Influence of Membrane Asymmetry on OmpF Insertion, Orientation and Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
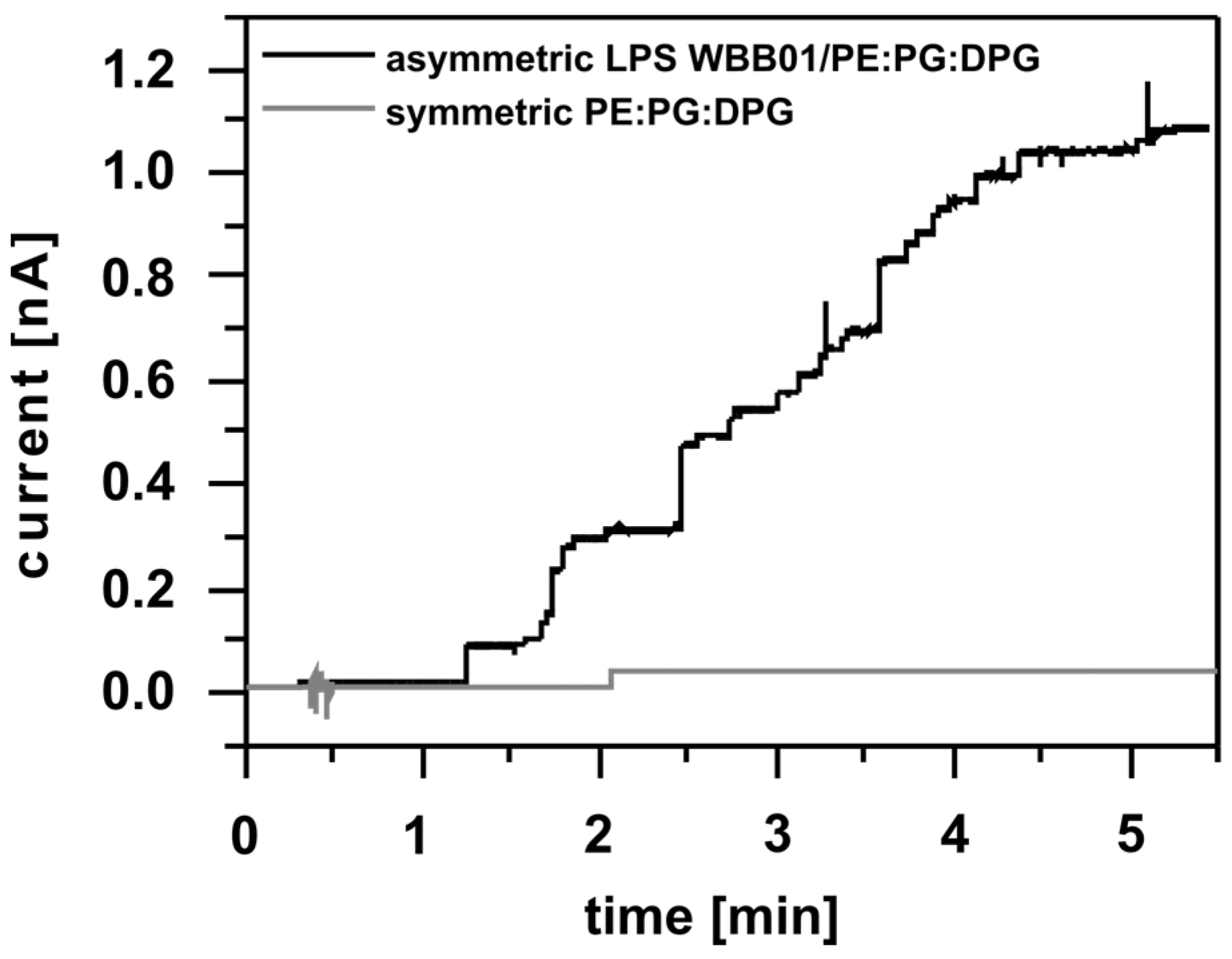
3.1. Insertion of OmpF into the Membranes
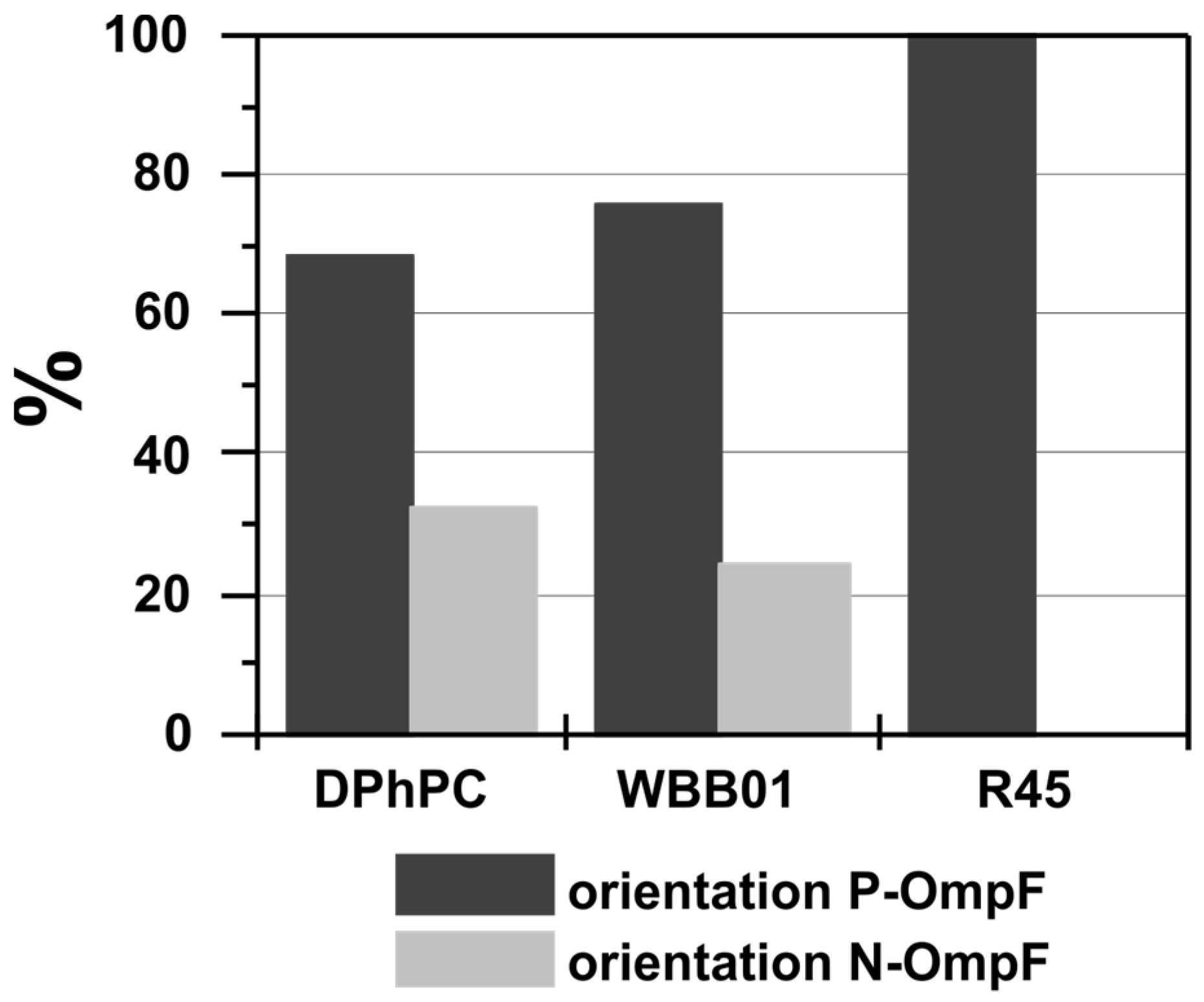
3.2. Oriented Insertion of OmpF into the Membranes
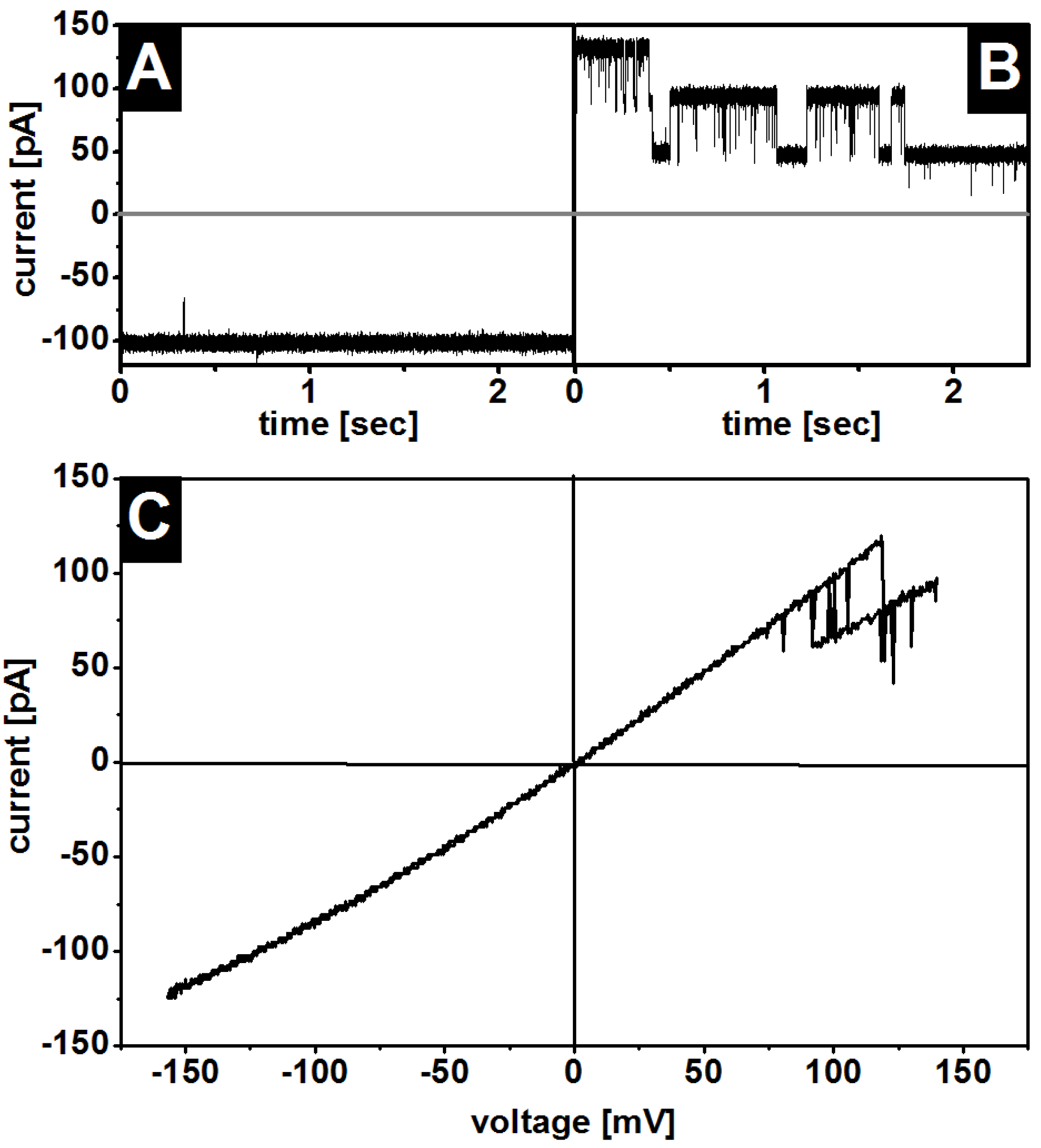
3.3. Gating
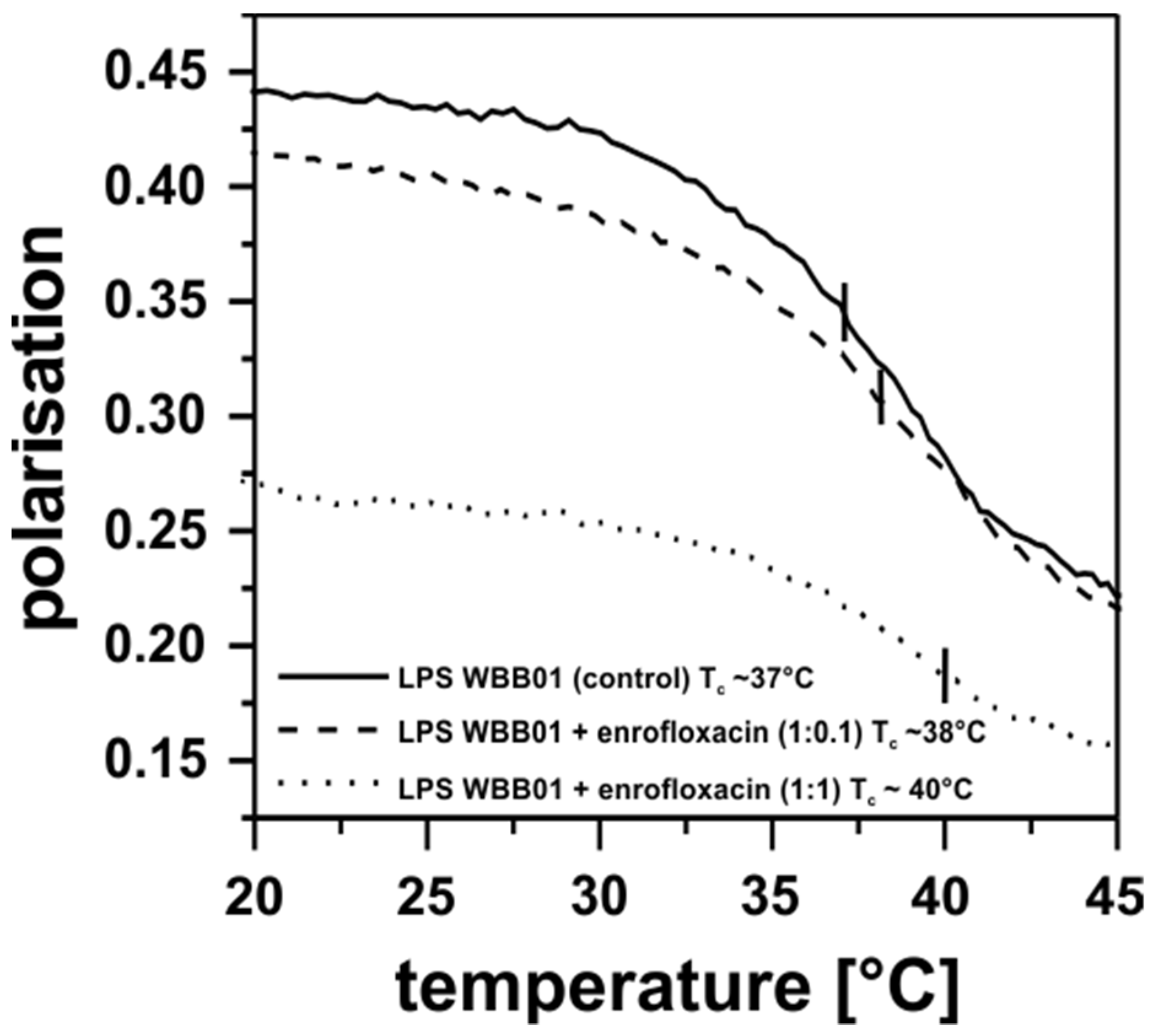
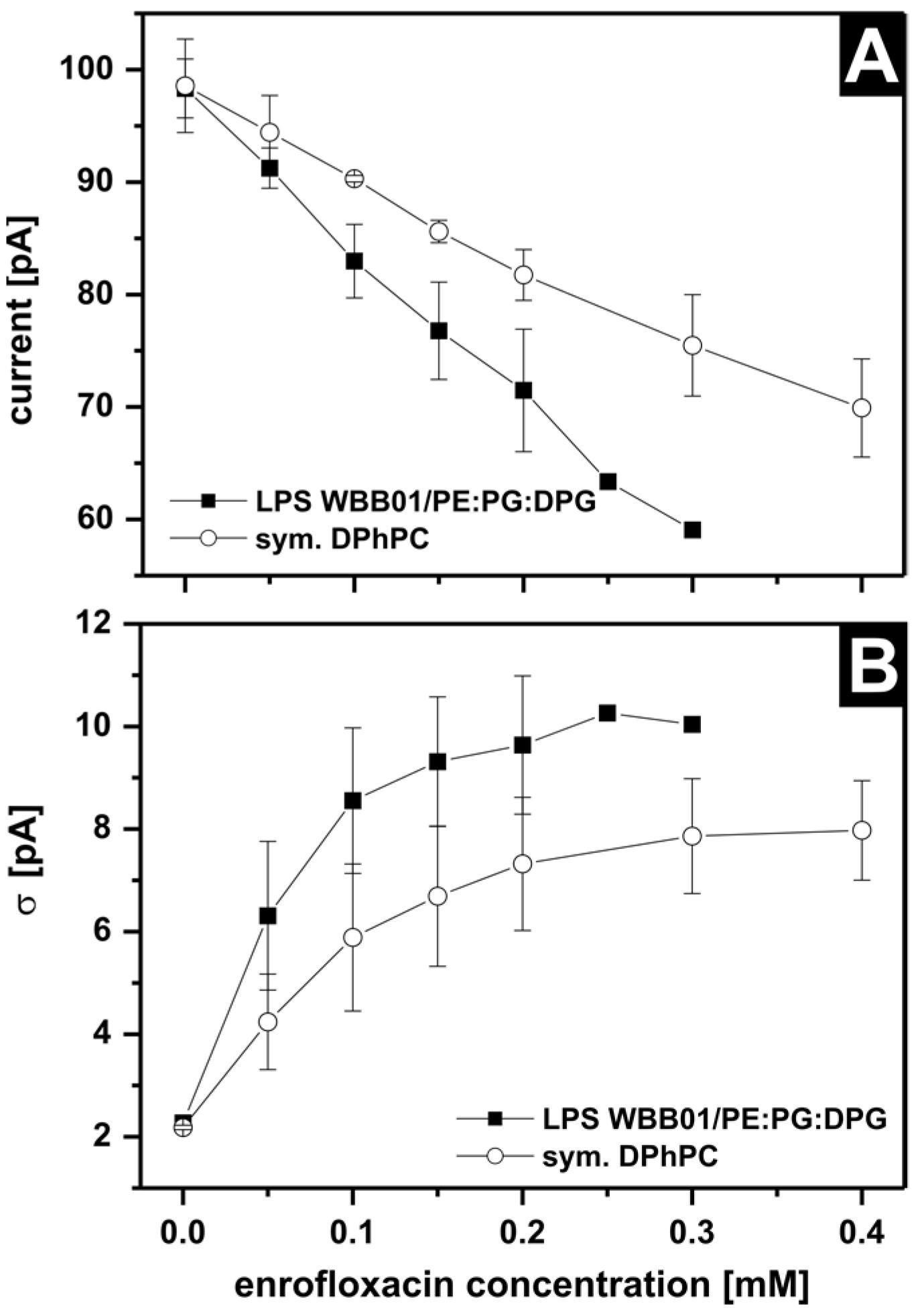
3.4. Antibiotic Interaction with Lipid Membranes
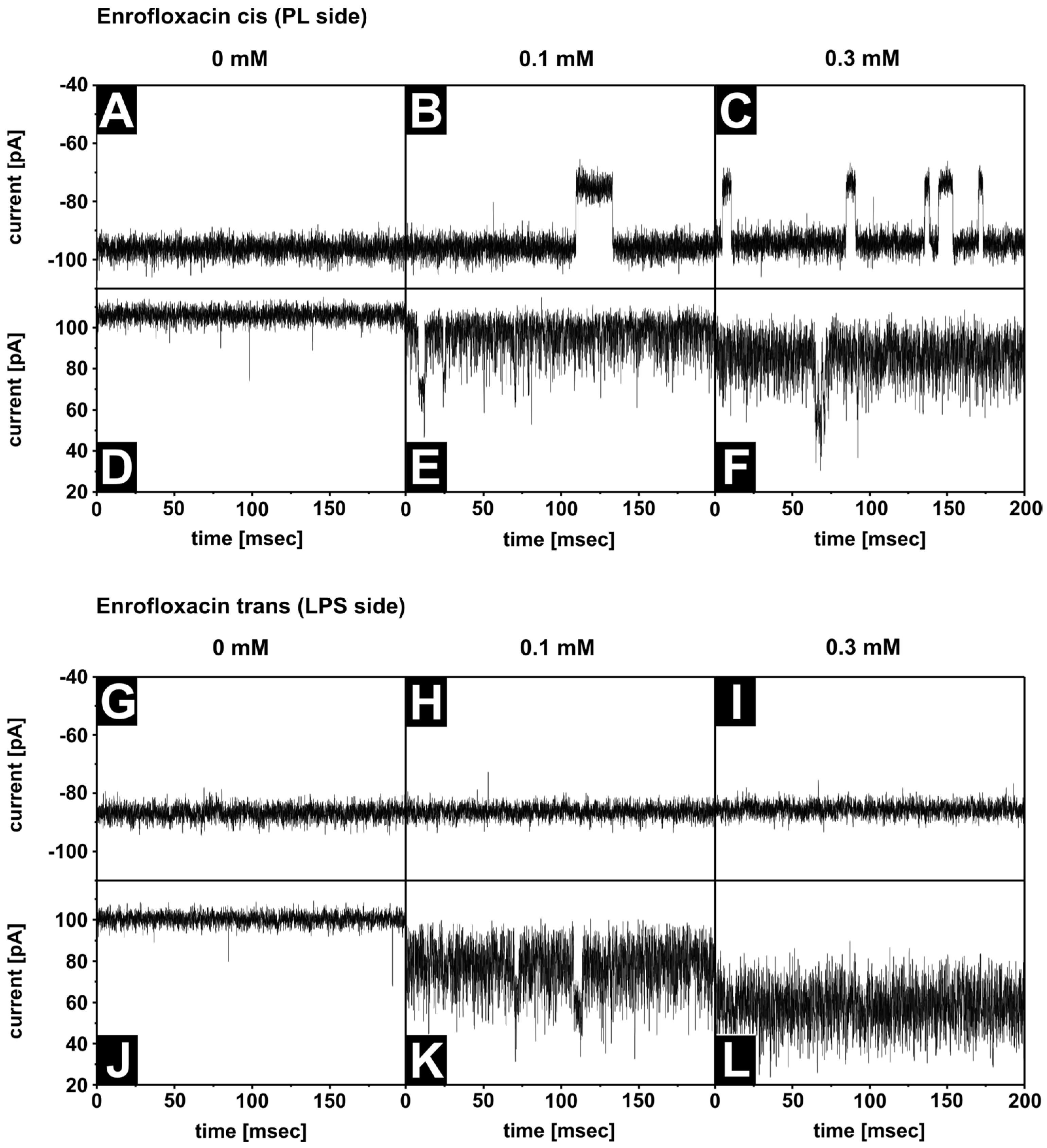
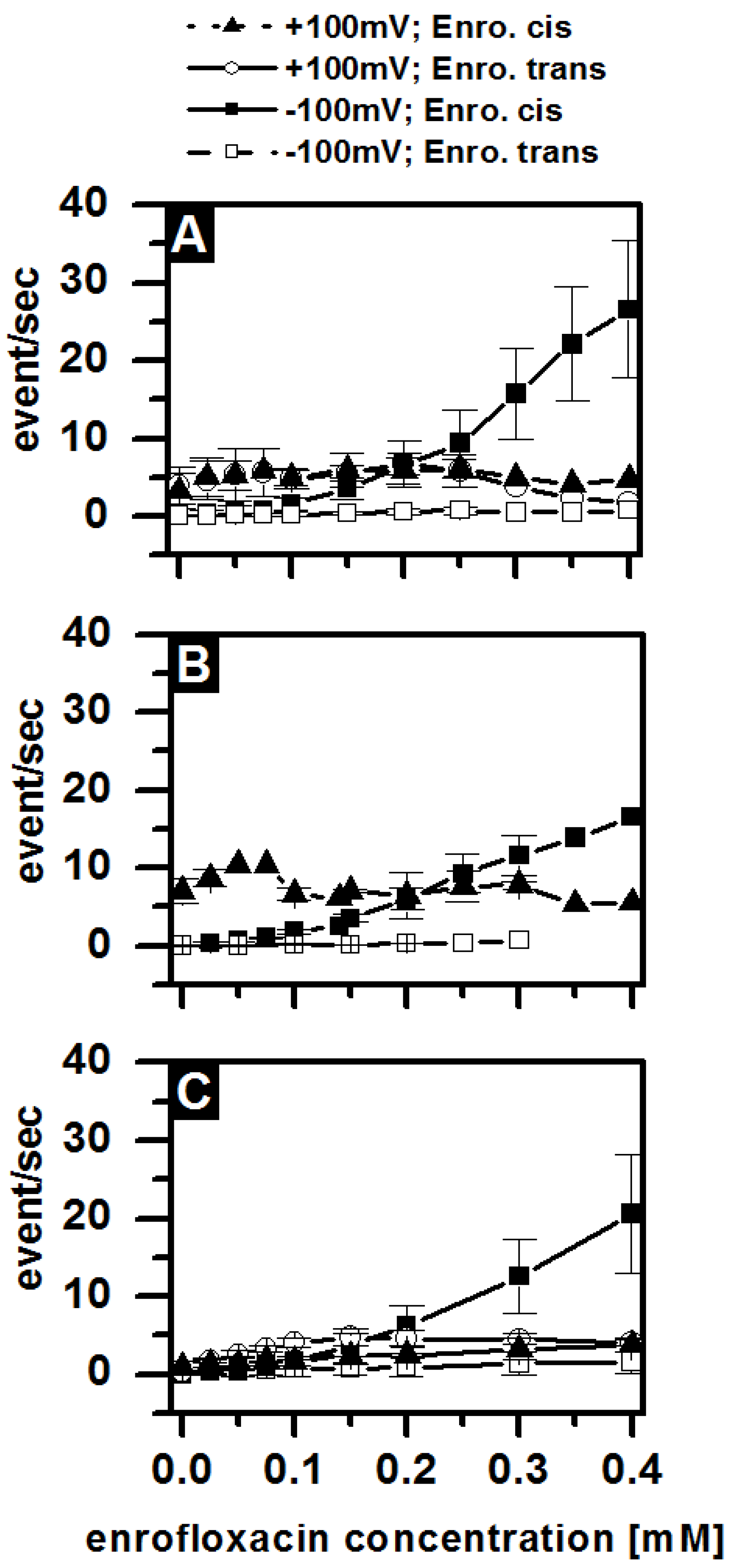
3.5. Antibiotic Interaction with OmpF
3.6. Antimicrobial Test
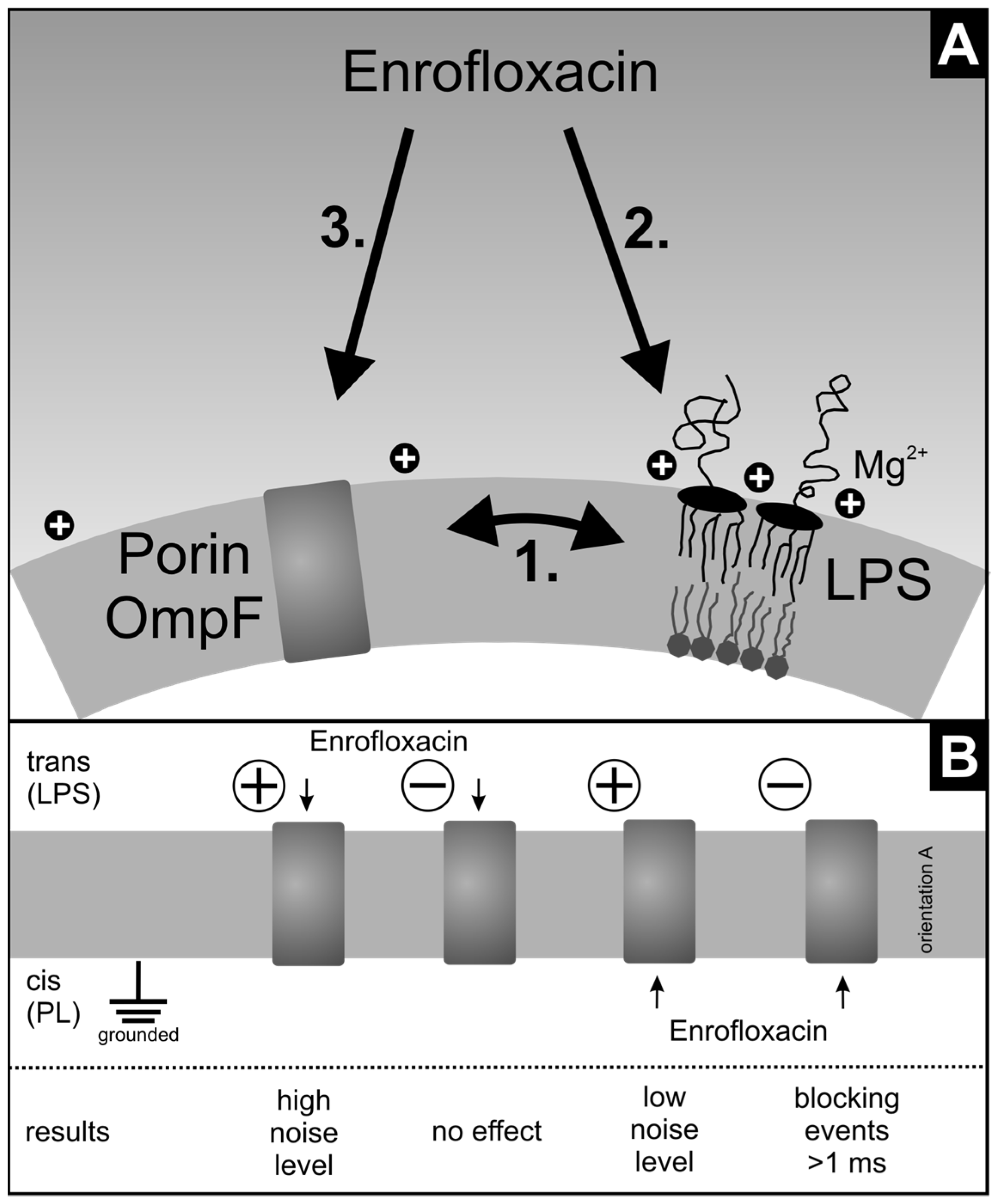
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pagès, J.M.; James, C.E.; Winterhalter, M. The porin and the permeating antibiotic: A selective diffusion barrier in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcour, A.H. Solute uptake through general porins. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, d1055–d1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, H. Molecular Basis of Bacterial Outer Membrane Permeability Revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 593–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, K.; Aoyama, H.; Irikura, T.; Iyobe, S.; Mitsuhashi, S. Differences in susceptibility to quinolones of outer membrane mutants of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1986, 29, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, K.; Aoyama, H.; Suzue, S.; Irikura, T.; Iyobe, S.; Mitsuhashi, S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1986, 30, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.C.; Wolfson, J.S.; Souza, K.S.; Tung, C.; McHugh, G.L.; Swartz, M.N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1986, 29, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, M.; Vergalli, J.; Ghai, I.; Barba-Bon, A.; Schembri, T.; Nau, W.M.; Lafitte, D.; Winterhalter, M.; Pagès, J.M. Cephalosporin translocation across enterobacterial OmpF and OmpC channels, a filter across the outer membrane. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, K.R.; Kreir, M.; Weingart, H.; Fertig, N.; Winterhalter, M. Permeation of antibiotics through Escherichia coli OmpF and OmpC porins: Screening for influx on a single-molecule level. J. Biomol. Screen. 2010, 15, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.R.; Ceccarelli, M.; Lovelle, M.; Winterhalter, M.; Mahendran, K.R. Antibiotic Permeation across the OmpF Channel: Modulation of the Affinity Site in the Presence of Magnesium. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 4433–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, K.R.; Hajjar, E.; Mach, T.; Lovelle, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Sousa, I.; Spiga, E.; Weingart, H.; Gameiro, P.; et al. Molecular basis of enrofloxacin translocation through OmpF, an outer membrane channel of Escherichia coli—When binding does not imply translocation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 5170–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, J.D.; Kleinekathöfer, U.; Winterhalter, M. How to Enter a Bacterium: Bacterial Porins and the Permeation of Antibiotics. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 5158–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauser, A.; Schroeder, I.; Gutsmann, T.; Cosentino, C.; Moroni, A.; Hansen, U.P.; Winterhalter, M. Modulation of enrofloxacin binding in OmpF by Mg2+ as revealed by the analysis of fast flickering single-porin current. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012, 140, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Terrasse, R.; Bafna, J.A.; Benier, L.; Winterhalter, M. Electrophysiological Characterization of Transport across Outer-Membrane Channels from Gram-Negative Bacteria in Presence of Lipopolysaccharides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 8517–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, E.; Zhalnina, M.V.; Zakharov, S.D.; Sharma, O.; Cramer, W.A. Crystal structures of the OmpF porin: Function in a colicin translocon. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, N.; Takayama, K.; Mascagni, P.; Honovich, J.; Wong, R.; Cotter, R.J. Complete structural determination of lipopolysaccharide obtained from deep rough mutant of Escherichia coli. Purification by high performance liquid chromatography and direct analysis by plasma desorption mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 11971–11976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestorovich, E.M.; Rostovtseva, T.K.; Bezrukov, S.M. Residue ionization and ion transport through OmpF channels. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 3718–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagge, S.O.; de Cock, H.; Gutsmann, T.; Beckers, F.; Seydel, U.; Wiese, A. Pore formation and function of phosphoporin PhoE of Escherichia coli are determined by the core sugar moiety of lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34247–34253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavito, R.M.; Rosenbusch, J.P. Isolation and crystallization of bacterial porin. Methods Enzym. 1986, 125, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanos, C.; Lüderitz, O.; Westphal, O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1969, 9, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, M.J.; Gander, J.E.; Parisi, E.; Carson, J. Mechanism and assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 3962–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montal, M.; Mueller, P. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 3561–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, A.; Seydel, U. Electrophysiological measurements on reconstituted outer membranes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 145, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, B.J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol. Rev. 1972, 36, 525–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Morooka, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Fujita, K.; Isono, K.; Choi, S.; Ohtsubo, E.; Baba, T.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H.; et al. Highly accurate genome sequences of Escherichia coli K-12 strains MG1655 and W3110. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 2006.0007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoenger, A.; Pagès, J.M.; Fourel, D.; Engel, A. The orientation of porin OmpF in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 233, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danelon, C.; Brando, T.; Winterhalter, M. Probing the orientation of reconstituted maltoporin channels at the single-protein level. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35542–35551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, W.; Roux, B. Ions and counterions in a biological channel: A molecular dynamics simulation of OmpF porin from Escherichia coli in an explicit membrane with 1 M KCl aqueous salt solution. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 319, 1177–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz, A.; Nestorovich, E.M.; Aguilella-Arzo, M.; Aguilella, V.M.; Bezrukov, S.M. Salting out the ionic selectivity of a wide channel: The asymmetry of OmpF. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, S.A.; Lee, S.; Housden, N.G.; Kaminska, R.; Kleanthous, C.; Bayley, H. Orientation of the OmpF Porin in planar Lipid Bilayers. Chembiochem 2017, 18, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, L.K.; Hong, H.; Liang, B. Folding and assembly of beta-barrel membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1666, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagge, S.O.; Wiese, A.; Seydel, U.; Gutsmann, T. Inner field compensation as a tool for the characterization of asymmetric membranes and Peptide-membrane interactions. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, K.; Hellman, J.; Nikaido, H. Porin channels in intact cells of Escherichia coli are not affected by Donnan potentials across the outer membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, H.; Vaara, M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbial. Rev. 1985, 49, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, T.; Neves, P.; Spiga, E.; Weingart, H.; Winterhalter, M.; Ruggerone, P.; Ceccarelli, M.; Gameiro, P. Facilitated permeation of antibiotics across membrane channels—Interaction of the quinolone moxifloxacin with the OmpF channel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13301–13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestorovich, E.M.; Danelon, C.; Winterhalter, M.; Bezrukov, S.M. Designed to penetrate: Time-resolved interaction of single antibiotic molecules with bacterial pores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9789–9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.P.; McMurry, L.M.; Hooper, D.C.; Wolfson, J.S.; Levy, S.B. Cross-resistance to fluoroquinolones in multiple-antibiotic-resistant (Mar) Escherichia coli selected by tetracycline or chloramphenicol: Decreased drug accumulation associated with membrane changes in addition to OmpF reduction. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1989, 33, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, A.H.; East, J.M.; Lee, A.G. Selectivity in lipid binding to the bacterial outer membrane protein OmpF. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 2066–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, L.K.; Kusumoto, S.; Zhang, H.; Rosenbusch, J.P. Plasticity of Escherichia coli porin channels. Dependence of their conductance on strain and lipid environment. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 24446–24450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, K.L.; Saint, N.; Prilipov, A.; Rummel, G.; Benson, S.A.; Rosenbusch, J.P.; Schirmer, T. Structural and functional characterization of OmpF porin mutants selected for larger pore size. I. Crystallographic analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20669–20675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint, N.; Prilipov, A.; Hardmeyer, A.; Lou, K.L.; Schirmer, T.; Rosenbusch, J.P. Replacement of the sole histidinyl residue in OmpF porin from E. coli by threonine (H21T) does not affect channel structure and function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 223, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, K.M.; Tieleman, D. Molecular basis of voltage gating of OmpF porin. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2002, 80, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestres, C.; Alsina, M.A.; Busquets, M.A.; Haro, I.; Reig, F. Interaction of enrofloxacin with phospholipid mono- and bilayers. Langmuir 1994, 10, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| τ (−100 mV) | τ (+100 mV) (Only the Long Blockages) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LPS R45/PL | enrofloxacin cis | 8.2 ms ± 5.3 ms | 1.1 ms ± 0.4 ms |
| enrofloxacin trans | no events | 1.6 ms ± 0.5 ms | |
| LPS WBB01/PL | enrofloxacin cis | 5.3 ms ± 2.4 ms | 0.9 ms ± 0.3 ms |
| enrofloxacin trans | no events | not resolvable | |
| DPhPC/DPhPC | enrofloxacin cis | 10.5 ms ± 3 ms | 1.1 ms ± 0.1 ms |
| enrofloxacin trans | no events | 0.8 ms ± 0.2 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donoghue, A.; Winterhalter, M.; Gutsmann, T. Influence of Membrane Asymmetry on OmpF Insertion, Orientation and Function. Membranes 2023, 13, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050517
Donoghue A, Winterhalter M, Gutsmann T. Influence of Membrane Asymmetry on OmpF Insertion, Orientation and Function. Membranes. 2023; 13(5):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050517
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonoghue, Annemarie, Mathias Winterhalter, and Thomas Gutsmann. 2023. "Influence of Membrane Asymmetry on OmpF Insertion, Orientation and Function" Membranes 13, no. 5: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050517
APA StyleDonoghue, A., Winterhalter, M., & Gutsmann, T. (2023). Influence of Membrane Asymmetry on OmpF Insertion, Orientation and Function. Membranes, 13(5), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050517





