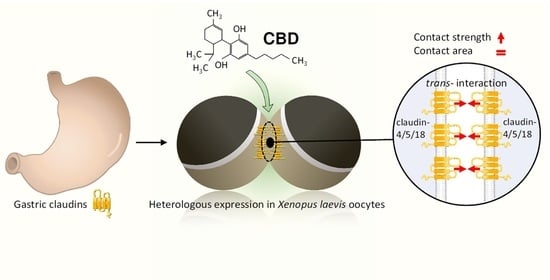
Cannabidiol Strengthening of Gastric Tight Junction Complexes Analyzed in an Improved Xenopus Oocyte Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Oocyte Harvesting
2.4. cRNA Preparation and Injection
2.5. Protein Extraction of the Oocyte Membrane Fractions
2.6. Protein Extraction of Stomach Tissue
2.7. Immunoblotting of Oocyte Membrane Fractions and Stomach Tissue
2.8. Immunohistochemistry of Oocytes and Porcine Stomach Tissue
2.9. Paired Oocyte Assay with CBD Treatment: Contact Area Monitoring
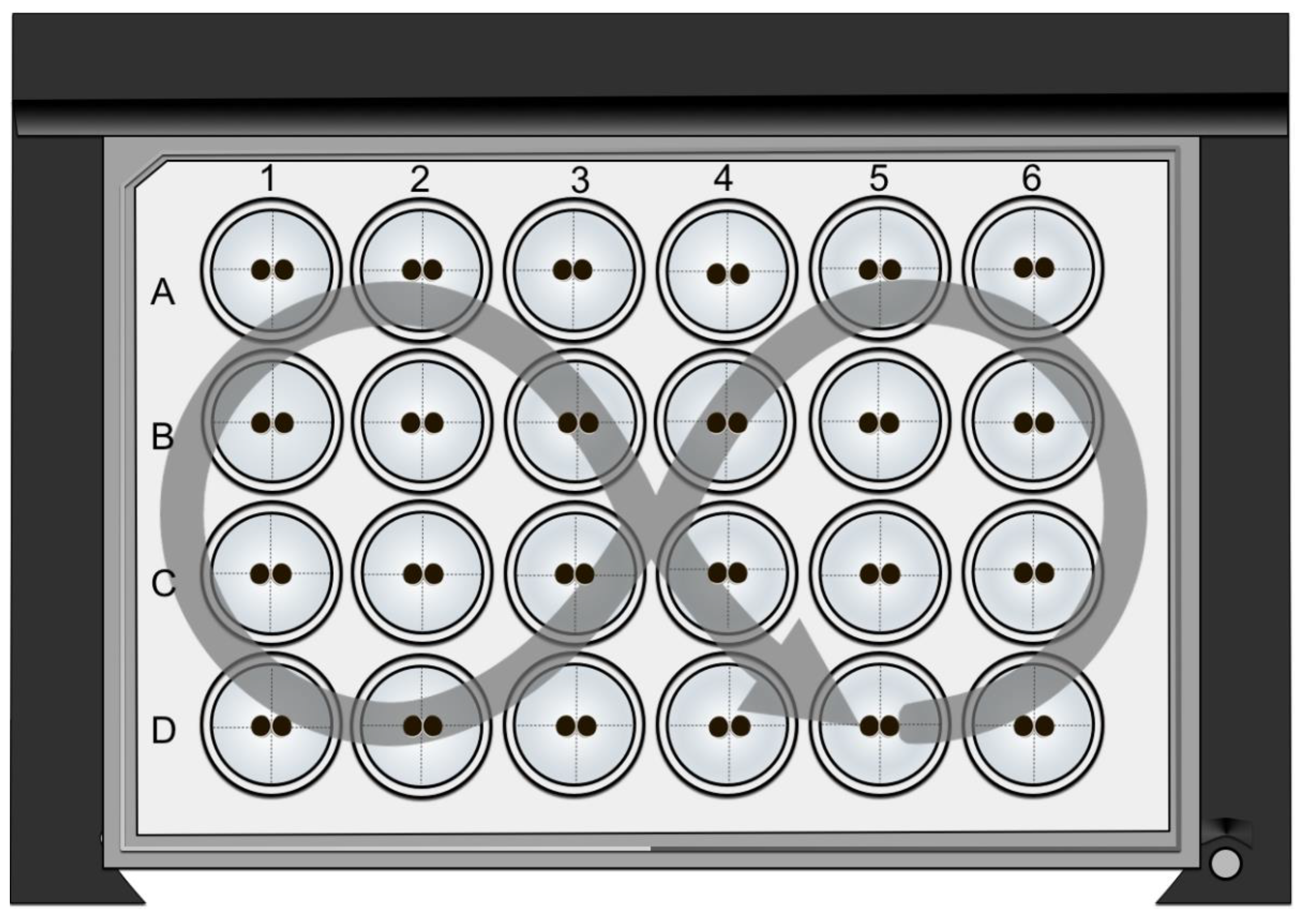
2.10. Double Orbital Challenge Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
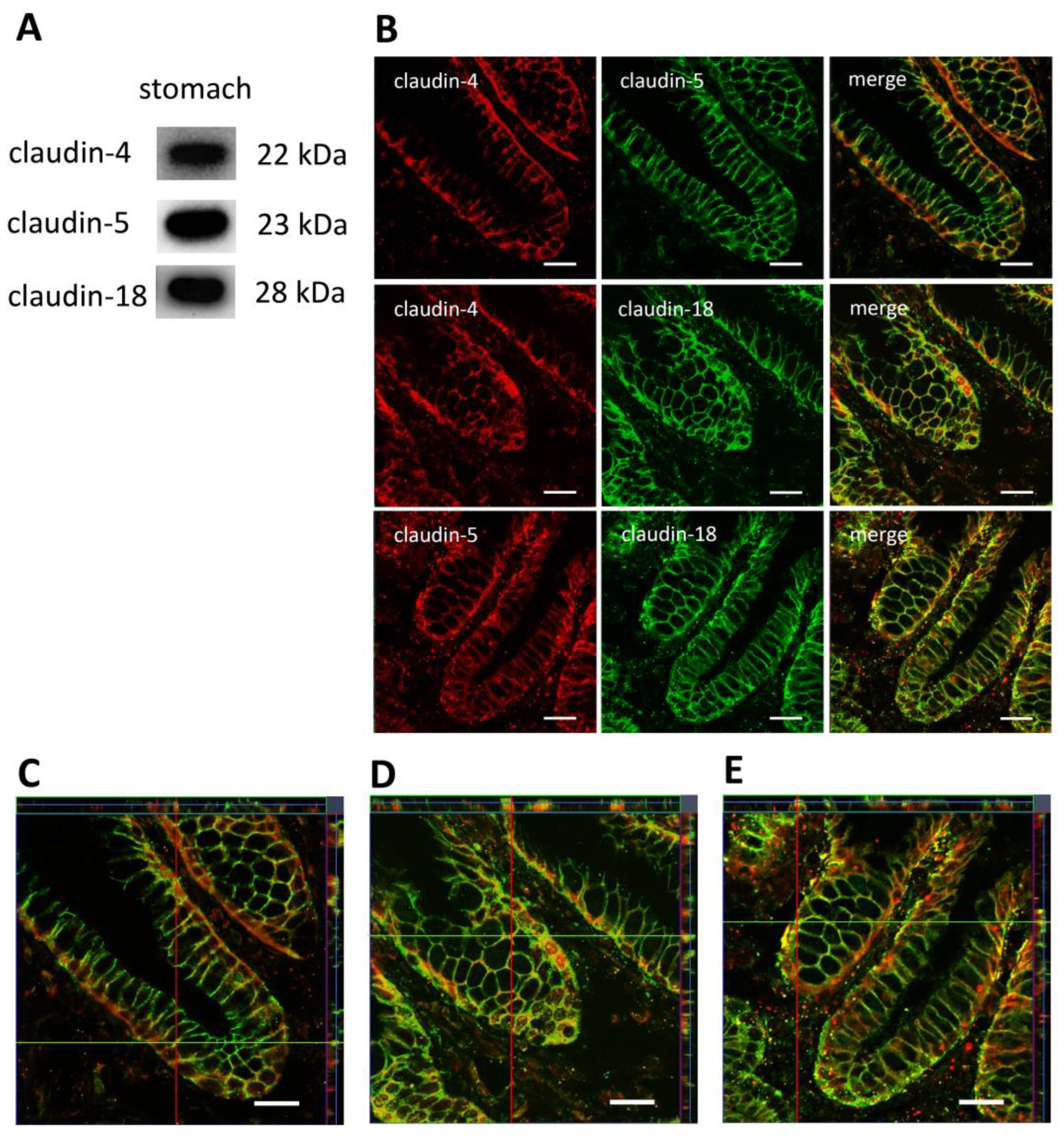
3.1. Expression of Claudins in the Stomach
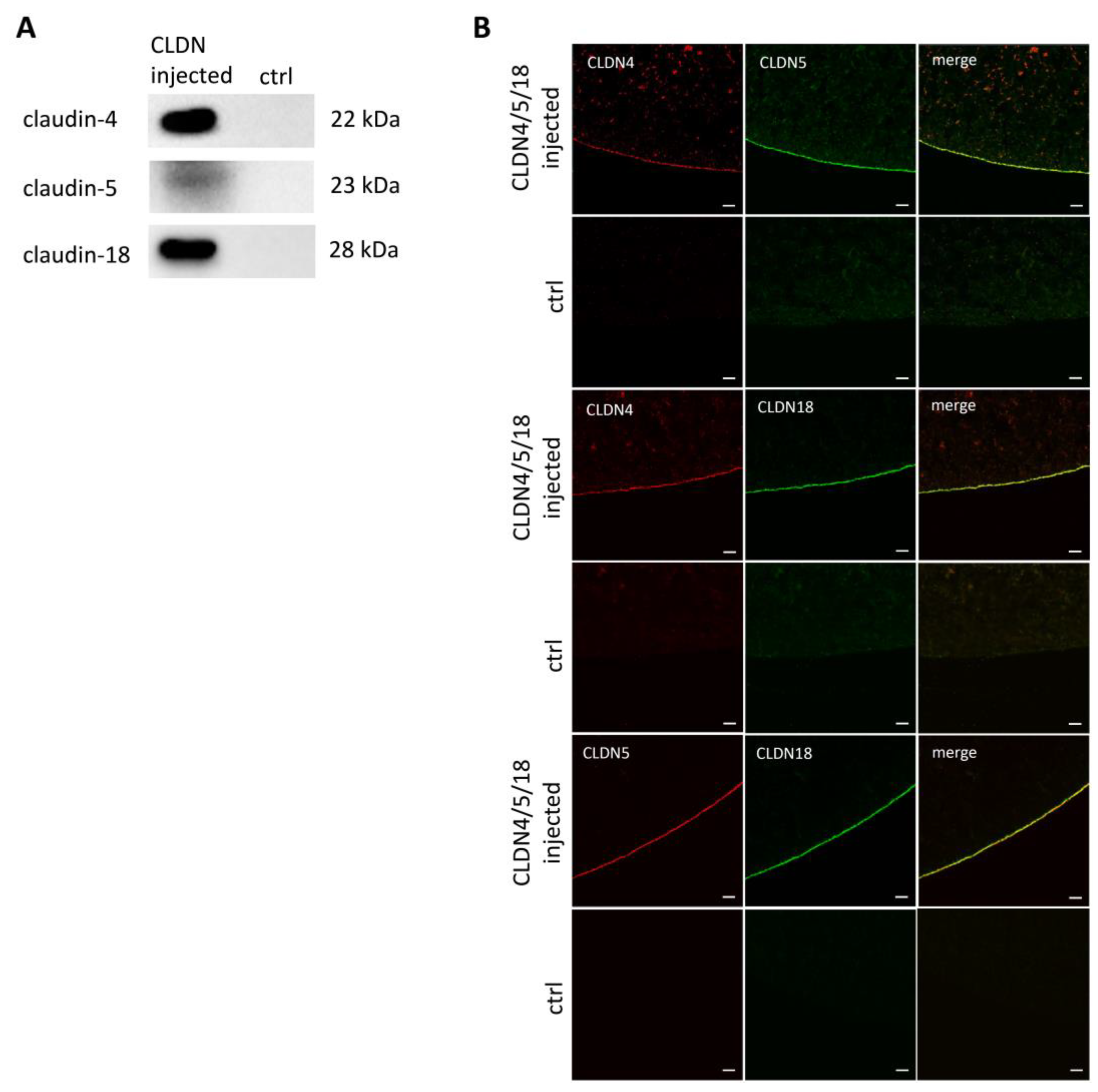
3.2. Heterologous Expression of Three Gastric Claudins in the Oocyte Membrane
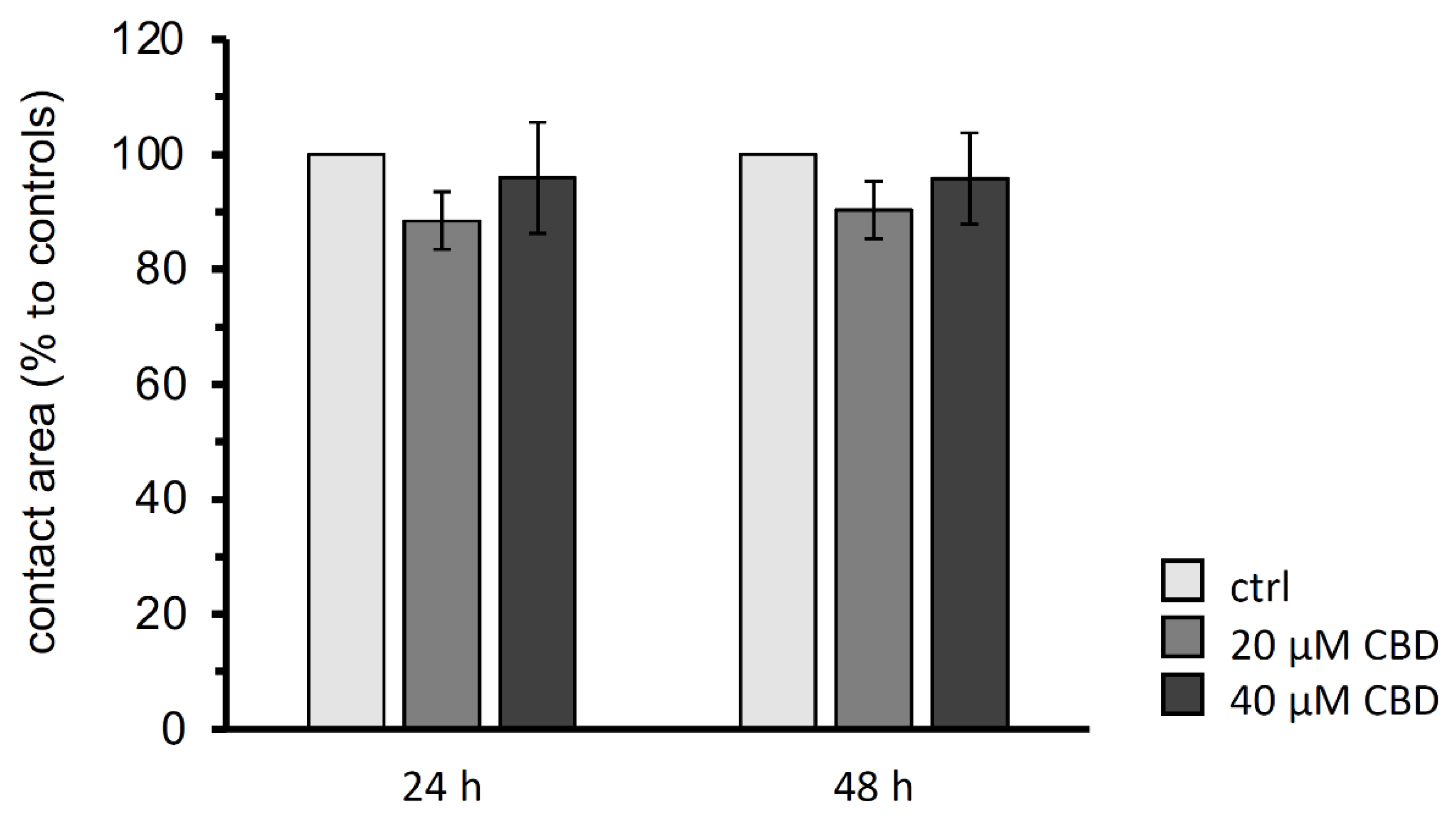
3.3. Paired Oocyte Assay for Contact Area Analysis
3.4. Double Orbital Challenge for Quantification of Contact Area Strength
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gurdon, J.B.; Lane, C.D.; Woodland, H.R.; Marbaix, G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature 1971, 233, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dascal, N.; Lotan, I. Expression of exogenous ion channels and neurotransmitter receptors in RNA-injected Xenopus oocytes. Protoc. Mol. Neurobiol. 1992, 13, 205–225. [Google Scholar]
- Keiper, B. Translation of mRNAs in Xenopus Oocytes. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Nature Publishing Company: London, UK, 2003; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Amasheh, S.; Wenzel, U.; Weber, W.M.; Clauss, W.; Daniel, H. Electrophysiological analysis of the function of the mammalian renal peptide transporter expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J. Physiol. 1997, 504, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasheh, S.; Wenzel, U.; Boll, M.; Dorn, D.; Weber, W.; Clauss, W.; Daniel, H. Transport of charged dipeptides by the intestinal H+/peptide symporter PepT1 expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J. Membr. Biol. 1997, 155, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reifarth, F.W.; Amasheh, S.; Clauss, W.; Weber, W. The Ca2+-inactivated Cl- channel at work: Selectivity, blocker kinetics and transport visualization. J. Membr. Biol. 1997, 155, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, K.I.; Jordan, J.R.; Beyer, E.C.; Paul, D.L. Formation of gap junctions by expression of connexins in Xenopus oocyte pairs. Cell 1989, 57, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, P.; Stebbings, L.A.; Baines, R.A.; Bacon, J.P.; Davies, J.A.; Ford, C. Drosophila Shaking-B protein forms gap junctions in paired Xenopus oocytes. Nature 1998, 391, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.A.; Friedrich, B.; Setiawan, I.; Lang, F.; Bröer, S. The use of Xenopus laevis oocytes for the functional characterization of heterologously expressed membrane proteins. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitzthum, C.; Stein, L.; Brunner, N.; Knittel, R.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Amasheh, S. Xenopus oocytes as a heterologous expression system for analysis of tight junction proteins. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 5312–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, N.; Stein, L.; Cornelius, V.; Knittel, R.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Amasheh, S. Blood-Brain Barrier Protein Claudin-5 Expressed in Paired Xenopus laevis Oocytes Mediates Cell-Cell Interaction. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, Y.; Wang, Z.W. Recording Gap Junction Current from Xenopus Oocytes. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 179, 63361. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, L.; Brunner, N.; Amasheh, S. Functional Analysis of Gastric Tight Junction Proteins in Xenopus laevis Oocytes. Membranes 2022, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, N.; Stein, L.; Amasheh, S. Cellular Distribution Pattern of tjp1 (ZO-1) in Xenopus laevis Oocytes Heterologously Expressing Claudins. J. Membr. Biol. 2023, 256, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 403–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piontek, J.; Winkler, L.; Wolburg, H.; Müller, S.L.; Zuleger, N.; Piehl, C.; Wiesner, B.; Krause, G.; Blasig, I.E. Formation of tight junction: Determinants of homophilic interaction between classic claudins. FASEB J. 2008, 1, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, T.; Furuse, M. Tight Junction Structure and Function Revisited. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 10, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, T.J.; Scott, K.E.; Fox, J.G.; Hagen, S.J. Tight junction disruption: Helicobacter pylori and dysregulation of the gastric mucosal barrier. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11411–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahner, C.; Mitic, L.L.; Anderson, J.M. Heterogeneity in expression and subcellular localization of claudins 2, 3, 4, and 5 in the rat liver, pancreas, and gut. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimi, T.; Nagashima, K.; Ward, J.M.; Minoo, P.; Zimonjic, D.B.; Popescu, N.C.; Kimura, S. Claudin-18, a Novel Downstream Target Gene for the T/EBP/NKX2.1 Homeodomain Transcription Factor, Encodes Lung- and Stomach-Specific Isoforms through Alternative Splicing. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 7380–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, A.; Yamazaki, Y.; Hayashi, D.; Suzuki, K.; Sentani, K.; Yasui, W.; Tsukita, S. Claudin-based paracellular proton barrier in the stomach. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1258, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Hernandez, V.; Quiros, M.; Nusrat, A. Intestinal epithelial claudins: Expression and regulation in homeostasis and inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1397, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Stüben, M.; Scheid, P. Demonstration of a pH gradient in the gastric gland of the acid-secreting guinea pig mucosa. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 279, G597–G604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forooghi Nia, F.; Rahmati, A.; Ariamanesh, M.; Saeidi, J.; Ghasemi, A.; Mohtashami, M. The Anti-Helicobacter pylori effects of Limosilactobacillus reuteri strain 2892 isolated from Camel milk in C57BL/6 mice. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, E.; Droessler, L.; Amasheh, S. Cannabidiol attenuates inflammatory impairment of intestinal cells expanding biomaterial-based therapeutic approaches. Mater. Today Bio. 2023, 23, 100808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M.; Itoh, M. Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 4, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radloff, J.; Falchuk, E.L.; Markov, A.G.; Amasheh, S. Molecular Characterization of Barrier Properties in Follicle-Associated Epithelium of Porcine Peyer’s Patches Reveals Major Sealing Function of Claudin-4. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasheh, S.; Schmidt, T.; Mahn, M.; Florian, P.; Mankertz, J.; Tavalali, S.; Gitter, A.H.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M. Contribution of claudin-5 to barrier properties in tight junctions of epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 321, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T.; Hata, M.; Gotoh, S.; Seo, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, D.; Tamura, A.; Tanaka, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, K.; Sentani, K.; Yasui, W.; Rakugi, H.; et al. Deficiency of claudin-18 causes paracellular H+ leakage, up-regulation of interleukin-1β, and atrophic gastritis in mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Sentani, K.; Tanaka, H.; Yano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Oshima, M.; Yasui, W.; Tamura, A.; Tsukita, S. Deficiency of Stomach-Type Claudin-18 in Mice Induces Gastric Tumor Formation Independent of H. pylori Infection. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovov, B.; Van Itallie, C.M.; Shaheen, N.J.; Carson, J.L.; Gambling, T.M.; Anderson, J.M.; Orlando, R.C. Claudin-18: A dominant tight junction protein in Barrett’s esophagus and likely contributor to its acid resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G1106–G1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, D.; Esposito, G.; Cirillo, C.; Cipriano, M.; De Winter, B.Y.; Scuderi, C.; Sarnelli, G.; Cuomo, R.; Steardo, L.; De Man, J.G.; et al. Cannabidiol reduces intestinal inflammation through the control of neuroimmune axis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, S. Cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogs: A review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigli, S.; Seguella, L.; Pesce, M.; Bruzzese, E.; D’Alessandro, A.; Cuomo, R.; Steardo, L.; Sarnelli, G.; Esposito, G. Cannabidiol restores intestinal barrier dysfunction and inhibits the apoptotic process induced by Clostridium difficile toxin A in Caco-2 cells. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.; Neuman, M.G. Cannabis and the gastrointestinal tract. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 23, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffolo, G.; Gaeta, A.; Cannata, B.; Pinzaglia, C.; Aronica, E.; Morano, A.; Cifelli, P.; Palma, E. GABAergic Neurotransmission in Human Tissues Is Modulated by Cannabidiol. Life 2022, 12, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, O. Gastric acid inhibitory and gastric protective effects of Cannabis and cannabinoids. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adejumo, A.C.; Akanbi, O.; Adejumo, K.L.; Bukong, T.N. Reduced Risk of Alcohol-Induced Pancreatitis with Cannabis Use. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayar, S.; Memarpoor-Yazdi, M.; Makky, A.; Eslami Sarokhalil, R.; D’Avanzo, N. Direct Regulation of Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic-Nucleotide Gated (HCN1) Channels by Cannabinoids. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 848540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.L.; Sudlow, L.C.; Berezin, M.Y. Using Xenopus oocytes in neurological disease drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stein, L.; Vollstaedt, M.-L.; Amasheh, S. Cannabidiol Strengthening of Gastric Tight Junction Complexes Analyzed in an Improved Xenopus Oocyte Assay. Membranes 2024, 14, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14010018
Stein L, Vollstaedt M-L, Amasheh S. Cannabidiol Strengthening of Gastric Tight Junction Complexes Analyzed in an Improved Xenopus Oocyte Assay. Membranes. 2024; 14(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleStein, Laura, Marie-Luise Vollstaedt, and Salah Amasheh. 2024. "Cannabidiol Strengthening of Gastric Tight Junction Complexes Analyzed in an Improved Xenopus Oocyte Assay" Membranes 14, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14010018
APA StyleStein, L., Vollstaedt, M.-L., & Amasheh, S. (2024). Cannabidiol Strengthening of Gastric Tight Junction Complexes Analyzed in an Improved Xenopus Oocyte Assay. Membranes, 14(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14010018