Performance and Impact of Crosslinking Level of Hierarchical Anion-Exchange Membranes on Demineralization of a Complex Food Solution by Electrodialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
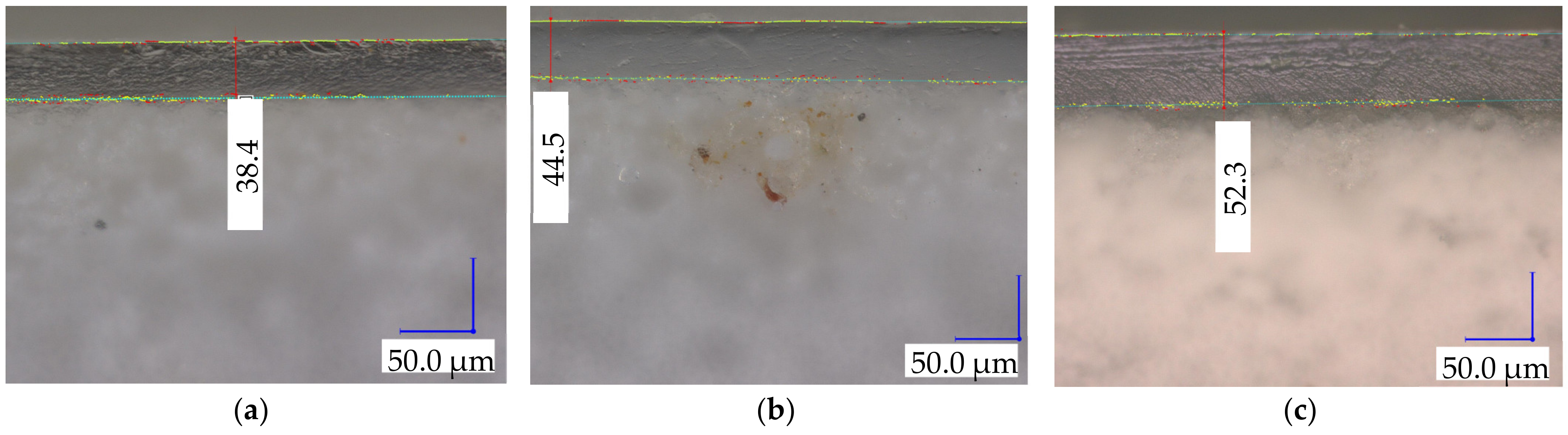
2.2.1. Characterization of Membrane and Morphology
Thickness
Microscopy
Roughness
Contact Angle
Ion-Exchange Capacity
Conductivity and Ionic Conductance
Selectivity
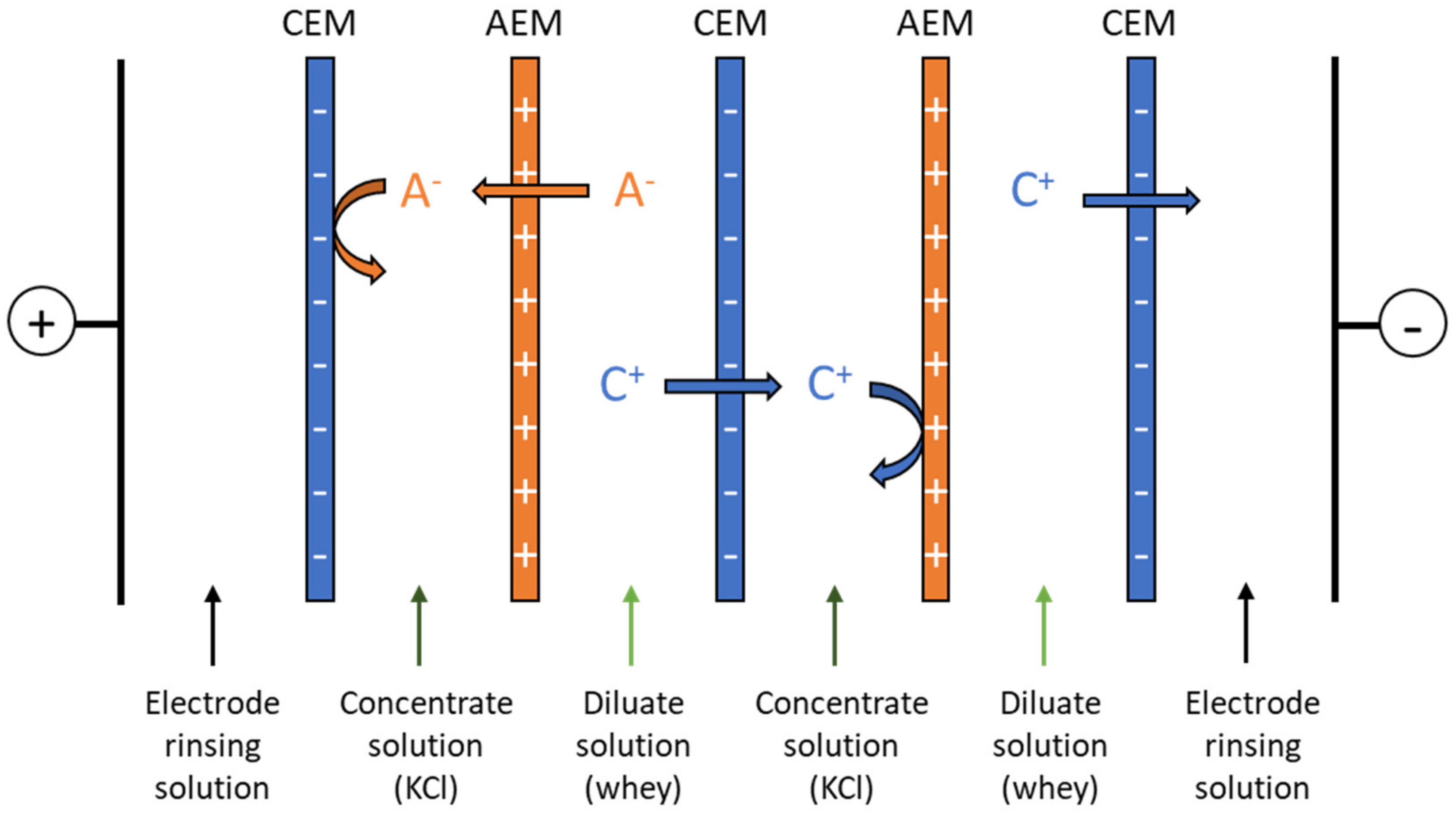
2.2.2. Electrodialysis Experiments
ED Set-Up and Configuration
Limiting Current Density
Performance Evaluation
- pH
- Conductivity
- Demineralization
- Mineral Concentration
Current Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Whey Demineralization
2.2.3. Fouling Assessment
SEM-EDS
ATR-FTIR
2.2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Membrane and Morphology
3.2. Electrodialysis Experiments
3.2.1. Limiting Current Density
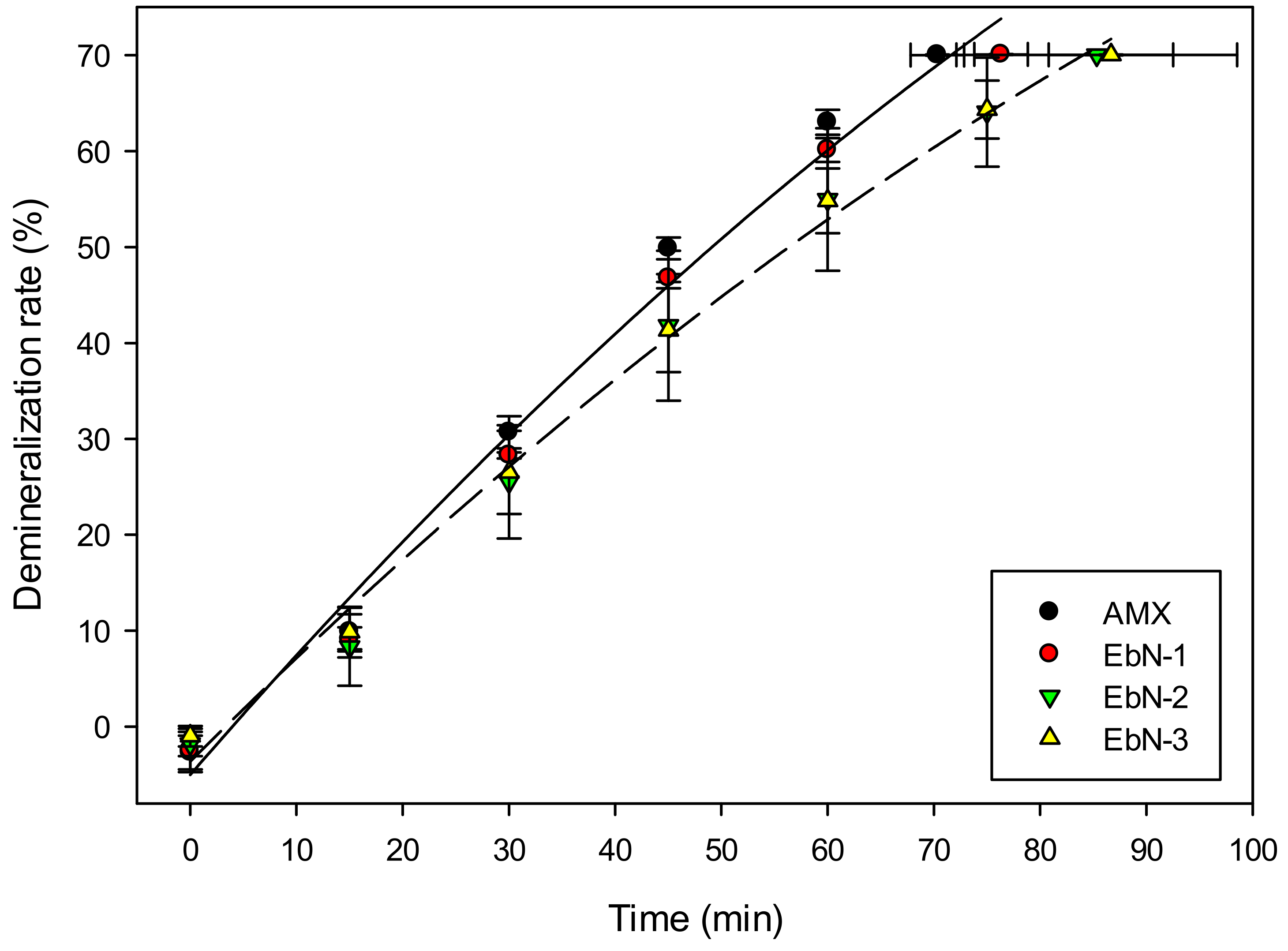
3.2.2. Demineralization of Whey
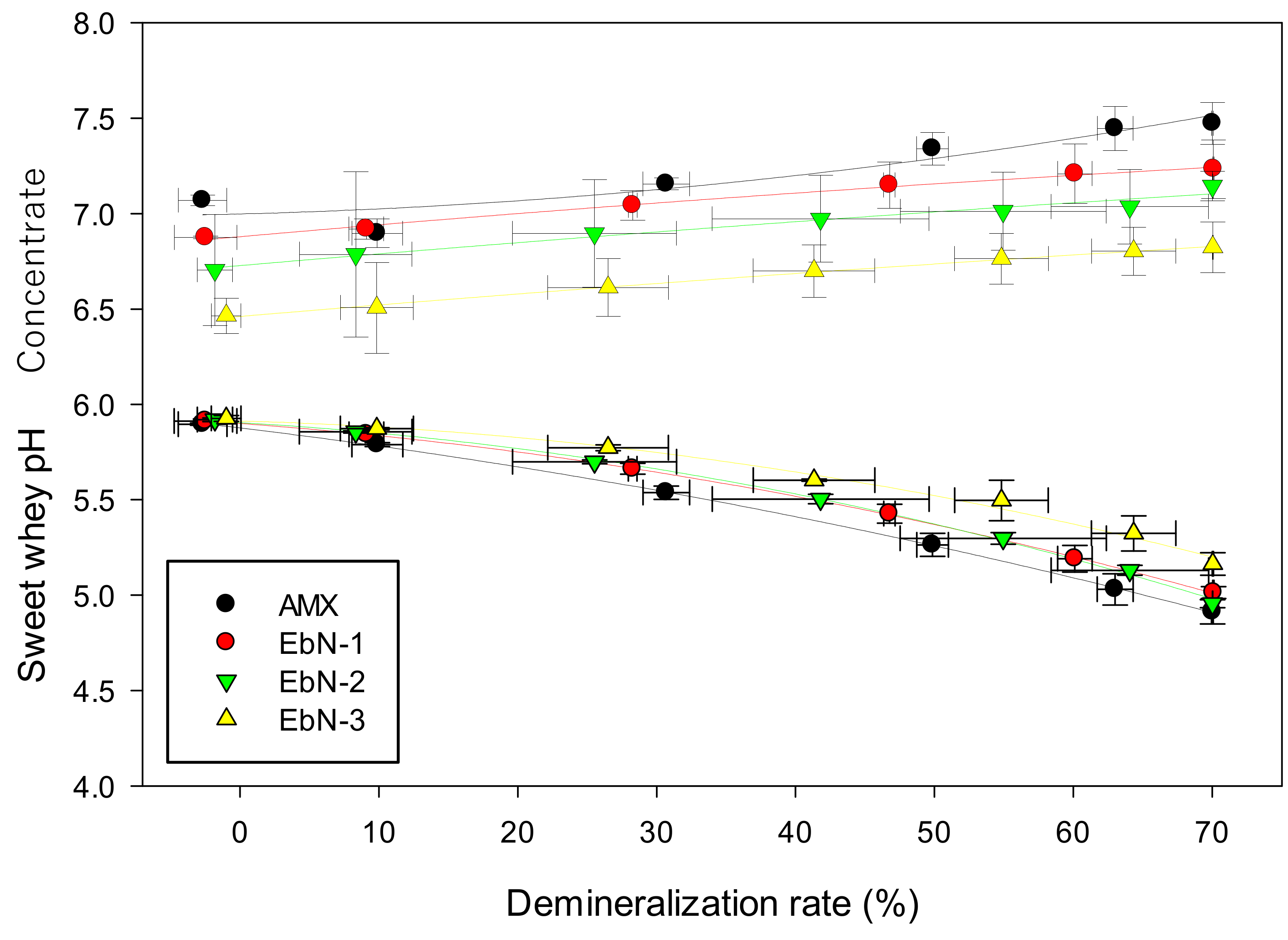
3.2.3. pH Variation
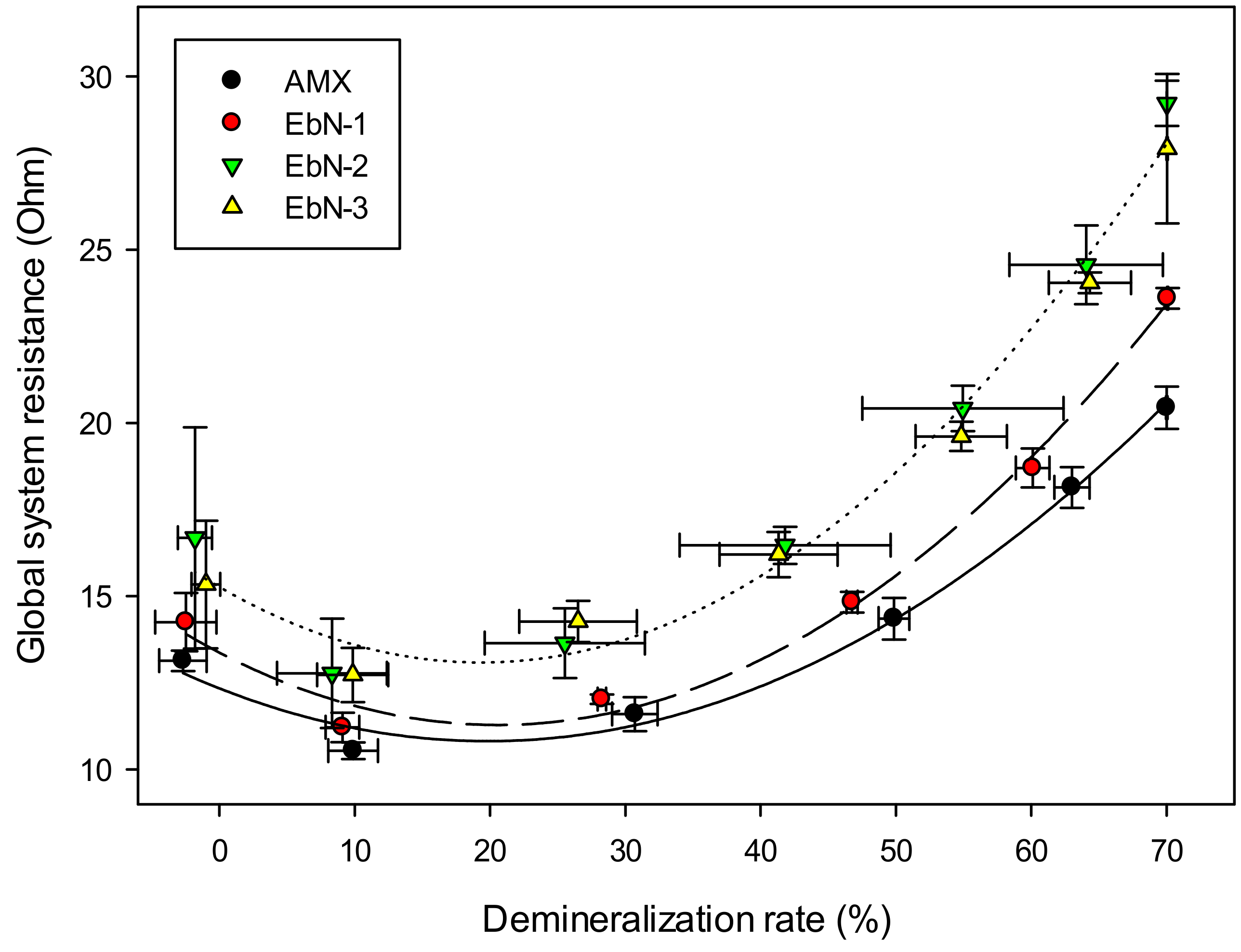
3.2.4. Global System Resistance
3.2.5. Energy Consumption and Current Efficiency
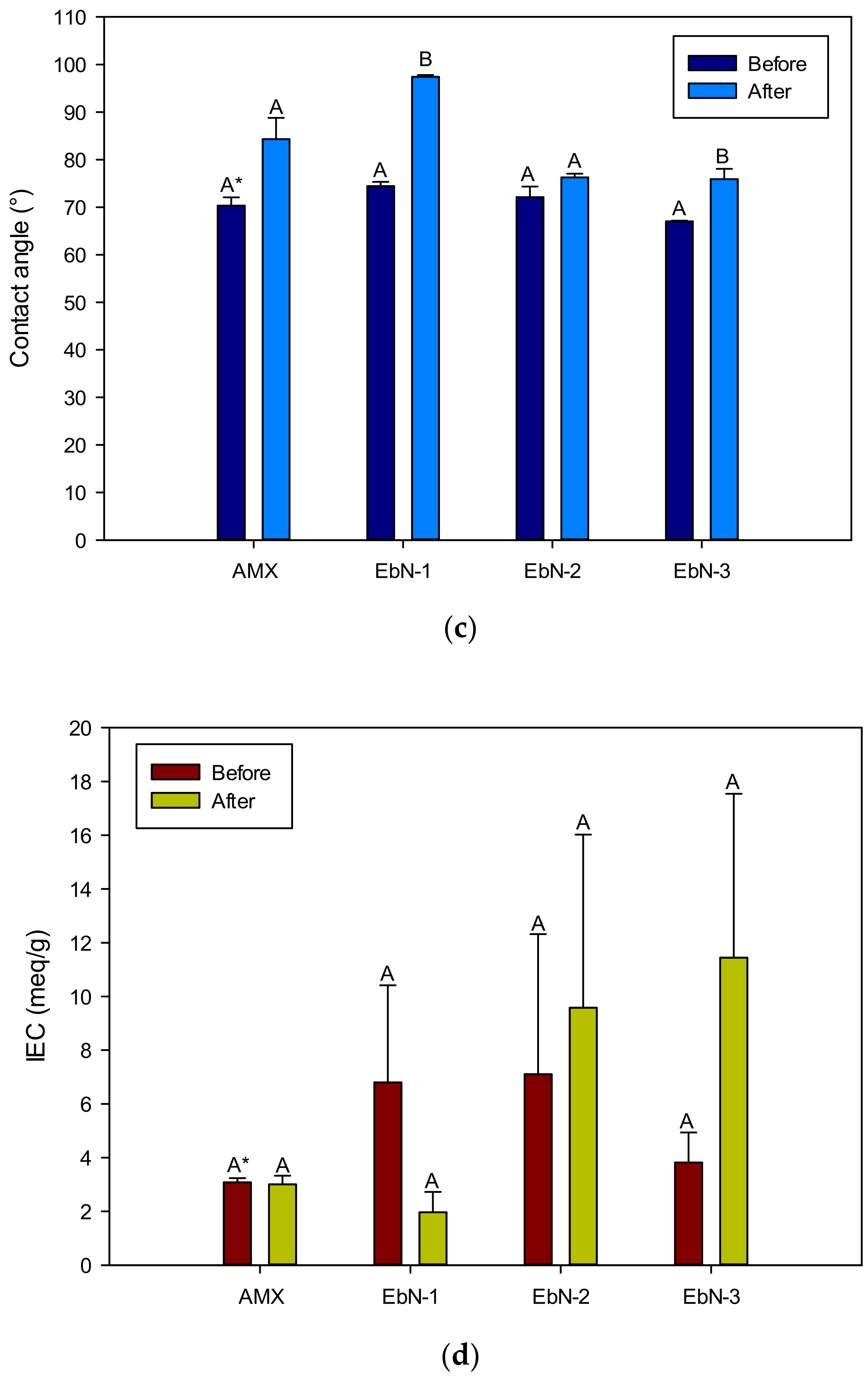
3.3. Change in Membrane Properties
3.4. Fouling Assessment
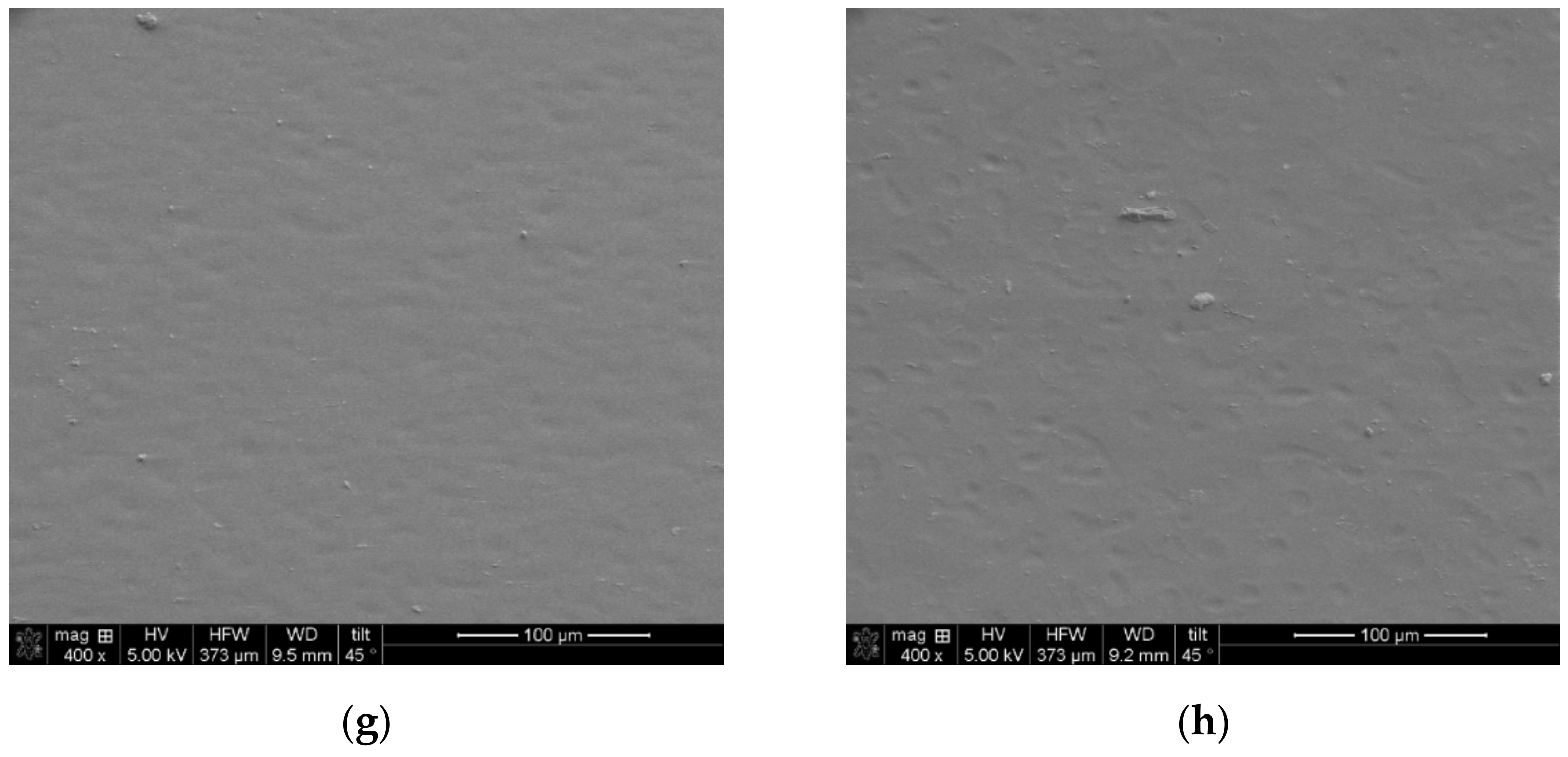
3.4.1. SEM-EDS
3.4.2. ATR-FTIR
3.5. Global Performances
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, L.; Chen, Q.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, P. Electrodialysis with Porous Membrane for Bioproduct Separation: Technology, Features, and Progress. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlJaberi, F.Y.; Ahmed, S.A.; Makki, H.F.; Naje, A.S.; Zwain, H.M.; Salman, A.D.; Juzsakova, T.; Viktor, S.; Van, B.; Le, P.-C.; et al. Recent Advances and Applicable Flexibility Potential of Electrochemical Processes for Wastewater Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ramasamy, D.L.; Sillanpää, M.; Repo, E. Separation and Concentration of Rare Earth Elements from Wastewater Using Electrodialysis Technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Sabur, G.M.; Akter, M.M.; Nam, S.Y.; Im, K.S.; Tijing, L.; Shon, H.K. Electrodialysis Desalination, Resource and Energy Recovery from Water Industries for a Circular Economy. Desalination 2024, 569, 117041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankoliya, D.; Mudgal, A.; Sinha, M.K.; Davies, P.; Park, K.; Alegre, R.R.; Patel, V.; Patel, J. Techno-Economic Analysis of Integrated Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis and Batch Reverse Osmosis for Water and Chemical Recovery from Dairy Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campione, A.; Gurreri, L.; Ciofalo, M.; Micale, G.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A. Electrodialysis for Water Desalination: A Critical Assessment of Recent Developments on Process Fundamentals, Models and Applications. Desalination 2018, 434, 121–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amshawee, S.; Yunus, M.Y.B.M.; Azoddein, A.A.M.; Hassell, D.G.; Dakhil, I.H.; Hasan, H.A. Electrodialysis Desalination for Water and Wastewater: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, Y.; Woo, Y.C.; Hwang, I. Water Management and Produced Water Treatment in Oil Sand Plant: A Review. Desalination 2023, 567, 116991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Geoffroy, T.R. Electrodialytic Processes: Market Overview, Membrane Phenomena, Recent Developments and Sustainable Strategies. Membranes 2020, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadel, S.; Deboli, F.; Perreault, V.; Donten, M.L.; Bazinet, L. Ionomer-coated Filtration Membranes as an Alternative to Ion-exchange Membranes for Demineralization by Electrodialysis. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 21, 2984–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboli, F.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Donten, M.L. A Versatile Chemistry Platform for the Fabrication of Cost-Effective Hierarchical Cation and Anion Exchange Membranes. Desalination 2022, 535, 115794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetsomphou, E.; Deboli, F.; Donten, M.L.; Bazinet, L. Impact of Hierarchical Cation-Exchange Membranes’ Chemistry and Crosslinking Level on Electrodialysis Demineralization Performances of a Complex Food Solution. Membranes 2023, 13, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, G.L.d.P.A.; Guimarães, J.T.; Pimentel, T.C.; da Cruz, A.G.; de Souza, S.L.Q.; Vendramel, S.M.R. Chapter 19—Whey: Generation, Recovery, and Use of a Relevant by-Product. In Valorization of Agri-Food Wastes and By-Products; Bhat, R., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 391–414. ISBN 978-0-12-824044-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ozel, B.; McClements, D.J.; Arikan, C.; Kaner, O.; Oztop, M.H. Challenges in Dried Whey Powder Production: Quality Problems. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P.M. Whey Powder, Demineralized Whey Powder and Delactosed Whey. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences (Third Edition); McSweeney, P.L.H., McNamara, J.P., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 174–185. ISBN 978-0-12-818767-8. [Google Scholar]
- Burling, H. Whey Processing—Demineralization. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Roginski, H., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 2745–2751. ISBN 978-0-12-227235-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrand, V.; Sundström, G.; Jönsson, A.-S. Fouling of Electrodialysis Membranes by Organic Substances. Desalination 2000, 128, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhovets, A.; Eliseeva, T.; Oren, Y. Fouling of Anion-Exchange Membranes in Electrodialysis of Aromatic Amino Acid Solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyati, S.; Takagi, R.; Fujii, A.; Ohmukai, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. Improvement of the Antifouling Potential of an Anion Exchange Membrane by Surface Modification with a Polyelectrolyte for an Electrodialysis Process. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Hong, M.-K.; Han, S.-D.; Cho, S.-H.; Moon, S.-H. Fouling of an Anion Exchange Membrane in the Electrodialysis Desalination Process in the Presence of Organic Foulants. Desalination 2009, 238, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pismenskaya, N.; Bdiri, M.; Sarapulova, V.; Kozmai, A.; Fouilloux, J.; Baklouti, L.; Larchet, C.; Renard, E.; Dammak, L. A Review on Ion-Exchange Membranes Fouling during Electrodialysis Process in Food Industry, Part 2: Influence on Transport Properties and Electrochemical Characteristics, Cleaning and Its Consequences. Membranes 2021, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, L.; Fouilloux, J.; Bdiri, M.; Larchet, C.; Renard, E.; Baklouti, L.; Sarapulova, V.; Kozmai, A.; Pismenskaya, N. A Review on Ion-Exchange Membrane Fouling during the Electrodialysis Process in the Food Industry, Part 1: Types, Effects, Characterization Methods, Fouling Mechanisms and Interactions. Membranes 2021, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L. A Review on Ion-Exchange Membranes Fouling and Antifouling During Electrodialysis Used in Food Industry: Cleanings and Strategies of Prevention. Chem. Afr. 2020, 3, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Feng, Z.; Liu, J.; Liao, S.; Li, X.; Yu, Y. Highly Conductive Anion Exchange Membrane with a Stable Double-Sided Anti-Fouling Structure for Electrodialysis Desalination of Protein Systems. Desalination 2023, 545, 116167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadel, S.; Pellerin, G.; Thibodeau, J.; Perreault, V.; Lainé, C.; Bazinet, L. How Molecular Weight Cut-Offs and Physicochemical Properties of Polyether Sulfone Membranes Affect Peptide Migration and Selectivity during Electrodialysis with Filtration Membranes. Membranes 2019, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagesteijn, K.F.L.; Jiang, S.; Ladewig, B.P. A Review of the Synthesis and Characterization of Anion Exchange Membranes. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 11131–11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lteif, R.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Auclair, B. Conductivitéélectrique Membranaire: Étude de l’effet de La Concentration, de La Nature de l’électrolyte et de La Structure Membranaire. Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, L.; Da Silva, E.; Pourcelly, G.; Métayer, M. Elaboration and Characterisation of Ion-Exchange Films Used in the Fabrication of Bipolar Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 227, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboli, F.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Donten, M.L. A Novel Concept of Hierarchical Cation Exchange Membrane Fabricated from Commodity Precursors through an Easily Scalable Process. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, D.A.; Brown, J.H. Effect of Turbulence on Limiting Current in Electrodialysis Cells. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1959, 51, 1445–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Bribiesca, E.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Nature Identification and Morphology Characterization of Cation-Exchange Membrane Fouling during Conventional Electrodialysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slade, S.; Campbell, S.A.; Ralph, T.R.; Walsh, F.C. Ionic Conductivity of an Extruded Nafion 1100 EW Series of Membranes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.; Andrés, L.J.; Álvarez, R.; Coca, J.; Hill, C.G., Jr. Electrodilaysis of Whey Permeates and Rententates Obtained by Ultrafiltration. J. Food Process Eng. 1994, 17, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabay, N.; Arda, M.; Kurucaovali, I.; Ersoz, E.; Kahveci, H.; Can, M.; Dal, S.; Kopuzlu, S.; Haner, M.; Demircioglu, M.; et al. Effect of Feed Characteristics on the Separation Performances of Monovalent and Divalent Salts by Electrodialysis. Desalination 2003, 158, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B.; Sager, J.; Rector, T.; Garland, J.; Strayer, R.F.; Levine, L.; Roberts, M.; Hummerick, M.; Bauer, J. Significance of Hydrated Radius and Hydration Shells on Ionic Permeability during Nanofiltration in Dead End and Cross Flow Modes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.M.; Aung, S.L.; Choi, J.; Cha, H.; Cho, J.; Byambaa, B.; Song, K.G. Behavior of Solutes and Membrane Fouling in an Electrodialysis to Treat a Side-Stream: Migration of Ions, Dissolved Organics and Micropollutants. Desalination 2023, 549, 116361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, A.; León, T.; Jofre, L.; Cortina, J.L.; Dvořák, L.; Ahrné, L. Steady-State Modeling of Water-Splitting and Multi-Ionic Transport of Skim Milk Electro-Acidification by Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis. J. Food Eng. 2024, 378, 112106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, T.; Sata, T.; Yang, W. Studies on Cation-Exchange Membranes Having Permselectivity between Cations in Electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 206, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, N.; Mikhaylin, S.; Mareev, S.; Pismenskaya, N.; Nikonenko, V.; Bazinet, L. How Demineralization Duration by Electrodialysis under High Frequency Pulsed Electric Field Can Be the Same as in Continuous Current Condition and That for Better Performances? J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 117878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbeke, R. La déminéralisation par électrodialyse du lactosérum doux de fromagerie. Le Lait 1975, 55, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkoula, N.-M.; Peijs, T. 2—Interface Engineering through Matrix Modification in Natural Fibre Composites. In Interface Engineering of Natural Fibre Composites for Maximum Performance; Zafeiropoulos, N.E., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 43–81. ISBN 978-1-84569-742-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hebbar, R.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F. Chapter 12—Contact Angle Measurements. In Membrane Characterization; Hilal, N., Ismail, A.F., Matsuura, T., Oatley-Radcliffe, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 219–255. ISBN 978-0-444-63776-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ghalloussi, R.; Chaabane, L.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Grande, D. Structural and Physicochemical Investigation of Ageing of Ion-Exchange Membranes in Electrodialysis for Food Industry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 123, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Dammak, L.; Chaabane, L.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Cleaning of Cation-Exchange Membranes Used in Electrodialysis for Food Industry by Chemical Solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allat, L.; Delimi, R.; Mehellou, A. Mitigation of an Anion Exchange Membrane Fouling by Coupling Electrodialysis to Anodic Oxidation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 186, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, A.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A. Infrared Spectroscopy: An Underexploited Analytical Tool for Assessing Physicochemical Properties of Food Products and Processing. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 49, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, M.; Mikhaylin, S.; Doyen, A.; Firdaous, L.; Hammami, R.; Bazinet, L. How Peptide Physicochemical and Structural Characteristics Affect Anion-Exchange Membranes Fouling by a Tryptic Whey Protein Hydrolysate. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwal, S.; Roblet, C.; Amiot, J.; Bazinet, L. Presence of Free Amino Acids in Protein Hydrolysate during Electroseparation of Peptides: Impact on System Efficiency and Membrane Physicochemical Properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, V.; Sarapulova, V.; Tsygurina, K.; Pismenskaya, N.; Bazinet, L. Understanding of Adsorption and Desorption Mechanisms of Anthocyanins and Proanthocyanidins on Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Cation-Exchange Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phukan, R.; Guttierez, L.; De Schepper, W.; Vanoppen, M.; Verbeken, K.; Raes, K.; Verliefde, A.; Cornelissen, E. Short Term Fouling Tests on Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Anion-Exchange Membranes from Food and Bio-Based Industrial Streams: Foulant Identification and Characterization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, S.; Noda, I. Analysis of Crystallized Lactose in Milk Powder by Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Two-Dimensional Correlation Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 974, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păucean, A.; Vodnar, D.C.; Mureșan, V.; Fetea, F.; Ranga, F.; Man, S.M.; Muste, S.; Socaciu, C. Monitoring Lactic Acid Concentrations by Infrared Spectroscopy: A New Developed Method for Lactobacillus Fermenting Media with Potential Food Applications. Acta Aliment. 2017, 46, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magan, J.B.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Mandal, R.; Hennessy, D.; Fenelon, M.A.; Wishart, D.S.; Kelly, A.L.; McCarthy, N.A. Impact of Bovine Diet on Metabolomic Profile of Skim Milk and Whey Protein Ingredients. Metabolites 2019, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, E.N.; Merkel, A.; Yazdi, S.R.; Ahrné, L. The Effect of Acid Whey Composition on the Removal of Calcium and Lactate during Electrodialysis. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 117, 104985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsermoula, P.; Bechshøft, M.R.; Friis, C.; Engelsen, S.B.; Khakimov, B. Screening of Non-Protein Nitrogen Compounds in Lactose Refining Streams from Industrial Whey Permeate Processing. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kuang, S.; Wang, X.; Kang, D.; Mao, D.; Qian, G.; Cai, X.; Tan, M.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. Transport of Amino Acids in Soy Sauce Desalination Process by Electrodialysis. Membranes 2021, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliseeva, T.; Kharina, A. Desalination of Neutral Amino Acid Solutions in an Electromembrane System. Membranes 2022, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiter, M.; Novalin, S.; Wendland, M.; Kulbe, K.-D.; Fischer, J. Desalination of Whey by Electrodialysis and Ion Exchange Resins: Analysis of Both Processes with Regard to Sustainability by Calculating Their Cumulative Energy Demand. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 210, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Eschbach, F.I.I.; Weeks, M.; Gras, S.L.; Kentish, S.E. Removal of Lactic Acid from Acid Whey Using Electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 158, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Kee, E.; Chen, G.Q.; Bathurst, K.; Kentish, S.E. Utilisation of Salty Whey Ultrafiltration Permeate with Electrodialysis. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 99, 104549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.N.; Skibsted, L.H.; Yazdi, S.R.; Merkel, A.; Ahrné, L.M. Improving Electrodialysis Separation Efficiency of Minerals from Acid Whey by Nano-Filtration Pre-Processing. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2022, 75, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, A.; Ashrafi, A.M. An Investigation on the Application of Pulsed Electrodialysis Reversal in Whey Desalination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | EBE3105 * | EBE830 |
|---|---|---|
| EbN-1 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
| EbN-2 | 0.15 | 0.30 |
| EbN-3 | 0.00 | 0.45 |
| Sample | Membrane Thickness (mm) | Coating Thickness (µm) | Ra (µm) | Rz (µm) | Conductivity (mS.cm−1) | Selectivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMX | 0.145 ± 0.002 b* | - | 0.26 ± 0.09 a | 3.43 ± 2.03 b | 6.06 ± 0.23 c | 89 ± 0 b |
| EbN-1 | 0.434 ± 0.002 a | 36.59 ± 4.41 b | 0.55 ± 0.26 a | 5.80 ± 0.73 a,b | 10.03 ± 0.18 a | 86 ± 0 a |
| EbN-2 | 0.417 ± 0.026 a | 45.48 ± 9.43 a,b | 0.59 ± 0.25 a | 10.31 ± 2.66 a | 8.71 ± 0.13 b | 91± 0 c |
| EbN-3 | 0.406 ± 0.009 a | 54.34 ± 2.67 a | 0.29 ± 0.08 a | 9.31 ± 2.56 a | 7.71 ± 0.49 b | 94 ± 0 d |
| Sample | Limiting Current Density (mA.cm−2) | Associated Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|
| AMX | 17.6 ± 0.21 a,* | 18.46 ± 0.39 a |
| EbN-1 | 16.9 ± 0.15 a | 18.61 ± 0.93 a |
| EbN-2 | 17.4 ± 0.10 a | 19.31 ± 1.77 a |
| Sample | Energy Consumption (Wh) | Current Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AMX | 15.10 ± 0.09 a,* | 27.45 ± 1.54 a |
| EbN-1 | 15.10 ± 0.16 a | 25.25 ± 1.51 a |
| EbN-2 | 14.60 ± 0.59 a | 26.19 ± 2.54 a |
| EbN-3 | 14.78 ± 0.43 a | 26.56 ± 3.08 a |
| Element | AMX (At%) | EbN-1 (At%) | EbN-2 (At%) | EbN-3 (At%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | Before | After | |
| S | 0.08 | 0.11 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cl | 2.22 | 0.63 | 1.06 | - | 0.98 | 0.09 | 0.99 | - |
| P | - | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.14 |
| O | 3.09 | 6.55 | 17.79 | 19.56 | 18.75 | 22.00 | 21.45 | 22.92 |
| C | 94.61 | 92.54 | 80.98 | 80.28 | 80.09 | 77.77 | 77.38 | 76.94 |
| AEM (Manufacturer) | Solution | ED Unit | Duration (min) | Demineralization Rate (%) | Energy Consumption | Current Efficiency (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA-1 | WPC (10.0 wt. %) | 10 cell pairs 100 cm2/membrane | 60 | 64.2 | 640 kWh/eq removed | 84.2 | Pérez et al. [33] |
| Neosepta CMX—homogeneous (Astom) | 1.50 L nanofiltered whey (18.0–20.0 wt. %) | 8 cell pairs 37 cm2/membrane | 260 | 90.0 | 26.5 kJ | 70.0 | Greiter et al. [58] |
| Neosepta AHA—homogeneous (Astom) | 1.20 L acid whey (5.2 wt. %) | 2 cell pairs 36 cm2/membrane | 180 | 90.0 | 0.014 kWh/g | 80.0–90.0 | Chen et al. [59] |
| Neosepta AHA—homogeneous (Astom) | 2.00 L sweet whey (6.5 wt. %) | 2 cell pairs 36 cm2/membrane | 180 | 75.0 | 5.9 kWh/ton of whey | Talebi et al. [60] | |
| AEM-PES—heterogeneous (MemBrain) | 30.00 kg acid whey (20.0% wt. %) | 50 cell pairs 400 cm2/membrane | 195 | 89.3 | 8.8 Wh/kg | Merkel et al. [62] | |
| Ralex AM-PES TR I—heterogeneous (MEGA) | 2.00 kg evaporated sweet whey (15.7 wt. %) | 10 cell pairs 64 cm2/membrane | 180 | 98.0 | 4.4 Wh/kg | Nielsen et al. [61] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khetsomphou, E.; Deboli, F.; Donten, M.L.; Bazinet, L. Performance and Impact of Crosslinking Level of Hierarchical Anion-Exchange Membranes on Demineralization of a Complex Food Solution by Electrodialysis. Membranes 2024, 14, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14070155
Khetsomphou E, Deboli F, Donten ML, Bazinet L. Performance and Impact of Crosslinking Level of Hierarchical Anion-Exchange Membranes on Demineralization of a Complex Food Solution by Electrodialysis. Membranes. 2024; 14(7):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14070155
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhetsomphou, Elodie, Francesco Deboli, Mateusz L. Donten, and Laurent Bazinet. 2024. "Performance and Impact of Crosslinking Level of Hierarchical Anion-Exchange Membranes on Demineralization of a Complex Food Solution by Electrodialysis" Membranes 14, no. 7: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14070155
APA StyleKhetsomphou, E., Deboli, F., Donten, M. L., & Bazinet, L. (2024). Performance and Impact of Crosslinking Level of Hierarchical Anion-Exchange Membranes on Demineralization of a Complex Food Solution by Electrodialysis. Membranes, 14(7), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14070155







