Pilot-Scale Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Patterned Membranes: Phase-Inversion Parametric Optimization on a Roll-to-Roll Casting System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dope Solution Preparation
2.2. Membrane Characterizations
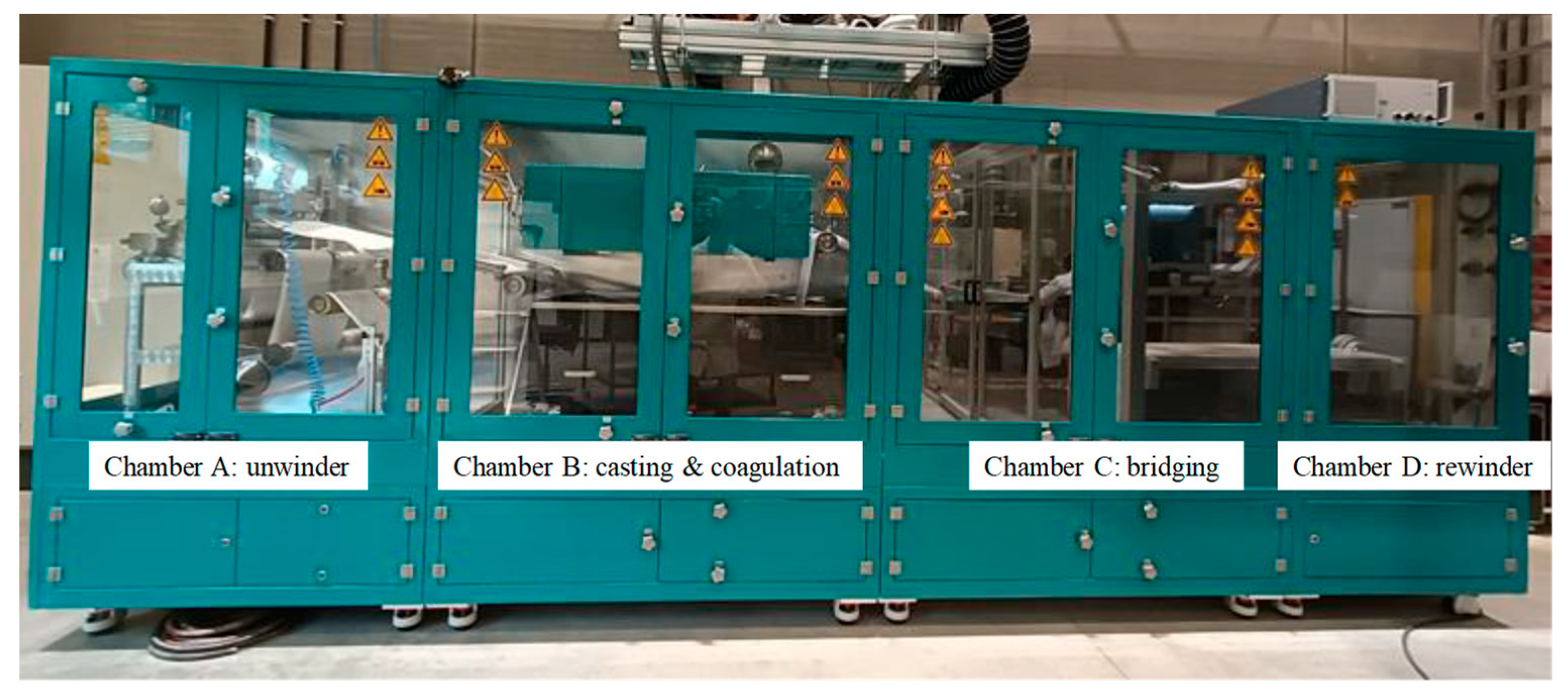
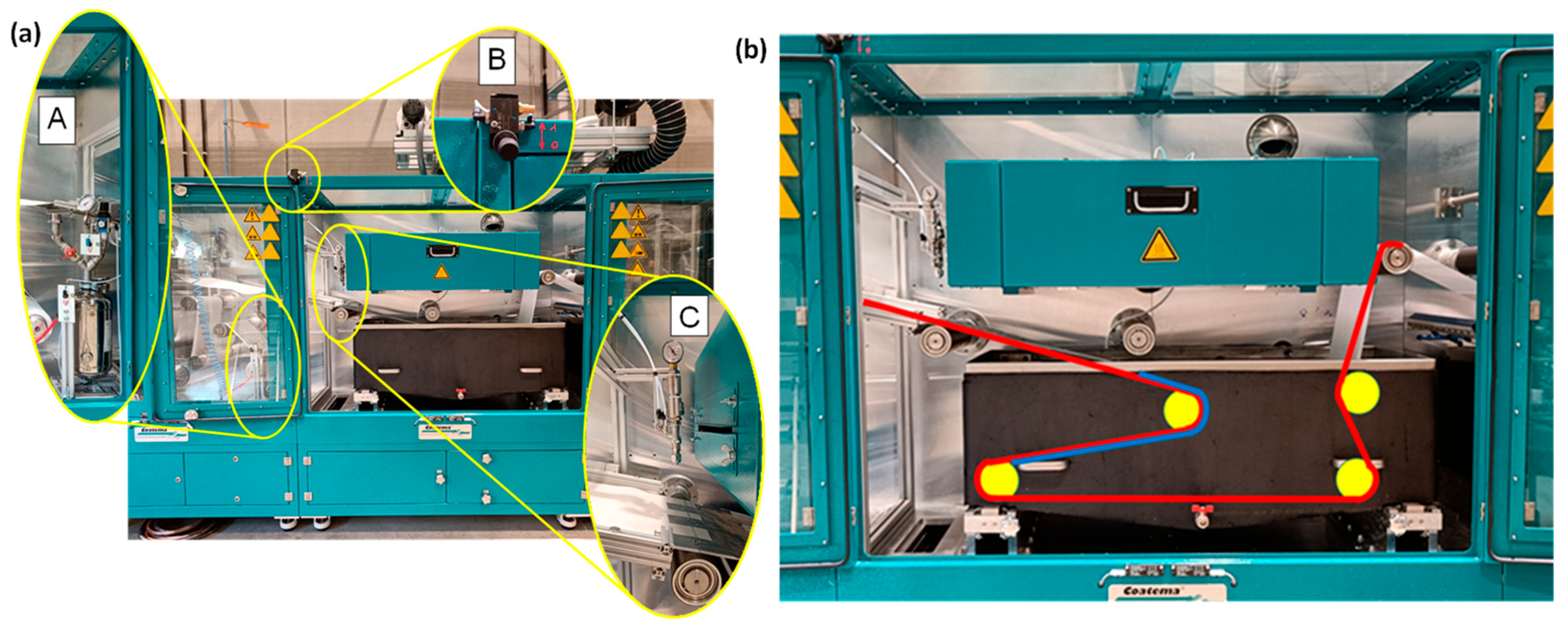
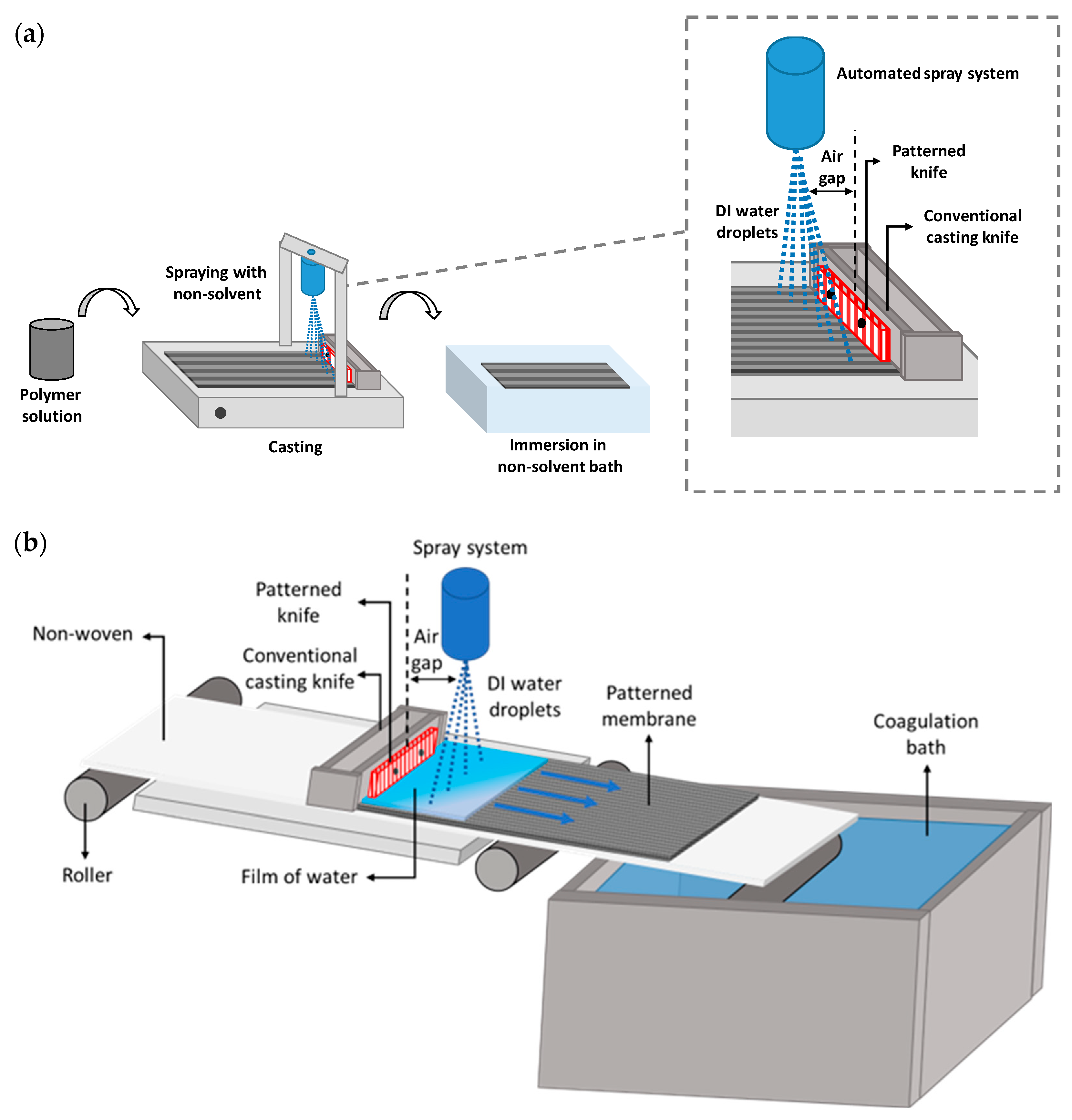
2.3. Roll-to-Roll (R2R) System Design
3. Results
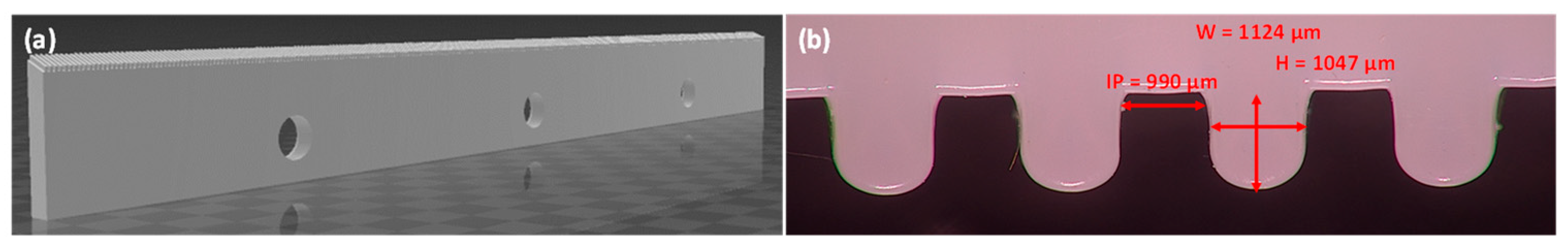
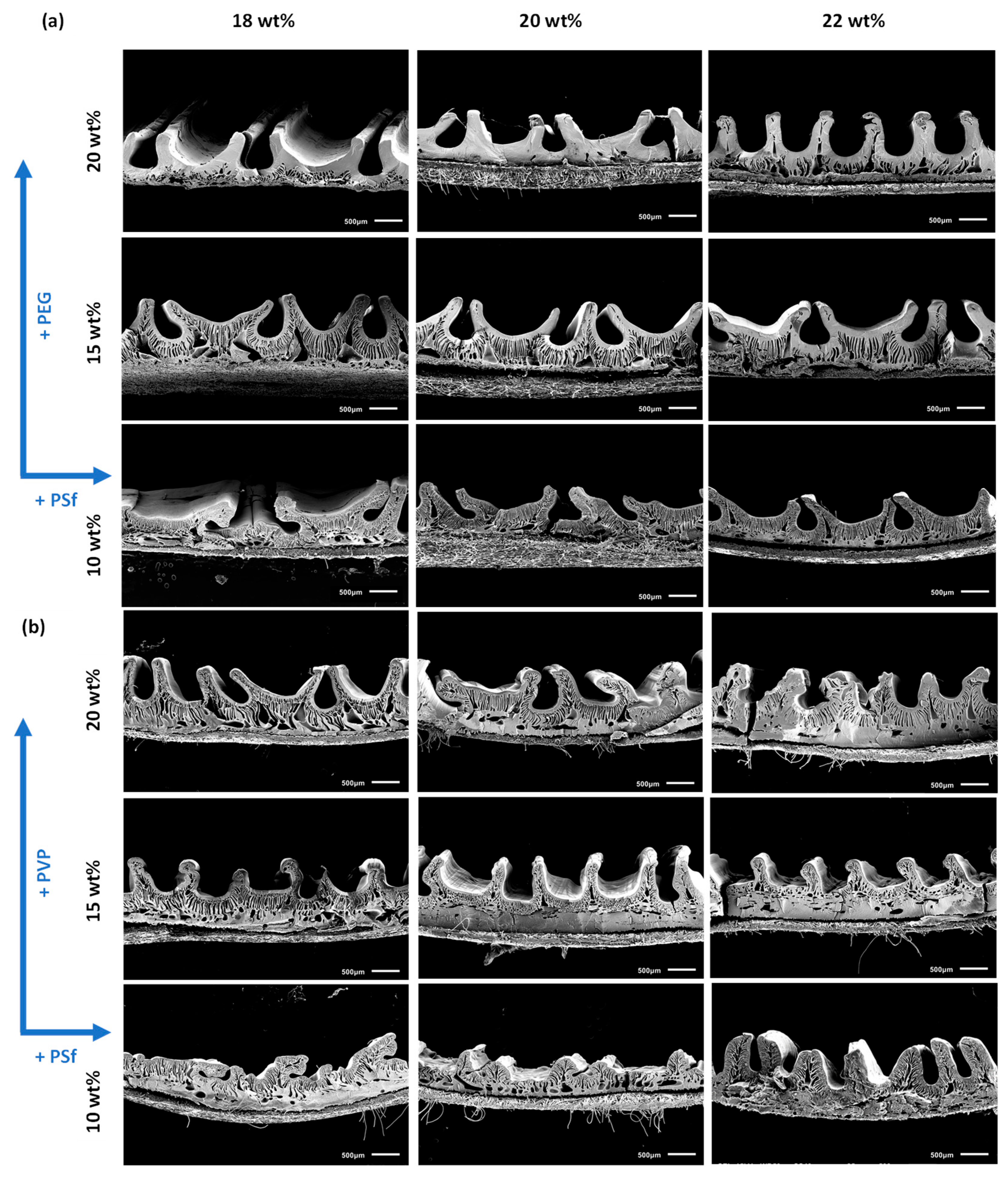
3.1. Patterned Membrane Preparation
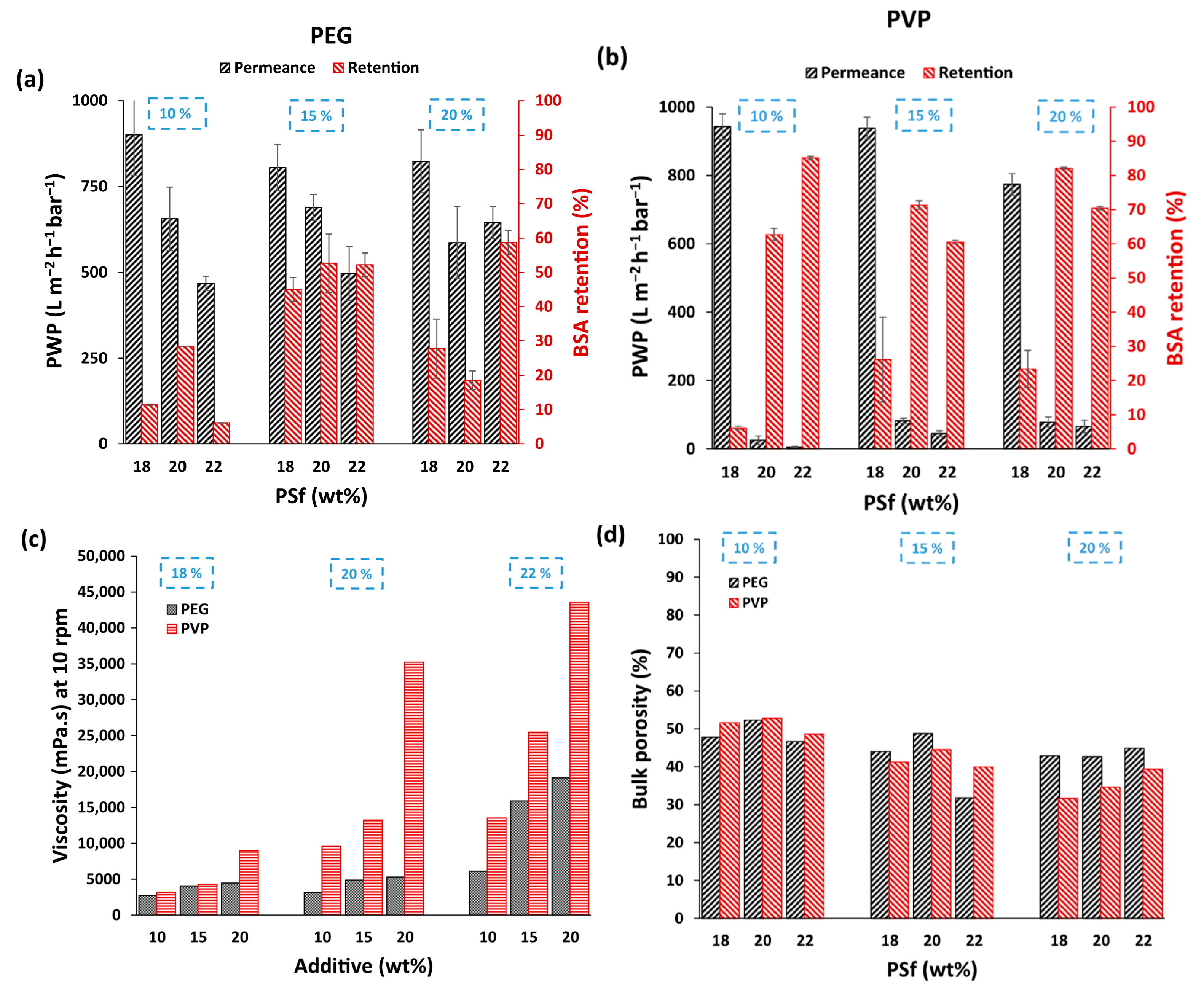
3.2. Performance Comparison for PEG and PVP-Based Membranes
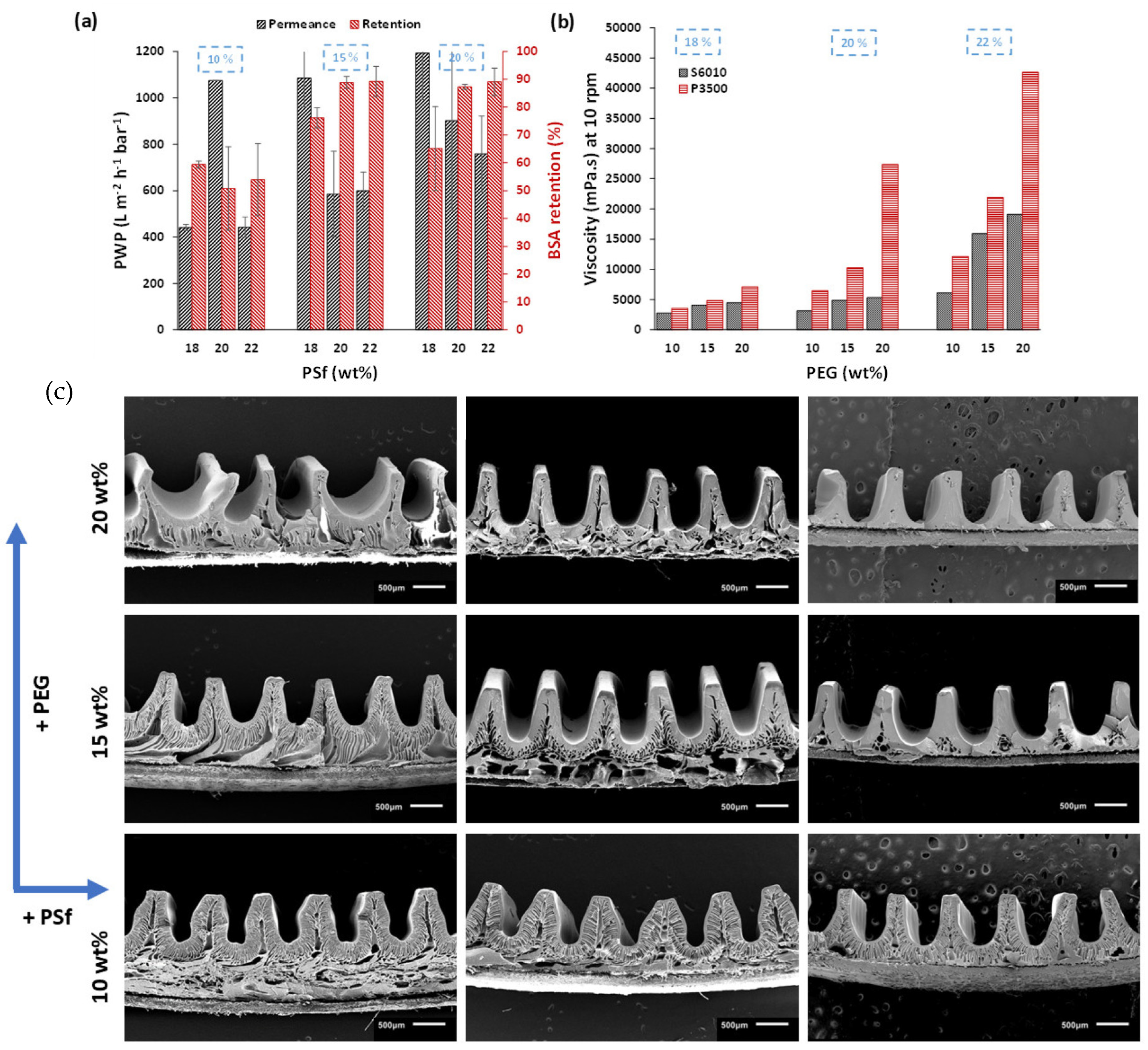
3.3. Effect of Polymer MW
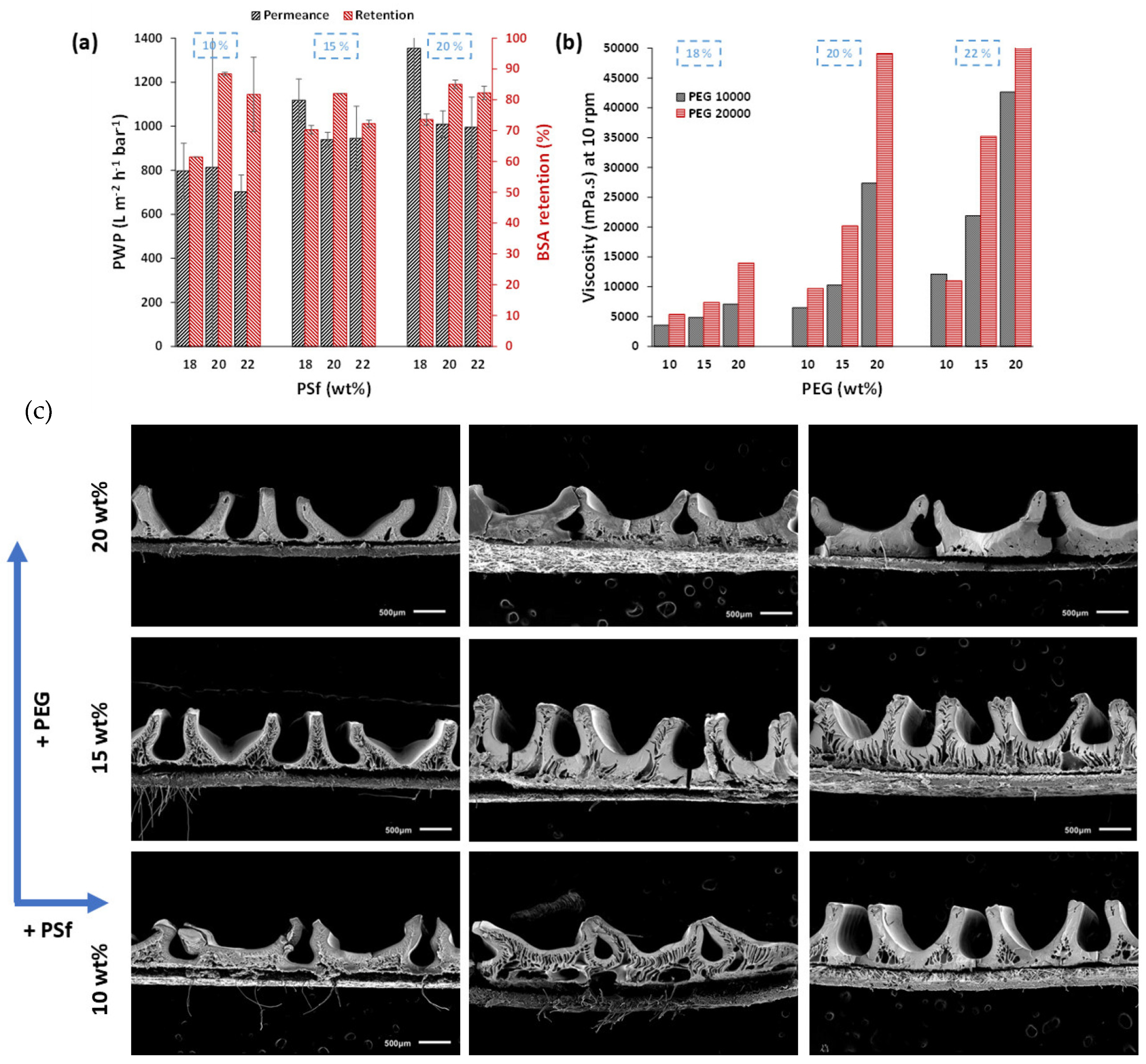
3.4. Effect of PEG MW
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, J.; Liu, N.; Li, L.; Lee, R. Organic fouling and regeneration of zeolite membrane in wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, T.; Shi, J.; Teng, K.; Wang, W.; Ma, M.; Li, J.; Qian, X.; Li, C.; Fan, J. Photocatalytic antifouling PVDF ultrafiltration membranes based on synergy of graphene oxide and TiO2 for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Xiong, X.; Gai, X.; Zeng, J.; Luan, G.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, J. Preparation of Ultrafiltration Membrane by Polyethylene Glycol Non-Covalent Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Application for HA Removal and Fouling Contro. Membranes 2021, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; He, F.; Wang, B.; Chung, T.-S.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A.; Tong, Y.W. An aquaporin-based vesicle-embedded polymeric membrane for low energy water filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2013, 1, 7592–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mama, L.; Pirkin-Benameur, J.; Bouad, V.; Fournier, D.; Woisel, P.; Lyskawa, J.; Aissou, K.; Quemener, D. Development of Thermo-Responsive and Salt-Adaptive Ultrafiltration Membranes Functionalized with PNIPAM-co-PDMAC Copolymer. Membranes 2025, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Heer, J.; Sankar, S.; Geiger, F.; Gukelberger, E.; Galiano, F.; Mancuso, R.; Gabriele, B.; Figoli, A.; Hoinkis, J. Study on UF PES Membranes Spray-Coated with Polymerizable Bicontinuous Microemulsion Materials for Low-Fouling Behavior. Membranes 2023, 13, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Understanding and guiding the phase inversion process for synthesis of solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.I.M.; Chean, H.M.; Shamsuddin, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Khan, A.L. Development of Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane Using Vapour Induced Phase Separation Method for Produced Water Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.P.; Culfaz-Emecen, P.Z.; Ramon, G.Z.; Visser, T.; Koops, G.H.; Jin, W.; Ulbricht, M. Thinking the future of membranes: Perspectives for advanced and new membrane materials and manufacturing processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbelia, L.; Ilyas, A.; Dierick, M.; Qian, J.; Achille, C.; Ameloot, R.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Preparation of patterned flat-sheet membranes using a modified phase inversion process and advanced casting knife construction techniques. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 597, 117621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, A.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Qian, J.; Reynaerts, D.; Kuhn, S.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Micro-patterned membranes prepared via modified phase inversion: Effect of modified interface on water fluxes and organic fouling. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 585, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, A.; Madhav, D.; Nulens, I.; Agrawal, K.V.; Van Goethem, C.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Influence of micro-patterned support properties and interfacial polymerization conditions on performance of patterned thin-film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 700, 122721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.H.; Hotz, N.; Hawkins, B.T.; Kabala, Z.J. Inducing Deep Sweeps and Vortex Ejections on Patterned Membrane Surfaces to Mitigate Surface Fouling. Membranes 2024, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, A.; Timmermans, L.; Vanierschot, M.; Smets, I.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Micro-patterned PVDF membranes and magnetically induced membrane vibration system for efficient membrane bioreactor operation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 662, 120978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, A.; Mertens, M.; Oyaert, S.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Synthesis of patterned PVDF ultrafiltration membranes: Spray-modified non-solvent induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandezande, P.; Li, X.; Gevers, L.E.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. High throughput study of phase inversion parameters for polyimide-based SRNF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 330, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, A.; Davenport, D.M.; Dysserinck, B.; Rombaut, K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Patterned Vibrating Membranes at Pilot-Scale: Membrane Preparation and Setup Design. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 369, 133143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.H. Effect of PEG additive on membrane formation by phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 138, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Koops, G.H.; Strathmann, H. Characterization of morphology controlled polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes by the addition of polyethylene glycol to the dope and bore liquid solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 223, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.L.; Yu, D.G.; Yang, M.C.; Jou, C.H. Effect of molecular weight and concentration of PEG additives on morphology and permeation performance of cellulose acetate hollow fibers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminasab, S.; Barzin, J.; Dehghan, R. High-performance hemodialysis membrane: Influence of polyethylene glycol and polyvinylpyrrolidone in the polyethersulfone membrane. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2020, 6, 438–448. [Google Scholar]
- Spindler, R.; Shriver, D.F. Physical and Spectroscopic Properties of Ternary Polymer Electrolytes Composed of Poly(vinylpyrrolidone), Poly(ethylene glycol), and Lithium Trifluoromethanesulfonate. Macromolecules 1986, 19, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasouri, K.; Shoushtari, A.M.; Mojtahedi, M.R.M. Thermodynamic Studies on Polyvinylpyrrolidone Solution Systems Used for Fabrication of Electrospun Nanostructures: Effects of the Solvent. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2015, 34, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yune, P.S.; Kilduff, J.E.; Belfort, G. Using co-solvents and high throughput to maximize protein resistance for poly(ethylene glycol)-grafted poly(ether sulfone) UF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, A.K.; De Roeck, M.; Hendrix, K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. The influence of polymer purity and molecular weight on the synthesis of integrally skinned polysulfone membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, H.; Shiki, S.; Kawakami, H. Fabrication study of polysulfone hollow-fiber microfiltration membranes: Optimal dope viscosity for nucleation and growth. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Component | δD | δP | δH | Ra (MPa1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMP | 18.0 | 12.3 | 7.2 | - |
| PEG | 15.4 | 7.6 | 8.7 | 7.1 |
| PVP | 15.5 | 11.7 | 8.6 | 5.2 |
| Additive Concentration (wt%) | PEG Mass Loss (%) | PVP Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 17.1 | 31.0 |
| 15 | 17.3 | 32.5 |
| 20 | 17.3 | 33.7 |
| Membrane (PSf-PEG) | Pattern Height * (µm) | Surface Area Increase (%) | PWPflat Membrane (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) | PWPpatterned Based on Real Area * (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) | PWPpatterned Based on Projected Area (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) | PEG Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18–15 | 725 ± 25 | 175 ± 17 | 239 ± 24 | 351 ± 39 | 1085 ± 124 | 20 |
| 20–15 | 783 ± 28 | 198 ± 16 | 219 ± 19 | 345 ± 32 | 585 ± 103 | 20 |
| 22–15 | 825 ± 15 | 200 ± 13 | 223 ± 17 | 236 ± 29 | 598± 90 | 22 |
| Additive Concentration (wt%) | PEG Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 27.1 |
| 15 | 27.1 |
| 20 | 27.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilyas, A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Pilot-Scale Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Patterned Membranes: Phase-Inversion Parametric Optimization on a Roll-to-Roll Casting System. Membranes 2025, 15, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080228
Ilyas A, Vankelecom IFJ. Pilot-Scale Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Patterned Membranes: Phase-Inversion Parametric Optimization on a Roll-to-Roll Casting System. Membranes. 2025; 15(8):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080228
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlyas, Ayesha, and Ivo F. J. Vankelecom. 2025. "Pilot-Scale Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Patterned Membranes: Phase-Inversion Parametric Optimization on a Roll-to-Roll Casting System" Membranes 15, no. 8: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080228
APA StyleIlyas, A., & Vankelecom, I. F. J. (2025). Pilot-Scale Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Patterned Membranes: Phase-Inversion Parametric Optimization on a Roll-to-Roll Casting System. Membranes, 15(8), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15080228







