Review of Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation: Exploring Fundamentals and Recent Advancements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material for HFMs
2.1. Rubbery Materials
2.2. Glassy Materials
2.3. Polymer Blends
2.4. Hollow Fiber Mixed-Matrix Membranes (HF-MMMs)
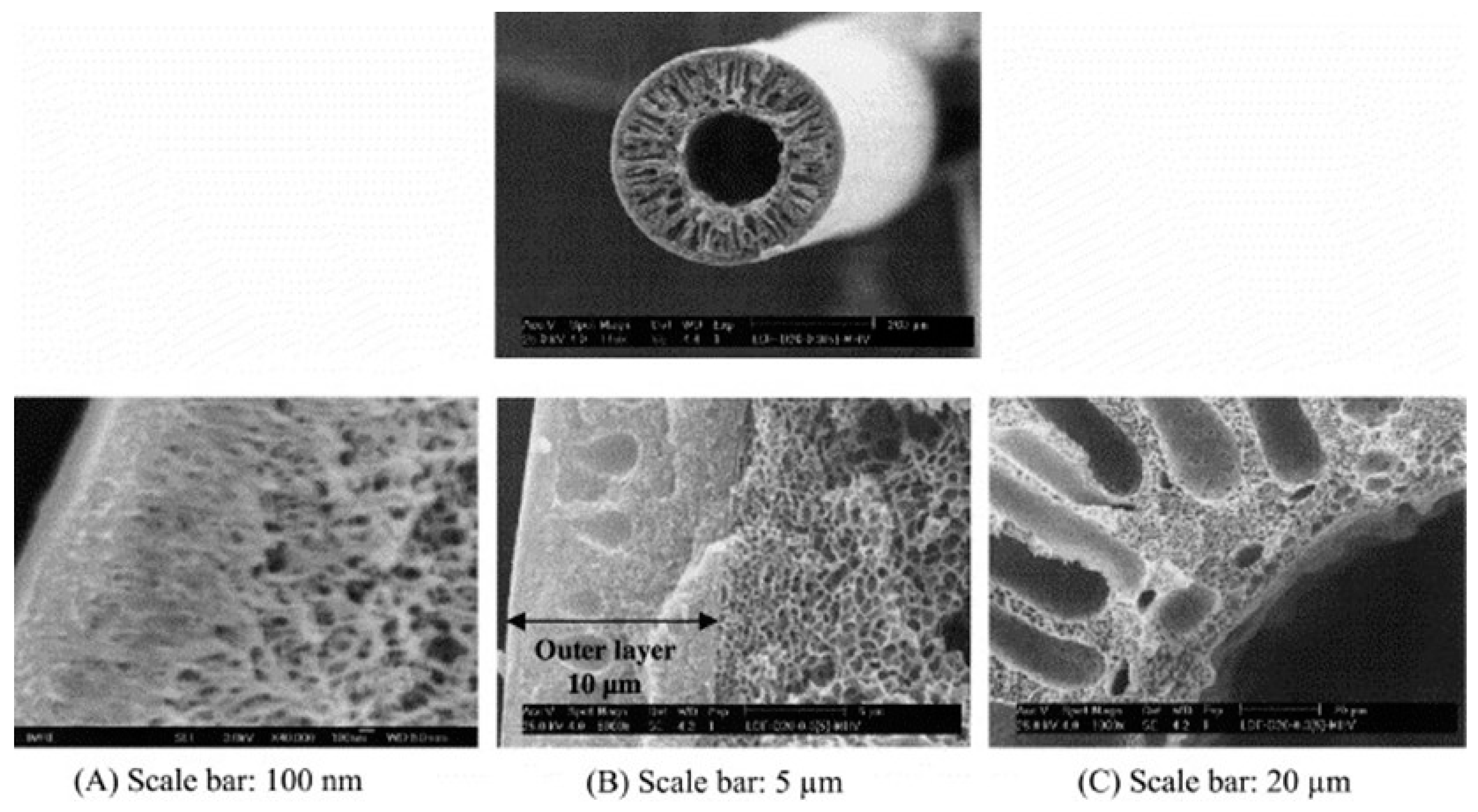
3. Preparation Methods and Impact on HFMs Structures
3.1. Dry–Wet Spinning
3.2. Melt Spinning
3.3. Dip Coating and Dynamic Coating
3.4. 3D Printing
3.5. Dual-Layer Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membranes
3.6. TFC-Hollow Fiber Membranes
3.6.1. Multi-Layer TFC-HF
3.6.2. TFCs by Dip Coating and Dynamic Coating
3.7. Green and Sustainable Development of HFMs Preparation
3.8. Critical Aspects in the Preparation of HFMs for Gas Separation
4. HF Properties and Characterization
4.1. Mechanical Properties
4.2. Swelling/Plasticization
4.3. Thermal Properties
4.4. Physical Aging
4.4.1. Basic Principle
4.4.2. Mitigation of Physical Aging
4.4.3. Exploitation of Physical Aging
4.5. Modeling
5. Industrial Scalability of Hollow Fibers for Gas Separation
5.1. Manufacturing Methods and Their Advantages
5.2. Cost–Benefit Considerations and Durability
5.3. Balancing Durability with Performance: The Role of Robeson Plots
6. Hollow Fibers for Gas Separation Processes
6.1. Helium Separation from Natural Gas
6.2. H2-Recovery
6.2.1. H2-Selective Hollow Fiber Membranes
6.2.2. CO2 Selective HFMs
6.3. O2/N2 Separation
6.4. H2O/Air
6.5. CO2 Separation Processes
6.5.1. Biogas Upgrading and CO2/CH4 Separation
6.5.2. CO2/N2 and Flue Gas Purification
6.6. Olefin/Paraffin Separation
6.6.1. Polymeric Membranes
6.6.2. Hybrid Supported Membranes
6.6.3. Hybrid Mixed-Matrix Membranes
7. Future Outlooks and Emerging Trends in Hollow Fiber Membranes
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATRP | Atom transfer radical polymerization |
| CA | Cellulose acetate |
| CDA | Cellulose diacetate |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| CH4 | Methane |
| CHFMs | Carbon hollow fiber membranes |
| CMS | Carbon molecular sieve |
| CNTs | Carbon nanotubes |
| CO2 | Carbone dioxide |
| COF | Covalent organic framework |
| COP | Coefficient of performance |
| CTA | Cellulose triacetate |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ECMO | Extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| GBL | Gamma-butyrolactone |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| GPU | Gas permeation unit |
| HF | Hollow fiber |
| HFMs | Hollow fiber membranes |
| ILs | Ionic liquids |
| IMMP | Interfacial microfluidic membrane processing |
| IP | Interfacial polymerization |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| ME | Mixed ester |
| ML | Machine learning |
| MMMs | Mixed-matrix membranes |
| MOF | Metal–organic framework |
| m-PBI | Meta-polybenzimidazole |
| MPD | M-phenylene diamine |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| N2 | Nitrogen |
| NIPS | Nonsolvent-induced phase separation |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| O2 | Oxygen |
| OEA | Oxygen-enriched air |
| OEG | Oxygen-enriched gas |
| PAI | Polyamide-imide |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| PBI | Polybenzimidazole |
| PDA | Poly(dopamine) |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| Pebax® | Poly(ether-block-amide |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| PEI | Polyethylenimine, Polyetherimide |
| PES | Polyethersulfone |
| PFPs | Perfluoropolymers |
| PI | Polyimide |
| PIMs | Polymers of intrinsic microporosity |
| PLA | Poly(lactic acid) |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PPO | Poly(phenyleneoxide |
| PSA | Pressure swing adsorption |
| PSF | Polyphenylsulfone |
| PS-PEGMA | Poly(styrene)-b-poly (ethylene glycol) methacrylate |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| PTMSP | Poly[1-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propyne] |
| TEP | Triethyl phosphate |
| TFC | Thin-film composite |
| TFC-HFMs | Thin-film composite hollow fiber membranes |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature |
| TIPS | Thermally induced phase separation |
| TFN | Thin-film nanocomposite |
| TMC | Trimesoyl chloride |
| TR | Thermally rearranged |
| STP | Standard temperature and pressure |
| VOCs | Volatile organic compounds |
References
- Naderi, A.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C. High Performance Dual-Layer Hollow Fiber Membrane of Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone/Polybenzimidazole for Hydrogen Purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T. XXII.-On the Absorpion and Dialytic Separation of Gases by Colloid Septa. J. Chem. Soc. 1867, 20, 235–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stannett, V. The Transport of Gases in Synthetic Polymeric Membranes—An Historic Perspective. J. Membr. Sci. 1978, 3, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, S.; Sourirajan, S. Sea Water Demineralization by Means of an Osmotic Membrane. Saline Water Convers.-II Adv. Chem. Ser. 1963, 38, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mahon, H.I. Permeability Separatory Apparatus, Permeability Separatory Membrane Element, Method of Making the Same and Process Utilizing the Same. US Patent 3228876A, 11 January 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Henis, J.M.; Tripodi, M.K. The Developing Technology of Gas Separating Membranes. Science 1983, 220, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, L.V. Saline Water Conversion. J. AOAC Int. 1961, 44, 374–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Future Directions of Membrane Gas Separation Technology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 1393–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, R.S.; Sankarshana, T.; Sridhar, S. Air Separation by Polymer-Based Membrane Technology. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2013, 42, 130–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Sheng, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Mao, S.; Wang, D.; Guo, B.; Ye, N.; et al. Membrane Technology for CO2 Capture: From Pilot-Scale Investigation of Two-Stage Plant to Actual System Design. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 624, 119137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sunarso, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, R. Current Status and Development of Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation: A Review. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 12, 84–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazali, N.; Mohamed, M.A.; Salleh, W.N.W. Membranes for Hydrogen Separation: A Significant Review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 1859–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorg, M.; Addis, B.; Piccialli, V.; Ramírez-Santos, Á.A.; Castel, C.; Pinnau, I.; Favre, E. Polymeric Membrane Materials for Nitrogen Production from Air: A Process Synthesis Study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 207, 1196–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himma, N.F.; Wardani, A.K.; Prasetya, N.; Aryanti, P.T.P.; Wenten, I.G. Recent progress and challenges in membrane-based O2/N2 separation. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Lasseuguette, E.; Rouch, J.C.; Remigy, J.C. Hollow-Fiber Coating: Application to Preparation of Composite Hollow-Fiber Membrane for Gas Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13146–13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulhairun, A.K.; Subramaniam, M.N.; Samavati, A.; Ramli, M.K.N.; Krishparao, M.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. High-Flux Polysulfone Mixed Matrix Hollow Fiber Membrane Incorporating Mesoporous Titania Nanotubes for Gas Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 180, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Paul, D.R. Gas Permeation in Poly(Ether Imide) Nanocomposite Membranes Based on Surface-Treated Silica. Part 2: With Chemical Coupling to Matrix. Polymer 2006, 47, 7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Ingole, P.G.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.K. Separation Performance of PEBAX/PEI Hollow Fiber Composite Membrane for SO2/CO2/N2 Mixed Gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 233, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Revuelta, D.; Fallanza, M.; Ortiz, A.; Gorri, D. Thin-Film Composite Matrimid-Based Hollow Fiber Membranes for Oxygen/Nitrogen Separation by Gas Permeation. Membranes 2023, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.A.; Gordeyev, S.A.; Shilton, S.J. Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Hollow Fibre Membranes for Gas Separation. Polymer 2011, 52, 901–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, I.; Morimoto, T.; Kusagawa, M. Development of a Silicon Hollow Fiber Membrane-Oxygenator; Blackwell Science Inc.: Malden, MA, USA, 1981; Volume 5, pp. 324–325. [Google Scholar]
- Farrukh, S.; Javed, S.; Hussain, A.; Mujahid, M. Blending of TiO2 Nanoparticles with Cellulose Acetate Polymer: To Study the Effect on Morphology and Gas Permeation of Blended Membranes. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 9, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Monteleone, M.; Fuoco, A.; Longo, M.; Jansen, J.C. Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation. In Hollow Fibers and Nanofibers in Membrane Science: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications; Figoli, A., Dorraji, S.S., Galiano, F., Eds.; Jenny Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2022; ISBN 978-981-4968-03-4. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; ISBN 978-1-119-68598-2. [Google Scholar]
- Comesaña-Gándara, B.; Chen, J.; Bezzu, C.G.; Carta, M.; Rose, I.; Ferrari, M.C.; Esposito, E.; Fuoco, A.; Jansen, J.C.; McKeown, N.B. Redefining the Robeson Upper Bounds for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 Separations Using a Series of Ultrapermeable Benzotriptycene-Based Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M.; Smith, Z.P.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R. Contributions of Diffusion and Solubility Selectivity to the Upper Bound Analysis for Glassy Gas Separation Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. In-Situ Grafting to Improve Polarity of Polyacrylonitrile Hollow Fiber-Supported Polydimethylsiloxane Membranes for CO2 Separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 510, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargari, A.; Rezaeinia, S. State-of-the-Art Modification of Polymeric Membranes by PEO and PEG for Carbon Dioxide Separation: A Review of the Current Status and Future Perspectives. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 84, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.F.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Shilton, S.J. Studies on Gas Permeation Performance of Asymmetric Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Mixed Matrix Membranes Using Nanosized Fumed Silica as Fillers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 86, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Xie, X. Proton Exchange Membranes Prepared via Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 30013–30028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Elimelech, M.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling Membranes for Sustainable Water Purification: Strategies and Mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5888–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilongo, T.G.; Remigy, J.C.; Clifton, M.J. Modification of Hollow Fibers by UV Surface Grafting. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittrakarn, T.; Tirawanichakul, Y.; Sirijarukul, S.; Yuenyao, C. Plasma Induced Graft Polymerization of Hydrophilic Monomers on Polysulfone Gas Separation Membrane Surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 296, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Askari, M.; Liang, C.Z.; Peng, N.; Farrukh, S.; Hussain, A.; Chung, T.S. Advanced Multiple-Layer Composite CTA/CDA Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2 Separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 625, 119124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, S.R.; Offord, G.T.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E. Co-Extruded Polymeric Films for Gas Separation Membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 39765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.Z.; Yong, W.F.; Chung, T.S. High-Performance Composite Hollow Fiber Membrane for Flue Gas and Air Separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.C.; Lai, S.O.; Lau, W.J.; Thiam, H.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Roslan, R.A. Preparation, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membrane with PEBAX or PDMS Coating for Oxygen Enhancement Process. Polymers 2018, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Tan, S.; Wan, Y. Plasma Modification of Substrate with Poly(Methylhydrosiloxane) for Enhancing the Interfacial Stability of PDMS/PAN Composite Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesswein, I.; Hirth, T.; Schiestel, T. Continuous Dip Coating of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes with PVA for Humidification. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-A.; Chen, Y.-L.; Huang, S.-H.; Hu, C.-C.; Hung, W.-S.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Preparation of Polyamide/Polyacrylonitrile Composite Hollow Fiber Membrane by Synchronous Procedure of Spinning and Interfacial Polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 551, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.-S.; An, X.; Ingole, P.G.; Choi, W.-K.; Park, Y.-S.; Lee, H.-K. CO2/CH4 Separation Using inside Coated Thin Film Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes Prepared by Interfacial Polymerization. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Tian, Z.; Xin, Q.; He, G.; Peng, D.; Chen, S.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Advances in High Permeability Polymer-Based Membrane Materials for CO2 Separations. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1863–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The Upper Bound Revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaidan, R.; Ghanem, B.; Pinnau, I. Fine-Tuned Intrinsically Ultramicroporous Polymers Redefine the Permeability/Selectivity Upper Bounds of Membrane-Based Air and Hydrogen Separations. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chakma, A.; Feng, X. Preparation of Hollow Fiber Poly(Ether Block Amide)/Polysulfone Composite Membranes for Separation of Carbon Dioxide from Nitrogen. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 105, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemifard, S.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; DashtArzhandi, M.R. Performance of Silicon Rubber Coated Polyetherimide Hollow Fibers for CO2 Removal via a Membrane Contactor. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48442–48455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, W.; Mansouri, J.; Li, H.; Chen, V. Improving CO2 Separation Performance of Thin Film Composite Hollow Fiber with Pebax®1657/Ionic Liquid Gel Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Thong, Z.; Li, P.; Chung, T.S. High Performance Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2/H2 and CO2/N2 Separation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5043–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Clarizia, G.; Bernardo, P.; Jansen, J.C.; Sedláková, Z.; Izák, P.; Curcio, S.; de Cindio, B.; Tasselli, F. Pebax®/PAN Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2015, 94, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrov, G.; Ivanov, M.; Semyashkin, M.; Sudin, V.; Kagramanov, G. High-Pressure Aging of Asymmetric Torlon® Hollow Fibers for Helium Separation from Natural Gas. Fibers 2018, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kujawski, W.; Knozowska, K.; Kujawa, J. The Effects of PEI Hollow Fiber Substrate Characteristics on PDMS/PEI Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2/N2 Separation. Membranes 2021, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnam, M.; Mukhtar, H.; Shariff, A. Investigation of Optimum Drying Conditions for Pure PES Membranes for Gas Separation. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2015, 9, 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Pientka, Z.; Peter, J.; Válek, R. Membrane Unit for Integrated Gas Separation—Membrane Bioreactor (GS-MBR) System. Hung. J. Ind. Chem. 2022, 50, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, P.M.; Ghanem, B.S.; Makhseed, S.; McKeown, N.B.; Msayib, K.J.; Tattershall, C.E. Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity (PIMs): Robust, Solution-Processable, Organic Nanoporous Materials. Chem. Commun. 2004, 4, 230–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jue, M.L.; Breedveld, V.; Lively, R.P. Defect-Free PIM-1 Hollow Fiber Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Monteleone, M.; Esposito, E.; Fuoco, A.; Tocci, E.; Ferrari, M.-C.; Comesaña-Gándara, B.; Malpass-Evans, R.; McKeown, N.B.; Jansen, J.C. Thin Film Composite Membranes Based on the Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity PIM-EA(Me2)-TB Blended with Matrimid®5218. Membranes 2022, 12, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zuo, J.; Chung, T. Formation of Defect-free Polyetherimide/PIM-1 Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 3848–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.F.; Li, F.Y.; Xiao, Y.C.; Chung, T.S.; Tong, Y.W. High Performance PIM-1/Matrimid Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2/CH4, O2/N2 and CO2/N2 Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 443, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.C.; Tasselli, F.; Tocci, E.; Drioli, E. High-Flux Composite Perfluorinated Gas Separation Membranes of Hyflon® AD on a Hollow Fibre Ultrafiltration Membrane Support. Desalination 2006, 192, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, C.A.; Ghosh, U.K. Review of Membranes for Helium Separation and Purification. Membranes 2017, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S.; Xu, Z.-L. Asymmetric Hollow fiber Membranes Prepared from Miscible Polybenzimidazole and Polyetherimide Blends. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 147, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Peng, N.; Chung, T.S. Gas Separation Membranes Developed through Integration of Polymer Blending and Dual-Layer Hollow Fiber Spinning Process for Hydrogen and Natural Gas Enrichments. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.F.; Zhang, H. Recent Advances in Polymer Blend Membranes for Gas Separation and Pervaporation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 116, 100713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.C.; Cheng, P.H.; Chou, S.C.; Lai, C.L.; Huang, S.H.; Tsai, H.A.; Hung, W.S.; Lee, K.R. Separation Behavior of Amorphous Amino-Modified Silica Nanoparticle/Polyimide Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Ma, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, H.; Ding, X.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X. Interface Engineering of Mixed Matrix Membrane via CO2-Philic Polymer Brush Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanosheets for Efficient Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 586, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Zheng, W.; Yang, K.; Dai, Y.; Ruan, X.; Yan, X.; He, G. Amino-Functional ZIF-8 Nanocrystals by Microemulsion Based Mixed Linker Strategy and the Enhanced CO2/N2 Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Caro, J.; Huang, A. A New UiO-66-NH2 Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes with High CO2/CH4 Separation Performance. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 274, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, K.; Izak, P.; Karaszova, M.; Pasichnyk, M.; Lanč, M.; Nikolaeva, D.; Luis, P.; Jansen, J. A Review on Ionic Liquid Gas Separation Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordoñez, M.J.C.; Balkus, K.J.; Ferraris, J.P.; Musselman, I.H. Molecular Sieving Realized with ZIF-8/Matrimid® Mixed-Matrix Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.H.; Lee, J.S.; Qiu, W.; Koros, W.J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. A High-Performance Gas-Separation Membrane Containing Submicrometer-Sized Metal-Organic Framework Crystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9863–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, C.E.; Qiao, G.G. Polymeric CO2/N2 Gas Separation Membranes for the Capture of Carbon Dioxide from Power Plant Flue Gases. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Prasad, B.; Ahn, Y.H. Recent Developments in Gas Separation Membranes Enhancing the Performance of Oxygen and Nitrogen Separation: A Comprehensive Review. Gas Sci. Eng. 2024, 123, 205256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Koros, W.J. Utilization of Nanoplatelets in Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Separation Materials: Separation Advantages and Formation Challenges. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2009, 40, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpan, E.I.; Shen, X.; Wetzel, B.; Friedrich, K. Design and Synthesis of Polymer Nanocomposites. In Polymer Composites with Functionalized Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 47–83. ISBN 978-0-12-814065-9. [Google Scholar]
- Darban, M.A.; Lock, S.S.M.; Ilyas, S.U.; Waqas, S.; Lim, L.G.; Lock, I.S.M.; Kang, D.-Y.; Othman, M.H.D.; Yiin, C.L.; Hira, N.E.; et al. A Critical Review on Advancements and Challenges in CO2 Gas Separation via 6FDA-Based Membranes. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2025, 15, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Z.X.; Budd, P.M.; McKeown, N.B.; Patterson, D.A. Gas Permeation Properties, Physical Aging, and Its Mitigation in High Free Volume Glassy Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 5871–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.T.; Koros, W.J. Non-Ideal Effects in Organic–Inorganic Materials for Gas Separation Membranes. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 739, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.F.; Chung, T.-S.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y. Fabrication of Fluoropolyimide/Polyethersulfone (PES) Dual-Layer Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 198, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Koros, W.J. Mixed Matrix Hollow Fiber Membranes Made with Modified HSSZ-13 Zeolite in Polyetherimide Polymer Matrix for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kujawa, J.; Knozowska, K.; Kareiva, A.; Favre, E.; Castel, C.; Kujawski, W. The Advancements in Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Functionalized MOFs and 2D Materials for CO2/N2 Separation and CO2/CH4 Separation. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah Buddin, M.M.H.; Ahmad, A.L. Synergistic Effect of 2D ZIF Loading and Ionic Liquid Modification on Improving Gas Separation Performance of PES-Based Mixed Matrix Hollow Fiber Membrane. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 16243–16261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Dai, Z.; Shao, L.; Eisen, M.S.; He, X. A Review from Material Functionalization to Process Feasibility on Advanced Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separations. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, R.A.; Lau, W.J.; Lai, G.S.; Zulhairun, A.K.; Yeong, Y.F.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. Impacts of Multilayer Hybrid Coating on Psf Hollow Fiber Membrane for Enhanced Gas Separation. Membranes 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-G.; Koops, G.H.; Mulder, M.H.V.; van den Boomgaard, T.; Smolders, C.A. Wet Spinning of Integrally Skinned Hollow Fiber Membranes by a Modified Dual-Bath Coagulation Method Using a Triple Orifice Spinneret. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 194, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, M.; Eminoglu, Y.; Mehling, N.; Walorski, J.; Roth, H.; Wessling, M. Rotation-in-a-Spinneret Integrates Static Mixers inside Hollow Fiber Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 656, 120599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Liu, W.; Wu, H.C.; Kato, N.; Sun, Y.; Jeon, S.; Matsuyama, H. Effect of Mixed Diluents during Thermally Induced Phase Separation Process on Structures and Performances of Hollow Fiber Membranes Prepared Using Triple-Orifice Spinneret. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 596, 117715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Wu, C. Effect of Preparation Methods on Crystallization Behavior and Tensile Strength of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Membranes. Membranes 2013, 3, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, X. Effect of Annealing on the Structure and Properties of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Hollow Fiber by Melt-spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Tasselli, F.; Jansen, J.C.; Barbieri, G.; Drioli, E. Effect of the Preparation Conditions on the Formation of Asymmetric Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Hollow Fibre Membranes with a Dense Skin. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twarowska-Schmidt, K.; Włochowicz, A. Melt-Spun Asymmetric Poly(4-Methyl-1-Pentene) Hollow Fibre Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 137, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, K.; Yue, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yan, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, C. Design of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes with Stable Crystalline and Porous Structure by Solvent-free Method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 141, e55691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karousos, D.S.; Chiesa, F.; Theodorakopoulos, G.V.; Bouroushian, M.; Favvas, E.P. Rapid Hollow Fiber-Coating Device for Thin Film Composite Membrane Preparation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2024, 95, 033906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, W.; Su, Y.; Du, Q.; Zhu, H.; Qin, X. Preparation and Characterization of Inner-Pressure Hollow Fiber Composite Membrane via Two-Way Coating Technique for CO2/CH4 Separation. Fibers Polym. 2016, 17, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, M.; Chen, B.; Fu, J.; et al. 3D Bioprinting of Vessel-like Structures with Multilevel Fluidic Channels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y. Magnetically-Driven Drug and Cell on Demand Release System Using 3D Printed Alginate Based Hollow Fiber Scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Hollow Fibers: From Fabrication to Applications. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 9166–9177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L. Structured Zeolite Monoliths with Ultrathin Framework for Fast CO2 Adsorption Enabled by 3D Printing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 8223–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluijter, S.N.; Boon, J.; James, J.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Lind, A.; Blom, R.; Andreassen, K.A.; Cormos, A.M.; Sandu, V.C.; De Boer, R. 3D-Printing of Adsorbents for Increased Productivity in Carbon Capture Applications (3D-CAPS). Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2021, 112, 103512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, E.R.; Xia, Q.; Gillespie, R.; Proschogo, N.; Doheny, P.W.; Solomon, M.B.; D’Alessandro, D.M. 3D Printing of Monoliths Using TIFSIX-Ni-Based Formulations for the Electric Swing Adsorption of CO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 32935–32944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafanelli, L.F.A.S.; Henrique, A.; Steldinger, H.; Diaz De Tuesta, J.L.; Gläsel, J.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Gomes, H.T.; Etzold, B.J.M.; Silva, J.A.C. 3D-Printed Activated Carbon for Post-Combustion CO2 Capture. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 335, 111818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajal, N.H. Gas separation membranes: Advances in polymer and mixed-matrix membranes for CO2 capture. Innov. Eng. J. 2024, 1, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, P.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Kato, N.; Sasaki, Y.; Shon, H.K.; Matsuyama, H. Hollow Fiber Membranes with Hierarchical Spherulite Surface Structure Developed by Thermally Induced Phase Separation Using Triple-Orifice Spinneret for Membrane Distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Venault, A.; Wang, S.; Shen, Q.; Jia, Y.; Fang, C.; Kato, N.; Chang, Y.; Matsuyama, H. One-Step Entrapment of a PS-PEGMA Amphiphilic Copolymer on the Outer Surface of a Hollow Fiber Membrane via TIPS Process Using Triple-Orifice Spinneret. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 638, 119712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Tasselli, F.; Clarizia, G. Hollow Fiber Polyimide Membranes Prepared in a Triple Orifice Spinneret: Effect of a Reduced Water Activity in the Bore Fluid on the Gas Separation Performance. Polymers 2021, 13, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, P.; Gonzales, R.R.; Li, B.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Shi, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, Z.; Guan, K.; Matsuyama, H. Fabrication of High-Permeance Polyketone (PK) Hollow Fiber Membrane Using Triple-Orifice Spinneret via the Thermally Induced Phase Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 695, 122511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karousos, D.S.; Theodorakopoulos, G.V.; Chiesa, F.; Barbe, S.; Bouroushian, M.; Favvas, E.P. CO2/CH4 and CO2/CO Selective Pebax-1657 Based Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes Prepared by a Novel Dip-Coating Technique. Separations 2025, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, G.; Ingole, P.G. Polymer-Based Hollow Fiber Membranes: A Modern Trend in Gas Separation Technologies. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 38, 102109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wong, J.W.; Liang, C.Z.; Wu, J.; Chung, T.S.; Zhang, S. Inner-Selective Polyethersulfone-Polydimethylsiloxane (PES-PDMS) Thin Film Composite Hollow Fiber Membrane for CO2/N2 Separation at High Pressures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 323, 124439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Tan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S. A Sustainable Method to Prepare Ultra-Thin MOF Hollow Fiber Membranes for H2 Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 721, 123794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuri, M.R.; Koros, W.J. Defect-Free Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membranes from Torlon®, a Polyamide-Imide Polymer, for High-Pressure CO2 Separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, X.; Duan, C.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, Q. Fabrication of an Asymmetric 4,4′-Oxydiphthalic Anhydride–2,4,6-Trimethyl-1,3-Phenylenediamine/2,6-Diaminotoluene Copolyimide Hollow Fiber Membrane and Its Performance for CO2 Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 4442–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Silver Ionic Modification in Dual-Layer Hollow Fiber Membranes with Significant Enhancement in CO2/CH4 and O2/N2 Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 350, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Johnson, J.R.; Karvan, O.; Sholl, D.S.; Koros, W.J. Ultem ®/ZIF-8 Mixed Matrix Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2/N2 Separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, R.A.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Kartohardjono, S. Recent 10-Year Development on Surface Modification of Polymeric Hollow Fiber Membranes via Surface Coating Approach for Gas Separation: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 10083–10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.T.; Lee, J.; Dong, G.; Kim, J.S.; Do, Y.S.; Hung, W.-S.; Lee, K.-R.; Barbieri, G.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Fabrication of Thermally Rearranged (TR) Polybenzoxazole Hollow Fiber Membranes with Superior CO2/N2 Separation Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Sultan, M.M.B.; Alsuwailem, A.A.; Zuabi, S.M. Preparation and Characterization of Multilayer Thin-Film Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes for Helium Extraction from Its Mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakariya, S.; Yeong, Y.F.; Jusoh, N.; Tan, L.S. Performance of Multilayer Composite Hollow Membrane in Separation of CO2 from CH4 in Mixed Gas Conditions. Polymers 2022, 14, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.Z.; Liu, J.T.; Lai, J.Y.; Chung, T.S. High-Performance Multiple-Layer PIM Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Xiao, Y.C.; Chung, T.-S. Multi-Layer Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes Derived from Poly(Ethylene Glycol) (PEG) Containing Hybrid Materials for CO2/N2 Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, T.; Li, H.; Dong, G.; Wong, W.; Chen, V. Enhancing Membrane Permeability for CO2 Capture Through Blending Commodity Polymers with Selected PEO and PEO-PDMS Copolymers and Composite Hollow Fibres. Energy Procedia 2014, 63, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, C.; Chung, T.S.; Pramoda, K.P. Fabrication of Dual-Layer Polyethersulfone (PES) Hollow Fiber Membranes with an Ultrathin Dense-Selective Layer for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.M.R.; Kumbharkar, S.C.; Groth, A.M.; Li, K. Ultrafiltration PVDF Hollow Fibre Membranes with Interconnected Bicontinuous Structures Produced via a Single-Step Phase Inversion Technique. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 407–408, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakopoulos, G.V.; Karousos, D.S.; Veziri, C.M.; Kouvelos, E.P.; Sapalidis, A.A.; Favvas, E.P. Green Chemistry-Based Fabrication of Hollow Fiber and Flat Sheet Polyimide Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation. J. Membr. Sci. Lett. 2023, 3, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Laínez, J.; Etxeberria-Benavides, M.; David, O.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Green Preparation of Thin Films of Polybenzimidazole on Flat and Hollow Fiber Supports: Application to Hydrogen Separation. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubashir, M.; Yeong, Y.F.; Lau, K.K.; Chew, T.L. Effect of Spinning Conditions on the Fabrication of Cellulose Acetate Hollow Fiber Membrane for CO2 Separation from N2 and CH4. Polym. Test. 2019, 73, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunder, N.; Fong, Y.Y.; Bustam, M.A.; Lau, W.J. Study on the Performance of Cellulose Triacetate Hollow Fiber Mixed Matrix Membrane Incorporated with Amine-Functionalized NH2-MIL-125(Ti) for CO2 and CH4 Separation. Separations 2023, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Lindbråthen, A.; Hillestad, M.; Sandru, M.; Favvas, E.P.; He, X. Screening Cellulose Spinning Parameters for Fabrication of Novel Carbon Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13330–13339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, A.; Maruyama, T.; Ohmukai, Y.; Sotani, T.; Matsuyama, H. Preparation of Poly(Lactic Acid) Hollow Fiber Membranes via Phase Separation Methods. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 342, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, H.Z.; Chung, T.S. The Effects of Substrate Characteristics and Pre-Wetting Agents on PAN-PDMS Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2/N2 and O2/N2 Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzarelli, F.; Bernardo, P.; Tasselli, F.; Clarizia, G.; Dzyubenko, V.G.; Vdovin, P.; Jansen, J.C. Multilayer Composite SBS Membranes for Pervaporation and Gas Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Dellamuzia, L.; Moretti, U.; Fuoco, A.; Giorno, L.; Jansen, J.C. Simultaneous Production of Biomethane and Food Grade CO2 from Biogas: An Industrial Case Study. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Yoshinaga, T.; Ninomiya, K.; Sakakibara, T.; Tamari, T. Relation of Gas Permeability with Structure of Aromatic Polyimides II. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 111, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; De Santo, M.P.; Esposito, E.; Fuoco, A.; Monteleone, M.; Giorno, L.; Comesaña-Gándara, B.; Chen, J.; Bezzu, C.G.; Carta, M.; et al. Correlating Gas Permeability and Young’s Modulus during the Physical Aging of Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity Using Atomic Force Microscopy. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 5381–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S.; Khean Teoh, S. The Ageing Phenomenon of Polyethersulphone Hollow Fibre Membranes for Gas Separation and Their Characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 152, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, A.; Rizzuto, C.; Tocci, E.; Monteleone, M.; Esposito, E.; Budd, P.M.; Carta, M.; Comesaña-Gándara, B.; McKeown, N.B.; Jansen, J.C. The Origin of Size-Selective Gas Transport through Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20121–20126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Ren, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Hua, K.; Deng, M. The Evolution of the Structure, Mechanical, and Gas Separation Properties of P84 Hollow Fiber Membranes from the Polymer to the Carbon Stage. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 256, 117741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, A.; Verma, S.K.; Bellare, J. Carboxylated Carbon Nanotubes/Polyethersulfone Hollow Fiber Mixed Matrix Membranes: Development and Characterization for Enhanced Gas Separation Performance. Materials Research Society. MRS Adv. 2018, 3, 3135–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirabedi, P.; Yegani, R.; Hesaraki, A.H. Hydrophobicity Optimization of Polypropylene Hollow Fiber Membrane by Sol–Gel Process for CO2 Absorption in Gas–Liquid Membrane Contactor Using Response Surface Methodology. Iran. Polym. J. 2017, 26, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahri, K.; Wong, K.C.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. Graphene Oxide/Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Mixed Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 89130–89139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjojo, N.; Chung, T.S.; Kulprathipanja, S. The Fabrication of Hollow Fiber Membranes with Double-Layer Mixed-Matrix Materials for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramanayake, S.; Hopkinson, D.; Myers, C.; Hong, L.; Feng, J.; Seol, Y.; Plasynski, D.; Zeh, M.; Luebke, D. Mechanically Robust Hollow Fiber Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes for CO2 Separation Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramanayake, S.; Hopkinson, D.; Myers, C.; Sui, L.; Luebke, D. Investigation of Transport and Mechanical Properties of Hollow Fiber Membranes Containing Ionic Liquids for Pre-Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 439, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.H.; Oh, P.C.; Jamil, A. Effect of Air Gap Interval on Polyvinylidene Fluoride Hollow Fiber Membrane Spinning for CO2 and CH4 Gas Separation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 2499–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbullah, H.; Kumbharkar, S.; Ismail, A.F.; Li, K. Preparation of Polyaniline Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membranes and Investigation towards Gas Separation Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 366, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontananova, E.; Jansen, J.C.; Cristiano, A.; Curcio, E.; Drioli, E. Effect of Additives in the Casting Solution on the Formation of PVDF Membranes. Desalination 2006, 192, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DashtArzhandi, M.R.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Ng, B.C.; Abdullah, M.S. Fabrication and Characterization of Porous Polyetherimide/Montmorillonite Hollow Fiber Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2 Absorption via Membrane Contactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.F.; Jo, H.J.; Park, H.; Seong, J.G.; Lee, Y.M. Densification-Induced Hollow Fiber Membranes Using Crosslinked Thermally Rearranged (XTR) Polymer for CO2 Capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jo, H.J.; Han, S.H.; Park, C.H.; Kim, S.; Budd, P.M.; Lee, Y.M. Mechanically Robust Thermally Rearranged (TR) Polymer Membranes with Spirobisindane for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulhameed, M.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Harun, Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Puteh, M.H.; Jaafar, J. Preparation and Characterisation of Inexpensive Porous Kaolin Hollow Fibre as Ceramic Membrane Supports for Gas Separation Application. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 53, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhlis, A. RahmanMohd Akmal GhazaliWan Muhammad Solehin Wan Abd AzizShow all 6 authors, Ahmad Fauzi IsmailAhmad Fauzi Ismail. Preparation of Titanium Dioxide Hollow Fiber Membrane Using Phase Inversion and Sintering Technique for Gas Separation and Water Purification. Sains Malays. 2015, 44, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Ackley, M.W. Medical Oxygen Concentrators: A Review of Progress in Air Separation Technology. Adsorption 2019, 25, 1437–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, J.E. Physical Properties of Polymers Handbook, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-387-31235-4. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.L.; Landel, R.F.; Ferry, J.D. The Temperature Dependence of Relaxation Mechanisms in Amorphous Polymers and Other Glass-Forming Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 3701–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissinger, R.G.; Paulaitis, M.E. Glass Transitions in Polymer/CO2 Mixtures at Elevated Pressures. J. Polym. Sci. 1991, 29, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, O.S.; Kazarian, S.G. Polymer Processing with Supercritical Fluids. In Supercritical Carbon Dioxide; Kemmere, M.F., Meyer, T., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 205–238. ISBN 978-3-527-31092-0. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, S.M.; Henson, M.A.; Koros, W.J. The effects of carbon dioxide conditioning on the permeation behavior of hollow fiber asymmetric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 54, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuri, M.R.; Koros, W.J. Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membranes for Separation of CO2 from Hydrocarbons and Fluorocarbons at High-Pressure Conditions Relevant to C2F4 Polymerization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 10577–10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fabio, S.; Giuseppe Marino, N.; Riccardo, C.; Deng, L. Field Test of a Pre-Pilot Scale Hollow Fiber Facilitated Transport Membrane for CO2 Capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2019, 86, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirkhan, F.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Wan Mustapa, W.N.F.; Halim, M.H.M.; Soh, W.K.; Yeo, S.Y. Recent Advances of Polymeric Membranes in Tackling Plasticization and Aging for Practical Industrial CO2/CH4 Applications—A Review. Membranes 2022, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C. Chemical Cross-Linking Modification of 6FDA-2,6-DAT Hollow Fiber Membranes for Natural Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 216, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Bai, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Luo, S. Dual Thermally Crosslinked Hollow Fiber Membranes for Plasticization-Resistant Helium Recovery from Natural Gas. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, J.G.; Lewis, J.C.; Matteson, J.A.; Craddock, E.; Martinez, U.; Thakkar, H.; Benavidez, A.D.; Berchtold, K.A.; Singh, R.P. Polybenzimidazole-Derived Carbon Molecular Sieve Hollow Fiber Membranes with Tailored Oxygen Selective Transport. Carbon 2022, 192, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struik, L.C.E. Physical Aging in Amorphous Polymers and Other Materials; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; ISBN 978-0-444-41655-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yampolskii, I.P.Y.; Pinnau, I.; Freeman, B.D. Materials Science of Membranes for Gas and Vapor Separation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-470-85345-X. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Sanyal, O.; Koros, W.J. Carbon Molecular Sieve Membrane Preparation by Economical Coating and Pyrolysis of Porous Polymer Hollow Fibers. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 12277–12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccaig, M.S.; Paul, D.R. Effect of Film Thickness on the Changes in Gas Permeability of a Glassy Polyarylate Due to Physical Aging Part, I. Experimental Observations. Polymer 2000, 41, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, G.; Tasselli, F.; Bernardo, P. Effect of Physical Aging on Gas Transport in Asymmetric Polyimide Hollow Fibers Prepared by Triple-Orifice Spinneret. Polymers 2020, 12, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, K.R.F.; Faupel, N.; Chaukura, P.M.; Budd, W.; Egger, W.; Ravelli, L. Aging and Free Volume in a Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity (PIM-1). J. Adhes. 2012, 88, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, N.; Handge, U.A.; Abetz, V. Physical Ageing and Lifetime Prediction of Polymer Membranes for Gas Separation Processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 516, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, L.; Meneguzzo, S.; Ligi, S.; Saccani, A.; Giorgini, L.; Orsini, A.; Pettinau, A.; De Angelis, M.G. Reducing Ageing of Thin PTMSP Films by Incorporating Graphene and Graphene Oxide: Effect of Thickness, Gas Type and Temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.F.; Chung, T.S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C. New Polyethersulfone (PESU) Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2 Capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Koros, W.J. Physical Aging of Ester-Cross-Linked Hollow Fiber Membranes for Natural Gas Separations and Mitigation Thereof. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 551, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapantaidakis, G.C.; Koops, G.H.; Wessling, M.; Kaldis, S.P.; Sakellaropulos, G.P. CO2 Plasticization of Polyethersulfone/Polyimide Gas-Separation Membranes. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, B.; Bisht, S.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Ismail, A.F.; Othman, M.H.D. Performance of Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes Encompassing ZIF-8, SiO2/ZIF-8, and Amine-Modified SiO2/ZIF-8 Nanofillers for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 Gas Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 264, 118471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutrisna, P.D.; Hou, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, V. Improved Operational Stability of Pebax-Based Gas Separation Membranes with ZIF-8: A Comparative Study of Flat Sheet and Composite Hollow Fibre Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.S.; Kim, H.J.; Johnson, J.R.; Kim, W.G.; Koros, W.J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Modified Mesoporous Silica Gas Separation Membranes on Polymeric Hollow Fibers. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3025–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jeong, H.K. Transforming Polymer Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules to Mixed-Matrix Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Propylene/Propane Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Vaughn, J.; Liu, G.; Xu, L.; Brayden, M.; Martinez, M.; Fitzgibbons, T.; Wenz, G.; Koros, W.J. Hyperaging Tuning of a Carbon Molecular-Sieve Hollow Fiber Membrane with Extraordinary Gas-Separation Performance and Stability. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 11826–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.L.H.; Lau, K.K.; Lau, W.J.; Ahmad, F. Holistic Review on the Recent Development in Mathematical Modelling and Process Simulation of Hollow Fiber Membrane Contactor for Gas Separation Process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 104, 231–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, M.; De Angelis, M.G.; Sarti, G.C. Predictive Calculations of Gas Solubility and Permeability in Glassy Polymeric Membranes: An Overview. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsalve-Bravo, G.M.; Bhatia, S.K. Modeling Permeation through Mixed-Matrix Membranes: A Review. Processes 2018, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, E.; Minelli, M.; De Angelis, M.G. Modelling Sorption and Transport of Gases in Polymeric Membranes across Different Scales: A Review. Membranes 2022, 12, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, T.; Lien, K.M. Design Studies of Membrane Permeator Processes for Gas Separation. Gas Sep. Purif. 1995, 9, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, D.T.; Freeman, B.D.; Fleming, G.K. Modeling Multicomponent Gas Separation Using Hollow-fiber Membrane Contactors. AIChE J. 1998, 44, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Suleiman, A.; Liu, G.; Perez, M.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, M.; Guo, R.; Luo, T. Superior Polymeric Gas Separation Membrane Designed by Explainable Graph Machine Learning. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 102067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, F.; Khosravi, A.; Karagöz, S.; Keshavarz, A. A Systematic Review of Recent Advances in the Application of Machine Learning in Membrane-Based Gas Separation Technologies. Appl. Energy 2025, 381, 125203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqassar Bani Almarjeh, R.; Attasi, Y. Boosting Polymeric Hollow-Fiber Membrane Gas Separation Process by Evaluating Its Performance Utilizing Ai Algorithms. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5070911 (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Wang, J.; Tian, K.; Li, D.; Chen, M.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Machine Learning in Gas Separation Membrane Developing: Ready for Prime Time. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 313, 123493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The Solution-Diffusion Model: A Review. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R.; Wesselingh, J.A. The Maxwell-Stefan Approach to Mass Transfer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1997, 52, 861–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, R.T.; Koros, W.J.; Fedkiw, P.S. Simulation of a Hollow-Fiber Gas Separator: The Effects of Process and Design Variables. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1985, 24, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M.; Harlacher, T.; Melin, T.; Wessling, M. Modeling Gas Permeation by Linking Nonideal Effects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, S.L.; Lin, T.T.; Chung, T.S. Characterization of Hollow Ber Membranes in a Permeator Using Binary Gas Mixtures. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, F.; Lin, G.; Tang, B.; Li, X.; Zhou, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y. The Enhancement of Separation Performance of Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules: From the Perspective of Membranes and Membrane Modules Structural Optimization Design. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 280, 119106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Younas, M.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ly, Q.V.; Li, J. A Review on Hollow Fiber Membrane Module towards High Separation Efficiency: Process Modeling in Fouling Perspective. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Freger, V.; He, X.; Wang, R.; Kong, B. Three-Dimensional CFD Modeling for Hollow Fiber Gas Separation Membrane Modules Based on a Dual Porous Media Model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 302, 120864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhong, D.; Du, X.; Zhang, J. Optimization of Mechanical Properties and Finite Element Simulation Analysis of Hollow Fiber Membranes in Gas-Liquid Membrane Separation Technology. Desalination 2025, 599, 118456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovvali, A.S.; Vemury, S.; Admassu, W. Modeling of Multicomponent Countercurrent Gas Permeators. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1994, 93, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsabadi, A.A.; Kargari, A.; Farshadpour, F.; Laki, S. Mathematical Modeling of CO2/CH4 Separation by Hollow Fiber Membrane Module Using Finite Difference Method. J. Memb. Sep. Technol. 2012, 1, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thundyil, M. Mathematical Modeling of Gas Separation Permeators—For Radial Crossflow, Countercurrent, and Cocurrent Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 125, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Lau, K.K.; Lock, S.S.M.; Rafiq, S.; Khan, A.U.; Lee, M. Hollow Fiber Membrane Model for Gas Separation: Process Simulation, Experimental Validation and Module Characteristics Study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1246–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Baik, K.J.; Kim, I.W.; Lee, H.K. Optimization of Membrane Process for Methane Recovery from Biogas. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhou, Z.; Ismail, N.; Tocci, E.; Figoli, A.; Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T.; Cui, Z.; Tavajohi, N. Membrane Formation by Thermally Induced Phase Separation: Materials, Involved Parameters, Modeling, Current Efforts and Future Directions. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 669, 121303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziresh, S.; Bouyer, D.; Tocci, E.; Tavajohi, N.; Vatanpour, V. Modeling Membrane Formation. In Polymeric Membrane Formation by Phase Inversion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 345–394. ISBN 978-0-323-95628-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ford, D.M.; Qian, X.; Cervellere, M.R.; Millett, P.C.; Wang, X. A Review on Models and Simulations of Membrane Formation via Phase Inversion Processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burganos, V.N. 1.03—Modeling and Simulation of Membrane Structure and Transport Properties. Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering; Drioli, E., Giorno, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 29–74. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, D.; Heuchel, M.; Yampolskii, Y.; Khotimskii, V.; Shantarovich, V. Free Volume Distributions in Ultrahigh and Lower Free Volume Polymers: Comparison between Molecular Modeling and Positron Lifetime Studies. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A. Modeling in Membranes and Membrane-Based Processes; John Wiley & Sons Incorporated: Newark, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-119-53606-2. [Google Scholar]
- Venable, R.M.; Krämer, A.; Pastor, R.W. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Membrane Permeability. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5954–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergadou, N.; Theodorou, D.N. Molecular Modeling Investigations of Sorption and Diffusion of Small Molecules in Glassy Polymers. Membranes 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Zhang, R.; Surampalli, Y.; Vigneswaran, S. The Values of Membrane Science and Technology: Introduction and Overview; ACSE library: Auckland, New Zealand, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, I.; Nam, S.Y.; Rizzuto, C.; Barbieri, G.; Tocci, E.; Kim, T.-H. PIM-Polyimide Multiblock Copolymer-Based Membranes with Enhanced CO2 Separation Performances. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Tocci, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. Thermal Treatment Effect on the Structure and Property Change between Hydroxy-Containing Polyimides (HPIs) and Thermally Rearranged Polybenzoxazole (TR-PBO). J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 12864–12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.; Burt, L.A.; Esposito, E.; Jansen, J.C.; Tocci, E.; Rizzuto, C.; Lanč, M.; Carta, M.; McKeown, N.B. A Highly Rigid and Gas Selective Methanopentacene-Based Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity Derived from Tröger’s Base Polymerization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocci, E.; De Lorenzo, L.; Bernardo, P.; Clarizia, G.; Bazzarelli, F.; Mckeown, N.B.; Carta, M.; Malpass-Evans, R.; Friess, K.; Pilnáček, K.; et al. Molecular Modeling and Gas Permeation Properties of a Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity Composed of Ethanoanthracene and Tröger’s Base Units. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 7900–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Tocci, E.; Kim, S.; Kumar, A.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. A Simulation Study on OH-Containing Polyimide (HPI) and Thermally Rearranged Polybenzoxazoles (TR-PBO): Relationship between Gas Transport Properties and Free Volume Morphology. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 2746–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satilmis, B.; Lanč, M.; Fuoco, A.; Rizzuto, C.; Tocci, E.; Bernardo, P.; Clarizia, G.; Esposito, E.; Monteleone, M.; Dendisová, M.; et al. Temperature and Pressure Dependence of Gas Permeation in Amine-Modified PIM-1. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Ma, H.; Wu, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y. Molecular Simulation for Guiding the Design and Optimization of Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs) in the Pervaporation Process. Langmuir 2023, 39, 5199–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, K.; Lock, S.S.M.; Taqvi, S.A.A.; Jusoh, N.; Yiin, C.L.; Chin, B.L.F.; Loy, A.C.M. A Molecular Simulation Study of Silica/Polysulfone Mixed Matrix Membrane for Mixed Gas Separation. Polymers 2021, 13, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupgan, G.; Abbott, L.J.; Hart, K.E.; Colina, C.M. Modeling Amorphous Microporous Polymers for CO2 Capture and Separations. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 5488–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahshoori, I.; Cacciotti, I.; Seyfaee, A.; Babapoor, A. Improvement Efficiency of the of Poly (Ether-Block-Amide) -Cellulose Acetate (Pebax-CA) Blend by the Addition of Nanoparticles (MIL-53 and NH2-MIL-53): A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, C.Y.; Lim, L.G.; Lock, S.S.M.; Jusoh, N.; Yiin, C.L.; Chin, B.L.F.; Chan, Y.H.; Loy, A.C.M.; Mubashir, M. A Systematic Review of the Molecular Simulation of Hybrid Membranes for Performance Enhancements and Contaminant Removals. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyertz, S.; Benes, N.E.; Brown, D. Molecular Simulations of Hybrid Cross-Linked Membranes for H2S Gas Separation at Very High Temperatures and Pressure: Binary 90%/10% N2/H2S and CH4/H2S, Ternary 90%/9%/1% N2/CO2/H2S and CH4/CO2/H2S Mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 687, 122092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.C.; Bhatia, S.K. Atomistic Investigation of Mixed-Gas Separation in a Fluorinated Polyimide Membrane. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuto, C.; Caravella, A.; Brunetti, A.; Park, C.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E.; Barbieri, G.; Tocci, E. Sorption and Diffusion of CO2/N2 in Gas Mixture in Thermally-Rearranged Polymeric Membranes: A Molecular Investigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillman, R. Chapter 13 Economics of Gas Separation Membrane Processes. In Membrane Separations Technology; Noble, R.D., Stern, S.A., Eds.; Membrane Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 589–667. [Google Scholar]
- León, N.E.; Liu, Z.; Irani, M.; Koros, W.J. How to Get the Best Gas Separation Membranes from State-of-the-Art Glassy Polymers. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kárászová, M.; Zach, B.; Petrusová, Z.; Červenka, V.; Bobák, M.; Šyc, M.; Izák, P. Post-Combustion Carbon Capture by Membrane Separation, Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, C.A.; Stevens, G.W.; Kentish, S.E. Membrane Gas Separation Applications in Natural Gas Processing. Fuel 2012, 96, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho-Bailo, F.; Caro, G.; Etxeberría-Benavides, M.; Karvan, O.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. MOF–Polymer Enhanced Compatibility: Post-Annealed Zeolite Imidazolate Framework Membranes inside Polyimide Hollow Fibers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5881–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Najari, S.; Kundu, P.K.; Tan, N.R.; Roodashti, S.M. Simulation and Sensitivity Analysis of Transport in Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membrane Permeators for Air Separation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 86359–86370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Recent Developments in Membranes for Efficient Hydrogen Purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 130–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Galiano, F.; Iulianelli, A.; Basile, A.; Figoli, A. Biopolymers for Sustainable Membranes in CO2 Separation: A Review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 213, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evonik SEPURAN® Noble Membrane Technology for Helium and Hydrogen Generation. 2011. Available online: https://Www.Membrane-Separation.Com/En/Helium-Recovery-with-Sepuran-Noble (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Ohya, H.; Kudryavtsev, V.V.; Semenova, S.I. Polyimide Membranes: Applications, Fabrications and Properties; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 1996; ISBN 978-90-5699-024-4. [Google Scholar]
- Tymen Visser, Markus Ungerank, J.B.; Führer, C. Method For Producing Polyimide Membranes. US Patent 2016/0144323 A1, 26 May 2015.
- GENERON® Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules. Available online: https://Www.Generon.Com/Product_type/Membrane-Modules/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Batoon, V.; Borsaly, A.; Casillas, C.; Hofmann, T.; Huang, I.; Kniep, J.; Merkel, T.; Paulaha, C.; Salim, W.; Westling, E. Scale-Up Testing of Advanced PolarisTM Membrane CO2 Capture Technology. SSRN J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. Carbon Dioxide Geological Storage: Monitoring Technologies Review. In Greenhouse Gases—Capturing, Utilization and Reduction; Liu, G., Ed.; InTech: Shanghai, China, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0192-5. [Google Scholar]
- Robust Polymer Composite Membranes for Hydrogen Separation. Available online: https://Pbipolymer.Com/Wp-Content/Uploads/2016/05/Polymer-Composite-Membranes-for-Hydrogen-Separation (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Nitro, U.P.H.; Dyes, N. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; Volume 12, pp. 149–174. [Google Scholar]
- Moriya, A.; Shoji, K.; Moriya, A. Method of Producing High-Purity Helium. US Patent 20030221448A1, 4 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Barsema, J. Preparation and Characterization of Highly Selective Dense and Hollow Fiber Asymmetric Membranes Based on BTDA-TDI/MDI Co-Polyimide. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 216, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Chung, T.-S.; Chng, M.L.; Aw, W. Evolution of Ultra-Thin Dense-Selective Layer from Single-Layer to Dual-Layer Hollow Fibers Using Novel Extem® Polyetherimide for Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrtsova, D.A.; Shalygin, M.G.; Teplyakov, V.V. Fluorinated Hollow Fiber Membranes Based on Matrimid 5218 and Their Application in the Process of Helium Recovery from Natural Gas. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogieglo, W.; Puspasari, T.; Ma, X.; Pinnau, I. Sub-100 Nm Carbon Molecular Sieve Membranes from a Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity Precursor: Physical Aging and near-Equilibrium Gas Separation Properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 597, 117752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.; Low, B.T. Gas Separation Membrane Materials: A Perspective. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6999–7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Lim, B. Hydrogen Separation Membranes: A Material Perspective. Molecules 2024, 29, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbharkar, S.C.; Liu, Y.; Li, K. High Performance Polybenzimidazole Based Asymmetric Hollow Fibre Membranes for H2/CO2 Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, M.; Kamali, S.M.; Mahdeyarfar, M.; Mohammadi, T. Separation of Hydrogen from Carbon Monoxide Using a Hollow Fiber Polyimide Membrane: Experimental and Simulation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2007, 30, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favvas, E.P.; Kapantaidakis, G.C.; Nolan, J.W.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. Preparation, Characterization and Gas Permeation Properties of Carbon Hollow Fiber Membranes Based on Matrimid® 5218 Precursor. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2007, 186, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, M.; Malpass-Evans, R.; Croad, M.; Rogan, Y.; Jansen, J.C.; Bernardo, P.; Bazzarelli, F.; McKeown, N.B. An Efficient Polymer Molecular Sieve for Membrane Gas Separations. Science 2013, 339, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Scorzafave, V.; Clarizia, G.; Tocci, E.; Jansen, J.C.; Borgogno, A.; Malpass-Evans, R.; McKeown, N.B.; Carta, M.; Tasselli, F. Thin Film Composite Membranes Based on a Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity Derived from TrÖger’s Base: A Combined Experimental and Computational Investigation of the Role of Residual Casting Solvent. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 569, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R. Fabrication of Novel Polyetherimide-Fluorinated Silica Organic-Inorganic Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes Intended for Membrane Contactor Application. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 443, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Berchtold, K.A.; David Huckaby, E. High Temperature Polymer-Based Membrane Systems for Pre-Combustion Carbon Dioxide Capture; Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL): Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2016.
- Singh, R.P.; Dahe, G.J.; Dudeck, K.W.; Berchtold, K.A. Macrovoid-Free High Performance Polybenzimidazole Hollow Fiber Membranes for Elevated Temperature H2/CO2 Separations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 27331–27345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Tong, F.; Lei, L.; Xu, Z. Ultraselective Carbon Hollow Fiber Membrane for H2 Extraction from Blended Natural Gas. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 302, 120717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Hagiwara, H.; Yanagishita, H.; Ito, K.; Tsuru, T. Structural Characterization of Thin-Film Polyamide Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxeberria-Benavides, M.; Johnson, T.; Cao, S.; Zornoza, B.; Coronas, J.; Sanchez-Lainez, J.; Sabetghadam, A.; Liu, X.; Andres-Garcia, E.; Kapteijn, F.; et al. PBI Mixed Matrix Hollow Fiber Membrane: Influence of ZIF-8 Filler over H2/CO2 Separation Performance at High Temperature and Pressure. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, O.C.; Gorri, D.; Nijmeijer, K.; Ortiz, I.; Urtiaga, A. Hydrogen Separation from Multicomponent Gas Mixtures Containing CO, N2 and CO2 Using Matrimid ® Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 419–420, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Yuan, J.; Shen, G.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Graphene Oxide Membranes Supported on the Ceramic Hollow Fibre for Efficient H2 Recovery. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W.; Li, N.-X.; Li, Z.-R.; Wang, J.-R.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.-S. Preparation and Gas Separation Properties of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks-8 (ZIF-8) Membranes Supported on Silicon Nitride Ceramic Hollow Fibers. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 8949–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Cen, K. Composites of Ionic Liquid and Amine-Modified SAPO 34 Improve CO2 Separation of CO2 -Selective Polymer Membranes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 410, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Morales, J.E.; Tapia-Venegas, E.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bakonyi, P.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Ruiz-Filippi, G. Evaluation of Two Gas Membrane Modules for Fermentative Hydrogen Separation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 14042–14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Lei, L.; Xu, Z. Oxygen-Enriched Carbon Molecular Sieve Hollow Fiber Membrane for Efficient CO2 Removal from Natural Gas. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 347, 127611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y. Combustion Behaviour and Mechanism of a Cu-Ni-Mn Alloy in an Oxygen Enriched Atmosphere. Corros. Sci. 2020, 163, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Lindbråthen, A.; Lie, J.A.; Carstensen, P.V.; Johannessen, T.; Hägg, M.-B. Vehicle Fuel from Biogas with Carbon Membranes; a Comparison between Simulation Predictions and Actual Field Demonstration. Green Energy Environ. 2018, 3, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan, W.M.; McDowell, D. Modified Atmosphere Packaging. In Food and Beverage Packaging Technology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchenko, M.V.; Karapuzikov, A.I.; Sherstov, I.V. Short Pulse Formation in a TEA CO2 Laser Using a CO2–N2–H2 Gas Mixture. Quantum Electron. 2001, 31, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjeev, K.; Ramesh, M.N. Low Oxygen and Inert Gas Processing of Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2006, 46, 423–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariono, D.; Wardani, A.K. Review of Membrane Oxygen Enrichment for Efficient Combustion. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 877, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, S.L.; Ward, W.J.; Kimura, S.G.; Browall, W.R. Membrane Oxygen Enrichment: II. Economic Assessment. J. Membr. Sci. 1986, 29, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.G.; Browall, W.R. Membrane Oxygen Enrichment: I. Demonstration of Membrane Oxygen Enrichment for Natural Gas Combustion. J. Membr. Sci. 1986, 29, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, C.Y.; Muhammad Anwar, S.N.B.; Weerachanchai, P.; Bae, T.-H.; Goh, K.; Wang, R. Scaling-up Defect-Free Asymmetric Hollow Fiber Membranes to Produce Oxygen-Enriched Gas for Integration into Municipal Solid Waste Gasification Process. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.M.; Feng, C.; Li, J.F.; Liu, J.Z.; Wu, Y.L. Water Vapor Permeation and Compressed Air Dehydration Performances of Modified Polyimide Membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 60, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Peng, N.; Liang, C.; Yong, W.; Chung, T.-S. Hollow Fiber Membrane Dehumidification Device for Air Conditioning System. Membranes 2015, 5, 722–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, W.H.; Bleikamp, L.K.; Kalthod, D.G. Hollow Fiber Membrane Dryer with Internal Sweep. Patent Number 5.525.143, 11 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Douglas LeVan, M. Water Transport Properties of Nafion Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 221, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Jin, L. Surface-Modified PVA/PVDF Hollow Fiber Composite Membrane for Air Dehumidification. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 5415–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingole, P.G.; Pawar, R.R.; Baig, M.I.; Jeon, J.D.; Lee, H.K. Thin Film Nanocomposite (TFN) Hollow Fiber Membranes Incorporated with Functionalized Acid-Activated Bentonite (ABn-NH) Clay: Towards Enhancement of Water Vapor Permeance and Selectivity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 20947–20958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, L.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Shahzad, M.W.; Syed, U.T.; Aristizábal, S.L.; Gorecki, R.; Nunes, S.P. Polyphenol-Coated Hollow Fiber System for Energy-Efficient Dehumidification in Air-Conditioning. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 692, 122215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, L.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Akhtar, F.H.; Falca, G.; Musteata, V.; Mahalingam, D.K.; Almansoury, R.; Ng, K.C.; Nunes, S.P. NEXARTM-Coated Hollow Fibers for Air Dehumidification. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Vinh-Thang, H.; Ramirez, A.A.; Rodrigue, D.; Kaliaguine, S. Membrane Gas Separation Technologies for Biogas Upgrading. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24399–24448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Chibwe, K.; Mantilla-Calderon, D.; Ling, F.; He, Z. Meta-Analysis of Biogas Upgrading to Renewable Natural Gas through Biological CO2 Conversion. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, M.S.; Kong, C.I.; Park, B.R.; Lee, Y.; Na, B.K.; Kim, J.H. Optimization of Pilot-Scale 3-Stage Membrane Process Using Asymmetric Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes for Production of High-Purity CH4 and CO2 from Crude Biogas. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, A.G.; Urbaniak, A.; Wawryniuk, K. Membrane Enrichment of Biogas from Two-Stage Pilot Plant Using Agricultural Waste as a Substrate. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 58, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, V.; Balster, F.J.; Balster, J. Method for Producing Polyimide Membranes. U.S. Patent US009873093B2 (12), 23 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, M.S.; Jung, K.H.; Kwag, J.H.; Jeon, Y.W. Biogas Separation Using a Membrane Gas Separator: Focus on CO2 Upgrading without CH4 Loss. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 129, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abejón, R.; Casado-Coterillo, C.; Garea, A. Techno-Economic Optimization of Multistage Membrane Processes with Innovative Hollow Fiber Modules for the Production of High-Purity CO2 and CH4 from Different Sources. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 8149–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Chu, Y.; Lindbråthen, A.; Hillestad, M.; Hägg, M.B. Carbon Molecular Sieve Membranes for Biogas Upgrading: Techno-Economic Feasibility Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Lei, L.; Avruscio, E.; Karousos, D.S.; Lindbråthen, A.; Kouvelos, E.P.; He, X.; Favvas, E.P.; Barbieri, G. Long-Term Performance of Highly Selective Carbon Hollow Fiber Membranes for Biogas Upgrading in the Presence of H2S and Water Vapor. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kraftschik, B.E.; Babu, V.P.; Bhuwania, N.; Chinn, D.; Koros, W.J. Natural Gas Sweetening Using TEGMC Polyimide Hollow Fiber Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 632, 119361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Qiu, W.; Koros, W.J. Cross-Linkable Semi-Rigid 6FDA-Based Polyimide Hollow Fiber Membranes for Sour Natural Gas Purification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 5333–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.; Yang, T.; Chung, T.-S. Natural Gas Purification and Olefin/Paraffin Separation Using Cross-Linkable Dual-Layer Hollow Fiber Membranes Comprising β-Cyclodextrin. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Koros, W.J. Ester-Cross-Linkable Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes for CO2 Removal from Natural Gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10495–10505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Chaikittisilp, W.; Jang, K.S.; Didas, S.A.; Johnson, J.R.; Koros, W.J.; Nair, S.; Jones, C.W. Aziridine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Membranes on Polymeric Hollow Fibers: Synthesis and Single-Component CO2 and N2 Permeation Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4407–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Q.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, J.Z.; Zhou, J.H.; Cen, K.F. Improvement on Surface Hydrophily of Hollow Fiber-Supported PDMS Gas Separation Membrane by PVP Modification. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Eng. Sci.) 2019, 53, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Pak, S.-H.; Jeon, Y.-W.; Shin, M.-S.; Koh, H.C. Preparation of Cellulose Acetate Hollow-Fiber Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.Y.; Nam, S.Y.; Koh, H.C.; Ha, S.Y.; Barbieri, G.; Drioli, E. The Effect of Operating Conditions on the Performance of Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for CO2/N2 Separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxeberria-Benavides, M.; Karvan, O.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J.; David, O. Fabrication of Defect-Free P84® Polyimide Hollow Fiber for Gas Separation: Pathway to Formation of Optimized Structure. Membranes 2019, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lively, R.P.; Dose, M.E.; Xu, L.; Vaughn, J.T.; Johnson, J.R.; Thompson, J.A.; Zhang, K.; Lydon, M.E.; Lee, J.-S.; Liu, L.; et al. A High-Flux Polyimide Hollow Fiber Membrane to Minimize Footprint and Energy Penalty for CO2 Recovery from Flue Gas. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukhov, A.V.; Pelzer, M.; Markova, S.Y.; Syrtsova, D.A.; Shalygin, M.G.; Gries, T.; Teplyakov, V.V. Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membranes Based on Poly(4-Methyl-1-Pentene) for Gas Separation. Fibers 2022, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liang, X.; Dou, H.; Ye, C.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Wu, H.; Guiver, M.D.; Jiang, Z. Membrane-Based Olefin/Paraffin Separations. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, R.; Li, K. Olefin/Paraffin Separation Using Membrane Based Facilitated Transport/Chemical Absorption Techniques. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 73, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Venna, S.R.; Rogers, G.; Tang, L.; Fitzgibbons, T.C.; Liu, J.; Mccurry, H.; Vickery, D.J.; Flick, D.; Fish, B. Membranes for Olefin-Paraffin Separation: An Industrial Perspective. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 2022194118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.C.; Thomas, S. Transport Phenomena through Polymeric Systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 985–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabelman, A.; Hwang, S.-T. Hollow fiber Membrane Contactors. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 159, 61–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K. Handbook of Industrial Membranes, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; ISBN 1856172333. Available online: http://site.ebrary.com/id/10203515 (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Calamur, N.; Carrera, M.E.; Devlin, D.J.; Archuleta, T. Methods of Forming and Using Porous Structures for Energy Efficient Separation of Light Gases by Capillary Condensation. Google Patents Number 6.039.792, 21 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Cussler, E.L. Hollow Fibers as Structured Distillation Packing. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 215, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cussler, E.L. Distillation in Hollow Fibers. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Barbero, R.S.; Devlin, D.J.; Cussler, E.L.; Colling, C.W.; Carrera, M.E. Hollow Fibers as Structured Packing for Olefin/Paraffin Separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Devlin, D.J.; Barbero, R.S. American Institute of Chemical Engineers. In Annual Meeting Thermal Stability of Hollow Fibers in Olefin/Paraffin Distillation; American Institute of Chemical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Devlin, D.J.; Barbero, R.S. Effect of Hollow Fiber Morphology and Compatibility on Propane/Propylene Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, P.S.; Chang, J.S.; Nam, S.E.; Park, Y.I. Preparation of Carbon Molecular Sieve Membranes on Low-Cost Alumina Hollow Fibers for Use in C3H6/C3H8 Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppler, R.J.; Timmons, D.J.; Fang, Q.R.; Li, J.R.; Makal, T.A.; Young, M.D.; Yuan, D.; Zhao, D.; Zhuang, W.; Zhou, H.C. Potential Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 3042–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.J.; Brunelli, N.A.; Eum, K.; Rashidi, F.; Johnson, J.R.; Koros, W.J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Interfacial Microfluidic Processing of Metal-Organic Framework Hollow Fiber Membranes. Science 2014, 345, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, K.; Ma, C.; Rownaghi, A.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. ZIF-8 Membranes via Interfacial Microfluidic Processing in Polymeric Hollow Fibers: Efficient Propylene Separation at Elevated Pressures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25337–25342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, K.; Ma, C.; Koh, D.Y.; Rashidi, F.; Li, Z.; Jones, C.W.; Lively, R.P.; Nair, S. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes Supported on Macroporous Carbon Hollow Fibers by Fluidic Processing Techniques. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.T.; Jeong, H.K. In Situ Synthesis of Thin Zeolitic-Imidazolate Framework ZIF-8 Membranes Exhibiting Exceptionally High Propylene/Propane Separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10763–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Kwon, H.T.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, J. Counter-Diffusion-Based in Situ Synthesis of ZIF-67 Membranes for Propylene/Propane Separation. Mater. Lett. 2020, 271, 127777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Su, P.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Ou, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, E. Ultrathin Metal-Organic Framework Membrane Production by Gel-Vapour Deposition. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koros, W.J.; Fleming, G.K. Membrane-Based Gas Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 83, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Xu, L.; Labreche, Y.; Kraftschik, B.; Koros, W.J. Highly Scalable ZIF-Based Mixed-Matrix Hollow Fiber Membranes for Advanced Hydrocarbon Separations. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 2625–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqassar Bani Almarjeh, R.; Atassi, Y. Enhancing Gas Separation Efficiency: A Comprehensive Experimental Database for AI-Driven Modeling of Polymeric Hollow-Fiber Membranes. Next Res. 2025, 2, 100417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DAM4CO2 Project. Available online: http://www.dam4co2.eu/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
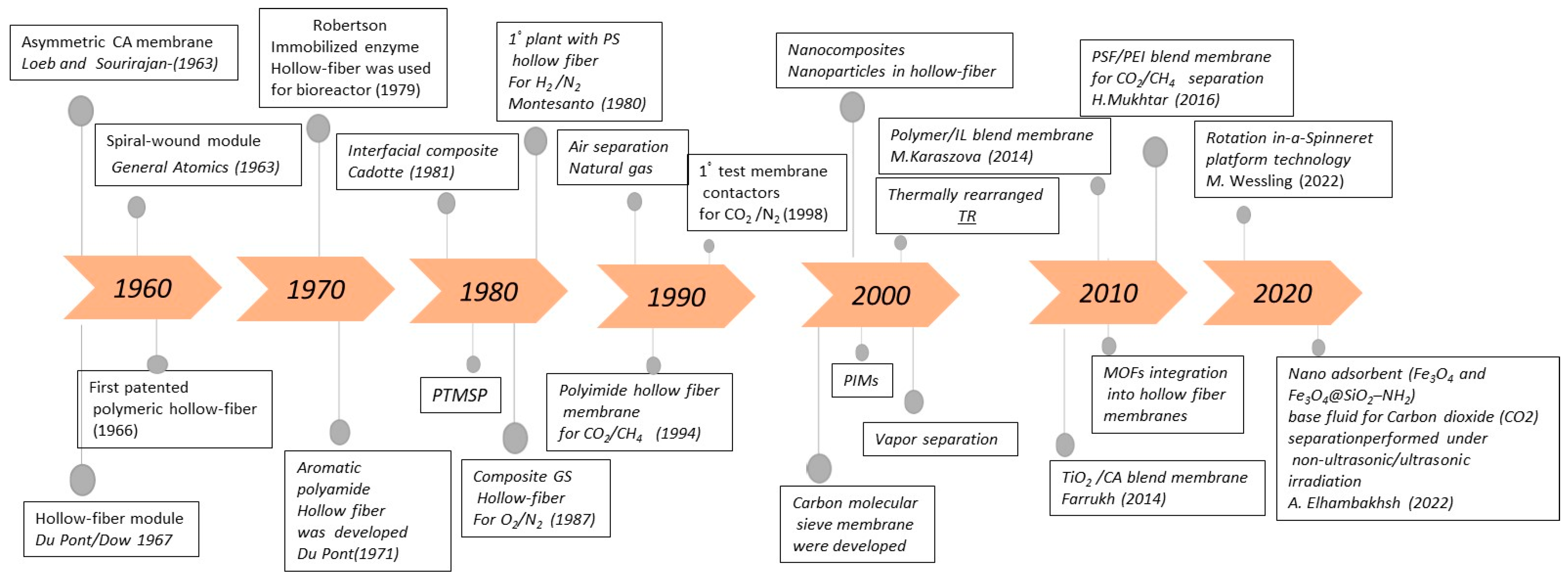
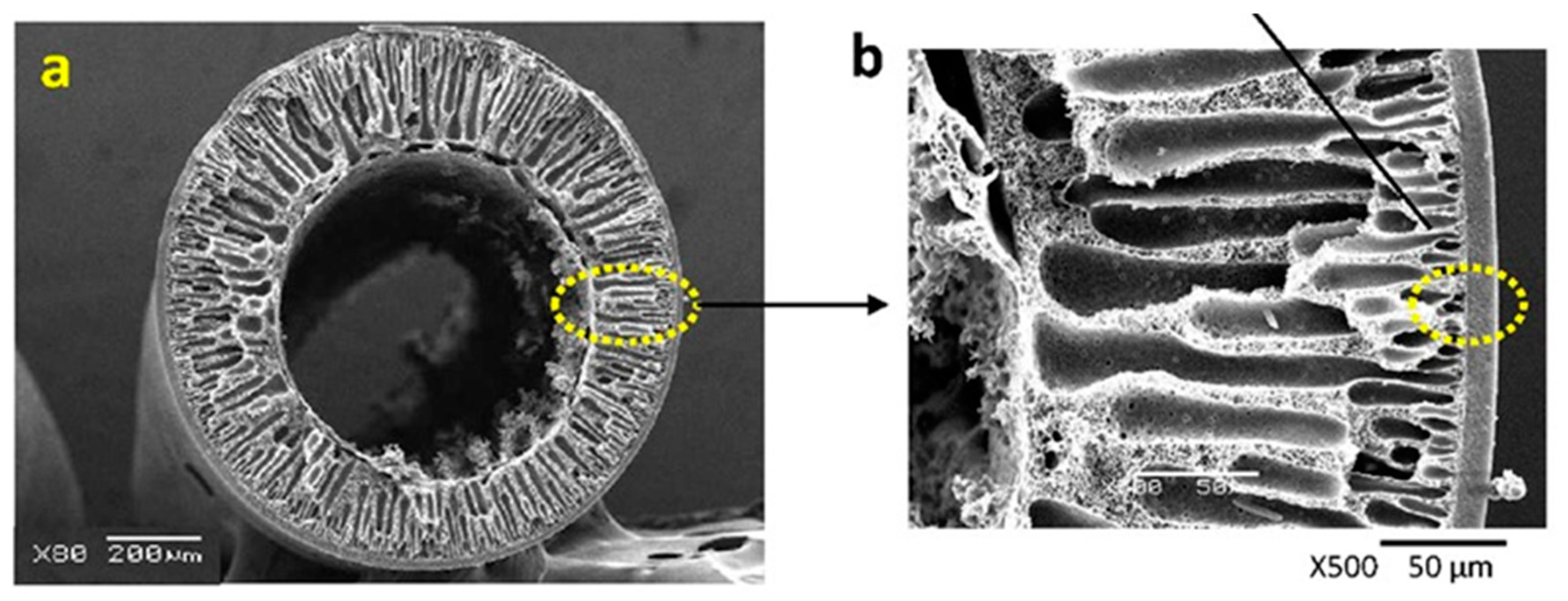
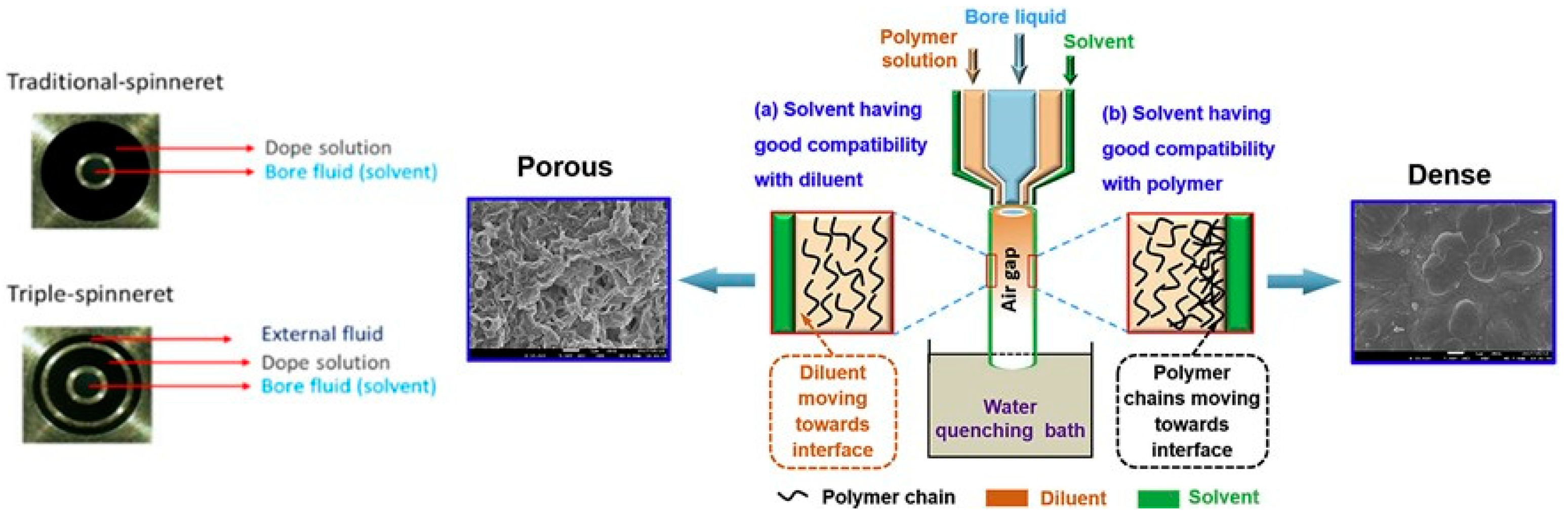
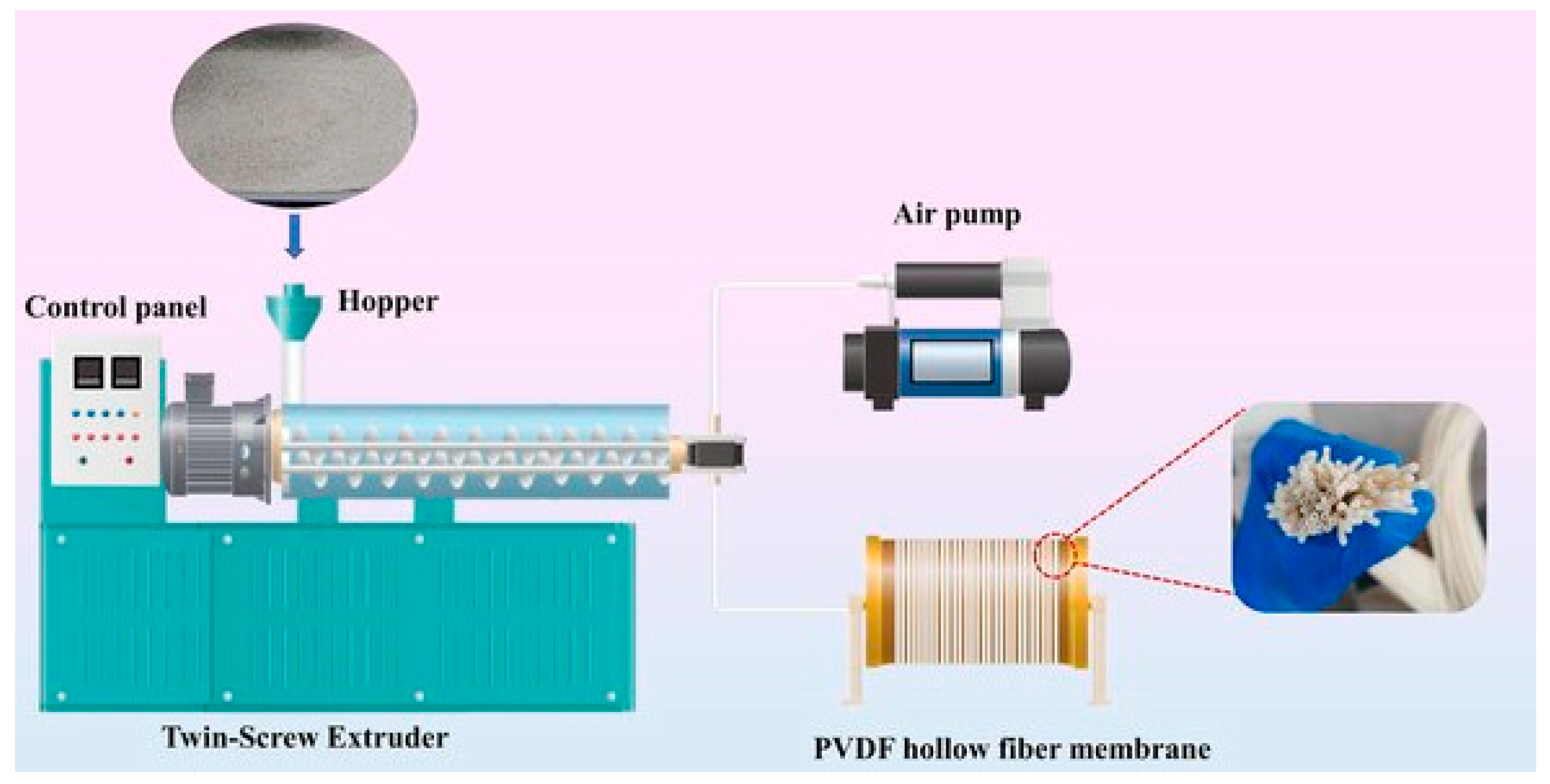
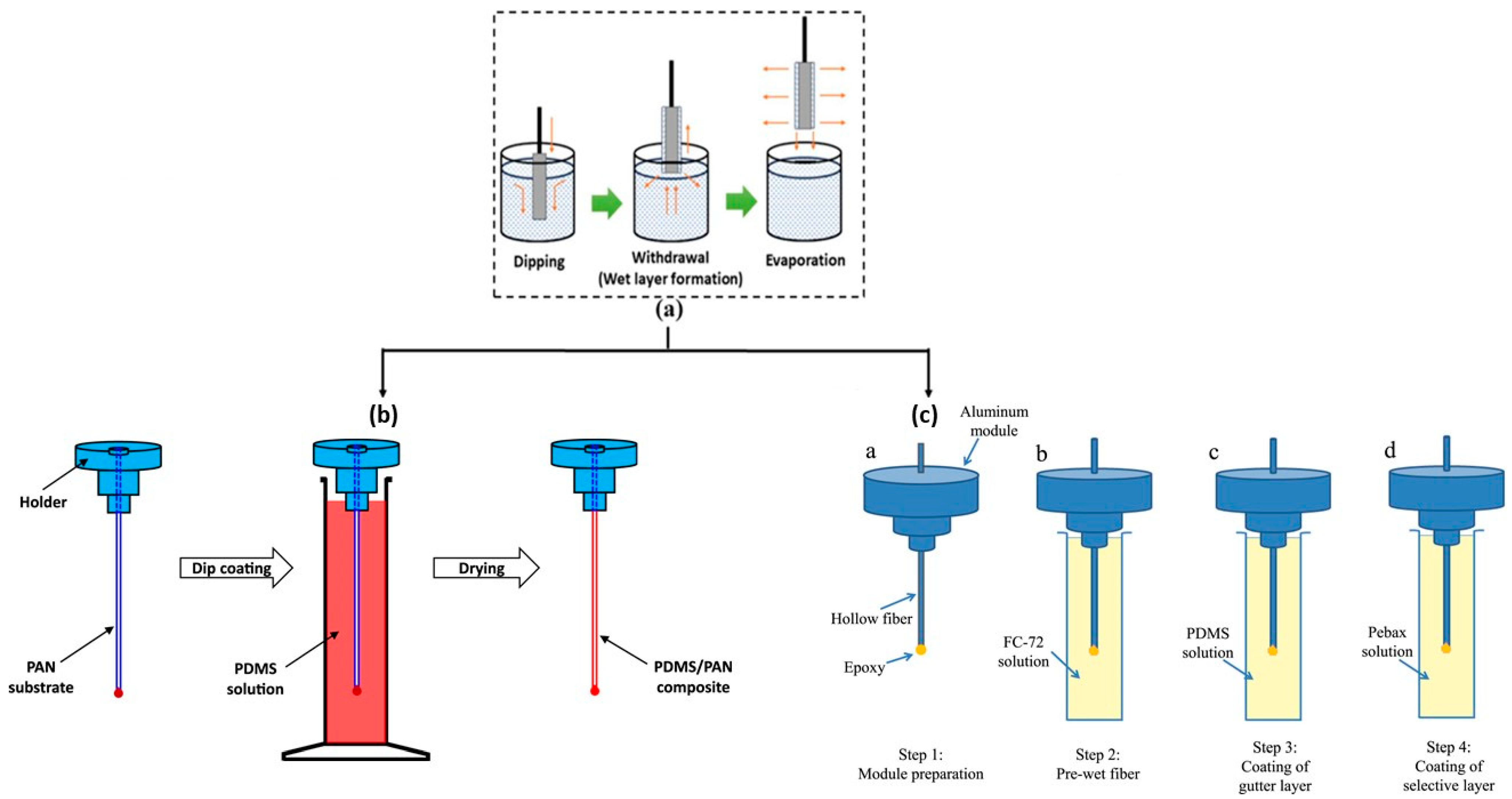
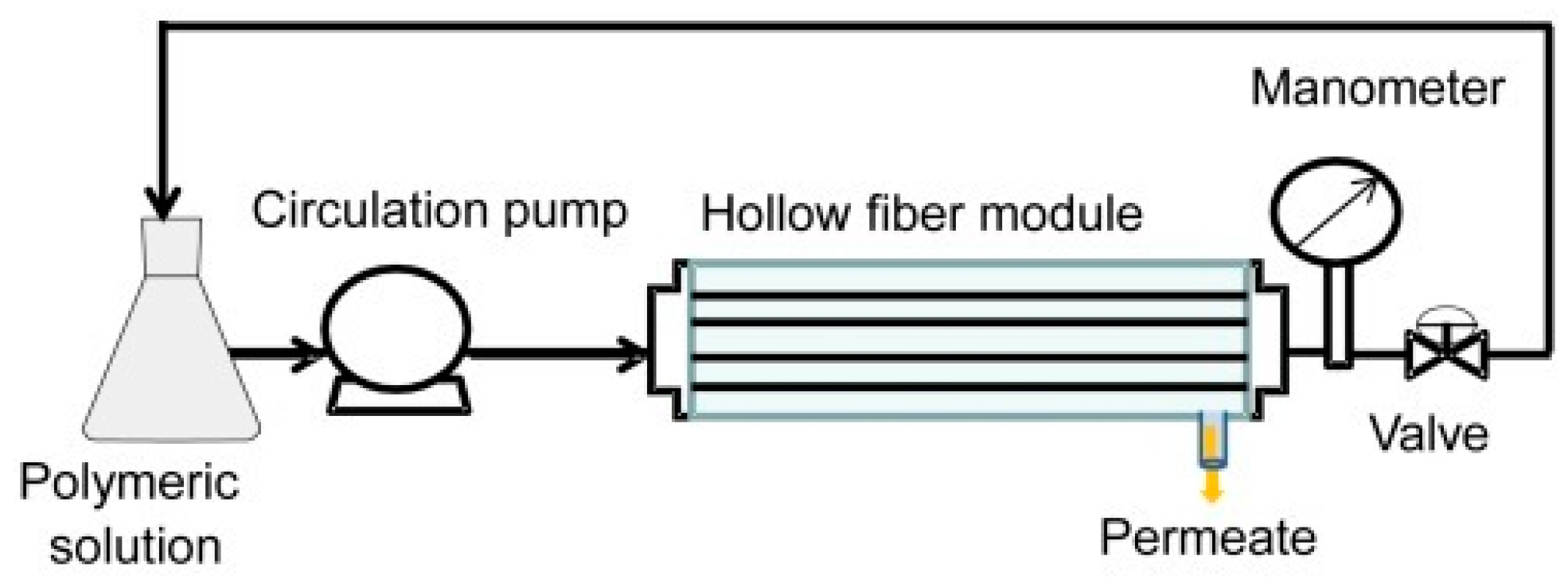
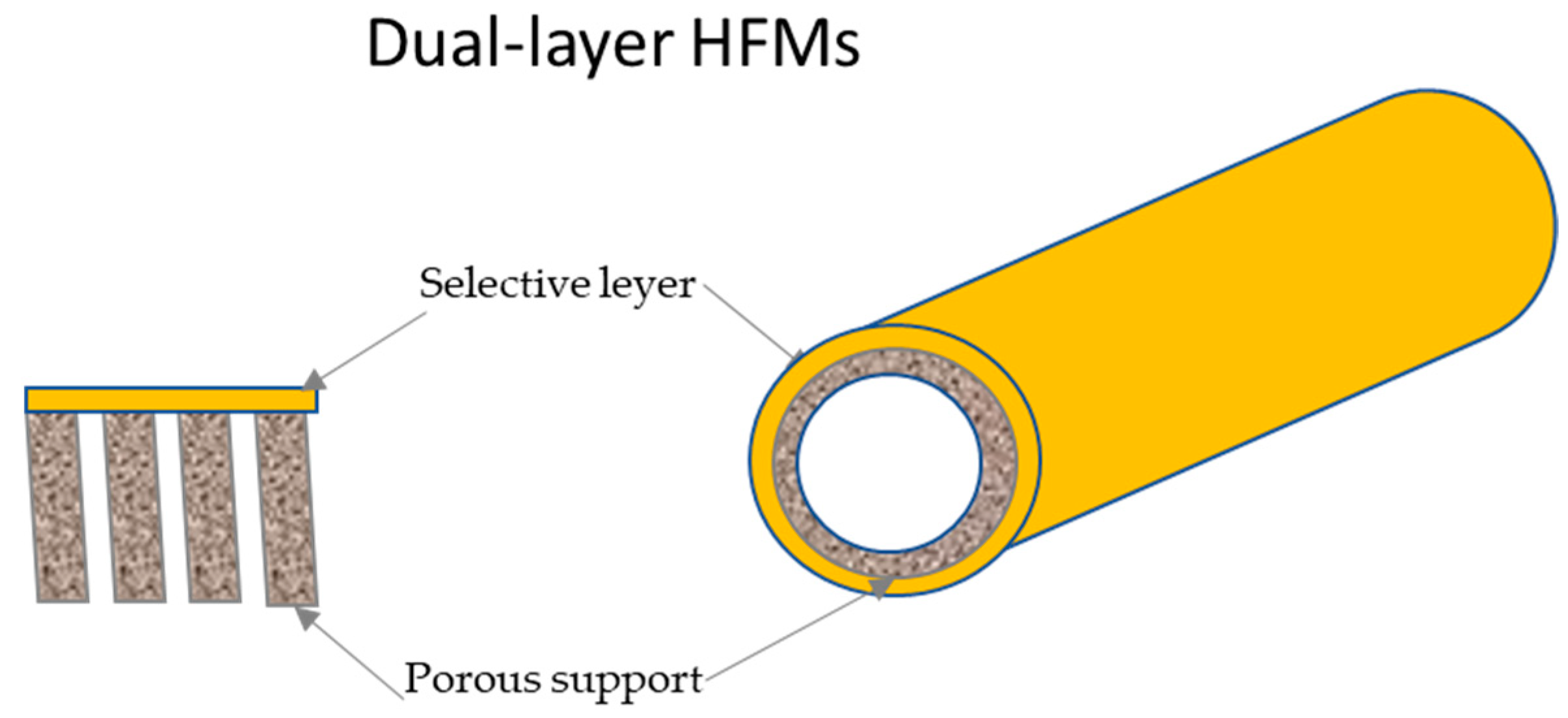
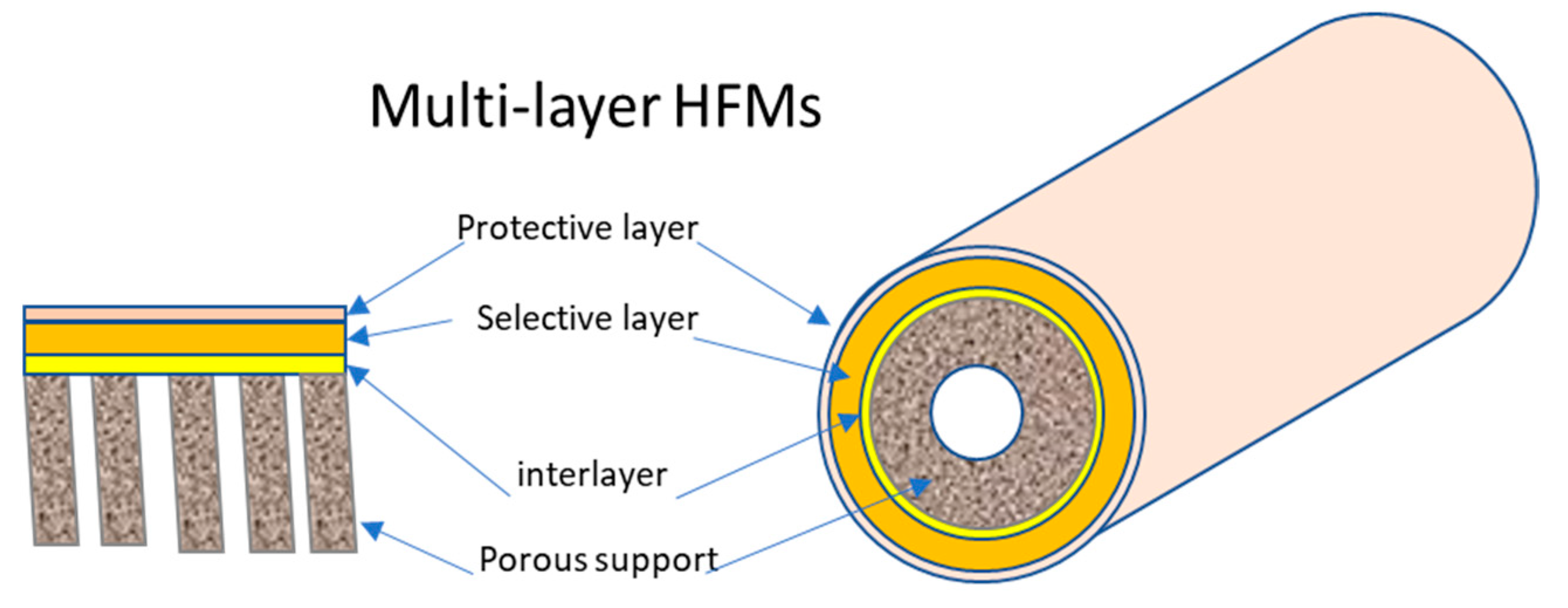
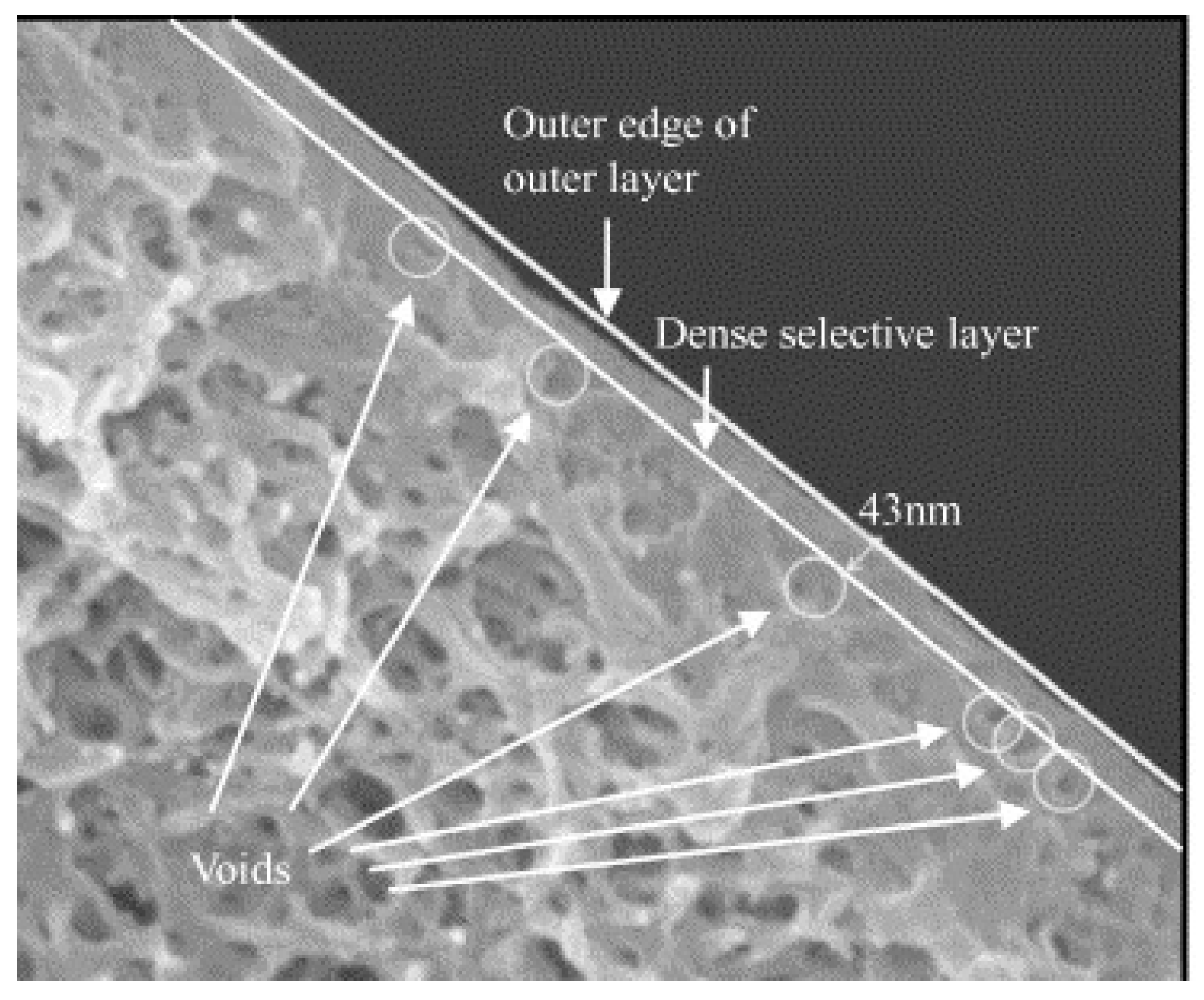
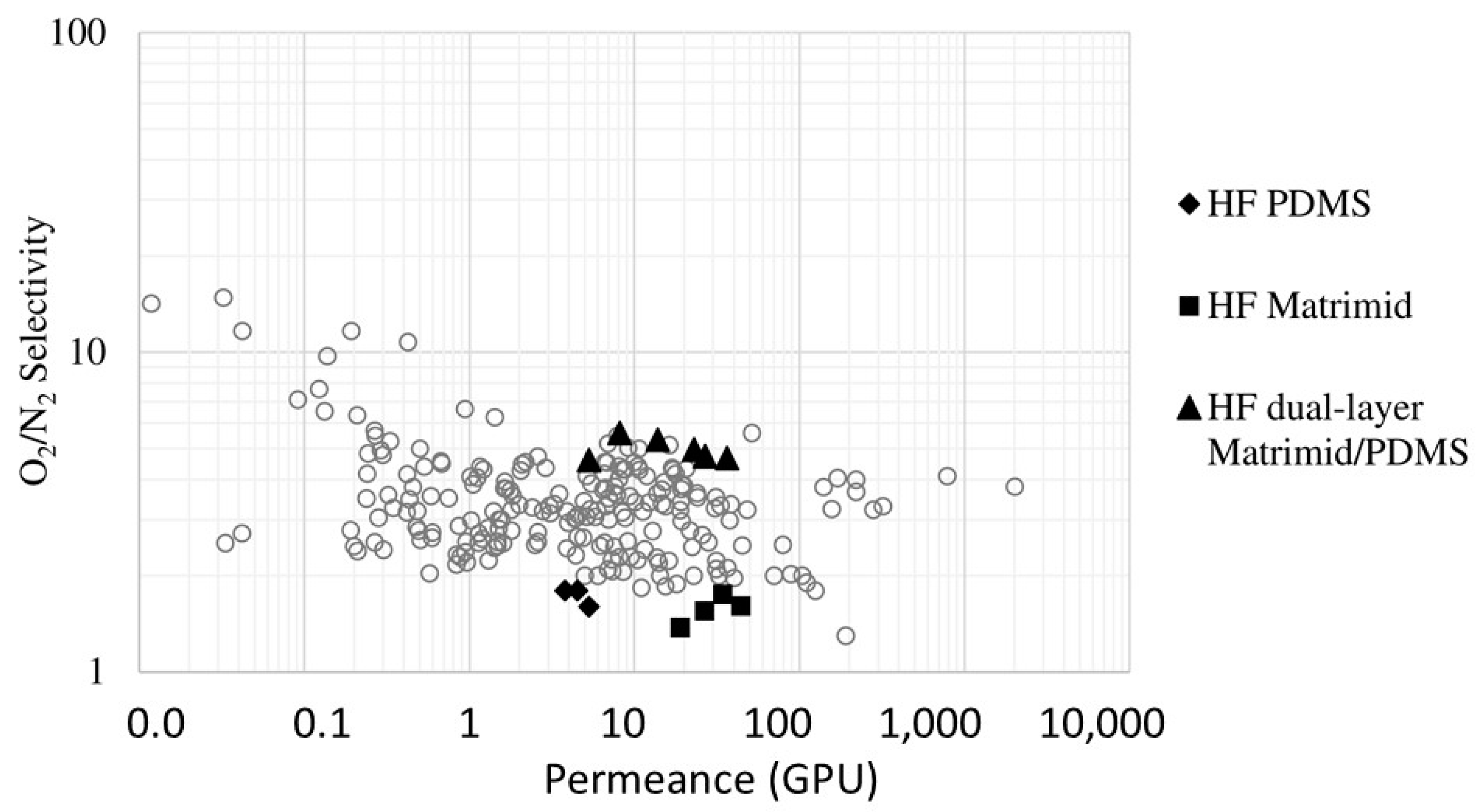
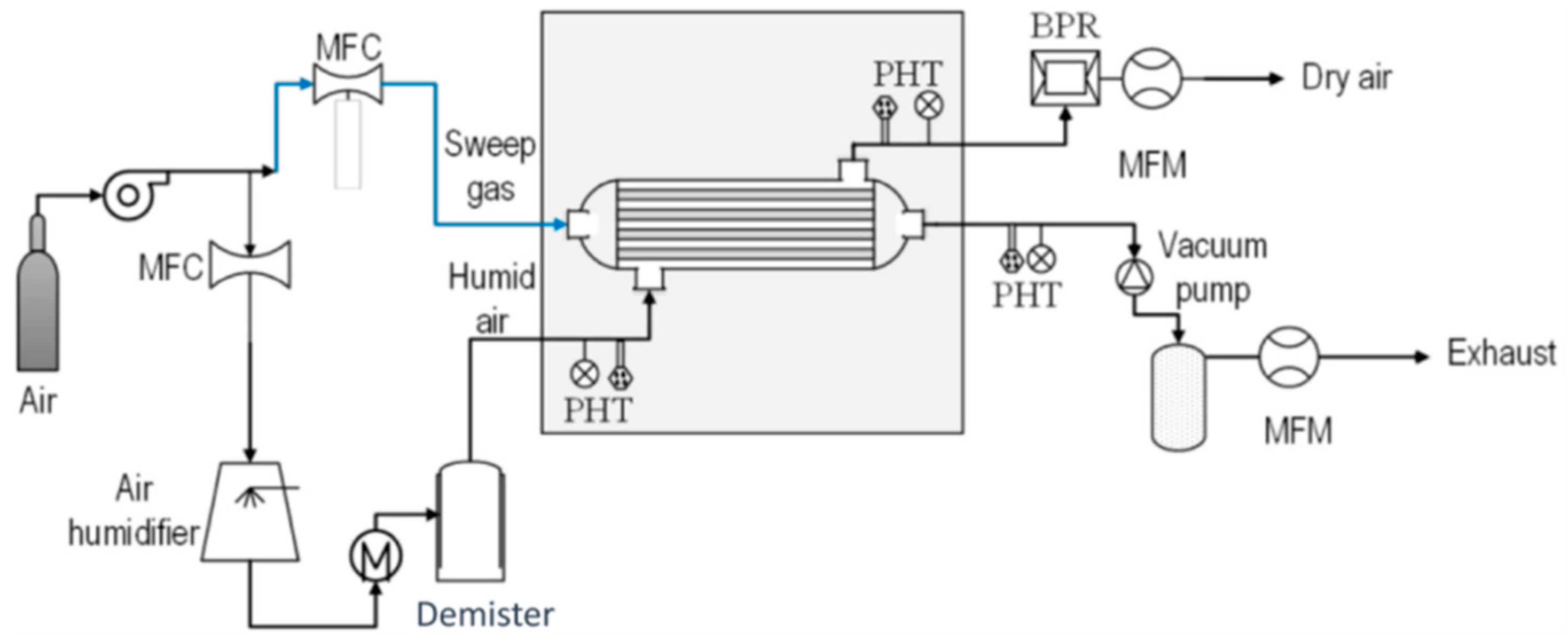
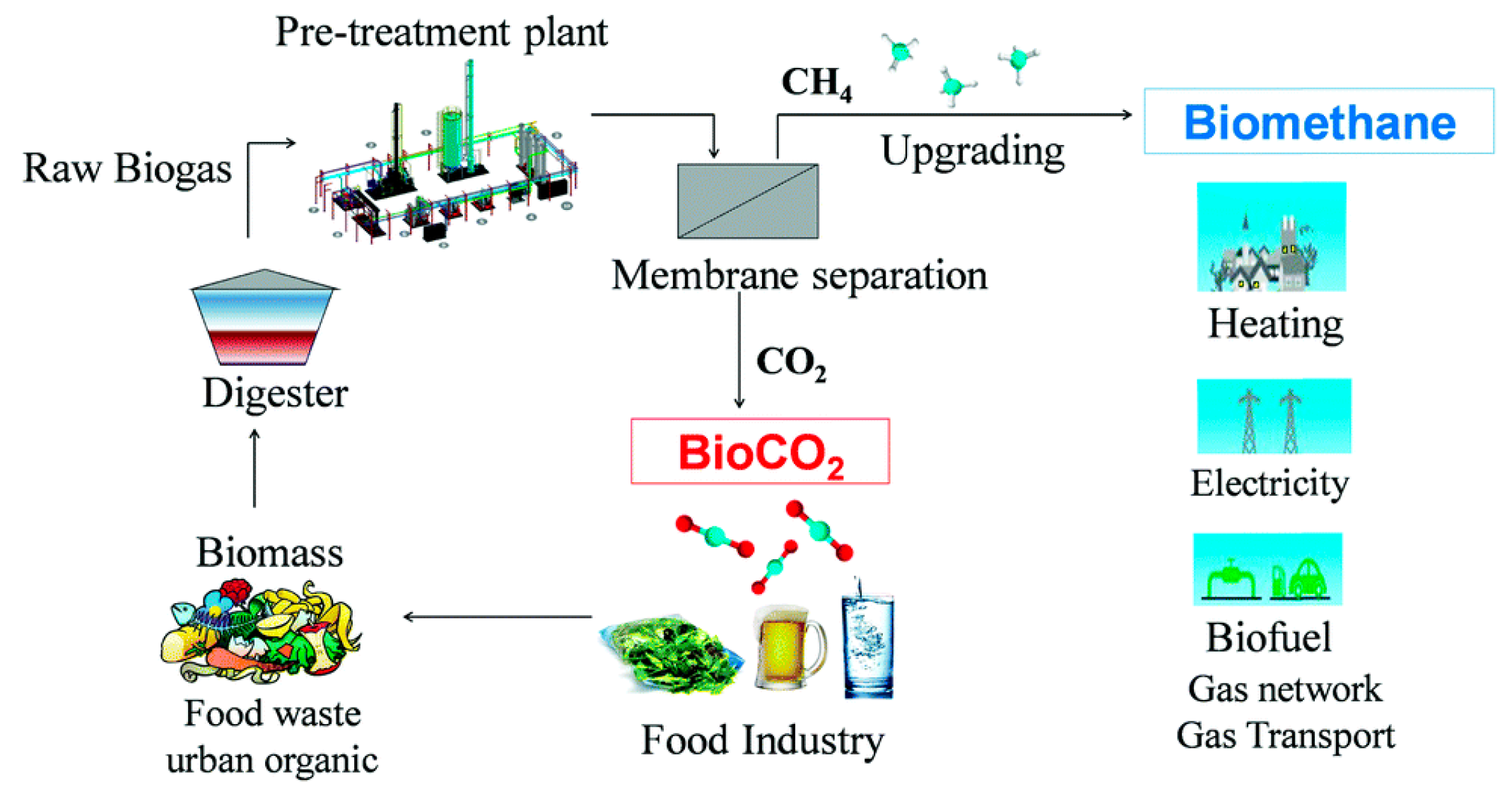
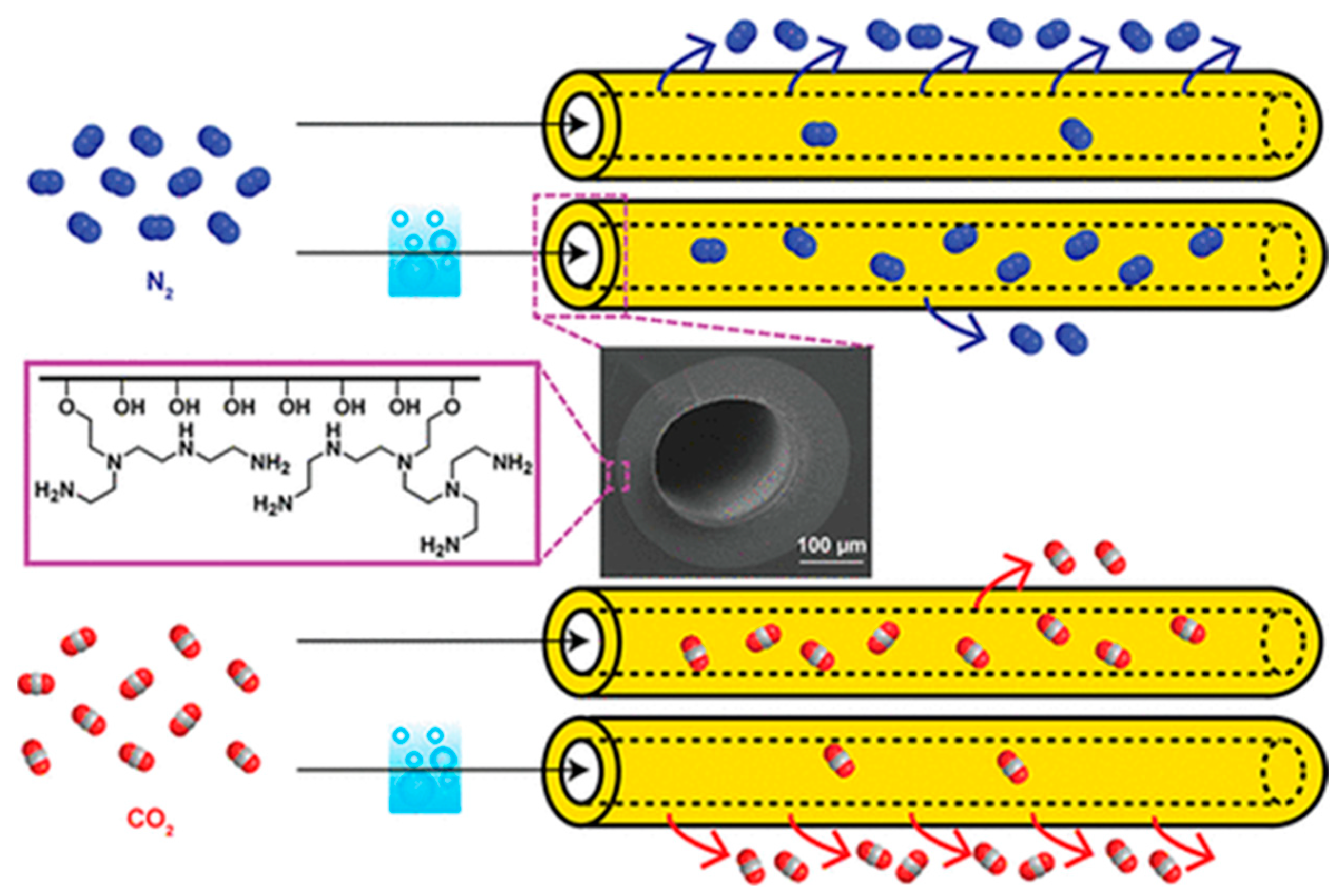
| Polymers | Top-Layer Thickness, [µm] | PCO2 [GPU] | Selectivity [-] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torlon® | 0.41 | 0.84 | CO2/N2 = 25 | [110] |
| Matrimid®+PIM-1 | 0.07 | 243 | CO2/N2 = 25 | [58] |
| ODPA−TMPDA/DAT Copolyimide | 0.27 | 39 | CO2/N2 = 44 | [111] |
| PES+Ag+ | 0.079 | 38 | CO2/N2 = 53 | [112] |
| Ultem®1010+PIM-1 | 0.10 | 49 | CO2/N2 = 21 | [113] |
| P84/PES-PEBA | n.a. | 1.42 | CO2/CH4 = 56.5 | [114] |
| PDMS/PEI | n.a. | 51 | CO2/N2 = 21 | [51] |
| TR-PBO | 0.19 | 2500 | CO2/N2 = 16 | [115] |
| HF | Top Layer | Thickness [µm] | PCO2 [GPU] | Selectivity [-] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | PEG | 0.15 | 30 | CO2/N2 = 50 | [119] |
| PAN | Pebax®1657 | 0.5 | 59 | CO2/CH4 = 12 | [49] |
| PVDF/PTMSP | Pebax®1657 | 1 | 111 | CO2/N2 = 92 | [120] |
| PVDF | Pebax®1657/[EmimBF4] | 4–5 | 306 | CO2/N2 = 36 | [47] |
| PSF | GO/Pebax®1657 | 0.3 | 28.08 | CO2/N2 = 43 | [83] |
| PES | PES/Silicone | 0.04 | (PO2 = 10) | O2/N2 = 6 | [121] |
| Solvent | Chemical Structure | Polymer | Separation [α] | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triethyl phosphate (TEP) |  | PVDF (as a support) | As a porous support | [122] |
| Gamma-butyrolactone (GBL) |  | P84 (as a support) | CO2/CH4 = 26; 25 °C | [123] |
| Ethanol (EtOH) |  | m-PBI (as a top layer) | H2/CO2 = 20.5; 150 °C 7 bar | [124] |
| EtOH/water (70/30 wt./wt.) mixture |  | Pebax®1657 (as a top layer) | CO2/CH4 18; 25 °C, 1–4 bar | [49] |
| Separation | Application Field | Main Brands and Suppliers | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helium separation | Helium purification | Sepuran® Noble (Evonik) | [234] |
| H2 separation | H2 recovery | Sepuran®Noble (Evonik) HH, UBE H2, (Ube Industry) | [235] |
| Polysep (UoP Honeywell company) PRISM® (Air Products) | [236] | ||
| O2/N2 | O2-enriched Air production Nitrogen generation | GENERON® Sepuran® N2 (Evonik) PRISM® (Air Products) Ims (Praxair) Medal (Air Liquide) Aquilo (Parker Hannifin) (Ube Industry) | [237] [8] |
| H2O/air | Gas/liquid separation Air dehydration | PRISM® (Air Products) Medal (Air Liquide) (Ube Industry) (Air Products) GENERON® | [8] [237] |
| CO2/CH4 | Biogas up-grading Natural gas treatment | Sepuran®green (Evonik) psf-based membrane (Airrane Co., Ltd.) GENERON® | [131] [237] |
| CO2/N2 | CO2 from flue gas | Polaris membranes (MTR) | [238] |
| CO2 separation | Acid gas treating Enhanced oil recovery Landfill gas upgrading | Cynara (Natco) Kvaerner (Grace Membrane System) (Ube Industry) (Air Products) GENERON® | [239] [237] |
| CO2/H2 | Celazole (PBI performance products inc.) | [240] |
| Polymer | Helium Permeability (GPU) | He/CH4 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torlon® | 7.4 | 370 | [110] |
| P84 | 14.3 | 304 | [243] |
| Ultem® | 55 | 98 | [79,244] |
| Matrimid®5218 | 195 | 12 | [245] |
| 6FDA-DAM-DABA | 340 | 20 | [161] |
| PBDI | 50 | 100 | [1] |
| PIM-PI/alumina precursor | 40.0 | 11.2 | [246] |
| PTMSP coated multi-layer TFC | 5.96 | 36.39 | [116] |
| Polymer | H2 Permeance (GPU) | H2/CO2 (-) | H2/CH4 (-) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTMSP/Polyamide/PAN | 7.79 | 28.3 | 40.1 | [258] |
| PBI-sPPSU/PSf | 16.7 | 9.7 | [1] | |
| PSf/TNT/PDMS | 120 | 57.86 | [16] | |
| PBI/ZIF-8/PDMS | 107 | 18.0 | - | [259] |
| Polyaniline | 5.0 | 7.9 | - | [144] |
| Matrimid | 66.05 | 5 | - | [260] |
| sPPSU/PBI | 16.7 | 9.7 | - | [1] |
| TNTs/PSf | 120 | 57.84 | [16] | |
| ZIF-8/PBI | 107 | 18 | - | [259] |
| GO/α-Al2O3 | 300 | 15 | 6.4 | [261] |
| ZIF-8/Si3N4 | 2505 | 7.6 | - | [262] |
| Polymer | CO2 [GPU] | CO2/CH4 [-] | H2S [GPU] | H2S/CH4 [-] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose triacetate-HF | 110 | 22 | 140 | 28 | [292] |
| 6FDA-based polyimides with bulky CF3 groups (PDMC−CF3) | 35 | 32 | 32 | 30 | [293] |
| Crosslinking-modified 6FDA-2,6-DAT-HFs | 55 | 60 | - | - | [160] |
| Co-polyimide grafted with β-Cyclodextrin-HFs | 130 | 15 | - | - | [294] |
| PDMC-ester-crosslinkable PI-HFs | 120 | 30 * | - | - | [295] [172] |
| Material for CO2/N2 | Membrane | CO2 [GPU] | CO2/N2 [-] | T [°C] | Press. [bar] | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDMS/PAN | PDMS/PAN composite HF membranes | 3700 | 10 | 25 | 1 | [129] | |
| PDMS/PAN composite-HF, PVP grafted | 2500 | 12 | - | - | [297] | ||
| PEG | PEG_HF-composite | 30 | 50 | 25 | 2 | [119] | |
| CA | Cellulose acetate | 13 | 39 | 25 | 3 | [298] | |
| PSF | PSF HF-commercialized by Airrane Co. (Daejeon, Republic of Korea) | 120 | 26 | 25 | [299] | ||
| TPESU (new pes) | 85 | 34 | 25 | 1 | [171] | ||
| PI | Matrimid® | 86 | 33 | 25 | 1 | [58] | |
| P84® (BTDA-TDI/MDI) co-polyimide | 23 | 40 | 35 | 1 | [300] | ||
| 6FDA-DAM-DABA | 520 | 24 | 30 | 2.3 | [301] | ||
| BTDA-TDI/MDI co-PI (P84) | 2.2 | 45–50 | - | 20 | [243] | ||
| PIMs | PIM-1 composite multi-layer-HF Blend polymers | 483 | 22 | [118] | |||
| PIM-1/Matrimid® | 235 | 25 | 25 | 1 | [58] | ||
| Thermoplastic Polyolefin | Poly(4-methyl-1-pentene) (PMP) | 68.4 | 13.5 | 25 | 1 | [302] | |
| Material for N2/CO2 | Membrane | N2 (GPU) | CO2 (GPU) | N2/CO2 [-] | T [°C] | Press. [bar] | Ref. |
| Mesoporous Silica | hyperbranched aminosilica (HAS_dry) | 12 | 1.8 | 6.7 | 35 | [296] | |
| hyperbranched aminosilica (HAS_wet) | 3.6 | 9.7 | 0.37 | 35 | [296] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grosso, V.; Rizzuto, C.; Tocci, E.; Fuoco, A.; Longo, M.; Monteleone, M.; Hajivand, P.; Jansen, J.C.; Esposito, E. Review of Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation: Exploring Fundamentals and Recent Advancements. Membranes 2025, 15, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080246
Grosso V, Rizzuto C, Tocci E, Fuoco A, Longo M, Monteleone M, Hajivand P, Jansen JC, Esposito E. Review of Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation: Exploring Fundamentals and Recent Advancements. Membranes. 2025; 15(8):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080246
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrosso, Valentina, Carmen Rizzuto, Elena Tocci, Alessio Fuoco, Mariagiulia Longo, Marcello Monteleone, Pegah Hajivand, Johannes C. Jansen, and Elisa Esposito. 2025. "Review of Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation: Exploring Fundamentals and Recent Advancements" Membranes 15, no. 8: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080246
APA StyleGrosso, V., Rizzuto, C., Tocci, E., Fuoco, A., Longo, M., Monteleone, M., Hajivand, P., Jansen, J. C., & Esposito, E. (2025). Review of Hollow Fiber Membranes for Gas Separation: Exploring Fundamentals and Recent Advancements. Membranes, 15(8), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080246













