Effect of NiO Addition on the Sintering and Electrochemical Properties of BaCe0.55Zr0.35Y0.1O3-δ Proton-Conducting Ceramic Electrolyte
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Single Cells Fabrication
2.3. Material Characterization
2.4. Electrical Property Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
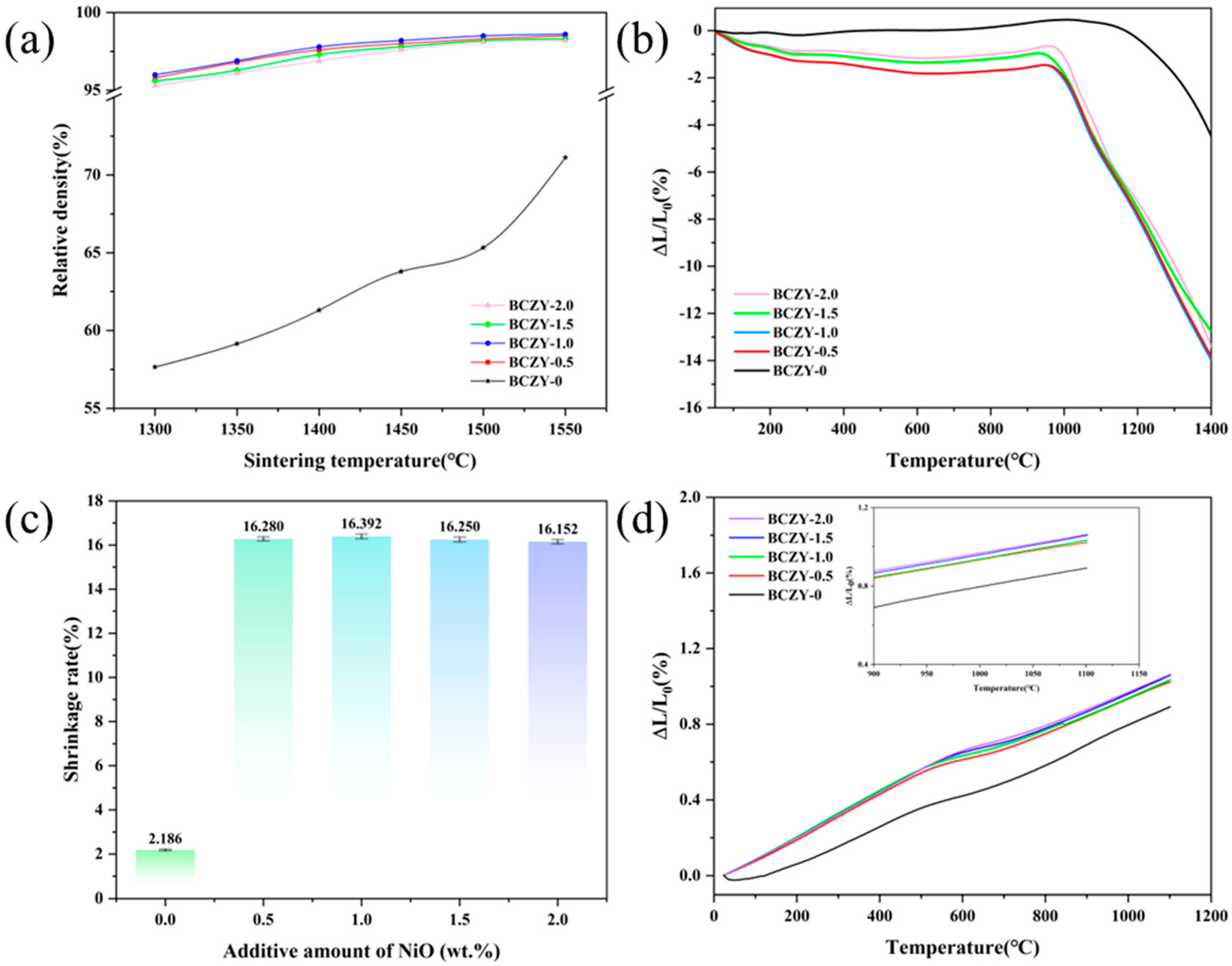
3.2. Sintering Behavior
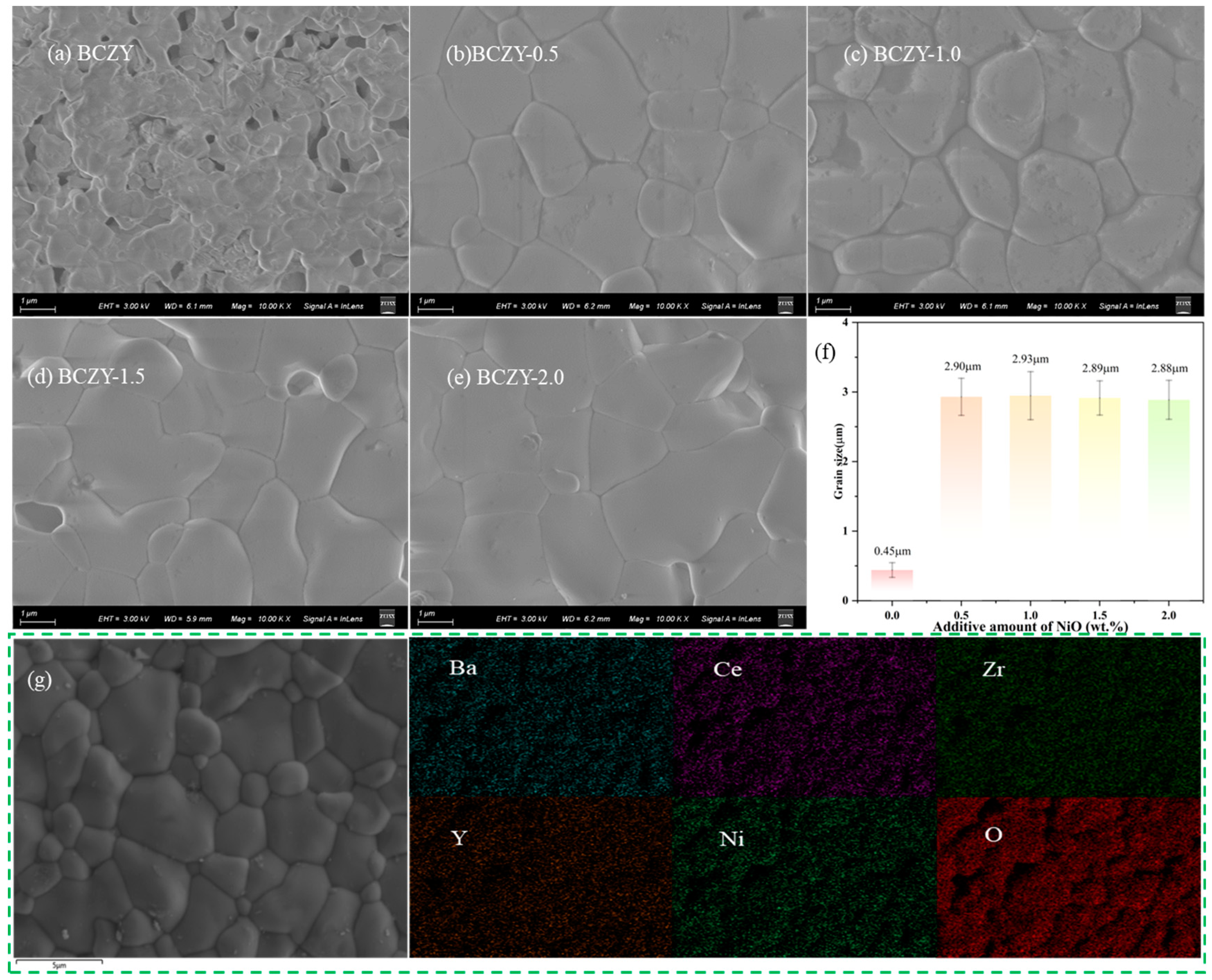
3.3. Surface Morphology
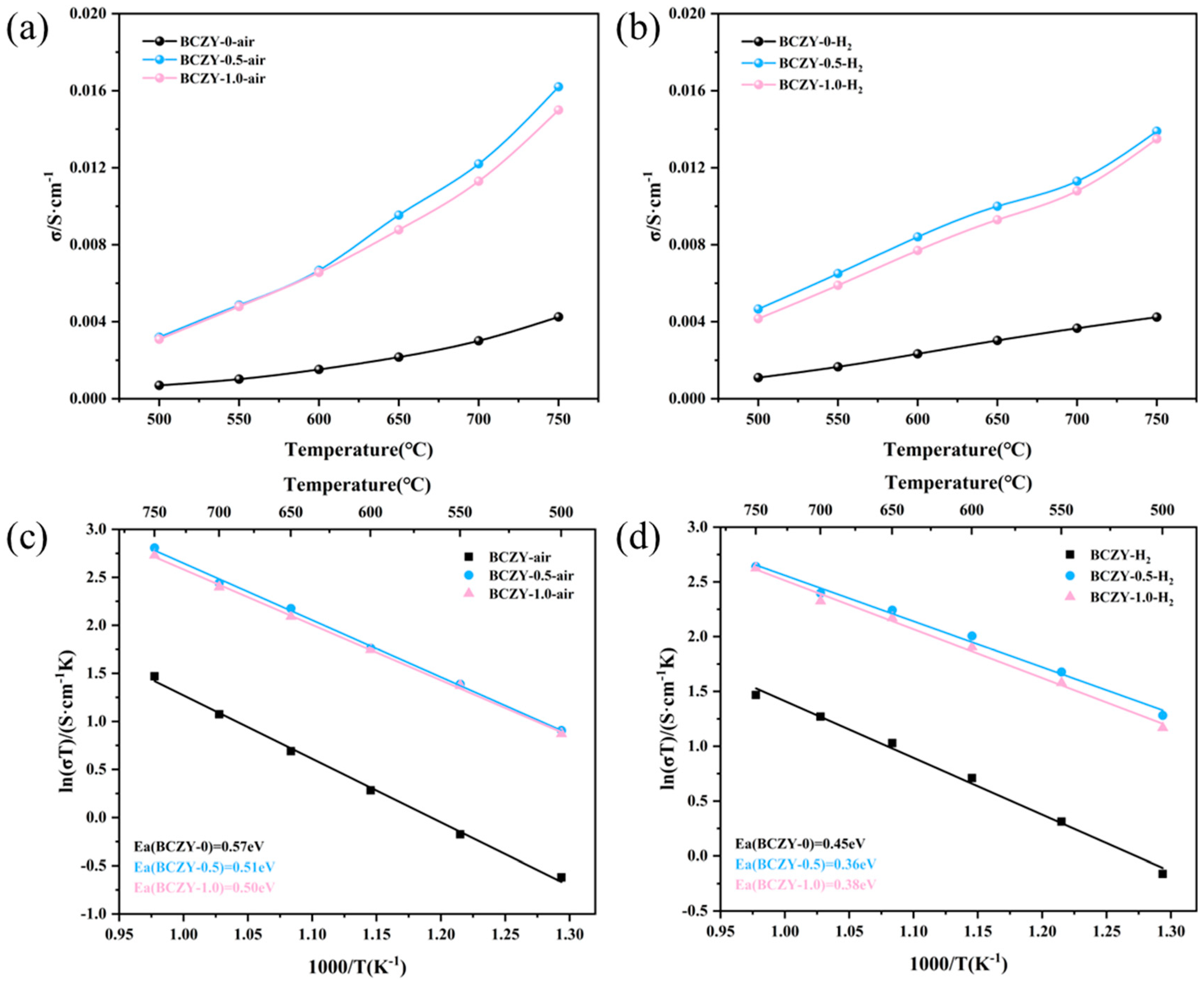
3.4. Conductivity
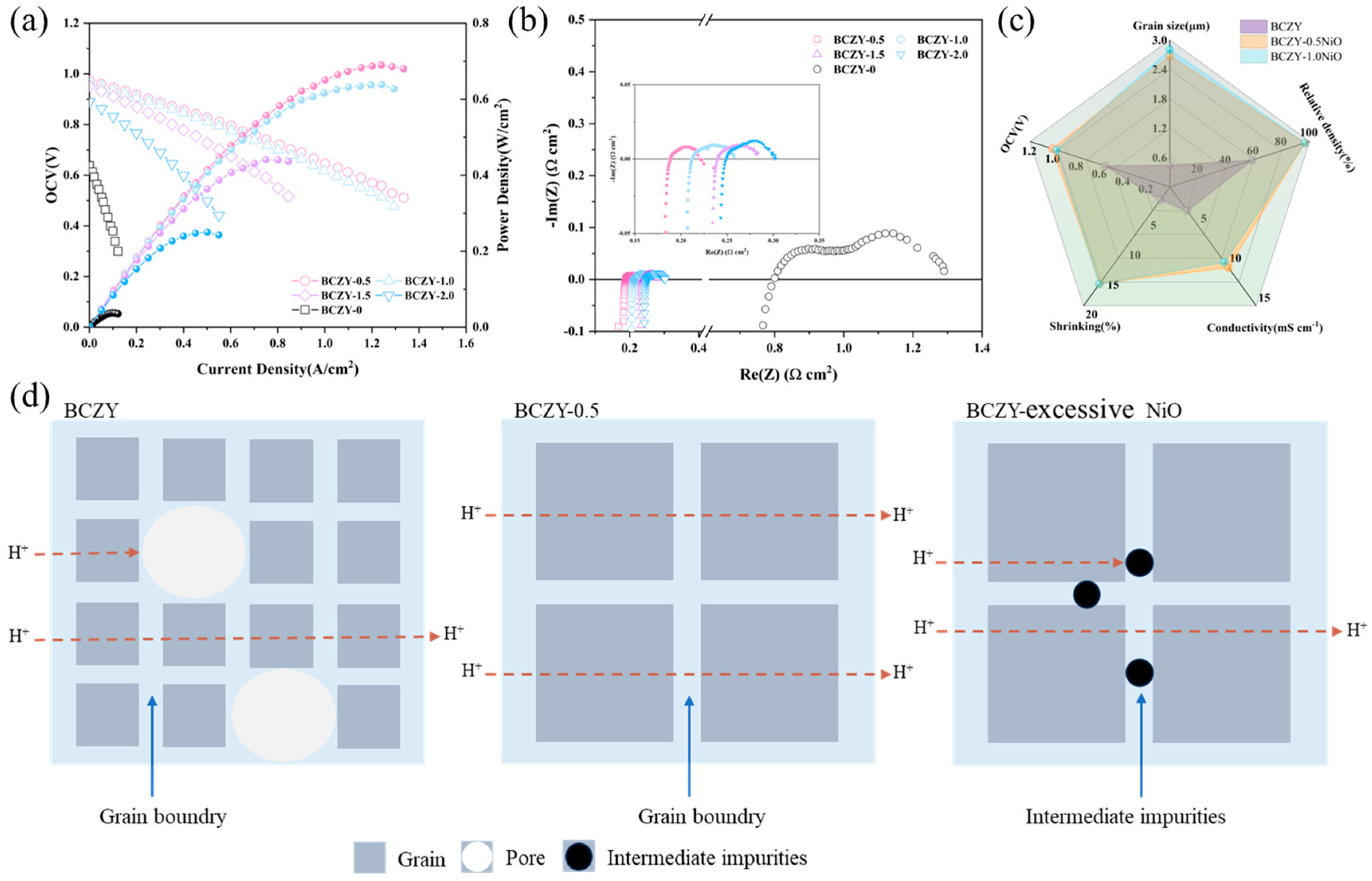
3.5. Electrochemical Performance of Single Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, M.; Shao, Z. Fuel cells that operate at 300° to 500 °C. Science 2020, 369, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Ji, Y.; Shao, Z. Perovskites for protonic ceramic fuel cells: A review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 2200–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Blinn, K.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, M. Enhanced sulfur and coking tolerance of a mixed ion conductor for SOFCs: BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2-xYbxO3-delta. Science 2009, 326, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Kucharczyk, C.J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Takeuchi, I.; Ji, H.-I.; Haile, S.M. Exceptional power density and stability at intermediate temperatures in protonic ceramic fuel cells. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papac, M.; Stevanović, V.; Zakutayev, A.; O’Hayre, R. Triple ionic–electronic conducting oxides for next-generation electrochemical devices. Nat. Mater. 2020, 20, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Leng, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhang, B.; Chu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, S. Synthesis and characterization of PrBa0.5Sr0·5Co2-xFexO5+δ (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0) as oxygen electrode for proton-conducting solid oxide cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 23655–23669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cadigan, C.; Duan, C.; Huang, J.; Bian, L.; Le, L.; Hernandez, C.H.; Avance, V.; O’Hayre, R.; Sullivan, N.P. Ammonia-fed reversible protonic ceramic fuel cells with Ru-based catalyst. Commun. Chem. 2021, 4, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Kee, R.; Zhu, H.; Sullivan, N.; Zhu, L.; Bian, L.; Jennings, D.; O’Hayre, R. Highly efficient reversible protonic ceramic electrochemical cells for power generation and fuel production. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatoo, M.A.; Habib, F.; Malik, A.H.; Qazi, M.J.; Ahmad, S.; Ganayee, M.A.; Ahmad, Z. Solid-oxide fuel cells: A critical review of materials for cell components. MRS Commun. 2023, 13, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikodemski, S.; Tong, J.; Duan, C.; O’Hayre, R. Ionic transport modification in proton conducting BaCe0.6Zr0.3Y0.1O3−δ with transition metal oxide dopants. Solid State Ion. 2016, 294, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Dai, M.; Chen, C.; Zhan, Z. Protonic ceramic cells with thin BaZr0.8Y0.2O3-δ electrolytes for stable separation of H2 from H2–CO2 mixtures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 12067–12073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, E.; Pergolesi, D.; D’Epifanio, A.; Di Bartolomeo, E.; Balestrino, G.; Licoccia, S.; Traversa, E. Design and fabrication of a chemically-stable proton conductor bilayer electrolyte for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells (IT-SOFCs). Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fop, S.; McCombie, K.S.; Wildman, E.J.; Skakle, J.M.S.; Irvine, J.T.S.; Connor, P.A.; Savaniu, C.; Ritter, C.; McLaughlin, A.C. High oxide ion and proton conductivity in a disordered hexagonal perovskite. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hua, B.; Luo, J.-l.; Jiang, S.P.; Pu, J.; Chi, B.; Jian, L. Carbon-tolerant Ni-based cermet anodes modified by proton conducting yttrium- and ytterbium-doped barium cerates for direct methane solid oxide fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21609–21617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, N.A.; Starostina, I.A.; Starostin, G.N.; Kasyanova, A.V.; Medvedev, D.A.; Shao, Z. Fundamental Understanding and Applications of Protonic Y- and Yb-Coped Ba(Ce,Zr)O3 Perovskites: State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhu, B.; Hong, L.; Xia, C.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Cai, H.; Rauf, S.; Huang, J.; Asghar, M.I.; et al. Designing High Interfacial Conduction beyond Bulk via Engineering the Semiconductor–Ionic Heterostructure CeO2−δ/BaZr0.8Y0.2O3 for Superior Proton Conductive Fuel Cell and Water Electrolysis Applications. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 15373–15384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Fabbri, E.; Bi, L.; Traversa, E.; Koc, R. Electrochemical Properties and Intermediate-Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Dense Yttrium-Doped Barium Zirconate with Calcium Addition. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 95, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Tang, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Yang, T.; Cheng, M.; Shao, Z. Preparation, characterization and application of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ for a high-performance and stable proton ceramic electrochemical cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 39747–39758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Lee, H.-W.; Kim, B.-K.; Son, J.-W.; Yoon, K.J.; Kim, H.; Shin, D.; Ji, H.-I.; Lee, J.-H. A 5 × 5 cm2 protonic ceramic fuel cell with a power density of 1.3 W cm–2 at 600 °C. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, B.; Besra, L.; Anwar, S.; Anwar, S. La2Ce2O7 based materials for next generation proton conducting solid oxide cells: Progress, opportunity and future prospects. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 28460–28501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bi, L.; Zhao, X.S. Exploring the role of NiO as a sintering aid in BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ electrolyte for proton-conducting solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2018, 399, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsmanand, E.D.; Lee, K.T. Lowering the Temperature of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Science 2011, 334, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Paik, J.; Kim, D.; Woo, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.; Lee, W. Exceptionally high performance of protonic ceramic fuel cells with stoichiometric electrolytes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 6476–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; An, J.; Liu, C. Stable and easily sintered BaCe0.5Zr0.3Y0.2O3−δ electrolytes using ZnO and Na2CO3 additives for protonic oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 95, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Seo, J.; Yu, J.H.; Yun, K.S.; Joo, J.H.; Moon, J.; Park, H.J. Effect of cerium on yttrium-doped barium zirconate with a ZnO sintering aid: Grain and grain boundary protonic conduction. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 32720–32726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babilo, P.; Haile, S.M. Enhanced Sintering of Yttrium-Doped Barium Zirconate by Addition of ZnO. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricote, S.; Bonanos, N. Enhanced sintering and conductivity study of cobalt or nickel doped solid solution of barium cerate and zirconate. Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Shen, Z.; Bokhari, A.; Ali, W.; Han, N. Effect of Co2O3 as sintering aid on perovskite BaCe0.8Y0.2O3-δ proton conductive membrane for hydrogen separation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 26551–26558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, J. Enhancing sinterability and electrochemical properties of Ba(Zr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2)O3-δ proton conducting electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells by addition of NiO. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 13501–13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, C.; Xu, Q.; Guo, M.; Bello, I.T.; Ni, M. Ethylene and power cogeneration from proton ceramic fuel cells (PCFC): A thermo-electrochemical modelling study. J. Power Sources 2022, 536, 231503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvonareva, I.; Fu, X.-Z.; Medvedev, D.; Shao, Z. Electrochemistry and energy conversion features of protonic ceramic cells with mixed ionic-electronic electrolytes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 439–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Kim, Y.-d.; Sanders, M.; Harvey, S.P.; Walker, M.; O’Hayre, R. Tuning the Co/Fe ratio in BaCoxFe0.8−xZr0.1Y0.1O3−δ, a promising triple ionic and electronic conducting oxide, to boost electrolysis and fuel cell performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 24839–24853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Akbar, M.; Jin, B.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Dong, W.; Afzal, M.; Wang, H.; Xia, C. Enhancing the Performance of the p-n Heterostructure Electrolyte for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells via A-Site-Deficiency Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 49154–49169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, W.; Wu, W.; Wang, B.; Tang, W.; Zhou, M.; Jin, C.; Ding, H.; Fan, W.; Dong, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Revitalizing interface in protonic ceramic cells by acid etch. Nature 2022, 604, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Gan, Y.; Yang, C.; Ren, C.; Xue, X. Fabrication and accelerated long-term stability test of asymmetrical hollow fiber-supported thin film oxygen separation membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 655, 120600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Clark, D.; Bernau, L.; Subramaniyan, A.; O’Hayre, R. Proton-conducting yttrium-doped barium cerate ceramics synthesized by a cost-effective solid-state reactive sintering method. Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Pang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Lei, Z.; Yang, Z. Structure, synthesis, properties and solid oxide electrolysis cells application of Ba(Ce, Zr)O3 based proton conducting materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, D.; Wang, K.; Xu, Q. Densification and electrical conducting behavior of BaZr0.9Y0.1O3-δ proton conducting ceramics with NiO additive. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, L.; Yu, S.; Xu, H.; Hao, X.; Sun, Y.; He, T. Effect of Two Different ZnO Addition Strategies on the Sinterability and Conductivity of the BaZr0.4Ce0.4Y0.2O3−δ Proton-Conducting Ceramic Electrolyte. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 3369–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, D.; Guan, R.; Kong, D.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, Z.; He, T. Sn–Dy–Cu Triply Doped BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3−δ: A Chemically Stable and Highly Proton-Conductive Electrolyte for Low-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 5352–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, G.; Lei, Y.; Yaowen, W.; Youcheng, X.; Rui, G.; Mengjiao, W.; Tianmin, H. Enhanced sintering and electrical properties of proton-conducting electrolytes through Cu doping in BaZr0.5Ce0.3Y0.2O3-δ. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 11793–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shi, Z.; Liu, M.; Bi, L.; Liu, W. An Easily Sintered, Chemically Stable, Barium Zirconate-Based Proton Conductor for High-Performance Proton-Conducting Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5695–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. A comparative investigation on protonic ceramic fuel cell electrolytes BaZr0.8Y0.2O3-δ and BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3-δ with NiO as sintering aid. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17208–17216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; He, B.; Wang, R.; Ling, Y.; Zhao, L. Effect of Co doping on sinterability and protonic conductivity of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3−δ for protonic ceramic fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 347, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Dong, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z. Achieving Robust Redox Stability of SOFC through Ni-YSZ Anode Layer Thinning and Inert Support Mechanical Compensation. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 5822–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Han, C.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, C.; Chen, C.; Lin, L.; Cai, G.; Jiang, L. Site-oriented design of spinel MgxNiMn2-xO4-δ as cathode material of intermediate-temperature direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2021, 503, 230020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Khan, K.; Wu, H.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, B. Enhanced ORR activity of A-site deficiency engineered BaCo0·4Fe0·4Zr0·1Y0·1O3-δ cathode in practical YSZ fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 5593–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, T.; Wang, H.; Yu, S.; Bi, L. Microwave sintering coupled with sintering aids for proton-conducting oxide membranes. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 19561–19568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Sunarso, J.; Song, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhang, J.; Gu, B.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. New reduced-temperature ceramic fuel cells with dual-ion conducting electrolyte and triple-conducting double perovskite cathode. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 13265–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

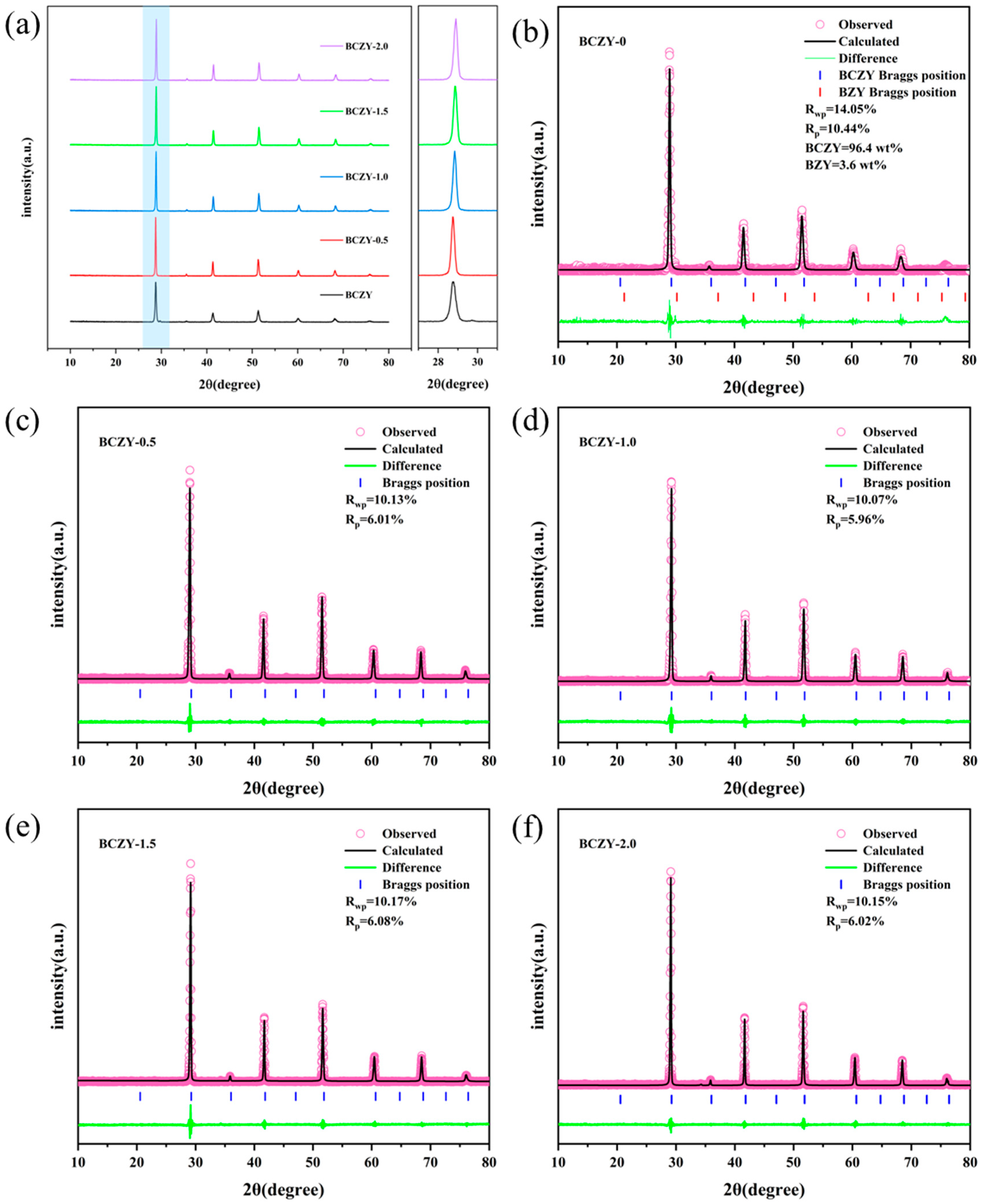

| Samples | Space Group | a (Å) | V (Å3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCZY-0 | Pm-3m | 4.3736 | 83.66 |
| BCZY-0.5 | Pm-3m | 4.3692 | 83.41 |
| BCZY-1.0 | Pm-3m | 4.3611 | 82.95 |
| BCZY-1.5 | Pm-3m | 4.3576 | 82.74 |
| BCZY-2.0 | Pm-3m | 4.3531 | 82.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, C.; Zhao, B.; Meng, X.; Ye, X.; Luo, T.; Xin, X.; Wen, Z. Effect of NiO Addition on the Sintering and Electrochemical Properties of BaCe0.55Zr0.35Y0.1O3-δ Proton-Conducting Ceramic Electrolyte. Membranes 2024, 14, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14030061
Peng C, Zhao B, Meng X, Ye X, Luo T, Xin X, Wen Z. Effect of NiO Addition on the Sintering and Electrochemical Properties of BaCe0.55Zr0.35Y0.1O3-δ Proton-Conducting Ceramic Electrolyte. Membranes. 2024; 14(3):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14030061
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Chengxin, Bingxiang Zhao, Xie Meng, Xiaofeng Ye, Ting Luo, Xianshuang Xin, and Zhaoyin Wen. 2024. "Effect of NiO Addition on the Sintering and Electrochemical Properties of BaCe0.55Zr0.35Y0.1O3-δ Proton-Conducting Ceramic Electrolyte" Membranes 14, no. 3: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14030061
APA StylePeng, C., Zhao, B., Meng, X., Ye, X., Luo, T., Xin, X., & Wen, Z. (2024). Effect of NiO Addition on the Sintering and Electrochemical Properties of BaCe0.55Zr0.35Y0.1O3-δ Proton-Conducting Ceramic Electrolyte. Membranes, 14(3), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14030061






