The Importance of Bilayer Asymmetry in Biological Membranes: Insights from Model Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling the Exoplasmic Leaflet of the Plasma Membrane
2.1. Triangular Phase Diagrams
2.2. Mapping the Coexistence Region Ld + Lo Phases
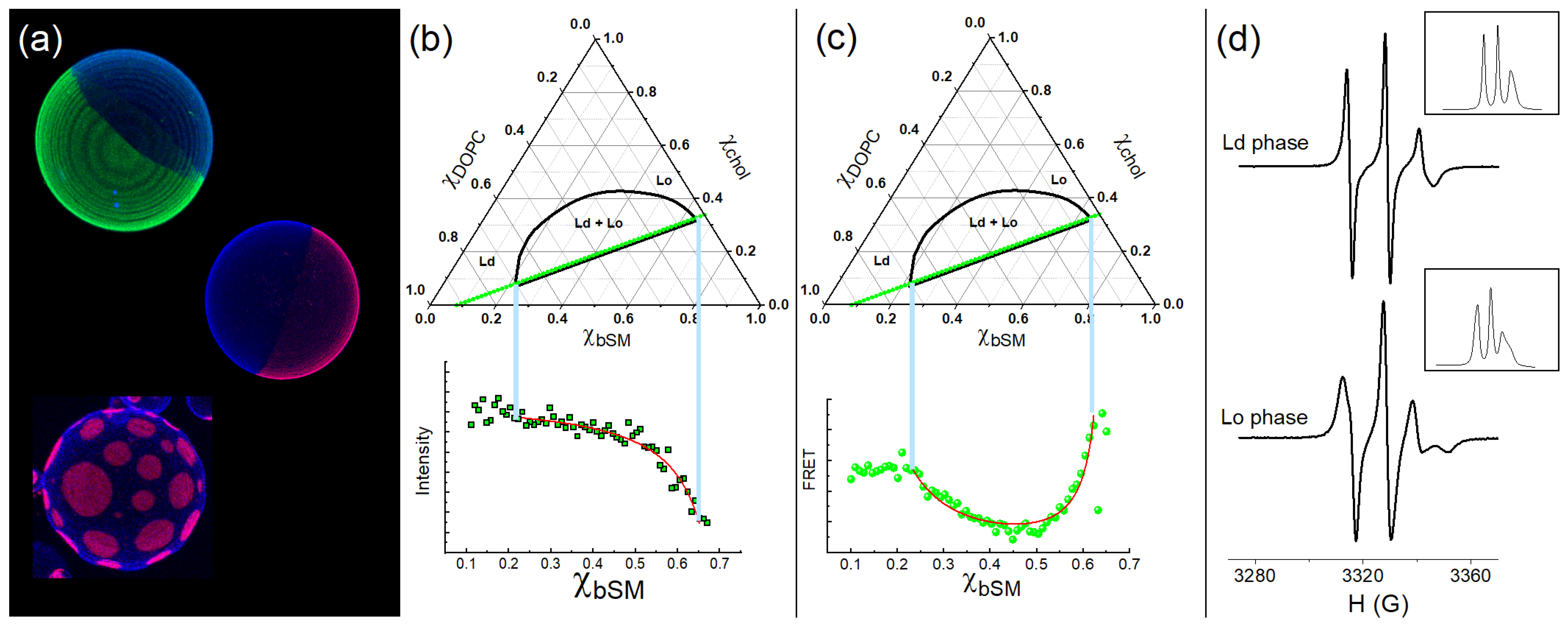
2.2.1. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.2.2. Steady-State Probe Partition Fluorescence
2.2.3. Steady-State Probe Partition—Förster Resonance Energy Transfer
2.2.4. Electron Spin Resonance to Monitor Lipid Packing/Order
2.2.5. Pros and Cons of These Techniques
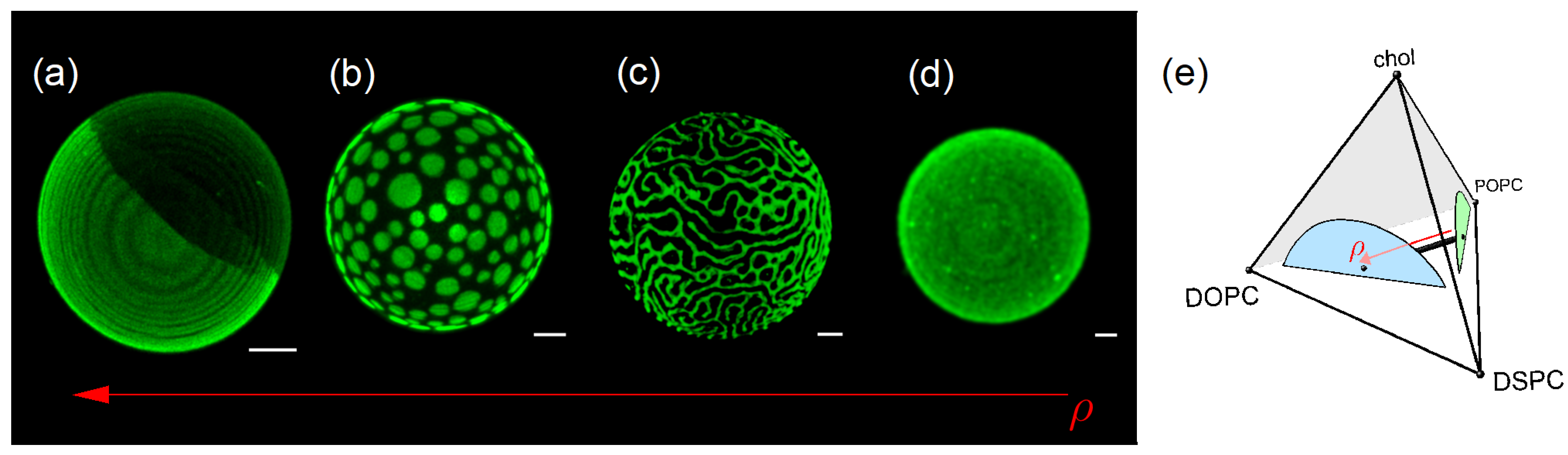
2.3. Alignment of Domains Within a Bilayer
2.4. Quaternary Phase Diagrams
2.5. Energetic Factors Driving Phase Separation and Competing Interactions
2.6. Membrane Phase Domains and Protein Partition
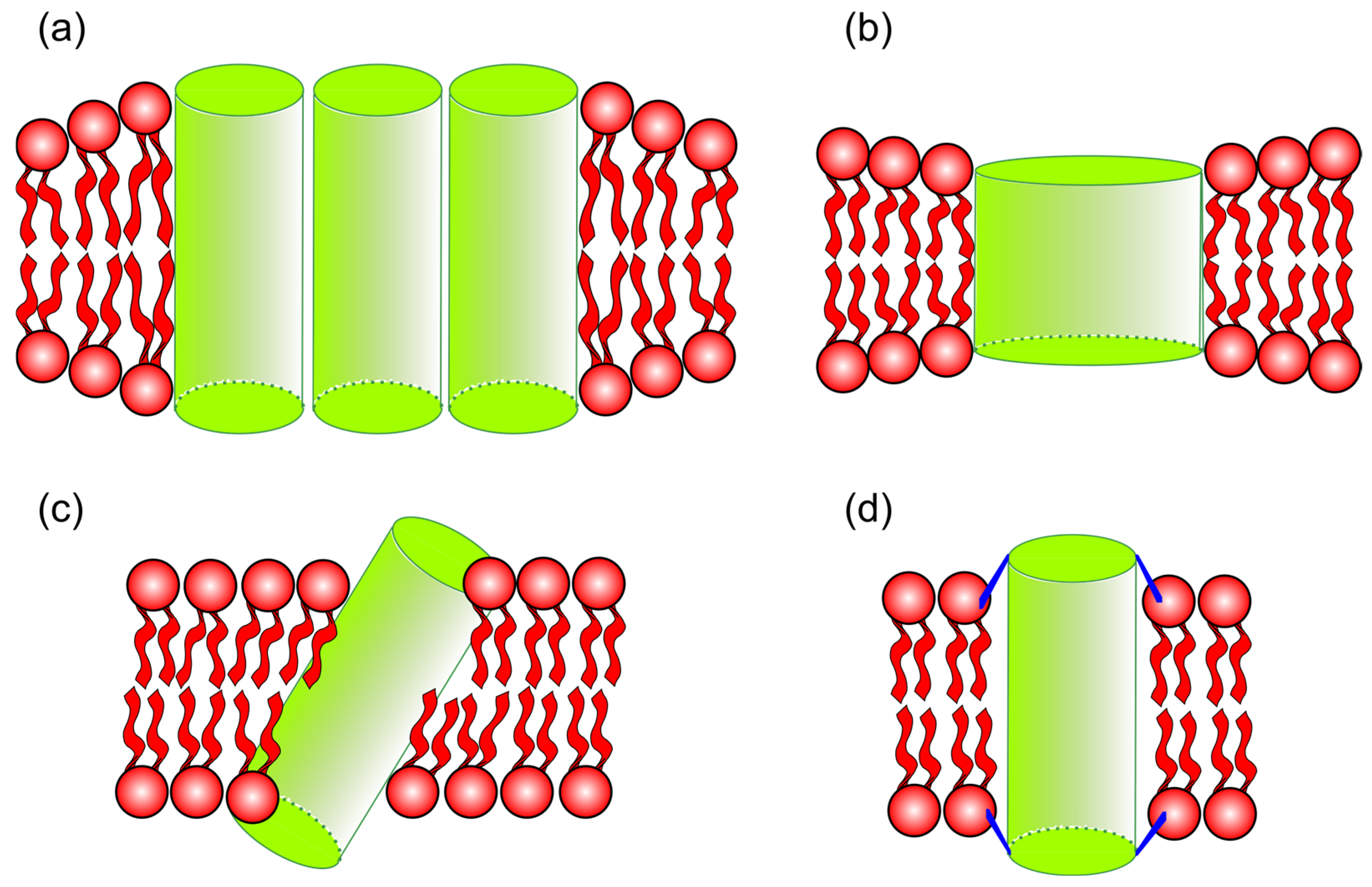
2.6.1. Transmembrane Peptide Mismatch
2.6.2. Protein Partition
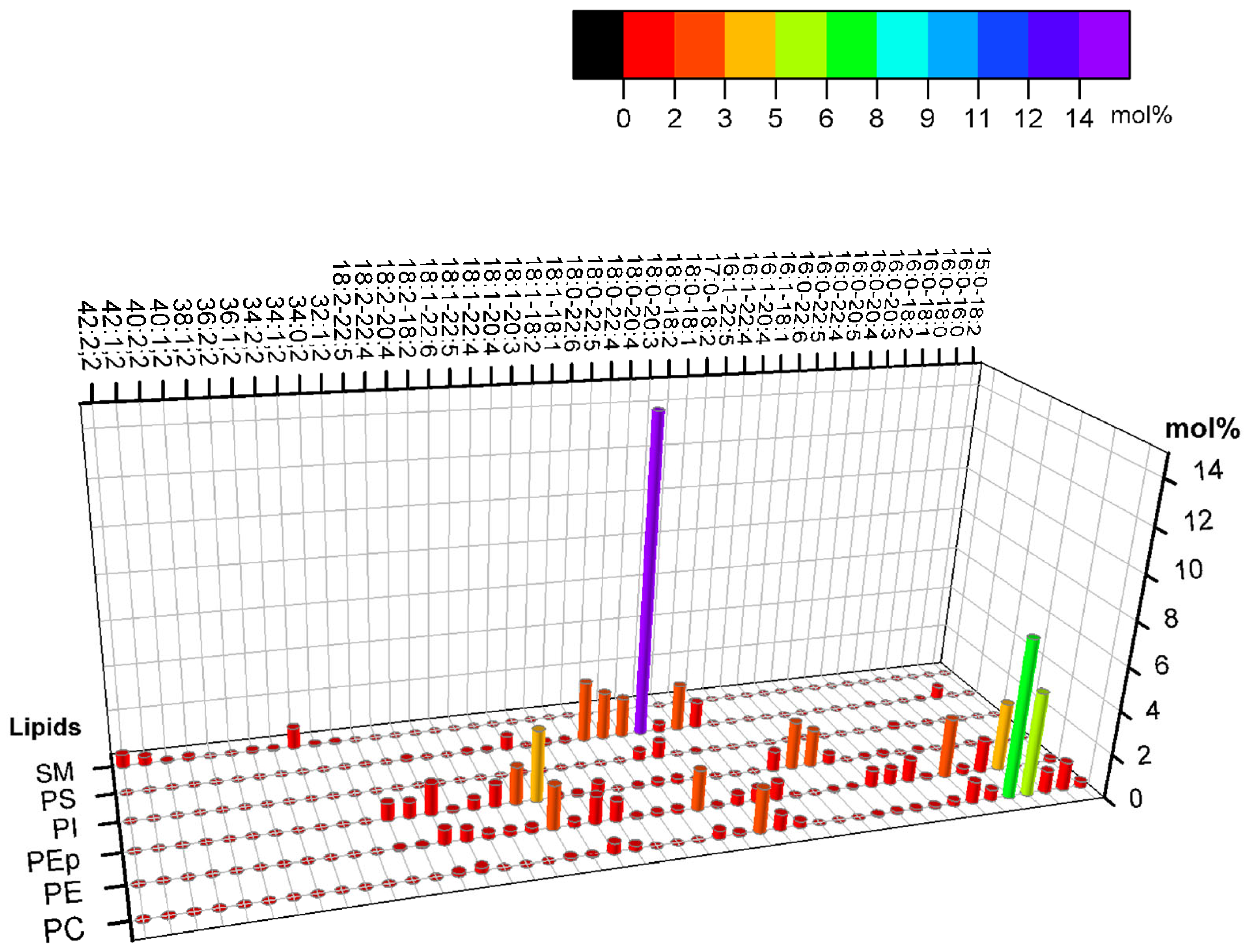
3. The Cytoplasmic Leaflet of the Plasma Membrane
4. The Asymmetric Membrane
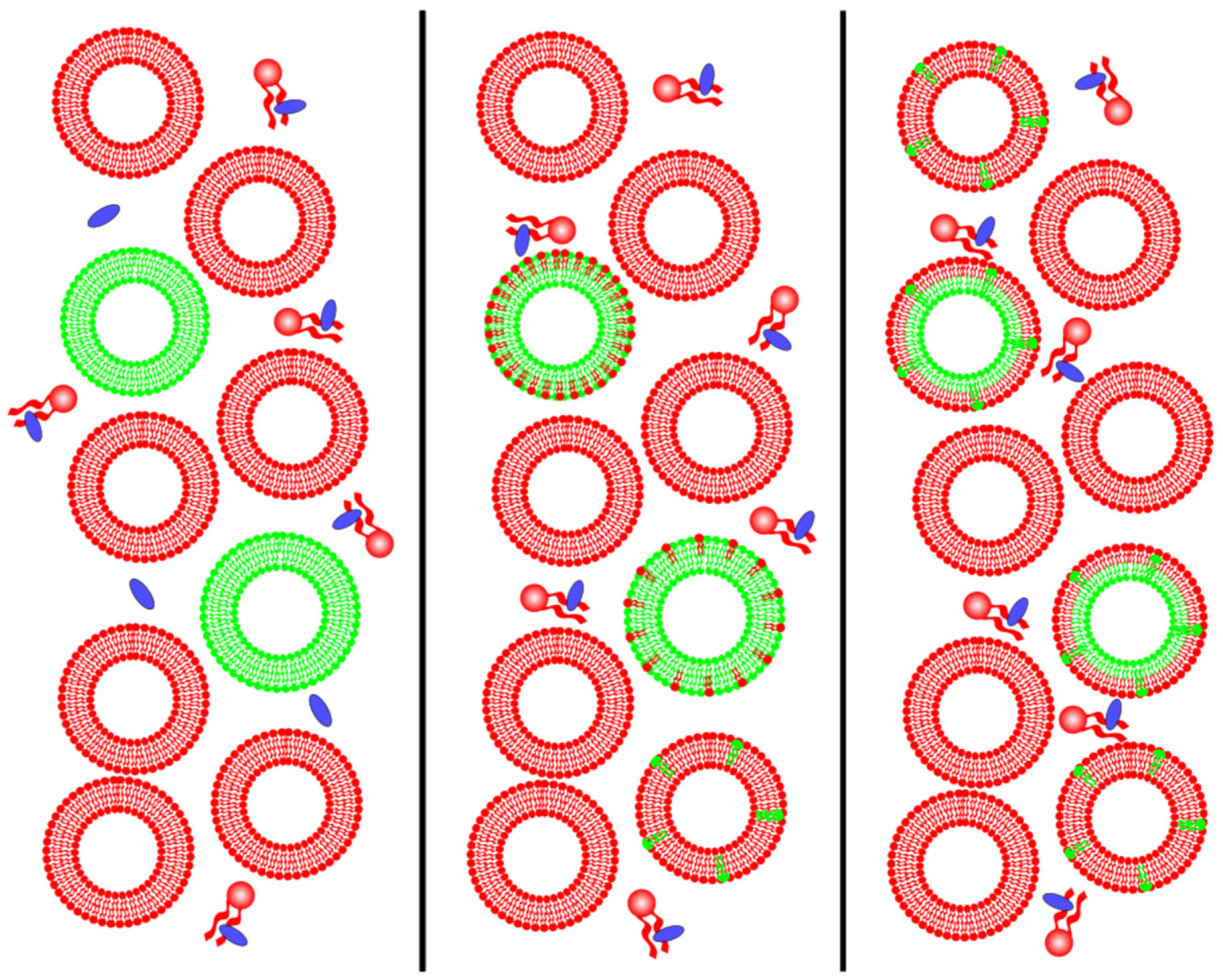
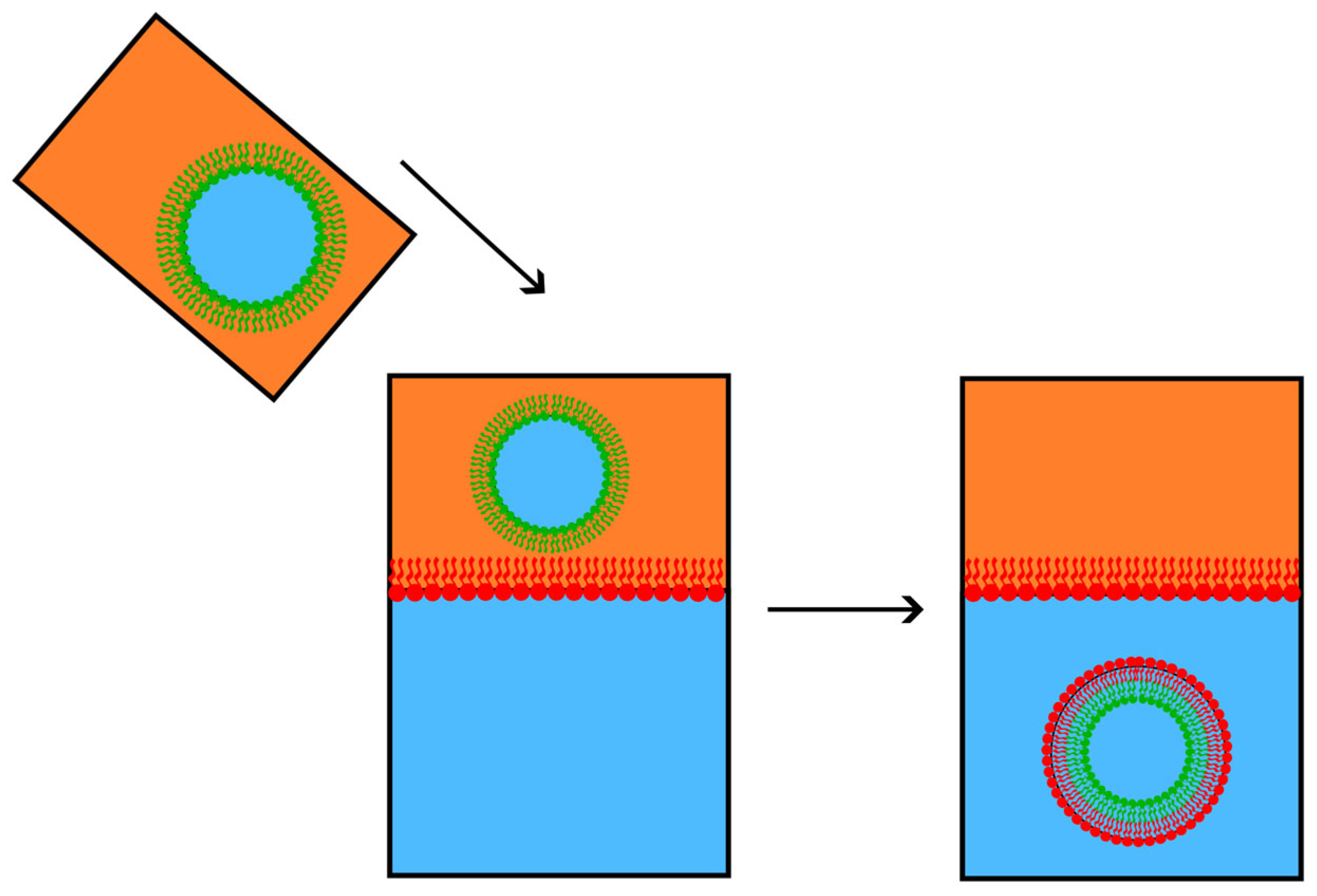
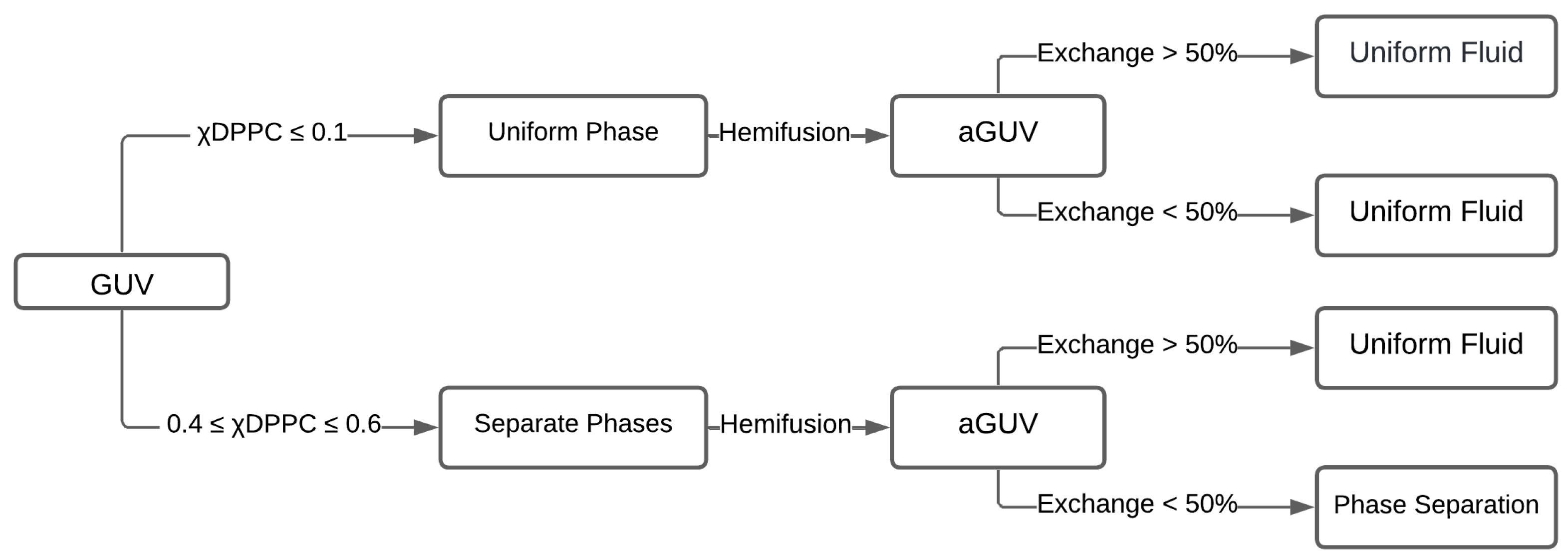
4.1. Experimental Procedures to Make Asymmetric Lipid Bilayer
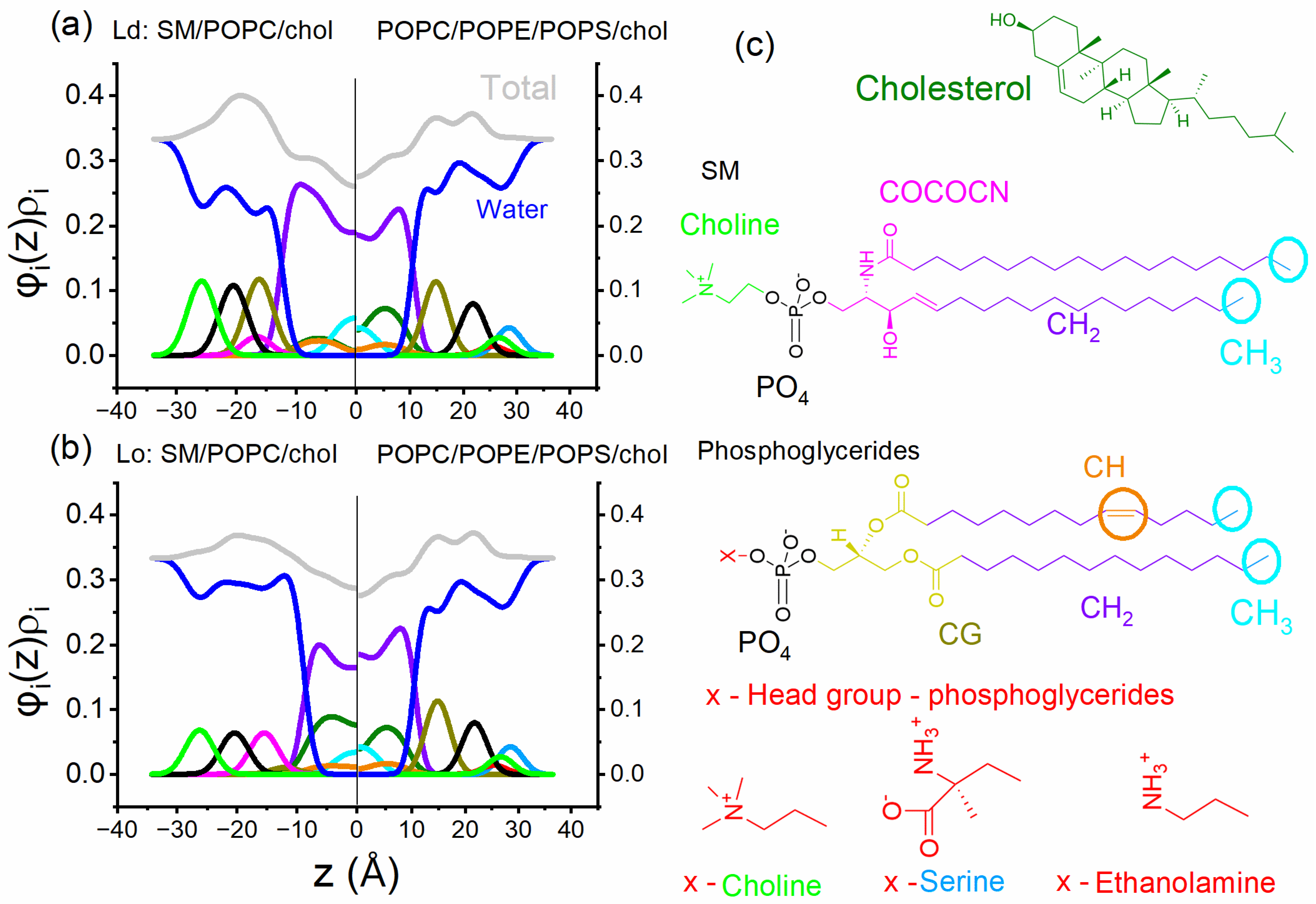
4.2. Electron Density Modeling for Asymmetric Bilayers
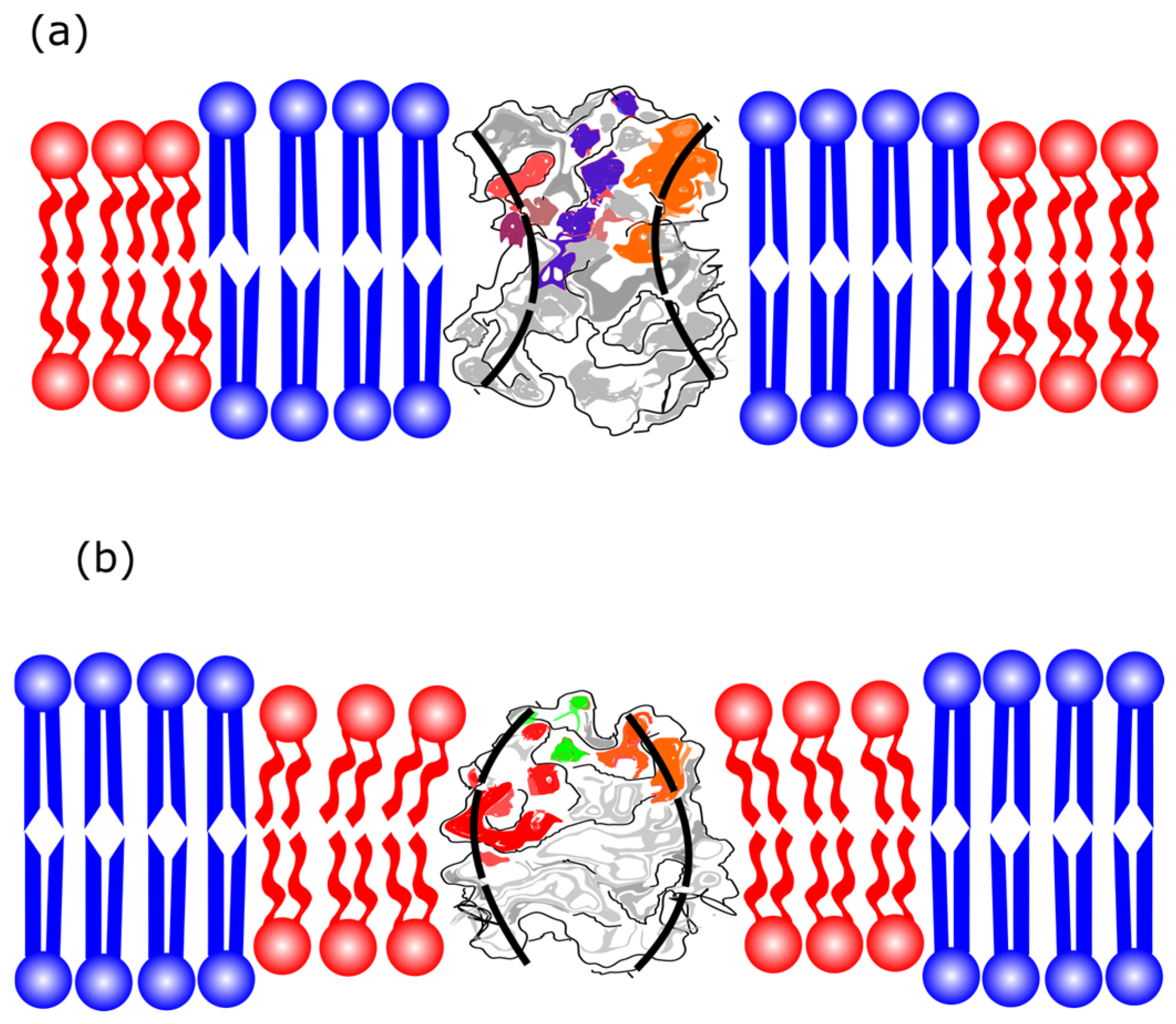
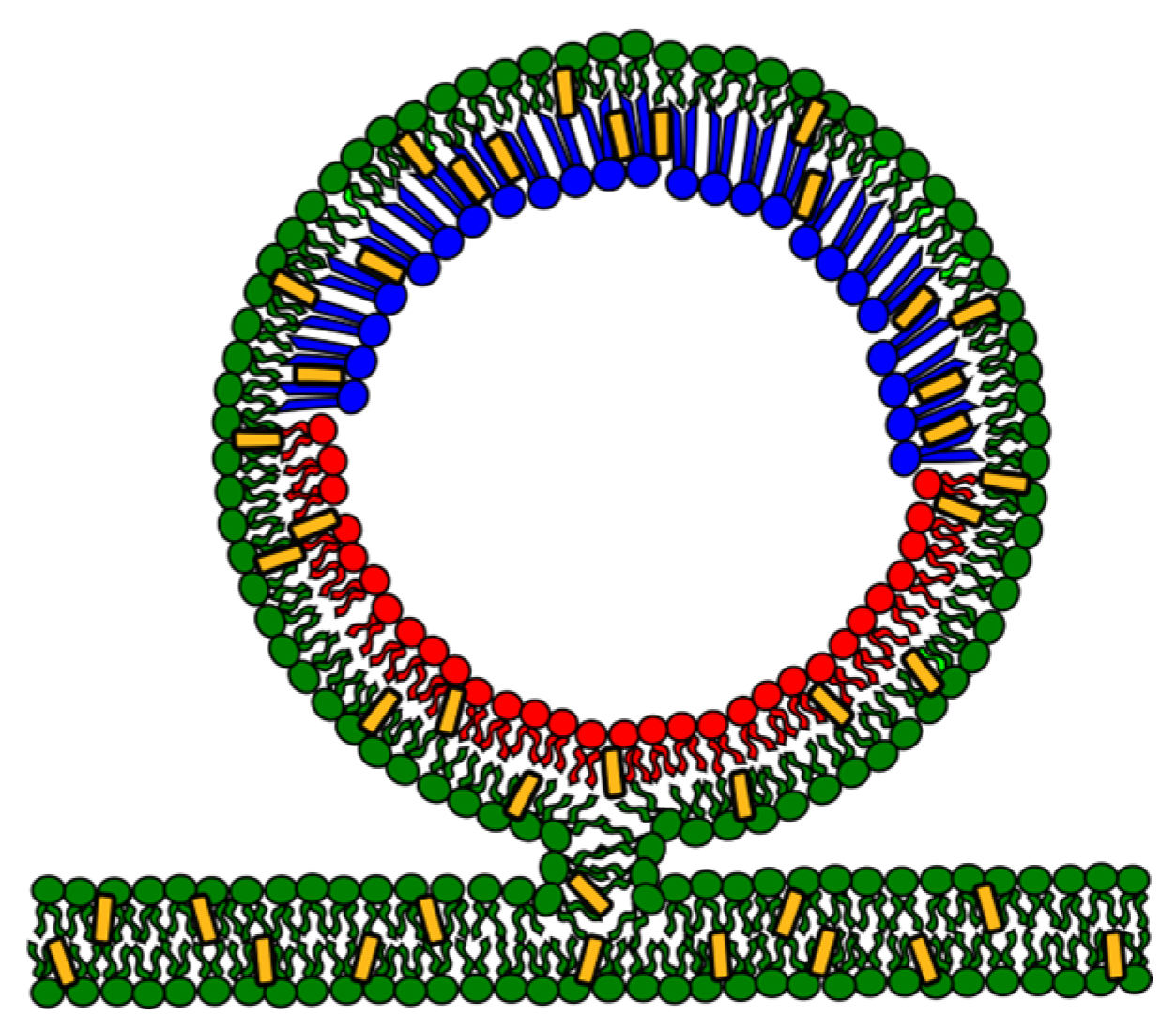
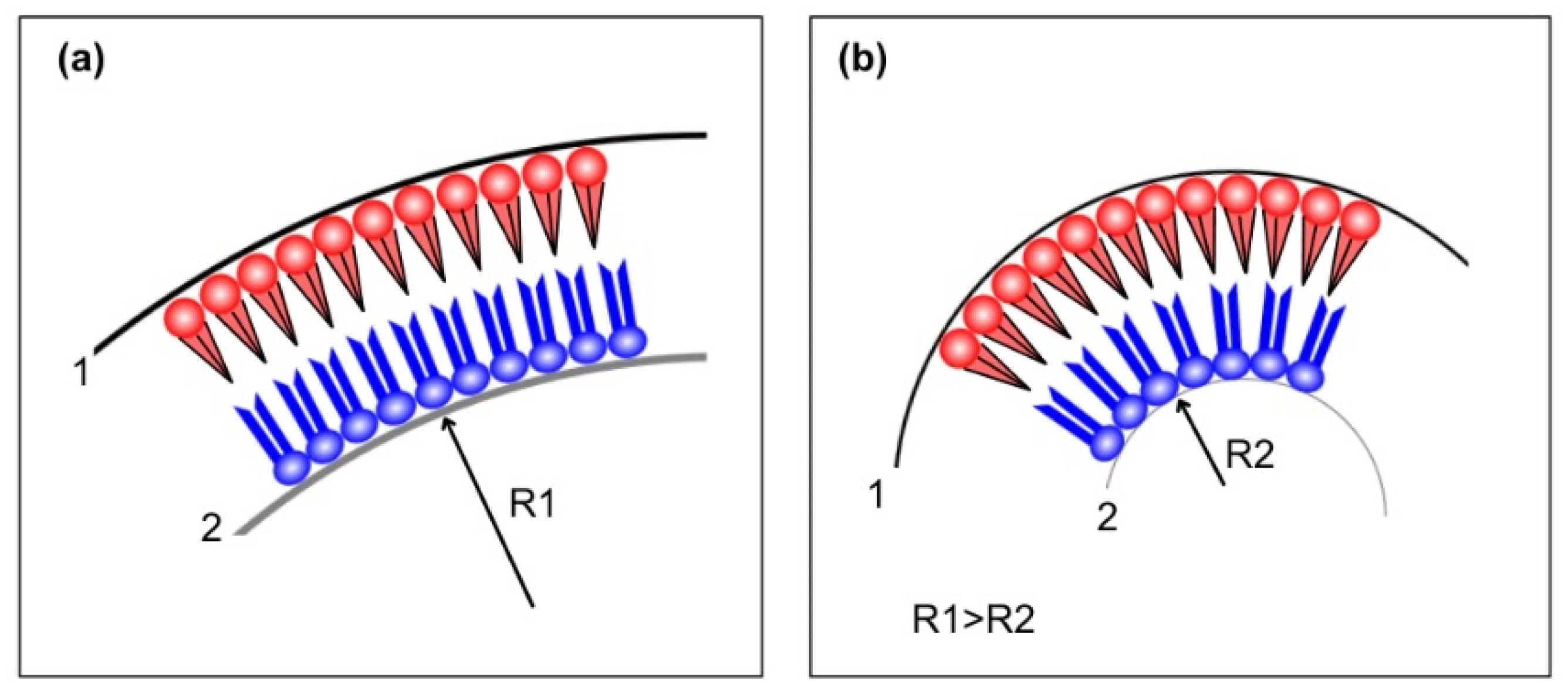
4.3. Experimental Phase Diagram of Asymmetric Lipid Bilayers: Domains and Coupling
4.4. Theoretical Minimal Models
5. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| aGUVs | Asymmetric Giant Unilamellar Vesicles |
| bSM | Brain Sphingomyelin |
| CDs | Cyclodextrins |
| Chol | Cholesterol |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| DHE | Dehydroergosterol |
| DOPC | 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| DOPE | 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine |
| DPPC | 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| DSPC | 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| ESR | Electron Spin Resonance |
| FRET | Förster Resonance Energy Transfer |
| GUV | Giant Unilamellar Vesicle |
| Kp | Partition Coefficient |
| LUV | Large Unilamellar Vesicle |
| Ld | Liquid disordered phase |
| Lo | Liquid ordered phase |
| MSDP | Modified Scattering Density Profile |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PEp | Phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogen |
| PLD | Phospholipase D |
| PM | Plasma Membrane |
| POPG | 1-Palmitoyl-2-Oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-[Phospho-rac-(1-glycerol)] |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| SANS | Small-Angle Neutron Scattering |
| SAXS | Small-Angle X-ray Scattering |
| SLB | Supported lipid bilayer |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| SSPP | Steady-State Probe Partition |
| TFPC | 1-palmitoyl-2-(dipyrrometheneboron difluoride)undecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
References
- Cockcroft, S. Mammalian Lipids: Structure, Synthesis and Function. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 813–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane Lipids: Where They Are and How They Behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Young, G.; Walkinshaw, M.D.; Darke, A. Order-Disorder Transition for a Bacterial Polysaccharide in Solution. A Role for Polysaccharide Conformation in Recognition between Xanthomonas Pathogen and Its Plant Host. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 110, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, H. Molecular Basis of Bacterial Outer Membrane Permeability Revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 593–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulowski, L.; Donoghue, A.; Nehls, C.; Groth, S.; Koistinen, M.; Hagge, S.O.; Böhling, A.; Winterhalter, M.; Gutsmann, T. The Beauty of Asymmetric Membranes: Reconstitution of the Outer Membrane of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretscher, M.S. Asymmetrical Lipid Bilayer Structure for Biological Membranes. Nat. New Biol. 1972, 236, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkleij, A.; Zwaal, R.F.; Roelofsen, B.; Comfurius, P.; Kastelijn, D.; Van Deenen, L.L. The Asymmetric Distribution of Phospholipids in the Human Red Cell Membrane. A Combined Study Using Phospholipases and Freeze-Etch Electron Microscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1973, 323, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.N.; Fernandes, F.; Fedorov, A.; Futerman, A.H.; Silva, L.C.; Prieto, M. A Combined Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Confocal and 2-Photon Microscopy Approach to Re-Evaluate the Properties of Sphingolipid Domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, P.F. Static and Dynamic Lipid Asymmetry in Cell Membranes. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, W.G.; Igbavboa, U.; Müller, W.E.; Eckert, G.P. Cholesterol Asymmetry in Synaptic Plasma Membranes. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorent, J.H.; Levental, K.R.; Ganesan, L.; Rivera-Longsworth, G.; Sezgin, E.; Doktorova, M.; Lyman, E.; Levental, I. Plasma Membranes Are Asymmetric in Lipid Unsaturation, Packing and Protein Shape. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohrbandt, M.; Lipski, A.; Grimshaw, J.W.; Buttress, J.A.; Baig, Z.; Herkenhoff, B.; Walter, S.; Kurre, R.; Deckers-Hebestreit, G.; Strahl, H. Low Membrane Fluidity Triggers Lipid Phase Separation and Protein Segregation in Living Bacteria. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaisson, E.H.; Heberle, F.A.; Doktorova, M. Building Asymmetric Lipid Bilayers for Molecular Dynamics Simulations: What Methods Exist and How to Choose One? Membranes 2023, 13, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiessling, V.; Wan, C.; Tamm, L.K. Domain Coupling in Asymmetric Lipid Bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Kiessling, V.; Tamm, L.K. Coupling of Cholesterol-Rich Lipid Phases in Asymmetric Bilayers. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenson, G.W.; Huang, J.; Enoki, T.A. An Unexpected Driving Force for Lipid Order Appears in Asymmetric Lipid Bilayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 21717–21722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, T.A.; Feigenson, G.W. Improving Our Picture of the Plasma Membrane: Rafts Induce Ordered Domains in a Simplified Model Cytoplasmic Leaflet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2022, 1864, 183995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, T.A.; Feigenson, G.W. Asymmetric Bilayers by Hemifusion: Method and Leaflet Behaviors. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.; Geier, B.; Pabst, G. Asymmetric Lipid Membranes: Towards More Realistic Model Systems. Membranes 2015, 5, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, B.; Marquardt, D.; Heberle, F.A.; Letofsky-Papst, I.; Rechberger, G.N.; Appavou, M.-S.; Katsaras, J.; Pabst, G. Intrinsic Curvature-Mediated Transbilayer Coupling in Asymmetric Lipid Vesicles. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, F.A.; Marquardt, D.; Doktorova, M.; Geier, B.; Standaert, R.F.; Heftberger, P.; Kollmitzer, B.; Nickels, J.D.; Dick, R.A.; Feigenson, G.W.; et al. Subnanometer Structure of an Asymmetric Model Membrane: Interleaflet Coupling Influences Domain Properties. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5195–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frewein, M.P.K.; Piller, P.; Semeraro, E.F.; Batchu, K.C.; Heberle, F.A.; Scott, H.L.; Gerelli, Y.; Porcar, L.; Pabst, G. Interdigitation-Induced Order and Disorder in Asymmetric Membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 2022, 255, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, E. Membrane Structure-Function Insights from Asymmetric Lipid Vesicles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2382–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; London, E. Preparation of Artificial Plasma Membrane Mimicking Vesicles with Lipid Asymmetry. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.T.; London, E. Preparation and Properties of Asymmetric Large Unilamellar Vesicles: Interleaflet Coupling in Asymmetric Vesicles Is Dependent on Temperature but Not Curvature. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiantia, S.; Schwille, P.; Klymchenko, A.S.; London, E. Asymmetric GUVs Prepared by MβCD-Mediated Lipid Exchange: An FCS Study. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, L1–L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D.; Keller, S.L. Tuning Lipid Mixtures to Induce or Suppress Domain Formation across Leaflets of Unsupported Asymmetric Bilayers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorova, M.; Heberle, F.A.; Eicher, B.; Standaert, R.F.; Katsaras, J.; London, E.; Pabst, G.; Marquardt, D. Preparation of Asymmetric Phospholipid Vesicles for Use as Cell Membrane Models. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 2086–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, T.A. The Use of Hemifusion to Create Asymmetric Giant Unilamellar Vesicles: Insights on Induced Order Domains. In Methods in Enzymology; Baumgart, T., Deserno, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Enoki, T.A.; Heberle, F.A.; Feigenson, G.W. Experimental Evidence That Bilayer Asymmetry Decreases Lo/Ld Line Tension. Biophys. J. 2020, 118, 386a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenson, G.W.; Buboltz, J.T. Ternary Phase Diagram of Dipalmitoyl-PC/Dilauroyl-PC/Cholesterol: Nanoscopic Domain Formation Driven by Cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 2775–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenson, G.W. Phase Diagrams and Lipid Domains in Multicomponent Lipid Bilayer Mixtures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2008, 1788, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenson, G.W. Phase Behavior of Lipid Mixtures. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Heberle, F.A.; Mills, T.T.; Klawitter, P.; Huang, G.; Costanza, G.; Feigenson, G.W. Phase Studies of Model Biomembranes: Complex Behavior of DSPC/DOPC/Cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 2764–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petruzielo, R.S.; Heberle, F.A.; Drazba, P.; Katsaras, J.; Feigenson, G.W. Phase Behavior and Domain Size in Sphingomyelin-Containing Lipid Bilayers Author’ s Personal Copy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoki, T.A.; Heberle, F.A.; Feigenson, G.W. FRET Detects the Size of Nanodomains for Coexisting Liquid-Disordered and Liquid-Ordered Phases. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppamoochikkal, P.; Tristram-Nagle, S.; Nagle, J.F. Orientation of Tie-Lines in the Phase Diagram of DOPC/DPPC/Cholesterol Model Biomembranes. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17363–17368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezlyepkina, N.; Gracià, R.S.; Shchelokovskyy, P.; Lipowsky, R.; Dimova, R. Phase Diagram and Tie-Line Determination for the Ternary Mixture DOPC/ESM/Cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konyakhina, T.M.; Wu, J.; Mastroianni, J.D.; Heberle, F.A.; Feigenson, G.W. Phase Diagram of a 4-Component Lipid Mixture: DSPC/DOPC/POPC/Chol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 2204–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usery, R.D.; Enoki, T.A.; Wickramasinghe, S.P.; Weiner, M.D.; Tsai, W.C.; Kim, M.B.; Wang, S.; Torng, T.L.; Ackerman, D.G.; Heberle, F.A.; et al. Line Tension Controls Liquid-Disordered + Liquid-Ordered Domain Size Transition in Lipid Bilayers. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, F.A.; Buboltz, J.T.; Stringer, D.; Feigenson, G.W. Fluorescence Methods to Detect Phase Boundaries in Lipid Bilayer Mixtures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2005, 1746, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konyakhina, T.M.; Feigenson, G.W. Phase Diagram of a Polyunsaturated Lipid Mixture: Brain Sphingomyelin/1-Stearoyl-2-Docosahexaenoyl-Sn-Glycero-3-Phosphocholine/Cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2015, 1858, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberle, F.A.; Wu, J.; Goh, S.L.; Petruzielo, R.S.; Feigenson, G.W. Comparison of Three Ternary Lipid Bilayer Mixtures: FRET and ESR Reveal Nanodomains. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 3309–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heftberger, P.; Kollmitzer, B.; Heberle, F.A.; Pan, J.; Rappolt, M.; Amenitsch, H.; Kučerka, N.; Katsaras, J.; Pabst, G. Global Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering Data Analysis for Multilamellar Vesicles: The Evolution of the Scattering Density Profile Model. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberle, F.A.; Petruzielo, R.S.; Pan, J.; Drazba, P.; Kučerka, N.; Standaert, R.F.; Feigenson, G.W.; Katsaras, J. Bilayer Thickness Mismatch Controls Domain Size in Model Membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 6853–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, F.A.; Doktorova, M.; Scott, H.L.; Skinkle, A.D.; Waxham, M.N.; Levental, I. Direct Label-Free Imaging of Nanodomains in Biomimetic and Biological Membranes by Cryogenic Electron Microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19943–19952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, C.E.; Mileant, A.; Thakkar, N.; Lee, K.K.; Keller, S.L. Direct Imaging of Liquid Domains in Membranes by Cryo-Electron Tomography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19713–19719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumasu, F.; Jin, A.J.; Feigenson, G.W.; Dvorak, J.A. Atomic Force Microscopy of Nanometric Liposome Adsorption and Nanoscopic Membrane Domain Formation. Ultramicroscopy 2003, 97, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumasu, F.; Jin, A.J.; Feigenson, G.W.; Dvorak, J.A. Nanoscopic Lipid Domain Dynamics Revealed by Atomic Force Microscopy. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buboltz, J.T. Steady-State Probe-Partitioning Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer: A Simple and Robust Tool for the Study of Membrane Phase Behavior. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2007, 76, 021903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Penningston, N.F.; Wu, J.; Farkas, E.R.; Goh, S.L.; Konyakhina, T.M.; Zheng, J.Y.; Webb, W.W.; Feigenson, G.W. GUV Preparation and Imaging: Minimizing Artifacts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2010, 1798, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.C.; Feigenson, G.W. Lowering Line Tension with High Cholesterol Content Induces a Transition from Macroscopic to Nanoscopic Phase Domains in Model Biomembranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konyakhina, T.M.; Goh, S.L.; Amazon, J.; Heberle, F.A.; Wu, J.; Feigenson, G.W. Control of a Nanoscopic-to-Macroscopic Transition: Modulated Phases in Four-Component DSPC/DOPC/POPC/Chol Giant Unilamellar Vesicles. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, L8–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.L.; Amazon, J.J.; Feigenson, G.W. Toward a Better Raft Model: Modulated Phases in the Four-Component Bilayer, DSPC/DOPC/POPC/CHOL. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-46312-4. (Online). [Google Scholar]
- Budil, D.E.; Sanghyuk, L.; Saxena, S.; Freed, J.H. Nonlinear-Least-Squares Analysis of Slow-Motion EPR Spectra in One and Two Dimensions Using a Modified Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm. J. Magn. Reson.-Ser. A 1996, 120, 155–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haataja, M.P. Lipid Domain Co-Localization Induced by Membrane Undulations. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimzyanov, T.R.; Kuzmin, P.I.; Pohl, P.; Akimov, S.A. Undulations Drive Domain Registration from the Two Membrane Leaflets. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, T.A.; Wu, J.; Heberle, F.A.; Feigenson, G.W. Investigation of the Domain Line Tension in Asymmetric Vesicles Prepared via Hemifusion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.; Heberle, F.A.; Miti, T.; Eicher, B.; London, E.; Katsaras, J.; Pabst, G. 1H NMR Shows Slow Phospholipid Flip-Flop in Gel and Fluid Bilayers. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3731–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, F.A.; Doktorova, M.; Goh, S.L.; Standaert, R.F.; Katsaras, J.; Feigenson, G.W. Hybrid and Nonhybrid Lipids Exert Common Effects on Membrane Raft Size and Morphology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14932–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veatch, S.L.; Keller, S.L. Separation of Liquid Phases in Giant Vesicles of Ternary Mixtures of Phospholipids and Cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 3074–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veatch, S.L.; Gawrisch, K.; Keller, S.L. Closed-Loop Miscibility Gap and Quantitative Tie-Lines in Ternary Membranes Containing Diphytanoyl PC. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 4428–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, T.; Hess, S.T.; Webb, W.W. Imaging Coexisting Fluid Domains in Biomembrane Models Coupling Curvature and Line Tension. Nature 2003, 425, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, C.; Tian, A.; Melamed, S.; Johnson, C.; Tee, S.-Y.; Baumgart, T. Flicker Spectroscopy of Thermal Lipid Bilayer Domain Boundary Fluctuations. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 3169–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seul, M.; Andelman, D. Domain Shapes and Patterns: The Phenomenology of Modulated Phases. Science 1995, 267, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazon, J.J.; Goh, S.L.; Feigenson, G.W. Competition between Line Tension and Curvature Stabilizes Modulated Phase Patterns on the Surface of Giant Unilamellar Vesicles: A Simulation Study. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2013, 87, 022708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazon, J.J.; Feigenson, G.W. Lattice Simulations of Phase Morphology on Lipid Bilayers: Renormalization, Membrane Shape, and Electrostatic Dipole Interactions. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2014, 89, 022702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, W. Elastic Properties of Lipid Bilayers: Theory and Possible Experiments. Z. Fur Naturforsch. Sect. C J. Biosci. 1973, 28, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, T.; Hammond, A.T.; Sengupta, P.; Hess, S.T.; Holowka, D.A.; Baird, B.A.; Webb, W.W. Large-Scale Fluid/Fluid Phase Separation of Proteins and Lipids in Giant Plasma Membrane Vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3165–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorent, J.H.; Diaz-Rohrer, B.; Lin, X.; Spring, K.; Gorfe, A.A.; Levental, K.R.; Levental, I. Structural Determinants and Functional Consequences of Protein Affinity for Membrane Rafts. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorent, J.H.; Levental, I. Structural Determinants of Protein Partitioning into Ordered Membrane Domains and Lipid Rafts. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 192, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, H.J.; Stevens, T.J.; Munro, S. A Comprehensive Comparison of Transmembrane Domains Reveals Organelle-Specific Properties. Cell 2010, 142, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killian, J.A.A. Synthetic Peptides as Models for Intrinsic Membrane Proteins. FEBS Lett. 2003, 555, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrashov, O.V.; Pinigin, K.V.; Akimov, S.A. Characteristic Lengths of Transmembrane Peptides Controlling Their Tilt and Lateral Distribution between Membrane Domains. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 104, 044411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frewein, M.; Kollmitzer, B.; Heftberger, P.; Pabst, G. Lateral Pressure-Mediated Protein Partitioning into Liquid-Ordered/Liquid-Disordered Domains. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 3189–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Vostrikov, V.V.; Greathouse, D.V.; Koeppe, R.E. Influence of Proline upon the Folding and Geometry of the WALP19 Transmembrane Peptide. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 11883–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, N.J.; Vostrikov, V.V.; Greathouse, D.V.; Grant, C.V.; Opella, S.J.; Koeppe, R.E. Tyrosine Replacing Tryptophan as an Anchor in GWALP Peptides. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, D.G.; Feigenson, G.W. Effects of Transmembrane α-Helix Length and Concentration on Phase Behavior in Four-Component Lipid Mixtures: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 4064–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Planque, M.R.R.; Greathouse, D.V.; Koeppe, R.E.; Schäfer, H.; Marsh, D.; Killian, J.A. Influence of Lipid/Peptide Hydrophobic Mismatch on the Thickness of Diacylphosphatidylcholine Bilayers. A 2H NMR and ESR Study Using Designed Transmembrane α-Helical Peptides and Gramicidin A. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 9333–9345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usery, R.D.; Enoki, T.A.; Wickramasinghe, S.P.; Nguyen, V.P.; Ackerman, D.G.; Greathouse, D.V.; Koeppe, R.E.; Barrera, F.N.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane Bending Moduli of Coexisting Liquid Phases Containing Transmembrane Peptide. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 2152–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efodili, E.; Knight, A.; Mirza, M.; Briones, C.; Lee, I.H. Spontaneous Transfer of Small Peripheral Peptides between Supported Lipid Bilayer and Giant Unilamellar Vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2024, 1866, 184256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H.L.; DiPasquale, M.; Rickeard, B.W.; Doktorova, M.; Heberle, F.A.; Scott, H.L.; Barrera, F.N.; Taylor, G.; Collier, C.P.; Stanley, C.B.; et al. Peptide-Induced Lipid Flip-Flop in Asymmetric Liposomes Measured by Small Angle Neutron Scattering. Langmuir 2019, 35, 11735–11744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levental, K.R.; Levental, I. Giant Plasma Membrane Vesicles: Models for Understanding Membrane Organization. Curr. Top. Membr. 2015, 75, 25–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, T.J.; Toombs, J.E.; Minna, J.D.; Brekken, R.A.; Udugamasooriya, D.G. Identification of Lipid-Phosphatidylserine (PS) as the Target of Unbiasedly Selected Cancer Specific Peptide-Peptoid Hybrid PPS1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30678–30690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.-Y.Y.; Silvius, J.R. Cholesterol Does Not Induce Segregation of Liquid-Ordered Domains in Bilayers Modeling the Inner Leaflet of the Plasma Membrane. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 2762–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krompers, M.; Heerklotz, H. A Guide to Your Desired Lipid-Asymmetric Vesicles. Membranes 2023, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.L.; Kennison, K.B.; Enoki, T.A.; Doktorova, M.; Kinnun, J.J.; Heberle, F.A.; Katsaras, J. Model Membrane Systems Used to Study Plasma Membrane Lipid Asymmetry. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsler, C.; Markones, M.; Choi, J.Y.; Frieling, N.; Fiedler, S.; Voelker, D.R.; Schubert, R.; Heerklotz, H. Preparation of Asymmetric Liposomes Using a Phosphatidylserine Decarboxylase. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaoka, R.; Kurosaki, H.; Nakao, H.; Ikeda, K.; Nakano, M. Formation of Asymmetric Vesicles via Phospholipase D-Mediated Transphosphatidylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.T.; Megha; London, E. Preparation and Properties of Asymmetric Vesicles That Mimic Cell Membranes. Effect upon Lipid Raft Formation and Transmembrane Helix Orientation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6079–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; London, E. Using Sterol Substitution to Probe the Role of Membrane Domains in Membrane Functions. Lipids 2015, 50, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiantia, S.; London, E. Acyl Chain Length and Saturation Modulate Interleaflet Coupling in Asymmetric Bilayers: Effects on Dynamics and Structural Order. Biophys. J. 2012, 103, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; London, E. Effect of Cyclodextrin and Membrane Lipid Structure upon Cyclodextrin-Lipid Interaction. Langmuir 2013, 29, 14631–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakuda, S.; Suresh, P.; Li, G.; London, E. Loss of Plasma Membrane Lipid Asymmetry Can Induce Ordered Domain (Raft) Formation. J. Lipid Res. 2022, 63, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pautot, S.; Frisken, B.J.; Weitz, D.A. Engineering Asymmetric Vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10718–10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leomil, F.S.C.; Stephan, M.; Pramanik, S.; Riske, K.A.; Dimova, R. Bilayer Charge Asymmetry and Oil Residues Destabilize Membranes upon Poration. Langmuir 2024, 40, 4719–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, J.; Paratore, T.A.; Ketelhohn, H.M.; DeCilio, B.C.; Ross, A.H.; Gericke, A. Engineering Phosphatidylserine Containing Asymmetric Giant Unilamellar Vesicles. Membranes 2024, 14, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papahadjopoulos, D.; Nir, S.; Düzgünes, N. Molecular Mechanisms of Calcium-Induced Membrane Fusion. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1990, 22, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papahadjopoulos, D.; Vail, W.J.; Newton, C.; Nir, S.; Jacobson, K.; Poste, G.; Lazo, R. Studies on Membrane Fusion. III. The Role of Calcium-Induced Phase Changes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 1977, 465, 579–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaus, J.; Stöckl, M.; Langosch, D.; Volkmer, R.; Herrmann, A. Direct Visualization of Large and Protein-Free Hemifusion Diaphragms. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, R.; Spinozzi, F.; Itri, R. Hydroperoxide and Carboxyl Groups Preferential Location in Oxidized Biomembranes Experimentally Determined by Small Angle X-Ray Scattering: Implications in Membrane Structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 2299–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinozzi, F.; Ferrero, C.; Ortore, M.G.; De Maria Antolinos, A.; Mariani, P. GENFIT: Software for the Analysis of Small-Angle X-Ray and Neutron Scattering Data of Macro-Molecules in Solution. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučerka, N.; Nagle, J.F.; Sachs, J.N.; Feller, S.E.; Pencer, J.; Jackson, A.; Katsaras, J. Lipid Bilayer Structure Determined by the Simultaneous Analysis of Neutron and X-Ray Scattering Data. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoki, T.A.; Wu, J.; Heberle, F.A.; Feigenson, G.W. Dataset of Asymmetric Giant Unilamellar Vesicles Prepared via Hemifusion: Observation of Anti-Alignment of Domains and Modulated Phases in Asymmetric Bilayers. Data Br. 2021, 35, 106927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenson, G.W.; Enoki, T.A. Nano-Scale Domains in the Plasma Membrane Are like Macroscopic Domains in Asymmetric Bilayers. Biophys. J. 2023, 122, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; London, E. Lipid Structure and Composition Control Consequences of Interleaflet Coupling in Asymmetric Vesicles. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.J.; Loew, S.; May, S. Influence of Monolayer-Monolayer Coupling on the Phase Behavior of a Fluid Lipid Bilayer. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 4268–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, S. Trans-Monolayer Coupling of Fluid Domains in Lipid Bilayers. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3148–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.J.; Olmsted, P.D. Effects of Passive Phospholipid Flip-Flop and Asymmetric External Fields on Bilayer Phase Equilibria. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.J.; Olmsted, P.D. Registered and Antiregistered Phase Separation of Mixed Amphiphilic Bilayers. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 1963–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.D. Interleaflet Coupling Mechanisms in Bilayers of Lipids and Cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, L32–L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzel, G.G.; Schick, M. Phase Behavior of a Model Bilayer Membrane with Coupled Leaves. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimburg, T. Thermal Biophysics of Membranes; Tutorials in Biophysics; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; ISBN 9783527611591. [Google Scholar]
- Doniach, S. Thermodynamic Fluctuations in Phospholipid Bilayers. J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 68, 4912–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, H.S.; Henriques, V.B. Lattice Solution Model for Order-Disorder Transitions in Membranes and Langmuir Monolayers. Phys. Rev. E-Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2014, 90, 052705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riske, K.A.; Barroso, R.P.; Vequi-Suplicy, C.C.; Germano, R.; Henriques, V.B.; Lamy, M.T. Lipid Bilayer Pre-Transition as the Beginning of the Melting Process. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akabori, K.; Nagle, J.F. Structure of the DMPC Lipid Bilayer Ripple Phase. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hiraki, S.; Feigenson, G.W. Calculation of Liquid-Disordered/Liquid-Ordered Line Tension from Pairwise Lipid Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 4949–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safran, S.A. Statistical Thermodynamics of Surfaces, Interfaces, and Membranes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 9780429965685. [Google Scholar]
- Risselad, H.J.; Marrink, S.J. The Molecular Face of Lipid Rafts in Model Membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17367–17372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Soft and Biological Structures. In Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 535–576. [Google Scholar]
- Deserno, M. Fluid Lipid Membranes: From Differential Geometry to Curvature Stresses. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 185, 11–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deserno, M. Biomembranes Balance Many Types of Leaflet Asymmetries. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2024, 87, 102832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, A.; Deserno, M. Spontaneous Curvature, Differential Stress, and Bending Modulus of Asymmetric Lipid Membranes. Biophys. J. 2020, 118, 624–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, I.S.; Pinheiro, G.X.; Sa, M.L.B.; Gurgel, P.H.L.O.; Pizzol, S.U.; Itri, R.; Henriques, V.B.; Enoki, T.A. The Importance of Bilayer Asymmetry in Biological Membranes: Insights from Model Membranes. Membranes 2025, 15, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030079
Oliveira IS, Pinheiro GX, Sa MLB, Gurgel PHLO, Pizzol SU, Itri R, Henriques VB, Enoki TA. The Importance of Bilayer Asymmetry in Biological Membranes: Insights from Model Membranes. Membranes. 2025; 15(3):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030079
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Igor S., Guilherme X. Pinheiro, Maria Luana B. Sa, Pedro Henrique L. O. Gurgel, Samuel U. Pizzol, Rosangela Itri, Vera B. Henriques, and Thais A. Enoki. 2025. "The Importance of Bilayer Asymmetry in Biological Membranes: Insights from Model Membranes" Membranes 15, no. 3: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030079
APA StyleOliveira, I. S., Pinheiro, G. X., Sa, M. L. B., Gurgel, P. H. L. O., Pizzol, S. U., Itri, R., Henriques, V. B., & Enoki, T. A. (2025). The Importance of Bilayer Asymmetry in Biological Membranes: Insights from Model Membranes. Membranes, 15(3), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15030079






