Identification of Suitable Internal Control miRNAs in Bovine Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles for Normalization in Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Status of the Cattle
2.1.1. Blood Collection
2.1.2. Measurement of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Isozymes
2.1.3. Identification of Anti-BLV Antibody in Serum
2.1.4. Extraction of DNA from WBCs
2.1.5. Detection of BLV Provirus and Measurement of BLV Proviral Load (PVL)
2.2. Milk Collection
2.2.1. Isolation and Characterization of Bovine Milk sEVs
2.2.2. Extraction of RNA from Bovine Milk sEVs
2.2.3. Selection of Candidate Internal Control miRNAs in Bovine Milk sEVs
2.2.4. Quantification of miRNAs in qPCR Analysis
2.2.5. Assessment of Stability of Candidate Internal Control miRNAs
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Status of the Cattle
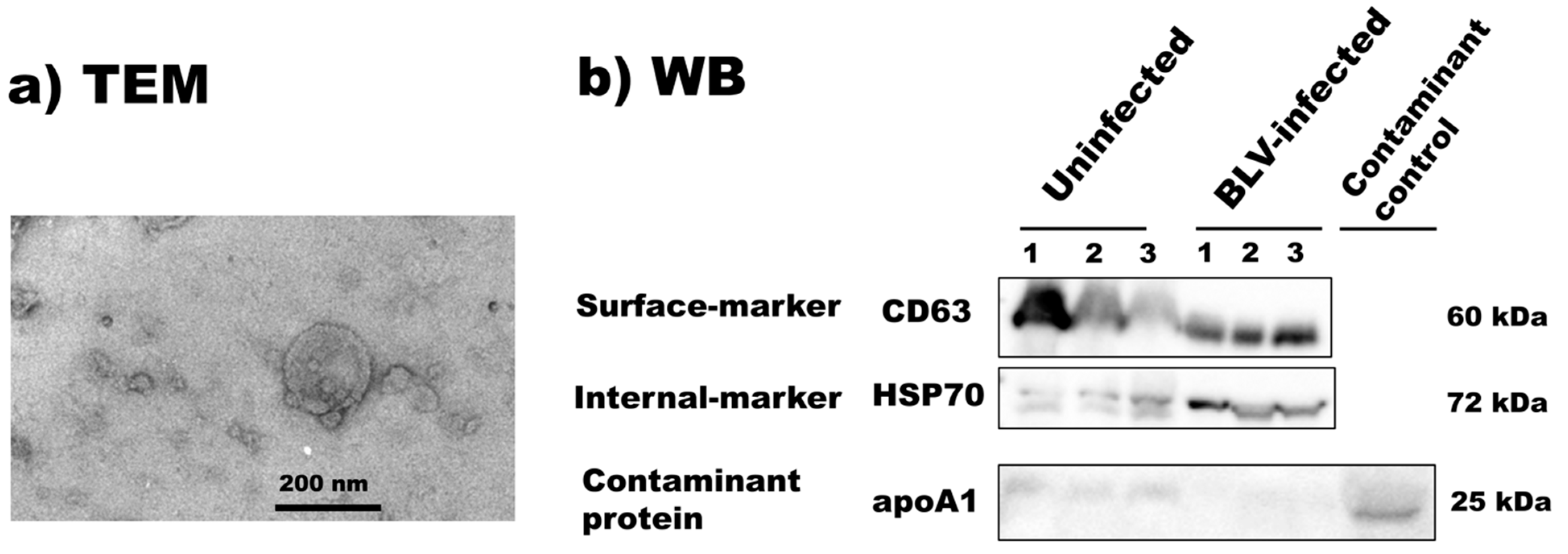
3.2. Isolation and Characterization of Bovine Milk sEVs
3.2.1. Selection of Candidate Internal Control miRNAs in Bovine Milk sEVs
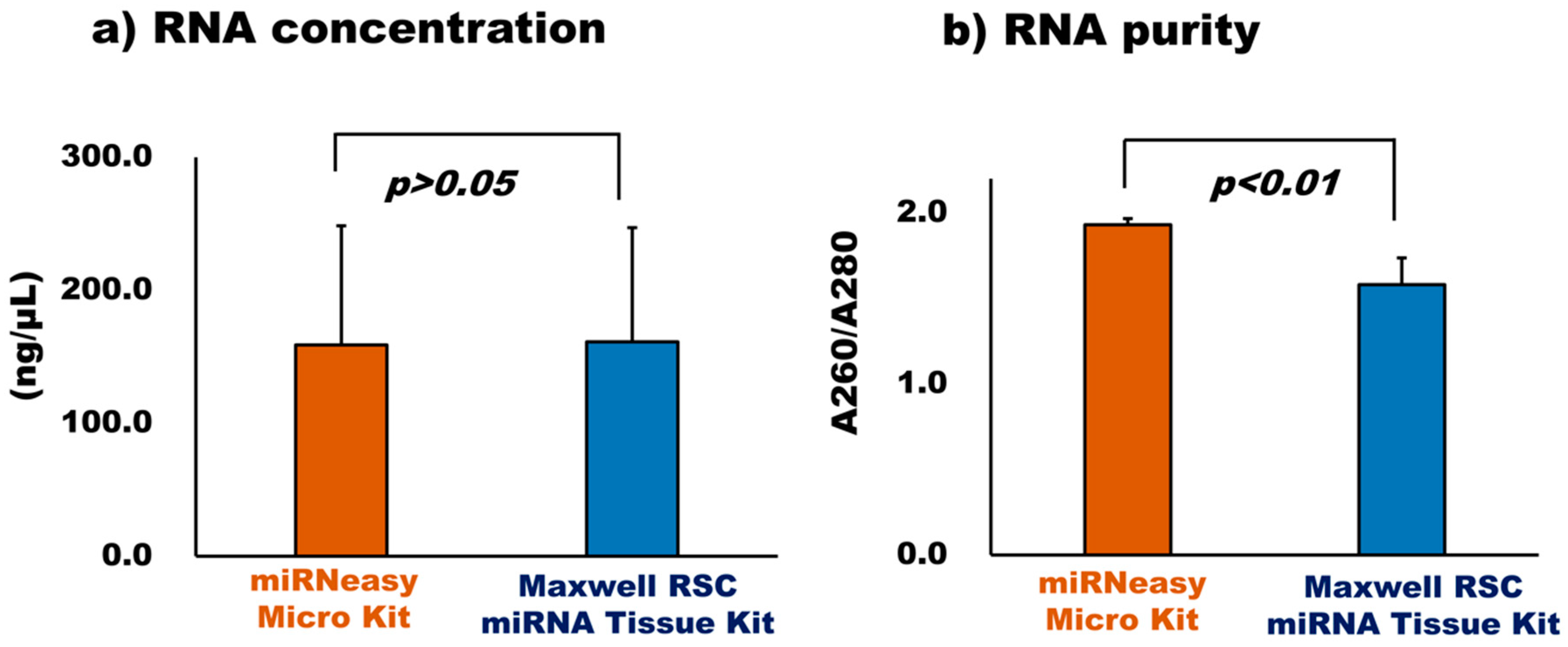
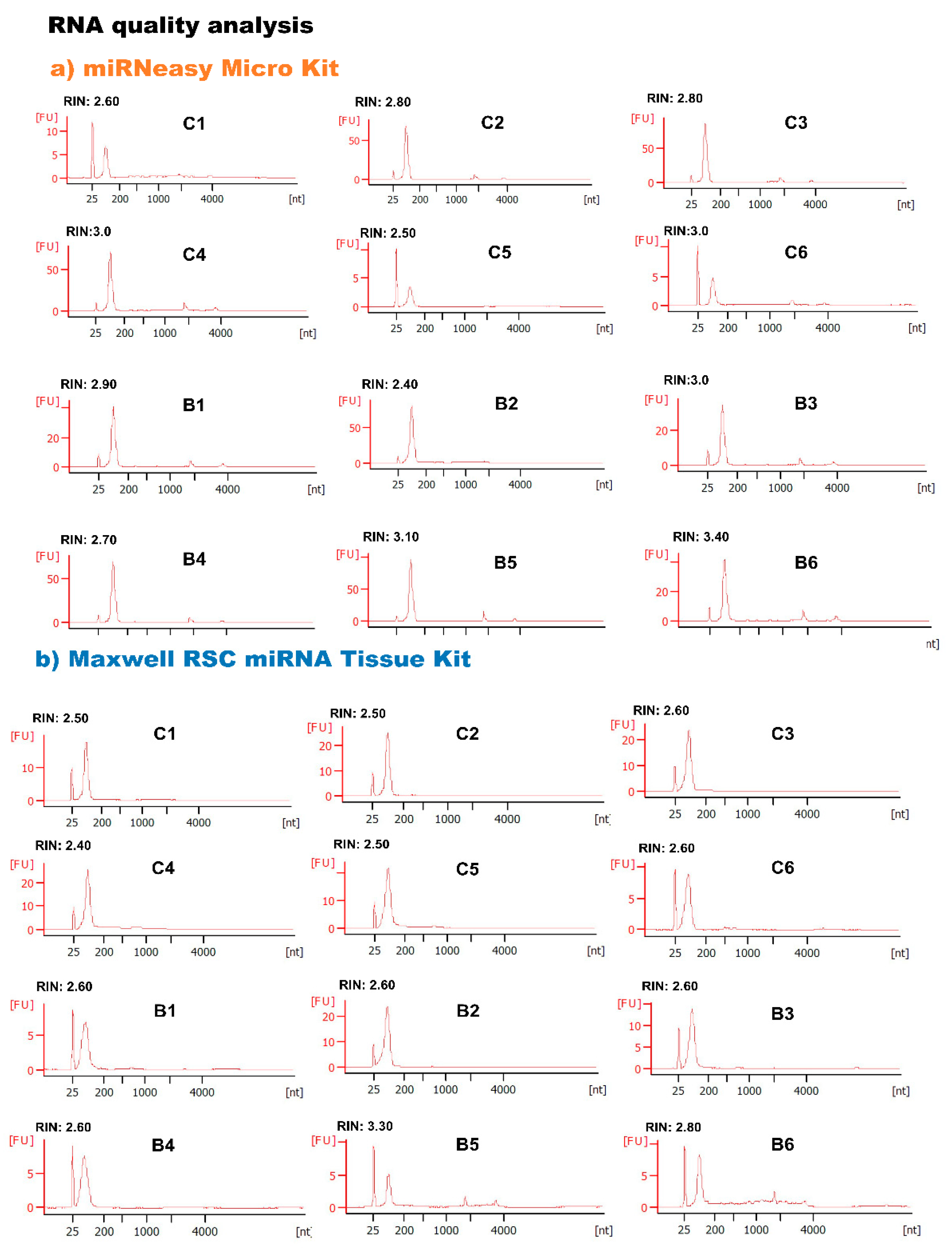
3.2.2. Comparison of RNA Extraction Kit
3.2.3. qPCR Analysis
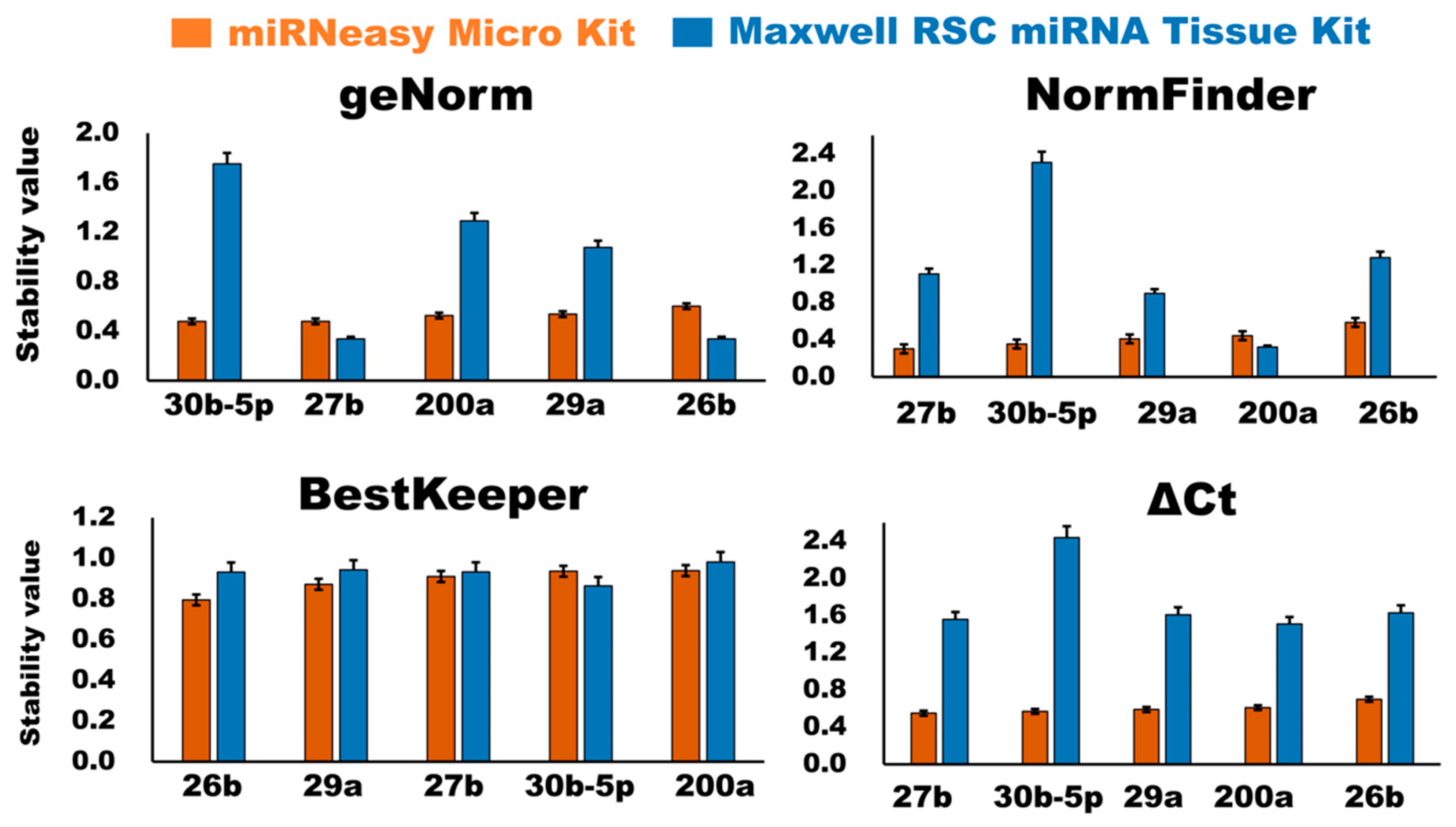
3.2.4. Evaluation of Stability of the Candidate Internal Control miRNAs
GeNorm Analysis
NormFinder Analysis
BestKeeper Analysis
ΔCt Analysis
RefFinder Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for extracellular vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, T.; Murakami, K.; Nakatani, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Aoki, N. Isolation of bovine milk-derived microvesicles carrying mRNAs and microRNAs. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Kim, S.; Park, H.T.; Park, H.E.; Choi, J.S.; Yoo, H.S. MicroRNA profiling in bovine serum according to the stage of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Aswath, K.; Schroeder, S.G.; Lippolis, J.D.; Reinhardt, T.A.; Sonstegard, T.S. MicroRNA expression profiles of bovine milk exosomes in response to Staphylococcus aureus infection. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, R.; Takashima, S.; Wakihara, Y.; Kamatari, Y.O.; Kitamura, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Okada, A.; Inoshima, Y. Comparing microRNA in milk small extracellular vesicles among healthy cattle and cattle at high risk for bovine leukemia virus transmission. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 5370–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, F.; Takashima, S.; Wakihara, Y.; Kamatari, Y.O.; Shimizu, K.; Okada, A.; Inoshima, Y. Characterization of miRNAs in milk small extracellular vesicles from enzootic bovine leukosis cattle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Hammerle-Fickinger, A.; Riedmaier, I.; Pfaffl, M.W. mRNA and microRNA quality control for RT-qPCR analysis. Methods 2010, 50, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourvinou, I.S.; Markou, A.; Lianidou, E.S. Quantification of circulating miRNAs in plasma: Effect of preanalytical and analytical parameters on their isolation and stability. J. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 15, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monleau, M.; Bonnel, S.; Gostan, T.; Blanchard, D.; Courgnaud, V.; Lecellier, C.H. Comparison of different extraction techniques to profile microRNAs from human sera and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Bai, Z.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Bi, J.; Ma, X.; Han, S.; Zhang, Z. Identification of suitable reference genes for qPCR analysis of serum microRNA in gastric cancer patients. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H.; Tsuda, M.; Sato, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Namba, K.; Takeda, Y. Bovine milk exosomes contain microRNA and mRNA and are taken up by human macrophages. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2920–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; Kubista, M.; Pfaffl, M.W. Reference gene validation software for improved normalization. In Real-Time PCR: Current Technology and Applications; Logan, J., Edwards, K., Saunders, N., Eds.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2009; Volume 47, p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, S.U.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Ulbrich, S.E. Normalization strategies for microRNA profiling experiments: A ‘normal’ way to a hidden layer of complexity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; da Silva, A.M.; Calin, G.; Pantel, K. Which is the accurate data normalization strategy for microRNA quantification? Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Xiang, G.; Jiang, D.; Pu, X. Identification of endogenous controls for analyzing serum exosomal miRNA in patients with hepatitis B or hepatocellular carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 893594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, research0034.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.L.; Jensen, J.L.; Orntoft, T.F. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, N.; Best, S.; Jiang, J.; Thein, S.L. Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol. Biol. 2006, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Xiao, P.; Chen, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, B. miRDeepFinder: A miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Okada, K.; Ikawa, Y.; Aida, Y. Bovine Leukemia virus induces CD5-B cell lymphoma in sheep despite temporarily increasing CD5+B cells in asymptomatic stage. Virology 1994, 202, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechner, H.; Blankenstein, P.; Looman, A.C.; Elwert, J.; Geue, L.; Albrecht, C.; Kurg, A.; Beier, D.; Marquardt, O.; Ebner, D. Provirus variants of the bovine leukemia virus and their relation to the serological status of naturally infected cattle. Virology 1997, 237, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Shimizu, K.; Yamauchi, M.; Takase, H.; Ugawa, S.; Okada, A.; Inoshima, Y. Acidification effects on isolation of extracellular vesicles from bovine milk. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Rahman, M.M.; Yamauchi, M.; Takashima, S.; Wakihara, Y.; Kamatari, Y.O.; Shimizu, K.; Okada, A.; Inoshima, Y. mRNA profile in milk extracellular vesicles from bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle. Viruses 2020, 12, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Takashima, S.; Kamatari, Y.O.; Badr, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Okada, A.; Inoshima, Y. Proteomic profiling of milk small extracellular vesicles from bovine leukemia virus-infected cattle. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammerickx, M.; Lorenz, R.J.; Straub, O.C.; Donnelly, W.J.; Flensburg, J.C.; Gentile, G.; Markson, L.M.; Ressang, A.A.; Taylor, S.M. Bovine hematology. III. Comparative breed studies on the leukocyte parameters of several European cattle breeds as determined in the common reference laboratory. Vet. Med. B. 1978, 25, 257–267. [Google Scholar]
- Moret, I.; Sánchez-Izquierdo, D.; Iborra, M.; Tortosa, L.; Navarro-Puche, A.; Nos, P.; Cervera, J.; Beltrán, B. Assessing an improved protocol for plasma microRNA extraction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.; Roberts, H.; Burton, J.; Pan, J.; States, V.; Rai, S.N.; Galandiuk, S. Assay reproducibility in clinical studies of plasma miRNA. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerson, A.; Ploug, T. Assessment of six commercial plasma small RNA isolation kits using qRT-PCR and electrophoretic separation: Higher recovery of microRNA following ultracentrifugation. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2016, 1, bpw003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.K.; MacMahon, M.; Woodside, J.V.; Simpson, D.A. A comparison of RNA extraction and sequencing protocols for detection of small RNA s in plasma. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoury, V.; Pierson, S.; Kaoma, T.; Bernardin, F.; Berchem, G. Assessing cellular and circulating miRNA recovery: The impact of the RNA isolation method and the quantity of input material. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldh, M.; Lötvall, J.; Malmhäll, C.; Ekström, K. Importance of RNA isolation methods for analysis of exosomal RNA: Evaluation of different methods. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 50, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, J.; Koehler, J.W.; Honko, A.N.; Minogue, T.D. Optimized microRNA purification from TRIzol-treated plasma. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirshova, A.N.; Shamovskaya, D.A.; Boyarskikh, U.A.; Kushlinskii, N.E.; Filipenko, M.L. One-phase phenol-free method for microRNA isolation from blood plasma. Methods 2018, 5, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, D.; Guo, X.; Chen, W.; Li, G.; Wang, G.; et al. MicroRNA-200a regulates grb2 and suppresses differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells into endoderm and mesoderm. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.Y.; Wang, L.F.; Wang, Q.; Yu, L.D. miR-26b inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis induction via the downregulation of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase-3 driven glycolysis in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yu, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Li, G. miR-29a regulates the proliferation and migration of human arterial smooth muscle cells in arteriosclerosis obliterans of the lower extremities. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2019, 44, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Fu, H.; Sun, F.; Zhang, H.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xing, R.; Sun, Z.; Zhenget, X. miR-16 family induces cell cycle arrest by regulating multiple cell cycle genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5391–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, H.N.N.; Vy, H.T.N.; Thanh, T.N.N.; Giang, D.T.N.; Nhan, T.N.; Hoang, N.P.; Hue, T.N. miRNA-16 as an internal control in breast cancer studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Biol. 2021, 55, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, M.D.C.G.; Coimbra, E.C.; Lima, R.D.C.P.D.; Guimarães, M.D.L.; Heráclio, S.D.A.; Silva Neto, J.D.C.; de Freitas, A.C. Quantifying mRNA and microRNA with qPCR in cervical carcinogenesis: A validation of reference genes to ensure accurate data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignotti, E.; Calza, S.; Tassi, R.A.; Zanotti, L.; Bandiera, E.; Sartori, E.; Odicino, F.E.; Ravaggi, A.; Todeschini, P.; Romani, C. Identification of stably expressed reference small non-coding RNAs for microRNA quantification in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma tissues. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, N.; Kulshreshtha, R. miR-191: An emerging player in disease biology. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, G.; Ma, N.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Jiao, Y.; Gao, X. Differential distribution of U6 (RNU6-1) expression in human carcinoma tissues demonstrates the requirement for caution in the internal control gene selection for microRNA quantification. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cattle | Age (Month) | ELISA | Nested PCR | PVL (Copies/105 WBC) | WBC (/µL) | Lymphocyte (/µL) | Key of EC | Total LDH (U/L) | LDH Isozyme (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 + 3 | 4 | 5 | |||||||||
| Uninfected cattle | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 19 | − | − | − | 4800 | 2700 | − | 881 | 51.5 | 26.4 | 14.9 | 41.3 | 4.9 | 2.3 |
| 2 | 20 | − | − | − | 9100 | 4400 | − | 955 | 50.0 | 25.9 | 15.4 | 41.3 | 5.2 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 31 | − | − | − | 8600 | 4200 | − | 876 | 52.4 | 22.6 | 15.7 | 38.3 | 5.2 | 4.1 |
| 4 | 66 | − | − | − | 6000 | 3100 | − | 839 | 58.8 | 25.1 | 12.4 | 37.5 | 2.8 | 0.9 |
| 5 | 42 | − | − | − | 5400 | 2100 | − | 778 | 57.5 | 25.6 | 12.6 | 38.2 | 2.9 | 1.4 |
| 6 | 115 | − | − | − | NT | NT | − | 723 | 63.9 | 16.6 | 13.0 | 29.6 | 4.3 | 2.2 |
| BLV-infected cattle | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 52 | + | + | 9057.53 | 7400 | 3656 | − | 882 | 55.9 | 22.0 | 13.6 | 35.6 | 5.0 | 3.5 |
| 2 | 22 | + | + | 21,589.79 | 12,300 | 6950 | − | 917 | 53.3 | 29.7 | 13.3 | 43.0 | 3.1 | 0.6 |
| 3 | 55 | + | + | 27,029.76 | 18,800 | 10,171 | + | 1124 | 60.7 | 22.9 | 9.7 | 32.6 | 2.6 | 4.1 |
| 4 | 41 | + | + | 31,802.33 | 10,600 | 7378 | ± | 1129 | 52.5 | 21.7 | 15.3 | 37.0 | 6.4 | 4.1 |
| 5 | 52 | + | + | 47,450.30 | 11,000 | 6666 | ± | 1221 | 60.3 | 22.2 | 11.0 | 33.2 | 4.4 | 2.1 |
| 6 | 53 | + | + | 87,417.31 | 24,400 | 13,713 | + | 1233 | 58.1 | 22.0 | 13.0 | 35.0 | 4.6 | 2.3 |
| miRNAs Name | Symbolic Presentation | Primers (Qiagen) | GeneGlobe ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| bta-miR-29a | 29a | bta-miR-29a miRCURY LNA miRNA PCR Assay | YP02114732 |
| bta-miR-200a | 200a | bta-miR-200a miRCURY LNA miRNA PCR Assay | YP02104134 |
| bta-miR-26b | 26b | bta-miR-26b miRCURY LNA miRNA PCR Assay | YP00205953 |
| bta-miR-27b | 27b | hsa-miR-27b-3p miRCURY LNA miRNA PCR Assay | YP00205915 |
| bta-miR-30b-5p | 30b-5p | hsa-miR-30b-5p miRCURY LNA miRNA PCR Assay | YP00204765 |
| Stability Ranking | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name of RNA extraction kit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| miRNeasy Micro Kit | miR-27b-3p | miR-30b-5p | miR-29a | miR-200a | miR-26b |
| Maxwell RSC miRNA Tissue kit | miR-200a | miR-27b-3p | miR-29a | miR-26b | miR-30b-5p |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.M.; Nakanishi, R.; Tsukada, F.; Takashima, S.; Wakihara, Y.; Kamatari, Y.O.; Shimizu, K.; Okada, A.; Inoshima, Y. Identification of Suitable Internal Control miRNAs in Bovine Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles for Normalization in Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Membranes 2023, 13, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020185
Rahman MM, Nakanishi R, Tsukada F, Takashima S, Wakihara Y, Kamatari YO, Shimizu K, Okada A, Inoshima Y. Identification of Suitable Internal Control miRNAs in Bovine Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles for Normalization in Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Membranes. 2023; 13(2):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020185
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md. Matiur, Ryoka Nakanishi, Fumi Tsukada, Shigeo Takashima, Yoshiko Wakihara, Yuji O. Kamatari, Kaori Shimizu, Ayaka Okada, and Yasuo Inoshima. 2023. "Identification of Suitable Internal Control miRNAs in Bovine Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles for Normalization in Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction" Membranes 13, no. 2: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020185
APA StyleRahman, M. M., Nakanishi, R., Tsukada, F., Takashima, S., Wakihara, Y., Kamatari, Y. O., Shimizu, K., Okada, A., & Inoshima, Y. (2023). Identification of Suitable Internal Control miRNAs in Bovine Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles for Normalization in Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Membranes, 13(2), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13020185







