Application of Online Flow Cytometry for Early Biofouling Detection in Reverse Osmosis Membrane Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Operating Conditions
2.4. Fouling Monitoring
2.4.1. Feed Channel Pressure Drop
2.4.2. Bacterial Cell Concentration in Water Using Online Flow Cytometry
2.5. Biomass Quantification on the Membrane
2.5.1. Total Bacterial Cell Count
2.5.2. Adenosine Triphosphate
3. Results
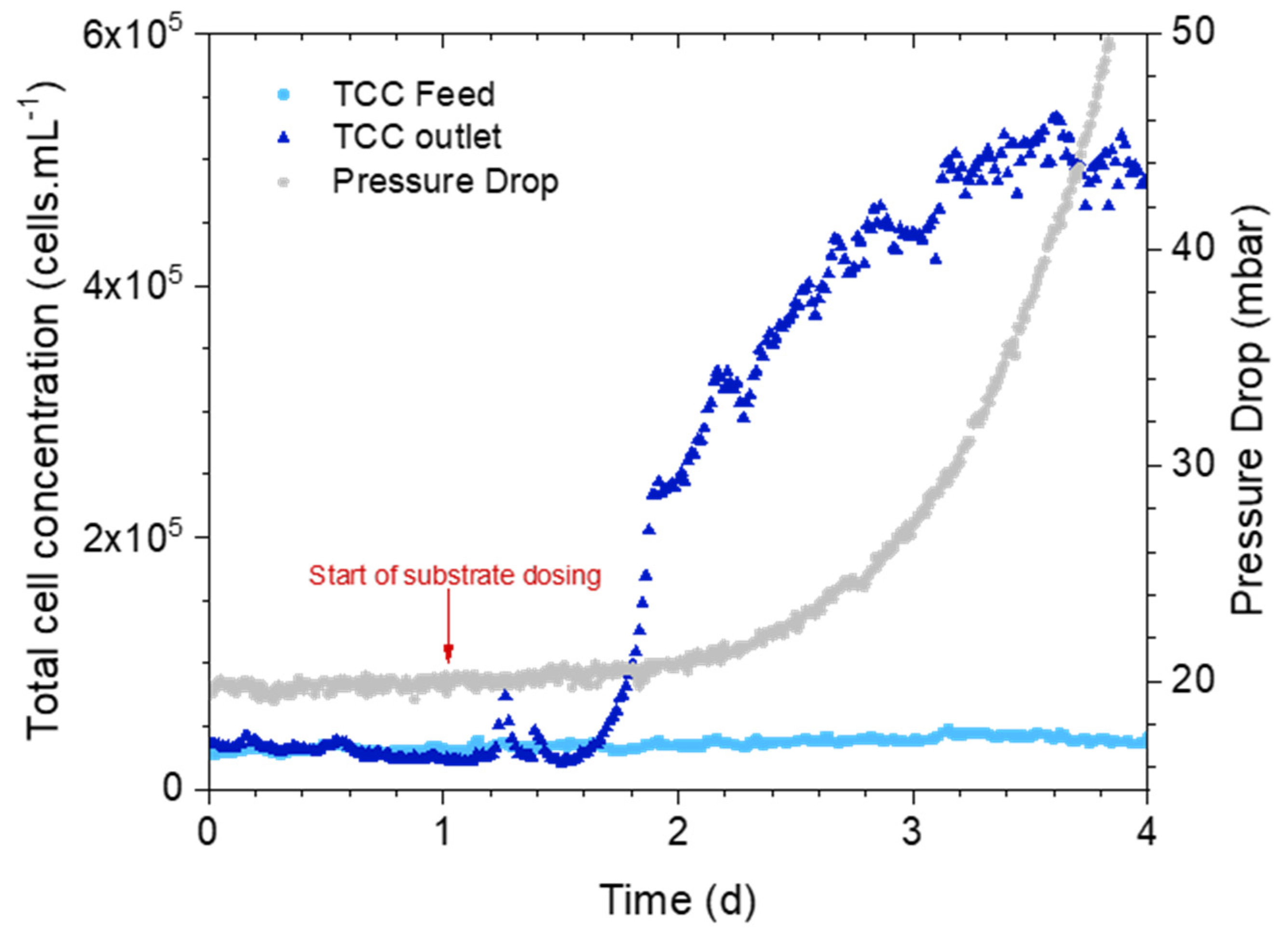
3.1. Can an Increase in Bacterial Cell Concentration in the Outlet Water Be Observed before the Pressure Drop Increases?
3.1.1. Online Measurements: Pressure Drop Versus Bacterial Cell Concentration
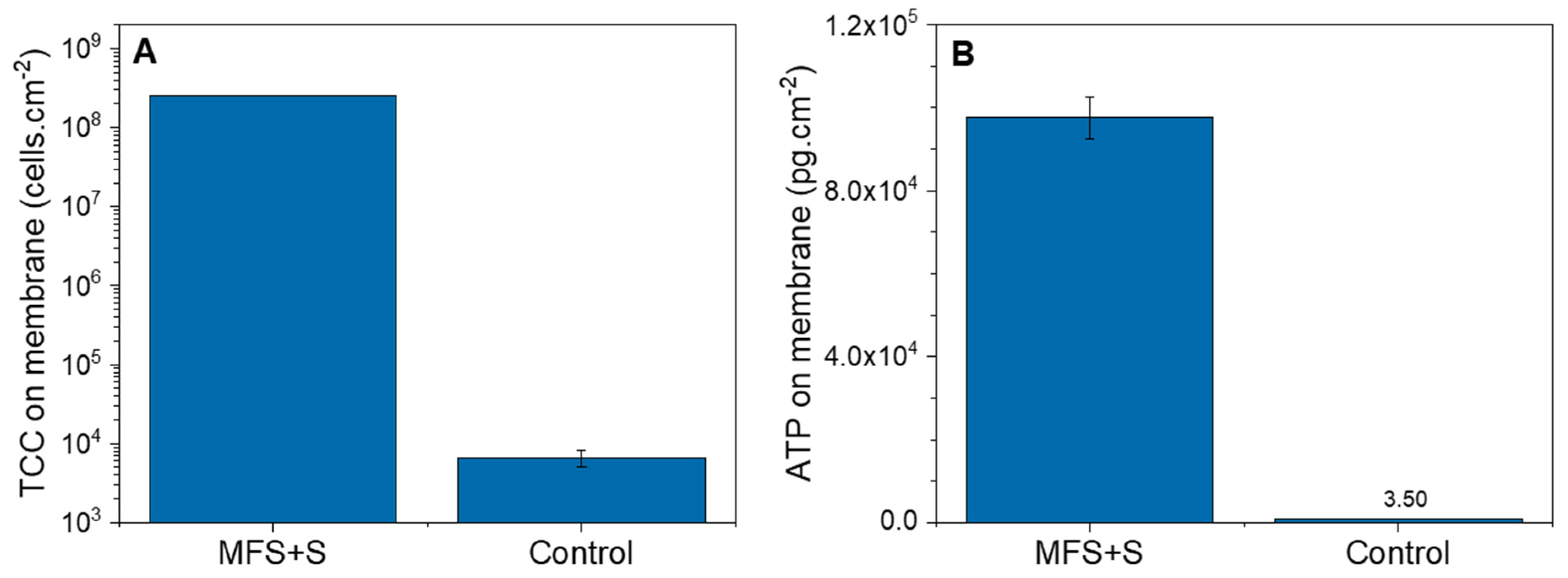
3.1.2. Biofilm Characterization
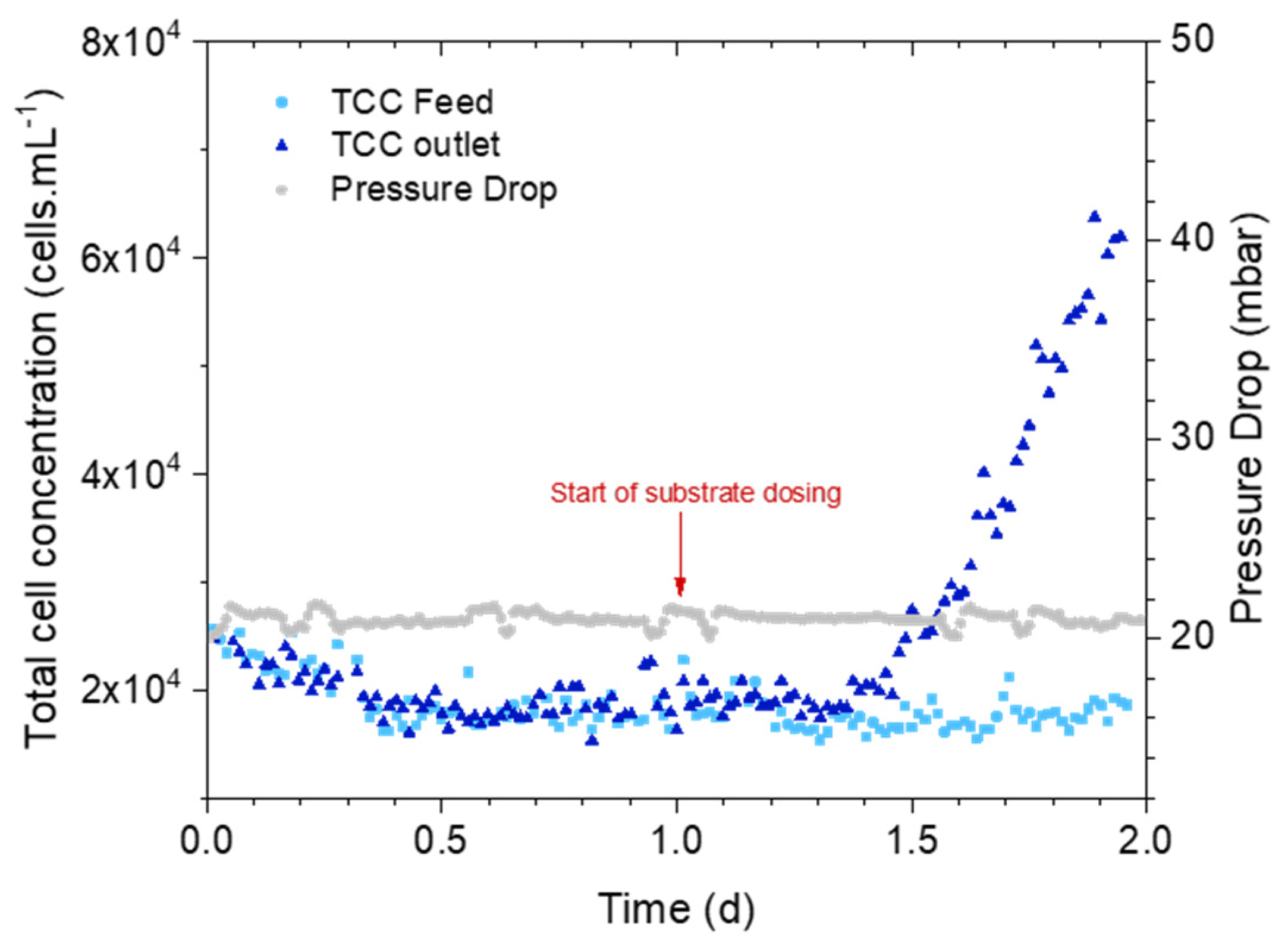
3.2. How Early Is the Cell Concentration Increase Detected?
3.2.1. Online Measurements: Pressure Drop Versus Bacterial Cell Concentration
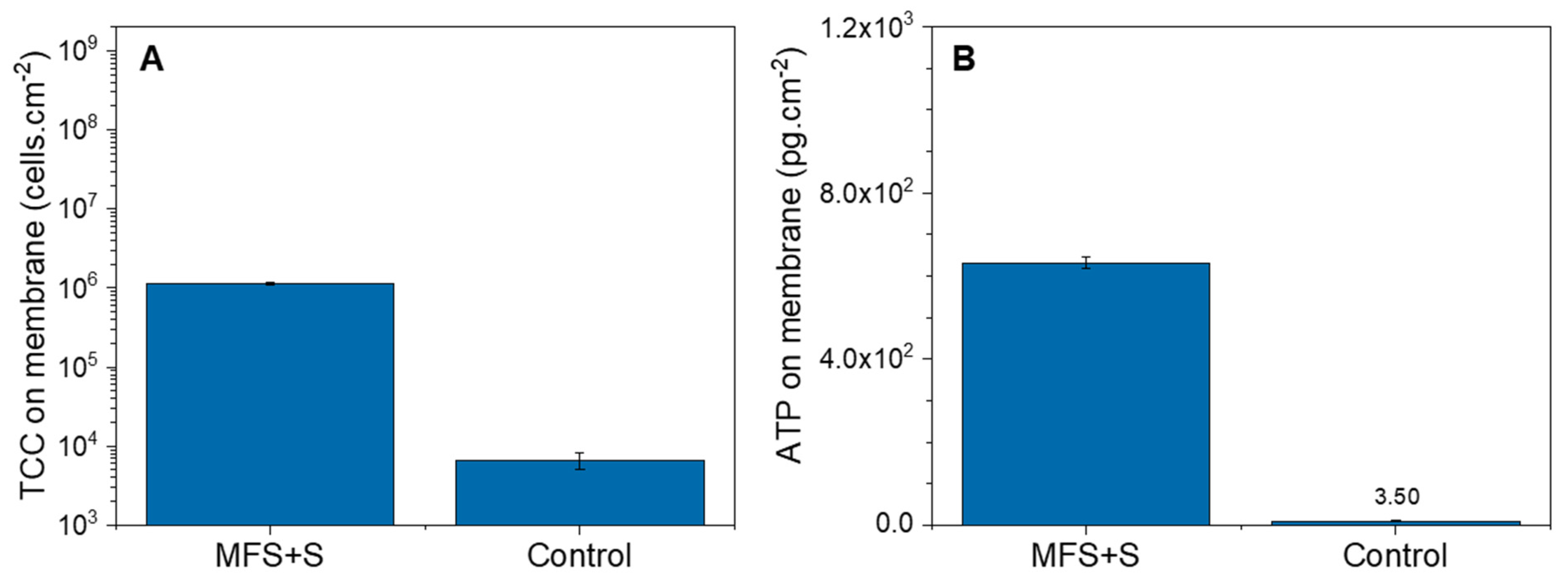
3.2.2. Biofilm Characterization
4. Discussion
4.1. Biofilm Detection in Membrane Systems: Total Cell Concentration in the Outlet as an Indication of Biofilm Growth
4.2. Accelerated Biofilm Development Timescale Translated to Reality
4.3. Early Detection of Biofilm on Membrane Systems
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Vliet, M.T.H.; Jones, E.R.; Flörke, M.; Franssen, W.H.P.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Yearsley, J.R. Global water scarcity including surface water quality and expansions of clean water technologies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 024020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; Qadir, M.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Smakhtin, V.; Kang, S.M. The state of desalination and brine production: A global outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayar, K.G.; Fernandes, J.; McGovern, R.K.; Dominguez, K.P.; McCance, A.; Al-Anzi, B.S.; Lienhard, V.J.H. Cost and energy requirements of hybrid RO and ED brine concentration systems for salt production. Desalination 2019, 456, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaka, K.; Katsura, T.; Iwahori, H.; Kamiyama, Y. Analysis of RO elements operated at more than 80 plants in Japan. Desalination 1994, 96, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Aleem, F.A.; Al-Sugair, K.A.; Alahmad, M.I. Biofouling problems in membrane processes for water desalination and reuse in Saudi Arabia. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1998, 41, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Laoui, T.; Falath, W.; Farooque, M. Fouling control in reverse osmosis for water desalination & reuse: Current practices & emerging environment-friendly technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142721. [Google Scholar]
- Siebdrath, N.; Farhat, N.; Ding, W.; Kruithof, J.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Impact of membrane biofouling in the sequential development of performance indicators: Feed channel pressure drop, permeability, and salt rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 585, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, N.; Skillman, L.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ho, G.; Li, D. Investigation of compounds that degrade biofilm polysaccharides on reverse osmosis membranes from a full scale desalination plant to alleviate biofouling. Desalination 2017, 403, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.S.; Dudley, L.Y. Biofouling in membrane systems—A review. Desalination 1998, 118, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.; Valavala, R.; Han, J.; Her, N.; Yoon, Y. Pretreatment in reverse osmosis seawater desalination: A short review. Environ. Eng. Res. 2011, 16, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Weigand, T.M.; Edalat, A. Reverse osmosis membrane biofouling: Causes, consequences and countermeasures. NPJ Clean Water 2022, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushaban, A.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Philibert, M.; Le Bouille, L.; Necibi, M.C.; Chehbouni, A. Biofouling potential indicators to assess pretreatment and mitigate biofouling in SWRO membranes: A short review. Desalination 2022, 527, 115543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.; Farhat, N.; Bucs, S.S.; Linares, R.V.; Picioreanu, C.; Kruithof, J.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Kidwell, J.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Development and characterization of 3D-printed feed spacers for spiral wound membrane systems. Water Res. 2016, 91, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Anvari, A.; Hoek, E.M.V.; McCutcheon, J.R. Advancements in conventional and 3D printed feed spacers in membrane modules. Desalination 2023, 556, 116518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, N.; Thomas, N.; Ghaffour, N.; Arafat, H.A. The evolution of feed spacer role in membrane applications for desalination and water treatment: A critical review and future perspective. Desalination 2023, 554, 116505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.-T.; Lee, D.-J.; Huang, C. Membrane Fouling Mitigation: Membrane Cleaning. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, J. Biofouling of polyamide membranes: Fouling mechanisms, current mitigation and cleaning strategies, and future prospects. Membranes 2019, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, N.M.; Staal, M.; Siddiqui, A.; Borisov, S.M.; Bucs, S.S.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Early non-destructive biofouling detection and spatial distribution: Application of oxygen sensing optodes. Water Res 2015, 83, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.K.; Fortunato, L.; Leiknes, T.O. Early biofouling detection using fluorescence-based extracellular enzyme activity. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2019, 120, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Behzad, A.R.; Farinha, A.S.F.; Zhao, C.; Bucs, S.S.; Nada, T.; Das, R.; Altmann, T.; Buijs, P.J.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Clinical Autopsy of a Reverse Osmosis Membrane Module. Front. Chem. Eng. 2021, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Bolto, B.; Gray, S.; Hoang, M.; Ostarcevic, E. An autopsy study of a fouled reverse osmosis membrane element used in a brackish water treatment plant. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3915–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Kruithof, J.; van Loosdrecht, M. Biofouling of spiral wound membrane systems. Water Intell. Online 2011, 10, 9781780400990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.T.V.; Krantz, W.B.; Chong, T.H.; Fane, A.G. Online monitor for the reverse osmosis spiral wound module—Development of the canary cell. Desalination 2015, 368, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.; Vanpassen, J.; Wessels, L.; Vandam, A.; Bakker, S. The Membrane Fouling Simulator: A practical tool for fouling prediction and control. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creber, S.A.; Pintelon, T.R.R.; Graf von der Schulenburg, D.A.W.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Johns, M.L. Magnetic resonance imaging and 3D simulation studies of biofilm accumulation and cleaning on reverse osmosis membranes. Food Bioprod. Process. 2010, 88, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeck, J. Early Studies on Ecto- and Extracellular Enzymes in Aquatic Environments. In Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments; Chróst, R.J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G. Enzyme activity in soil: Location and a possible role in microbial ecology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C. The BiofilmMode of Life. In Ecological Biochemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah, H.; Chogle, A. Biofouling in reverse osmosis: Phenomena, monitoring, controlling and remediation. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, F.; Berney, M.; Wang, Y.; Vital, M.; Köster, O.; Egli, T. Flow-cytometric total bacterial cell counts as a descriptive microbiological parameter for drinking water treatment processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besmer, M.D.; Weissbrodt, D.G.; Kratochvil, B.E.; Sigrist, J.r.A.; Weyland, M.S.; Hammes, F. The feasibility of automated online flow cytometry for in-situ monitoring of microbial dynamics in aquatic ecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, N.; Kim, L.H.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Online characterization of bacterial processes in drinking water systems. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.B.; Lasslett, S.; Pelekani, C. Destructive and non-destructive methods for biofouling analysis investigated at the Adelaide Desalination Pilot Plant. Desalination 2012, 296, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, F.A.; Egli, T. New Method for Assimilable Organic Carbon Determination Using Flow-Cytometric Enumeration and a Natural Microbial Consortium as Inoculum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3289–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, L.; Proctor, C.R.; Walser, J.-c.; Hammes, F. Small-Scale Heterogeneity in Drinking Water Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celsis, AdvanceTM Luminometer. Operator Manual. Available online: https://www.criver.com/sites/default/files/resources/doc_a/CelsisAdvanceII%E2%84%A2SystemforRapidMicrobialScreening.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Prihasto, N.; Liu, Q.F.; Kim, S.H. Pre-treatment strategies for seawater desalination by reverse osmosis system. Desalination 2009, 249, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, J. Reverse Osmosis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Badrelzaman, M.; Darwish, N.N.; Darwish, N.A.; Hilal, N. Reverse osmosis desalination: A state-of-the-art review. Desalination 2019, 459, 59–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C. Reverse osmosis membrane biofouling. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1997, 14, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-c. Biofilms, Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (ELS); John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereschenko, L.A.; Stams, A.J.M.; Euverink, G.J.W.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Biofilm formation on reverse osmosis membranes is initiated and dominated by Sphingomonas spp. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2010, 76, 2623–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, K.R.; Asteriadou, K.; Robbins, P.T.; Fryer, P.J. Fouling and Cleaning Studies in the Food and Beverage Industry Classified by Cleaning Type. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Manolarakis, S.A.; van der Hoek, J.P.; van Paassen, J.A.M.; van der Meer, W.G.J.; van Agtmaal, J.M.C.; Prummel, H.D.M.; Kruithof, J.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Quantitative biofouling diagnosis in full scale nanofiltration and reverse osmosis installations. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4856–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, N.; Judd, S. Chemical cleaning of potable water membranes: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, F.; Laurinonyte, J.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Stams, A.J.M.; Plugge, C.M. Membrane Fouling and Chemical Cleaning in Three Full-Scale. Hindawi 2017, 2017, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Hijnen, W.A.M.; Castillo, C.; Brouwer-Hanzens, A.H.; Harmsen, D.J.H.; Cornelissen, E.R.; van der Kooij, D. Quantitative assessment of the efficacy of spiral-wound membrane cleaning procedures to remove biofilms. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6369–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanawar, H.; Kim, L.H.; Farhat, N.M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Periodic chemical cleaning with urea: Disintegration of biofilms and reduction of key biofilm-forming bacteria from reverse osmosis membranes. Water Res. X 2021, 13, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngene, I.S.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; van de Ven, W.J.C.; Wessels, L.P.; Wessling, M.; Van der Meer, W.G.J. CO2 Nucleation in Membrane Spacer Channels Remove Biofilms and Fouling Deposits. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 10034–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayarathne, H.N.P.; Choi, J.; Jang, A. Enhancement of cleaning-in-place (CIP) of a reverse osmosis desalination process with air micro-nano bubbles. Desalination 2017, 422, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pulido Beltran, L.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Farhat, N. Application of Online Flow Cytometry for Early Biofouling Detection in Reverse Osmosis Membrane Systems. Membranes 2024, 14, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090185
Pulido Beltran L, Vrouwenvelder JS, Farhat N. Application of Online Flow Cytometry for Early Biofouling Detection in Reverse Osmosis Membrane Systems. Membranes. 2024; 14(9):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090185
Chicago/Turabian StylePulido Beltran, Laura, Johannes S. Vrouwenvelder, and Nadia Farhat. 2024. "Application of Online Flow Cytometry for Early Biofouling Detection in Reverse Osmosis Membrane Systems" Membranes 14, no. 9: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090185
APA StylePulido Beltran, L., Vrouwenvelder, J. S., & Farhat, N. (2024). Application of Online Flow Cytometry for Early Biofouling Detection in Reverse Osmosis Membrane Systems. Membranes, 14(9), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090185






