Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate—HBA/Poly Sulfone Blend for Water Treatment Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments
2.2. Chemicals
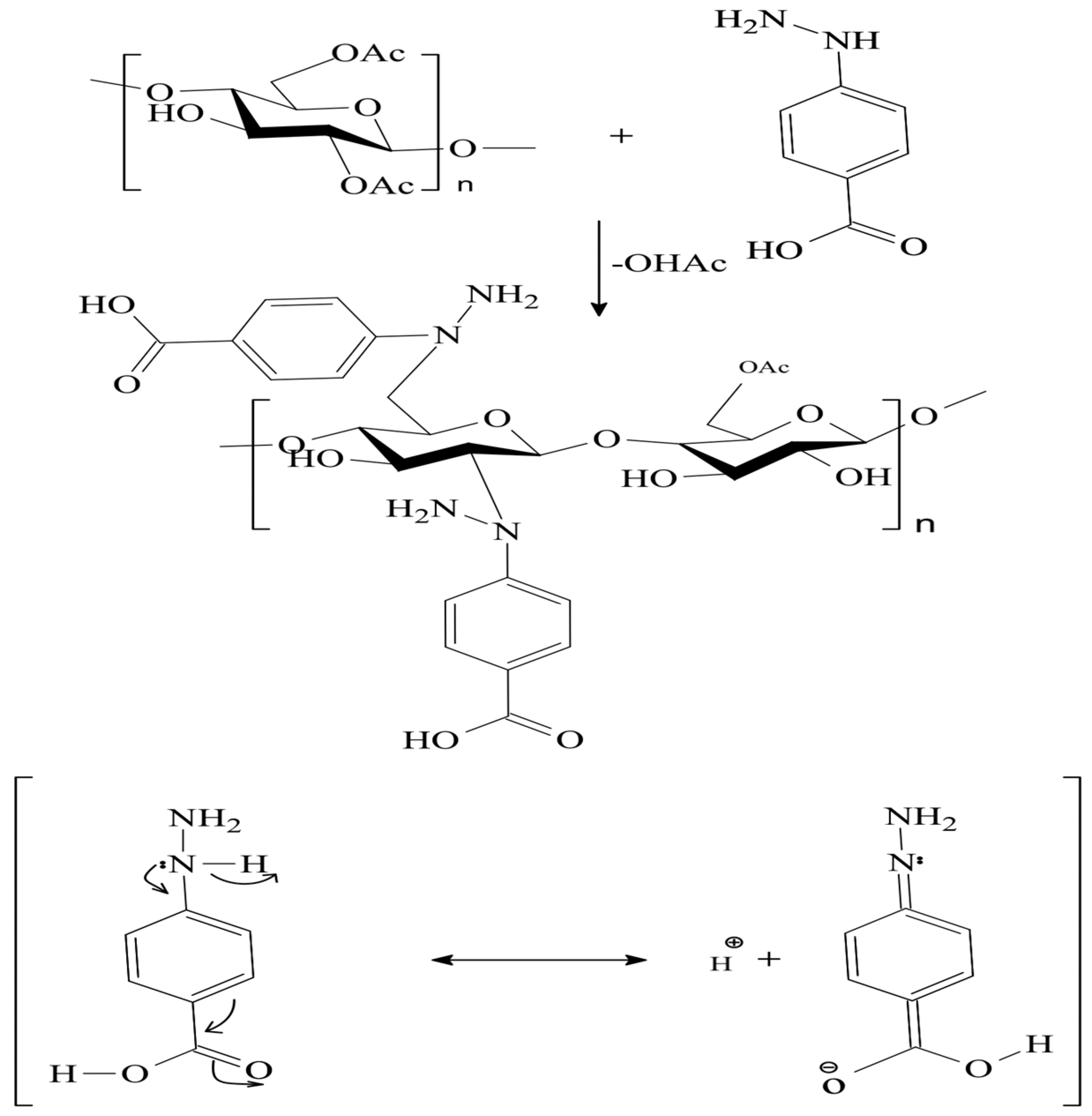
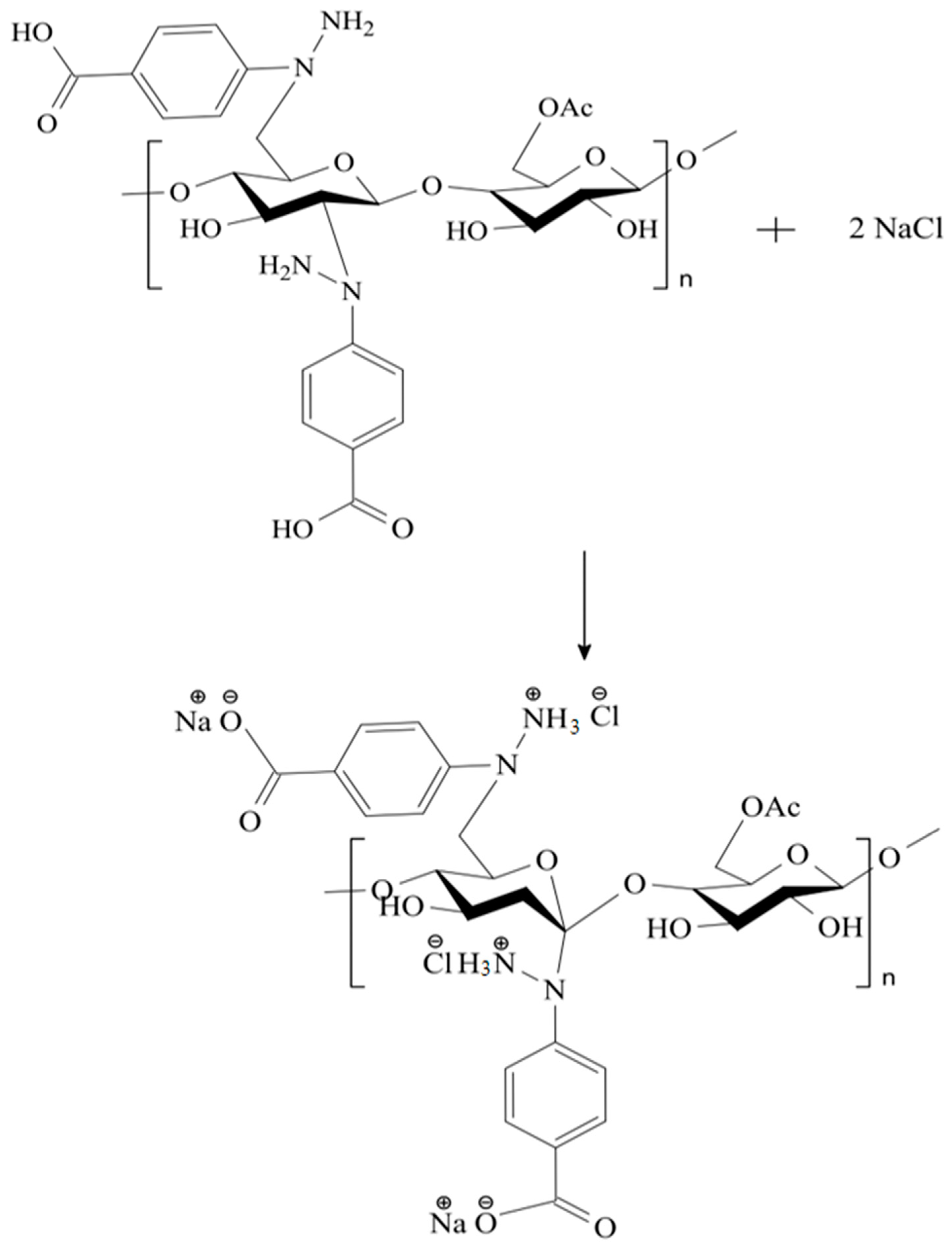
2.3. Synthesis of the CA–HBA Modified Polymer
2.4. General Preparation of Stock Solution of Metal Ions
2.5. Procedures
2.5.1. Fabrication of Membrane
2.5.2. Surface Hydrophilicity and Contact Angle Measurement
2.5.3. Method of Metal Ion Removal
2.5.4. Water Flux
2.5.5. Membrane Porosity and Pore Size
2.5.6. Regeneration of Metal Ions
2.5.7. Preparation of the NaCl Solution
2.5.8. Desalination Process
3. Results
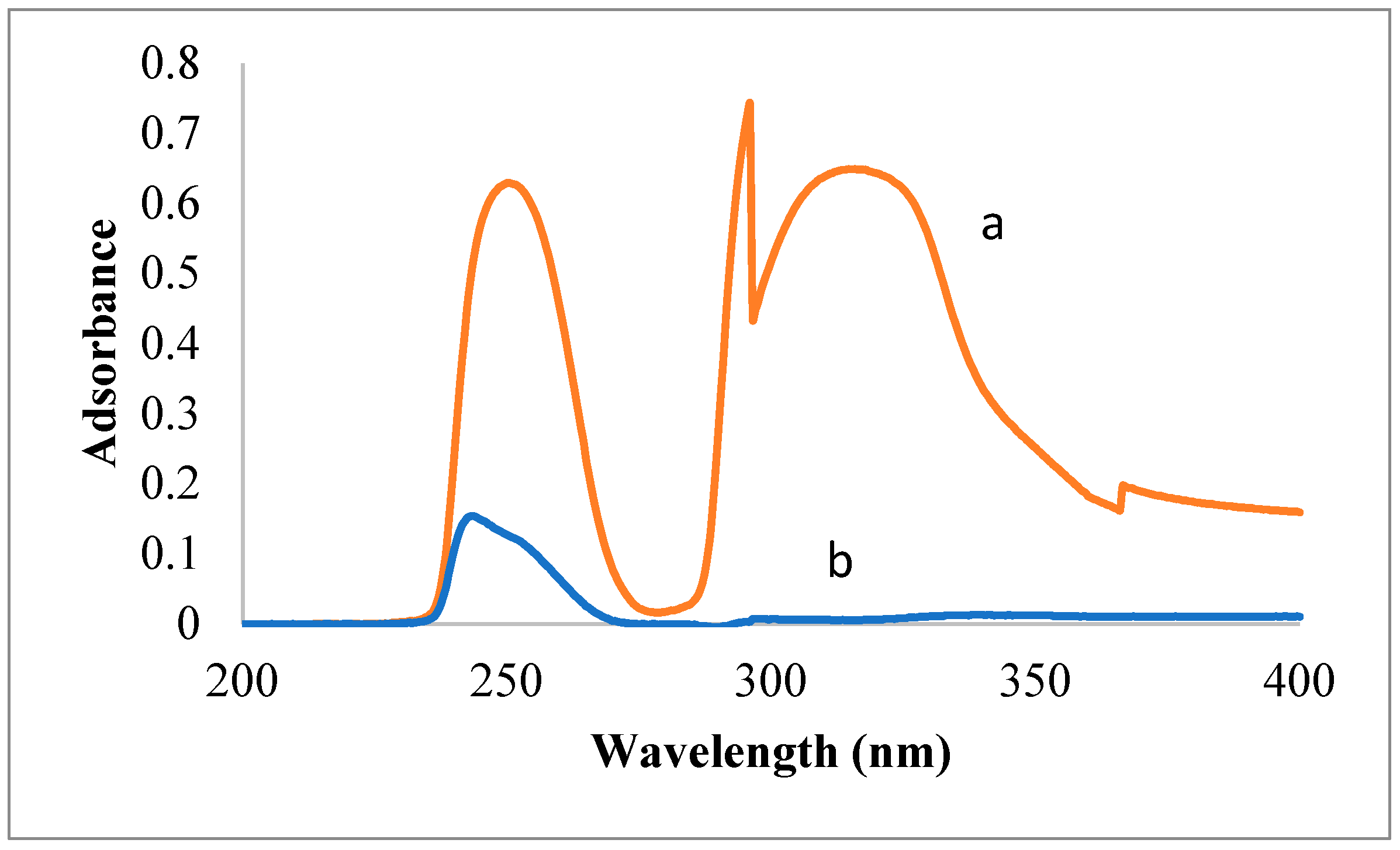
3.1. Spectroscopic Analysis
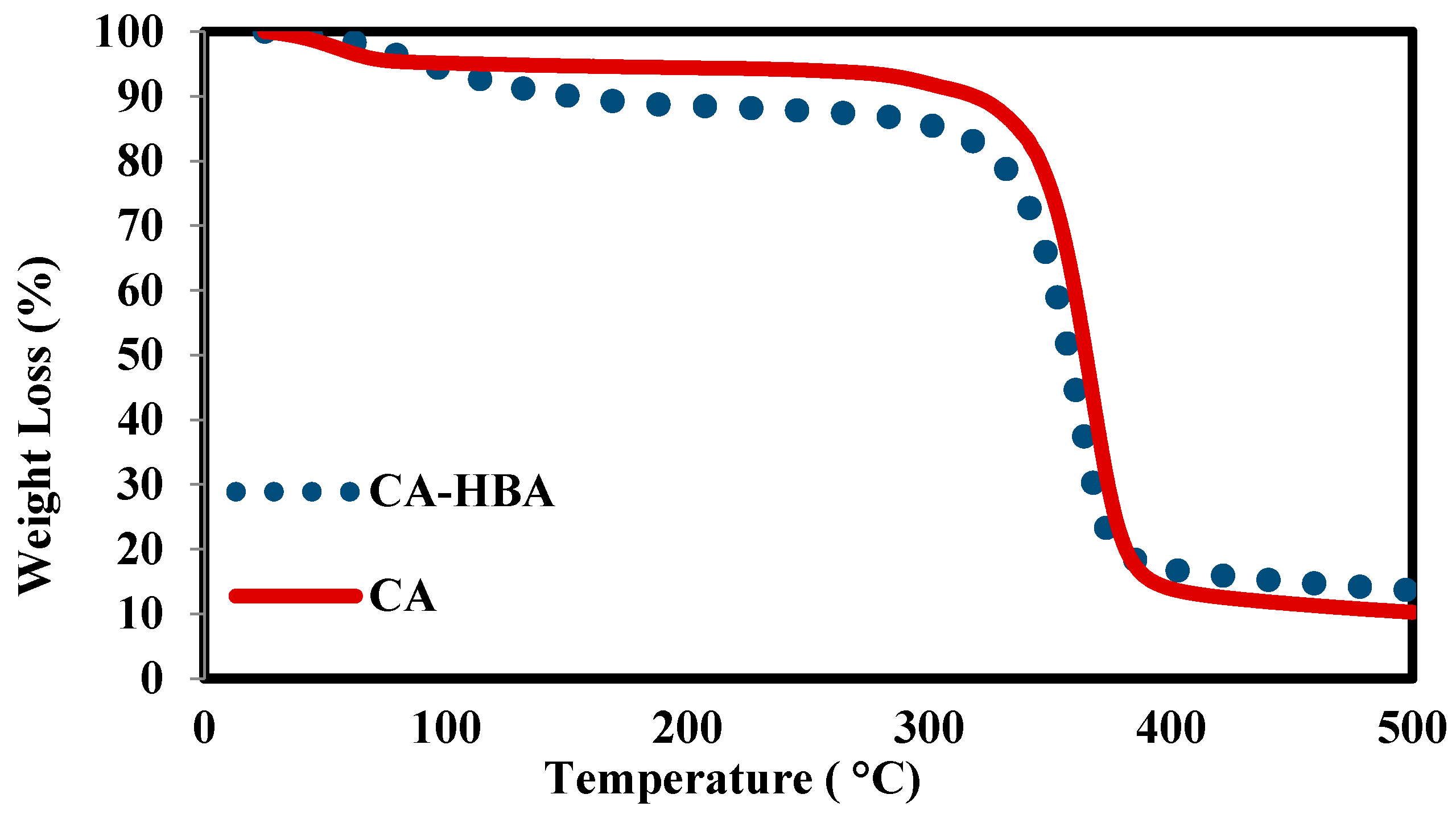
3.2. Thermal Stability
3.3. Crystallinity
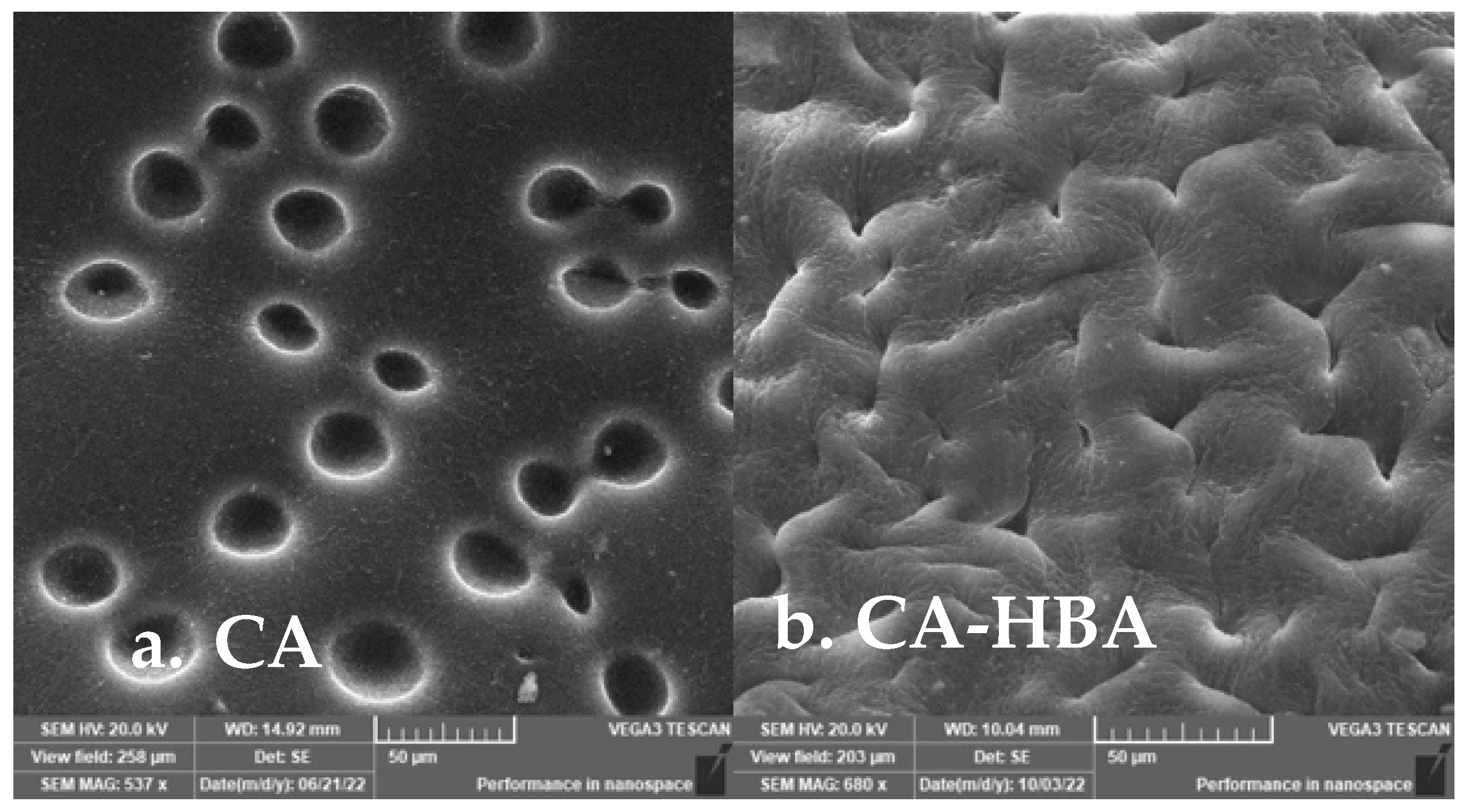
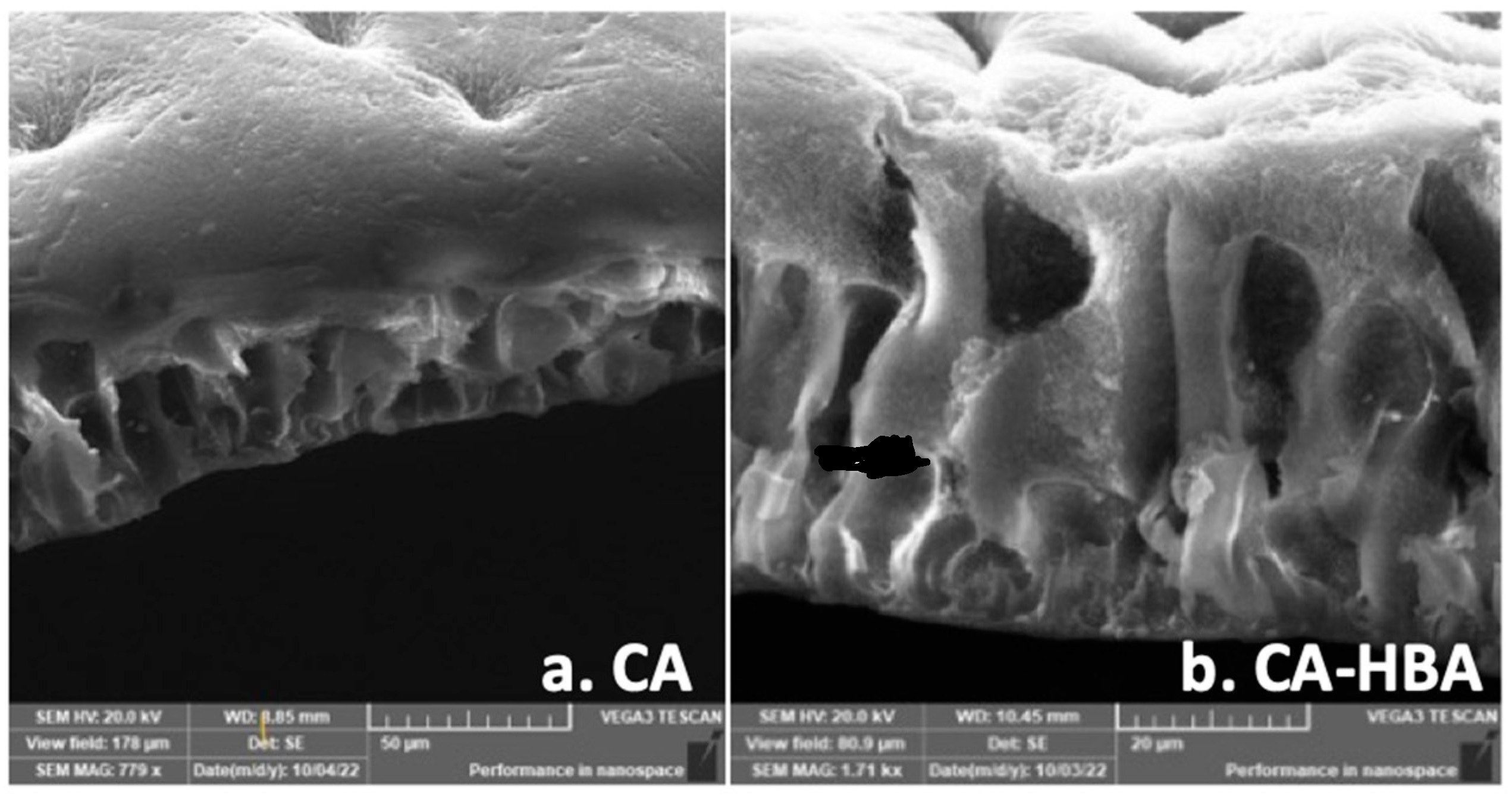
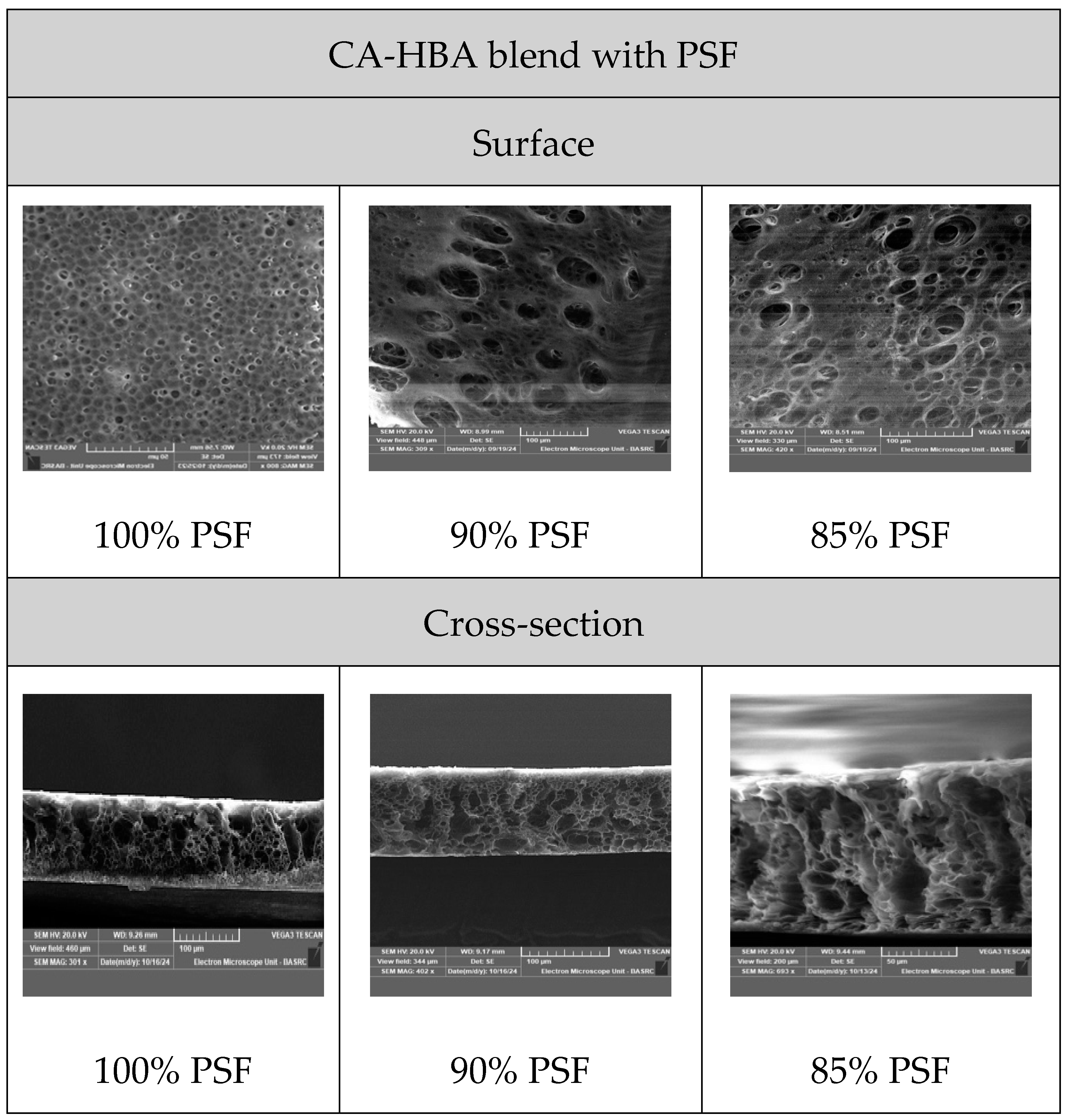
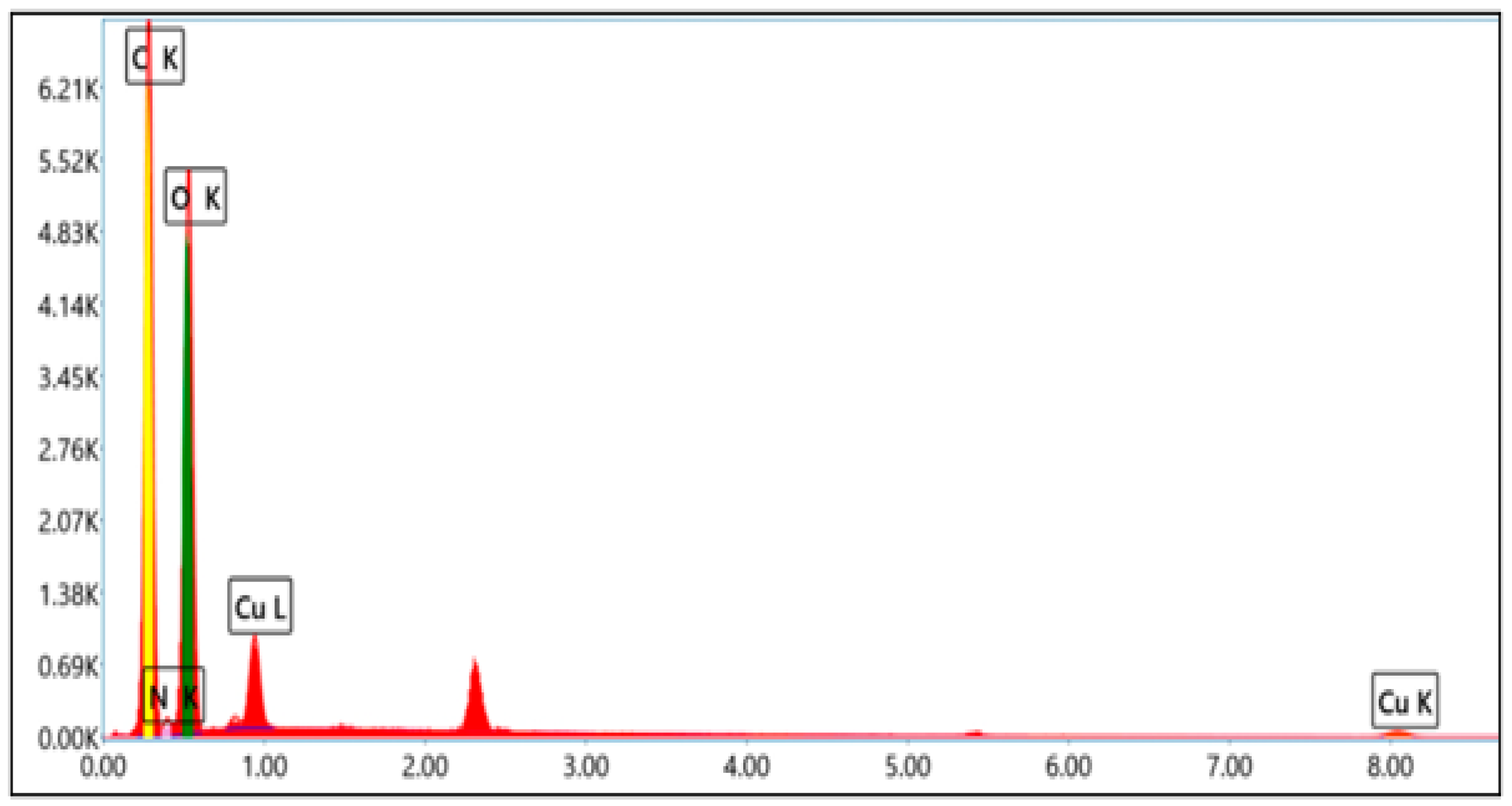
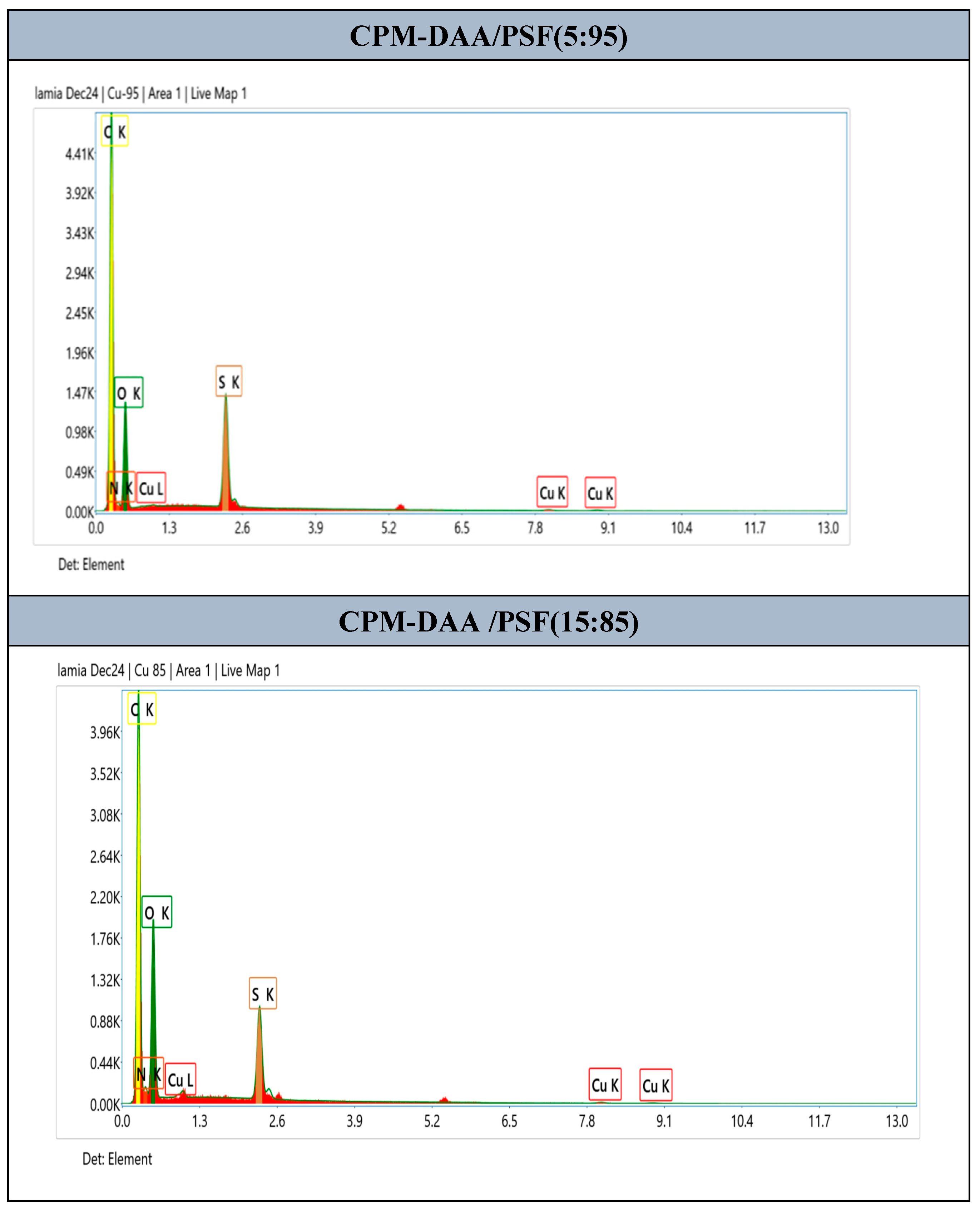
3.4. Morphological Characterization
3.5. Contact Angle and Surface Hydrophilicity
3.6. Membrane Performance
3.6.1. Water Flux
3.6.2. Membrane Porosity and Pore Size
3.6.3. Removal of Cu (II) Ions
3.7. Parameters Affecting Membrane Performance
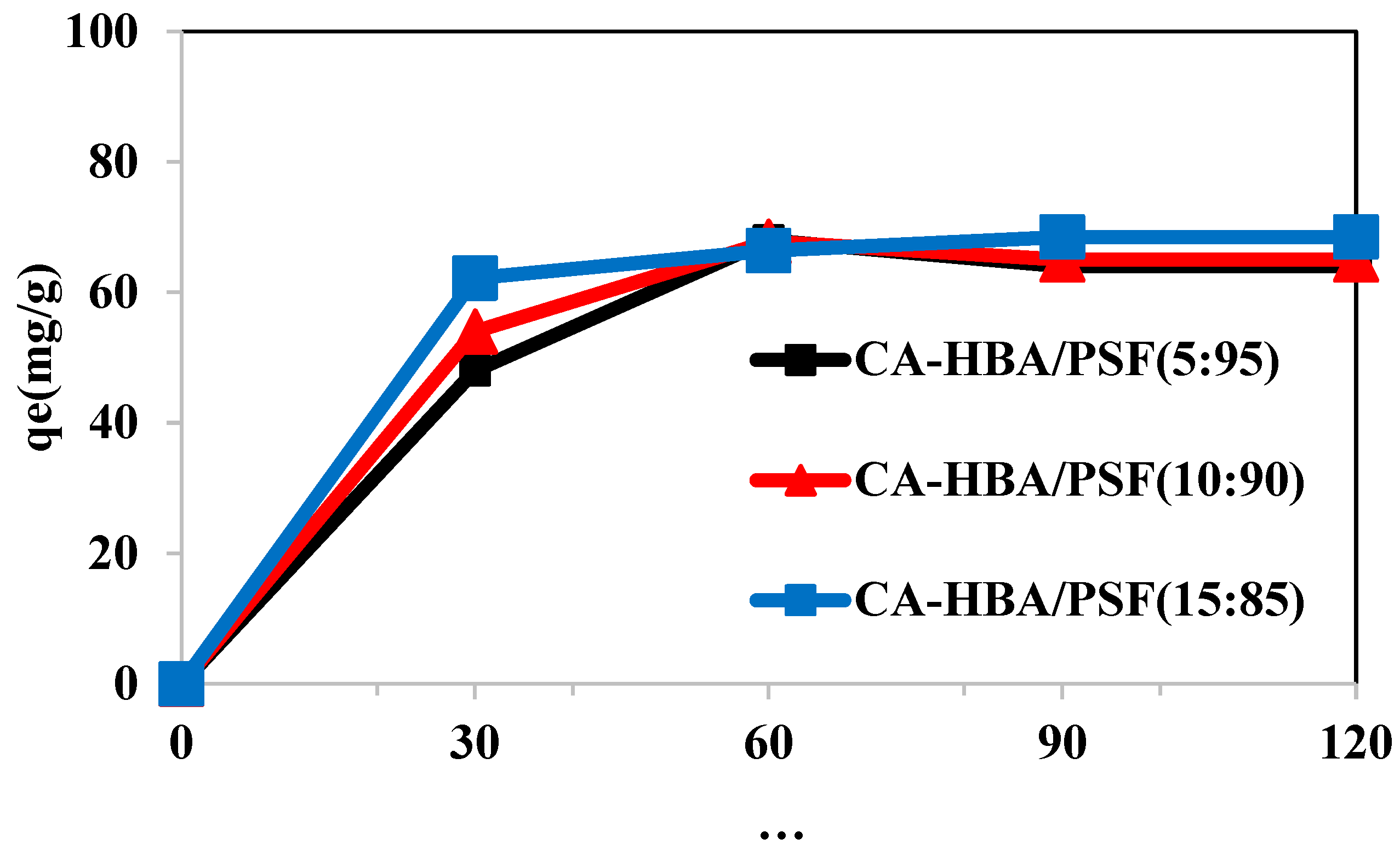
3.7.1. Contact Time
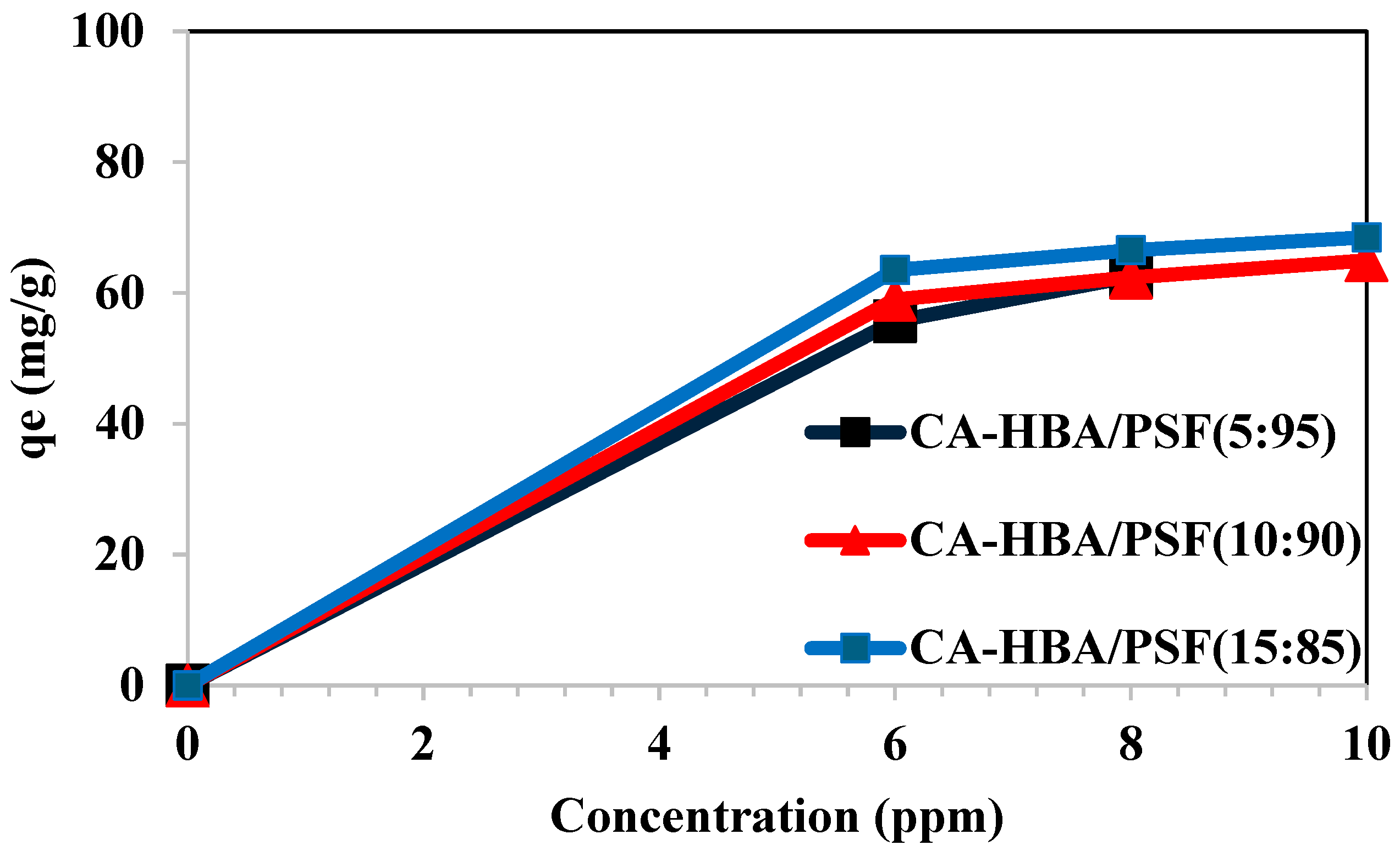
3.7.2. Effect of Adsorbate Concentration
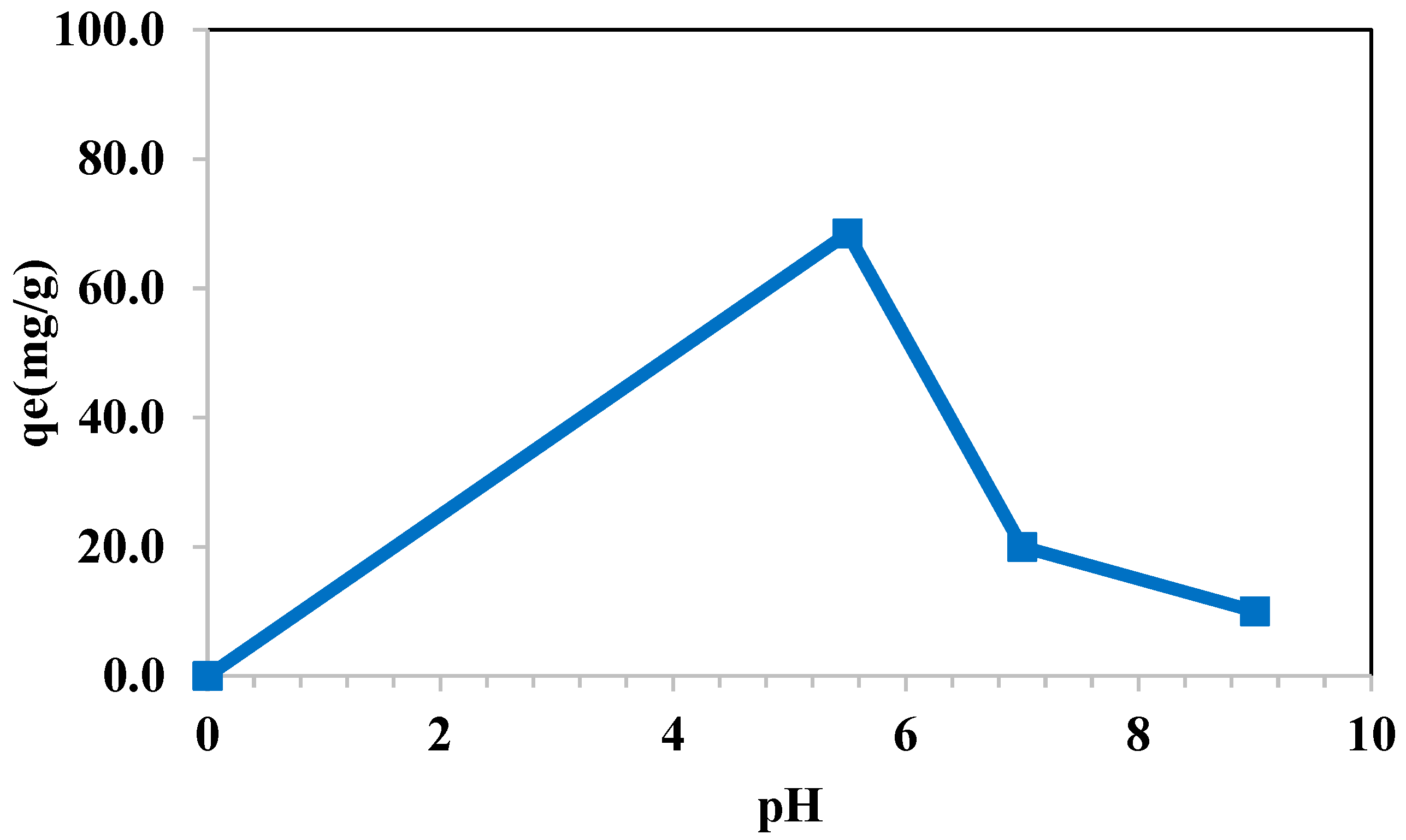
3.7.3. Effect of pH
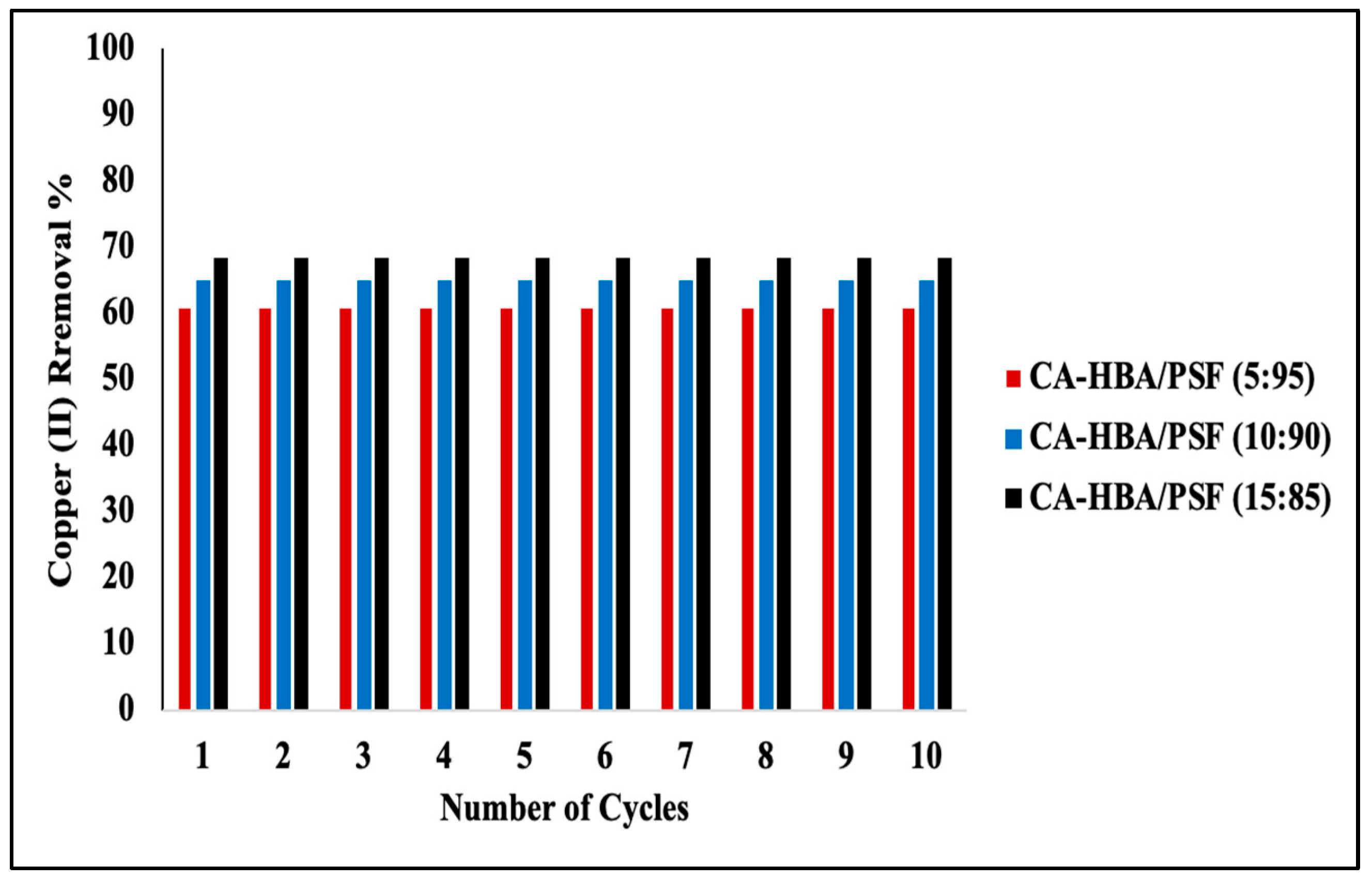
3.8. Desorption of Metal Ions and Reusability of the CA-HBA/PSF Membranes
3.9. Desalination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Ji, D.; Zhang, H. One-step facile fabrication of PVDF/graphene composite nanofibrous membrane with enhanced oil affinity for highly efficient gravity-driven emulsified oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrao, C.; Strippoli, R.; Lagioia, G.; Huisingh, D. Water scarcity in agriculture: An overview of causes, impacts and approaches for reducing the risks. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, K.H.H.; Mustafa, F.S.; Omer, K.M.; Hama, S.; Hamarawf, R.F.; Rahman, K.O. Heavy metal pollution in the aquatic environment: Efficient and low-cost removal approaches to eliminate their toxicity: A review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 17595–17610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Khan, M.; Sheikh, T.M.M.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Chohan, T.A.; Shamim, S.; Liu, Y. Zinc essentiality; toxicity, and its bacterial bioremediation: A comprehensive insight. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 900740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean. Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbanescu, O.S.; Voicu, S.I.; Thakur, V.K. Polysulfone functionalized membranes: Properties; challenges. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; García, R.G.; Martínez, J.D.H.; Briones, C.M.; Ramos, A.M.M.; Tamez, M.F.L.; Del Valle, B.G.; Segura, F.J.M. Recent advances in designing fibrous biomaterials for the domain of biomedical, clinical, and environmental applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 3690–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jia, Y.; Bai, S. Polysulfone foam with high expansion ratio prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide assisted molding foaming method. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2880–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, X.J.; Show, P.L.; Katsuda, T.; Chen, W.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Surface grafting techniques on the improvement of membrane bioreactor: State-of-the-art advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, L.; Shen, M.-H.; Van, Y.-T. Microbial synthesis of poly (ε-lysine) and its various applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Mahmud, N.; Benamor, A.; Mahmoudi, E.; Takriff, M.S.; Mohammad, A.W. Improved properties and salt rejection of polysulfone membrane by incorporation of hydrophilic cobalt-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Emergent Mater. 2024, 7, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, O.T.; Mamba, G.; Mamba, B.B. A facile synthesis approach for GO-ZnO/PES ultrafiltration mixed matrix photocatalytic membranes for dye removal in water: Leveraging the synergy between photocatalysis and membrane filtration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.H.; Al-Anbari, R.H.; Haider, A. Polysulfone/TiO2 thin film nanocomposite for commercial ultrafiltration membranes. J. Appl. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2022, 2, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, R.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F. Preparation of antifouling polyetherimide/hydrolysed PIAM blend nanofiltration membranes for salt rejection applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55773–55780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, M.Z.; Ismail, A.F.; Goh, P.S.; Kadir, S.H.S.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hasbullah, H.; Abdullah, M.S.; Ng, B.C.; Kamal, F.; Mustafar, R. Immobilizing chitosan nanoparticles in polysulfone ultrafiltration hollow fibre membranes for improving uremic toxins removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, A.T.; Benamor, A.; Hawari, A.H.; Mahmoudi, E. Graphene oxide/chitosan doped polysulfone membrane for the treatment of industrial wastewater. Emergent Mater. 2023, 6, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasibiselahchin, A.; Soltanolkottabi, F. Surface modification of polysulfone reverse osmosis membrane with chitosan-modified zinc oxide for water desalination. Environ. Technol. 2023, 45, 3912–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zurayk, R.; Alnairat, N.; Khalaf, A.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Halaweh, G. Cellulose Acetate Membranes: Fouling Types and Antifouling Strategies—A Brief Review. Processes 2023, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Pasaoglu, M.E.; Barzegar, H.; Teber, O.O.; Kaya, R.; Bastug, M.; Khataee, A.; Koyuncu, I. Cellulose acetate in fabrication of polymeric membranes: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Feng, X.; Hu, D. From asymmetry to symmetry: Biomimetic multi-channel structures for enhanced desalination using co-dissolving porogens. J. Memb. Sci. 2023, 685, 121914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ansari, Z.; Vega, L.F.; Zou, L. Emulsified oil fouling resistant cellulose acetate-MoS2-nanocomposite membrane for oily wastewater remediation. Desalination 2024, 575, 117335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, E.S.; Abdallah, H.; Shaban, A.M. Development of TiO2/polyvinyl alcohol-cellulose acetate nanocomposite reverse osmosis membrane for groundwater-surface water interfaces purification. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 289, 116222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Rahman, R. Electrospun nanofiber composite membranes based on cellulose acetate/nano-zeolite for the removal of oil from oily wastewater. Emergent Mater. 2022, 5, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatiatun; Bakar, S.A.; Mohamed, A.; Kusuma, H.H.; Muqoyyanah; Mohamat, R.; Kumar, V.V.; Ali, K.; Nuryadi, R.; Azis, M.N.A. High Methylene Blue Adsorption Efficiency of Cellulose Acetate-Based Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes Modified with Graphene Oxide and Zeolite. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2025, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, M.; Voicu, S.I. Cellulose acetate-based membranes for the removal of heavy metals from water in the context of circular economy. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 206, 117716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswari, A.; Christy, E.J.S.; Mary, G.I.C.; Jayaraj, K.; Pius, A. Cellulose acetate based biopolymeric mixed matrix membranes with various nanoparticles for environmental remediation-A comparative study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diainabo, K.J.; Mthombeni, N.H.; Motsa, M. Preparation and characterization of hybrids of cellulose acetate membranes blended with polysulfone and embedded with silica for Copper(II), Iron(II) and Zinc(II) removal from contaminated solutions. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3587–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelizz, H.A.; Taie, H.A.A.; Bakheit, A.H.; Mostafa, G.A.E.; Marzouk, M.; Rashid, H.; Al-Salahi, R. Investigation of 4-hydrazinobenzoic acid derivatives for their antioxidant activity: In vitro screening and DFT study. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 31993–32004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Abdel-Naby, A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Al-Shahrani, N. Graft copolymerization of Diallylamine onto starch for water treatment use characterization, removal of Cu (II) cations and antibacterial activity. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bai, Q.; Liang, T.; Bai, H.; Liu, X. Two-sided surface oxidized cellulose membranes modified with PEI: Preparation, characterization and application for dyes removal. Polymers 2017, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrivel, S.; Saraswathi, M.S.A.; Rana, D.; Nagendran, A. Fabrication of cellulose acetate nanocomposite membranes using 2D layered nanomaterials for macromolecular separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyati, S.; Aprilia, S.; Muchtar, S.; Syamsuddin, Y.; Rosnelly, C.M.; Bilad, M.R.; Samsuri, S.; Ismail, N.M. Fabrication of Polyvinylidene Difluoride Membrane with Enhanced Pore and Filtration Properties by Using Tannic Acid as an Additive. Polymers 2022, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndlwana, L.; Sikhwivhilu, K.; Moutloali, R.M.; Ngila, J.C. Heterogeneous functionalization of polyethersulfone: A new approach for pH-responsive microfiltration membranes with enhanced antifouling properties. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2020, 6, 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Naby, A.; Alabdullatif, B.A.; Aldulaijan, S.; Alqarni, Y. Synthesis and characterization of p-carboxy phenyl amino maleimide-g-cellulose acetate/ZrO2 nanocomposite membrane for water desalination. Water Reuse 2023, 13, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hou, J.; Ye, Y.; Mansouri, J.; Chen, V. Composite PVA/PVDF pervaporation membrane for concentrated brine desalination: Salt rejection, membrane fouling and defect control. Desalination 2017, 422, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.; Stalmach, U.; Kolshorn, H. Effective conjugation length and UV/vis spectra of oligomers. Acta Polym. 1997, 48, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Naby, A.S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Effect of crystallinity on the thermal and photo-stabilization of PVC/poly (AN-DAA) blend. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2020, 25, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Naby, A.S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Chemical modification of cellulose acetate by diallylamine. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-naby, A.S.I. Method for Removing Metal Ions from Water with a Nanocomposite Film. U.S. Patent 2023312379-A1, 23 August 2021. [Google Scholar]

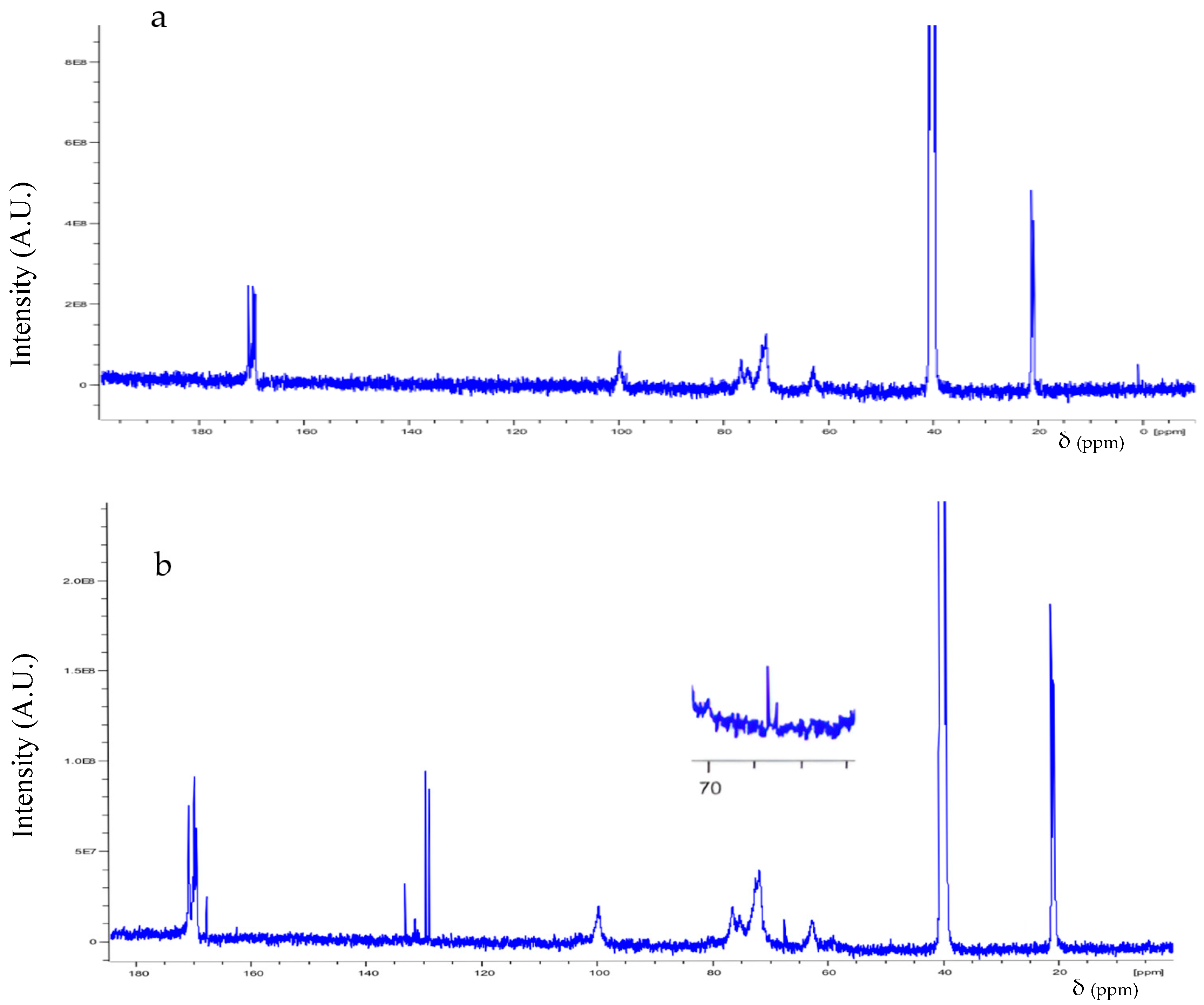


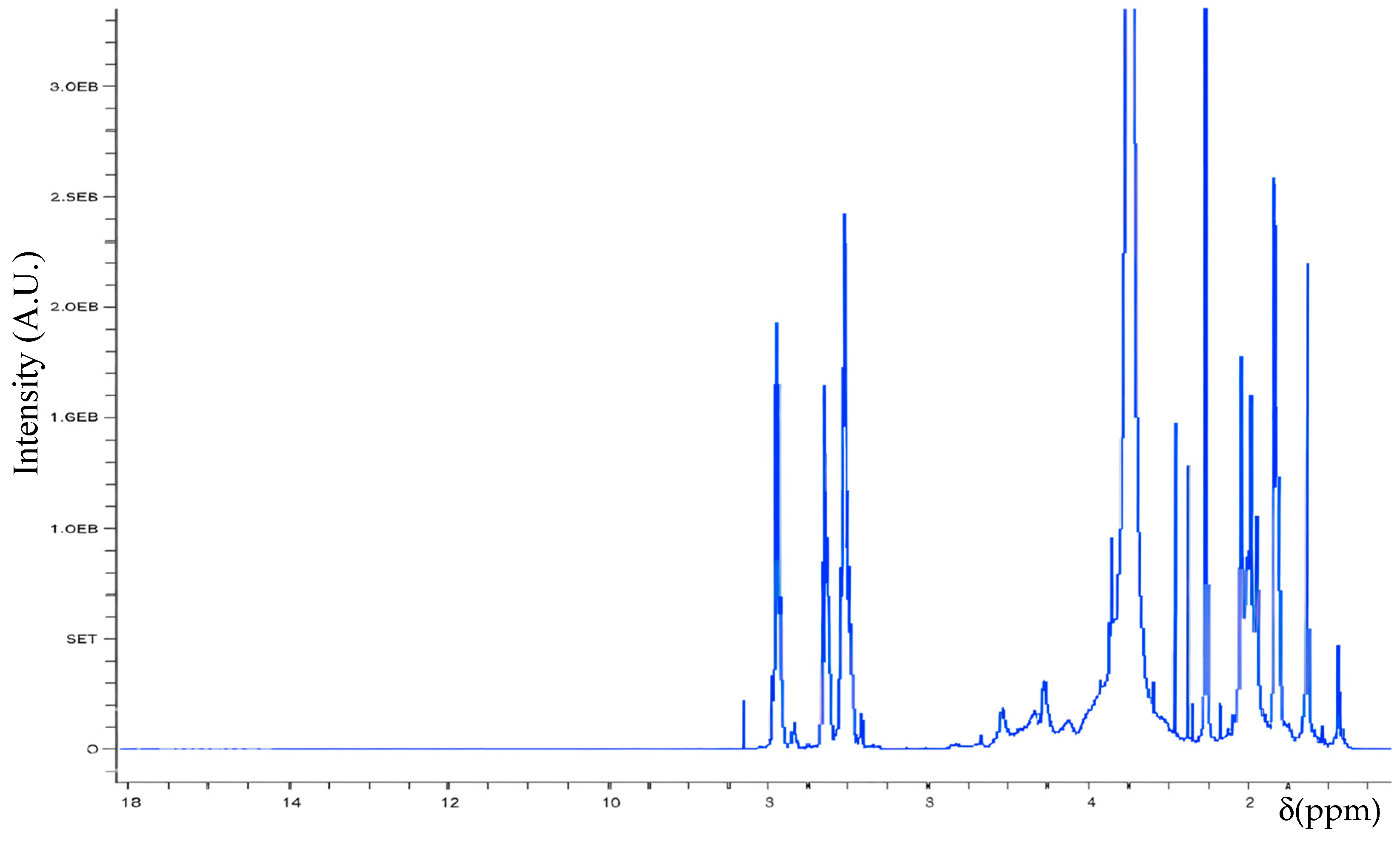
| Structure | H Atom | δ (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
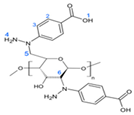 | 1 | 10.3 |
| 2 | 7.9 | |
| 3 | 7.4 | |
| 4 | 4.3 | |
| 5 | 3.3 | |
| 6 | 3.1 |
| Structure | C atom | δ (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
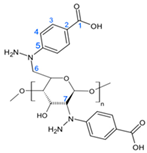 | 1 | 168 |
| 2 | 130 | |
| 3 | 131.5 | |
| 4 | 129 | |
| 5 | 133.5 | |
| 6 | 67 | |
| 7 | 67.5 |
| Membrane | Contact Angle | Image |
|---|---|---|
| PSF | 94° |  |
| CA | 81° |  |
| CA-HBA/PSF (5:95) | 87° |  |
| CA-HBA/PSF (10:90) | 78° |  |
| CA-HBA/PSF (15:85) | 69° |  |
| Membrane Composition | Water Flux (L/m2.h) |
|---|---|
| 85% CA-HBA | 30.2 |
| 90% CA-HBA | 19.6 |
| 95% CA-HBA | 9.8 |
| 100% PSF | 0.1 |
| Membrane Composition | T° (°C) | Weight Loss% at 500 °C |
|---|---|---|
| 100% CA-HBA | 330 | 87% |
| 15% CA-HBA | 500 | 4% |
| 10% CA-HBA | 509 | 0% |
| 5% CA-HBA | 510 | 0% |
| 100% PSF | 510 | 0% |
| Membrane Composition | Porosity % | Pore Size (µm) | Water Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA-HBA | 72 | 0.192 | 86.8 |
| PSF 85% | 58 | 0.139 | 70.8 |
| PSF 90% | 53 | 0.137 | 66.7 |
| PSF 95% | 50 | 0.071 | 50 |
| PSF | 32 | 0.047 | 54 |
| Membrane | Removal % |
|---|---|
| PSF | 8.2 |
| CA-HBA/PSF 95% | 52.5 |
| CA-HBA/PSF 90% | 66.6 |
| CA-HBA/PSF 85% | 89.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsulaiman, L.; Abdel-Naby, A.S.; Alharthi, S.; ALabdullatif, B.; Al-Dossary, A.; Al-Mughrabi, W.; Alqarni, Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate—HBA/Poly Sulfone Blend for Water Treatment Applications. Membranes 2025, 15, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15020038
Alsulaiman L, Abdel-Naby AS, Alharthi S, ALabdullatif B, Al-Dossary A, Al-Mughrabi W, Alqarni Y. Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate—HBA/Poly Sulfone Blend for Water Treatment Applications. Membranes. 2025; 15(2):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15020038
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsulaiman, Lamai, Abir S. Abdel-Naby, Salha Alharthi, Bushra ALabdullatif, Abeer Al-Dossary, Wafa Al-Mughrabi, and Yanallah Alqarni. 2025. "Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate—HBA/Poly Sulfone Blend for Water Treatment Applications" Membranes 15, no. 2: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15020038
APA StyleAlsulaiman, L., Abdel-Naby, A. S., Alharthi, S., ALabdullatif, B., Al-Dossary, A., Al-Mughrabi, W., & Alqarni, Y. (2025). Synthesis and Characterization of Cellulose Acetate—HBA/Poly Sulfone Blend for Water Treatment Applications. Membranes, 15(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15020038







