reaction between hydrophobic silver nanoparticles and aqueous chloroaurate ions at the air-water interface. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 19620–19626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Shimomura, M.; Yabu, H. Dispersion of Al2O3 nanoparticles stabilized with mussel-inspired amphiphilic copolymers in organic solvents and formation of hierarchical porous films by the breath figure technique. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6081–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Shimomura, M.; Yabu, H. Breath figures of nanoscale bricks: A universal method for creating hierarchic porous materials from inorganic nanoparticles stabilized with mussel-inspired copolymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Wu, L. Polyoxometalate/polymer hybridmaterials: Fabrication and properties. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proust, A.; Thouvenot, R.; Gouzerh, P. Functionalization of polyoxometalates: Towards advanced applications in catalysis and materials science. Chem. Commun. 2008, 1837, 1837–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; You, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, E.; Huang, C. A new polyoxometalate-templated Mo/V-oxide-based organic–inorganic hybrid framework with a honeycomb-like structure. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2721, 2721–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, H.; Bu, W.; Xu, M.; Wu, L. Self-organized microporous structures based on surfactant-encapsulated polyoxometalate complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 24847–24854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, W.; Wollenberg, L.; Li, B.; Wu, L.; Li, F.; Xu, L. Self-organized honeycomb structures of Mn12 single-molecule magnets. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 14674–14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.; Jia, X.; Tang, P.; Hao, J.; Liu, T. Self-patterning of hydrophobic materials into highly ordered honeycomb nanostructures at the air/water interface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 3342–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Hao, J. Formation mechanism and morphology modulation of honeycomb hybrid films made of polyoxometalates/surfactants at the air/water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 333, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Hao, J. Macroporous honeycomb films of surfactant-encapsulated polyoxometalates at air/water interface and their electrochemical properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 161, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Hao, J. Photoluminescent honeycomb films templated by microwater droplets. Langmuir 2010, 26, 3843–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Jia, X.; Fan, D.; Wang, L.; Hao, J. Surface charges of hedgehog-shaped polyoxomolybdate modified by a cationic surfactant and the inorganic/organic complex. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 312, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, H.; Chen, S. Quantum-dot-embedded ionomer-derived films with ordered honeycomb structures via breath figures. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7376–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeotti, F.; Mróz, W.; Bolognesi, A. CdTe nanocrystal assemblies guided by breath figure templates. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3832–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böker, A; Lin, Y.; Chiapperini, K.; Horowitz, R.; Thompson, M.; Carreon, V.; Xu, T.; Abetz, C.; Skaff, H.; Dinsmore, A.D.; et al. Hierarchical nanoparticle assemblies formed by decorating breath figures. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 302–306. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; Hao, J. Directionally electrodeposited gold nanoparticles into honeycomb macropores and their Surface-Enhanced Raman scattering. New J. Chem. 2010, 34, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Hao, J. Porphyrin-based honeycomb films and their antibacterial activity. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6419–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shang, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Nanostructured 2D diporphyrin honeycomb film: Photoelectrochemistry, photodegradation, and antibacterial activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11783–11791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Men, X.; Sun, H.; She, P.; Zhang, W.; Wu, C.; Qin, W.; Chen, X. Enhanced photocurrent generation of bio-inspired graphene/ZnO composite films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12016–12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Lv, C.; Yu, W.; Mao, Z.; Wan, L.; Xu, Z. Fabrication of perforated isoporous membranes via a transfer-free strategy: Enabling high-resolution separation of cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22400–22407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Lee, C.; Kim, B.; Kwak, C.; Yoon, J.; Jeong, H.; Lee, J. Honeycomb-like periodic porous LaFeO3 thin film chemiresistors with enhanced gas-sensing performances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16217–16226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Wan, L.; Xu, Z. In-situ immobilization of silver nanoparticles on self-assembled honeycomb-patterned films enables Surface-Enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 11478–11484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dou, Y.; Jin, M.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L. Breath Figure Method for Construction of Honeycomb Films. Membranes 2015, 5, 399-424. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5030399
Dou Y, Jin M, Zhou G, Shui L. Breath Figure Method for Construction of Honeycomb Films. Membranes. 2015; 5(3):399-424. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5030399
Chicago/Turabian StyleDou, Yingying, Mingliang Jin, Guofu Zhou, and Lingling Shui. 2015. "Breath Figure Method for Construction of Honeycomb Films" Membranes 5, no. 3: 399-424. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5030399
APA StyleDou, Y., Jin, M., Zhou, G., & Shui, L. (2015). Breath Figure Method for Construction of Honeycomb Films. Membranes, 5(3), 399-424. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5030399





