The Charged Superhydrophilic Polyelectrolyte/TiO2 Nanofiltration Membrane for Self-Cleaning and Separation Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
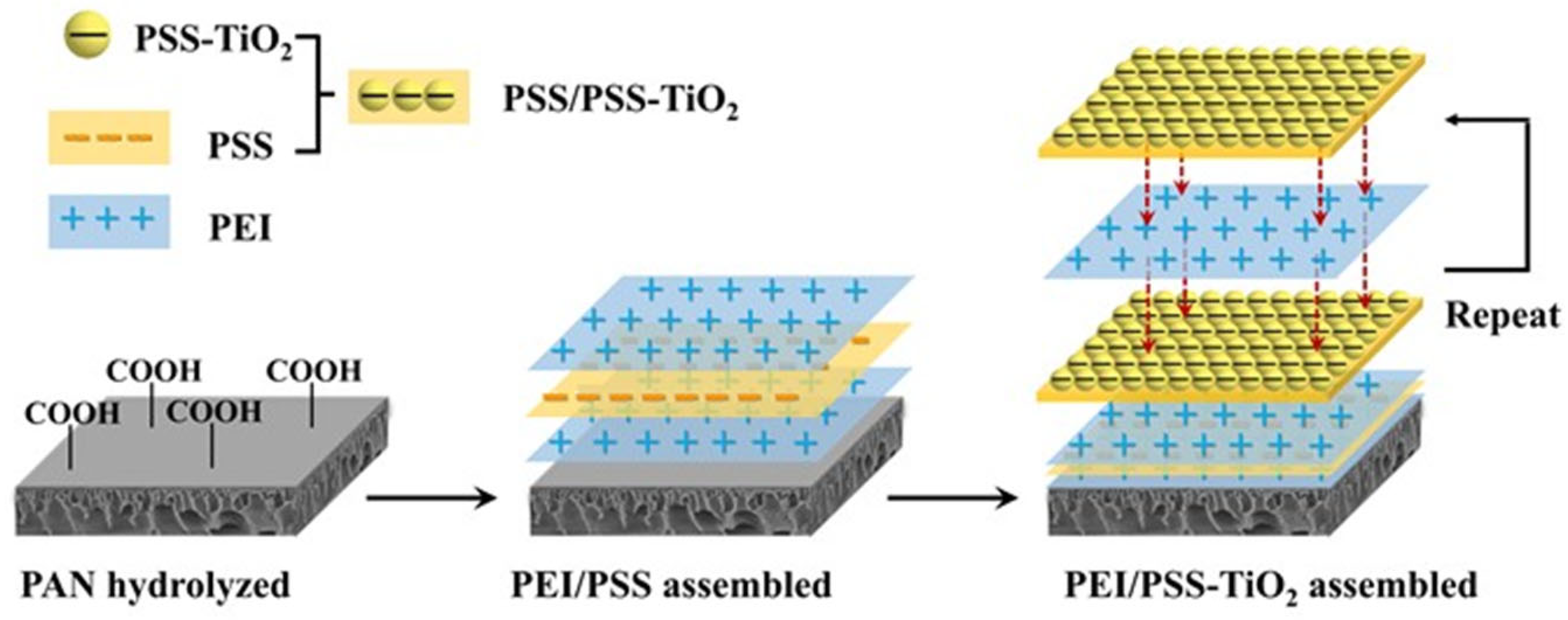
2.2. Preparation of TiO2 Hybrid Membrane by Self-Assembly
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.4. Nanofiltration Performance
3. Results and Discussions
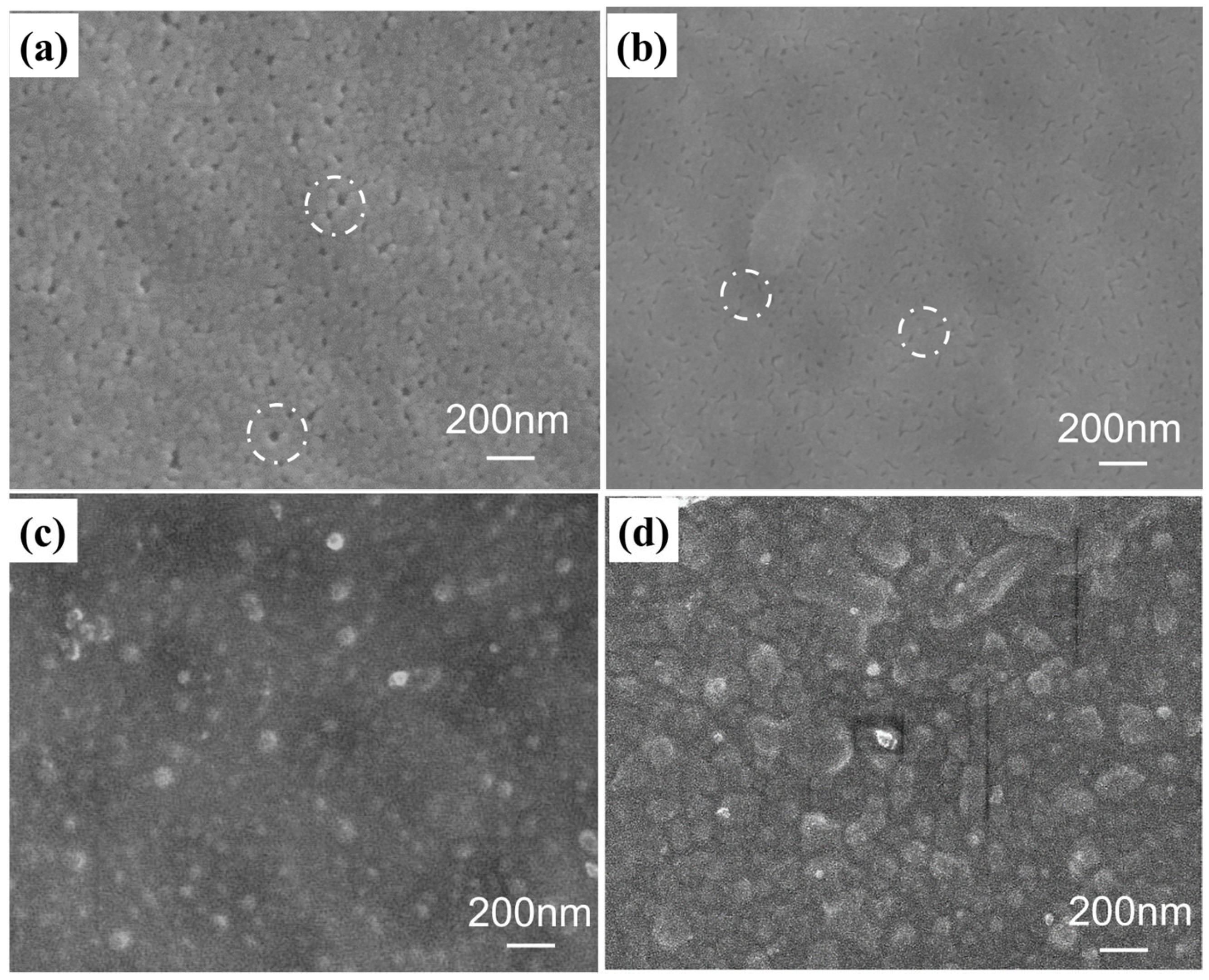
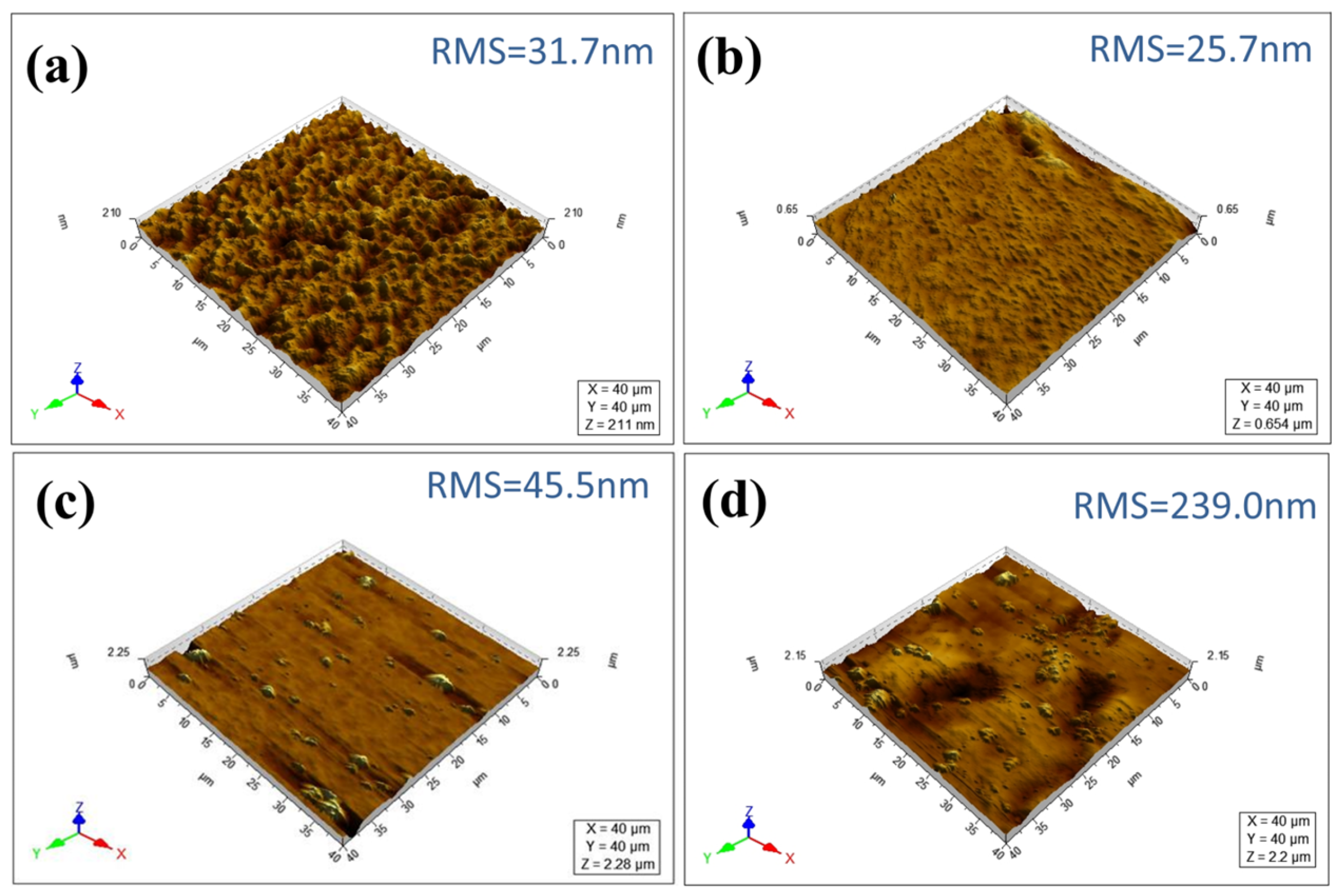
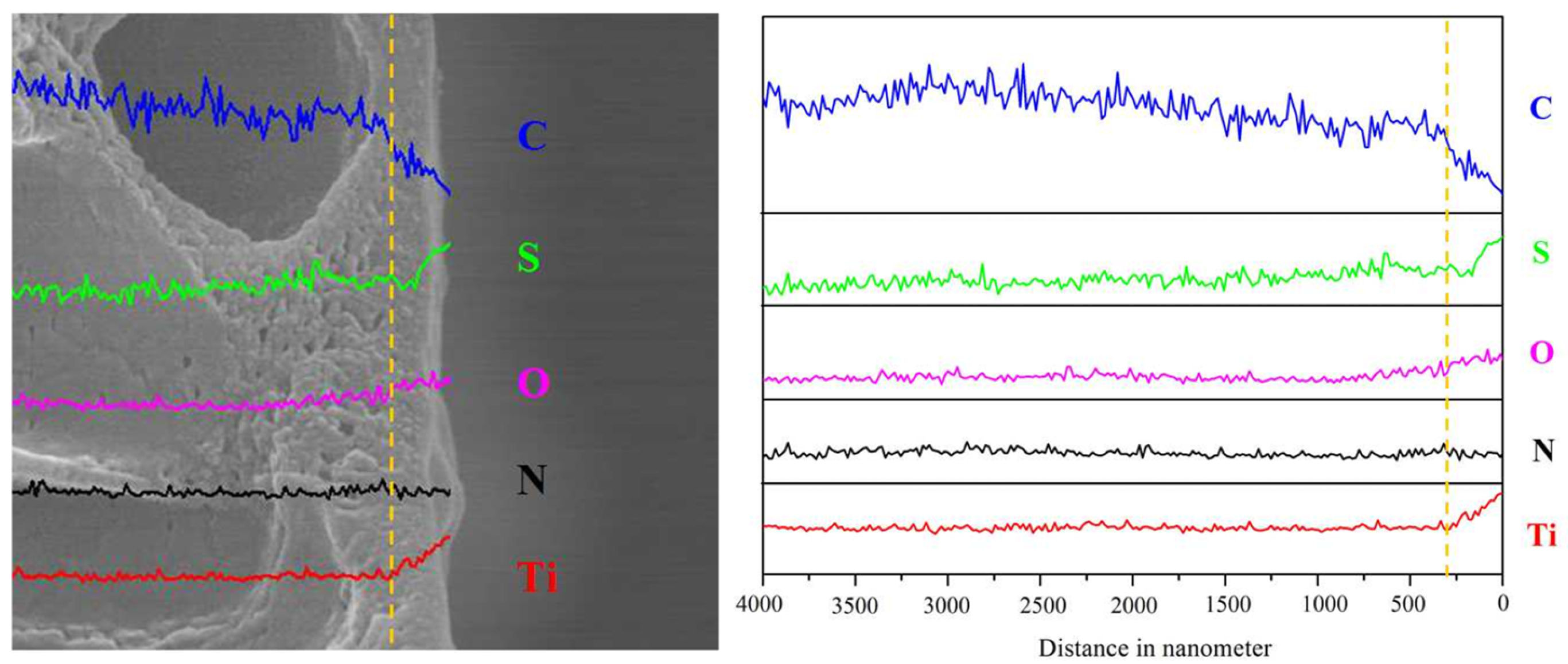
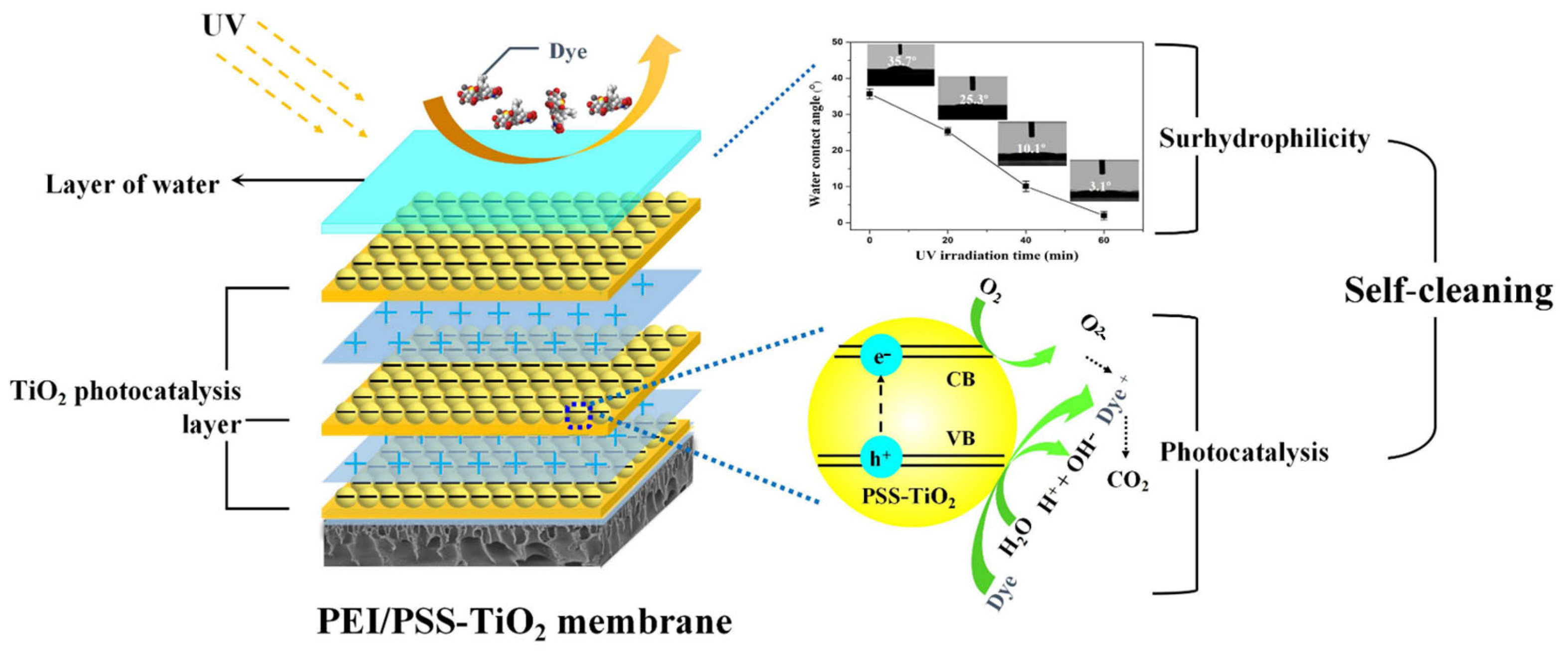
3.1. Self-Assembly of the Charged PE-TiO2 Hybrid Membrane
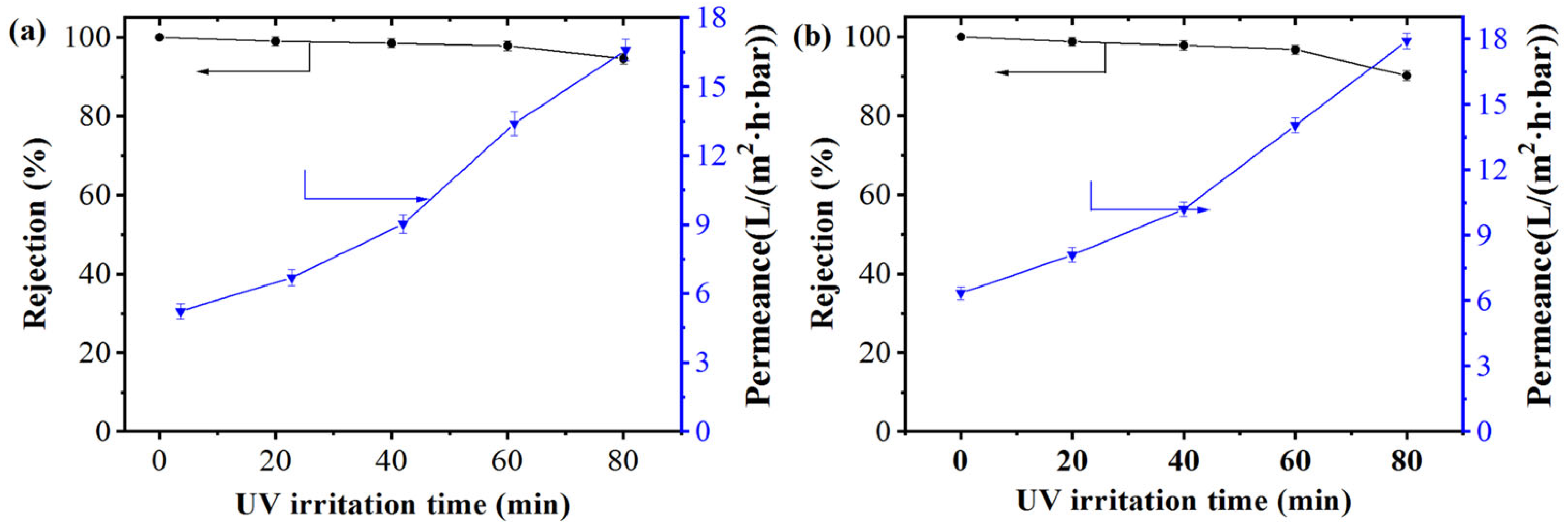
3.2. Wettability and Charge of the Membrane Under UV Irradiation
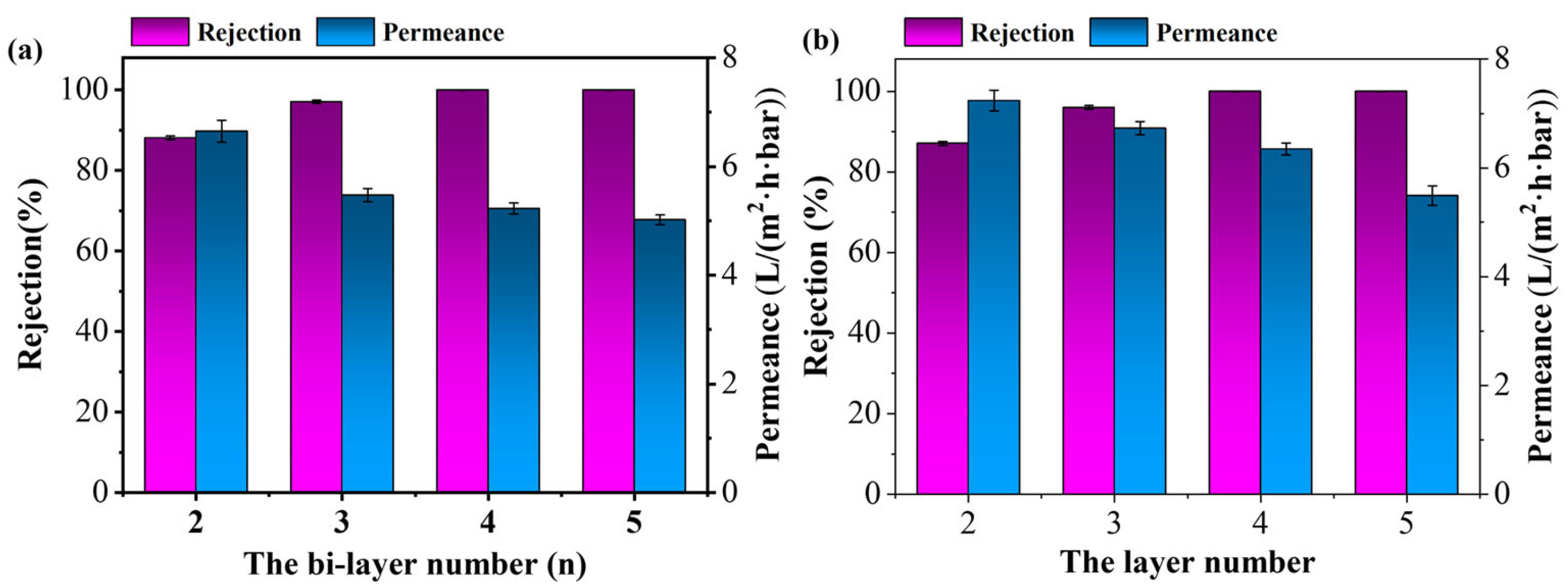
3.3. Nanofiltration Performance of the Membranes
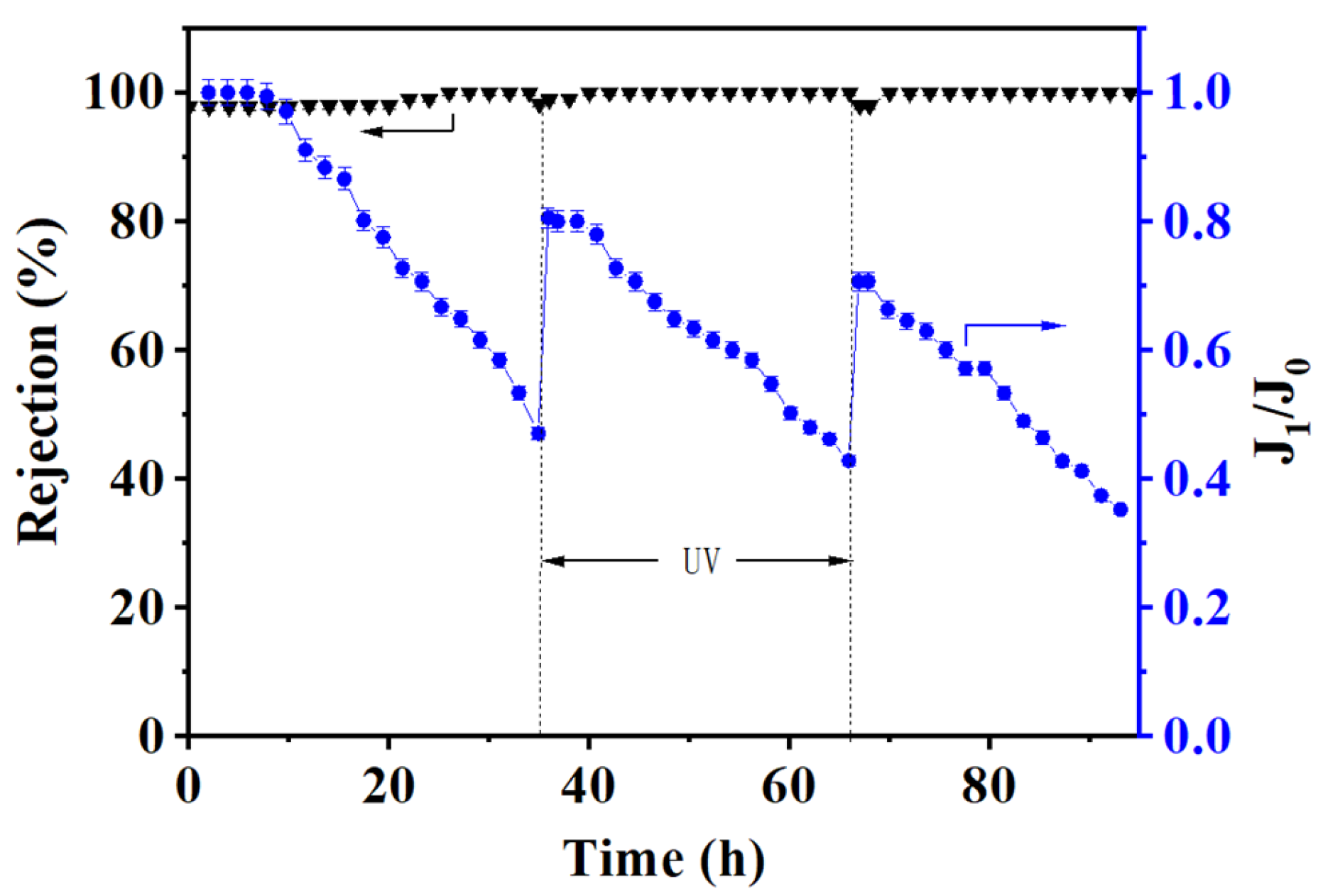
3.4. Self-Cleaning of the (PEI/PSS-TiO2)4.0 Membrane
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NF | Nanofiltration |
| PAN | polyacrylonitrile |
| PEI | Poly(ethyleneimine) |
| PSS | poly(sodium4-styrenesulfonate) |
| XO | Xylenol orange |
| EbT | eriochrome black T |
| SM | new substrate membrane |
| WCA | water contact angle |
References
- Labban, O.; Liu, C.; Chong, H.; Lienhard, V.J. Fundamentals of low-pressure nanofiltration: Membrane characterization, modeling, and understanding the multi-ionic interactions in water softening. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 521, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhu, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Su, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, X.; Xue, Y.; et al. Preparation of hybrid nanofiltration membranes based on Schiff base reaction for hard water softening. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 717, 123578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, Y.; Boo, C.; Hong, S. Performance, limitation, and opportunities of acid-resistant nanofiltration membranes for industrial wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 666, 121142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Nymann, M.C.; Christensen, M.L.; Quist-Jensen, C.A. Industrial Wastewater Treatment by Nanofiltration—A Case Study on the Anodizing Industry. Membranes 2020, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Tang, X.; Xiong, C.; Tang, M.; Lu, Y. A dually charged nanofiltration membrane by pH-responsive polydopamine for pharmaceuticals and personal care products removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Shao, L. Bio-inspired loose nanofiltration membranes with optimized separation performance for antibiotics removals. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Guo, S.; Wu, Y.; Wan, Y. Separation of sucrose and reducing sugar in cane molasses by nanofiltration. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Yao, Z.; Mei, Y.; Peng, L.; Yang, Z.; Shao, S.; Tang, C. Nanofiltration for drinking water treatment: A review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. Polymeric nanofiltration membranes for textile dye wastewater treatment: Preparation, performance evaluation, transport modelling, and fouling control—A review. Desalination 2009, 245, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Preparation and characterization of anti-fouling β-cyclodextrin/polyester thin film nanofiltration composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Matsuura, T. Surface modifications for antifouling membranes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2448–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Du, C. Fabrication and characterization of a novel TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembly membrane with improved fouling resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrabi, H.; Yekavalangi, M.E.; Vatanpour, V.; Shockravi, A.; Safarpour, M. Improvement in desalination performance of thin film nanocomposite nanofiltration membrane using amine-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube. Desalination 2016, 394, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhu, C.; Xiong, P.; Guo, J.; Zhao, K. Calcium alginate-coated electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate/carbon nanotubes composite nanofibers as nanofiltration membrane for dye removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 53, 14801–14820. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, V.R.; Isloor, A.M.; Bhat, U.K.; Ismail, A.; Obaid, A.; Fun, H. Preparation and performance studies of polysulfone-sulfated nano-titania (S-TiO2) nanofiltration membranes for dye removal. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53874–53885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhuo, H.; Bao, M.; Li, Y.; Lu, J. Fabrication of organic-inorganic nanofiltration membrane using ordered stacking SiO2 thin film as rejection layer assisted with layer-by-layer method. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Mahmood, A.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.H. Graphene oxide modified polyamide nanofiltration membrane with improved flux and antifouling properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.M.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; León, G.; Miguel, B.; Gago, I.; Martínez, P. Ibuprofen Removal by Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Coated Polysulfone Nanofiltration Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Deng, S.; Zhao, S.; Shi, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, G.; Xu, Z. High permeability Performance TFC Nanofiltration Membrane with Two dimensional Nanochannels Support Layer Fabricated by Dissolving of Nanosheets. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, H.; Akbari, A. Hierarchical nanostructures as novel antifouling agents in nanofiltration process. Desalination 2015, 375, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Shao, L.; Li, X.; Zeng, H. A novel photocatalytic self-cleaning TiO2 nanorods inserted graphene oxide based nanofiltration membrane. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 749, 137424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlet, M.; Permpoon, S.; Riassetto, D.; Berthomé, G.; Pernot, E.; Joud, J.C. Photocatalytic activity and photo-induced superhydrophilicity of sol–gel derived TiO2 films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2006, 181, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.H.; Tak, T.M. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on fouling mitigation of ultrafiltration membranes for activated sludge filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 249, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodar, R.A.; You, S.J.; Chou, H.H. Study the self cleaning, antibacterial and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 entrapped PVDF membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A.; Madaeni, S.; Taheri, A.; Mansourpanah, Y. Coupling TiO2 nanoparticles with UV irradiation for modification of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 313, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Shao, J.; He, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhong, X. Natural organic matter removal and flux decline with PEG–TiO2-doped PVDF membranes by integration of ultrafiltration with photocatalysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 405, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Study on the modification of positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane by TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalination 2013, 313, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, P.; Sun, W. Preparation and characterization of PVDF/TiO2 hybrid membranes with different dosage of nano-TiO2. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, A.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. The effects of mechanical and chemical modification of TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface chemistry, structure and fouling performance of PES ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaoui, O.T.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Mbareck, C.; Rhlalou, T. Elaboration and study of poly (vinylidene fluoride)–anatase TiO2 composite membranes in photocatalytic degradation of dyes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 358, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Combs, Z.A.; Gupta, M.K.; Davis, R.; Tsukruk, V.V. In situ growth of silver nanoparticles in porous membranes for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3333–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Li, J.; Ji, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z. In situ ultraviolet-light-induced TiO2 nanohybrid superhydrophilic membrane for pervaporation dehydration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.J.; Semblante, G.U.; Lu, S.C.; Damodar, R.A.; Wei, T.C. Evaluation of the antifouling and photocatalytic properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride) plasma-grafted poly (acrylic acid) membrane with self-assembled TiO2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 237, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bet-Moushoul, E.; Mansourpanah, Y.; Farhadi, K.; Tabatabaei, M. TiO2 nanocomposite based polymeric membranes: A review on performance improvement for various applications in chemical engineering processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kwak, S.Y.; Sohn, B.H.; Park, T.H. Design of TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane as an approach to solve biofouling problem. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.S. Hybrid organic/inorganic reverse osmosis (RO) membrane for bactericidal anti-fouling. 1. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2388–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, P.; Sun, W. Preparation and characterization of PVDF/TiO2 hybrid membranes with ionic liquid modified nano-TiO2 particles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, D.N.; Modak, J.M.; Raichur, A.M. LbL Fabricated Poly(Styrene Sulfonate)/TiO2 Multilayer Thin Films for Environmental Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 2684–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Geng, C.; Guo, H.; Du, Z.; Zhang, G.; Ji, S. Synthesis of positively charged polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes for removal of divalent metal ions. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Guo, H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Ji, S.; Zeng, T. Low-Temperature Synthesis of Anatase TiO2, Nanoparticles with Tunable Surface Charges for Enhancing Photocatalytic Activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Zhang, J.; Horiuchi, Y.; Anpo, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Understanding TiO2 Photocatalysis: Mechanisms and Materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9919–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Im, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.P.; Min, B.R. Polyamide thin-film nanofiltration membranes containing TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalination 2008, 219, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogman, K.C.; Zacharia, N.S.; Grillo, D.M.; Hammond, P.T. Photocatalytic Layer-by-Layer Coatings for Degradation of Acutely Toxic Agents. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1924–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Cheng, L.; Liu, F.; Li, J. TiO2-Decorated Photocatalytic Nanofiltration Membranes for Enhanced Self-Cleaning and Separation Performance. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 3418–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Wang, N.; Fang, X.; Cao, J.; Tao, M.; Cao, Z. Interfacial Polymerization Nanofiltration Membrane with Visible Light Photocatalytic Self-cleaning Performance By Incorporation of CQD/TiO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Huo, L.; Ma, C.; Lu, J. Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide-TiO2 membranes forenhanced photocatalytic and self-cleaning performance. Process Saf. Environ. 2019, 130, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Yu, H.; Quan, X. A multifunctional graphene-based nanofiltration membrane under photoassistance for enhanced water treatment based on layer-by-layer sieving. Appl. Cat. B Environ. 2018, 224, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, W.; Han, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, H.; Qin, Z.; Guo, H. The Charged Superhydrophilic Polyelectrolyte/TiO2 Nanofiltration Membrane for Self-Cleaning and Separation Performance. Membranes 2025, 15, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060179
Gu W, Han L, Li Y, Wang J, Yan H, Qin Z, Guo H. The Charged Superhydrophilic Polyelectrolyte/TiO2 Nanofiltration Membrane for Self-Cleaning and Separation Performance. Membranes. 2025; 15(6):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060179
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Weiliang, Lei Han, Ye Li, Jiayi Wang, Haihong Yan, Zhenping Qin, and Hongxia Guo. 2025. "The Charged Superhydrophilic Polyelectrolyte/TiO2 Nanofiltration Membrane for Self-Cleaning and Separation Performance" Membranes 15, no. 6: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060179
APA StyleGu, W., Han, L., Li, Y., Wang, J., Yan, H., Qin, Z., & Guo, H. (2025). The Charged Superhydrophilic Polyelectrolyte/TiO2 Nanofiltration Membrane for Self-Cleaning and Separation Performance. Membranes, 15(6), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15060179




