Fabrication and Evaluation of Ceramic-Based Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Hemodialysis Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
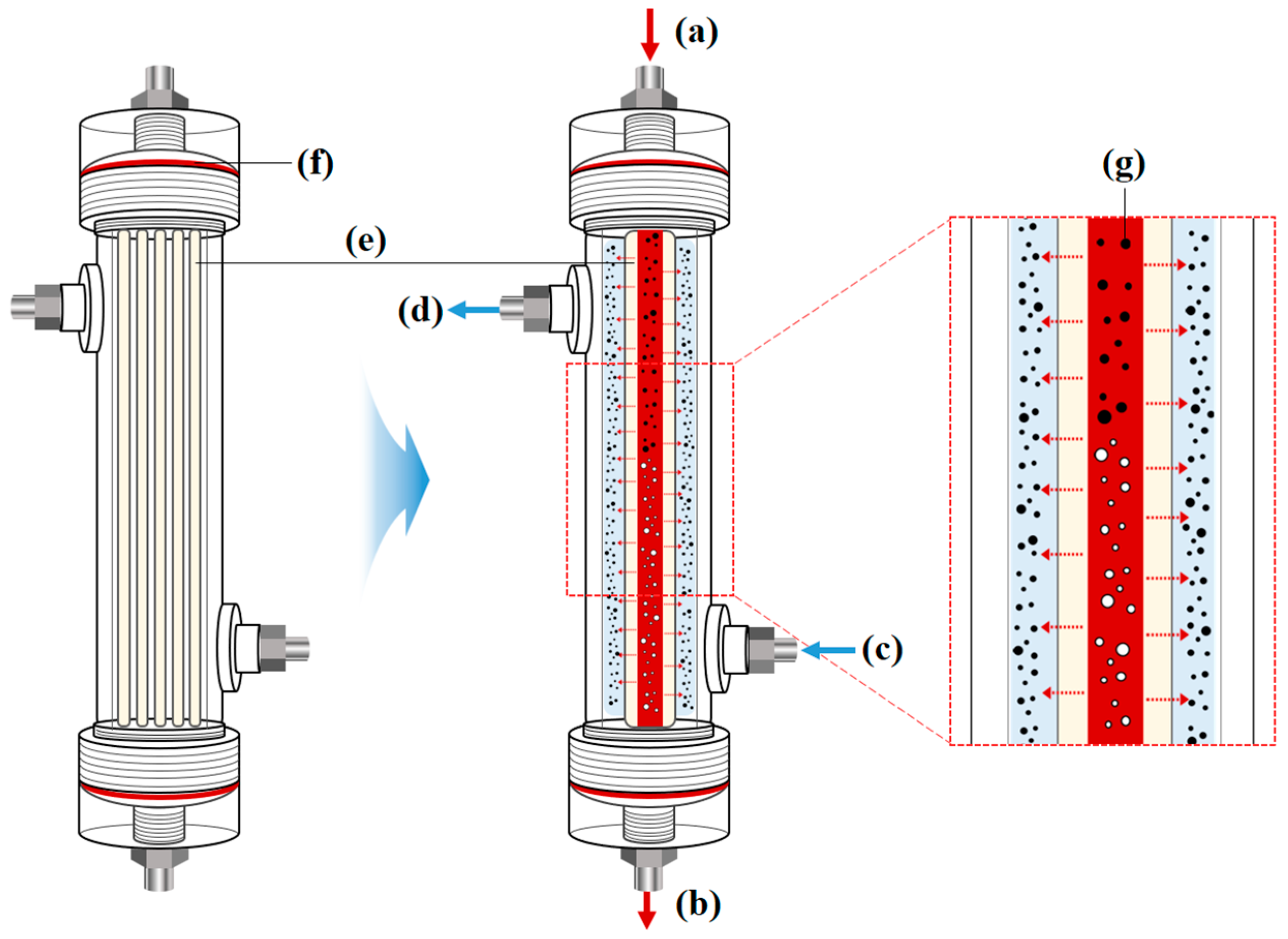
2.2. Preparation of Al2O3 Hollow Fiber Membranes and Lab-Scale Hemodialyzer
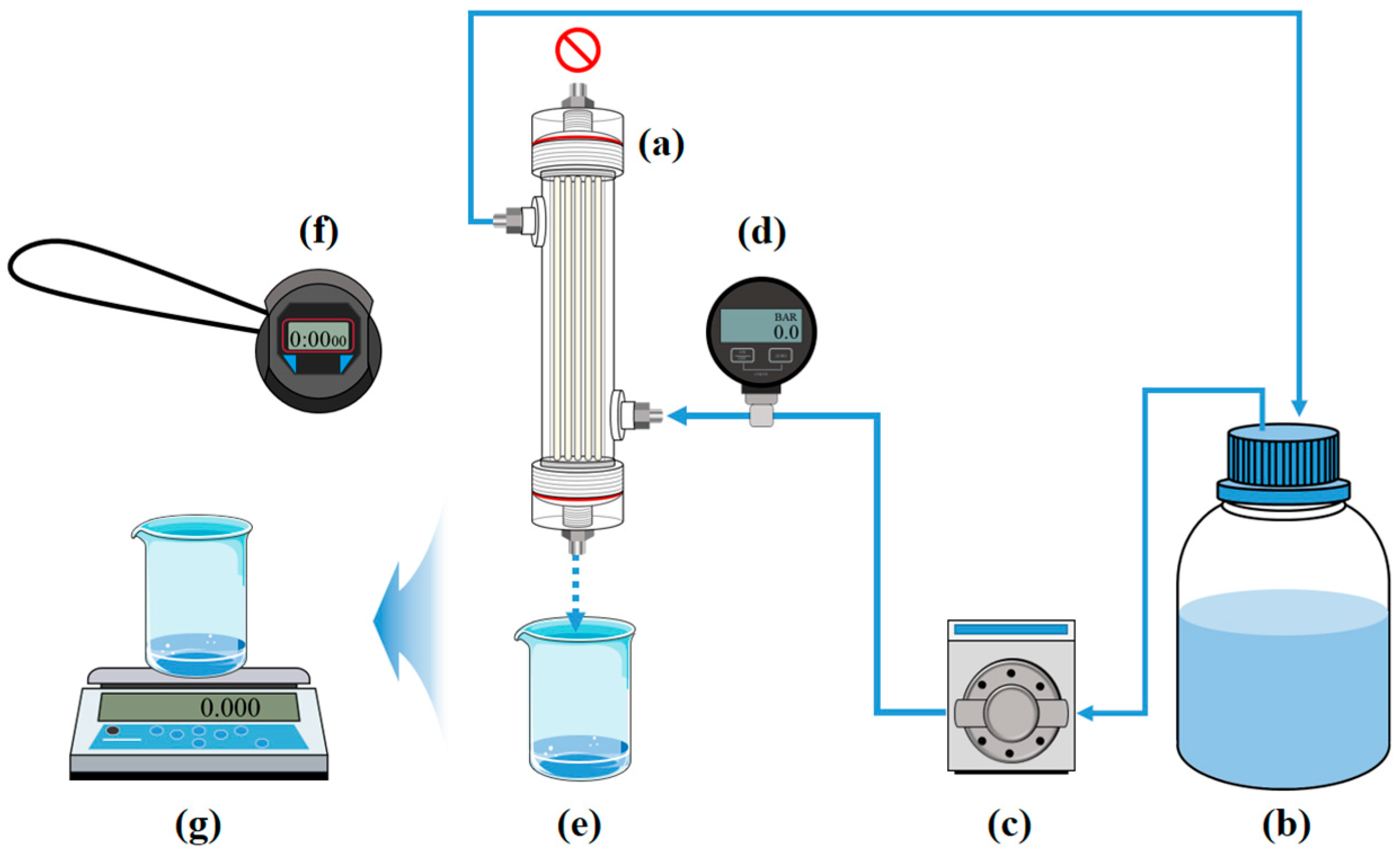
2.3. Characterization of Al2O3 Hollow Fiber Membranes and Lab-Scale Hemodialyzer
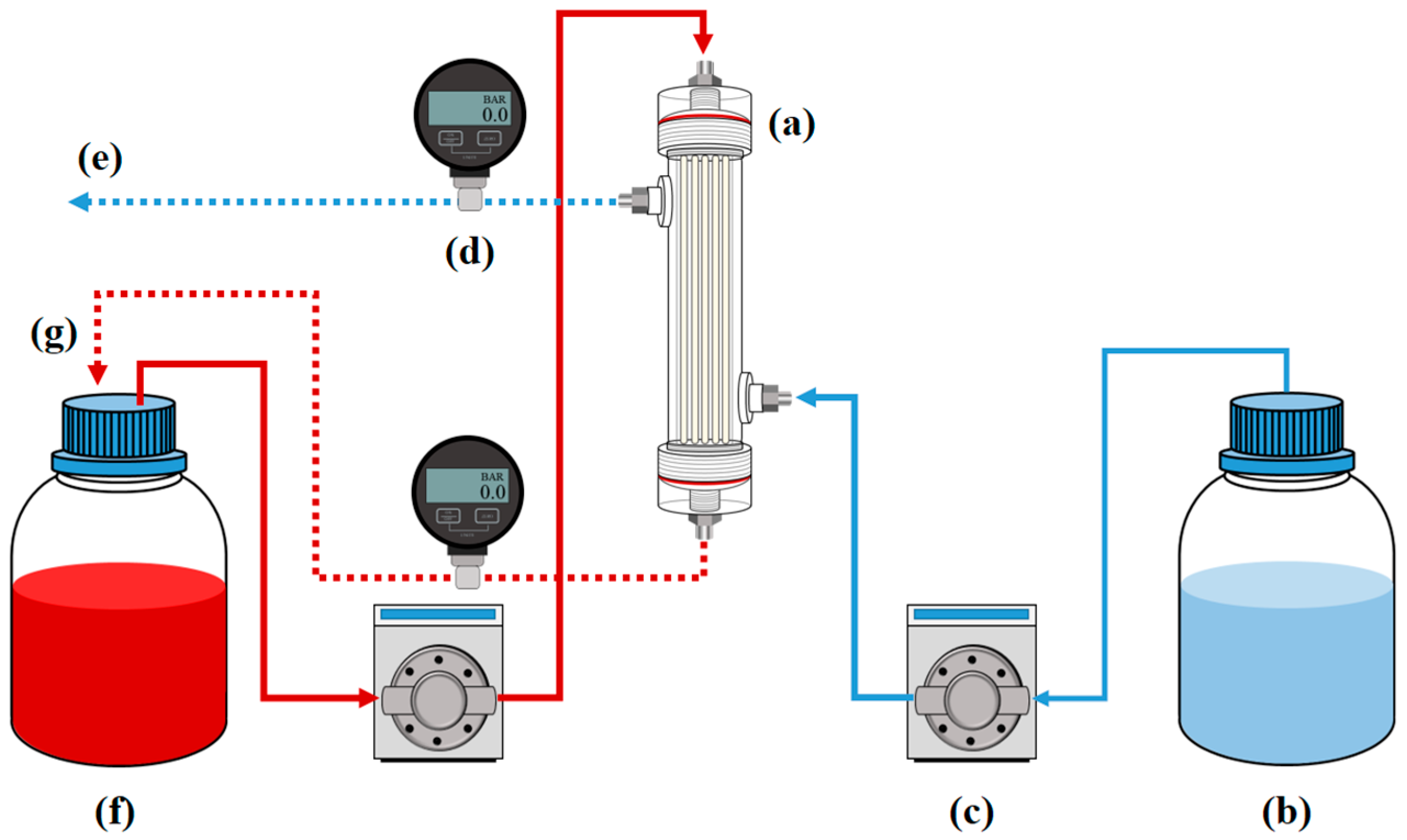
2.4. Hemodialysis Experiment of Lab-Scale Hemodialyzer
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure and Surface Characteristics of Al2O3 Hollow Fiber Membranes
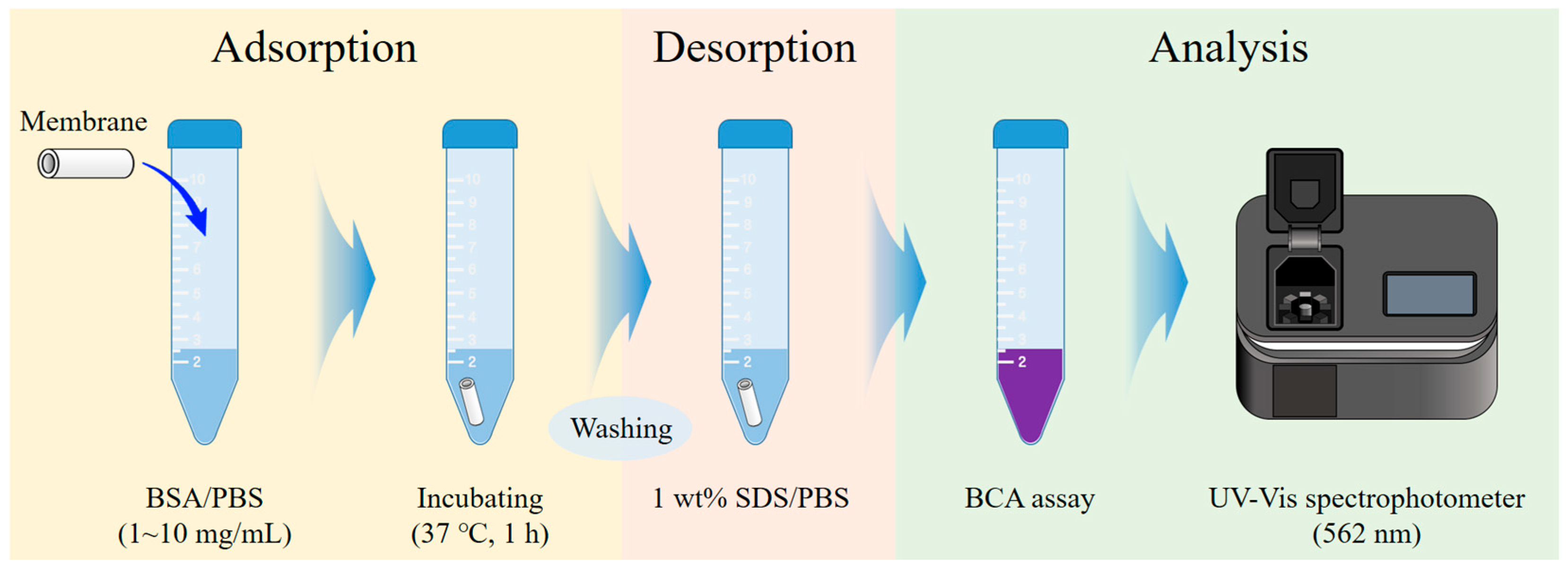
3.2. Protein Adsorption Test Result of Ceramic Hollow Fiber Membranes
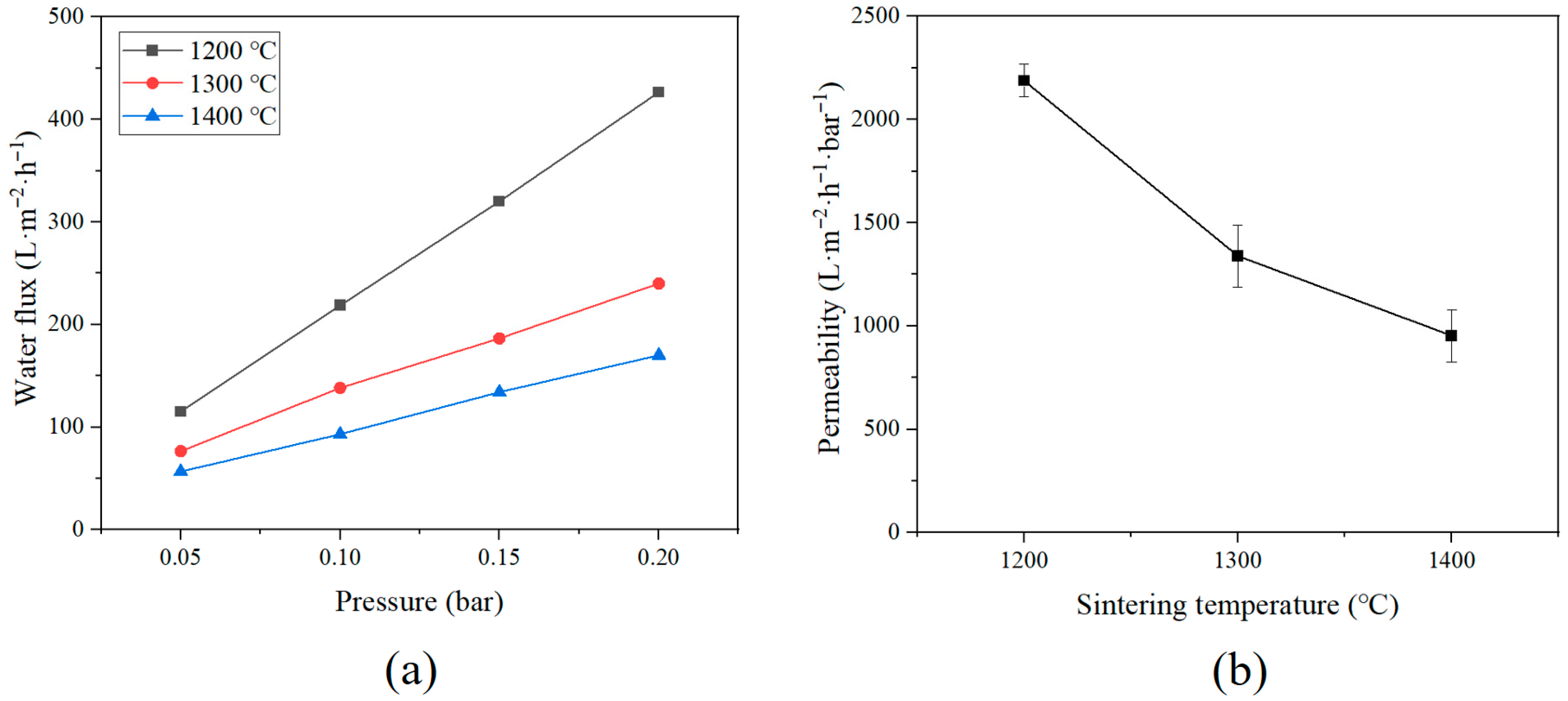
3.3. Water Flux and Permeability of Lab-Scale Hemodialyzer
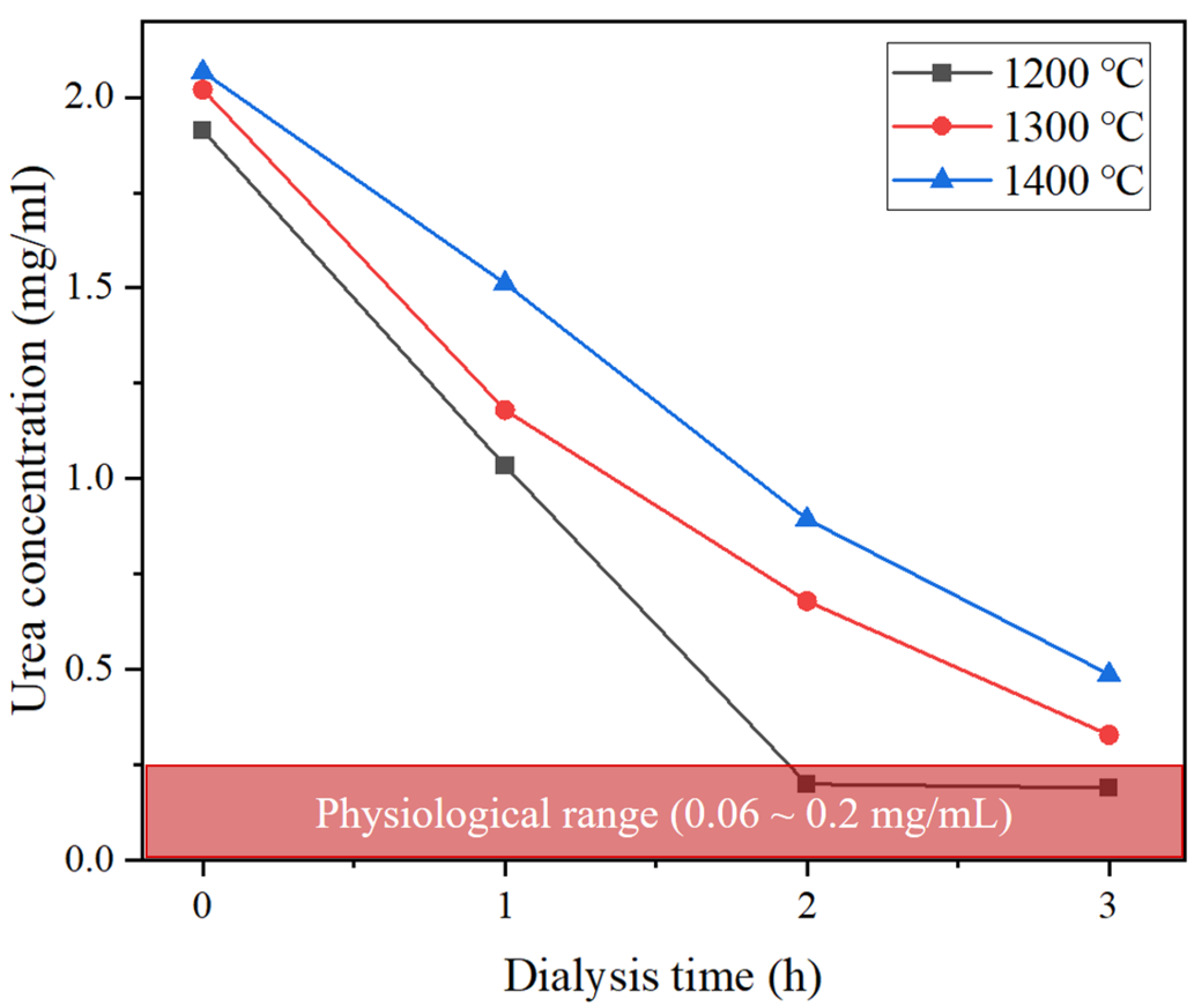
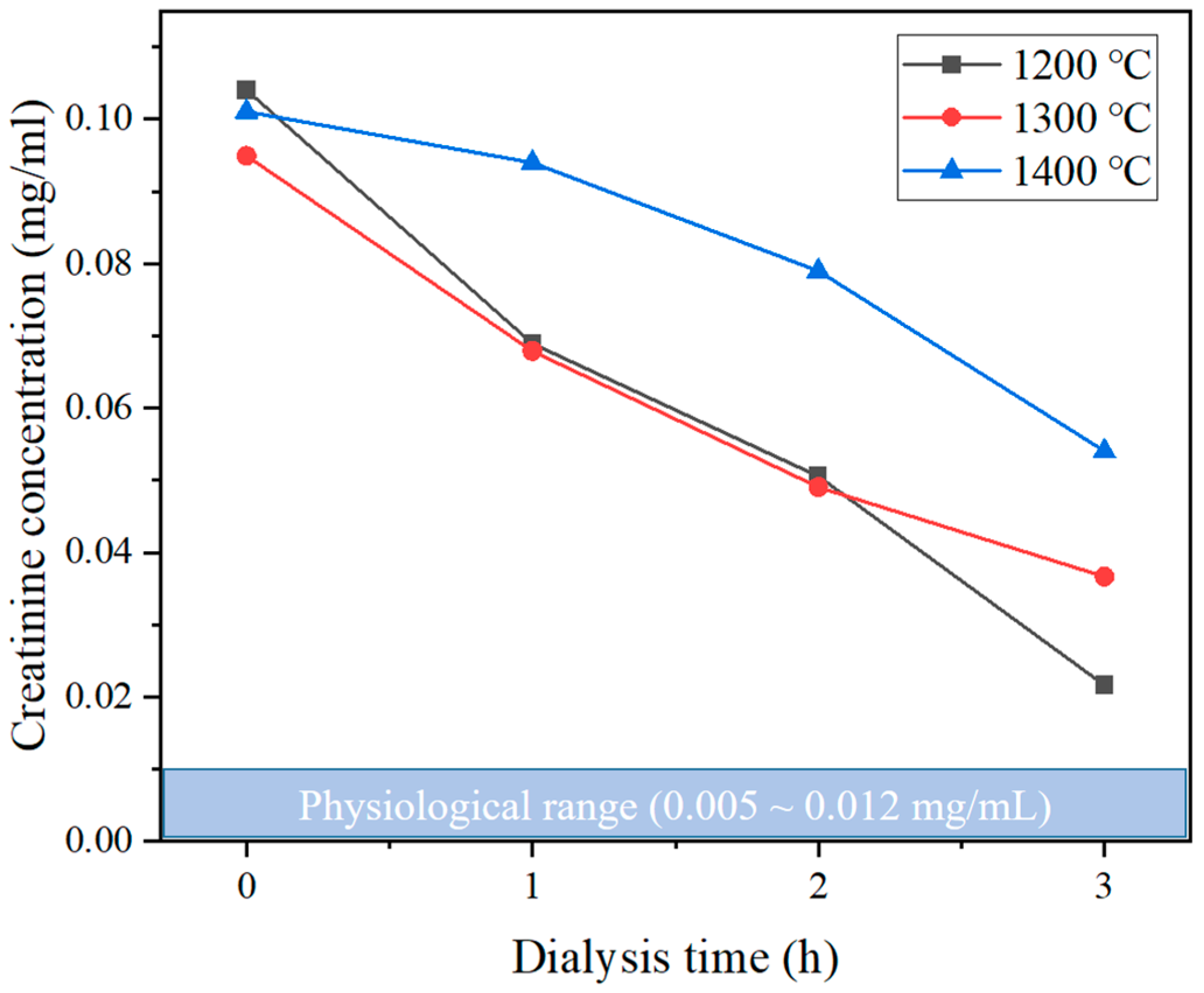
3.4. Hemodialysis Performance Evaluation of Lab-Scale Hemodialyzer
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Shu, G.; Ni, F.; Li, K.; Kong, X.; Zheng, S.; Ma, R.; Li, T.; Liu, H.; et al. Structure design and performance study on filtration-adsorption bifunctional blood purification membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins Costa, A.; Halfwerk, F.R.; Thiel, J.-N.; Wiegmann, B.; Neidlin, M.; Arens, J. Effect of hollow fiber configuration and replacement on the gas exchange performance of artificial membrane lungs. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 680, 121742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, Z.; Chen, L.; Han, H. Macrophage membrane-coated nanoscale allicin for the targeted treatment of drug-resistant bacterial pneumonia. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2025, 8, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, N.; Jahanbekam, S.; Ashrafi, H.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Azadi, A. Recent biomaterial-assisted approaches for immunotherapeutic inhibition of cancer recurrence. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 1207–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Reis, T.; Husain-Syed, F. Management of acute kidney injury in patients with COVID-19. Blood Purif. 2021, 50, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardowski, Z.J. History of hemodialyzers’ designs. Hemodial. Int. 2008, 12, 173–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, C.W.; Fellner, S.K. History of the science of dialysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 1997, 17, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagg, C.R. Willem Kolff and the artificial kidney. Lancet 2001, 358, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, H.D.; Fissell, W.H.; Tiranathanagul, K. The future of hemodialysis membranes. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Ou, S.-M.; Lin, C.-C. Influence of dialysis membranes on clinical outcomes: From history to innovation. Membranes 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, S.C.; Derebail, V.K.; Poulton, C.L.; Bunch, D.O.; Roy-Chaudhury, P.; Key, N.S. Hemodialysis-related complement and contact pathway activation and cardiovascular risk: A narrative review. Kidney Med. 2021, 3, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olafiranye, F.; Kyaw, W.; Olafiranye, O. Resolution of dialyzer membrane-associated thrombocytopenia with use of cellulose triacetate membrane: A case report. Case Rep. Med. 2011, 2011, 134295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.C.; Togo, K. Blood compatibility in various hemodialysis membrane materials: A review. J. Clin. Haematol. 2021, 2, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, T.; Zhao, H.; Mo, Q.; Pan, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, H.; Hu, B.; Song, H. From cellulose to cellulose nanofibrils—A comprehensive review of the preparation and modification of cellulose nanofibrils. Materials 2020, 13, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, E.R.; Voicu, S.I. Functionalized hemodialysis polysulfone membranes with improved hemocompatibility. Polymers 2022, 14, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Ji, H.; Zhao, W.; Sun, S.; Zhao, C. Hemocompatibility enhancement of polyethersulfone membranes: Strategies and challenges. Adv. Membr. 2021, 1, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani, B.; Oghyanous, F.A.; Karsaz, M.; Golkar, M.; Etemadi, H.; Khosroshahi, H.T.; Yegani, R. Fabrication and characterization of novel PES-based nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes for the hemodialysis process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, N.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y. Additive-free preparation of hemodialysis membranes from silibinin-modified polysulfone polymer with enhanced performance in anti-oxidative stress and hemocompatibility. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 713, 123345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, H.; Sayed, K.S.; Gharib, M.S. Effect of dialyzer geometry on coagulation activation in the extracorporeal circuit in maintenance hemodialysis patients: Prospective randomized trial. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2023, 27, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.; Lau, W.J.; Ho, Y.-C.; Lim, S.K.; Abidin, M.N.Z.; Ismail, A.F. A Review of Commercial Developments and Recent Laboratory Research of Dialyzers and Membranes for Hemodialysis Application. Membranes 2021, 11, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutov, E.; Mishin, O. Evaluation of the Effect of the PMMA Dialysis Membrane on the Level of Inflammation in Patients on Hemodialysis. Blood Purif. 2023, 52 (Suppl. S1), 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlerding, G.; Ries, W.; Kempkes-Koch, M.; Ziegler, E.; Erlenkötter, A.; Zawada, A.M.; Kennedy, J.P.; Ottillinger, B.; Stauss-Grabo, M.; Lang, T. Randomized comparison of three high-flux dialyzers during high-volume online hemodiafiltration—The comPERFORM study. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.D.; Mehdi, M.S.; Ullah, H.; Arshad, A. The novel amine functionalized TiO2-polyvinylpyrrolidone k-25 composite biomaterial-based polysulfone membranes for dialysis; an experimental study. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2025, 65, 3259–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoako, K.; Ukita, R.; Cook, K.E. Antifouling Zwitterionic Polymer Coatings for Blood-Bearing Medical Devices. Langmuir 2025, 41, 2994–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, A. Siloxane-Based Segmented Poly(urethane-urea) Elastomers with Enhanced Mechanical Properties, Hydrophobicity and Anti-Calcification Based on Hierarchical Phase Separation for Potential Applications of Polymeric Heart Valve. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 218, 113349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.K.; Wang, X.; Yu, M.; Pantrangi, M.; Sun, Z.; Ran, F. Sulphated Natural Bio-Polysaccharide Grafted Magnetic Nanoparticles: Experimental and Simulation towards Safe and Biocompatible Polymeric Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 712, 123224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Abdeltasoul, A. Impact of Membrane Modification and Surface Immobilization Techniques on the Hemocompatibility of Hemodialysis Membranes: A Critical Review. Membranes 2022, 12, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, E.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, S.M.; Heo, H.J.; Han, D.; Kim, J.F.; Park, A.; Choi, D.H.; Park, Y.; Park, H.; et al. Superamphiphobic Blood-Repellent Surface Modification of Porous Fluoropolymer Membranes for Blood Oxygenation Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 648, 120363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Abdelsrasoul, A. Surface Zwitterionization of Hemodialysis Membranes for Hemocompatibility Enhancement and Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion: A Critical Review. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 2022, 3, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomini, M.; Piscitani, L.; Di Liberato, L.; Sirolli, V. Biocompatibility of Surface-Modified Membranes for Chronic Hemodialysis Therapy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, P.; Sundarrajan, S.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Seshan, S.; Das, D.B.; Ismail, A.F. Advancements in Modification of Membrane Materials over Membrane Separation for Biomedical Applications—Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 204 Pt B, 112045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Magnone, E. Study on Design Strategies and on New Structure–Performance Relationships for CO2 Capture in Gas–Liquid Hollow Fiber Membrane Contactors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Park, C.-G.; Yeo, I.-S.; Park, J.H.; Magnone, E. Successful Removal of Phenol from Industrial Wastewater Using Novel Hydrophobic Modified Ceramic Hollow Fiber Membrane Contactors with Remarkably High Stability. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 114, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnone, E.; Lee, J.I.; Shin, M.C.; Zhuang, X.; Hwang, J.Y.; Han, S.W.; Park, J.H. Synergistic Approach to High-Performance Ultra-Thin Supported Pd-Based Membranes: Sacrificial Graphene Oxide Interlayer and Vacuum-Assisted Dip-Coating. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 699, 122660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobloth, A.-M.; Mersiowsky, M.J.; Kliemt, L.; Schell, H.; Dienelt, A.; Pfitzner, B.M.; Burgkart, R.; Detsch, R.; Wulsten, D.; Boccaccini, A.R.; et al. Bioactive Coating of Zirconia Toughened Alumina Ceramic Implants Improves Cancellous Osseointegration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, E.; Li, B. From Innovation to Application: Safety Concerns in Nanomaterial Implant Coatings. Nanomedicine 2025, 20, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mthisi, A.; Popoola, A.P.I.; Kanyane, L.R.; Raji, S.A.; Malatji, N. The Possibility of Using Laser Surface Engineered Titanium Alloy Implants as a Treatment for Cardiovascular Diseases. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 2024, 8, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yue, Y.; Huang, X.; Meng, D. Protein adsorption on blood-contact membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 222, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghnani, R.; Kumar, M.; Pugazhendhi, G.; Dhakshinamoorthy, V. Synthesis of Ceramic Membrane Using Inexpensive Precursors and Evaluation of Its Biocompatibility for Hemofiltration Application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 256, 117814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mzyk, A.; Imbir, G.; Trembecka-Wójciga, K.; Lackner, J.M.; Plutecka, H.; Jasek-Gajda, E.; Kawalko, J.; Major, R. Rolling or Two-Stage Aggregation of Platelets on the Surface of Thin Ceramic Coatings under In Vitro Simulated Blood Flow Conditions. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 898–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tang, S.M.; Yu, J.; Lai-Fook, S.J.; Gao, D. A Study of a New Ceramic Membrane for Use in Hemodialysis. In Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 13–19 November 2004; pp. 669–675, Paper No. IMECE2004-59404. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Gao, D. Nanoporous Alumina Membranes for Enhancing Hemodialysis. J. Med. Devices 2007, 1, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Attaluri, A.C.; Belwalkar, A.; Van Geertruyden, W.; Gao, D.; Misiolek, W. An Experimental Study of Transport Properties of Ceramic Membranes for Use in Hemodialysis. In Proceedings of the ASME 2008 Summer Bioengineering Conference, Marco Island, FL, USA, 25–29 June 2008; pp. 459–460, SBC2008-192808. [Google Scholar]
- Roshni, M.; Pugazhendhi, G.; Periyasamy, R.; Vasanth, D. Synthesis of ceramic tubular membrane from low-cost clay precursors for blood purification application as substitute of commercial dialysis membrane. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 2128–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, H.; Pflanzen, A.; Saunders, N.; Czermak, P.; Catapano, G.; Vienken, J. Membranes for Endotoxin Removal from Dialysate: Considerations on Feasibility of Commercial Ceramic Membranes. Artif. Organs 2000, 24, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czermak, P.; Ebrahimi, M.; Catapano, G. New Generation Ceramic Membranes have the Potential of Removing Endotoxins from Dialysis Water and Dialysate. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2005, 28, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K.M.; Gekas, V.; Trägårdh, G. Study of membrane compaction and its influence on ultrafiltration water permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


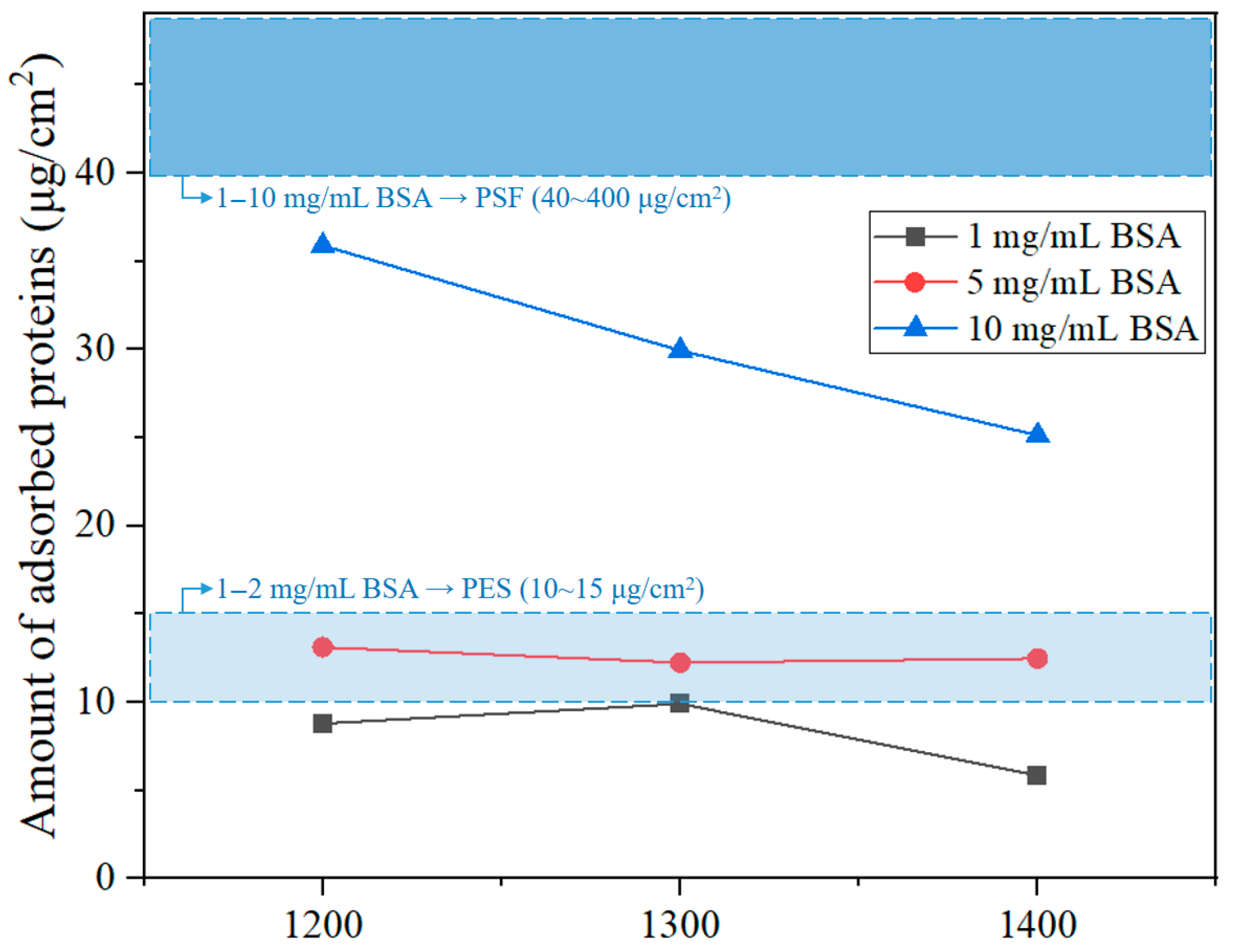
| BSA Concentration (mg/mL) | Sintering Temperature (°C) | Adsorbed Protein (μg/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1200 | 8.79 |
| 1300 | 9.91 | |
| 1400 | 5.84 | |
| 5 | 1200 | 13.12 |
| 1300 | 12.24 | |
| 1400 | 12.48 | |
| 10 | 1200 | 35.88 |
| 1300 | 29.94 | |
| 1400 | 25.12 |
| BSA Concentration (mg/mL) | Sintering Temperature (°C) | Surface Area (cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1200 | 2.42 |
| 1300 | 2.53 | |
| 1400 | 2.37 | |
| 5 | 1200 | 2.46 |
| 1300 | 2.65 | |
| 1400 | 2.41 | |
| 10 | 1200 | 2.74 |
| 1300 | 2.64 | |
| 1400 | 2.32 |
| Sintering Temperature (°C) | 1200 | 1300 | 1400 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Removal rate (%) (h = 1) | 45.96 | 41.58 | 26.82 |
| Initial concentration (mg/dL) | 191.321 | 202.014 | 206.665 |
| Extraction ratio (E) | 0.4596 | 0.4155 | 0.2681 |
| K (L/min) | 0.0184 | 0.0166 | 0.0107 |
| Kt/V (direct) (t = 60) | 1.10 | 1.00 | 0.64 |
| Kt/V (log model) (t = 60) | 0.61 | 0.53 | 0.31 |
| Sintering Temperature (°C) | 1200 | 1300 | 1400 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEM observation | Finger-like pores, loose bonding | Reduced pores, denser structure | Dense, compact structure |
| Contact angle (°) | 23.10 | 27.96 | 34.13 |
| AFM Ra (nm) | 123 | 97.2 | 78.2 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 7.03 ± 0.83 | 32.19 ± 0.36 | 87.74 ± 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, J.Y.; Han, S.W.; Huh, S.H.; Park, S.H.; Park, S.M.; Park, J.H. Fabrication and Evaluation of Ceramic-Based Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Hemodialysis Applications. Membranes 2025, 15, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090251
Hwang JY, Han SW, Huh SH, Park SH, Park SM, Park JH. Fabrication and Evaluation of Ceramic-Based Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Hemodialysis Applications. Membranes. 2025; 15(9):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090251
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Jae Yeon, Sung Woo Han, Seung Hee Huh, So Hee Park, Sang Min Park, and Jung Hoon Park. 2025. "Fabrication and Evaluation of Ceramic-Based Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Hemodialysis Applications" Membranes 15, no. 9: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090251
APA StyleHwang, J. Y., Han, S. W., Huh, S. H., Park, S. H., Park, S. M., & Park, J. H. (2025). Fabrication and Evaluation of Ceramic-Based Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Hemodialysis Applications. Membranes, 15(9), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090251








