Interaction of Hyaluronan Acid with Some Proteins in Aqueous Solution as Studied by NMR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
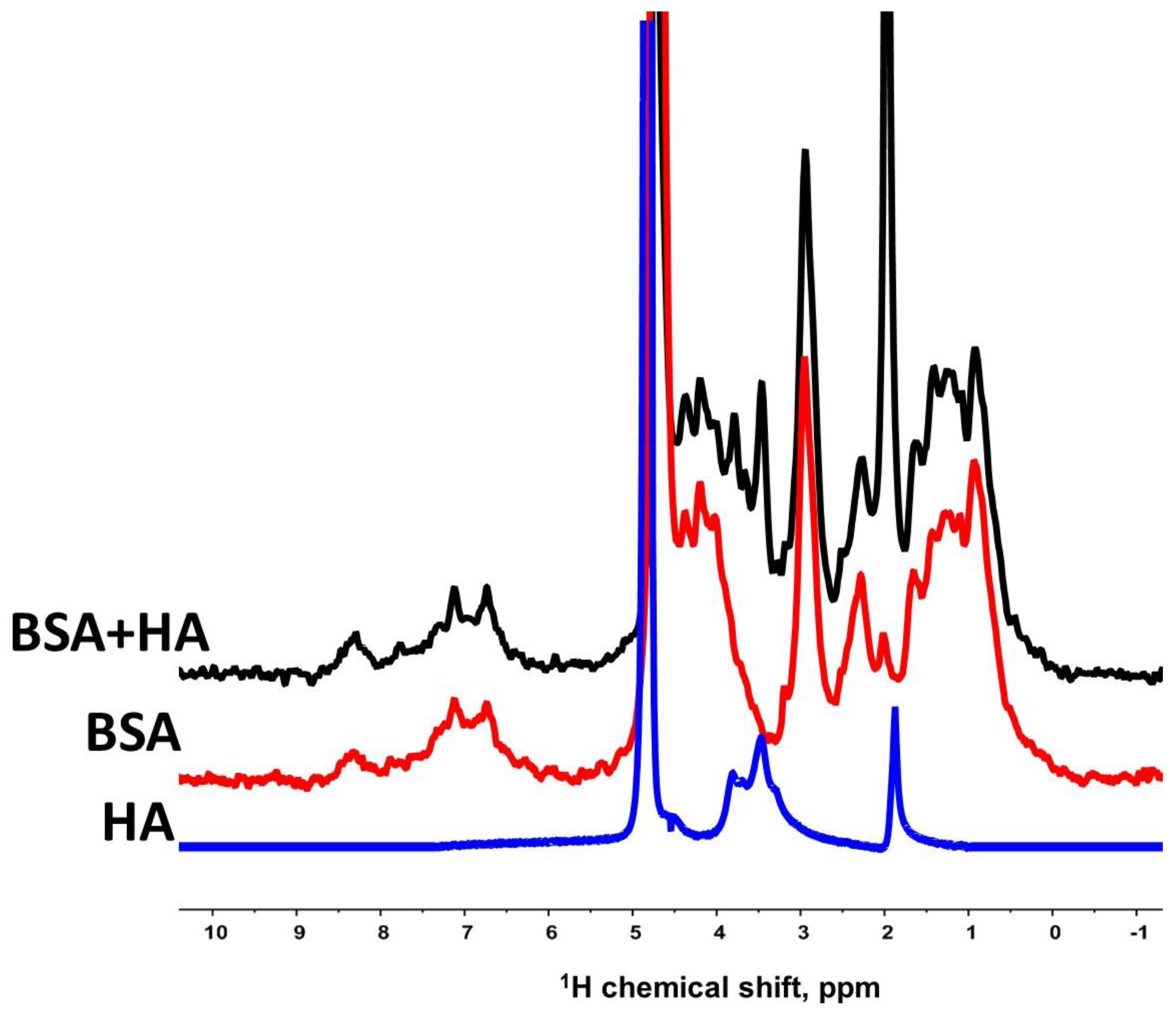
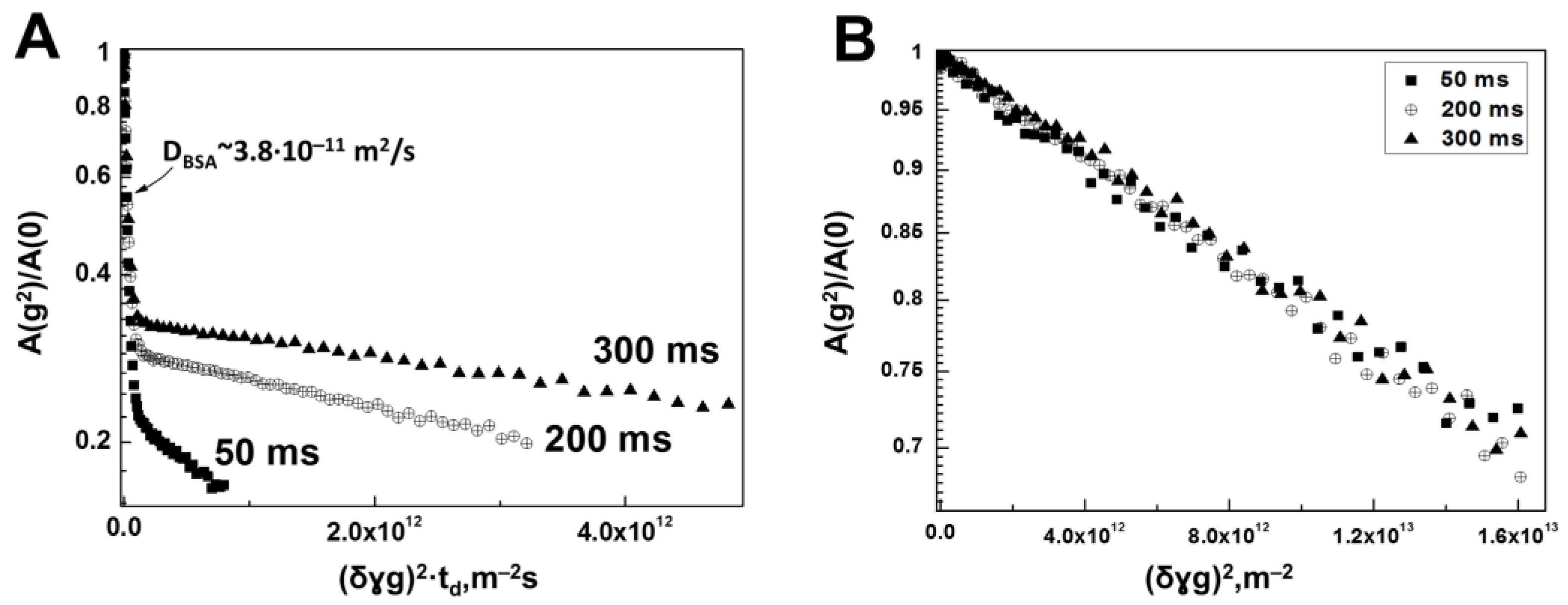
3.1. Interaction of Bovine Serum Albumin with Hyaluronic Acid Molecules
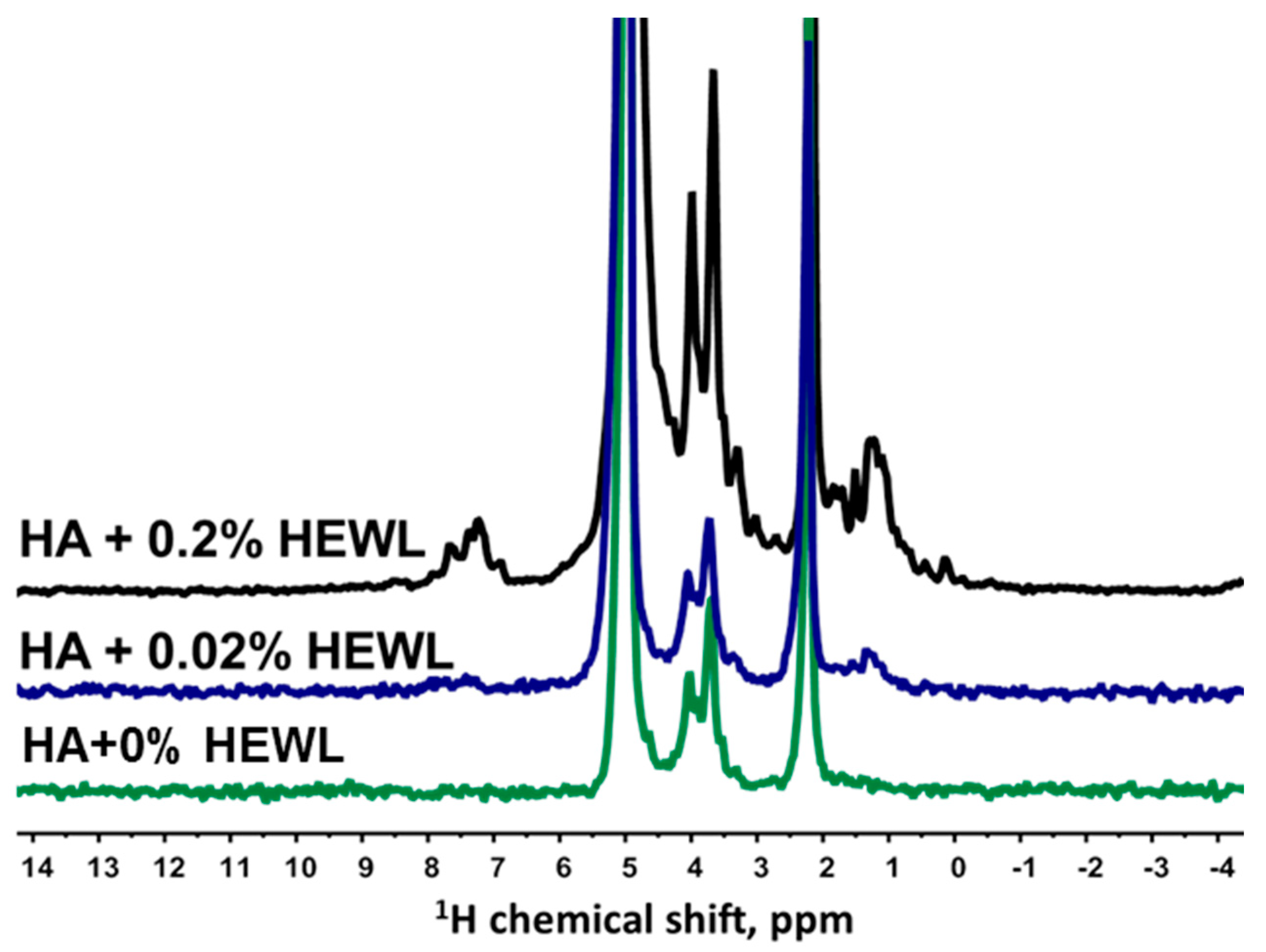
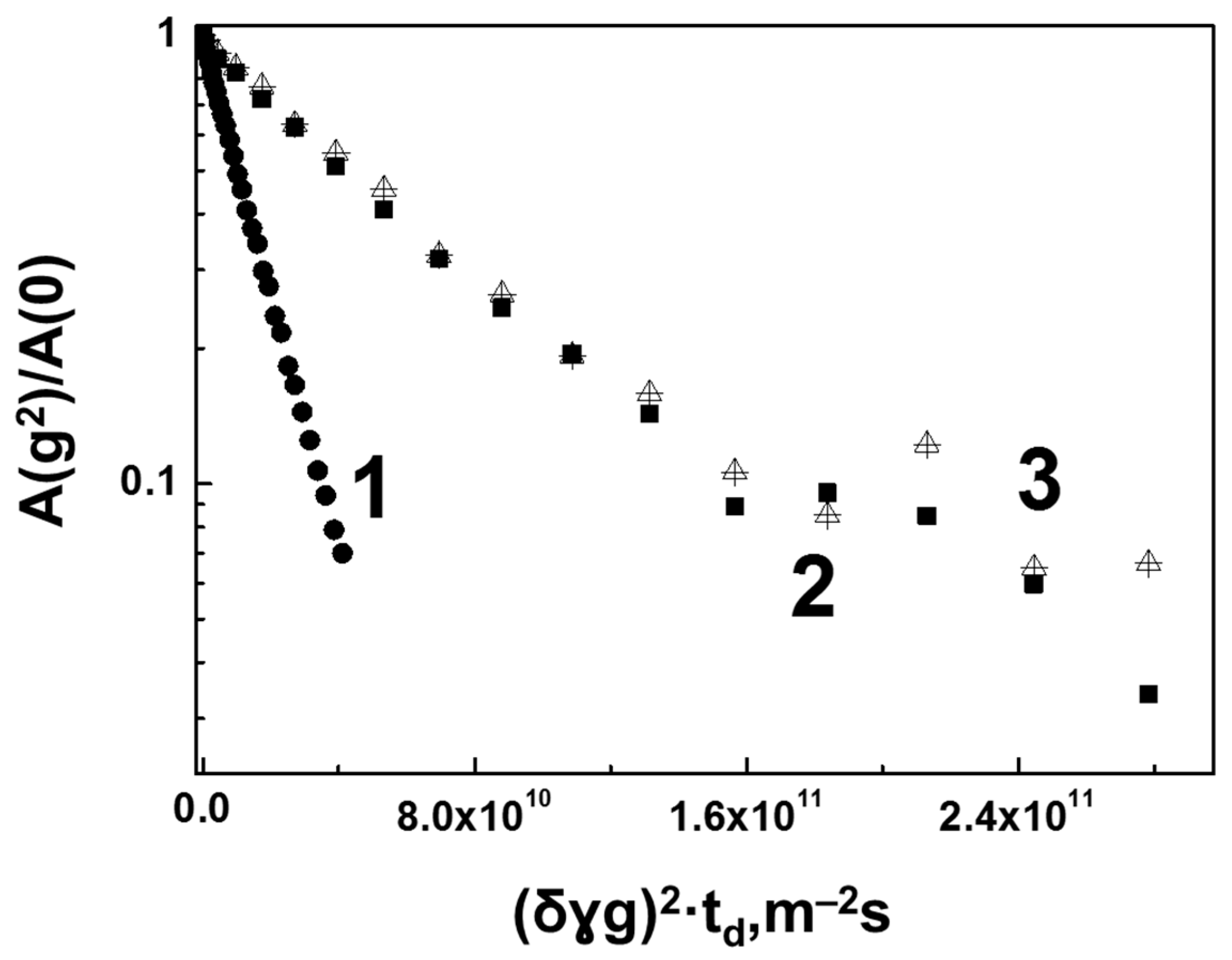
3.2. Interaction of Hen Egg-White Lysozyme (HEWL) with Hyaluronic Acid Molecules
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheetz, M.P. Cellular plasma membrane domains. Mol. Membr. Biol. 1995, 12, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtke, D.W.; Diamond, S.L. Direct observation of membrane tethers formed during neutrophil attachment to platelets or P-selectin under physiological flow. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, A.; Cappello, G.; Cartaud, J.; Prost, J.; Goud, B.; Bassereau, P. A minimal system allowing tubulation with molecular motors pulling on giant liposomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5394–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustom, A.; Saffrich, R.; Markovic, I.; Walther, P.; Gerdes, H.H. Nanotubular highways for intercellular organelle transport. Science 2004, 303, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, G.; VanDuijn, M.; Hofs, B.; Dogterom, M. Membrane tube formation from giant vesicles by dynamic association of motor proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15583–15588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afratis, N.; Gialeli, C.; Nikitovic, D.; Tsegenidis, T.; Karousou, E.; Theocharis, A.D.; Pavao, M.S.; Tzanakakis, G.N.; Karamanos, N.K. Glycosaminoglycans: Key players in cancer cell biology and treatment. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1177–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Noble, P.W. Hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 221–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigetti, D.; Rizzi, M.; Moretto, P.; Deleonibus, S.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Karousou, E.; Viola, M.; Clerici, M.; Hascall, V.C.; Ramoni, M.F.; et al. Glycosaminoglycans and glucose prevent apoptosis in 4-methylumbelliferone-treated human aortic smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 34497–34503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicker, K.T.; Gurski, L.A.; Pradhan-Bhatt, S.; Witt, R.L.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Jia, X. Hyaluronan: A simple polysaccharide with diverse biological functions. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikova, D.L.; Skirda, V.D.; Nesmelova, I.V. Effect of Intrinsic Disorder and Self-Association on the Translational Diffusion of Proteins: The Case of α-Casein. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 2980–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesmelova, I.V.; Skirda, V.D.; Fedotov, V.D. Generalized concentration dependence of globular protein self-diffusion coefficients in aqueous solutions. Biopolymers 2002, 63, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyadevi, P.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Butorac, R.R.; Cowley, A.H.; Bhuvanesh, N.S.; Dharmaraj, N. Effect of substitution and planarity of the ligand on DNA/BSA interaction, free radical scavenging and cytotoxicity of diamagnetic Ni(II) complexes: A systematic investigation. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 9690–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, M.; Curry, S.; Terreno, E.; Galliano, M.; Fanali, G.; Narciso, P.; Notari, S.; Ascenzi, P. The extraordinary ligand binding properties of human serum albumin. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Galiniak, S.; Bartosz, G. Kinetics of glycoxidation of bovine serum albumin by methylglyoxal and glyoxal and its prevention by various compounds. Molecules 2014, 19, 4880–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinskaia, D.A.; Voronina, P.A.; Goncharov, N.V. Integrative Role of Albumin: Evolutionary, Biochemical and Pathophysiological Aspects. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 57, 1419–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jha, A.K.; Harrington, D.A.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Jia, X. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels: From a Natural Polysaccharide to Complex Networks. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3280–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribitsch, G.; Schurz, J.; Ribitsch, V. Investigation of the solution structure of hyaluronic acid by light scattering, SAXS, and viscosity measurements. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1980, 258, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heatley, F.; Scott, J.E. A water molecule participates in the secondary structure of hyaluronan. Biochem. J. 1988, 254, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.E.; Cummings, C.; Brass, A.; Chen, Y. Secondary and tertiary structures of hyaluronan in aqueous solution, investigated by rotary shadowing-electron microscopy and computer simulation. Hyaluronan is a very efficient network-forming polymer. Biochem. J. 1991, 274, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.E.; Heatley, F. Hyaluronan forms specific stable tertiary structures in aqueous solution: A 13C NMR study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4850–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramani, S.; Truntzer, J.; Coleman, D.R. Thermal stability of high concentration lysozyme across varying pH: A Fourier Transform Infrared study. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2013, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.N.; Cheetham, J.; McLaughlin, P.J.; Acharya, K.R.; Barford, D.; Phillips, D.C. Protein-oligosaccharide interactions: Lysozyme, phosphorylase, amylases. In Carbohydrate-Protein Interaction; Part of the Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology Book Series (CT MICROBIOLOGY); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; Volume 139, pp. 81–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B.A.; Svensson, B.; Collins, M.E.; Rastall, R.A. Polysaccharide degradation. In Glycoscience; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 2325–2375. ISBN 978-3-540-36154-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoni, A.; Neglia, R.G.; Baschieri, M.C.; Cermelli, C.; Caratozzolo, M.; Righi, E.; Palmieri, B.; Blasi, E. Influence of hyaluronic acid on bacterial and fungal species, including clinically relevant opportunistic pathogens. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, A.J.; Prestwich, G.D. Hyaluronan-binding proteins: Tying up the giant. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4585–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, B.P. Hyaluronan: From extracellular glue to pericellular cue. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T. Lipid raft-mediated regulation of hyaluronan–CD44 interactions in inflammation and cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naor, D.; Sionov, R.V.; Ish-Shalom, D. CD44: Structure, function and association with the malignant process. Adv. Cancer Res. 1997, 71, 241–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponta, H.; Sherman, L.; Herrlich, P.A. CD44: From adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.E. Use of the stimulated echo in NMR diffusion studies. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 52, 2523–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maklakov, A.I.; Skirda, V.D.; Fatkullin, N.F. Self-Diffusion in Polymer Solutions and Melts; Kazan University Press: Kazan, Russia, 1987; p. 224. [Google Scholar]
- Sadler, P.J.; Tucker, A. Proton NMR studies of bovine serum albumin. Assignment of spin systems. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 205, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinskaia, D.A.; Voronina, P.A.; Shmurak, V.I.; Vovk, M.A.; Batalova, A.A.; Jenkins, R.O.; Goncharov, N.V. The Universal Soldier: Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant Functions of Serum Albumin. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, I.; Agrahari, V.; Murowchick, J.B.; Youan, B.B. Uptake and cytotoxicity of docetaxel-loaded hyaluronic acid-grafted oily core nanocapsules in MDA-MB 231 cancer cells. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 2439–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gafurov, I.R.; Skirda, V.D.; Maklakov, A.I.; Perevezentseva, S.P.; Zimkin, Y.A. NMR Study of the Structure of Aqueous Gelatine Gels and the Process of Their Formation. Polym. Sci. 1989, 31, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.L.; Skirda, V.D.; Nesmelova, I.V. Effect of Reducing Agent TCEP on Translational Diffusion and Supramolecular Assembly in Aqueous Solutions of α-Casein. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.; Artamonova, M.; Rudakova, M.; Gimatdinov, R.; Skirda, V. Self-diffusion in a hyaluronic acid-albumin-water system as studied by NMR. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2012, 50, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masschalck, B.; Michiels, C.W. Antimicrobial properties of lysozyme in relation to foodborne vegetative bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 29, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minones Conde, M.; Conde, O.; Trillo, J.M.; Minones, J., Jr. Interactions in monolayers: A study of the behavior of poly(methyl methacrylate)-lysozyme mixed films from surface pressure-area and ellipsometric measurements. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 8667–8678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, P.; Speranza, B.; Del Nobile, M.A.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M. A study on the antimicrobial activity of thymol intended as a natural preservative. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Dubin, P.L.; Hoagland, D.A.; Sun, L. Protein-selective coacervation with hyaluronic acid. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelner, R.A.; Yeong, V.; Obermeyer, A.C. Molecular determinants of protein-based coacervates. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 52, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.W.; Lytle, T.K.; Radhakrishna, M.; Madinya, J.J.; Vélez, J.; Sing, C.E.; Perry, S.L. Sequence and entropy-based control of complex coacervates. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brangwynne, C.P.; Eckmann, C.R.; Courson, D.S.; Rybarska, A.; Hoege, C.; Gharakhani, J.; Jülicher, F.; Hyman, A.A. Germline P granules are liquid droplets that localize by controlled dissolution/condensation. Science 2009, 324, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunde, B.M.; Moore, C.; Varani, G. RNA-binding proteins: Modular design for efficient function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Kedersha, N. RNA granules. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malay, O.; Bayraktar, O.; Batigün, A. Complex coacervation of silk fibroin and hyaluronic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 40, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izutsu, K.I.; Usui, A.; Yamamoto, E.; Abe, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Goda, Y. Effect of Complex Coacervation with Hyaluronic Acid on Protein Transition in a Subcutaneous Injection Site Model System. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, R.E.; Geis, I. Structure and Action of Proteins; Benjamin-Cummings Publishing Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Proctor, V.A.; Cunningham, F.E.; Fung, D.Y.C. The chemistry of lysozyme and its use as a food preservative and a pharmaceutical. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1988, 26, 359–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarter, J.D.; Withers, G.S. Mechanisms of enzymatic glycoside hydrolysis. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1994, 4, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaman, C.; Nakai, S.; Aminlari, M. Effect of pH, temperature and sodium bisulfite or cysteine on the level of Maillard-based conjugation of lysozyme with dextran, galactomannan and mannan. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masschalck, B.; Van Houdt, R.; Van Haver, E.G.; Michiels, C.W. Inactivation of gram-negative bacteria by lysozyme, denatured lysozyme, and lysozyme-derived peptides under high hydrostatic pressure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraboschi, P.; Ciceri, S.; Grisenti, P. Applications of lysozyme, an innate immune defense factor, as an alternative antibiotic. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melnikova, D.; Khisravashirova, C.; Smotrina, T.; Skirda, V. Interaction of Hyaluronan Acid with Some Proteins in Aqueous Solution as Studied by NMR. Membranes 2023, 13, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040436
Melnikova D, Khisravashirova C, Smotrina T, Skirda V. Interaction of Hyaluronan Acid with Some Proteins in Aqueous Solution as Studied by NMR. Membranes. 2023; 13(4):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040436
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelnikova, Daria, Catherine Khisravashirova, Tatiana Smotrina, and Vladimir Skirda. 2023. "Interaction of Hyaluronan Acid with Some Proteins in Aqueous Solution as Studied by NMR" Membranes 13, no. 4: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040436
APA StyleMelnikova, D., Khisravashirova, C., Smotrina, T., & Skirda, V. (2023). Interaction of Hyaluronan Acid with Some Proteins in Aqueous Solution as Studied by NMR. Membranes, 13(4), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13040436






