Revisiting the Endocytosis of the M2 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Fluorescent Fusion Proteins of M2 Receptor Undergo Agonist-Stimulated Endocytosis
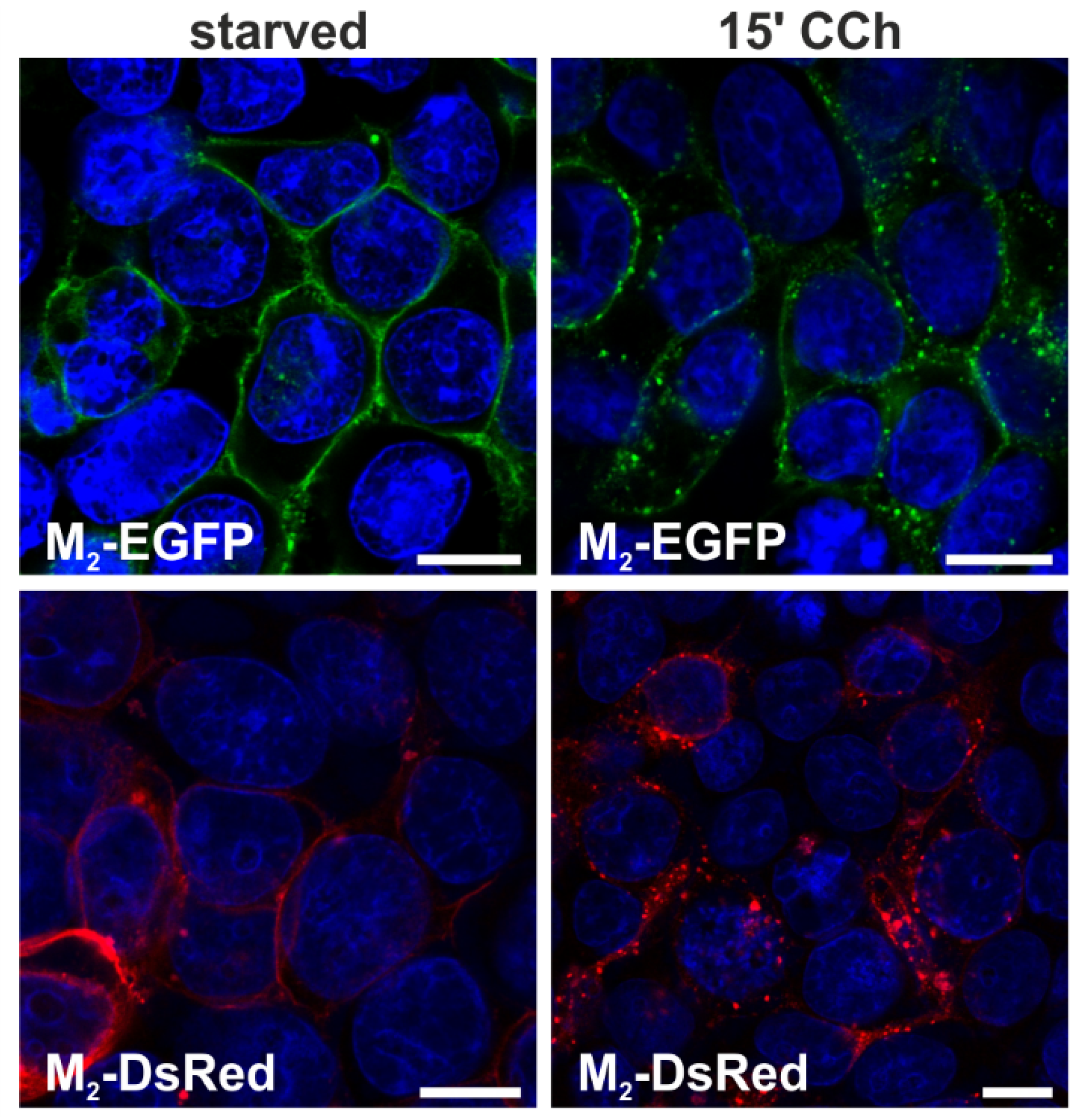
2.1.2. Knockdown of Clathrin Heavy Chain Impairs M2 Endocytosis

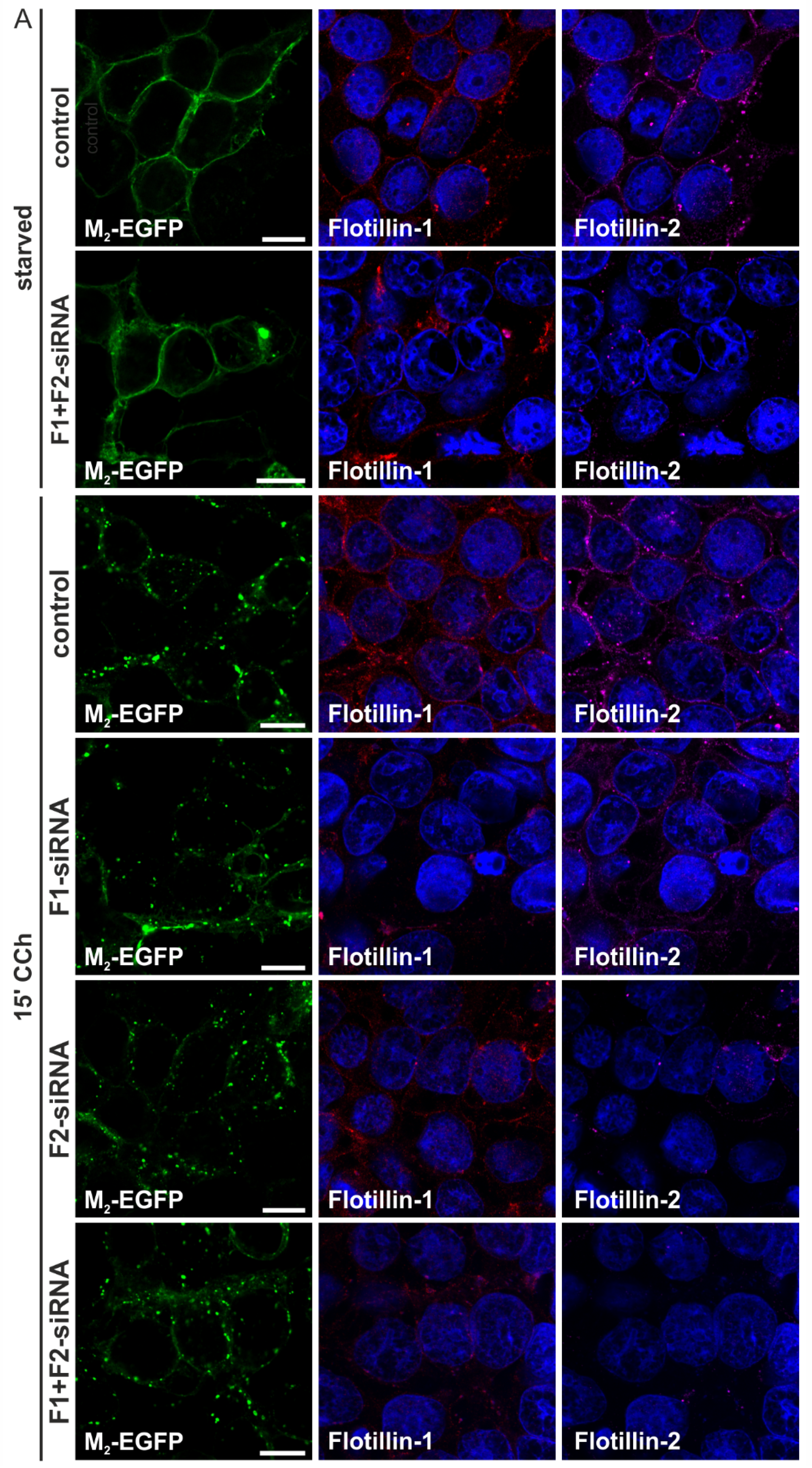
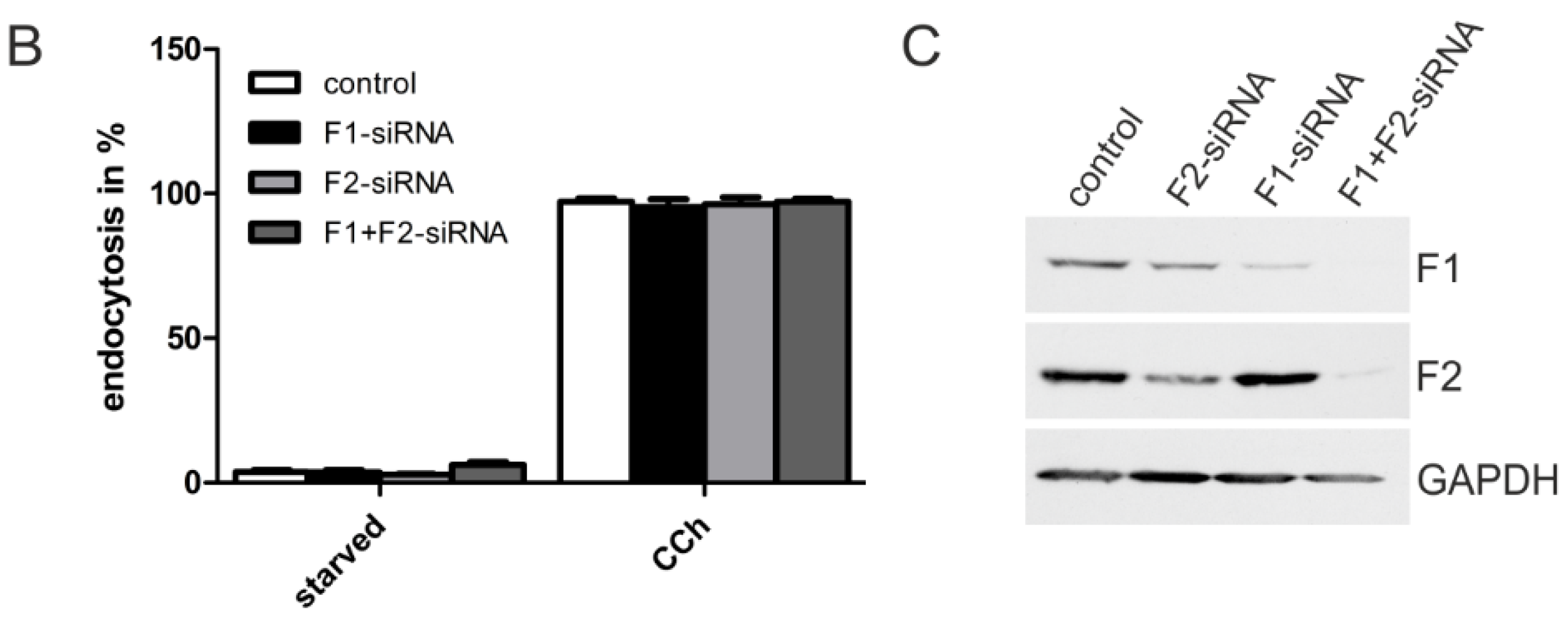
2.1.3. M2 Endocytosis Is Independent of Flotillins
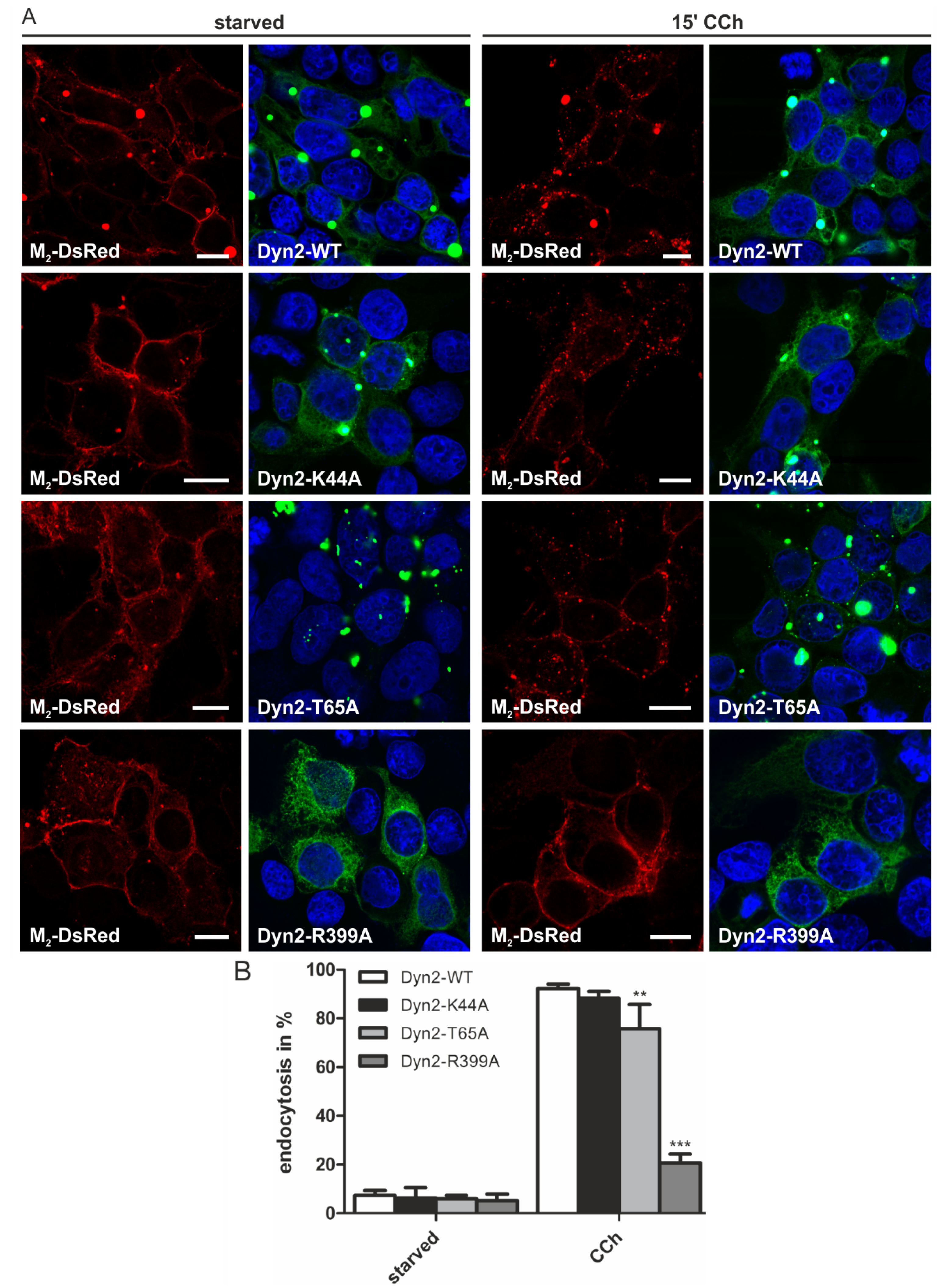
2.1.4. Dynamin-2 Mutants and Inhibitors Display Different Effects on M2 Endocytosis
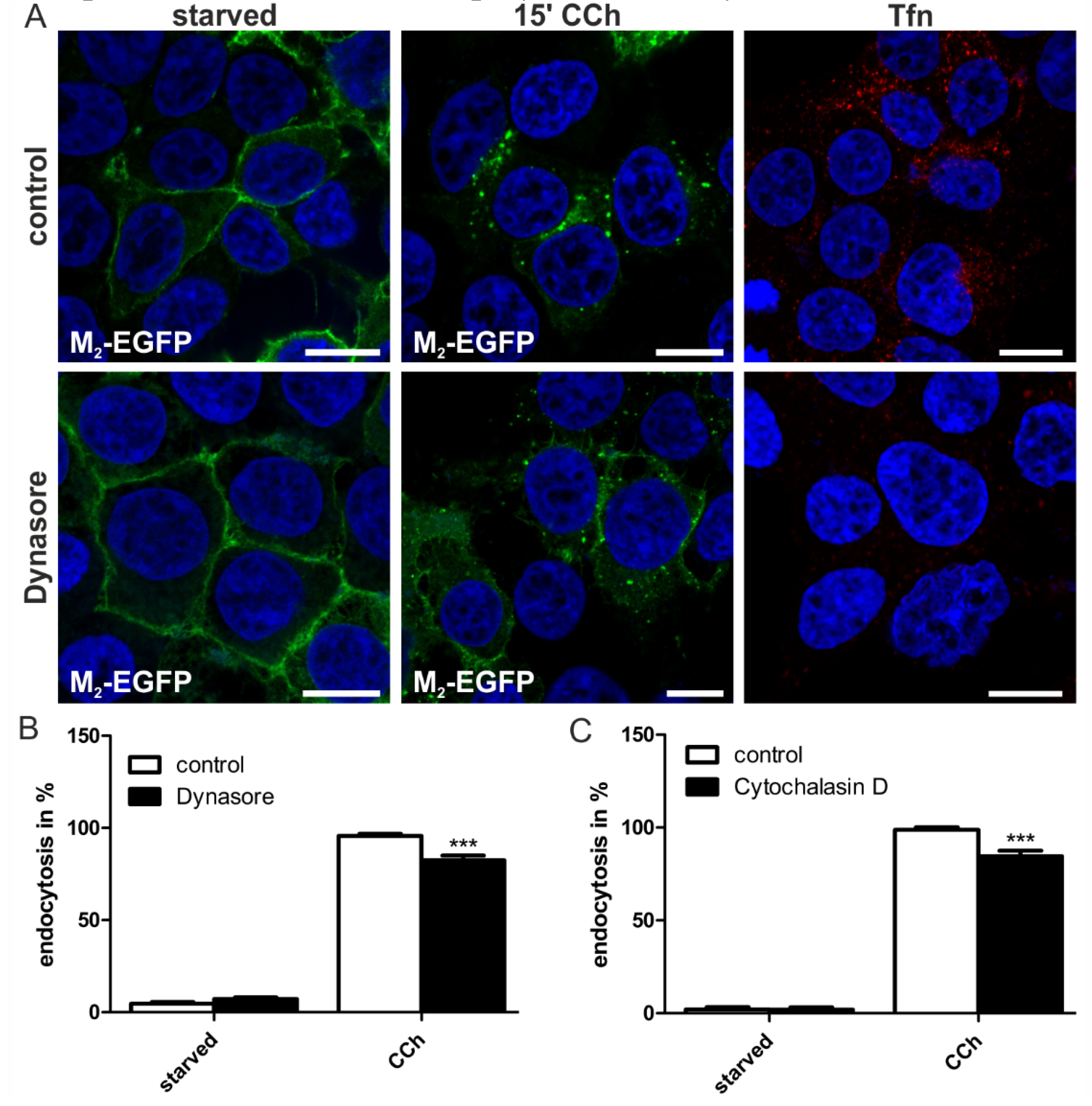
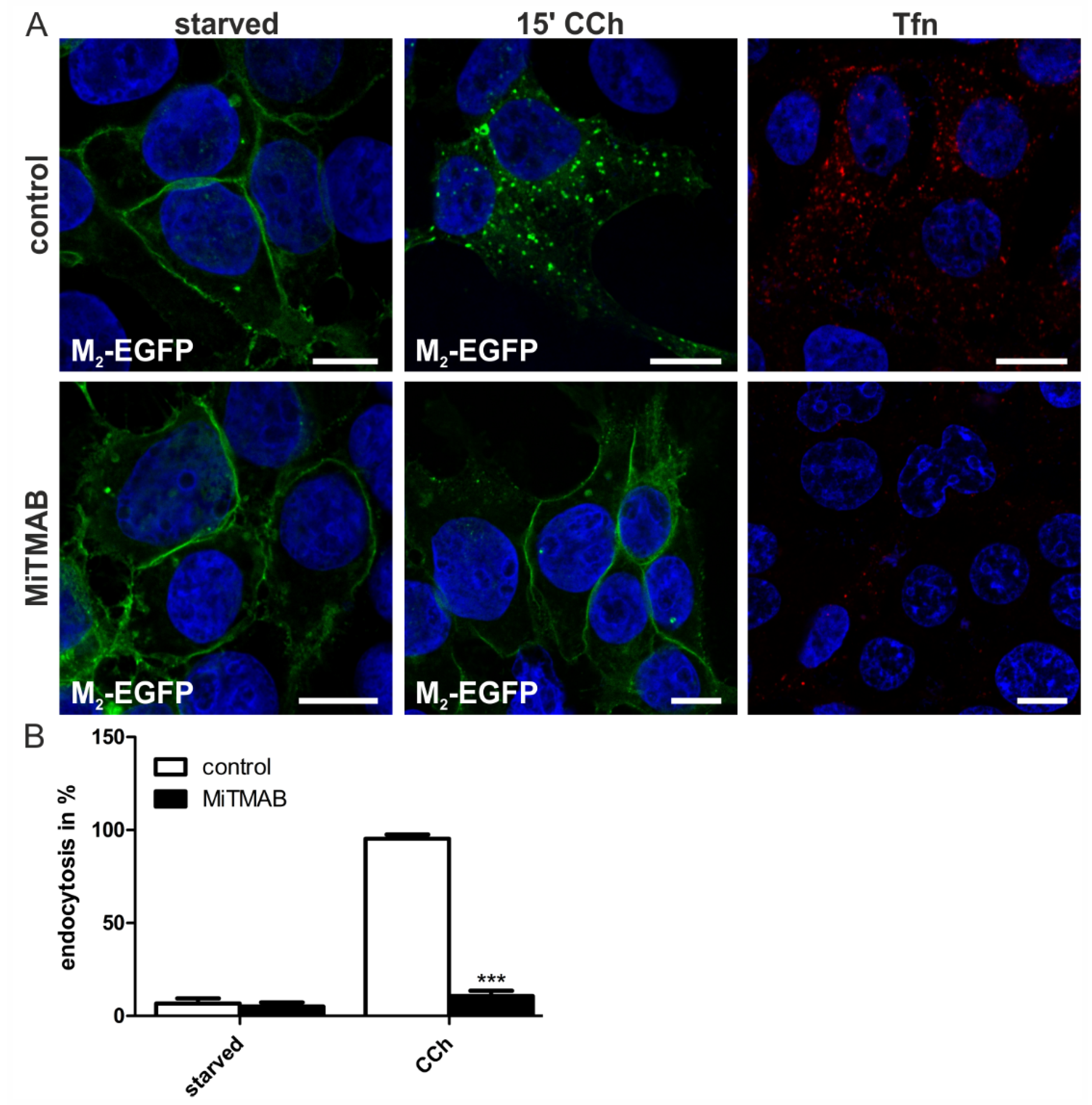
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture, Transfection and siRNA Knockdown
3.2. Constructs and Plasmid Cloning
3.3. Antibodies
3.4. Immunofluorescence
3.5. Inhibitor Treatment
3.6. Cell Lysis, Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blot
3.7. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ockenga, W.; Kühne, S.; Bocksberger, S.; Banning, A.; Tikkanen, R. Non-neuronal functions of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Genes 2013, 4, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roseberry, A.G.; Hosey, M.M. Trafficking of M(2) muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33671–33676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thangaraju, A.; Sawyer, G.W. Comparison of the kinetics and extent of muscarinic M1-M5 receptor internalization, recycling and downregulation in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogler, O.; Bogatkewitsch, G.S.; Wriske, C.; Krummenerl, P.; Jakobs, K.H.; van Koppen, C.J. Receptor subtype-specific regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor sequestration by dynamin. Distinct sequestration of M2 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12155–12160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuga, H.; Kameyama, K.; Haga, T.; Honma, T.; Lameh, J.; Sadee, W. Internalization and down-regulation of human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 subtypes. Role of third intracellular M2 loop and G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5323–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogler, O.; Nolte, B.; Voss, M.; Schmidt, M.; Jakobs, K.H.; van Koppen, C.J. Regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor sequestration and function by beta-arrestin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 12333–12338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucrot, E.; Ferreira, A.P.; Almeida-Souza, L.; Debard, S.; Vallis, Y.; Howard, G.; Bertot, L.; Sauvonnet, N.; McMahon, H.T. Endophilin marks and controls a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway. Nature 2015, 517, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, H.F.; Simunovic, M.; Lemiere, J.; Boucrot, E.; Garcia-Castillo, M.D.; Arumugam, S.; Chambon, V.; Lamaze, C.; Wunder, C.; Kenworthy, A.K.; et al. Endophilin-A2 functions in membrane scission in clathrin-independent endocytosis. Nature 2015, 517, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pals-Rylaarsdam, R.; Gurevich, V.V.; Lee, K.B.; Ptasienski, J.A.; Benovic, J.L.; Hosey, M.M. Internalization of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Arrestin-independent and -dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 23682–23689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pals-Rylaarsdam, R.; Hosey, M.M. Two homologous phosphorylation domains differentially contribute to desensitization and internalization of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 14152–14158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pals-Rylaarsdam, R.; Xu, Y.; Witt-Enderby, P.; Benovic, J.L.; Hosey, M.M. Desensitization and internalization of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor are directed by independent mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 29004–29011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlador, M.L.; Grubbs, R.D.; Nathanson, N.M. Multiple topological domains mediate subtype-specific internalization of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23295–23302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlador, M.L.; Nathanson, N.M. Synergistic regulation of M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor desensitization and sequestration by G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 and beta-arrestin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18882–18890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.B.; Pals-Rylaarsdam, R.; Benovic, J.L.; Hosey, M.M. Arrestin-independent internalization of the M1, M3, and M4 subtypes of muscarinic cholinergic receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12967–12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.T.; Echeverry, M.; Mosser, V.A.; Gates, A.; Jackson, D.A. Agonist mediated internalization of M2 mAChR is beta-arrestin-dependent. J. Mol. Signal. 2006, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, K.A.; Murph, M.M.; Brown, L.M.; Radhakrishna, H. Transfer of M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors to clathrin-derived early endosomes following clathrin-independent endocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33439–33446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houndolo, T.; Boulay, P.L.; Claing, A. G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis in ADP-ribosylation factor 6-depleted cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5598–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, C.; Nathanson, N.M. The internalization of the M2 and M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors involves distinct subsets of small G-proteins. Life Sci. 2008, 82, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseberry, A.G.; Hosey, M.M. Internalization of the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor proceeds through an atypical pathway in HEK293 cells that is independent of clathrin and caveolae. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Achiriloaie, M.; Barylko, B.; Albanesi, J.P. Essential role of the dynamin pleckstrin homology domain in receptor-mediated endocytosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herskovits, J.S.; Burgess, C.C.; Obar, R.A.; Vallee, R.B. Effects of mutant rat dynamin on endocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werbonat, Y.; Kleutges, N.; Jakobs, K.H.; van Koppen, C.J. Essential role of dynamin in internalization of M2 muscarinic acetylcholine and angiotensin AT1A receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21969–21974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, C.L.; McCullar, J.S.; Kow, R.L.; Le, J.H.; Goodlett, D.R.; Nathanson, N.M. RACK1 associates with muscarinic receptors and regulates M2 receptor trafficking. PLoS One 2010, 5, e13517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.H.; Marks, M.S.; Brodsky, F.M. A dominant-negative clathrin mutant differentially affects trafficking of molecules with distinct sorting motifs in the class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) pathway. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 140, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseberry, A.G.; Bunemann, M.; Elavunkal, J.; Hosey, M.M. Agonist-dependent delivery of M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors to the cell surface after pertussis toxin treatment. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meister, M.; Tikkanen, R. Endocytic trafficking of membrane-bound cargo: A flotillin point of view. Membranes 2014, 4, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glebov, O.O.; Bright, N.A.; Nichols, B.J. Flotillin-1 defines a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway in mammalian cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanwick, C.C.; Shapiro, M.E.; Yi, Z.; Chang, K.; Wenthold, R.J. NMDA receptors interact with flotillin-1 and -2, lipid raft-associated proteins. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1226–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhne, S.; Ockenga, W.; Banning, A.; Tikkanen, R. Cholinergic Transactivation of the EGFR in HaCaT Keratinocytes Stimulates a Flotillin-1 Dependent MAPK-Mediated Transcriptional Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6447–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damke, H.; Baba, T.; Warnock, D.E.; Schmid, S.L. Induction of mutant dynamin specifically blocks endocytic coated vesicle formation. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 915–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, B.; Stowell, M.H.; Vallis, Y.; Mills, I.G.; Gibson, A.; Hopkins, C.R.; McMahon, H.T. GTPase activity of dynamin and resulting conformation change are essential for endocytosis. Nature 2001, 410, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, R.; Surka, M.; Chappie, J.S.; Fowler, D.M.; Foss, T.R.; Song, B.D.; Schmid, S.L. The dynamin middle domain is critical for tetramerization and higher-order self-assembly. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhausen, T.; Macia, E.; Pelish, H.E. Use of dynasore, the small molecule inhibitor of dynamin, in the regulation of endocytosis. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 438, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macia, E.; Ehrlich, M.; Massol, R.; Boucrot, E.; Brunner, C.; Kirchhausen, T. Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, A.; McGeachie, A.B.; Keating, D.J.; van Dam, E.M.; Rusak, J.; Chau, N.; Malladi, C.S.; Chen, C.; McCluskey, A.; Cousin, M.A.; et al. Myristyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and octadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide are surface-active small molecule dynamin inhibitors that block endocytosis mediated by dynamin I or dynamin II. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, R.J.; Shen, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Ferguson, S.M.; de Camilli, P. Dynamin triple knockout cells reveal off target effects of commonly used dynamin inhibitors. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5305–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.H.; Wong, M.L.; Craik, C.S.; Brodsky, F.M. Regulation of clathrin assembly and trimerization defined using recombinant triskelion hubs. Cell 1995, 83, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puthenveedu, M.A.; von Zastrow, M. Cargo regulates clathrin-coated pit dynamics. Cell 2006, 127, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, F.; Gaidarov, I.; Keen, J.H. G protein-coupled receptor/arrestin3 modulation of the endocytic machinery. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 156, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.A.; Green, F.A.; Enns, C.A. Saturation of the endocytic pathway for the transferrin receptor does not affect the endocytosis of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2116–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.A.; Green, F.A.; Stenberg, P.E.; Enns, C.A. Distinct saturable pathways for the endocytosis of different tyrosine motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 17056–17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, C.; Tosoni, D.; Comai, R.; Rabellino, A.; Segat, D.; Caneva, F.; Luzzi, P.; di Fiore, P.P.; Tacchetti, C. Relationships between EGFR signaling-competent and endocytosis-competent membrane microdomains. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 2704–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosoni, D.; Puri, C.; Confalonieri, S.; Salcini, A.E.; de Camilli, P.; Tacchetti, C.; di Fiore, P.P. TTP specifically regulates the internalization of the transferrin receptor. Cell 2005, 123, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.T.; Mays, R.W.; von Zastrow, M. Regulated endocytosis of G-protein-coupled receptors by a biochemically and functionally distinct subpopulation of clathrin-coated pits. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24592–24602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundborger, A.C.; Fang, S.; Heymann, J.A.; Ray, P.; Chappie, J.S.; Hinshaw, J.E. A dynamin mutant defines a superconstricted prefission state. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlovsky, Y.; Kozlov, M.M. Membrane fission: Model for intermediate structures. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, M.; Zuk, A.; Tikkanen, R. Role of dynamin and clathrin in the cellular trafficking of flotillins. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 2956–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ockenga, W.; Tikkanen, R. Revisiting the Endocytosis of the M2 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Membranes 2015, 5, 197-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020197
Ockenga W, Tikkanen R. Revisiting the Endocytosis of the M2 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Membranes. 2015; 5(2):197-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020197
Chicago/Turabian StyleOckenga, Wymke, and Ritva Tikkanen. 2015. "Revisiting the Endocytosis of the M2 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor" Membranes 5, no. 2: 197-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020197
APA StyleOckenga, W., & Tikkanen, R. (2015). Revisiting the Endocytosis of the M2 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor. Membranes, 5(2), 197-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes5020197






