Fabrication and Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Chitosan-Coated Membranes for Enhanced Oil Emulsion Filtration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
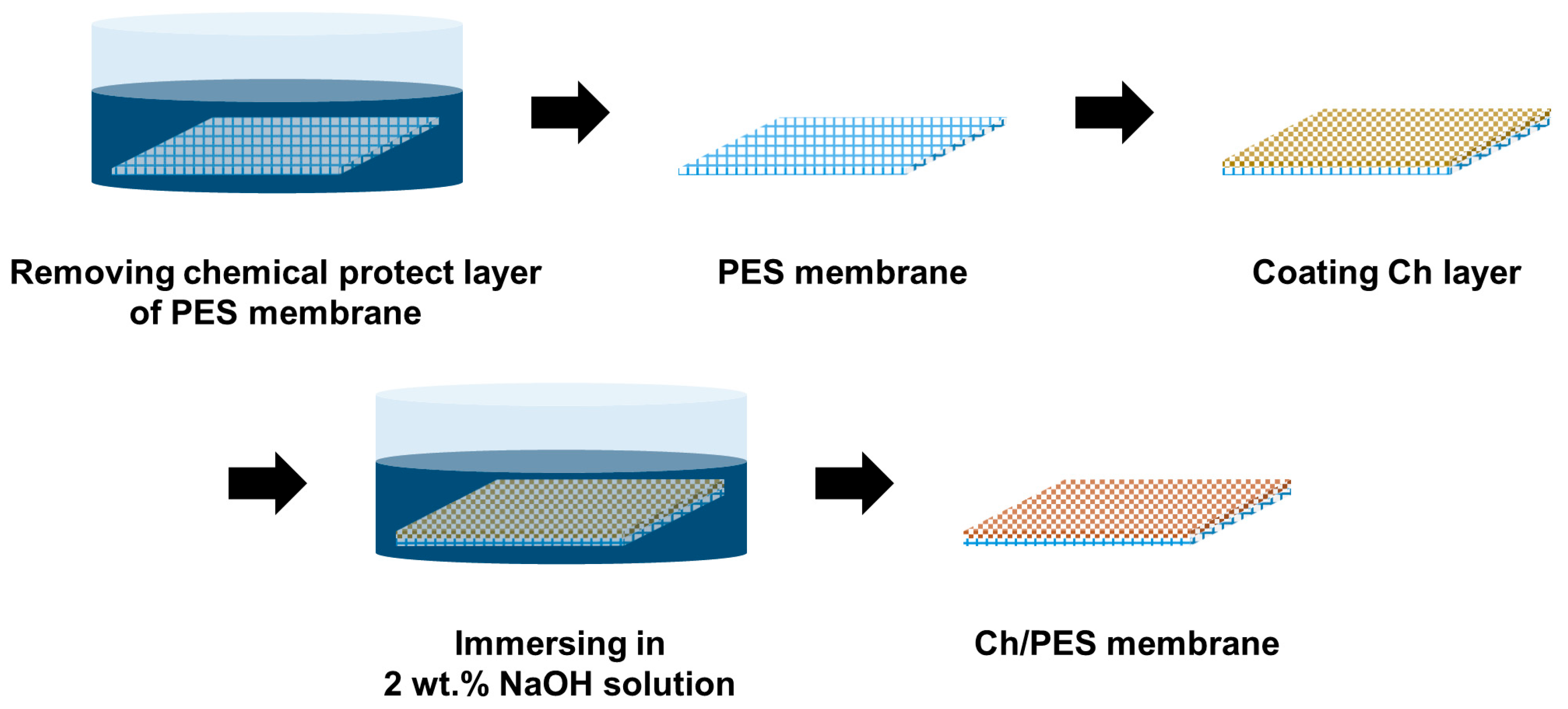
2.2. Fabrication of Ch/PES Membrane
2.3. Characterization of Ch/PES Membranes
2.4. Oil–Water Separation Performance of Ch/PES Membrane
3. Results and Discussion
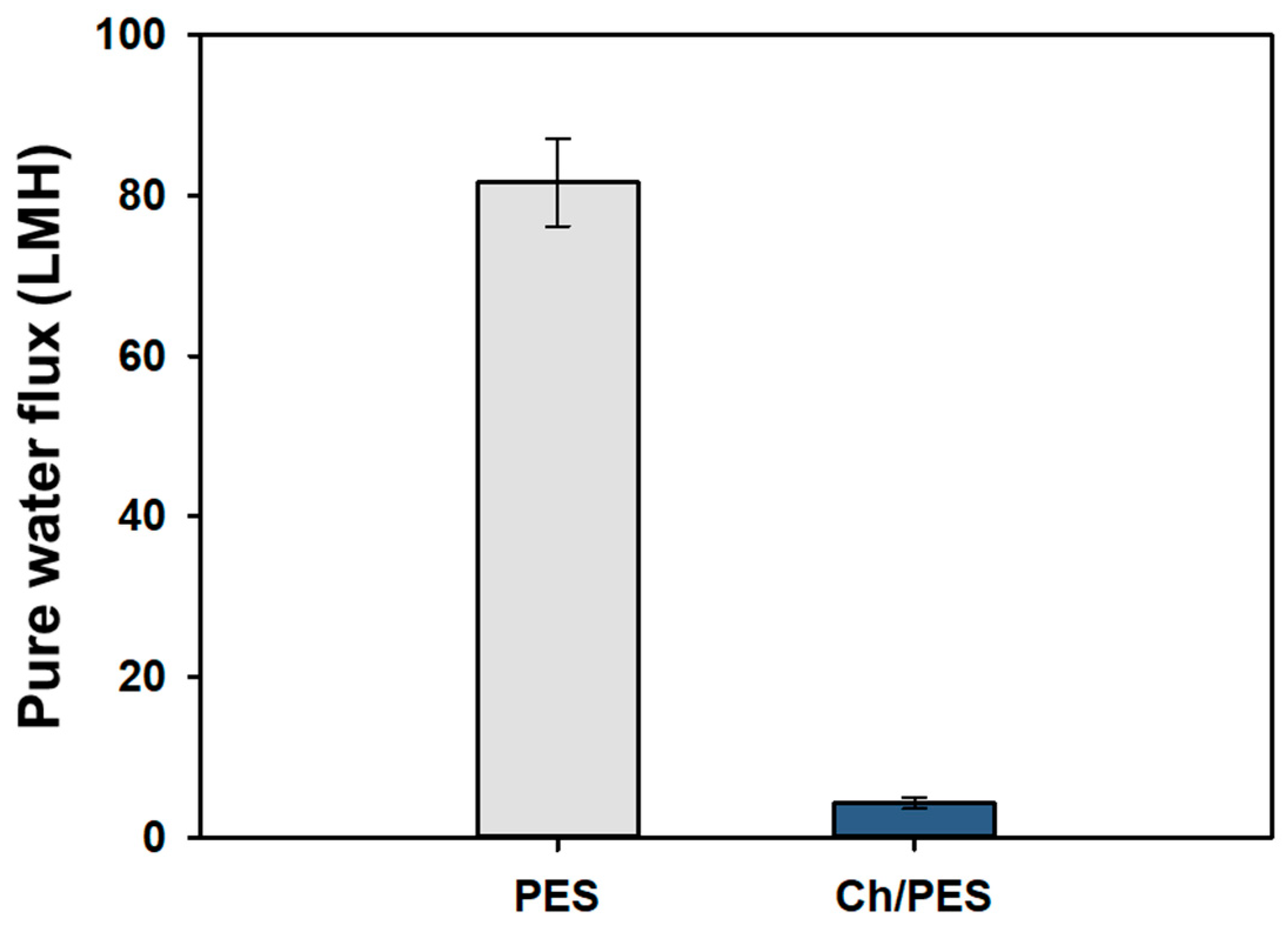
3.1. Characterization of Ch/PES Membrane
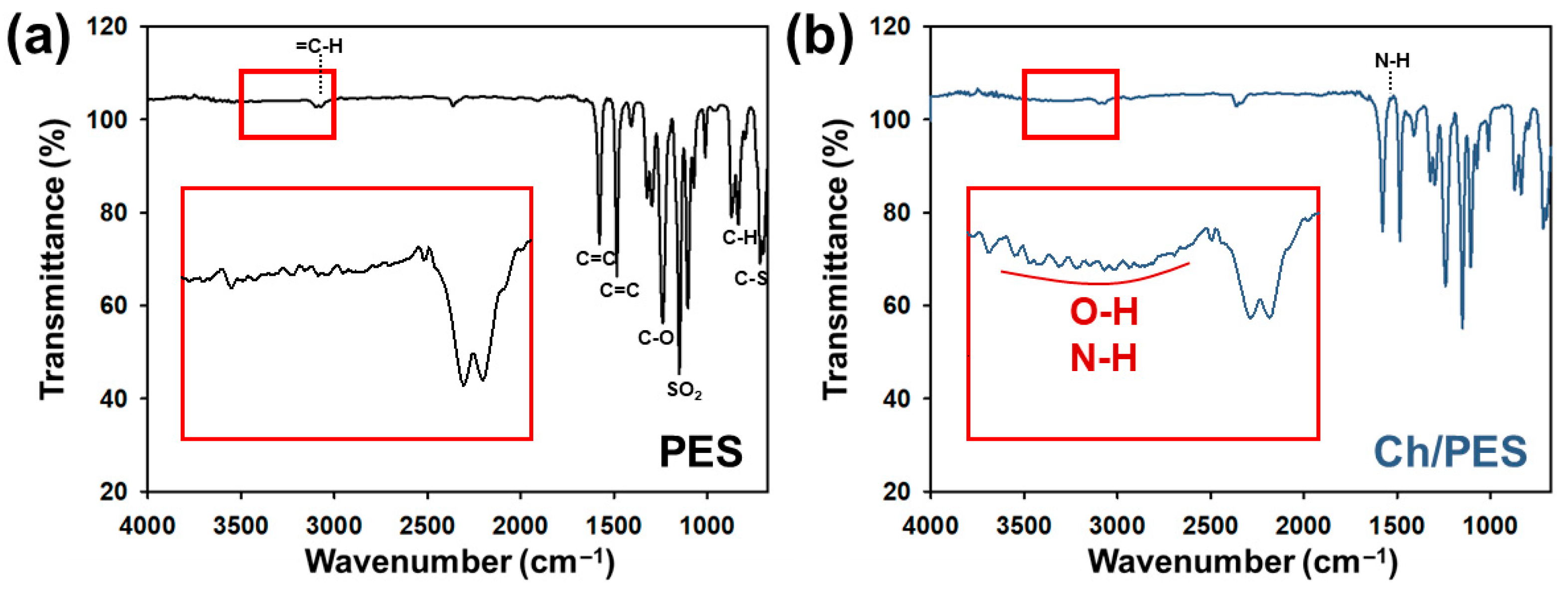
3.1.1. Chemical Characterization of Ch/PES Membrane
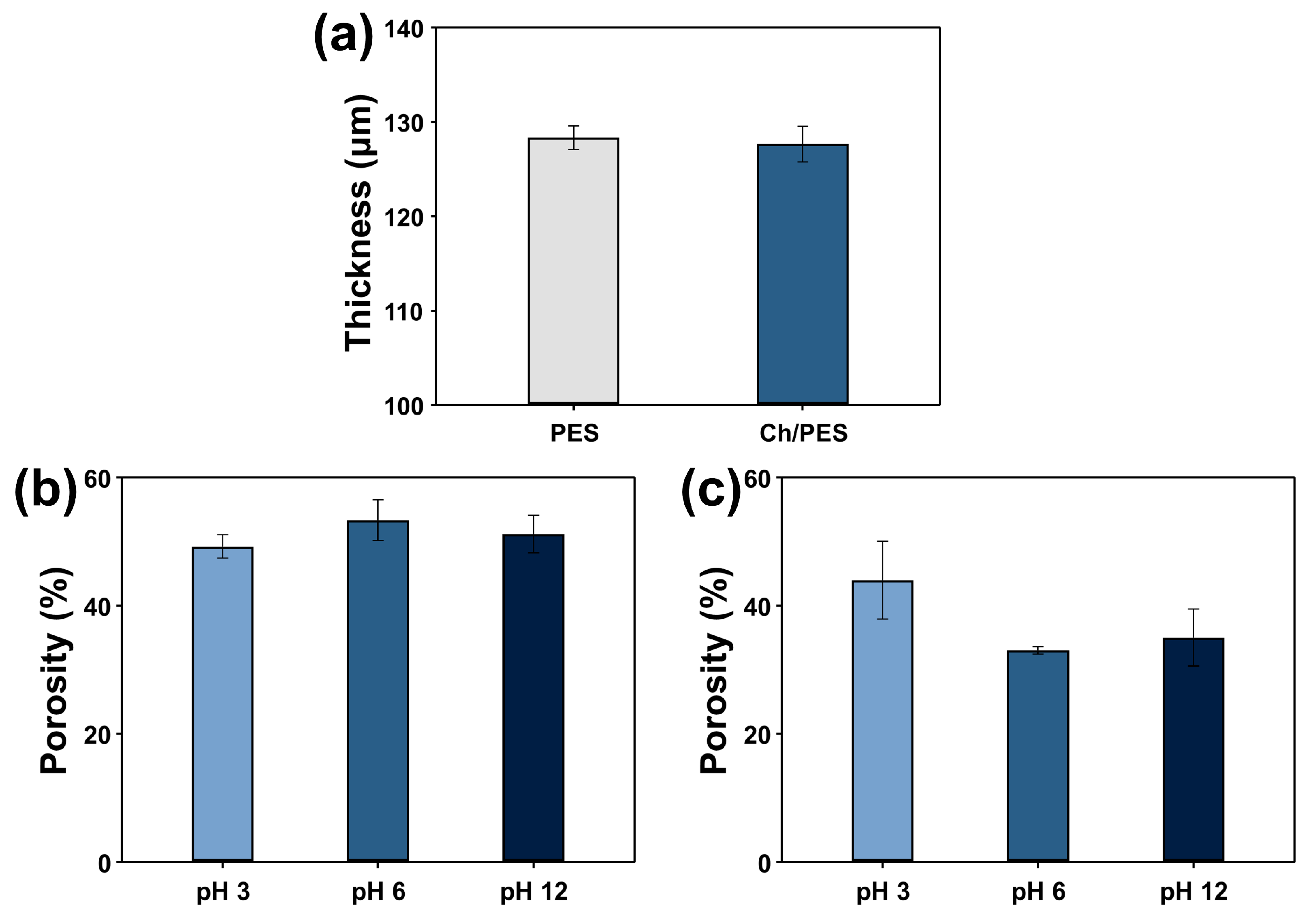
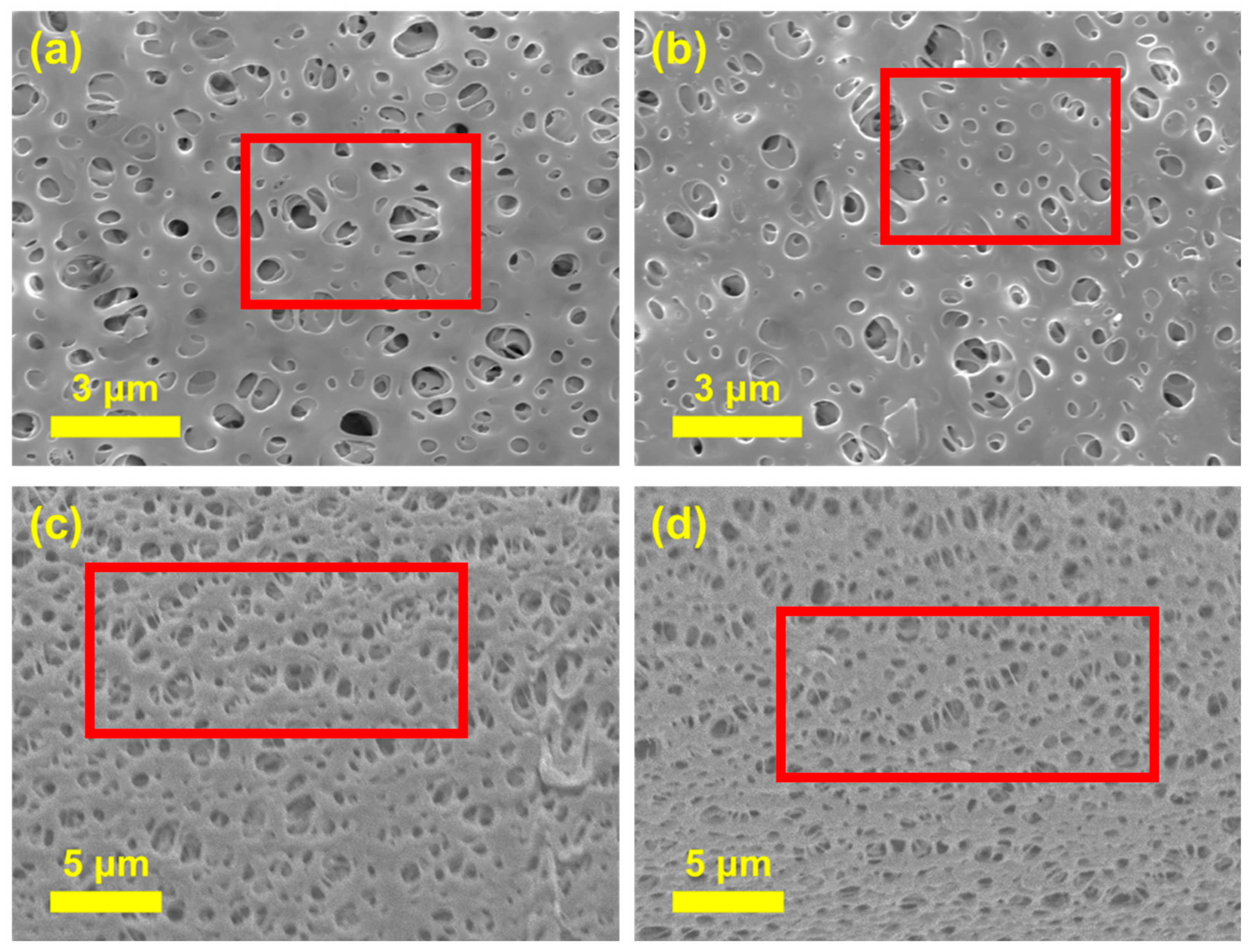
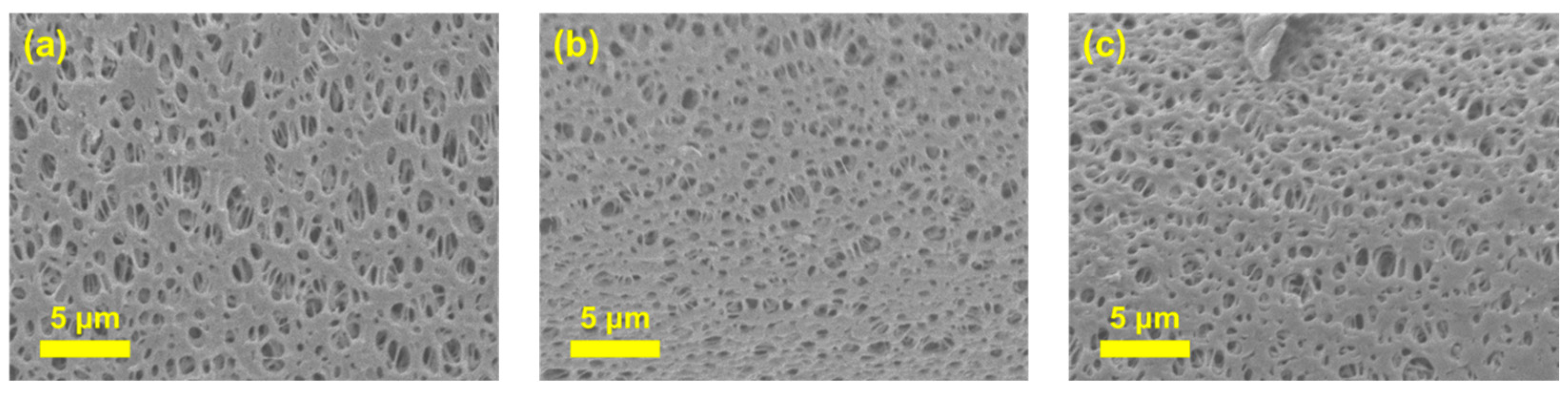
3.1.2. Physical Characterization of Ch/PES Membrane
3.1.3. Swelling Behavior of Ch/PES Membrane Under Different pH Conditions
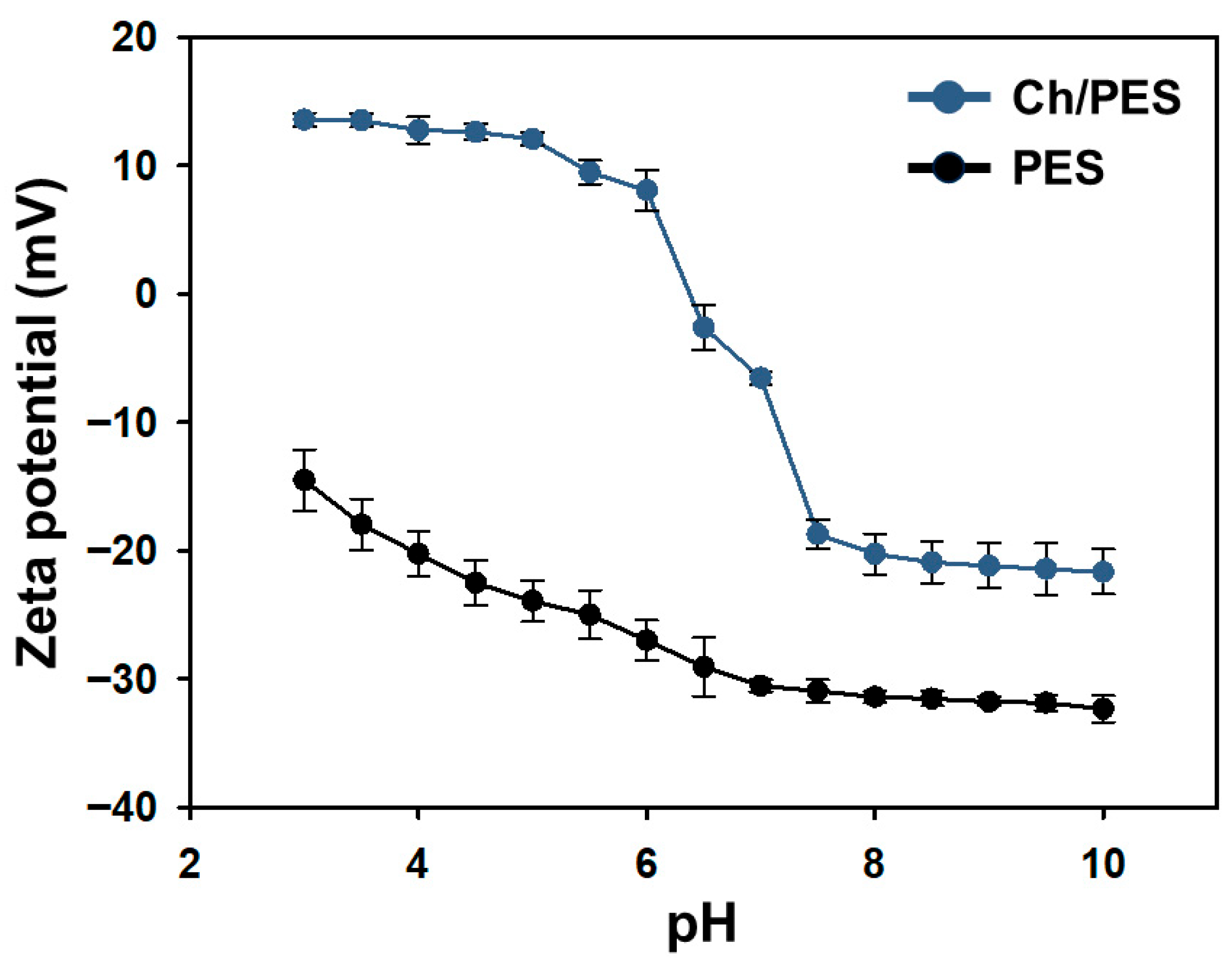
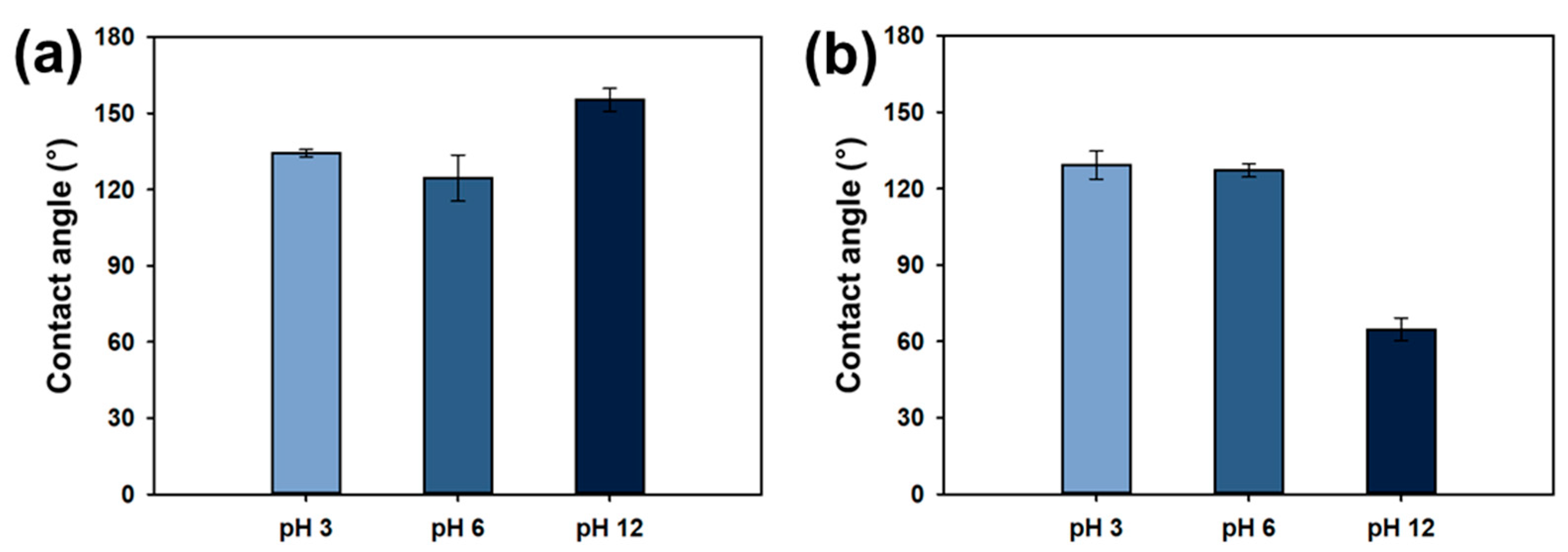
3.1.4. Zeta Potential and Wettability of Ch/PES Membrane at Different pH Levels
3.2. Emulsified-Oil Separation Performance of the Ch/PES Membrane
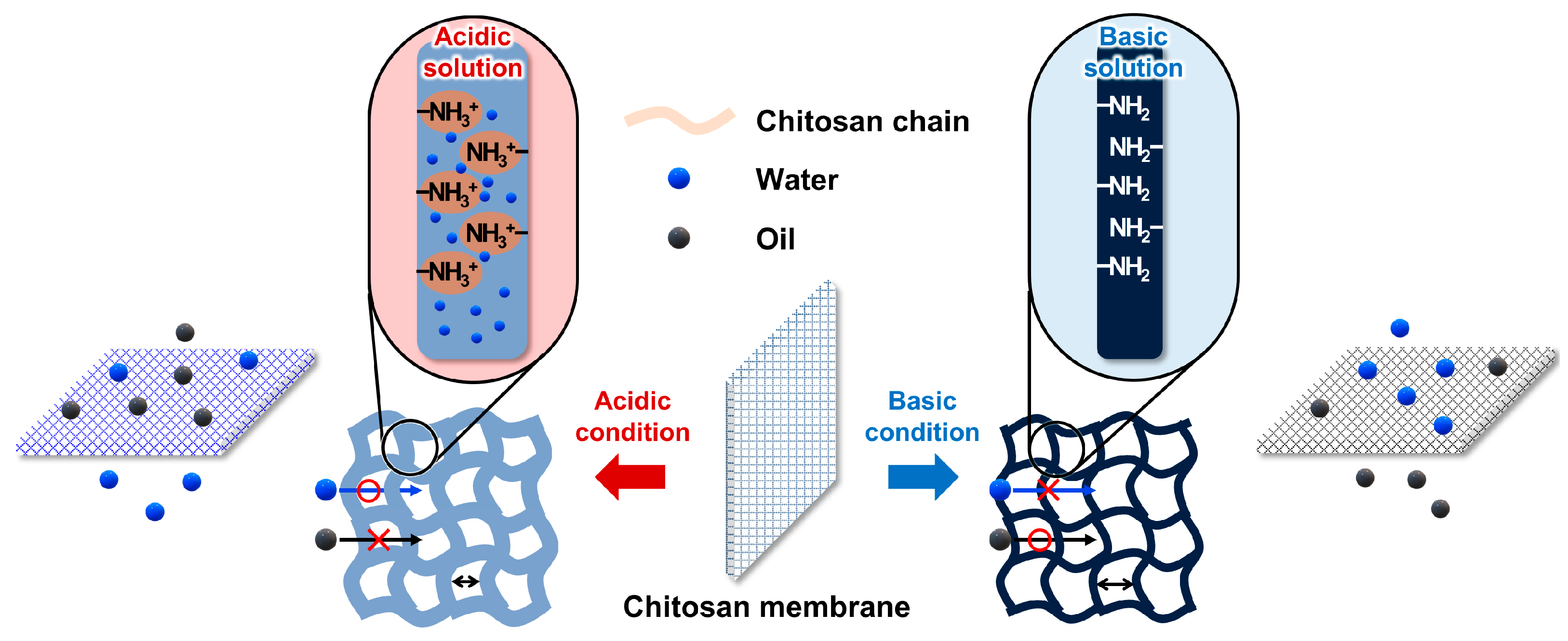
3.3. Mechanism of Oil/Water Separation Using the Ch/PES Membrane
3.4. Implications of the pH-Responsive Ch/PES Membrane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ch/PES | Chitosan-coated polyethersulfone |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| MF | Microfiltration |
| UF | Ultrafiltration |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| GA | Glutaraldehyde |
| HAc | Acetic acid |
| IPA | Isopropyl alcohol |
| NaOH | Sodium hydroxide beads |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| DI | Deionized |
| OCA | Oil contact angle |
Appendix A
| Type | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Density (g/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| Canola oil | 46 | 0.920 |
References
- Carpintero-Tepole, V.; Brito-de la Fuente, E.; Torrestiana-Sánchez, B. Microfiltration of oil in water (O/W) emulsions: Effect of membrane microstructure and surface properties. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 126, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.-H.T.; Lee, B.-K. Novel fabrication of a robust superhydrophobic PU@ ZnO@ Fe3O4@ SA sponge and its application in oil-water separations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorokhta, M.; Khalakhan, I.; Václavů, M.; Kovács, G.; Kozlov, S.M.; Kúš, P.; Skála, T.; Tsud, N.; Lavková, J.; Potin, V. Surface composition of magnetron sputtered Pt-Co thin film catalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 365, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-R.; Ma, W.-X.; Han, X.-Y.; Chen, G.-E.; Xu, Z.-L. Intelligent pH-responsive PMIA membrane with reversible wettability for controllable oil/water and emulsion separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 615, 156392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukupally, P.; Sun, W.; Williams, D.; Ozin, G.; Bilton, A. Wax-wetting sponges for oil droplets recovery from frigid waters. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saththasivam, J.; Loganathan, K.; Sarp, S. An overview of oil–water separation using gas flotation systems. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; He, S.; Shao, W. Sustainable, highly efficient and superhydrophobic fluorinated silica functionalized chitosan aerogel for gravity-driven oil/water separation. Gels 2021, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempoonsert, J.; Tansel, B.; Laha, S. Effect of temperature and pH on droplet aggregation and phase separation characteristics of flocs formed in oil–water emulsions after coagulation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 353, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambiella, A.; Benito, J.; Pazos, C.; Coca, J. Centrifugal separation efficiency in the treatment of waste emulsified oils. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2006, 84, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ran, X.; Sun, L.; Bi, H.; Wu, X. Recent advances in membrane technologies applied in oil–water separation. Discov. Nano 2024, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasouli, S.; Rezaei, N.; Hamedi, H.; Zendehboudi, S.; Duan, X. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic membranes for oil-water separation application: A comprehensive review. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N.; Salhi, B.; Sajid, M.; Aljundi, I.H. Recent progress in microfiltration/ultrafiltration membranes for separation of oil and water emulsions. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, e202100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Long, J.; Peng, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, G.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, T.; Wen, Y.; Li, J. Oil/water separation using elastic bio-aerogels derived from bagasse: Role of fabrication steps. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Sun, L. Zwitterionic nanogels modified nanofibrous membrane for efficient oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Cao, X.; Tan, C.; Yin, Z.; Lu, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H. Carbon microbelt aerogel prepared by waste paper: An efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents. Small 2014, 10, 3544–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Al-Zoubi, H.; Darwish, N.; Mohamma, A.; Arabi, M.A. A comprehensive review of nanofiltration membranes: Treatment, pretreatment, modelling, and atomic force microscopy. Desalination 2004, 170, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drioli, E.; Macedonio, F. Membrane engineering for water engineering. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 10051–10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eykamp, W. Microfiltration and ultrafiltration. In Membrane Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.-J.; Xu, Z.-K. Wettability Switchable Membranes for Separating Both Oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 624, 118976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, B.; Li, J.; Liang, S.; Bai, Y.; Xu, J.; Rao, D. Scalable and switchable CO2-responsive membranes with high wettability for separation of various oil/water systems. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D. A smart fabric with reversibly switchable wettability for controllable oil/water separation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2025, 201, 109116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, Z. Biomimetic materials in oil/water separation: Focusing on switchable wettabilities and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 320, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Fang, C.; Chen, L.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Cai, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Li, Y.; et al. A bio-inspired green method to fabricate pH-responsive sponge with switchable surface wettability for multitasking and effective oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 602, 154192. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Tao, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, Y. CO2-responsive nanofibrous membranes with gas-tunable wettability for switchable oil/water separation. React. Funct. Polym. 2023, 182, 105481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Ning, X. Robustly wettability-switchable polylactic acid nanofibrous membranes bearing CO2-responsive trigger and emulsion breaker for versatile oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Ding, S.; Wang, S.; Xiao, W.; Shi, S.; Chen, C. Electro-driven multi-functional catalysis separation membrane reactor with switchable wettability for efficient water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 16667–16676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yang, K.; Huang, C.; Yang, K.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Pi, P.; Wen, X. Novel pH-responsive smart fabric: From switchable wettability to controllable on-demand oil/water separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. An active and pH-responsive film developed by sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol doped with rose anthocyanin extracts. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinejad, Z.; Raeesi, M.; Mahdavian, A.R. Enhanced cysteine sensor based on modified gold nanoparticles with synergistic role of pH-responsive poly (N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate). Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 211, 113031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Su, Z.; Hou, K.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Nunes, S.P. Advanced stimuli-responsive membranes for smart separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 4173–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatinia, Z.; Jalali, A.M. Chitosan-based hydrogels: Preparation, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 194–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, X.; Hua, T.; Fu, J.; Koo, M.; Chan, W.; Poon, T. Chitosan natural polymer material for improving antibacterial properties of textiles. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 4014–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, C.; Wilhelms, T.; Kulicke, W.-M. Formation and characterization of chitosan membranes. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3210–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel Jacob, K.; Senthil Kumar, S.; Thanigaivelan, A.; Tarun, M.; Mohan, D. Sulfonated polyethersulfone-based membranes for metal ion removal via a hybrid process. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Olvera, I.G.; Villafana-Lopez, L.; Reyes-Aguilera, J.A.; Ávila-Rodríguez, M.; Razo-Lazcano, T.A.; González-Muñoz, M.P. Surface modification of polyethersulfone membranes with goethite through self-assembly. Desalin. Water Treat 2017, 65, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machodi, M.J.; Daramola, M.O. Synthesis and performance evaluation of PES/chitosan membranes coated with polyamide for acid mine drainage treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowska-Czubenko, J.; Gierszewska, M.; Pieróg, M. pH-responsive hydrogel membranes based on modified chitosan: Water transport and kinetics of swelling. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Ma, K.; Cai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y. Low temperature electrophoretic deposition of porous chitosan/silk fibroin composite coating for titanium biofunctionalization. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7705–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, Q.; Guan, Y.; Li, W.; Xie, S.; Tong, J.; Li, M.; Ren, L. Synthesis and characterization of porous chitosan/saccharomycetes adsorption microspheres. Polymers 2022, 14, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelkmann, M.; Menzel, C.; Baus, R.A.; Ausserhofer, P.; Baecker, D.; Gust, R.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Chitosan: The one and only? Aminated cellulose as an innovative option for primary amino groups containing polymers. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 4059–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias, B.S.; Junior, T.R.S.A.C.; de Almeida Pinto, L.A. Chitosan-functionalized nanofibers: A comprehensive review on challenges and prospects for food applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shaeli, M.; Benkhaya, S.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Koyuncu, I.; Vatanpour, V. pH-responsive membranes: Mechanisms, fabrications, and applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 173865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, N.; Abdulazeez, I.; Aljundi, I.H. Low-pressure-driven special wettable graphene oxide-based membrane for efficient separation of water-in-oil emulsions. npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhovskii, R.A.; Ivanov, A.N.; Lengert, E.V.; Tulyakova, K.A.; Shilyagina, N.Y.; Ermakov, A.V. Current principles, challenges, and new metrics in pH-responsive drug delivery systems for systemic cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, F.; Hegab, H.M.; Banat, F.; Arafat, H.A.; Hasan, S.W. Development of sustainable pH-responsive adsorptive modified mangrove-based polylactic acid ultrafiltration membrane for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Gao, C.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Jiao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xin, Q.; Li, H. Dual-gating pH-responsive membranes with the heterogeneous structure for whey protein fractionation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Armstrong, D.L.; Finnerty, C.; Zheng, S.; Hu, M.; Torrents, A.; Mi, B. Understanding the pH-responsive behavior of graphene oxide membrane in removing ions and organic micropollulants. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, E.; Byun, S.; Jeong, S. Fabrication and Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Chitosan-Coated Membranes for Enhanced Oil Emulsion Filtration. Membranes 2025, 15, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090252
Choi E, Byun S, Jeong S. Fabrication and Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Chitosan-Coated Membranes for Enhanced Oil Emulsion Filtration. Membranes. 2025; 15(9):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090252
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Eunseo, Siyoung Byun, and Sanghyun Jeong. 2025. "Fabrication and Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Chitosan-Coated Membranes for Enhanced Oil Emulsion Filtration" Membranes 15, no. 9: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090252
APA StyleChoi, E., Byun, S., & Jeong, S. (2025). Fabrication and Evaluation of pH-Sensitive Chitosan-Coated Membranes for Enhanced Oil Emulsion Filtration. Membranes, 15(9), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090252







