Reverse Solute Diffusion Enhances Sludge Dewatering in Dead-End Forward Osmosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
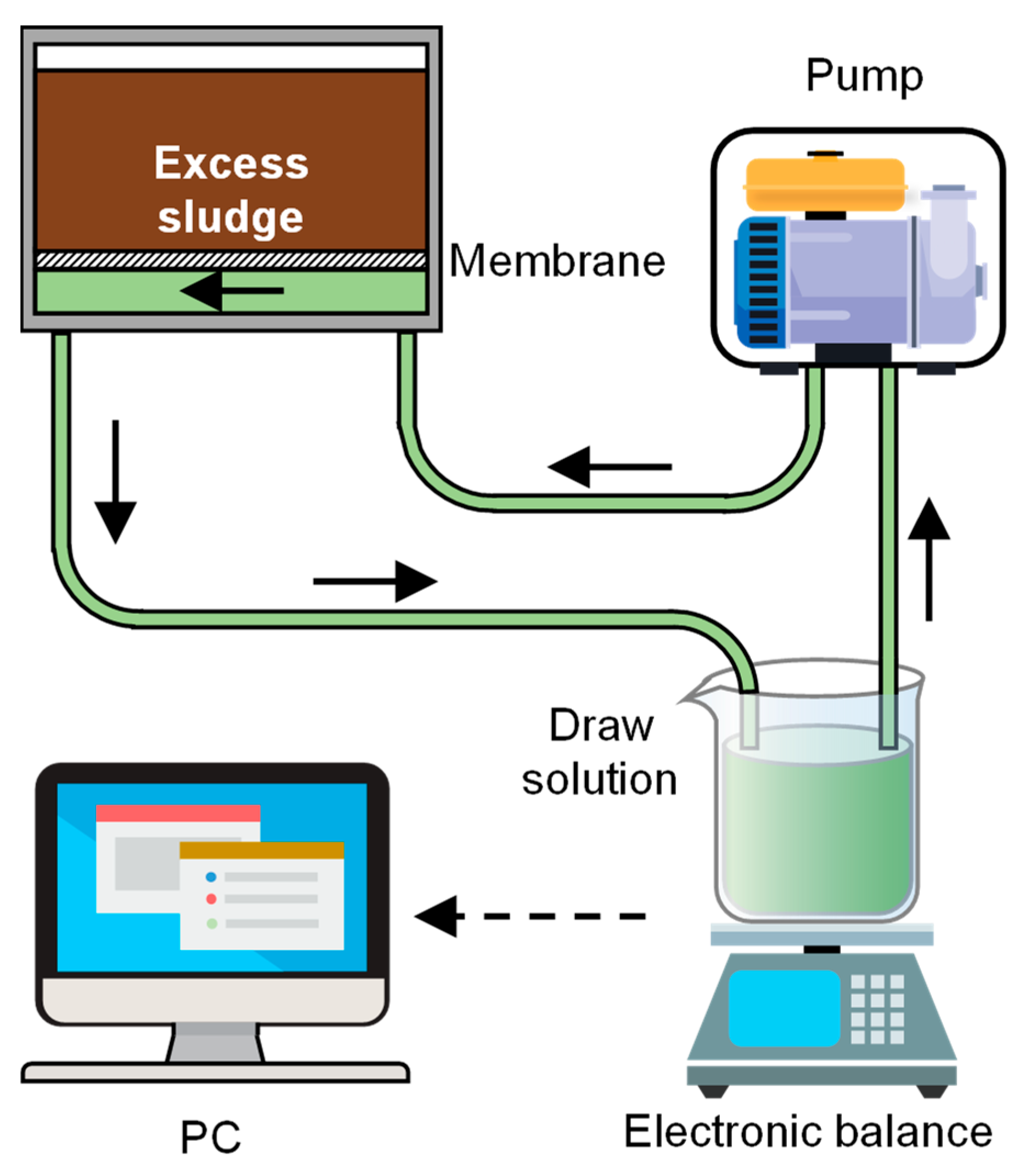
2.2. Experimental Equipment and Operating Conditions
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Measurement of Moisture and Metal Ions in Filter Cake
2.3.2. Physicochemical Properties of Sludge
3. Results and Discussion
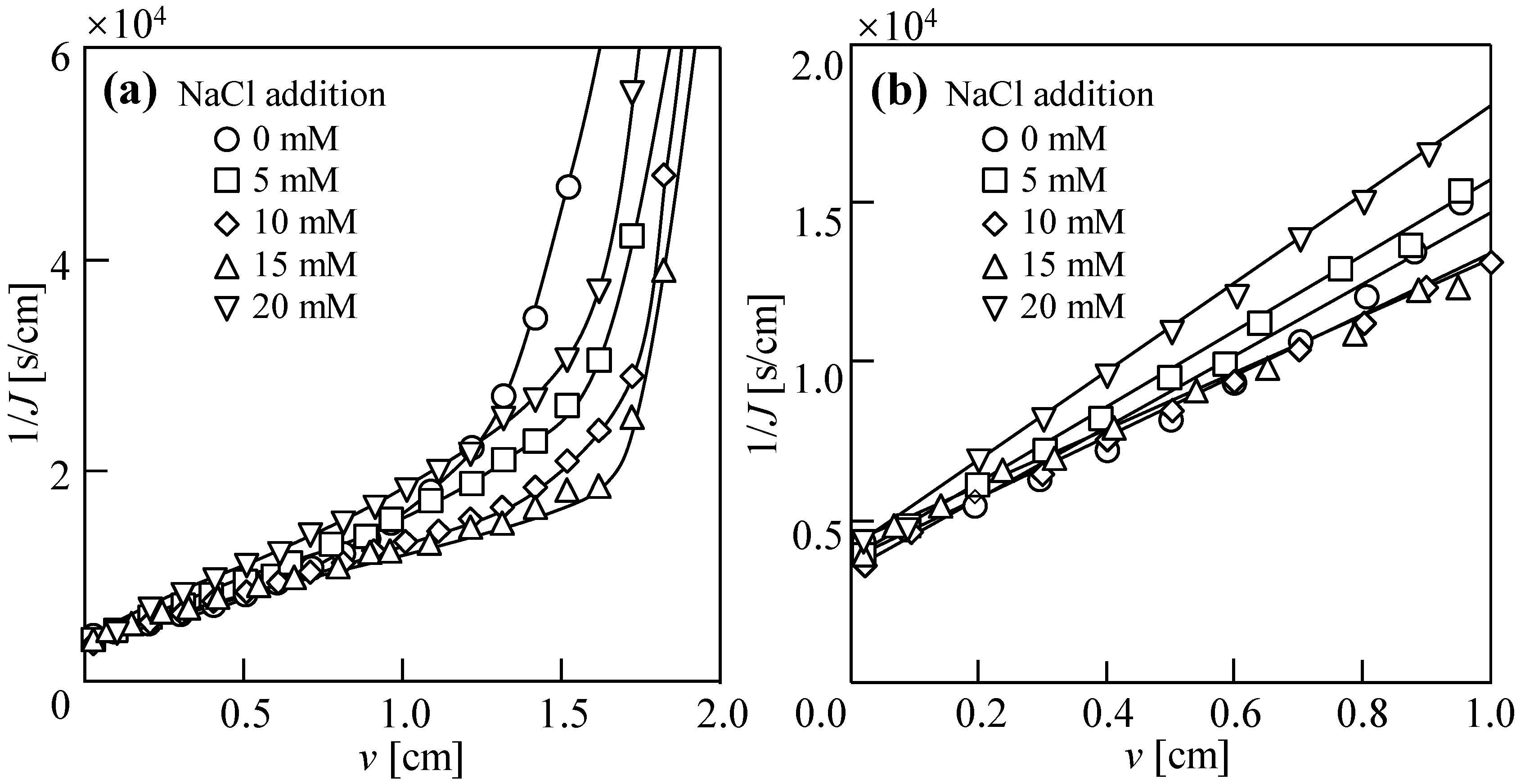
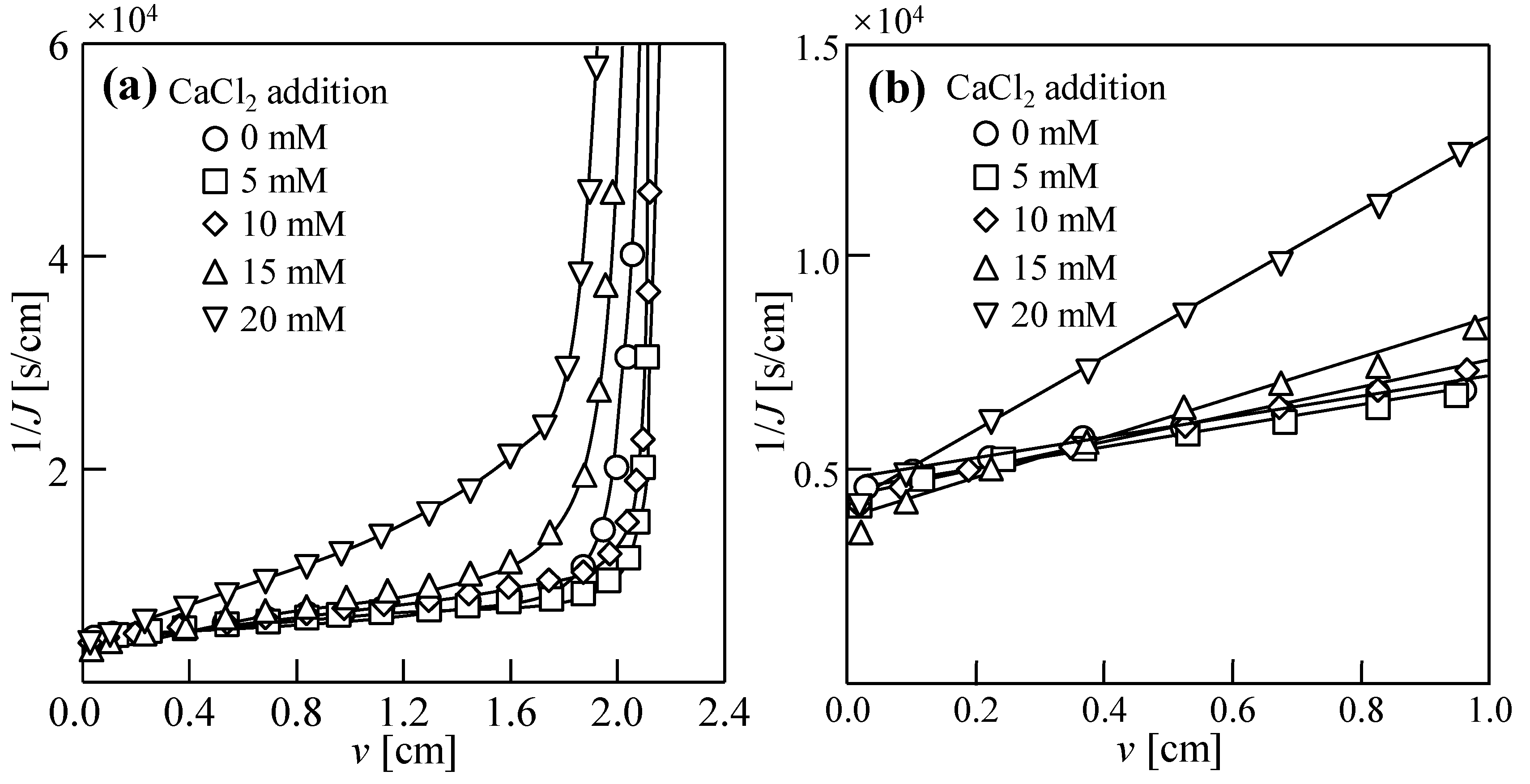
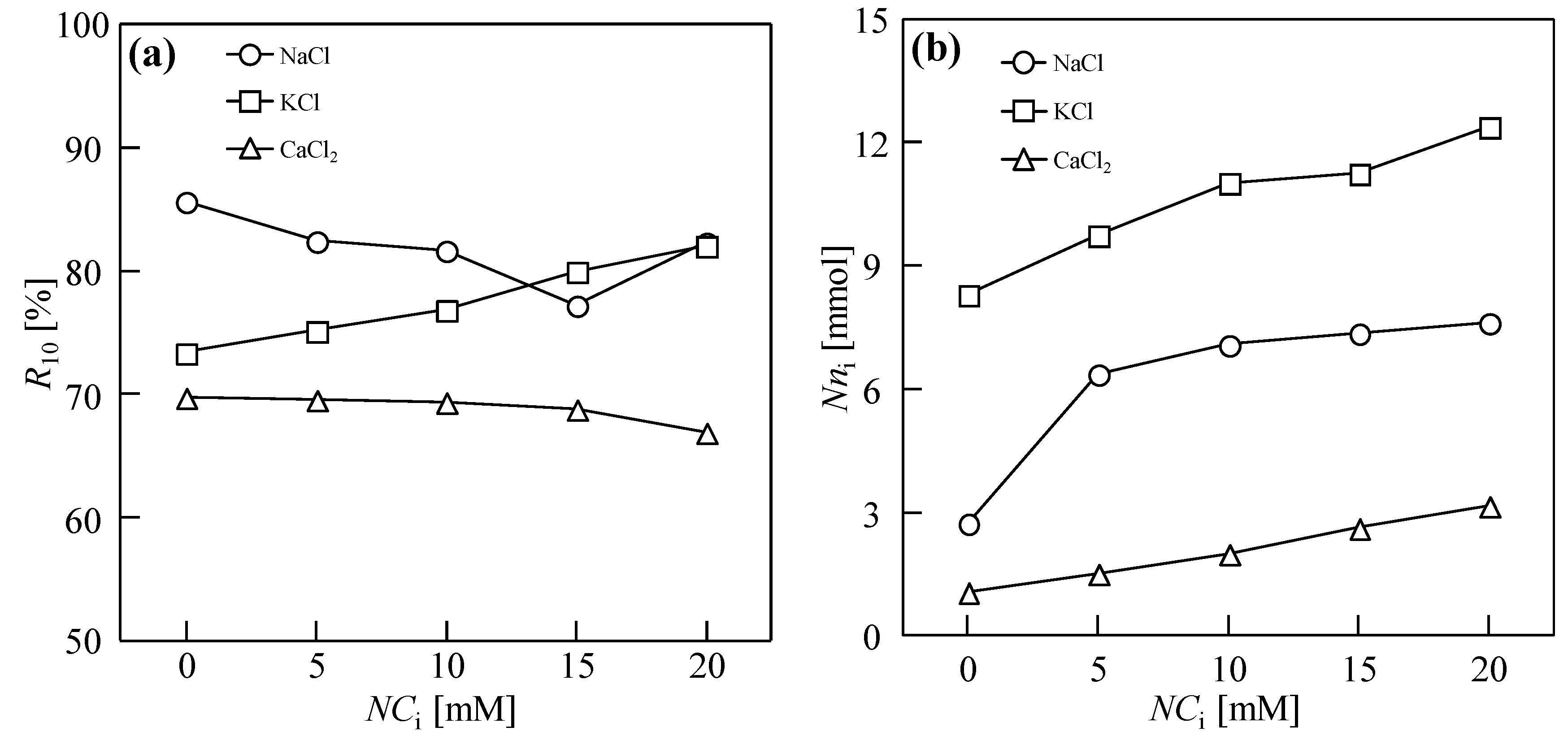
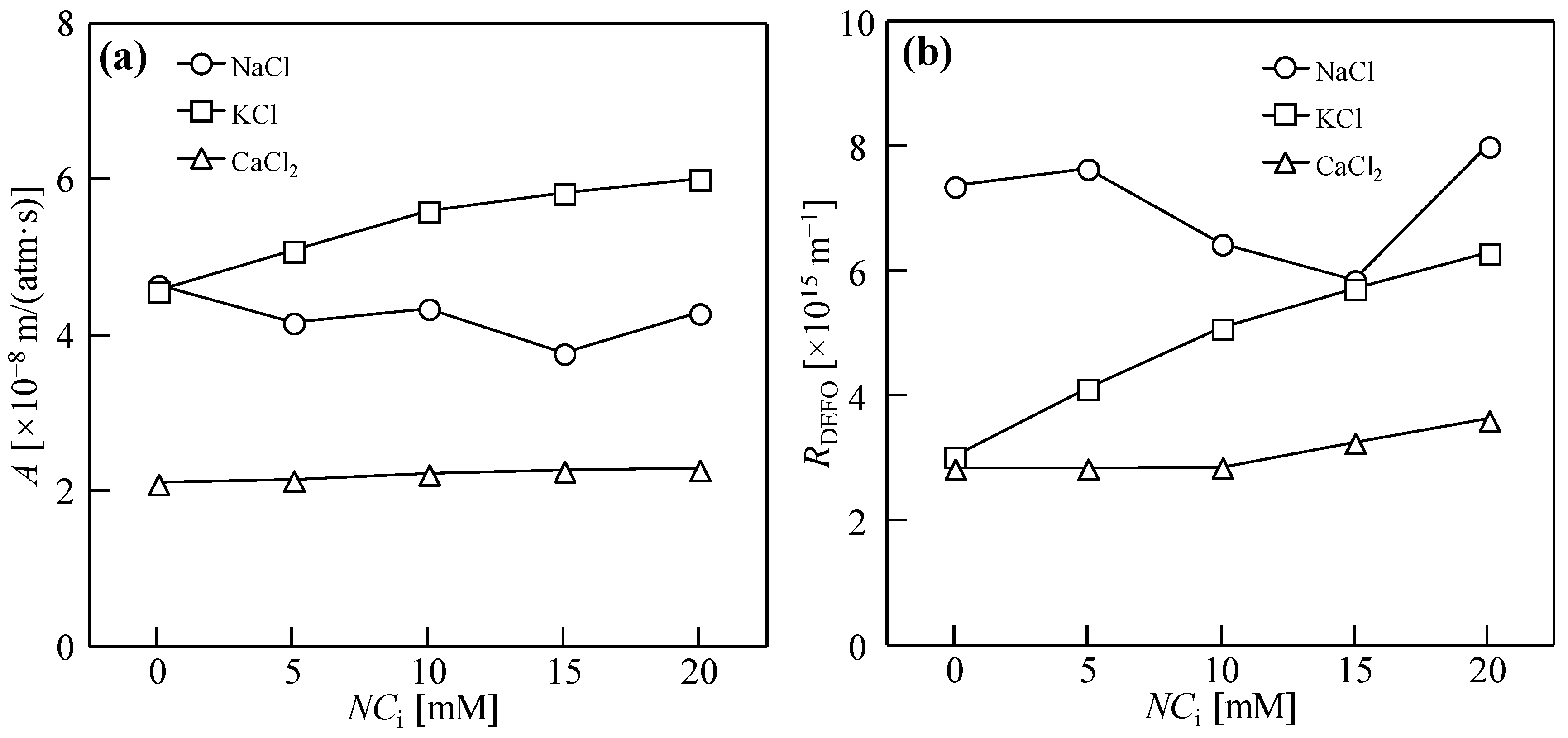
3.1. Dewatering Behaviors of Sludge with Single Salt
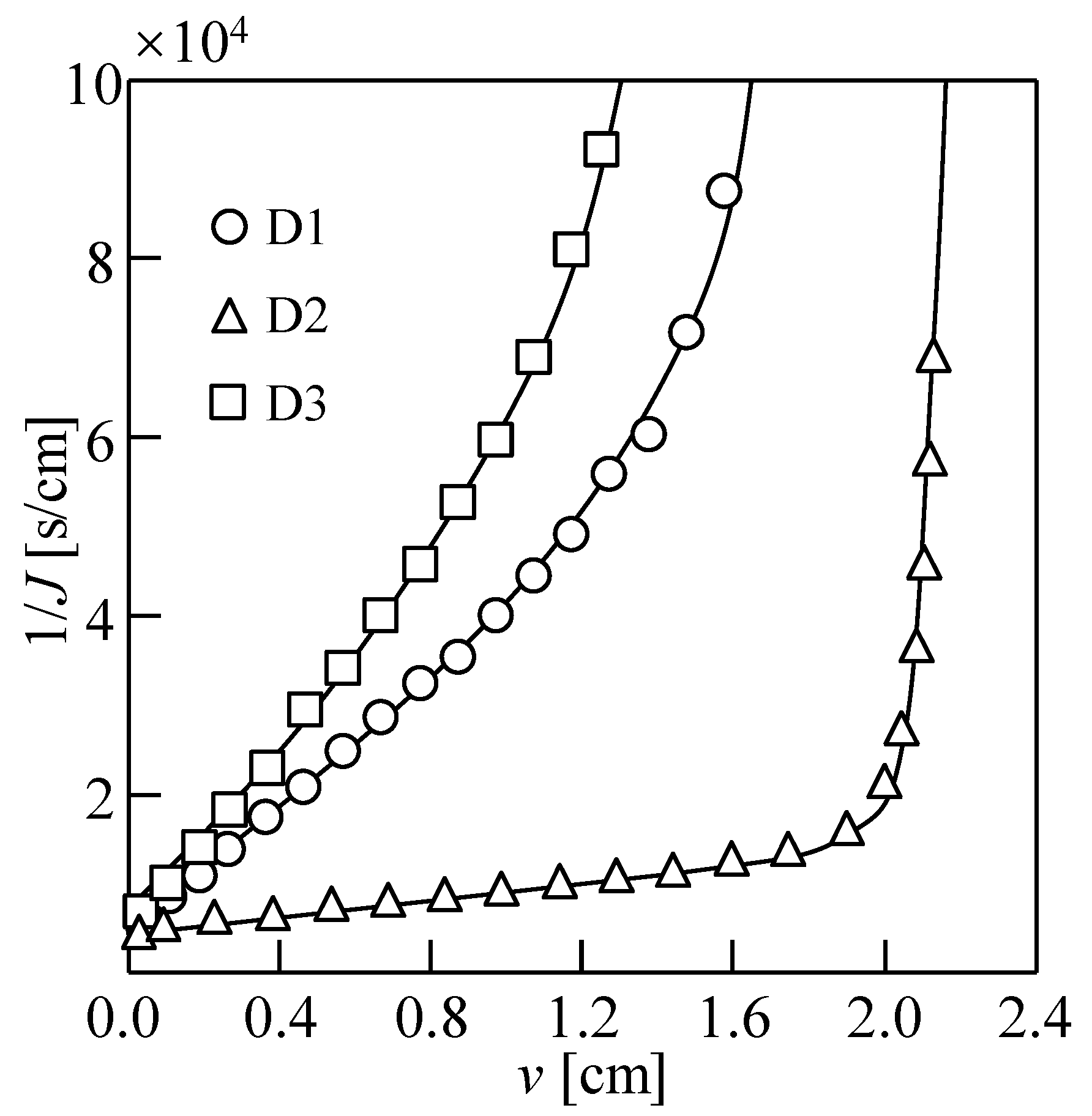
3.2. Water Permeability Coefficient and Osmosis Resistance in DEFO
3.3. Properties of Sludge Dewatering in DEFO with Binary Draw Solutes
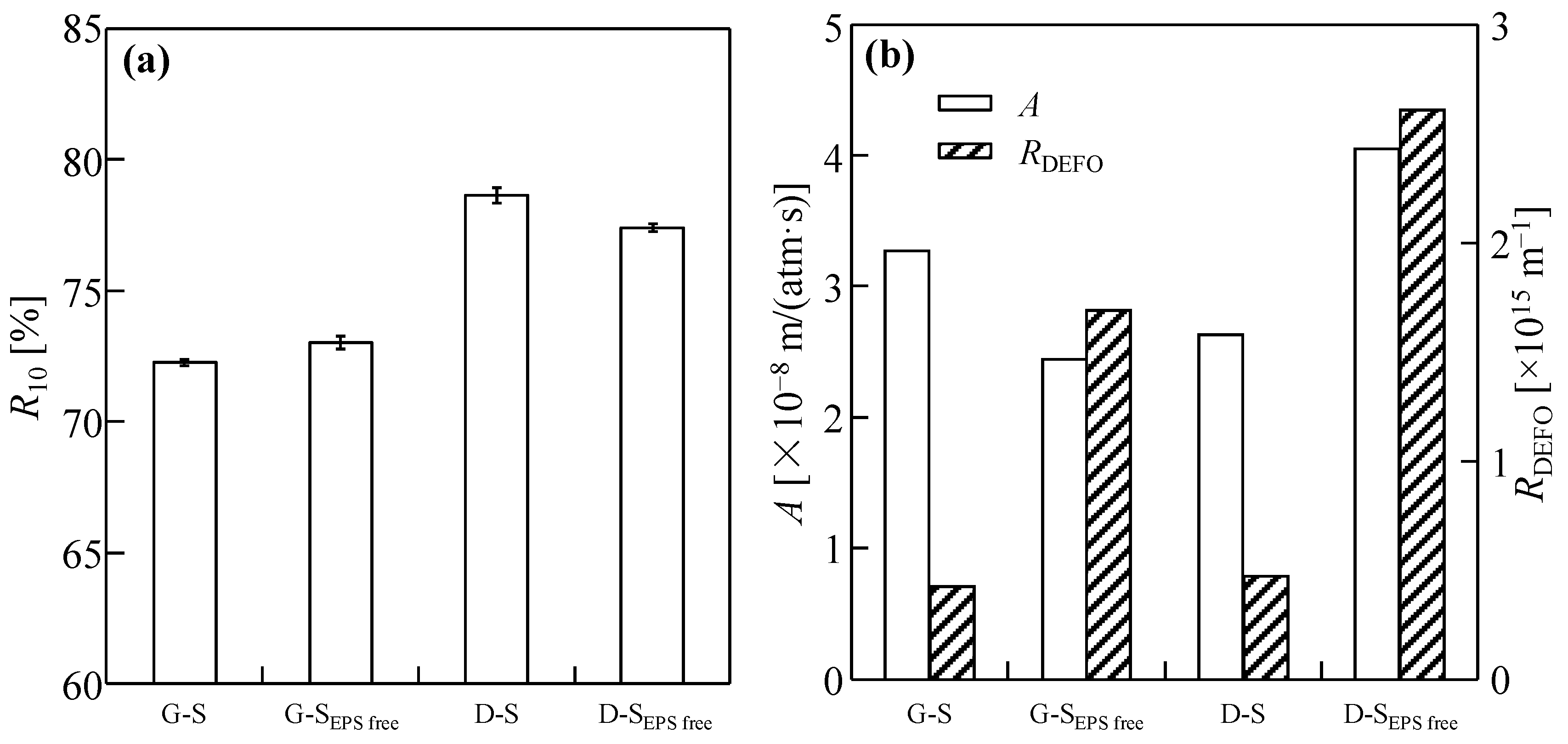
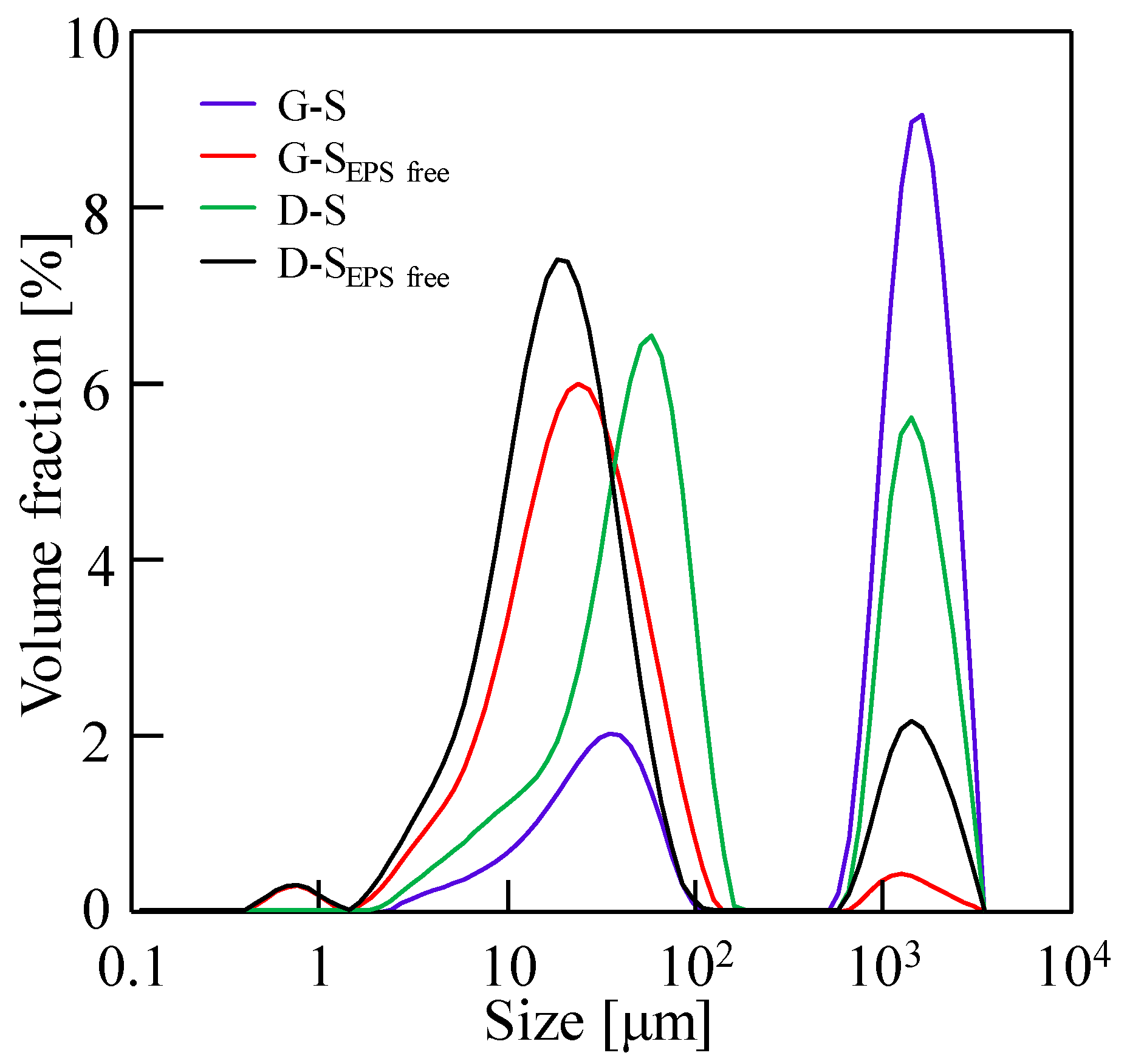
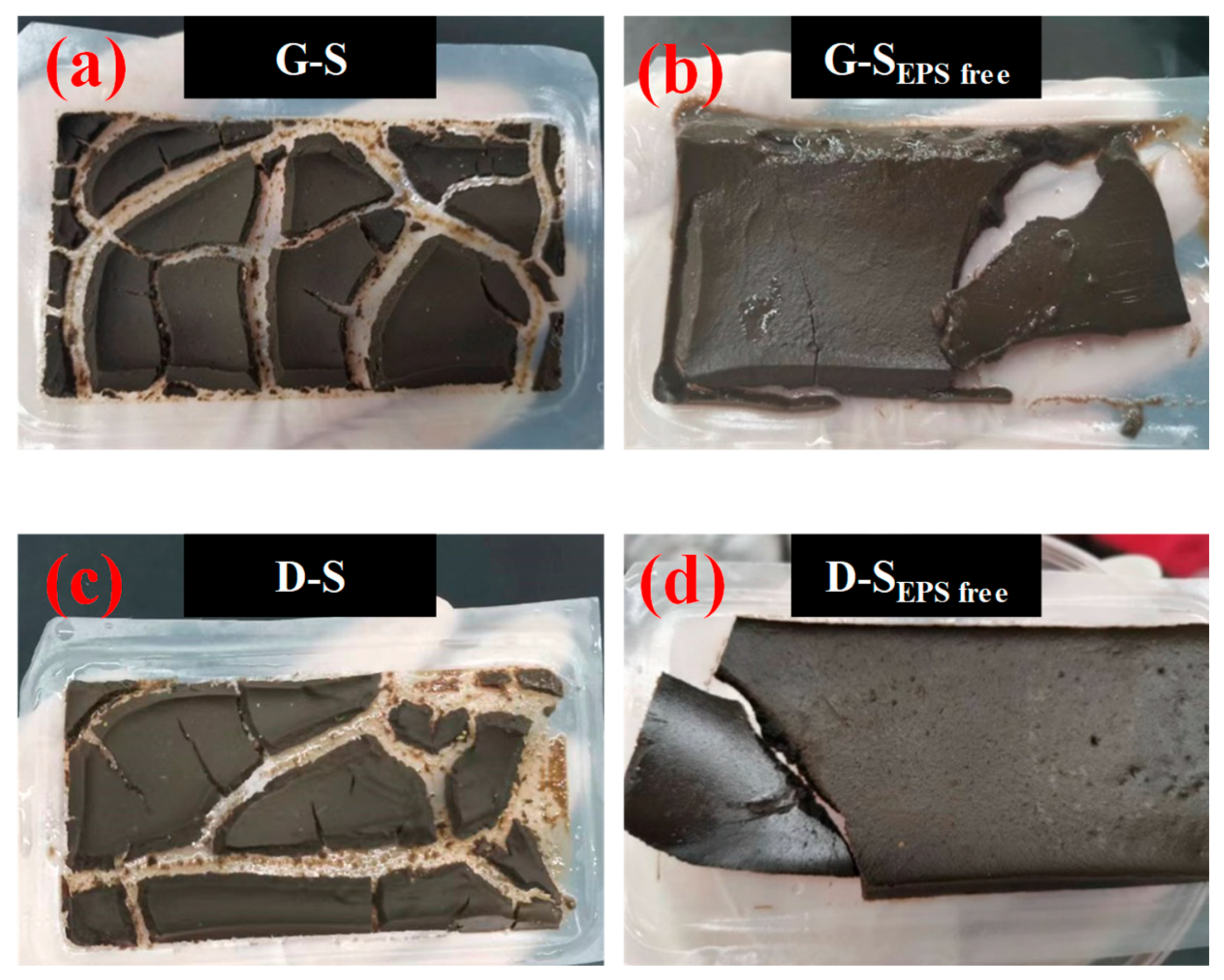
3.4. Effect of EPSs on Dewatering Behaviors of Sludge
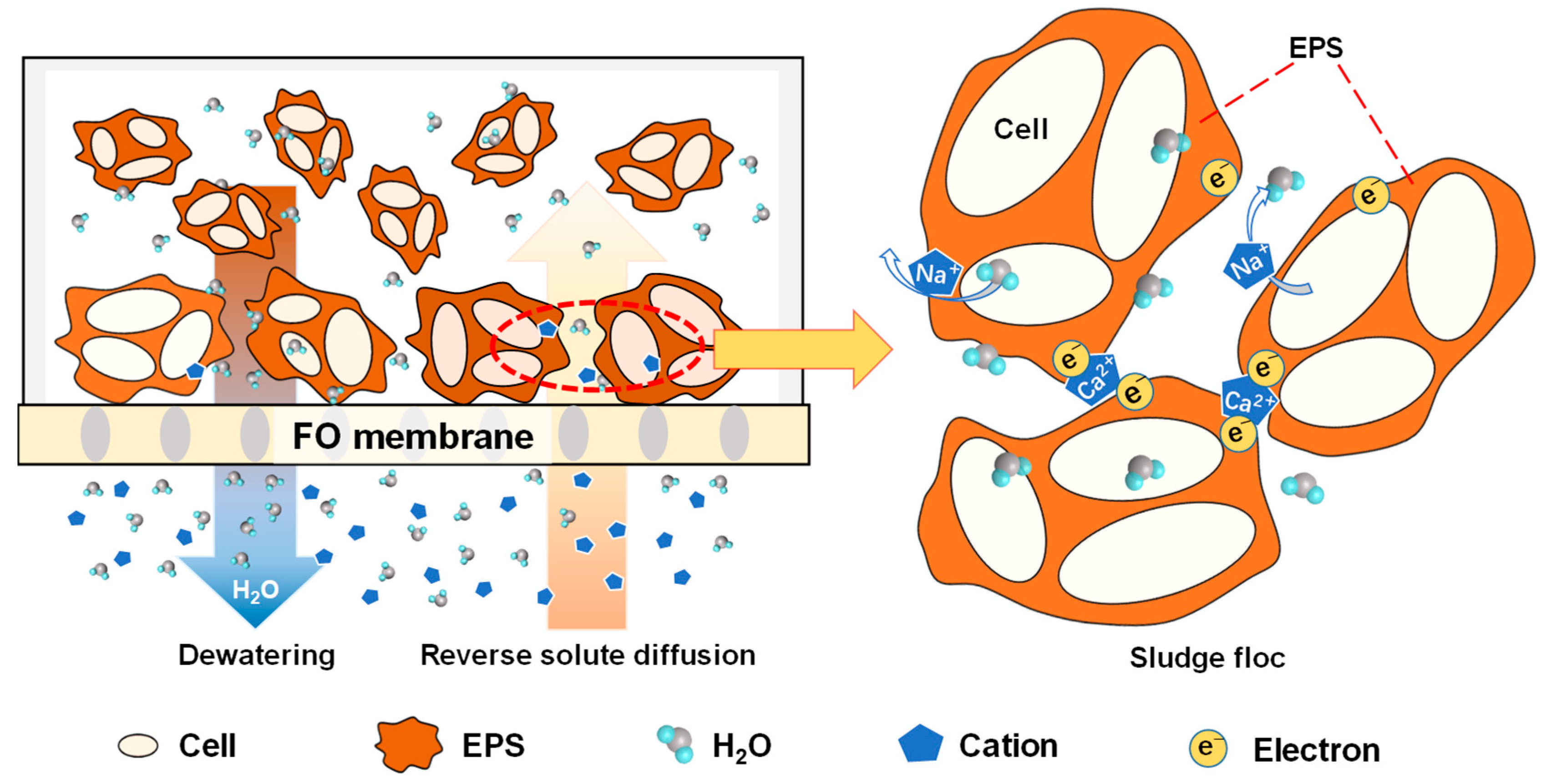
3.5. Mechanisms of DEFO Sludge Dewatering Enhancement
3.6. Effectivity of Practical Draw Solutions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, D.-Q.; Liu, H.; Tian, F.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Hao, X.-D.; Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N. Dead-end forward osmosis as an alternative for deep sludge dewatering: Evaluation method and characteristics analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, G.; Hu, W. Thoughts on the development direction of sludge treatment and resource recovery under the background of carbon neutrality. Water Wastewater Eng. 2021, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Li, A.H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, D. Safe disposal and resource recovery of urban sewage sludge in China. Eng. Sci. 2022, 24, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G.; Callegari, A. Energy and resources recovery from excess sewage sludge: A holistic analysis of opportunities and strategies. RCR Adv. 2023, 19, 200184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.-Q.; Song, X.; Fang, X.-M.; Yang, W.-Y.; Hao, X.-D.; Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N. Membrane filtration-based recovery of extracellular polymer substances from excess sludge and analysis of their heavy metal ion adsorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladejo, J.; Shi, K.; Luo, X.; Yang, G.; Wu, T. A review of sludge-to-energy recovery methods. Energies 2018, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-B.; Cayetano, R.D.A.; Park, J.; Jo, Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Pandey, A.; Kim, S.-H. Impact of thermal pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of dewatered sludge from municipal and industrial wastewaters and its economic feasibility. Energy 2022, 254, 124345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Wilén, B.-M.; Lant, P. Impacts of morphological, physical and chemical properties of sludge flocs on dewaterability of activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 98, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, A. Hydrothermal treatment coupled with mechanical expression at increased temperature for excess sludge dewatering: The dewatering performance and the characteristics of products. Water Res. 2015, 68, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, J.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chenxi, S. Current situation and prospect of sludge mechanical dewatering technology. Environ. Eng. 2016, 34, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yuan, S.; Chen, S.; Ci, H.; Dai, X.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Dong, B. Life-cycle assessment of two sewage sludge-to-energy systems based on different sewage sludge characteristics: Energy balance and greenhouse gas-emission footprint analysis. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Enhanced technology based for sewage sludge deep dewatering: A critical review. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Cui, G.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y. Effects of voltage and pressure on sludge electro-dewatering process and the dewatering mechanisms investigation. Env. Res. 2022, 212, 113490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Yang, C.-Z.; Pu, W.-H.; Yang, J.-K.; Shi, Y.-F.; Wang, J.; Bai, J.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Jiang, G.-S.; Li, C.-Y. The stability of aerobic granular sludge treating municipal sludge deep dewatering filtrate in a bench scale sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhu, N. Progress of improving waste activated sludge dewaterability: Influence factors, conditioning technologies and implications and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 912, 168605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Wydro, U.; Serra-Majem, L.; Butarewicz, A.; Wołejko, E. Studies on the cytotoxicity of filtrates obtained from sewage sludge from the municipal wastewater treatment plant. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 186, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Li, M. Adsorption and regeneration characteristics of phosphorus from sludge dewatering filtrate by magnetic anion exchange resin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34233–34247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Qiu, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, R.; Hernandez, B.V.; Ji, C.; Liu, G.; Zhao, X.; Ge, L. Efficient organic enrichment from sludge filtrate via a forward osmosis membrane process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bień, B.; Bień, J.D. Analysis of reject water formed in the mechanical dewatering process of digested sludge conditioned by physical and chemical methods. Energies 2022, 15, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Bian, S.; Su, X.; Xiao, K.; Liang, S.; Yuan, S. Evaluation of sludge deep-dewatering filtrate recirculation to wastewater treatment plant by toxicity detection with microbial fuel cells. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.-Q.; Jin, Y.; Liu, H.; Lei, S.-C.; Song, Y.-X.; Han, J.-L.; Hao, X.-D.; Ma, M.-G.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, R. Concentration properties of biopolymers via dead-end forward osmosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, H.; Meng, F. A unified thermodynamic fouling mechanism based on forward osmosis membrane unique properties: An asymmetric structure and reverse solute diffusion. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Qin, M.; He, Z. Tackle reverse solute flux in forward osmosis towards sustainable water recovery: Reduction and perspectives. Water Res. 2019, 149, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Wu, X.; Fan, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Xie, Z. Effect of different draw solutions on concentration polarization in a forward osmosis process: Theoretical modeling and experimental validation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 3672–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferby, M.; Zou, S.; He, Z. Reduction of reverse solute flux induced solute buildup in the feed solution of forward osmosis. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. 2020, 6, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; She, Q.; Yan, X.; Tang, C.Y. Effect of reverse solute diffusion on scaling in forward osmosis: A new control strategy by tailoring draw solution chemistry. Desalination 2017, 401, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; He, Z. Electrolysis-assisted recovery of reverse-fluxed solutes in forward osmosis. Desalination 2021, 520, 115346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, Z. Smart utilisation of reverse solute diffusion in forward osmosis for water treatment: A mini review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, C.; Lin, H. Novel molecular level insights into forward osmosis membrane fouling affected by reverse diffusion of draw solutions based on thermodynamic mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Zhang, H.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M. Synergistic fouling behaviors and thermodynamic mechanisms of proteins and polysaccharides in forward osmosis: The unique role of reverse solute diffusion. Desalination 2022, 536, 115850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Ngo, H.H.; Nan, J.; Li, G.; Ma, J.; He, X.; Ding, A. Deep mechanism of enhanced dewaterability of residual sludge by Na+: Comprehensive analyses of intermolecular forces, hydrophilicity and water-holding capacity of EPS. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Molina, V.; Esplugas, S.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. Ultrafiltration of aqueous solutions containing dextran. Desalination 2006, 188, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Elimelech, M. Relating organic fouling of reverse osmosis membranes to intermolecular adhesion forces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoufidou, K.; Yiantsios, S.; Karabelas, A. Experimental study of ultrafiltration membrane fouling by sodium alginate and flux recovery by backwashing. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zou, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Li, B.; Tang, X.; Xiao, X. Metal ions-induced structural modification of extracellular polymers: Impact of the valence on sludge biodegradability and dewaterability. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 174, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.-Q.; Sun, X.-Z.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Ji, Y.-T.; Yang, X.-X.; Hao, X.-D. News on alginate recovery by forward osmosis: Reverse solute diffusion is useful. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.-Q.; Tang, K.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Chang, C.; Han, J.-L.; Tian, F.; Hao, X.-D. Calcium alginate production through forward osmosis with reverse solute diffusion and mechanism analysis. Membranes 2023, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Gao, T.; Teng, J. Impacts of applied voltage on forward osmosis process harvesting microalgae: Filtration behaviors and lipid extraction efficiency. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekre, K.M.; Tiburcio, D.; Ronen, A.; Suri, R.; Andaluri, G.; Yuan, H. Electrically charged forward osmosis: Promoting reverse salt flux to enhance water recovery and struvite precipitation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 186, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wen, X.; Huang, X. Feasibility of applying forward osmosis to the simultaneous thickening, digestion, and direct dewatering of waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.-Q.; Hao, X.-D.; Wang, Z.; Song, X.; Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N. Membrane recovery of alginate in an aqueous solution by the addition of calcium ions: Analyses of resistance reduction and fouling mechanism. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 535, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.-Q.; Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N. Properties of filter cake formed during dead-end microfiltration of O/W emulsion. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2013, 46, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouaux, E.; MacKinnon, R. Principles of selective ion transport in channels and pumps. Science 2005, 310, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morth, J.P.; Pedersen, B.P.; Toustrup-Jensen, M.S.; Sørensen, T.L.-M.; Petersen, J.; Andersen, J.P.; Vilsen, B.; Nissen, P. Crystal structure of the sodium–potassium pump. Nature 2007, 450, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevere, A.; Guibaud, G.; Van Hullebusch, E.; Boughzala, W.; Lens, P. Effect of Na+ and Ca2+ on the aggregation properties of sieved anaerobic granular sludge. Colloids Surf. A 2007, 306, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobeck, D.C.; Higgins, M.J. Examination of three theories for mechanisms of cation-induced bioflocculation. Water Res. 2002, 36, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Critical review on dewatering of sewage sludge: Influential mechanism, conditioning technologies and implications to sludge re-utilizations. Water Res. 2020, 180, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, P.; Zhang, D.; Chen, G.; Zeng, S.; He, Q. Population balance modeling of activated sludge flocculation: Investigating the influence of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) content and zeta potential on flocculation dynamics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematzadeh, M.; Samimi, A.; Mohebbi-Kalhori, D.; Shokrollahzadeh, S.; Bide, Y. Forward osmosis dewatering of seawater and pesticide contaminated effluents using the commercial fertilizers and zinc-nitrate blend draw solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sludge Sources | pH | Zeta Potential [eV] | Average Particle Size [µm] | Viscosity [mPa·s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G-S | 8.0 | −19.7 | 1194.4 | 10.3 |
| G-SEPS free | 8.3 | −26.2 | 73.5 | 11.6 |
| D-S | 7.1 | −22.4 | 583.0 | 12.2 |
| D-SEPS free | 8.2 | −24.3 | 236.0 | 15.6 |
| Draw Solution | NaCl [mg/L] | CaCl2 [mg/L] | MgCl2·6H2O [mg/L] | NaHCO3 [mg/L] | Na2SO4 [mg/L] | R [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 25,053 | 1215 | 11,946 | 192 | 3168 | 90.3 |
| D2 | 35,790 | 1735 | 17,066 | 274 | 4526 | 65.7 |
| D3 | – | – | – | – | – | 88.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, D.-Q.; Lei, S.-C.; Liu, H.; Jin, Y.; Wu, Y.-F.; Cui, Y.; Wu, R. Reverse Solute Diffusion Enhances Sludge Dewatering in Dead-End Forward Osmosis. Membranes 2024, 14, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090196
Cao D-Q, Lei S-C, Liu H, Jin Y, Wu Y-F, Cui Y, Wu R. Reverse Solute Diffusion Enhances Sludge Dewatering in Dead-End Forward Osmosis. Membranes. 2024; 14(9):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090196
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Da-Qi, Shi-Cheng Lei, Hui Liu, Yan Jin, Yun-Feng Wu, Yuehua Cui, and Rongling Wu. 2024. "Reverse Solute Diffusion Enhances Sludge Dewatering in Dead-End Forward Osmosis" Membranes 14, no. 9: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090196
APA StyleCao, D.-Q., Lei, S.-C., Liu, H., Jin, Y., Wu, Y.-F., Cui, Y., & Wu, R. (2024). Reverse Solute Diffusion Enhances Sludge Dewatering in Dead-End Forward Osmosis. Membranes, 14(9), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090196








