Advancement in Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes Modification and Their Application in Water Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
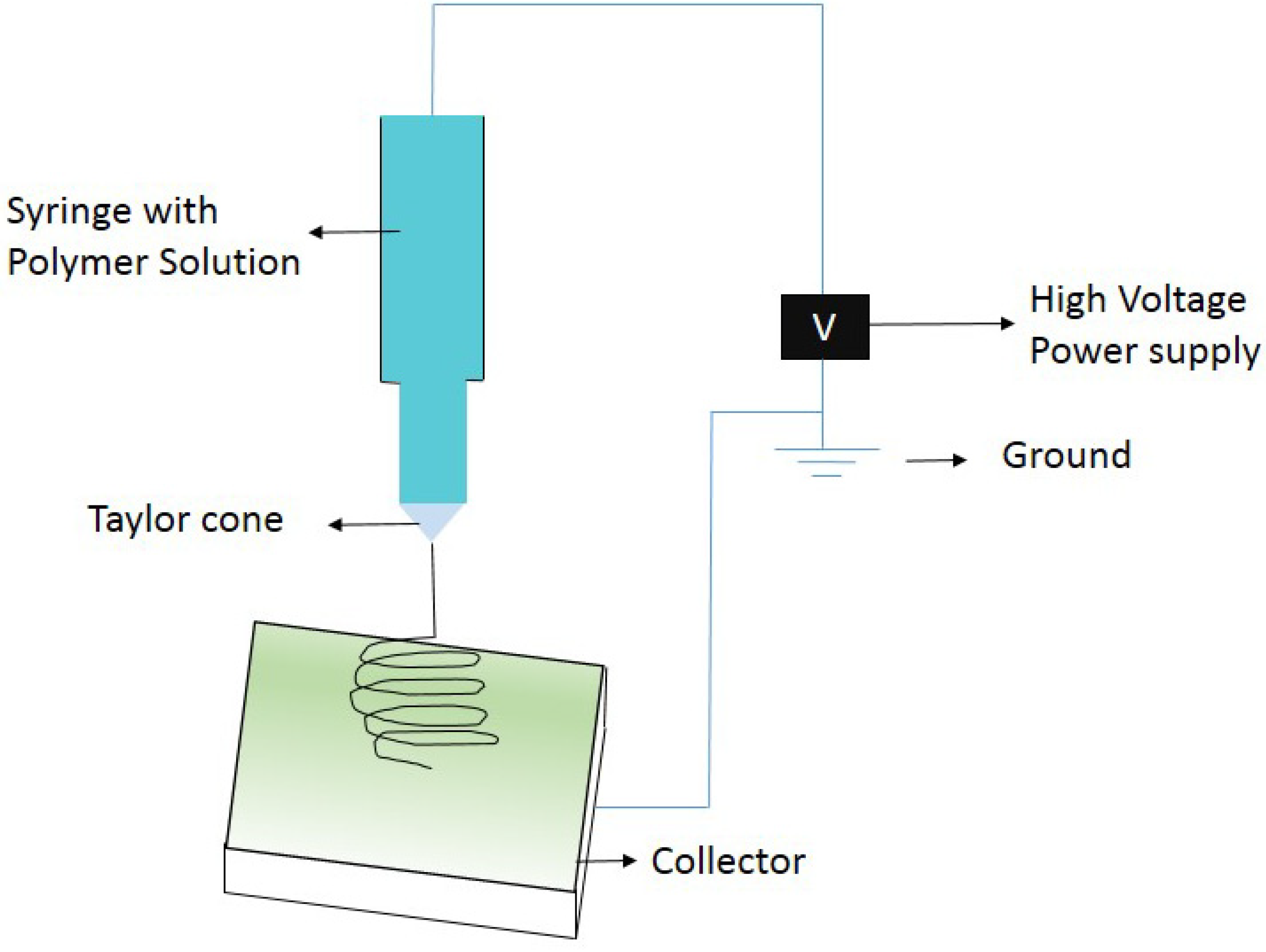
2. Nanofiber Preparation—Electrospinning Technique
3. Modifications of Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes (ENMs)
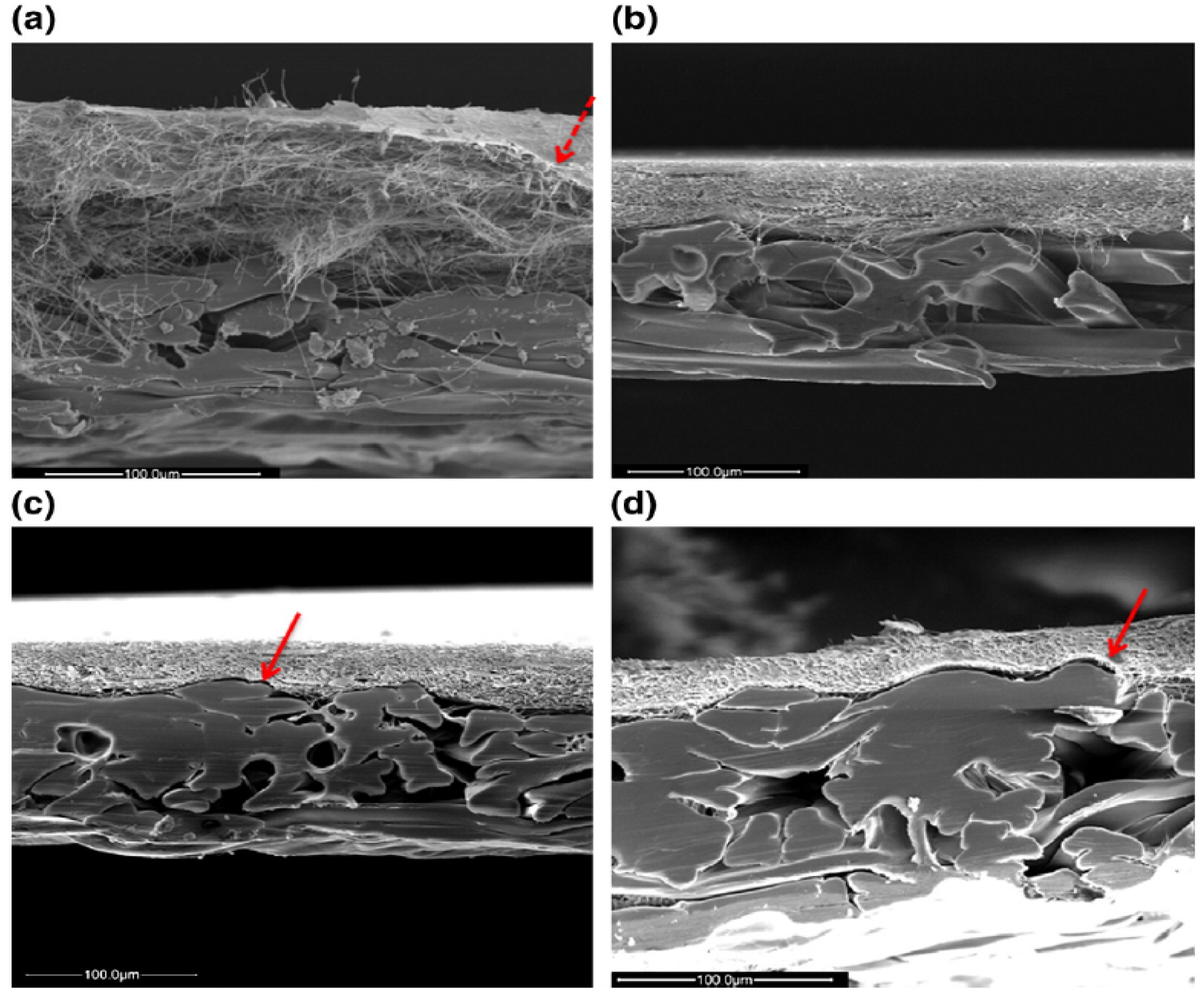
3.1. Surface Modification of ENMs
| S. No | Material | Modification | Active group | Target metal | Removal | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | chitosan | neutralization with K2CO3 | –NH2–, amine | Cu(II) | 485.44 mg/g | [37] |
| Pb(II) | 263.15 mg/g | |||||
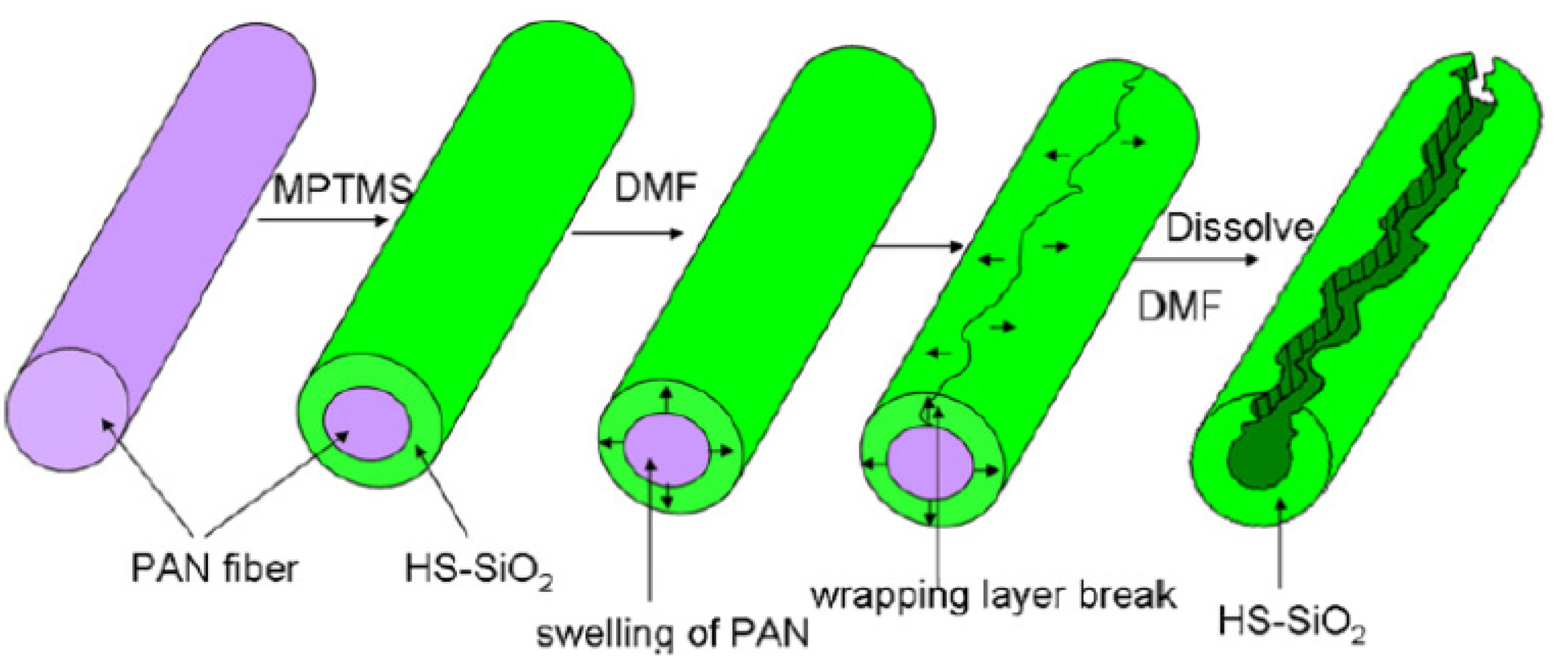
| 2 | silica | zonal dissolution of PAN | –SH–, Thiol | Hg(II) | 57.49 mg/g | [38] |
| 3 | cellulose acetate | In situ polymerization | fluorinated polybenzoxazine | oil water | maximum | [39] |
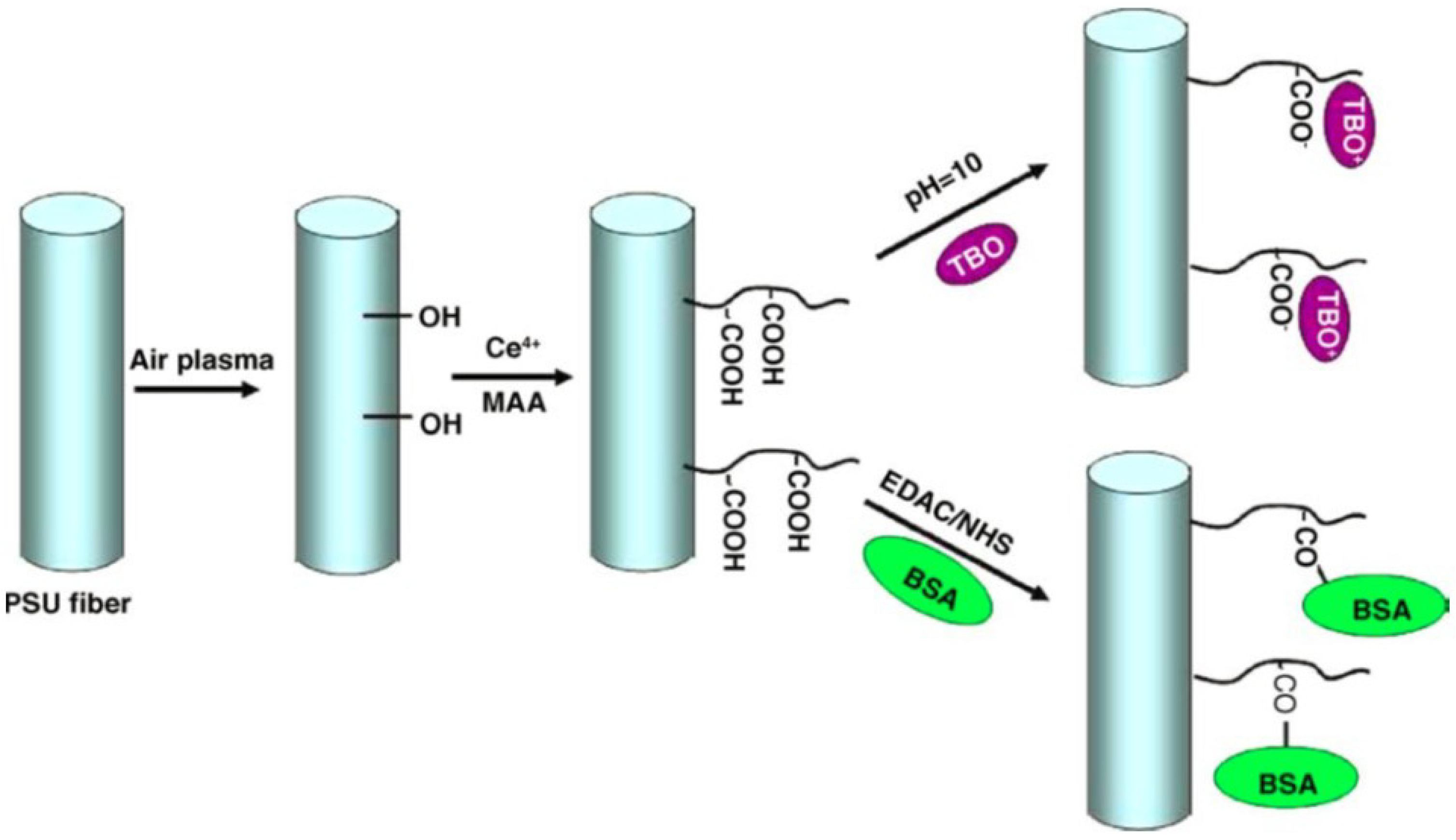
| 4 | poly sulfone | graft copolymerization | carboxyl group | toluidine blue O,BSA | 380 nmol of TBO/mg of TBO | [40] |
| 5 | poly ether sulfone | 1. solvent induced fusion | carbonyl | waste water | 1. flux: 2626 L/m2h psi | [41] |
| 2. oxidation | 2. flux: 2913 L/m2h psi | |||||
| 6 | PETE, PCTE, PTFC, PA | AgNO3 reduction | Ag | pathogen, waste water | turbidity removal: 99.25% | [42] |
| COD: 94.73% | ||||||
| NH4+: 93.98% | ||||||
| 7 | poly lactic acid | annealing | –COOH– | TiO2 removal | 85% rejection | [43] |
| 8 | polyacrylo nitrile | hot press interfacial polymerization | –CN– | salt rejection MgSO4 | 86.5% | [44] |
| 9 | polyacrylo nitrile | coupling | –NH2– | antibacterial | 53.7%–99.9% | [45] |
3.2. Interfacial Polymerization
3.3. Other Modifications
4. Application of ENMs in Water Treatment
4.1. Heavy Metal Removal
4.2. Microbial Removal
| Polymer | Membrane diameter (nm) | Properties | Antibacterial activity | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly acrylonitrile (PAN) | 100 | Mean Pore Size: 0.22 ± 0.01 µm | Flux: 1.5 L/m2h | E. coli | [66] | |||
| Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) | 50 | Mean Pore Size: 0.4 µm | – | S. aureus | [67] | |||
| E. coli | ||||||||
| Nylon-6 | 650 | OD culture at 600 nm | S. aureus E. coli | [68,69] | ||||
| E. coli | Pristine-3.4 | |||||||
| Mat 1-1.57 | ||||||||
| Mat 2-1.75 | ||||||||
| S. aureus | Pristine-2.55 | |||||||
| Mat 1-1.68 | ||||||||
| Mat 2-1.88 | ||||||||
| Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) | 200 | Zone inhibition (mm) | B. subtiliss S. aureus E. coli | [70] | ||||
| Microorganism | NaBH4 reduction | Heated @160 °C | Heated @80°C | |||||
| B. subtilis | 7.5 | 6 | 10 | |||||
| S. aureus | 9 | 10 | 10 | |||||
| E. coli | – | 6 | 9 | |||||
4.3. Desalination
| Middle layer (electrospun nanofiber) | Third layer | Solute | Method | Flux (L/m2/h) | Rejection (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/MWNT or Pebax/MWNT over PET substrate | none | oil/water | TFNC by coating | 330 or 160 | n.a. | [71] |
| PVA or Pebax over PET substrate | none | oil/water | TFNC by coating | 130 or 58 | PVA coated >99.5 | [72] |
| 10 and 4 wt % of PAN over PET substrate, rotating collector | none | oil/water | TFNC by coating | TFNC an order of magnitude > com. | 99.5%, better than com. NF | [73] |
| PAN | polyamides | MgSO4 | TFNC by Interfacial | TFNC 38% > com. NF 270 | TFNC and com. are comparable | [49] |
| PVDF | polyamides | MgSO4 | TFNC by Interfacial | 0.66 | 75.7 | [74] |
| NaCl | 0.66 | 70.2 | ||||
| PAN | polyamides | MgSO4 | Interfacial | [45] | ||
| TFNC1 | – | 88 | ||||
| TFNC2 | 81 | 84.2 | ||||
| first layer 8 or 10 wt % PAN | polyamides | MgSO4 | Interfacial | 220 | 89 | [75] |
| second layer 4 or 6 or 8 wt % PAN | NaCl | 200 | 89 | |||
| PVDF | n.a. | 6 wt % NaCl | AGMD | 11–12 kg/(m2 h) | n.a. | [76] |
| PVDF | n.a. | NaCl | DCMD | n.a. | 98.27 | [52] |
| PVDF-clay nanocomposites | 99.95 | |||||
| PET/PS | polyamide | NaCl | Interfacial | 1.13 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 | – | [21] |
4.4. Other Application
5. Future Directions and Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Guo, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M. Preparation of continuous alumina nanofibers via electrospinning of PAN/DMF solution. Mater. Lett. 2012, 74, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bromberg, L.; Hatton, T.A.; Rutledge, G.C. Catalytic hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate by electrospun polyacrylamidoxime nanofibers. Polymer 2007, 48, 4675–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijenska, E.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Swieszkowski, W.; Kurzydlowski, K.J.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun bio-composite (PLLA-CL)/collagen I/collagen III scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. J. Bio. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100B, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katepalli, H.; Bikshapathi, M.; Sharma, C.S.; Verma, N.; Sharma, A. Synthesis of hierarchical fabrics by electrospinning of PAN nanofibers on activated carbon microfibers for environmental remediation applications. Chem. Eng. 2011, 171, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.A.M.; Abadir, M.F.; Sheikh, F.A.; Kanjwal, M.A.; Park, S.J.; Kim, H.Y. Polymeric nanofibers containing solid nanoparticles prepared by electrospinning and their applications. Chem. Eng. 2010, 156, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.K.; Lee, S.-K.; Hwang, S.-H.; Kim, H. Photocatalytic deposition of silver nanoparticles onto organic/inorganic composite nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, D.; Bhuvaneshwari, N.; Indira, J. A novel green template assisted synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanorods and their spectral characterization. Spectrochim. Acta AMol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 107, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Dong, Y.; Fan, H.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Q. Preparation of polysulfone membranes via vapor-induced phase separation and simulation of direct-contact membrane distillation by measuring hydrophobic layer thickness. Desalination 2013, 316, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, J. Enhancing the permselectivity of pervaporation membrane by constructing the active layer through alternative self-assembly and spin-coating. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Li, M. Preparation, characterization of P(VDF-HFP)/[bmim]BF4 ionic liquids hybrid membranes and their pervaporation performance for ethyl acetate recovery from water. Desalination 2012, 295, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Cao, J. Shell element formulation of multi-step inverse analysis for axisymmetric deep drawing process. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2001, 50, 681–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liewhiran, C.; Phanichphant, S. Doctor-bladed thick films of flame-made Pd/ZnO nanoparticles for ethanol sensing. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2008, 8, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent trends in nanofibrous membranes and their suitability for air and water filtrations. Membranes 2011, 1, 232–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T.; Tabe, S.; Ismail, A.F. Preparation and characterization of electro-spun nanofiber membranes and their possible applications in water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 102, 118–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Seeram, R. New directions in nanofiltration applications—Are nanofibers the right materials as membranes in desalination? Desalination 2013, 308, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazargan, A.M.; Keyanpour-Rad, M.; Hesari, F.A.; Esmaeilpour, M.G. A study on the microfiltration behavior of self-supporting electrospun nanofibrous membrane in water using an optical particle counter. Desalination 2011, 265, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Performance of ultrafiltration membranes in ethanol–water solutions: Effect of membrane conditioning. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 198, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarrajan, S.; Balamurugan, R.; Kaur, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Potential of engineered electrospun nanofiber membranes for nanofiltration applications. Dry. Technol. 2013, 31, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, T.; Khan, S.J.; McDonald, J.A.; Roux, A.; Poussade, Y.; Drewes, J.E.; Nghiem, L.D. N-nitrosamine rejection by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: The importance of membrane characteristics. Desalination 2013, 316, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, L.A.; Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M. Nanofibers in thin-film composite membrane support layers: Enabling expanded application of forward and pressure retarded osmosis. Desalination 2013, 308, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, Y.; Marquez, M.; Thorsen, T. Multijet electrospinning of conducting nanofibers from microfluidic manifolds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 3171–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Upward needleless electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, M.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, B. Thioether-functionalized mesoporous fiber membranes: Sol-gel combined electrospun fabrication and their applications for Hg2+ removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 355, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, B.; Tan, H.; Chen, T.; Xu, J. A novel nanofiltration membrane prepared with PAMAM and TMC by in situ interfacial polymerization on PEK-C ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 269, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Hsiao, B.S. High flux low pressure thin film nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes based on nanofibrous substrates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, S.; Vanhulsel, A.; Buekenhoudt, A.; Weyten, H.; Kuypers, S.; Chen, H.; Bryjak, M.; Gevers, L.E.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Jacobs, P.A. Plasma-treated PDMS-membranes in solvent resistant nanofiltration: Characterization and study of transport mechanism. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 275, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Yang, X.; Xie, L.; Li, J.; Hou, Z.; Yao, S.; Liang, G.; Sheng, K.; Huang, Q. Microfiltration membranes with pH dependent property prepared from poly(methacrylic acid) grafted polyethersulfone powder. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 330, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Xu, Z.L.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y.M.; Wu, W.Z.; Chen, D.G. Preparation and characterization of PVDF-P(PEGMA-r-MMA) ultrafiltration blend membranes via simplified blend method. Desalination 2013, 319, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kango, S.; Kalia, S.; Celli, A.; Njuguna, J.; Habibi, Y.; Kuma, R. Surface modification of inorganic nanoparticles for development of organic–inorganic nanocomposites—A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1232–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyadhi, L.; Liu, J.C. Oxidation–microfiltration removal of Fe(II) from water. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.; Prabhavathy, C.; De, S.; Dasgupta, S. Flux enhancement by argon on Technology (II) from wet polyethersulfone membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, M.; Hsiao, B.; Chu, B. Membrane development of hydrophilic barrier layer on nanofibrous substrate as composite membrane via a facile route. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 356, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, K. Preparation and characterization of high flux ultrafiltration composite membrane based on nanofibrous substrate and cellulose acetate coating. In Proceedings of 2009 International Conference on Advanced Fibers and Polymer Materials, Shanghai, China, 21–24 October 2009.
- Stephen, M.; Catherine, N.; Brenda, M.; Andrew, K.; Leslie, P.; Corrine, G. Oxolane-2,5-dione modified electrospun cellulose nanofibers for heavy metals adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, J.D.; Schauer, C.L. Cross-linking chitosan nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
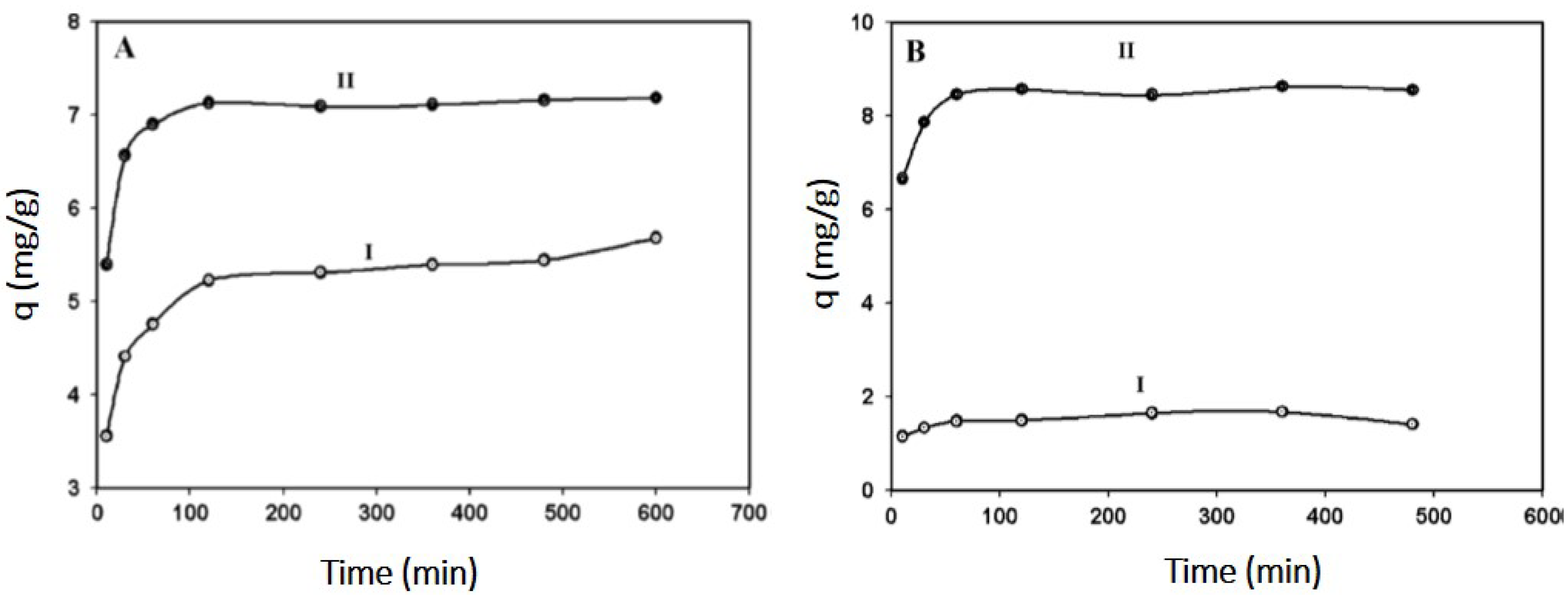
- Haider, S.; Park, S.Y. Preparation of the electrospun chitosan nanofibers and their applications to the adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from an aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yue, X.; Jing, Y.; Bai, S.; Dai, Z. Fabrication of zonal thiol-functionalized silica nanofibers for removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Colloid Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 380, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Si, Y.; Raza, A.; Yang, L.; Mao, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. An in situ polymerization approach for the synthesis of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes for oil–water separation. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7847–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kotak, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Surface modified nonwoven polysulphone (PSU) fiber mesh by electrospinning: A novel affinity membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 272, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Formation of functional polyethersulfone electrospun membrane for water purification by mixed solvent and oxidation processes. Polymer 2009, 50, 2893–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorge, D.; Daels, N.; de Vrieze, S.; Dejans, P.; van Camp, T.; Audenaert, W.; Hogie, J.; Westbroek, P.; de Clerck, K.; van Hulle, S.W.H. Performance assessment of electrospun nanofibers for filter applications. Desalination 2009, 249, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hashaikeh, R.; Arafat, H.A. Development of eco-efficient micro-porous membranes via electrospinning and annealing of poly (lactic acid). J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Barhate, R.; Sundarrajan, S.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Hot pressing of electrospun membrane composite and its influence on separation performance on thin film composite nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2011, 279, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Yao, C.; Fan, K.; Li, X. Surface modification of polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membranes with superior antibacterial and easy-cleaning properties through hydrophilic flexible spacers. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Han, C.C. High performance ultrafiltration membrane based on modified chitosan coating and electrospun nanofibrous PVDF scaffolds. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394–395, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.J. Composite reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 83, 81–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High flux nanofiltration membranes based on interfacially polymerized polyamide barrier layer on polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous scaffolds. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, L.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Yoon, K.; Wang, R.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Fabrication of thin-film nanofibrous composite membranes by interfacial polymerization using ionic liquids as additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Preparation and characterization of anti-fouling b-cyclodextrin/polyester thin film nanofiltration composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Sundarrajan, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Preparation and characterization of surface modified electrospun membranes for higher filtration flux. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390–391, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, J.A.; Singh, G.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Anbharasi, V.; Shanmugasundaram, T.S. Preparation and characterization of highly hydrophobic poly(vinylidene fluoride)—Clay nanocomposite nanofiber membranes (PVDF–clay NNMs) for desalination using direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 397–398, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Engineering superhydrophobic surface on poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 440, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High flux ultrafiltration nanofibrous membranes based on polyacrylonitrile electrospun scaffolds and crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol coating. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 338, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Manickam, S.S.; McCutcheon, J.R. Increasing strength of electrospun nanofiber membranes for water filtration using solvent vapor. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Surface modification of commercial aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membranes by graft polymerization of 3-allyl-5,5-dimethylhydantoin. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 351, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoji, H.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Tabe, S.; Feng, C. Development of plasma and/or chemically induced graft co-polymerized electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes for solute separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 108, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.A.; Wu, Y.N.; Wang, H.; Li, F. Preparation and application of functionalized cellulose acetate/silica composite nanofibrous membrane via electrospinning for Cr(VI) ion removal from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.A.; Qiao, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, B. Preparation and application of amino functionalized mesoporous nanofiber membrane via electrospinning for adsorption of Cr3+ from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Cai, W.; Tian, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Liang, C. Polyacrylonitrile/ferrous chloride composite porous nanofibers and their strong Cr-removal performance. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 991–997. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.J.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, J.N.; Cheng, J. PA6@FexOy nanofibrous membrane preparation and its strong Cr (VI)-removal performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.R.; Wang, J.N.; Li, C.J. Preparation of hierarchically nanofibrous membrane and its high adaptability in hexavalent chromium removal from water. Chem. Eng. J 2012, 198–199, 10–317. [Google Scholar]
- Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M.; Ismaeili, J.; Piri, H.; Parnian, M.J. Electrospun nanofiber membrane of PEO/Chitosan for the adsorption of nickel, cadmium, lead and copper ions from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Vitchuli, N.; Nowak, J.; Caldwell, J.M.; Breidt, F.; Bourham, M.; Zhang, X.; McCord, M. Durable antibacterial Ag/polyacrylonitrile (Ag/PAN) hybrid nanofibers prepared by atmospheric plasma treatment and electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Menkhaus, T.J.; Varadaraju, H.; Sun, Y.; Fong, H. Antimicrobial nano-fibrous membranes developed from electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes for high flux microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 392–393, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daels, N.; de Vrieze, S.; Sampers, I.; Decostere, B.; Westbroek, P.; Dumoulin, A.; Dejans, P.; de Clerck, K.; van Hulle, S.W.H. Potential of a functionalised nanofibre microfiltration membrane as an antibacterial water filter. Desalination 2011, 275, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, M.; Malekzadeh, S.B. Electrospun antibacterial nylon nanofibers through in situ synthesis of nanosilver: Preparation and characteristics. J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9980:1–9980:6. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, B.; Pant, H.R.; Pandeya, D.R.; Panthi, G.; Nam, K.T.; Hong, S.T.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, H.Y. Characterization and antibacterial properties of Ag NPs loaded nylon-6 nanocomposite prepared by one-step electrospinning process. Colloid Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. 2012, 395, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, A.; Grag, N.; Nayak, B.P.; Mishra, B.G.; Hota, G. Studies on the synthesis of electrospun PAN-Ag composite nanofibers for antibacterial application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Yoon, K.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High flux filtration medium based on nanofibrous substrate with hydrophilic nanocomposite coating. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7684–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, D.; Yoon, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High performance ultrafiltration composite membranes based on poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel coating on crosslinked nanofibrous poly(vinyl alcohol) scaffold. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Kim, K.; Wang, X.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High flux ultrafiltration membranes based on electrospun nanofibrous PAN scaffolds and chitosan coating. Polymer 2006, 47, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Sundarrajan, S.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Influence of electrospun fiber size on the separation efficiency of thin film nanofiltration composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 392, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T.; Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Khayet, M. Production of drinking water from saline water by air-gap membrane distillation using polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Pan, C.; Wang, L.; Dong, Q.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, J. Activated carbon nanofiber webs made by electrospinning for capacitive deionization. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 69, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Sundarrajan, S.; Gopal, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Formation and characterization of polyamide composite electrospun nanofibrous membranes for salt separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, E205–E215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-H.; Wang, S.-Y. Electrospun nanofibers from crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) and its filtration efficiency. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.S.; Buhr, K.; Ebert, K. Polyethersulfone electrospun nanofibrous composite membrane for liquid filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Huang, M.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Sun, G. Robust polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membrane reinforced with jute cellulose nanowhiskers for water purification. Desalination 2013, 361, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasreen, S.A.A.N.; Sundarrajan, S.; Nizar, S.A.S.; Balamurugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Advancement in Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes Modification and Their Application in Water Treatment. Membranes 2013, 3, 266-284. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040266
Nasreen SAAN, Sundarrajan S, Nizar SAS, Balamurugan R, Ramakrishna S. Advancement in Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes Modification and Their Application in Water Treatment. Membranes. 2013; 3(4):266-284. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040266
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasreen, Shaik Anwar Ahamed Nabeela, Subramanian Sundarrajan, Syed Abdulrahim Syed Nizar, Ramalingam Balamurugan, and Seeram Ramakrishna. 2013. "Advancement in Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes Modification and Their Application in Water Treatment" Membranes 3, no. 4: 266-284. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040266
APA StyleNasreen, S. A. A. N., Sundarrajan, S., Nizar, S. A. S., Balamurugan, R., & Ramakrishna, S. (2013). Advancement in Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes Modification and Their Application in Water Treatment. Membranes, 3(4), 266-284. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes3040266







