Remediation of Micro- and Nanoplastics by Membrane Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
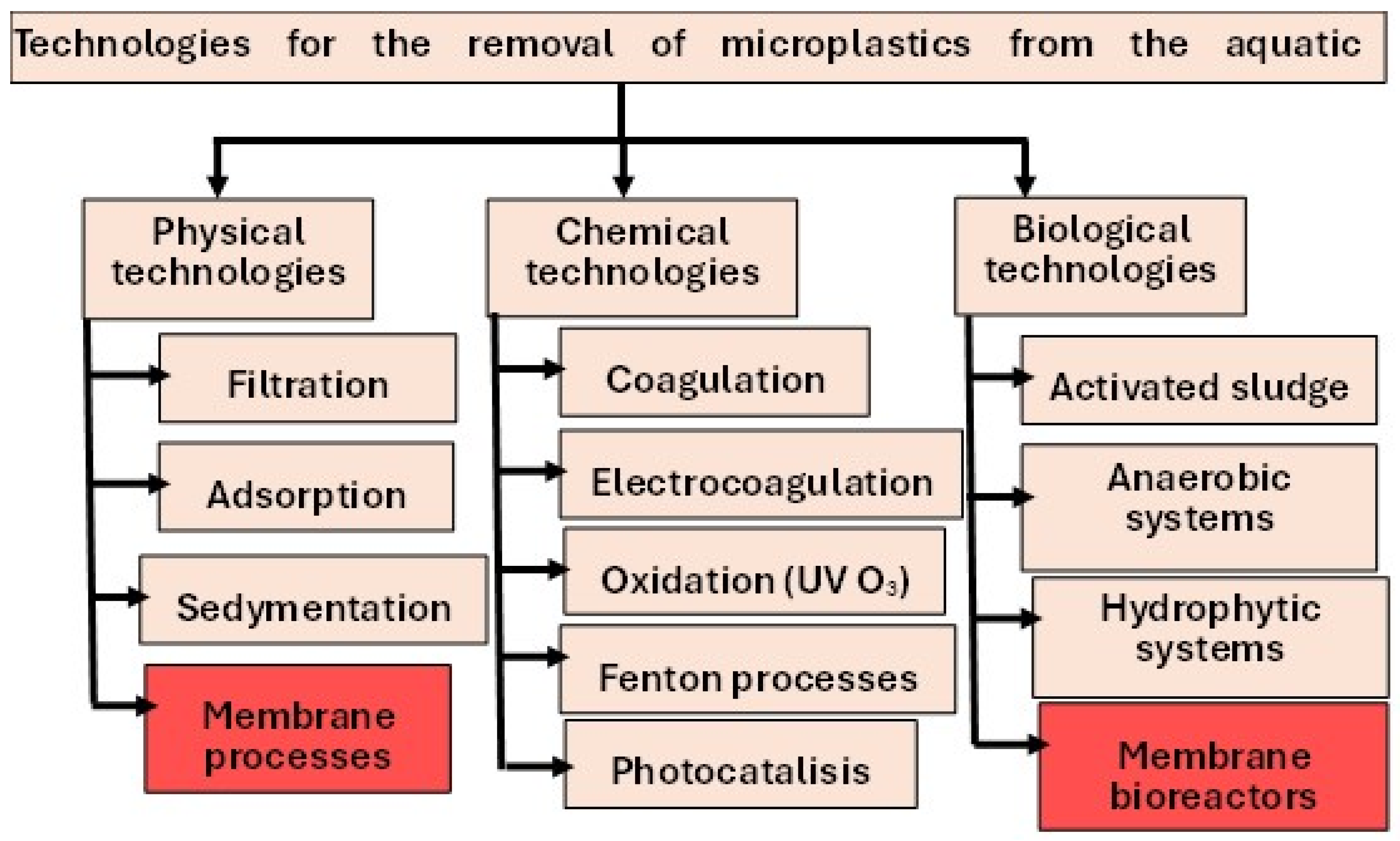
2. Overview of Technologies for the Removal of Microplastics from the Aquatic Environment
2.1. Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTP)
2.2. Drinking Water Treatment Plants (DWTP)
3. Membrane Techniques
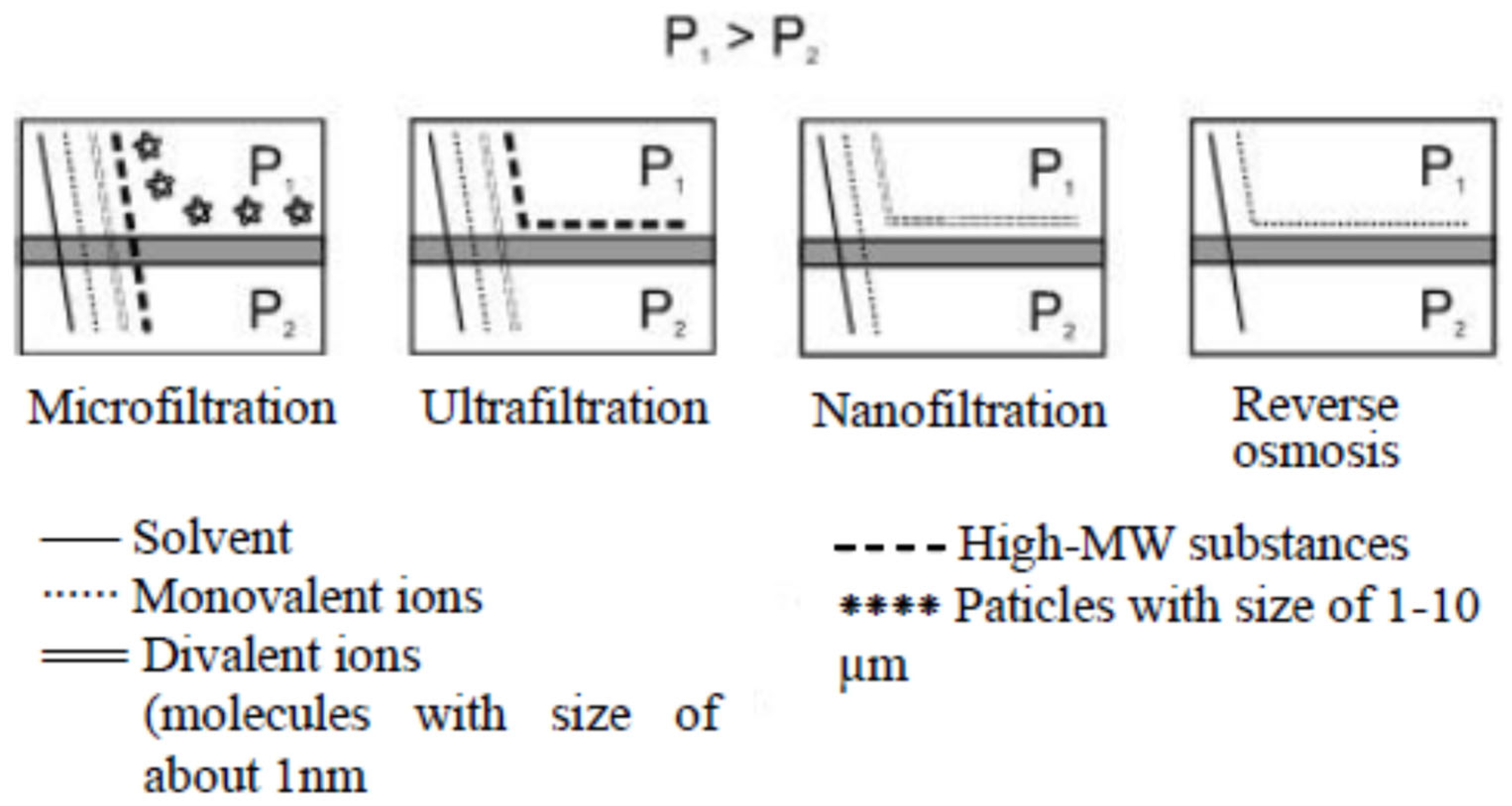
3.1. Fundamentals of Pressure-Driven Membrane Techniques
3.2. Membrane Methods for Removal of MPs and NPs
3.2.1. Micro- and Ultrafiltration
3.2.2. Nanofiltration
3.2.3. Reverse Osmosis
3.2.4. Forward Osmosis
3.2.5. Membrane Bioreactors
3.2.6. Membrane Fouling and Its Impact on the Removal of MPs/NPs
4. Recycling and Reuse of Polymeric Membranes
- (1)
- Innovation, development, and use of new polymers with improved durability compared to existing single-use products and with reusability and recyclability.
- (2)
- The elimination or significant reduction in the passage of MPs and NPs into the environment throughout the life cycle of a given product, and new-generation polymers should have a significantly shorter time to return to the environment compared to existing polymers.
- (3)
- Efforts to recycle plastic products must not result in an increase in the release of MPs and NPs into the environment, and recycling activities should be the responsibility of the producer.
5. Concluding Remarks
- (1)
- Efforts to develop and refine hybrid methods for MPs/NPs removal should be increased, especially the degradation and/or transformation of MPs in MBR should be investigated.
- (2)
- The number of studies on the removal of MPs and NPs in DWTP and WWTP under full industrial scale conditions should be increased, as most studies are carried out under controlled conditions in the laboratory or on a pilot scale, whereas under real conditions there is a high probability of reduced efficiency.
- (3)
- Alternative methods to prevent membrane fouling due to MPs/NPs should be developed, and the focus should be on producing membranes with MPs/NPs anti-fouling and self-cleaning properties.
- (4)
- There is a need for more research in the future on the use of inorganic material membranes in the removal of MPs/NPs. Currently, polymeric membranes are more widely used in DWTP and WWTP than inorganic membranes due to their low cost and ease of manufacture.
- (5)
- During polymeric membrane processes, there is a possibility of MPs/NPs release (attrition) into water/wastewater not only through porous membranes but even through dense osmotic membranes such as for RO. Further research is needed on the conditions for the release and permeation of MPs from polymeric membranes into water/wastewater and how to minimize this phenomenon.
- (6)
- There is also a paucity of research on MPs passing into retentate (concentrate), even though membrane filtration of MPs is highly effective.
- (7)
- Actions concerning the elimination or reduction in MPs/NPs pollution, which can act simultaneously, include mainly raising public awareness of pollution policies, limiting the use of single-use plastics and banning plastics in personal care products, and implementing processes based on the use of biodegradable materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A2O | anaerobic-anoxic-oxygen |
| AnMBR | anaerobic membrane bioreactor |
| AS | activated sludge |
| BAF | biologically active filter |
| BOD | biochemical oxygen demand |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CA | cellulose acetate |
| DS | draw solution |
| DWTPs | drinking water treatment plants |
| ED | electrodialysis |
| FDFO | fertilizer-driven forward osmosis |
| FO | forward osmosis |
| FS | feed solution |
| GF | granular filter |
| HRT | hydraulic retention time |
| IEMs | ion exchange membranes |
| IMS | integrated membrane system |
| MBR | membrane bioreactor |
| MF | microfiltration |
| MPs | microplastics |
| MW | molecular-weight |
| NF | nanofiltration |
| NPs | nanoplastics |
| O3 | ozone |
| OD | oxidation ditch |
| P | pressure |
| PA | polyamides |
| PAHs | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PAM | polyacrylamide |
| PAN | polyacrylonitrile |
| PC | polycarbonate |
| PCBs | polychlorinated biphenyls |
| PE | polyethylene |
| PES | polyethersulfone |
| PEs | polyester |
| PET | polyethylene terephthalate |
| PFASs | per-/polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| PP | polypropylene |
| PS | polystyrene |
| PTFE | politetrafluoroetylen |
| PVC | polyvinyl chloride |
| RC | regenerated cellulose |
| rGO | reduced graphene oxide |
| RO | reverse osmosis |
| RSF | rapid sand filter |
| SR | synthetic rubber |
| SRT | sludge retention time |
| TMP | transmembrane pressure |
| UF | ultrafiltration |
| USA | the United States of America |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| WWTPs | wastewater treatment plants |
References
- Krishnan, Y.; Manikandan, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Karmegam, N.; Kim, W.; Govarthanan, M. Recent approaches and advanced wastewater treatment technologies for mitigating emerging microplastics contamination—A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parashar, N.; Hait, S. Recent advances on microplastics pollution and removal from wastewater systems: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 340, 118014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noornama, M.; Abidin, N.M.Z.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Hashim, N.A. Removal of emerging microplastics from water by innovative and advanced non-membrane and membrane-based techniques. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.K.; Uddin, M.; Jamal, M. Detection and removal of microplastics in wastewater: Evolution and impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16925–16947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumari, S.; Chopade, R.L.; Pandit, P.P.; Rai, A.R.; Nagar, V.; Awasthi, G.; Singh, A.; Awasthi, K.K.; Sankhla, M.S. An assessment of the impact of structure and type of microplastics on ultrafiltration technology for microplastic remediation. Sci. Prog. 2023, 106, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poerio, T.; Piacentini, E.; Mazzei, R. Membrane processes or microplastic removal. Molecules 2019, 24, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K.; Hansson, L.A.; Cedervall, T. Nano-plastics in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, F.S.; Bhatti, M.S.; Anuar, N.; Anur, N.; Mohan, P.; Periathamby, A. World-wide distribution and abundance of microplastic: How dire is the situation? Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 873–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acarer, S. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Sources, properties, removal efficiency, removal mechanisms, and interactions with pollutants. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 685–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtiniemi, M.; Hartikainen, S.; Näkki, P.; Engström-Öst, J.; Koistinen, A.; Setälä, O. Size matters more than shape: Ingestion of primary and secondary microplastics by small predators. Food Webs 2018, 16, e00097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.A.; Arellano, J.M.; Albendín, G.; Rodríguez-Barroso, R.; Quiroga, J.M.; Coello, M.D. Microplastic pollution in wastewater treatment plants in the city of Cádiz: Abundance, removal efficiency and presence in receiving water body. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.A.; Garneau, D.; Sutton, R.; Chu, Y.; Ehmann, K.; Barnes, J.; Fink, P.; Papazissimos, D.; Rogers, D.L. Microplastic pollution is widely detected in US municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, X.; Zhong, X. Occurrence and identification of microplastics in tap water from China. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuth, M.; Mason, S.A.; Wattenberg, E.V. Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and sea salt. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.A.; Welch, V.G.; Neratko, J.J. Synthetic polymer contamination in bottled water. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.; Löder, M.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G.J. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egessa, R.; Nankabirwa, A.; Ocaya, H.; Pabire, W.G. Microplastic pollution in surface water of lake Victoria. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samandra, S.; Johnston, J.M.; Jaeger, J.E.; Symons, B.; Xie, S.; Currell, M.; Ellis, A.V.; Clarke, B.O. Microplastic contamination of an unconfined groundwater aquifer in Victoria, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Saad, M.; Renault, N.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 2, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, A.; Hoellein, T.J.; Mason, S.A.; Schluep, J.; Kelly, J. Microplastic is an abundant and distinct microbial habitat in an urban river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11863–11871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A. Plastic debris in 29 great lakes tributaries: Relations to watershed attributes and hydrology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperi, J.; Wright, S.L.; Dris, R.; Collard, F.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Kelly, F.J.; Tassin, B. Microplastics in air: Are we breathing it in? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, M.; Guerranti, C.; Blašković, A. Microplastic contents from maricultured and natural mussels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Lei, L.J. Microplastics in soils: Analytical methods, pollution characteristics and ecological risks. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballent, A.; Corcoran, P.L.; Madden, O.; Helm, P.A.; Longstaffe, F.J. Sources and sinks of microplastics in Canadian Lake Ontario Nearshore, tributary and beach sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, C. Microplastics in surface water and sediments of Chongming Island in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEachern, K.; Alegria, H.; Kalagher, A.L.; Hansen, C.; Morrison, S.; Hastings, D. Microplastics in Tampa Bay, Florida: Abundance and variability in estuarine waters and sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 148, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, A.; Forster, S.; Gerdts, G.; Schubert, H. Microplastic concentrations in beach sediments along the german baltic coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, Y.Y.; Mak, C.W.; Liebich, C.; Lam, S.W.; Sze, E.T.-P.; Chan, K.M. Microplastic pollution in the marine waters and sediments of Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianello, A.; Boldrin, A.; Guerriero, P.; Moschino, V.; Rella, R.; Sturaro, A.; Da Ros, L. Microplastic particles in sediments of Lagoon of Venice, Italy: First observations on occurrence, spatial patterns and identification. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaker, P.L.; Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A.; Reneau, P.C.; Scott, J.W. vertical distribution of microplastics in the water column and surficial sediment from the Milwaukee River Basin to Lake Michigan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12227–12237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koistinen, A.; Setala, O. Solutions to microplastic pollution, Removal of microplastics from wastewater effluent with advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, E.; Nowack, B.; Mitrano, D.M. Polyester textiles as a source of microplastics from households: A mechanistic study to understand microfiber release during washing. Environ. Sci Technol. 2017, 51, 7036–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Löder, M.G.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lares, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpää, M. Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res. 2018, 133, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Pan, Z.; Wang, W.; Ren, J.; Yu, X.; Lin, L.; Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Jin, X. Microplastic abundance, characteristics, and removal in wastewater treatment plants in a coastal city of China. Water Res. 2019, 155, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.J.C. Gaps in aquatic toxicological studies of microplastics. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; Pereira, R. Morphological and Physical Characterization of Microplastics. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 49–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Neale, P.A.; Rintoul, L.; Leusch, F.D. Wastewater Treatment plants as a pathway for microplastics: Development of a new approach to sample wastewater-based microplastics. Water Res. 2017, 112, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazour, M.; Terki, S.; Rabhi, K.; Jemaa, S.; Khalaf, G.; Amara, R. Sources of microplastics pollution in the marine environment: Importance of wastewater treatment plant and coastal landfill. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.; Welden, N.; Sobral, P.; Cole, M. Sampling, isolating and identifying microplastics ingested by fish and invertebrates. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Pu, S.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mandal, S.; Xing, B. Microplastics in aquatic environments: Toxicity to trigger ecological consequences. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Lubchenco, J.; Melillo, J.M. Human domination of Earth’s ecosystems. Science 1997, 277, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, T.; Pietro, B.; Pedà, C.; Consoli, P.; Andaloro, F.; Fossi, M.C. first evidence of presence of plastic debris in stomach of large pelagic fish in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 5, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, D.A.; de Carvalho-Souza, G.F. Are We Eating Plastic-ingesting Fish? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 103, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Sinclair, C.; Boxall, A. Occurrence, degradation, and effect of polymer-based materials in the environment. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 227, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Paul-Pont, I.; Tallec, K.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, C.; Lambert, C.; Vincent, D.; Mazurais, D.; Zambonino-Infante, J.-L.; Brotons, G.; Lagarde, F.; Fabioux, C.J. Constraints and priorities for conducting experimental exposures of marine organisms to microplastics. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, S.; Mestre, N.C.; Abel, S.; Fonseca, T.G.; Carteny, C.C.; Cormier, B.; Keiter, S.H.; Bebianno, M.J. Ecotoxicological effects of chemical contaminants adsorbed to microplastics in the clam Scrobicularia plana. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.; Frias, J.; Micaelo, A.; Sobral, P. Resin pellets from beaches of the Portuguese coast and adsorbed persistent organic pollutants. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Vieira, L.R.; Branco, V.; Figueiredo, N.; Carvalho, F.; Carvalho, C.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics cause neurotoxicity, oxidative damage and energy-related changes and interact with the bioaccumulation of mercury in the European Seabass, Dicentrarchus Labrax (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 195, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Inam, M.A.; Khan, S.; Park, D.R.; Yeom, I.T. Interaction between persistent organic pollutants and zno nps in synthetic and natural waters. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, E.; Ferreira, P.; Guilhermino, L.J. Temperature rise and microplastics interact with the toxicity of the antibiotic cefalexin to juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps): Post-exposure predatory behaviour, acetylcholinesterase activity and lipid peroxidation. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 180, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, J. Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products to polyethylene debris. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8819–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.H.; Liang, Y.; Kim, M.; Byun, J.; Choi, H. Microplastics with adsorbed contaminants: Mechanisms and Treatment. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.; Napoli, S.; Grasso, A.; Zuccarello, P.; Cristaldi, A.; Copat, C. Toxicology, systematic review of arsenic in fresh seafood from the Mediterranean Sea and European Atlantic Coasts: A health risk assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 126, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.; Chan, K.Y.K. Microplastics reduced posterior segment regeneration rate of the polychaete perinereis aibuhitensis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Garcia, A.R.; Pereira, B.P.; Fonseca, M.; Mestre, N.C.; Fonseca, T.G.; Ilharco, L.M.; Bebianno, M.J. Microplastics effects in scrobicularia plana. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, M.N.; Stack, M.E.; Fields, D.M.; Shaw, S.D.; Matrai, P.A. Microplastic fiber uptake, ingestion, and egestion rates in the blue mussel (Mytilus Edulis). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzek, M.; Pohl, A. Removal of microplastics in unit processes used in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2022, 48, 102–128. [Google Scholar]
- Bodzek, M.; Pohl, A. Possibilities of removing microplastics from the aquatic environment using, membrane processes. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 288, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau-Soler, J.; Ballesteros-Cano, R.; Boleda, M.R.; Paraira, M.; Ferrer, N.; Lacorte, S. Microplastics from headwaters to tap water: Occurrence and removal in a drinking water treatment plant in Barcelona metropolitan area (Catalonia, ne Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59462–59472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.J.; Das Sarkar, S.; Das, B.K.; Praharaj, J.K.; Mahajan, D.K.; Purokait, B.; Mohanty, T.R.; Mohanty, D.; Gogoi, P.; Kumar, V.S.; et al. Microplastics removal efficiency of drinking water treatment plant with pulse clarifier. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Hamid, A.K.; Krebsbach, S.A.; He, J.; Wang, D. Critical review of microplastics removal from the environment. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qiu, R.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; He, D. Biodegradation and disintegration of expanded polystyrene by land snails Achatina fulica. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, I.; Bacha, A.U.; Li, K.; Cheng, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Ajmal, S.; Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L. Complete photocatalytic mineralization of microplastic on TiO2 nanoparticle film. iScience 2020, 23, 01326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.L.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, H.B.; Choi, J.H.; Tsang, Y.F.; Baek, K. Occurrence and removal of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and drinking water purification facilities: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, T. A review of the removal of microplastics in global wastewater treatment plants: Characteristics and mechanisms. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith, N.; Arumugam, S.; Parthasarathy, S.; Manupoori, S.; Janakiraman, S. Global distribution of microplastics and its impact on marine environment—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25970–25986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater treatment works (WwTW) as a source of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.K.; Fok, L. Characterisation of plastic microbeads in facial scrubs and their estimated emissions in Mainland China. Water Res. 2017, 122, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Mei, Q.; Dong, B.; Dai, X.; Ding, G.; Zeng, E.Y. Microplastics in sewage sludge from the wastewater treatment plants in China. Water Res. 2018, 142, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, W.; Di, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Transfer and fate of microplastics during the conventional activated sludge process in one wastewater treatment plant of China. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralikrishna, I.V.; Manickam, V. Wastewater Treatment Technologies. In Environmental Management; Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 249–293. [Google Scholar]
- Ranade, V.V.; Bhandari, V.M. Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Dong, Q.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, W.M. Microplastics in a municipal wastewater treatment plant: Fate, dynamic distribution, removal efficiencies, and control strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.L.; Pramanik, B.K.; Shah, K.; Roychand, R. Pathway, classification and removal efficiency of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.G.; Senthilkumar, R.; Byrne, J.A.; Feroz, S. Wastewater Treatment: Advanced Processes and Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bendell, L.I.; Chan, K.; Crevecoeur, S.; Prigent, C. Changes in ammonium and pH within intertidal sediments in relation to temperature and the occurrence of non-indigenous bivalves. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 4, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Weber, A.; Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. Interactions of microplastics with freshwater biota. In Freshwater Microplastics. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 153–180. [Google Scholar]
- Rummel, C.D.; Jahnke, A.; Gorokhova, E.; Kühnel, D.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. Impacts of biofilm formation on the fate and potential effects of microplastic in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tang, W.; Wu, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, C. Fate and effects of microplastics in wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorhemen, O.T.; Hamza, R.A.; Tay, J.H. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology for wastewater treatment and reclamation: Membrane fouling. Membranes 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Jiao, W.; Qiu, L.; Zhong, J.; Sun, W. Research on lateral flow treatment technology to enhance phosphorus removal of AAO process. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 53, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Tang, S.; Gu, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xin, Z. Simulation and performance evaluation of the anoxic/anaerobic/aerobic process for biological nutrient removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Lu, S.; Qiu, R.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Bigalke, M.; Shi, H.; He, D. A method for extracting soil microplastics through circulation of sodium bromide solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, L.; Li, R.; Xu, L.; Shen, Y.; Li, S.; Tu, C.; Wu, L.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y. Microplastics in an agricultural soil following repeated application of three types of sewage sludge: A field study. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Setälä, O.; Heinonen, M.; Koistinen, A. How well is microlitter purified from wastewater?–A detailed study on the stepwise removal of microlitter in a tertiary level wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2017, 109, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.Y.; Groth, A.; Gray, S.; Duke, M. Enhanced abrasion resistant PVDF/nanoclay hollow fibre composite membranes for water reatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzek, M.; Pohl, A.; Rosik-Dulewska, C. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Characteristics, occurrence and removal technologies. Water 2024, 16, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Heinonen, M.; Paaakkonen, J.P.; Vahtera, E.; Mikola, A.; Setala, O.; Vahala, R. Do wastewater treatment plants act as a potential point source of microplastics? Preliminary study in the coastal Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielssen, M.R.; Michielssen, E.R.; Ni, J.; Duhaime, M.B. Fate of microplastics and other small anthropogenic litter (SAL) in wastewater treatment plants depends on unit processes employed. Environ. Sci.–Wat. Res. 2016, 2, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, Q.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Ni, B.-J. Microplastic in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res. 2019, 152, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerba, C.P.; Pepper, I.L. Drinking Water Treatment. In Environmental and Pollution Science, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 435–454. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Xue, W.; Ding, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Removal characteristics of microplastics by Fe-based coagulants during drinking water treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 78, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xue, W.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Li, L. Characteristics of microplastic removal via coagulation and ultrafiltration during drinking water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of microplastics in raw and treated drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, T.; Chen, W. Occurrence and removal of microplastics in an advanced drinking water treatment plant (ADWTP). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Diehl, A.; Lewandowski, A.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Baker, T. Removal efficiency of micro- and nanoplastics (180 nm–125 μm) during drinking water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzek, M. Membrane separation techniques—Removal of inorganic and organic admixtures and impurities from water environment—Review. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2019, 45, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.L.; Nunes, S.P. Materials and membrane technologies for water and energy sustainability. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Ghaffar, M.A.; Tieama, H.A. A Review of Membranes Classifications, Configurations, Surface Modifications, Characteristics and Its Applications in Water Purification. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2017, 2, 57–82. [Google Scholar]
- Enfrin, M.; Dumée, L.F.; Lee, J. Nano/microplastics in water and wastewater treatment processes—Origin, impact and potential solutions. Water Res. 2019, 161, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewuyi, A.; Campbell, A.J.; Adeyemi, O.G. The potential role of membrane technology in the removal of microplastics from wastewater. J. Appl. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2021, 25, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, C.; Kumbur, H.; Kideys, A.E. Removal of microplastics from wastewater through electrocoagulation-electroflotation and membrane filtration processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1648–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; García-Pacheco, R.; Molina, S.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Rabadán, J.; García-Calvo, E. Fouling prevention, preparing for re-use and membrane re- cycling. Towards circular economy in RO desalination. Desalination 2016, 393, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C. Fate of microplastics in a coastal wastewater treatment plant: Microfibers could partially break through the integrated membrane system. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luogo, B.D.P.; Salim, T.; Zhang, W.; Hartmann, N.B.; Malpei, F.; Candelario, V.M. Reuse of Water in Laundry Applications with Micro and Ultrafiltration Ceramic Membrane. Membranes 2022, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahyanezhad, N.; Bardi, M.J.; Aminirad, H. An evaluation of microplastics fate in the wastewater treatment plants: Frequency and removal of microplastics by microfiltration membrane. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfrin, M.; Lee, J.; Le-Clech, P.; Ludovic, F.D. Kinetic and mechanistic aspects of ultrafiltration membrane fouling by o- and microplastics. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 601, 117890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzichetti, A.R.P.; Pablos, C.; Álvarez-Fernández, C.; Reynolds, K.; Stanley, S.; Marugán, J. Evaluation of membranes performance for microplastic removal in a simple and low-cost filtration system, Case Studies in Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 3, 100075. [Google Scholar]
- Fryczkowska, B.; Przywara, L. Removal of microplastics from industrial wastewater utilising an ultrafiltration composite membrane rGO/PAN application. Des. Water Treat. 2021, 214, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Monnot, M.; Sun, Y.; Asia, L.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Doumenq, P.; Moulin, P. Microplastics in different water samples (seawater, freshwater, and wastewater): Removal efficiency of membrane treatment processes. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Camejo, J.; Morales, A.; Peña-Lamas, J.; Lafita, C.; Enguídanos, S.; Seco, A.; Martí, N. Feasibility of rapid gravity filtration and membrane ultrafiltration for the removal of microplastics and microlitter in sewage and wastewater from plastic industry. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2023, 51, 103452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, S.; Ocaña-Biedma, H.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J. Experimental evaluation of the process performance of MF and UF membranes for the removal of nanoplastics. Membranes 2023, 13, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.; Ma, B.; Chen, J.P. Ultrafiltration membrane fouling by microplastics with raw water: Behaviors and alleviation methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 410, 128174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, D.; Song, K.; Zhou, Y. Performance evaluation of MBR in treating microplastics polyvinylchloride contaminated polluted Surface water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.C.; Ball, H.; Cross, R.; Horton, A.A.; Jürgens, M.D.; Read, D.S.; Vollertsen, J.; Svendsen, C. Identification and quantification of microplastics in potable water and their sources within water treatment works in England and Wales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12326–12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.J.; Liu, Y.N.; Xing, L.I.; Yao, J.J. Drinking water production by ultrafiltration of Songhuajiang River with PAC adsorption. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Marinas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decade. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breite, D.; Went, M.; Thomas, I.; Prager, A.; Schulze, A. Particle adsorption on a polyether sulfone membrane: How electrostatic interactions dominate membrane fouling. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65383–65391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Lai, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Kuang, K.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Liu, L. Enhanced membrane fouling by microplastics during nanofiltration of secondary effluent considering secretion, interaction and deposition of extracellular polymeric substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, P.K.; Pandey, S.K.; Yadav, S.K.; Shukla, P.; Srivastava, A.; Giri, R. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube-Based Freestanding Filters for Efficient Removal of Fine Particulate Matters (PM0.3), Microplastics (MP0.3), and Bioaerosols. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 9306–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, N.; Sari Erkan, H.; Onkal Engin, G. Characterization and Removal of Microplastics in Landfill Leachate Treatment Plants in Istanbul, Turkey. Anal. Lett. 2022, 56, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, A.; Russo, B.; Lavorato, C.; Argurio, P.; Figoli, A.; Molinari, R.; Poerio, T. Integrated nanofiltration and photocatalytic processes for the removal of polystyrene nanoplastics waste in water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 131232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, J.-S.; Dris, R.; Lecarpentier, C.; Raymond, V.; Delabre, K.; Thibert, S.; Tassin, B.; Gasperi, J. Microplastic occurrence after conventional and nanofiltration processes at drinking water treatment plants: Preliminary results. Front. Water 2022, 4, 886703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenvi, S.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A. A review on RO membrane technology: Developments and challenges. Desalination 2015, 368, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.; Low, J.H.; Gray, S.; Childress, A.E.; Le-Clech, P.; Leslie, G. Scale formation and control in high pressure membrane water treatment systems: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellasamy, G.; Kiriyanthan, R.M.; Maharajan, T.; Radha, A.; Yun, K. Remediation of microplastics using bionanomaterials: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhu, Z.R.; Li, W.H.; Yan, X.; Wang, L.K.; Zhang, L.; Jin, J.; Dai, X.; Ni, B.J. Revisiting microplastics in landfill leachate: Unnoticed tiny microplastics and their fate in treatment works. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malankowska, M.; Echaide-Gorriz, C.; Coronas, J. Microplastics in marine environment: A review on sources, classification, and potential remediation by membrane technology. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.J.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Lai, S.O. Ultrafiltration as a pretreatment for seawater desalination: A review. Membr. Water Treat. 2014, 5, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Approaching the environmental problem of microplastics: Importance of WWTP treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ji, M.; Zhai, H.; Liu, Y. Occurrence of phthalate esters and microplastics in urban secondary effluents, receiving water bodies and reclaimed water treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugbe, E.O.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.-V.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Adha, R.S.; Zheng, L.; Bui, X.-T.; Ma, X.; Vo, H.N.P. Chapter 20—Forward Osmosis: Principle and Applications in Sustainable Water and Energy Development. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Bui, X.-T., Guo, W., Chiemchaisri, C., Pandey, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 463–491. [Google Scholar]
- Suwaileh, W.; Pathak, N.; Shon, H.; Hilal, N. Forward osmosis membranes and processes: A comprehensive review of research trends and outlook. Desalination 2020, 485, 114455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaileh, W.; Johnson, D.J.; Sarp, S.; Hilal, N. Advances in forward osmosis membranes: Altering the sub-layer structure via recent fabrication and chemical modification approaches. Desalination 2018, 436, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golgoli, M.; Khiadani, M.; Sen, T.K.; Razmjou, A.; Johns, M.L.; Zargar, M. Synergistic effects of microplastics and organic foulants on the performance of forward osmosis membranes. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartanto, Y.; Zargar, M.; Cui, X.; Jin, B.; Dai, S. Non-ionic copolymer microgels as high-performance draw materials for forward osmosis desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares Linares, R.; Yangali-Quintanilla, V.; Li, Z.; Amy, G. Rejection of micropollutants by clean and fouled forward osmosis membrane. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6737–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, N.T.; Xu, P.; Heil, D.M.; Bellona, H.C.; Cath, T.Y. Comprehensive bench- and pilot-scale investigation of trace organic compounds rejection by forward osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8483–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Shan, J.; Wang, C.; Wei, J.; Tang, C.Y. Rejection of pharmaceuticals by forward osmosis membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227–228, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.-J.; Shon, H.K.; Kim, I.S.; Jang, A. The effects of naturally occurring operation factors on the removal mechanism of major algae metabolized materials in forward osmosis process. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, I.S.; Shon, H.K.; Jang, A. Removal behaviors and fouling mechanisms of charged antibiotics and nanoparticles on forward osmosis membrane. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 247, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Im, S.-J.; Park, J.H.; Jang, A. Removal and transport behavior of trace organic compounds and degradation byproducts in forward osmosis process: Effects of operation conditions and membrane properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Li, S.; Chekli, L.; Woo, Y.C.; Wei, C.-H.; Phuntsho, S.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.; Shon, H.K. Assessing the removal of organic micro-pollutants from anaerobic membrane bioreactor effluent by fertilizer-drawn forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 533, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, K.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Liu, T.; Al-Namazi, M.A.; Li, S. Removal and Fouling Influence of Microplastics in. Fertilizer Driven Forward Osmosis for Wastewater Reclamation. Membranes 2021, 11, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kim, Y.; Chekli, L.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K.; Leiknes, T.; Ghaffour, N. Impact of reverse nutrient diffusion on membrane biofouling in fertilizer-drawn forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 539, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Lianga, S.; Wanga, X.; Chena, C.; Huanga, X. Current state, and challenges of full-scale membrane bioreactor applications: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helcoski, R.; Yonkos, L.T.; Sanchez, A.; Baldwin, A.H. Wetland soil microplastics are negatively related to vegetation cover and stemdensity. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S. The status of industrial and municipal effluent treatment with membrane bioreactor technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 305, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, J.; López-Castellanos, J.; Olmos, S. Membrane bioreactor and rapid sand filtration for the removal of microplastics in an urban wastewater treatment plant. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H.A.; Brandsma, S.H.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics en route: Field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Cosenza, A.; Rebouças, T.F. A plant-wide modelling comparison between membrane bioreactors and conventional activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalčíková, G.; Alič, B.; Skalar, T.; Bundschuh, M.; Gotvajn, A.Ž. Wastewater treatment plant effluents as source of cosmetic polyethylene microbeads to freshwater. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, R.M.; Waldron, S.; Gauchotte-Lindsay, C. Average daily flow of microplastics through a tertiary wastewater treatment plant over a ten-month period. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, C.; Wu, R.; Lam, P.K. A preliminary screening of HBCD nantiomers transported by microplastics inwastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wong, C.S.; Chen, D.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Zeng, E.Y. Interaction of toxic chemicals with microplastics: A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Kekre, K.A.; Tao, G.; Oo, M.H.; Wai, M.N.; Lee, T.C.; Viswanath, B.; Seah, H. New option of MBRRO process for production of NEWater from domestic sewage. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 272, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolar, D.; Gros, M.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Moreno, J.; Comas, J.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Barcelo, D. Removal of emerging contaminants from municipal wastewater with an integrated membrane system, MBR–RO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 239, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, E.L.; Howe, K.J.; Thomson, B.M. Effect of membrane bioreactor solids retention time on reverse osmosis membrane fouling for wastewater reuse. Water Res. 2014, 49, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padervand, M.; Lichtfouse, E.; Robert, D.; Wang, C. Removal of microplastics from the environment. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 807–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baresel, C.; Harding, M.; Fång, J. Ultrafiltration/granulated active carbon-biofilter: Efficient removal of a broad range of micropollutants. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, K.; Cui, S.; Kang, Y.; An, L.; Lei, K. Removal of microplastics in municipal sewage from China’s largest water reclamation plant. Water Res. 2019, 155, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayaturrahman, H.; Lee, T.-G. A study on characteristics of microplastic in wastewater of South Korea: Identification, quantification, and fate of microplastics during treatment process. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magni, S.; Binelli, A.; Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. The fate of microplastics in an Italian Wastewater Treatment Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyare, P.U.; Ouki, S.K.; Bond, T. Microplastics removal in wastewater treatment plants: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2664–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.G. Effects of microplastics on wastewater and sewage sludge treatment and their removal: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122955–122970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, C.; González-Pleiter, M.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Fate of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and their environmental dispersion with effluent and sludge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.H.; Fang, T.; Xu, P.; Zhu, L.X.; Li, D.J. Source and potential risk assessment of suspended atmospheric microplastics in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, G. Fundamental understanding of organic matter fouling of membranes. Desalination 2008, 231, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Introduction to membrane technology. In Membrane Technology and Engineering for Water Purification, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Upadhyay, P.; Prajapati, S.K. Impact of microplastics on riverine greenhouse gas emissions: A view point. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 107300–107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohana, A.A.; Farhad, S.M.; Haque, N.; Pramanik, B.K. Understanding the fate of nano-plastics in wastewater treatment plants and their removal using membrane processes. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkwachukwu, O.I.; Chima, C.H.; Ikenna, A.O.; Albert, L. Focus on potential environmental issues on plastic world towards a sustainable plastic recycling in developing countries. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2013, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.R.; Horgen, F.D.; Orski, S.V.; Rodriguez, V.C.; Beers, K.L.; Balazs, G.H.; Jones, T.T.; Work, T.M.; Brignac, K.C.; Royer, S.-J.; et al. Validation of ATR FT-IR to identify polymers of plastic marine debris, including those ingested by marine organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 127, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Dimzon, I.K.; Eubeler, J.; Knepper, T.P. Analysis, Occurrence, and Degradation of Microplastics in the Aqueous Environment. In Freshwater Microplastics. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 58. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. Characterisation of nanoplastics during the degradation of polystyrene. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Kumar, D.; Yoo, C.G.; Gitsov, I.; Majumder, E.L.-W. Conversion and removal strategies for microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and landfills. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 406, 126715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisay, E.J.; Al-Tayawi, A.N.; László, Z.; Kertész, S. Recent advances in organic fouling control and mitigation strategies in membrane separation processes: A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfrin, M.; Lee, J.; Fane, A.G.; Dumée, L.F. Mitigation of membrane particulate fouling by nano/microplastics via physical cleaning strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enfrin, M.; Wang, J.; Merenda, A.; Dumée, L.F.; Lee, J. Mitigation of membrane fouling by nano/microplastics via surface chemistry control. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 633, 119379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, T.; Yin, W.; Zhou, J.; Lu, D. Effect of sodium hypochlorite disinfection on polyvinylidene fluoride membranes in microplastic ultrafiltration. Water 2025, 17, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Bond, T.; Siddique, M.S.; Yu, W. The stimulation of microbial activity by microplastic contributes to membrane fouling in ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Siddique, M.S.; Graham, N.J.D.; Yu, W. Towards microplastics contribution for membrane biofouling and disinfection by-products precursors: The effect on microbes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Lee, H.-S.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; McGrath, J.E.; Paul, D.R. Water purification by membranes: The role of polymer science. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1685–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Membrane Filtration Market 2023 by Manufacturers, Regions, Type and Application, Forecast to 2029—GlobalInfoResearch. Available online: https://www.globalinforesearch.com/reports/992477/membrane-filtration (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Lawler, W.; Bradford-Hartke, Z.; Cran, M.J.; Duke, M.; Leslie, G.; Ladewig, B.P.; Le-Clech, P. Towards new opportunities for reuse, recycling and disposal of used reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2012, 299, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syberga, K.; Nielsen, M.B.; Oturai, N.B.; Clausen, L.P.W.; Ramos, T.M.; Hansen, S.F. Circular economy and reduction of micro(nano)plastics contamination. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 5, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, N.K.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Khatri, M.; Ahmed, F.E.; Ibrahim, Y.; Hilal, N. Sustainability in membrane technology: Membrane recycling and fabrication using recycled waste. Membranes 2024, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejarazu-Larrañaga, A.; Molina, S.; Ortiz, J.M.; Navarro, R.; García-Calvo, E. Circular economy in membrane technology: Using end-of-life reverse osmosis modules for preparation of recycled anion exchange membranes and validation in electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 593, 117423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achievements and Conclusions of the Life Transfomem. Project on the Recycling of Disposed Membranes. Available online: https://www.water.imdea.org/news/2018/achievements-and-conclusions-life-transfomemproject-recycling-disposed-membranes (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- RO Membrane Recycling. We Are Your Global Partner for Your Membrane Recycling. Available online: https://www.memre.de/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Galiano, F.; Ghanim, A.H.; Rashid, K.T.; Marino, T.; Simone, S.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Figoli, A. Preparation and characterization of green polylactic acid (PLA) membranes for organic/organic separation by pervaporation. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Source | Country | Surface water (m−3) | Sediment (kg−1) | Dominant MPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jangcy River, Shores, and Island Chongming | China | 0–259 | 10–60 | Polyethylene, polypropylene, α-cellulose |
| Tampa Bay | USA | 940 | 30–790 | No data available |
| The Baltic coast | Germany | 0–5000 | No data available | No data available |
| Drinking water treatment plants | Germany | 0–7 | No data available | Polyethylene, polyamide, polyester, polyvinyl chloride |
| Stream, river, and lake | USA | 0.06–19.10 | 32.9–6229 | Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyethylene terephthalate |
| Seine | Francee | 3–108 | No data available | Fibers |
| Rivers | USA | 1.94–17.93 | No data available | Fibers |
| Great Lakes | USA | 0.05–32 | No data available | Fibers |
| Surface water and sediments | Hong Kong | 51–27,909 | 49–279 | Polypropylene, polyethylene, ethylene, propylene, styrene, acrylonitrile |
| Venetian lagoon | Italy | No data available | 672–2175 | Polypropylene, polyethylene |
| Purification Process | Removal of MPs (%) | Location of WWTP |
|---|---|---|
| I treatment stage/AS | 99.9 | Sweden |
| I treatment stage/AS | 88.1 | France |
| I treatment stage/AS | 99.9 | USA |
| I treatment stage/AS | 98.4 | Scotland |
| I treatment stage/AS | 11–94 | Netherlands |
| I treatment stage/AS | 95.6 | USA |
| I treatment stage/AnMBR | 98.3 | Finland |
| I treatment stage/MBR | 99.4 | Finland |
| I, II, and III treatment stage (GF) | 99.3 | USA |
| I, II, and III treatment stage (BAF) | 97.8 | Finland |
| Microfiltration | Ultrafiltration | Nanofiltration | Reverse osmosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle separation (e.g., bacteria and viruses) | Separation of high-MW and colloidal substances (e.g., proteins) | Separation of multi-valent ions and organic compounds with MW > 300 | Separation of low-MW substances (e.g., salts) |
| Osmotic pressure—may be omitted | Osmotic pressure—may be omitted | Osmotic pressure—plays a role | High osmotic pressure: 0.5–2.5 MPa |
| Low TMP (<0.2 MPa) | Low TMP (0.1–1.0 MPa) | The TMP is 0.5–2.0 MPa | High TMP (1.0–6.0 MPa) |
| Symmetric membrane structure | Asymmetric membrane structure | Asymmetric membrane structure | Asymmetric membrane structure |
| Thickness of the separation layer (epidermal): 10–150 μm. | Thickness of the separation layer: 0.1–1.0 μm | Thickness of the separation layer: 0.1–1.0 μm | Thickness of the separation layer: 0.1–1.0 μm |
| Separation mechanism—sieve | Separation mechanism—sieve | Dissolution and diffusion separation | Dissolution and diffusion separation |
| Membrane | MPs | Concentration MPs [1/L] | Medium Size of MPs [μm] | Removal Efficiency [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | PA | 127,000 | 15.66 | 99.6 |
| PS | 33,000 | 37.40 | 96.8 | |
| CA | PA | 27,000 | 20.58 | 99.8 |
| PS | 8000 | 75.51 | 94.3 | |
| PTFE | PA | 46,000 | 21.72 | 99.6 |
| PS | 47,000 | 29.49 | 96.0 |
| Membrane Material | Characteristics of PS | PS Retention (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Size | ||
| UF—regenerated cellulose: 30 kDa | PS 120 | 120 nm | 100 |
| PS 500 | 500 nm | 100 | |
| BSA | 66 kDa | - | |
| PS 120 + BSA | Mixture | 100 | |
| PS 500 + BSA | Mixture | 100 | |
| UF—polyethersulfone: 30 kDa | PS 120 | 120 nm | 100 |
| PS 500 | 500 nm | 100 | |
| BSA | 66 kDa | - | |
| PS 120 + BSA | Mixture | 100 | |
| PS 500 + BSA | Mixture | 100 | |
| MF—chlorinated polyethylene: 0.4 μm | PS 120 | 120 nm | 26.72 |
| PS 500 | 500 nm | 100 | |
| BSA | 66 kDa | - | |
| PS 120 + BSA | Mixture | 0 | |
| PS 500 + BSA | Mixture | 100 | |
| Treatment Technology | Raw Wastewater (MPs/L) | Treated Wastewater (MPs/L) | Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disk filter: 10 µm as a third stage of treatment | 0.5 | 0.3 | 40.0 |
| Disk filter: 20 µm as at third stage of treatment | 2.0 | 0.03 | 98.5 |
| Rapid sand filter as a third stage of treatment | 0.7 | 0.02 | 97.1 |
| Flotation (airborne) as a second stage of treatment | 2.0 | 0.1 | 95.0 |
| MBR | 6.9 | 0.005 | 99.9 |
| Treatment Type | Effectiveness (%) | Type of MPs in Wastewater |
|---|---|---|
| MBR, AS, and settling tank | 83.1–91.9 | Fragments |
| AS and clarification | 92 | Fragments, fibers |
| AS | 93.8 | Microgranules |
| AS | 89.8 | Microgranules |
| MBR | 79.01 | Fibers, PP, PS |
| A2O | 71.67 ± 11.58 | No data available |
| AS, sedimentation | 64 | Fibers |
| MBR | 99 | Fragments, fibers from PVC |
| Hydrophytic treatment plant | 97 | Fragments, fibers |
| AS | 52 | PE < 100 µm |
| Aerated biological filter | 99 | PE100–300 µm |
| A2O | 54.4 | - |
| A2O | 28.1 | PET, PE, PES, PAN, PAA |
| AS | 66.7 | PS |
| MBR | 99.9 | 20–100 μm MPs |
| MBR | 97.6 | PES fibers and PE fragments |
| A2O | 93.7 | PE, PP, PE |
| MBR | 99.4 | PES, PE, PA, and PP |
| AS | 98.3 | Different types of MPs |
| AS | 75–91.9 | Different types of MPs |
| Submerged MBR | 100.0 | |
| Submerged anaerobic MBR | 99.4 | |
| Submerged MBR (KUBOTA) | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bodzek, M.; Bodzek, P. Remediation of Micro- and Nanoplastics by Membrane Technologies. Membranes 2025, 15, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030082
Bodzek M, Bodzek P. Remediation of Micro- and Nanoplastics by Membrane Technologies. Membranes. 2025; 15(3):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030082
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodzek, Michał, and Piotr Bodzek. 2025. "Remediation of Micro- and Nanoplastics by Membrane Technologies" Membranes 15, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030082
APA StyleBodzek, M., & Bodzek, P. (2025). Remediation of Micro- and Nanoplastics by Membrane Technologies. Membranes, 15(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030082








